Sedentary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sedentary lifestyle is a lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and/or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while engaged in an activity like socializing, watching TV, playing video games, reading or using a mobile phone or computer for much of the day. A sedentary lifestyle contributes to poor health quality, diseases as well as many preventable causes of death.
Sitting time is a common measure of a sedentary lifestyle. A global review representing 47% of the global adult population found that the average person sits down for 4.7 to 6.5 hours a day with the average going up every year. The
 Sedentary behavior is not the same as physical inactivity: sedentary behavior is defined as "any waking behavior characterized by an energy expenditure less than or equal to 1.5 metabolic equivalents (METs), while in a sitting, reclining or lying posture". Spending most waking hours sitting does not necessarily mean that an individual is sedentary, though sitting and lying down most frequently are sedentary behaviors. Esmonde-White defines a sedentary lifestyle as a lifestyle that involves "longer than six hours a day" of sedentary behavior.
Sedentary behavior is not the same as physical inactivity: sedentary behavior is defined as "any waking behavior characterized by an energy expenditure less than or equal to 1.5 metabolic equivalents (METs), while in a sitting, reclining or lying posture". Spending most waking hours sitting does not necessarily mean that an individual is sedentary, though sitting and lying down most frequently are sedentary behaviors. Esmonde-White defines a sedentary lifestyle as a lifestyle that involves "longer than six hours a day" of sedentary behavior.
*
 Physical inactivity reduces the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Sluggish blood flow allows for the accumulation of
Physical inactivity reduces the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Sluggish blood flow allows for the accumulation of
WHO fact sheet on physical activity
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sedentary Lifestyle Lifestyles Obesity Medical terminology
CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
found that 25.3% of all American adults are physically inactive.
Screen time Screen time is the amount of time electronic devices are used.
Screen time, Screentime or Screen Time may also refer to:
* Screen Time, an iOS and macOS feature that tracks how long devices are used
* Screentime, an Australian-based television pr ...
is a term for the amount of time a person spends looking at a screen such as a television, computer monitor, or mobile device. Excessive screen time is linked to negative health consequences.
Definition
 Sedentary behavior is not the same as physical inactivity: sedentary behavior is defined as "any waking behavior characterized by an energy expenditure less than or equal to 1.5 metabolic equivalents (METs), while in a sitting, reclining or lying posture". Spending most waking hours sitting does not necessarily mean that an individual is sedentary, though sitting and lying down most frequently are sedentary behaviors. Esmonde-White defines a sedentary lifestyle as a lifestyle that involves "longer than six hours a day" of sedentary behavior.
Sedentary behavior is not the same as physical inactivity: sedentary behavior is defined as "any waking behavior characterized by an energy expenditure less than or equal to 1.5 metabolic equivalents (METs), while in a sitting, reclining or lying posture". Spending most waking hours sitting does not necessarily mean that an individual is sedentary, though sitting and lying down most frequently are sedentary behaviors. Esmonde-White defines a sedentary lifestyle as a lifestyle that involves "longer than six hours a day" of sedentary behavior.
Health effects
Effects of a sedentary work life or lifestyle can be either direct or indirect. One of the most prominent direct effect of a sedentary lifestyle is an increasedbody mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
(BMI) leading to obesity. A lack of physical activity is one of the leading causes of preventable death worldwide.
At least 300,000 premature deaths, and $90 billion in direct healthcare costs are caused by obesity and sedentary lifestyle per year in the US alone. The risk is higher among those that sit still more than per day. It is shown to be a risk factor on its own independent of hard exercise and BMI. People that sit still more than per day have a higher risk than those that sit fewer than per day. However, those that exercise at least per week are as healthy as those that sit fewer than per day.
Indirectly, an increased BMI due to a sedentary lifestyle can lead to decreased productivity and increased absenteeism from necessary activities like work.
A sedentary lifestyle contributes to or can be a risk factor for:*
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
* Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
* Migraines
* Breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
* Colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
* Computer vision syndrome (only from excessive electronic use)
* Depression
* Gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of pain in a red, tender, hot, and Joint effusion, swollen joint, caused by the deposition of needle-like crystals of uric acid known as monosodium urate crysta ...
* High blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
* Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
disorders
* Skin problems such as hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
* Mortality in adults
* Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
* Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
* Scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others ...
* Spinal disc herniation
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
(low back pain
Low back pain or wiktionary:lumbago#Etymology, lumbago is a common musculoskeletal disorders, disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can var ...
