Scolex on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the
 The scolex, which attaches to the intestine of the definitive host, is often minute in comparison with the proglottids. It is typically a four-sided knob, armed with suckers or hooks or both. In some species, the scolex is dominated by bothria, or "sucking grooves" that function like suction cups. Cyclophyllid cestodes can be identified by the presence of four suckers on their scolices."Flatworm". ''Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2010. Other species have ruffled or leaflike scolices, and there may be other structures to aid attachment.
In the larval stage the scolex is similarly shaped and is known as the protoscoleces.
The scolex, which attaches to the intestine of the definitive host, is often minute in comparison with the proglottids. It is typically a four-sided knob, armed with suckers or hooks or both. In some species, the scolex is dominated by bothria, or "sucking grooves" that function like suction cups. Cyclophyllid cestodes can be identified by the presence of four suckers on their scolices."Flatworm". ''Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2010. Other species have ruffled or leaflike scolices, and there may be other structures to aid attachment.
In the larval stage the scolex is similarly shaped and is known as the protoscoleces.
 Once anchored to the host's intestinal wall, tapeworms absorb nutrients through their surface as their food flows past them. Cestodes are unable to synthesise lipids, which they use for reproduction, and are therefore entirely dependent on their hosts.
The tapeworm body is composed of a series of segments called ''proglottids''. These are produced from the neck by mitotic growth, which is followed by transverse constriction. The segments become larger and more mature as they are displaced backwards by newer segments. Each proglottid contains an independent reproductive tract, and like some other flatworms, cestodes excrete waste through flame cells (''protonephridia'') located in the proglottids. The sum of the proglottids is called a strobila, which is thin and resembles a strip of tape; from this is derived the common name "tapeworm". Proglottids are continually being produced by the neck region of the scolex, as long as the scolex is attached and alive.
Mature proglottids are essentially bags of eggs, each of which is infective to the proper intermediate host. They are released and leave the host in feces, or migrate outwards as independent motile proglottids. The number of proglottids forming the tapeworm ranges from three to four thousand. Their layout comes in two forms: craspedote, meaning any given proglottid is overlapped by the previous proglottid, or acraspedote, indicating the proglottids do not overlap.
Once anchored to the host's intestinal wall, tapeworms absorb nutrients through their surface as their food flows past them. Cestodes are unable to synthesise lipids, which they use for reproduction, and are therefore entirely dependent on their hosts.
The tapeworm body is composed of a series of segments called ''proglottids''. These are produced from the neck by mitotic growth, which is followed by transverse constriction. The segments become larger and more mature as they are displaced backwards by newer segments. Each proglottid contains an independent reproductive tract, and like some other flatworms, cestodes excrete waste through flame cells (''protonephridia'') located in the proglottids. The sum of the proglottids is called a strobila, which is thin and resembles a strip of tape; from this is derived the common name "tapeworm". Proglottids are continually being produced by the neck region of the scolex, as long as the scolex is attached and alive.
Mature proglottids are essentially bags of eggs, each of which is infective to the proper intermediate host. They are released and leave the host in feces, or migrate outwards as independent motile proglottids. The number of proglottids forming the tapeworm ranges from three to four thousand. Their layout comes in two forms: craspedote, meaning any given proglottid is overlapped by the previous proglottid, or acraspedote, indicating the proglottids do not overlap.
/ref> The fossil Rugosusivitta, which was found in China at base of the Cambrian deposits in Yunnan just above the Ediacaran-Cambrian border, has great similarities to present day Cestodians. If correct, this would be the earliest example of a Platyzoan and also one of the earliest bilaterian body-fossils and might thus provide an insight to the living mode of Cestodians before they became specialized parasites.

 The evolutionary history of the Cestoda has been studied using
The evolutionary history of the Cestoda has been studied using

Tapeworm Infection
2005 * Mayo Clinic Website on infectious diseases
''Mayo Clinic - Tapeworm Infection''
2006 * Medline Plus
* University of South Carolina - School of Medicine
{{Authority control Guadalupian first appearances Extant Permian first appearances
flatworm
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegme ...
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclatu ...
(Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda (the other subclass is Cestodaria). Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cestodar ...
; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish infecting parasites.
All cestodes are parasitic; many have complex life histories
Life history may refer to:
* Life history theory, a theory of biological evolution that seeks to explain aspects of organisms' anatomy and behavior by reference to the way that their life histories have been shaped by natural selection
* Life h ...
, including a stage in a definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
Th ...
e develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, ''Diphyllobothrium
''Diphyllobothrium'' is a genus of tapeworms which can cause diphyllobothriasis in humans through consumption of raw or undercooked fish. The principal species causing diphyllobothriasis is ''D. latum'', known as the broad or fish tapeworm, or b ...
'' has at least two intermediate hosts, a crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
and then one or more freshwater fish; its definitive host is a mammal. Some cestodes are host-specific, while others are parasites of a wide variety of hosts. Some six thousand species have been described; probably all vertebrates can host at least one species.
The adult tapeworm has a scolex (head), a short neck, and a strobila (segmented body) formed of proglottids
Cestoda is a Class (biology), class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodi ...
. Tapeworms anchor themselves to the inside of the intestine of their host using their scolex, which typically has hooks, suckers, or both. They have no mouth, but absorb nutrients directly from the host's gut. The neck continually produces proglottids, each one containing a reproductive tract; mature proglottids are full of eggs, and fall off to leave the host, either passively in the feces or actively moving. All tapeworms are hermaphrodites, with each individual having both male and female reproductive organs.
Humans are subject to infection by several species of tapeworms if they eat undercooked meat such as pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved ...
(''Taenia solium
''Taenia solium'', the pork tapeworm, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm that uses humans as its definitive host and p ...
''), beef (''T. saginata
''Taenia saginata'' (synonym ''Taeniarhynchus saginatus''), commonly known as the beef tapeworm, is a zoonotic tapeworm belonging to the order Cyclophyllidea and genus ''Taenia''. It is an intestinal parasite in humans causing taeniasis (a ...
''), and fish (''Diphyllobothrium
''Diphyllobothrium'' is a genus of tapeworms which can cause diphyllobothriasis in humans through consumption of raw or undercooked fish. The principal species causing diphyllobothriasis is ''D. latum'', known as the broad or fish tapeworm, or b ...
''), or if they live in, or eat food prepared in, conditions of poor hygiene ('' Hymenolepis'' or ''Echinococcus
''Echinococcus'' is a genus within Cestoda, a parasitic class of the platyhelminthes phylum (colloquially known as flatworms). Human echinococcosis is an infectious disease caused by the following species: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, ...
'' species). The unproven concept of using tapeworms as a slimming aid has been touted since around 1900.
Diversity and habitat
All 6,000 species of Cestoda areparasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of lif ...
s, mainly intestinal; their definitive hosts are vertebrates, both terrestrial and marine, while their intermediate hosts include insects, crustaceans, molluscs, and annelids as well as other vertebrates.
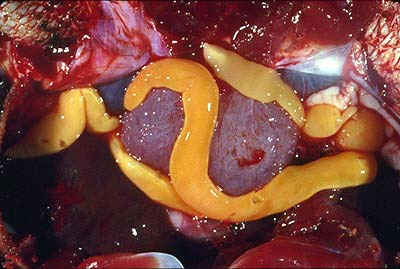
''T. saginata'', the beef tapeworm, can grow up to 20 m (65 ft); the largest species, the whale tapeworm '' Tetragonoporus calyptocephalus'', can grow to over 30 m (100 ft). Species with small hosts tend to be small. For example, vole and lemming tapeworms are only in length, and those parasitizing shrews only .
Anatomy
Cestodes have no gut or mouth and absorb nutrients from the host's alimentary tract through their specialised neodermal cuticle, ortegument
Tegument may refer to:
* Integumentary system, a protective organ system forming the outermost layer of an animal's body
* Tegument (helminth) Tegument is a term in helminthology for the outer body covering of members of the phylum Platyhelminthe ...
, through which gas exchange also takes place. The tegument also protects the parasite from the host's digestive enzymes and allows it to transfer molecules back to the host.
