In
decision theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical ...
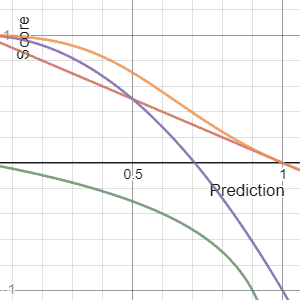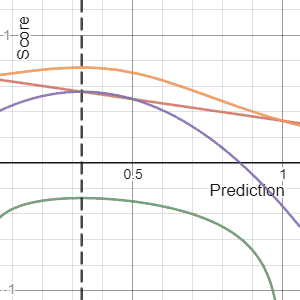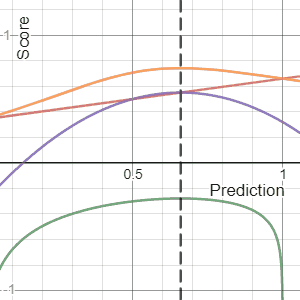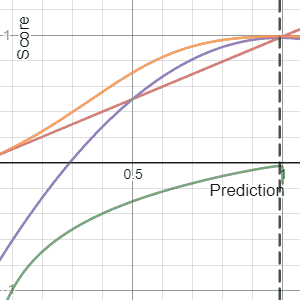
, a scoring rule
[
] provides a summary measure for the evaluation of
probabilistic predictions or forecasts. It is applicable to tasks in which predictions assign probabilities to events, i.e. one issues a probability distribution
as prediction. This includes probabilistic classification of a set of mutually exclusive outcomes or
classes.
On the other side, a scoring function
[
] provides a summary measure for the evaluation of point predictions, i.e. one predicts a property or functional
, like the
expectation
Expectation or Expectations may refer to:
Science
* Expectation (epistemic)
* Expected value, in mathematical probability theory
* Expectation value (quantum mechanics)
* Expectation–maximization algorithm, in statistics
Music
* ''Expectation' ...
or the
median.
Scoring rules and scoring functions can be thought of as "cost function" or "
loss function
In mathematical optimization and decision theory, a loss function or cost function (sometimes also called an error function) is a function that maps an event or values of one or more variables onto a real number intuitively representing some "co ...
". They are evaluated as empirical mean of a given sample, simply called score. Scores of different predictions or models can then be compared to conclude which model is best.
If a cost is levied in proportion to a proper scoring rule, the minimal expected cost corresponds to reporting the true set of probabilities. Proper scoring rules are used in meteorology, finance, and pattern classification where a forecaster or algorithm will attempt to minimize the average score to yield refined, calibrated probabilities (i.e. accurate probabilities).
Definition
Consider a
sample space
In probability theory, the sample space (also called sample description space, possibility space, or outcome space) of an experiment or random trial is the set of all possible outcomes or results of that experiment. A sample space is usually de ...
, a
σ-algebra of subsets of
and a convex class
of probability measures on
. A function defined on
and taking values in the extended real line,
 In
In  In
In