)
* Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
* Weight gain
Weight gain is an increase in body weight. This can involve an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, excess fluids such as water or other factors. Weight gain can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Description
Weight gain occurs ...
Brain function
Extended periods of sitting reduce overall blood circulation. This diminished blood flow leads to reduced oxygen delivery to the brain (cerebral hypoxia
Cerebral hypoxia is a form of Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia (reduced supply of oxygen), specifically involving the human brain, brain; when the brain is completely deprived of oxygen, it is called ''cerebral anoxia''. There are four categories of c ...
), impairing cognitive functions such as concentration and alertness. The brain relies heavily on a continuous supply of oxygen and glucose for optimal performance; decreased circulation hampers this supply, resulting in cognitive sluggishness and decreased mental sharpness.

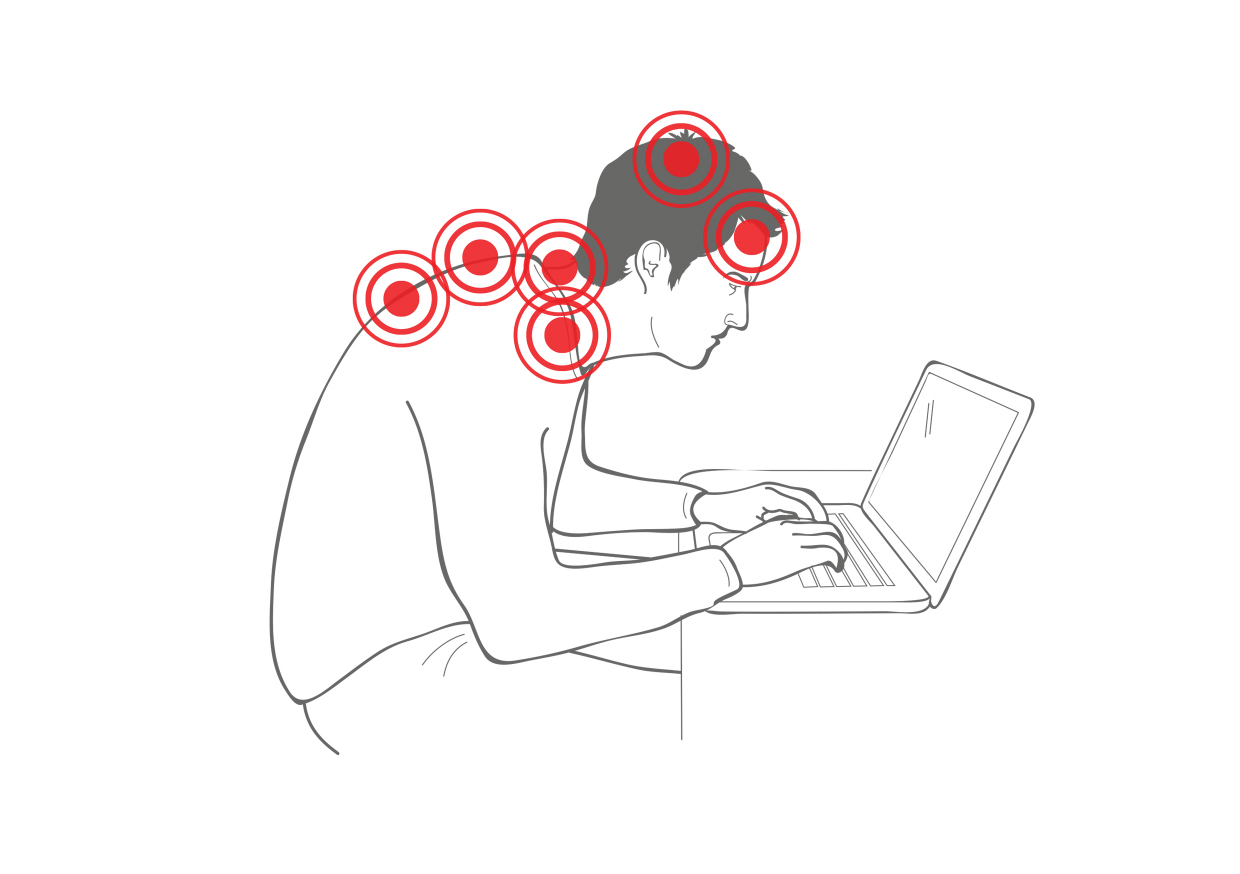
Neck and shoulders
Sitting, particularly with poor posture, often involves craning the neck forward to look at screens or documents. Such forward head posture puts excessive strain on thecervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
, leading to muscle tension and pain in the neck and shoulders. Over time, this can cause the cervical vertebrae to become misaligned permanently, leading to chronic neck pain and potential nerve impingement.