The body form of adult eucestodes is simple, with a scolex, or grasping head, adapted for attachment to the definitive host, a short neck, and a strobila, or segmented trunk formed of proglottids, which makes up the worm's body. Members of the subclass Cestodaria, the Amphilinidea and Gyrocotylidea, are wormlike but not divided into proglottids. Amphilinids have a muscular proboscis at the front end; Gyrocotylids have a sucker or proboscis which they can pull inside or push outside at the front end, and a holdfast rosette at the posterior end.
The Cestodaria have 10 larval hooks while Eucestoda have 6 larval hooks.
Scolex
 The scolex, which attaches to the intestine of the definitive host, is often minute in comparison with the proglottids. It is typically a four-sided knob, armed with suckers or hooks or both. In some species, the scolex is dominated by bothria, or "sucking grooves" that function like suction cups. Cyclophyllid cestodes can be identified by the presence of four suckers on their scolices."Flatworm". ''Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2010. Other species have ruffled or leaflike scolices, and there may be other structures to aid attachment.
In the larval stage the scolex is similarly shaped and is known as the protoscoleces.
The scolex, which attaches to the intestine of the definitive host, is often minute in comparison with the proglottids. It is typically a four-sided knob, armed with suckers or hooks or both. In some species, the scolex is dominated by bothria, or "sucking grooves" that function like suction cups. Cyclophyllid cestodes can be identified by the presence of four suckers on their scolices."Flatworm". ''Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2010. Other species have ruffled or leaflike scolices, and there may be other structures to aid attachment.
In the larval stage the scolex is similarly shaped and is known as the protoscoleces.
Body systems
Circular and longitudinal muscles lie under the neodermis, beneath which further longitudinal, dorso-ventral and transverse muscles surround the central parenchyma. Protonephridial cells drain into the parenchyma. There are four longitudinal collection canals, two dorso-lateral and two ventro-lateral, running along the length of the worm, with a transverse canal linking the ventral ones at the posterior of each segment. When the proglottids begin to detach, these canals open to the exterior through the terminal segment. The main nerve centre of a cestode is a cerebral ganglion in its scolex. Nerves emanate from the ganglion to supply the general body muscular and sensory endings, with two lateral nerve cords running the length of the strobila. The cirrus and vagina are innervated, and sensory endings around the genital pore are more plentiful than in other areas. Sensory function includes both tactoreception (touch) and chemoreception (smell or taste).Proglottids
 Once anchored to the host's intestinal wall, tapeworms absorb nutrients through their surface as their food flows past them. Cestodes are unable to synthesise lipids, which they use for reproduction, and are therefore entirely dependent on their hosts.
The tapeworm body is composed of a series of segments called ''proglottids''. These are produced from the neck by mitotic growth, which is followed by transverse constriction. The segments become larger and more mature as they are displaced backwards by newer segments. Each proglottid contains an independent reproductive tract, and like some other flatworms, cestodes excrete waste through flame cells (''protonephridia'') located in the proglottids. The sum of the proglottids is called a strobila, which is thin and resembles a strip of tape; from this is derived the common name "tapeworm". Proglottids are continually being produced by the neck region of the scolex, as long as the scolex is attached and alive.
Mature proglottids are essentially bags of eggs, each of which is infective to the proper intermediate host. They are released and leave the host in feces, or migrate outwards as independent motile proglottids. The number of proglottids forming the tapeworm ranges from three to four thousand. Their layout comes in two forms: craspedote, meaning any given proglottid is overlapped by the previous proglottid, or acraspedote, indicating the proglottids do not overlap.
Once anchored to the host's intestinal wall, tapeworms absorb nutrients through their surface as their food flows past them. Cestodes are unable to synthesise lipids, which they use for reproduction, and are therefore entirely dependent on their hosts.
The tapeworm body is composed of a series of segments called ''proglottids''. These are produced from the neck by mitotic growth, which is followed by transverse constriction. The segments become larger and more mature as they are displaced backwards by newer segments. Each proglottid contains an independent reproductive tract, and like some other flatworms, cestodes excrete waste through flame cells (''protonephridia'') located in the proglottids. The sum of the proglottids is called a strobila, which is thin and resembles a strip of tape; from this is derived the common name "tapeworm". Proglottids are continually being produced by the neck region of the scolex, as long as the scolex is attached and alive.
