Sea levels on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an
 Precise determination of a "mean sea level" is difficult because of the many factors that affect sea level. US National Research Council, ''Bulletin of the National Research Council 1932'' page 270 Instantaneous sea level varies substantially on several scales of time and space. This is because the sea is in constant motion, affected by the tides,
Precise determination of a "mean sea level" is difficult because of the many factors that affect sea level. US National Research Council, ''Bulletin of the National Research Council 1932'' page 270 Instantaneous sea level varies substantially on several scales of time and space. This is because the sea is in constant motion, affected by the tides,
 It is often necessary to compare the local height of the mean sea surface with a "level" reference surface, or geodetic datum, called the
It is often necessary to compare the local height of the mean sea surface with a "level" reference surface, or geodetic datum, called the
 Several terms are used to describe the changing relationships between sea level and dry land.
* "relative" means change relative to a fixed point in the sediment pile.
* "eustatic" refers to global changes in sea level relative to a fixed point, such as the centre of the earth, for example as a result of melting ice-caps.
* "steric" refers to global changes in sea level due to
Several terms are used to describe the changing relationships between sea level and dry land.
* "relative" means change relative to a fixed point in the sediment pile.
* "eustatic" refers to global changes in sea level relative to a fixed point, such as the centre of the earth, for example as a result of melting ice-caps.
* "steric" refers to global changes in sea level due to
 Local mean sea level (LMSL) is defined as the height of the sea with respect to a land benchmark, averaged over a period of time long enough that fluctuations caused by
Local mean sea level (LMSL) is defined as the height of the sea with respect to a land benchmark, averaged over a period of time long enough that fluctuations caused by
 Many factors can produce short-term changes in sea level, typically within a few metres, in timeframes ranging from minutes to months:
Many factors can produce short-term changes in sea level, typically within a few metres, in timeframes ranging from minutes to months:
Sec. 91.121
Sea Level Rise:Understanding the past – Improving projections for the futurePermanent Service for Mean Sea LevelMeasuring Sea Level from SpaceRising Tide Video: Scripps Institution of OceanographySea Levels Online: National Ocean Service (CO-OPS)Système d'Observation du Niveau des Eaux Littorales (SONEL)Sea level rise – How much and how fast will sea level rise over the coming centuries?
{{Authority control Geodesy Physical oceanography Oceanographical terminology Vertical datums
average
In colloquial, ordinary language, an average is a single number or value that best represents a set of data. The type of average taken as most typically representative of a list of numbers is the arithmetic mean the sum of the numbers divided by ...
surface level of one or more among Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's coastal bodies of water
A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more ra ...
from which heights such as elevation
The elevation of a geographic location (geography), ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational equipotenti ...
may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datum
In geodesy, surveying, hydrography and navigation, vertical datum or altimetric datum is a reference coordinate surface used for vertical positions, such as the elevations of Earth-bound features (terrain, bathymetry, water level, and built stru ...
a standardised geodetic datum
A geodetic datum or geodetic system (also: geodetic reference datum, geodetic reference system, or geodetic reference frame, or terrestrial reference frame) is a global datum reference or reference frame for unambiguously representing the positi ...
that is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
and marine navigation
Marine navigation is the art and science of steering a ship from a starting point (sailing) to a destination, efficiently and responsibly. It is an art because of the skill that the navigator must have to avoid the dangers of navigation, and it ...
, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013. ...
is measured to calibrate
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known ...
altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight level
In aviation, a flight level (FL) is an aircraft's altitude as determined by a pressure altimeter using the International Standard Atmosphere. It is expressed in hundreds of feet or metres. The altimeter setting used is the ISA sea level pressur ...
s. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead a long-term average of tide gauge
A tide gauge is a device for measuring the change in sea level relative to a vertical datum. It is also known as a mareograph, marigraph, and sea-level recorder.
When applied to freshwater continental water body, water bodies, the instrument may ...
readings at a particular reference location.
The term ''above sea level'' generally refers to the height above mean sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of a location's vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) in reference to a vertical datum based on a historic mean sea level. In geodesy, it is formalized as orthometric height. The zero level v ...
(AMSL). The term APSL means above present sea level, comparing sea levels in the past with the level today.