Upper body and back
Theintervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the ver ...
s, which act as cushions between the vertebrae, are subjected to constant pressure when sitting for prolonged periods. This compression can lead to disc degeneration and herniation. Additionally, collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
, a primary structural protein in tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue that connects skeletal muscle, muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tensi ...
s and ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s, tends to harden when not regularly stretched and mobilized, which leads to decreased flexibility
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a ...
and increased risk of injury in the back.
Heart disease
 Physical inactivity reduces the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Sluggish blood flow allows for the accumulation of
Physical inactivity reduces the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Sluggish blood flow allows for the accumulation of fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s and lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s in the blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s. These deposits can adhere to the vessel walls, forming plaques (atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
), which eventually narrow the arteries and restrict blood flow. This condition increases the risk of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
and heart attacks
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retr ...
as the heart struggles to receive adequate oxygen and nutrients.
One study found that interrupting sitting with 20 minutes of light-intensity walking each hour significantly reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
in healthy participants or 3 minutes of light intensity walking every 30 minutes.
Overproductive pancreas
A sedentary lifestyle contributes to decreased muscle activity, which affects glucose metabolism. Reduced muscle activity leads to lower insulin sensitivity, prompting thepancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
to produce more insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
to maintain normal blood glucose levels (metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
). Chronic overproduction of insulin can exhaust the pancreas and contribute to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
.
Leg problems
Prolonged sitting impedes venous return from the legs to the heart, leading to venous stasis (slow blood flow in the veins). This can cause fluid to pool in the lower extremities, resulting in swelling (edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
) and varicose veins
Varicose veins, also known as varicoses, are a medical condition in which superficial veins become enlarged and twisted. Although usually just a cosmetic ailment, in some cases they cause fatigue, pain, itch, itching, and cramp, nighttime leg cram ...
. Also, sluggish blood flow increases the risk of clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
formation, potentially leading to deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enl ...
(DVT), a condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, which can travel to the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s and cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
.
Mitigation
Adults and children spend long amounts of time sitting in a workplace or at a school, which is why interventions have been focused in these two areas.Mass media
Mass media include the diverse arrays of media that reach a large audience via mass communication.
Broadcast media transmit information electronically via media such as films, radio, recorded music, or television. Digital media comprises b ...
campaigns might also be able to reduce the amount of time spent sitting or lying down and positively affect the intention to be active physically.
Recent innovations in AI technology have led to the development of exercise prescription systems designed to reduce sedentary behavior. These systems deliver personalized exercise plans by analyzing individual health metrics, potentially decreasing the prevalence of a sedentary lifestyle and its associated health risks.
In urban spaces
Some evidence has been found of a negative association between exposure to an existing urbanmotorway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms ...
and moderate to vigorous physical activity. The proportion of physically active individuals was higher in high- versus low-walkability
In urban planning, walkability is the accessibility of amenities within a reasonable walking distance. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it s ...
neighborhoods. Rising rates of being overweight, obesity, and physical inactivity in China's rapidly growing cities and urban populations have been due to urban development
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of peop ...
practices and policies.
In a work environment
Occupational sedentary behaviour accounts for a significant proportion of sitting time for many adults. Some workplaces have implemented exercise classes at lunch, walking challenges among coworkers, or allowing employees to stand rather than sit at their desks during work. Workplace interventions such as alternative activity workstations, sit-stand desks, and promotion of stair use are among measures implemented to counter the harms of a sedentary workplace.Research
A 2018Cochrane review
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes ...
concluded that "At present there is low‐quality evidence that sit‐stand desks may reduce sitting at work in the first year of their use. However, the effects are likely to reduce with time. There is generally insufficient evidence to draw conclusions about such effects for other types of interventions and for the effectiveness of reducing workplace sitting over periods longer than one year."
An intervention to encourage office workers to stand and move reduced their sitting time by 22 minutes after 1 year; the effect was 3-times greater when the intervention included a sit-to-stand desk. The intervention also led to small improvements in stress, wellbeing and vigor.
In education
The majority of time children are in a classroom, they are seated (60% of the time). Children who regularly engage inphysical activity
Physical activity is defined as any voluntary movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure.Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health, 2009. World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland. Accessed 13/07/2018 ...
are more likely to become healthy adults; children benefit both physically and mentally when they replace sedentary behavior with active behavior. Despite this knowledge and due in part to an increase in sedentary behaviors, as of 2018 children have 8 fewer hours of free play each week than they did 20 years before.
