Schmitt Gillenwater Kelly Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Schmitt Gillenwater Kelly syndrome is a rare
 Another symptom of the individuals with the syndrome was Bilaterally symmetrical triphalangeal thumbs had three phalanges rather than two, and a longer finger like appearance. The thumbs were non-opposable.
Another symptom of the individuals with the syndrome was Bilaterally symmetrical triphalangeal thumbs had three phalanges rather than two, and a longer finger like appearance. The thumbs were non-opposable.
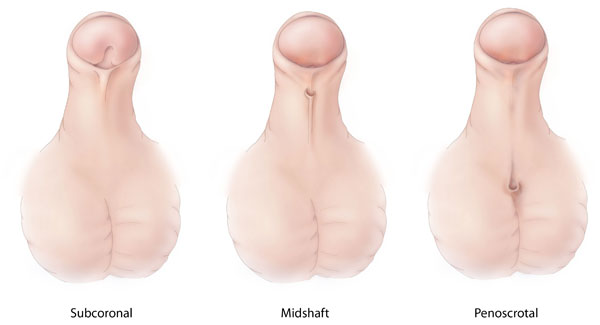 In the males,
In the males,
 The family also had Anterior Maxillary Diastema, a space between the upper incisors.
The family also had Anterior Maxillary Diastema, a space between the upper incisors.
autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in au ...
dominant congenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
consisting of radial hypoplasia, triphalangeal thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
s, hypospadias
Hypospadias is a common variation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location in the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth abnormality of the male reproductive system, affecting abou ...
, and maxillary diastema
A diastema (plural diastemata, from Greek διάστημα, space) is a space or gap between two teeth. Many species of mammals have diastemata as a normal feature, most commonly between the incisors and molars. More colloquially, the condition ...
.
Discovery
It was first identified by Edward Schmitt, Jay Y. Gillenwater, Thadeus E. Kelly, and John M. Opitz in 1962, where they published their results in a case study. The family was found to be minimally restricted in normal functions, and lived relatively normal lives. The symptoms were consistent throughout all the members of the family, with the exception of all three of the boys havinghypospadias
Hypospadias is a common variation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location in the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth abnormality of the male reproductive system, affecting abou ...
.
Radial Hypoplasia
Signs and Symptoms
The family had hypoplastic radii, which resulted in approximately 50% shorterradii
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
. Because of this, the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
was bowed outwards with outermost part of the ulna being pushed towards the skin. This resulted in a shorter reach.
Causes
Although more research is needed, the genetic cause of radial hypoplasia is believed to come from a rare allele of theSonic hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog protein (SHH) is encoded for by the ''SHH'' gene. The protein is named after the character ''Sonic the Hedgehog''.
This signaling molecule is key in regulating embryonic morphogenesis in all animals. SHH controls organogenesis and ...
(Shh) gene. This gene produces the Shh protein that induces development of the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
, and the index, middle, ring, and pinky fingers while increasing the expression of fibroblast growth factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in the ...
(FGF), another signaling molecule, which induces development of the radius and thumb. Both Shh and FGF are widely expressed during early embryo development. When this rare allele of Shh gene is expressed, the result is reduced Shh protein production, which hampers FGF expression, potentially leading to radial hypoplasia.
Treatment and Prognosis
Treatment usually begins after birth and minor cases involve stretching, manipulation, and splinting. The goal of surgery is to increase length and straighten forearm and thumb reconstruction.Triphalangeal thumbs
Signs and Symptoms
 Another symptom of the individuals with the syndrome was Bilaterally symmetrical triphalangeal thumbs had three phalanges rather than two, and a longer finger like appearance. The thumbs were non-opposable.
Another symptom of the individuals with the syndrome was Bilaterally symmetrical triphalangeal thumbs had three phalanges rather than two, and a longer finger like appearance. The thumbs were non-opposable.
Causes
The cause of this condition is understood to be genetic in nature, but the exact mechanism is unknown. However, research has shown that the gene of interest is located inchromosome 7
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 159 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total DN ...
, with potential candidate genes including EN2 and the human homologs
A couple of homologous chromosomes, or homologs, are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during fertilization. Homologs have the same genes in the same locus (genetics), loci where they pr ...
of mouse genes Hx and Hm.
Treatment and Prognosis
Surgery is done to correct any variations in the thumb and improve appearance; methods would vary on a case by case basisHypospadia
Signs and Symptoms
 In the males,
In the males, Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a common variation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location in the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth abnormality of the male reproductive system, affecting abou ...
was seen, which is the opening of the urethra was at the underside of the penis rather than at the tip.
Causes
Hypospadias can come about as a result of imbalances in the Wnt, Shh, Hox, and BMP pathways during fetal development. The Wnt, Shh, Hox, and BMP families are widely expressed throughout development. During the development of male external genitalia, Shh acts as a central cue, indirectly activatingHoxa13
Homeobox protein Hox-A13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HOXA13'' gene.
Function
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four sep ...
and Hoxd13
Homeobox protein Hox-D13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HOXD13'' gene. This gene belongs to the homeobox family of genes. The homeobox genes encode a highly conserved family of transcription factors that play an important role in ...
by binding to the Patched
Patched (Ptc) is a conserved 12-pass transmembrane protein receptor that plays an obligate negative regulatory role in the Hedgehog signaling pathway in insects and vertebrates. Patched is an essential gene in embryogenesis for proper segm ...
receptor, and directly activating BMP2, Fgf10
Fibroblast growth factor 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGF10'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell s ...
, Wnt5a
Protein Wnt-5a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WNT5A'' gene.
Function
The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes that encode secreted signaling lipid modified glycoproteins. These proteins have been implicated i ...
, and BMP4
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by ''BMP4'' gene. BMP4 is found on chromosome 14q22-q23.
BMP4 is a member of the bone morphogenetic protein family which is part of the transforming growth factor-beta superfami ...
. Fgf10 induces further Shh expression, while BMP4 represses Wnt5a expression. Rare allelic expression of any one of these genes can result in hypospadias.
Treatment and Prognosis
Minor forms do not require reconstructive surgery; Interventions include: correcting the location of urethral opening, repairing skin near the urethra opening, and straightening penile shaft.Maxillary diastema
Signs and Symptoms
 The family also had Anterior Maxillary Diastema, a space between the upper incisors.
The family also had Anterior Maxillary Diastema, a space between the upper incisors.
Causes
It highly likely this condition is caused by a genetic factor, but the exact gene is unknown.Treatment and Prognosis
Treatment is centered around closing the gap between the incisors: either by veneers, braces, implants, or boding to conceal the gap.Similar diseases
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints a ...
- Is another autosomal dominant congenital condition. Symptoms consist of curved spine, thumb abnormalities, heart disease. Like Schmitt Gillenwater Kelly syndrome, surgery is done for cosmetic and reconstructive purposes. Unlike Schmitt GIllenwater Kelly Syndrome, Marfan syndrome has a higher likelihood of developing life-threatening complications.
References
External links
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system Autosomal dominant disorders Genetic disorders with OMIM but no gene Syndromes Rare diseases