Earth's radius at sea level is 6,378.137 km (3,963.191 mi) at the equator. It is 6,356.752 km (3,949.903 mi) at the poles and 6,371.001 km (3,958.756 mi) on average. This flattened spheroid, combined with local gravity anomalies, defines the geoid
The geoid ( ) is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is exte ...
of the Earth, which approximates the local mean sea level for locations in the open ocean. The geoid includes a significant depression in the Indian Ocean, whose surface dips as much as below the global mean sea level (excluding minor effects such as tides and currents).
Measurement
 Precise determination of a "mean sea level" is difficult because of the many factors that affect sea level. US National Research Council, ''Bulletin of the National Research Council 1932'' page 270 Instantaneous sea level varies substantially on several scales of time and space. This is because the sea is in constant motion, affected by the tides,
Precise determination of a "mean sea level" is difficult because of the many factors that affect sea level. US National Research Council, ''Bulletin of the National Research Council 1932'' page 270 Instantaneous sea level varies substantially on several scales of time and space. This is because the sea is in constant motion, affected by the tides, wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heatin ...
, atmospheric pressure, local gravitational differences, temperature, salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
, and so forth. The mean sea level at a particular location may be calculated over an extended time period and used as a datum
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous value (semiotics), values that convey information, describing the quantity, qualitative property, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols t ...
. For example, hourly measurements may be averaged over a full Metonic 19-year lunar cycle
The Metonic cycle or enneadecaeteris (from , from ἐννεακαίδεκα, "nineteen") is a period of almost exactly 19 years after which the lunar phases recur at the same time of the year. The recurrence is not perfect, and by precise obser ...
to determine the mean sea level at an official tide gauge
A tide gauge is a device for measuring the change in sea level relative to a vertical datum. It is also known as a mareograph, marigraph, and sea-level recorder.
When applied to freshwater continental water body, water bodies, the instrument may ...
.
''Still-water level'' or ''still-water sea level'' (SWL) is the level of the sea with motions such as wind waves
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of Body of water, bodies of water as a result of the wind blowing over the water's surface. The contact distance in the wind directi ...
averaged out.
Then MSL implies the SWL further averaged over a period of time such that changes due to, e.g., the tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s, also have zero mean.
''Global MSL'' refers to a spatial average over the entire ocean area, typically using large sets of tide gauges and/or satellite measurements.
One often measures the values of MSL with respect to the land; hence a change in ''relative MSL'' or (relative sea level Relative sea level (RSL) is defined as the sea level that is observed with respect to a land-based reference frame. It is often contrasted with eustatic sea level, which is a measure of the total mass or volume of the oceans. Relative sea level can ...
) can result from a real change in sea level, or from a change in the height of the land on which the tide gauge operates, or both.
In the UK, the ordnance datum
An ordnance datum (OD) is a vertical datum used by an ordnance survey as the basis for deriving altitudes on maps. A spot height may be expressed as above ordnance datum (AOD). Usually mean sea level (MSL) at a particular place is used for the d ...
(the 0 metres height on UK maps) is the mean sea level measured at Newlyn
Newlyn () is a seaside town and fishing port in south-west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 203 ''Land's End'' It is the largest fishing port in England.
Newlyn lies on the shore of Mount's Bay and for ...
in Cornwall between 1915 and 1921. Before 1921, the vertical datum
In geodesy, surveying, hydrography and navigation, vertical datum or altimetric datum is a reference coordinate surface used for vertical positions, such as the elevations of Earth-bound features (terrain, bathymetry, water level, and built stru ...
was MSL at the Victoria Dock, Liverpool.
Since the times of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and its other former parts, now independent states, the sea level is measured from the zero level of Kronstadt
Kronstadt (, ) is a Russian administrative divisions of Saint Petersburg, port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg, near the head ...
Sea-Gauge.
In Hong Kong, "mPD" is a surveying term meaning "metres above Principal Datum" and refers to height of above chart datum and below the average sea level.