Mature proglottids are essentially bags of eggs, each of which is infective to the proper intermediate host. They are released and leave the host in feces, or migrate outwards as independent motile proglottids. The number of proglottids forming the tapeworm ranges from three to four thousand. Their layout comes in two forms: craspedote, meaning any given proglottid is overlapped by the previous proglottid, or acraspedote, indicating the proglottids do not overlap.
Reproduction
Cestodes are exclusivelyhermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have ...
s, with both male and female reproductive systems in each body. The reproductive system includes one or more testes, cirri, vas deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled t ...
, and seminal vesicles as male organs, and a single lobed or unlobed ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the bod ...
with the connecting oviduct
The oviduct in mammals, is the passageway from an ovary. In human females this is more usually known as the Fallopian tube or uterine tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, ...
and uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
as female organs. The common external opening for both male and female reproductive systems is known as the genital pore, which is situated at the surface opening of the cup-shaped atrium.Cheng, T.C. (1986). ''General Parasitology (2nd edn)''. Academic Press, Division of Hardcourt Brace & Company, USA, pp. 402–416. Though they are sexually hermaphroditic and cross-fertilization is the norm, self-fertilization sometimes occurs and makes possible the reproduction of a worm when it is the only individual in its host's gut. During copulation, the cirri of one individual connect with those of the other through the genital pore, and then spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell (biology), cell, or moving form of the ploidy, haploid cell (biology), cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon Fertilization, joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote ...
are exchanged.
Life cycle
Cestodes are parasites of vertebrates, with each species infecting a single definitive host or group of closely related host species. All but amphilinids and gyrocotylids (which burrow through the gut or body wall to reach the coelom) are intestinal, though some life-cycle stages rest in muscle or other tissues. The definitive host is always a vertebrate but in nearly all cases, one or more intermediate hosts are involved in the lifecycle, typicallyarthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s or other vertebrates. Infections can be long-lasting; in humans, tapeworm infection may last as much as 30 years. No asexual phases occur in the lifecycle, as they do in other flatworms, but the lifecycle pattern has been a crucial criterion for assessing evolution among Platyhelminthes.
Cestodes produce large numbers of eggs, but each one has a low probability of finding a host. To increase their chances, different species have adopted various strategies of egg release. In the Pseudophyllidea, many eggs are released in the brief period when their aquatic intermediate hosts are abundant (semelparity). In contrast, in the terrestrial Cyclophyllidea, proglottids are released steadily over a period of years, or as long as their host lives (iteroparity). Another strategy is to have very long-lived larvae; for example, in ''Echinococcus'', the hydatid larvae can survive for ten years or more in humans and other vertebrate hosts, giving the tapeworm an exceptionally long time window in which to find another host.
Many tapeworms have a two-phase lifecycle with two types of host. The adult ''Taenia saginata'' lives in the gut of a primate such as a human, its definitive host. Proglottids leave the body through the anus and fall to the ground, where they may be eaten with grass by a grazing animal such as a cow. This animal then becomes an intermediate host, the oncosphere boring through the gut wall and migrating to another part of the body such as the muscle. Here it encysts, forming a cysticercus. The parasite completes its lifecycle when the intermediate host passes on the parasite to the definitive host, usually when the definitive host eats contaminated parts of the intermediate host, for example a human eating raw or undercooked meat. Another two-phase lifecycle is exhibited by '' Anoplocephala perfoliata'', the definitive host being an equine and the intermediate host an oribatid mite
Oribatida (formerly Cryptostigmata), also known as oribatid mites, moss mites or beetle mites, are an order of mites, in the "chewing Acariformes" clade Sarcoptiformes. They range in size from . There are currently 12,000 species that have been i ...
.
''Diphyllobothrium
''Diphyllobothrium'' is a genus of tapeworms which can cause diphyllobothriasis in humans through consumption of raw or undercooked fish. The principal species causing diphyllobothriasis is ''D. latum'', known as the broad or fish tapeworm, or b ...
'' exhibits a more complex, three-phase lifecycle. If the eggs are laid in water, they develop into free-swimming oncosphere larvae. After ingestion by a suitable freshwater crustacean such as a copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have p ...
