Scorpius–Centaurus association on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
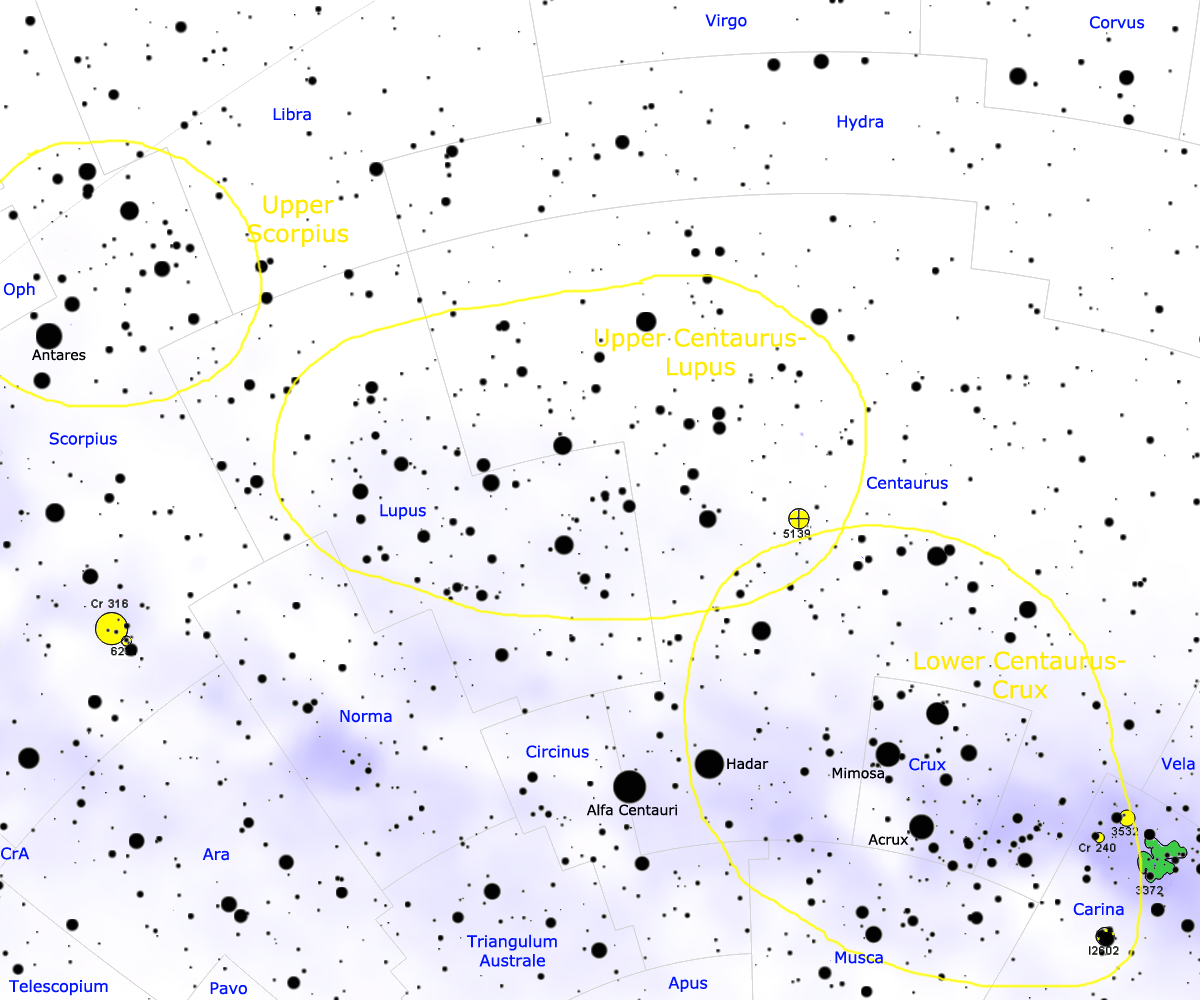
 The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130
The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130 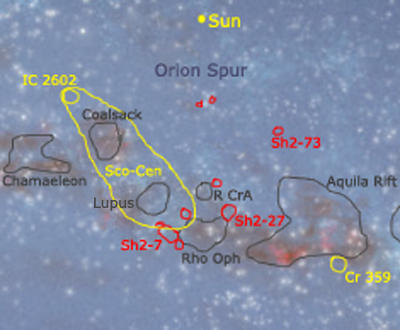 In December 2021, around 70 new
In December 2021, around 70 new
research paper
The subgroups of the Scorpius-Centaurus association contains the youngest transiting exoplanets: K2-33 b (11 Myrs), TOI-1227 b (11 Myrs) and HIP 67522 b (17 Myrs). It also contains directly imaged exoplanets such as UScoCTIO 108 b and the PDS 70 system.