In France, the Marégraphe in Marseilles measures continuously the sea level since 1883 and offers the longest collated data about the sea level. It is used for a part of continental Europe and the main part of Africa as the official sea level. Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
uses the reference to measure heights below or above sea level at Alicante
Alicante (, , ; ; ; officially: ''/'' ) is a city and municipalities of Spain, municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean port. The population ...
, while the European Vertical Reference System is calibrated to the Amsterdam Peil elevation, which dates back to the 1690s.
Satellite altimeters have been making precise measurements of sea level since the launch of TOPEX/Poseidon in 1992. A joint mission of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
and CNES
CNES () is the French national space agency. Headquartered in central Paris, the agency is overseen by the ministries of the Armed Forces, Economy and Finance and Higher Education, Research and Innovation.
It operates from the Toulouse Spac ...
, TOPEX/Poseidon was followed by Jason-1 in 2001 and the Ocean Surface Topography Mission on the Jason-2 satellite in 2008.
Height above mean sea level
''Height above mean sea level'' (''AMSL'') is the elevation (on the ground) or altitude (in the air) of an object, relative to a reference datum for mean sea level (MSL). It is also used in aviation, where some heights are recorded and reported with respect to mean sea level (contrast withflight level
In aviation, a flight level (FL) is an aircraft's altitude as determined by a pressure altimeter using the International Standard Atmosphere. It is expressed in hundreds of feet or metres. The altimeter setting used is the ISA sea level pressur ...
), and in the atmospheric sciences
Atmospheric science is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study ...
, and in land surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the land, terrestrial Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional or Three-dimensional space#In Euclidean geometry, three-dimensional positions of Point (geom ...
. An alternative is to base height measurements on a reference ellipsoid
An Earth ellipsoid or Earth spheroid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximation ...
approximating the entire Earth, which is what systems such as GPS do. In aviation, the reference ellipsoid known as WGS84 is increasingly used to define heights; however, differences up to exist between this ellipsoid height and local mean sea level. Another alternative is to use a geoid
The geoid ( ) is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is exte ...
-based vertical datum
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous value (semiotics), values that convey information, describing the quantity, qualitative property, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols t ...
such as NAVD88 and the global EGM96 (part of WGS84). Details vary in different countries.
When referring to geographic
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
features such as mountains, on a topographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
variations in elevation are shown by contour line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, isoquant or isarithm) of a Function of several real variables, function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a ...
s. A mountain's highest point or summit is typically illustrated with the AMSL height in metres, feet or both. In unusual cases where a land location is below sea level, such as Death Valley, California, the elevation AMSL is negative.
Difficulties in use
geoid
The geoid ( ) is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is exte ...
. In the absence of external forces, the local mean sea level would coincide with this geoid surface, being an equipotential surface of the Earth's gravitation
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
al field which, in itself, does not conform to a simple sphere or ellipsoid and exhibits gravity anomalies such as those measured by NASA's GRACE satellites. In reality, the geoid surface is not directly observed, even as a long-term average, due to ocean currents, air pressure variations, temperature and salinity variations, etc. The location-dependent but time-persistent separation between local mean sea level and the geoid is referred to as (mean) ocean surface topography. It varies globally in a typical range of ±.
Dry land
thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
and salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
variations.
* "isostatic" refers to changes in the level of the land relative to a fixed point in the earth, possibly due to thermal buoyancy or tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
effects, disregarding changes in the volume of water in the oceans.
The melting of glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s at the end of ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
s results in isostatic post-glacial rebound
Post-glacial rebound (also called isostatic rebound or crustal rebound) is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound an ...
, when land rises after the weight of ice is removed. Conversely, older volcanic islands experience relative sea level Relative sea level (RSL) is defined as the sea level that is observed with respect to a land-based reference frame. It is often contrasted with eustatic sea level, which is a measure of the total mass or volume of the oceans. Relative sea level can ...
rise, due to isostatic subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope mov ...
from the weight of cooling volcanos. The subsidence of land due to the withdrawal of groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
is another isostatic cause of relative sea level rise.
On planets that lack a liquid ocean, planetologists can calculate a "mean altitude" by averaging the heights of all points on the surface. This altitude, sometimes referred to as a "sea level" or zero-level elevation, serves equivalently as a reference for the height of planetary features.