, the first intermediate host, they develop into procercoid larvae. When the copepod is eaten by a suitable second intermediate host, typically a minnow or other small freshwater fish, the procercoid larvae migrate into the fish's flesh where they develop into plerocercoid larvae. These are the infective stages for the mammalian definitive host. If the small fish is eaten by a predatory fish, its muscles too can become infected.
'' Schistocephalus solidus'' is another three-phase example. The intermediate hosts are copepods and small fish, and the definitive hosts are waterbirds. This species has been used to demonstrate that cross-fertilisation produces a higher infective success rate than self-fertilisation.
Host immunity
Hosts can become immune to infection by a cestode if the lining, the mucosa, of the gut is damaged. This exposes the host'simmune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
to cestode antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
s, enabling the host to mount an antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and Viral disease, viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique m ...
defence. Host antibodies can kill or limit cestode infection by damaging their digestive enzymes, which reduces their ability to feed and therefore to grow and to reproduce; by binding to their bodies; and by neutralising toxins that they produce. When cestodes feed passively in the gut, they do not provoke an antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and Viral disease, viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique m ...
reaction.
Evolution and phylogeny
Fossil history
Parasite fossils are rare, but recognizable clusters of cestode eggs, some with an operculum (lid) indicating that they had not erupted, one with a developing larva, have been discovered in fossil shark coprolites dating to thePermian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Pale ...
, some 270 million years ago."Tapeworm Eggs Discovered in 270-Million-Year-Old Fossil Shark faeces", ''ScienceDaily'', 30 January 2013/ref> The fossil Rugosusivitta, which was found in China at base of the Cambrian deposits in Yunnan just above the Ediacaran-Cambrian border, has great similarities to present day Cestodians. If correct, this would be the earliest example of a Platyzoan and also one of the earliest bilaterian body-fossils and might thus provide an insight to the living mode of Cestodians before they became specialized parasites.
External
The position of the Cestoda within the Platyhelminthes and otherSpiralia
The Spiralia are a morphologically diverse clade of protostome animals, including within their number the molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths and other taxa. The term ''Spiralia'' is applied to those phyla that exhibit canonical spiral cleavage, a ...
n phyla based on genomic analysis is shown in the phylogenetic tree. The non-parasitic flatworms, traditionally grouped as the "Turbellaria
The Turbellaria are one of the traditional sub-divisions of the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms), and include all the sub-groups that are not exclusively parasitic. There are about 4,500 species, which range from to large freshwater forms mor ...
", are paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
, as the parasitic Neodermata including the Cestoda arose within that grouping. The approximate times when major groups first appeared is shown in millions of years ago.
Internal


 The evolutionary history of the Cestoda has been studied using
The evolutionary history of the Cestoda has been studied using ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
, mitochondrial
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
and other DNA, and morphological analysis and continues to be revised. " Tetraphyllidea" is seen to be paraphyletic; " Pseudophyllidea" has been broken up into two orders, Bothriocephalidea
Bothriocephalidea is an order of Cestoda (tapeworms). Members of this order are gut parasites
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host ...
and Diphyllobothriidea. Hosts, whose phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spe ...
often mirrors that of the parasites (Fahrenholz's rule
Cospeciation is a form of coevolution in which the speciation of one species dictates speciation of another species and is most commonly studied in host-parasite relationships. In the case of a host-parasite relationship, if two hosts of the sam ...
), are indicated in italics and parentheses, the life-cycle sequence (where known) shown by arrows as ''(intermediate host1 �� intermediate host2 → definitive host)''. Alternatives, generally for different species within an order, are shown in square brackets.
The Taeniidae, including species such as the pork tapeworm and the beef tapeworm that often infect humans, may be the most basal of the 12 orders of the Cyclophyllidea.