 The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130
The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130 parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, a ...
s or 420 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 101 ...
s. Using improved Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial obj ...
data, Rizzuto and colleagues analysed nearby stars more closely, bringing the number of known members to 436. They doubt the need to add a subclassification because they found a more continuous spread of stars.
The Sco–Cen subgroups range in age from 11 million years (Upper Scorpius) to roughly 15 million years (Upper Centaurus–Lupus and Lower Centaurus–Crux). Many of the bright star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make ...
s in the constellations Scorpius, Lupus, Centaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. I ...
, and Crux
Crux () is a constellation of the southern sky that is centred on four bright stars in a cross-shaped asterism commonly known as the Southern Cross. It lies on the southern end of the Milky Way's visible band. The name ''Crux'' is Latin for ...
are members of the Sco–Cen association, including Antares (the most massive member of Upper Scorpius), and most of the stars in the Southern Cross. Hundreds of star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make ...
s have been identified as members of Sco-Cen, with masses ranging from roughly 15 solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass o ...
es (Antares) down to below the hydrogen-burning limit (i.e. brown dwarfs), and the total stellar population in each of the three subgroups is probably of the order 1000–2000.
The Sco–Cen OB association appears to be the most pronounced part of a large complex of recent (<20 million years) and ongoing star-formation. The complex contains several star-forming molecular clouds in Sco–Cen's immediate vicinity—the Rho Oph, Pipe Nebula, Barnard 68, Chamaeleon, Lupus, Corona Australis, and Coalsack cloud complexes (all at distances of ~120-200 parsecs), and several less populous, young stellar groups on the periphery of Sco–Cen, including the ~3–5 million-year-old epsilon Cha group, ~7 million-year-old eta Chamaeleontis cluster (also called Mamajek 1), ~8 million-year-old TW Hydrae association, ~12 million-year-old Beta Pictoris moving group, and possibly the ~30–50 million-year-old IC 2602 open cluster.
The stellar members of the Sco–Cen association have convergent proper motions of approximately 0.02–0.04 arcseconds
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
per year, indicative that the stars have nearly parallel velocity vectors, moving at about 20 km/s with respect to the Sun. The dispersion of the velocities within the subgroups are only of order 1–2 km/s, and the group is most likely gravitationally unbound. Several supernovae have exploded in Sco–Cen over the past 15 million years, leaving a network of expanding gas superbubbles around the group, including the Loop I Bubble
The Loop I Bubble is a cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm of the Milky Way. From our Sun's point of view, it is situated towards the Galactic Center of the Milky Way galaxy. Two conspicuous tunnels connect the Local Bubble wit ...
.
To explain the presence of radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consi ...
60 Fe in deep ocean ferromanganese crusts and in biogenic magnetite crystals within Pacific Ocean sediments it has been hypothesized that a nearby supernova, possibly a member of Sco–Cen, exploded in the Sun's vicinity roughly 3 million years ago, causing the Pliocene–Pleistocene boundary marine extinction. However, other findings cite the distance at which this supernova occurred at more than 100 parsec, maintaining that it is not likely not to have contributed to this extinction through the mechanism of what is known as the ultra-violet B (UV-B) catastrophe.
In 2019, researchers found interstellar iron in Antarctica which they relate to the Local Interstellar Cloud, which might have been formed near the Sco-Cen association.
 In December 2021, around 70 new
In December 2021, around 70 new rogue planet
A rogue planet (also termed a free-floating planet (FFP), interstellar, nomad, orphan, starless, unbound or wandering planet) is an interstellar object of planetary-mass, therefore smaller than fusors (stars and brown dwarfs) and without a ...
s were discovered in the Upper Scorpius association. See also attacheresearch paper
The subgroups of the Scorpius-Centaurus association contains the youngest transiting exoplanets: K2-33 b (11 Myrs), TOI-1227 b (11 Myrs) and HIP 67522 b (17 Myrs). It also contains directly imaged exoplanets such as UScoCTIO 108 b and the PDS 70 system.
See also
*List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups
This is a list of nearby stellar associations and moving groups. A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than an open cluster. A moving group is the remnant of such a stellar association. Members of stellar associations an ...
* β Pictoris moving group
* Ursa Major Moving Group
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Scorpius-Centaurus Association Stellar associations Scorpius (constellation) Centaurus (constellation) Lupus (constellation) Crux (constellation)