Change
Local and eustatic
 Local mean sea level (LMSL) is defined as the height of the sea with respect to a land benchmark, averaged over a period of time long enough that fluctuations caused by
Local mean sea level (LMSL) is defined as the height of the sea with respect to a land benchmark, averaged over a period of time long enough that fluctuations caused by waves
United States Naval Reserve (Women's Reserve), better known as the WAVES (for Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service), was the women's branch of the United States Naval Reserve during World War II. It was established on July 21, 1942, ...
and tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s are smoothed out, typically a year or more. One must adjust perceived changes in LMSL to account for vertical movements of the land, which can occur at rates similar to sea level changes (millimetres per year).
Some land movements occur because of isostatic adjustment to the melting of ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
s at the end of the last ice age. The weight of the ice sheet depresses the underlying land, and when the ice melts away the land slowly rebounds. Changes in ground-based ice volume also affect local and regional sea levels by the readjustment of the geoid
The geoid ( ) is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is exte ...
and true polar wander
True polar wander is a solid-body rotation (or reorientation) of a planet or moon with respect to its spin axis, causing the geographic locations of the north and south poles to change, or "wander". In rotational equilibrium, a planetary body ha ...
. Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013. ...
, ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s and local ocean temperature changes can affect LMSL as well.
Eustatic sea level change (global as opposed to local change) is due to change in either the volume of water in the world's oceans or the volume of the oceanic basin
In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, most of the ocean basins are large Structural basin, geologic basins that are below sea level.
Most commonly the ocea ...
s. Two major mechanisms are currently causing eustatic sea level rise. First, shrinking land ice, such as mountain glaciers and polar ice sheets, is releasing water into the oceans. Second, as ocean temperatures rise, the warmer water expands.
Short-term and periodic changes
 Many factors can produce short-term changes in sea level, typically within a few metres, in timeframes ranging from minutes to months:
Many factors can produce short-term changes in sea level, typically within a few metres, in timeframes ranging from minutes to months:
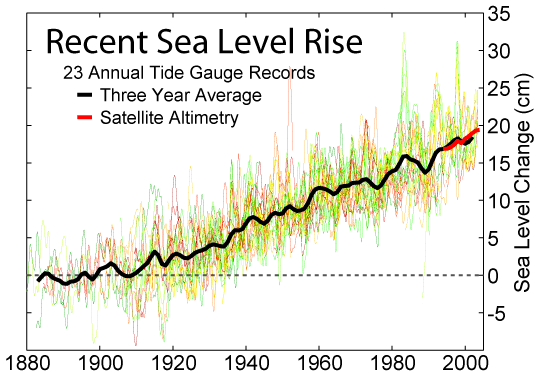
Recent changes
Aviation
Pilots can estimate height above sea level with analtimeter
An altimeter or an altitude meter is an instrument used to measure the altitude of an object above a fixed level. The measurement of altitude is called altimetry, which is related to the term bathymetry, the measurement of depth under water.
Ty ...
set to a defined barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.2 ...
. Generally, the pressure used to set the altimeter is the barometric pressure that would exist at MSL in the region being flown over. This pressure is referred to as either QNH or "altimeter" and is transmitted to the pilot by radio from air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled air ...
(ATC) or an automatic terminal information service
Automatic terminal information service, or ATIS, is a continuous broadcast of recorded aeronautical information in busier terminal areas. ATIS broadcasts contain essential information, such as current weather information, active runways, availabl ...
(ATIS). Since the terrain elevation is also referenced to MSL, the pilot can estimate height above ground by subtracting the terrain altitude from the altimeter reading. Aviation charts are divided into boxes and the maximum terrain altitude from MSL in each box is clearly indicated. Once above the transition altitude, the altimeter is set to the international standard atmosphere
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is a static atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes or elevations. It has been established to provide ...
(ISA) pressure at MSL which is 1013.25 hPa or 29.92 inHg.US Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is a Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation that regulates civil aviation in t ...
, Code of Federal RegulationSec. 91.121
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * (UK and Ireland) * * * * * *References
External links
Sea Level Rise:Understanding the past – Improving projections for the future
{{Authority control Geodesy Physical oceanography Oceanographical terminology Vertical datums