Interactions with humans

Infection and treatment
Like other species of mammal, humans can become infected with tapeworms. There may be few or no symptoms, and the first indication of the infection may be the presence of one or more proglottids in the stools. The proglottids appear as flat, rectangular, whitish objects about the size of a grain of rice, which may change size or move about. Bodily symptoms which are sometimes present include abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, increased appetite and weight loss. There are several classes of anthelminthic drugs, some effective against many kinds of parasite, others more specific; these can be used both preventatively and to treat infections. For example, praziquantel is an effective treatment for tapeworm infection, and is preferred over the older niclosamide. While accidental tapeworm infections in developed countries are quite rare, such infections are more likely to occur in countries with poor sanitation facilities or where food hygiene standards are low.History and culture
Inancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, the comic playwright Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; grc, Ἀριστοφάνης, ; c. 446 – c. 386 BC), son of Philippus, of the deme Kydathenaion ( la, Cydathenaeum), was a comic playwright or comedy-writer of ancient Athens and a poet of Old Attic Comedy. Eleven of his fo ...
and philosopher Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
described the lumps that form during cysticercosis as "hailstones". In Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
times, in '' The Canon of Medicine'', completed in 1025, the Persian physician Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islam ...
recorded parasites including tapeworms. In the Early Modern period, Francesco Redi
Francesco Redi (18 February 1626 – 1 March 1697) was an Italian physician, naturalist, biologist, and poet. He is referred to as the "founder of experimental biology", and as the "father of modern parasitology". He was the first person to c ...
described and illustrated many parasites, and was the first to identify the cysts of '' Echinococcus granulosus'' seen in dogs and sheep as parasitic in origin; a century later, in 1760, Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810.
Life and work
Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son ...
correctly suggested that these were the larvae of tapeworms.
Tapeworms have occasionally appeared in fiction
In Fiction were an Australian five-piece melodic rock band from Adelaide.
Having formed in 2005, In Fiction signed to Boomtown Records in 2006 with their debut release '' The Four Letter Failure'' and featured as Triple J's "Next Crop" artist ...
. Peter Marren and Richard Mabey
Richard Thomas Mabey (born 20 February 1941) is a writer and broadcaster, chiefly on the relations between nature and culture.
Education
Mabey was educated at three independent schools, all in Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire. The first was at Roth ...
in ''Bugs Britannica'' write that Irvine Welsh's sociopathic policeman in his 1998 novel '' Filth'' owns a talking tapeworm, which they call "the most attractive character in the novel"; it becomes the policeman's ''alter ego
An alter ego (Latin for "other I", "doppelgänger") means an alternate self, which is believed to be distinct from a person's normal or true original personality. Finding one's alter ego will require finding one's other self, one with a differe ...
'' and better self. Mira Grant
Seanan McGuire (pronounced SHAWN-in; born January 5, 1978 in Martinez, California) is an American author and filker. McGuire is known for her urban fantasy novels. She uses the pseudonym Mira Grant to write science fiction/ horror and the pseudon ...
's 2013 novel ''Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of lif ...
'' envisages a world where people's immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
s are maintained by genetically engineered tapeworms. Tapeworms are prominently mentioned in the System of a Down
System of a Down (also known as SoaD or simply System) is an Armenian-American heavy metal band formed in Glendale, California, in 1994. Since 1997, the band has consisted of Serj Tankian (lead vocals, keyboards); Daron Malakian (guitar, v ...
song " Needles": their inclusion within the song result in a lyrical dispute among band members.
There are unproven claims that, around 1900, tapeworm eggs were marketed to the public as slimming tablets. A full-page coloured image, purportedly from a women's magazine of that period, reads "Fat: the enemy ... that is banished! How? With sanitized tape worms. Jar packed. No ill effects!" When television presenter Michael Mosley
Michael Hugh Mosley (22 March 1957 – 5 June 2024) was a British television and radio journalist, producer, presenter and writer who worked for the BBC from 1985 until his death. He presented television programmes on biology and medicine a ...
deliberately infected himself with tapeworms he gained weight due to increased appetite. Dieters still sometimes risk intentional infection, evidenced by a 2013 warning on American television.
Notes
References
Further reading
* ''Merck Manual of Medication' Information'', Second Home Edition, Online VersionTapeworm Infection
2005 * Mayo Clinic Website on infectious diseases
''Mayo Clinic - Tapeworm Infection''
2006 * Medline Plus
* University of South Carolina - School of Medicine
{{Authority control Guadalupian first appearances Extant Permian first appearances