Several studies have examined the effects of adding height-adjustable standing desk
A standing desk or stand-up desk is a desk conceived for writing, reading or drawing while Standing, standing up or while sitting on a high stool.
History
Several writers and statesmen wrote standing up: Thomas Jefferson, Charles Dickens, Win ...
s to classrooms, which have reduced the time spent sitting. However, associating the reduction in sitting with health effects is challenging. In one study conducted on Australian school children, known as the Transform-Us! study, interventions reduced the amount of time children spent sitting in the classroom, which was associated with lower body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
and waist circumference
The waist is the part of the Human abdomen, abdomen between the rib cage and Hip (anatomy), hips. Normally, it is the narrowest part of the torso.
''Waistline'' refers to the horizontal line where the waist is narrowest, or to the general appe ...
. The interventions used in the study included stand-up desks and easel
An easel is an upright support used for displaying and/or fixing something resting upon it, at an angle of about 20° to the vertical. In particular, painters traditionally use an easel to support a painting while they work on it, normally stan ...
s, the use of timers, and sport and circus equipment in the classroom. Teachers also made lessons more active, and added breaks to lessons to promote active time. In the US, another intervention for children is promoting the use of active transportation to and from school, such as through the Safe Routes to School program.
History
Over the last hundred years, there has been a large shift from manual labor jobs (e.g. farming, manufacturing, building) to office jobs which is due to many contributing factors including globalization,outsourcing
Outsourcing is a business practice in which companies use external providers to carry out business processes that would otherwise be handled internally. Outsourcing sometimes involves transferring employees and assets from one firm to another ...
of jobs and technological advances (specifically internet and computers). In 1960, there was a decline of jobs requiring moderate physical activity from 50% to 20%, and one in two Americans had a physically demanding job, while in 2011 this ratio was one in five. From 1990 to 2016, there was a decrease of about one third in manual labor jobs/employment. In 2008, the United States American National Health Interview Survey found that 36% of adults were inactive, and 59% of adult respondents never participated in vigorous physical activity lasting more than 10 minutes per week. According to a 2018 study, office based workers typically spend 70-85% sitting. In the US population, prevalence of sitting watching television or videos at least 2 h/d was high in 2015-2016 (ranging from 59% to 65%); the estimated prevalence of computer use outside school or work for at least 1 h/d increased from 2001 to 2016 (from 43% to 56% for children, from 53% to 57% among adolescents, and from 29% to 50% for adults); and estimated total sitting time increased from 2007 to 2016 (from 7.0 to 8.2 h/d among adolescents and from 5.5 to 6.4 h/d among adults).
See also
* Active design *Active mobility
Active mobility, soft mobility, active travel, active transport or active transportation is the transport of people or goods, through non-motorized means, based around human physical activity. The best-known forms of active mobility are walking ...
* Car dependency
* Childhood obesity
Childhood obesity is a condition where excess adipose tissue, body fat negatively affects a child's health or well-being. As methods to determine body fat directly are difficult, the diagnosis of obesity is often based on Body mass index, BMI. ...
* Couch potato
* Cyclability
* Cycling advocacy
* Effects of cars
* Effects of the car on societies
* Exercise trends
* Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
* Green exercise
* Healthy city
Healthy city is a term used in public health and urban design to stress the impact of policy on human health. It is a municipality that continually improves on a physical and a social level until environmental and pathological conditions are reac ...
* Lack of physical education
* Laziness
* Neurobiological effects of physical exercise
* Obesity and walking
* Physical activity
Physical activity is defined as any voluntary movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure.Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health, 2009. World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland. Accessed 13/07/2018 ...
* Preventable causes of death
* Simple living
Simple living refers to practices that promote simplicity in one's lifestyle. Common practices of simple living include reducing the number of possessions one owns, depending less on technology and services, and spending less money. In addition t ...
* Societal effects of cars
* Street reclamation
* Walkability
In urban planning, walkability is the accessibility of amenities within a reasonable walking distance. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it s ...
* Walking audit
* Workaholic
A workaholic is a person who works Compulsive behavior, compulsively. A workaholic experiences an inability to limit the amount of time they spend on work despite negative consequences such as damage to their relationships or health.
There is no ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
WHO fact sheet on physical activity
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sedentary Lifestyle Lifestyles Obesity Medical terminology