Schlesien Verwaltungsgliederung 1905 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes,
 In the fourth century BC from the south, through the Kłodzko Valley, the Celts entered Silesia, and settled around Mount Ślęża near modern Wrocław, Oława and Strzelin.
Germanic peoples, Germanic Lugii tribes were first recorded within Silesia in the 1st century. West Slavs and Lechites arrived in the region around the 7th century, and by the early ninth century, their settlements had stabilized. Local West Slavs started to erect boundary structures like the Silesian Przesieka and the Silesia Walls. The eastern border of Silesian tribes, Silesian settlement was situated to the west of the Bytom, and east from Racibórz and Cieszyn. East of this line dwelt a closely related Lechitic tribe, the Vistulans. Their northern border was in the valley of the Barycz (river), Barycz River, north of which lived the Polans (western), Western Polans tribe who gave Name of Poland, Poland its name.R. Żerelik(in:) M. Czpliński (red.) Historia Śląska, Wrocław 2007, s. 21–22
The first known states in Silesia were Greater Moravia and Duchy of Bohemia, Bohemia. In the 10th century, the Polish ruler Mieszko I of the Piast dynasty incorporated Silesia into the newly established Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polish state. In 1000, the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Wrocław, Diocese of Wrocław was established as the oldest Catholic diocese in the region, and one of the oldest dioceses in Poland, subjugated to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Gniezno. Poland repulsed German invasions of Silesia in 1017 at Siege of Niemcza, Niemcza and in 1109 at Siege of Głogów, Głogów. During the History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Fragmentation of Poland, Silesia and the rest of the country were divided into Duchies of Silesia, many smaller duchies ruled by various Silesian Dukes of Silesia, dukes. During this time, German cultural and ethnic Germanization, influence increased as a result of Ostsiedlung, immigration from German-speaking states of the Holy Roman Empire. In 1178, parts of the Duchy of Kraków around Bytom, Oświęcim, Chrzanów, and Siewierz were transferred to the Silesian Piasts, although their population was primarily Vistulan and not of Silesian descent.
In 1241, the Mongol Empire, Mongols conducted their First Mongol invasion of Poland, first invasion of Poland, causing widespread panic and mass flight. They looted much of the region and defeated the combined Polish, Moravian and German forces led by Duke Henry II the Pious at the Battle of Legnica, which took place at Legnickie Pole near the Silesian city of Legnica. Upon the death of Orda Khan, the Mongols chose not to press forward further into Europe, but returned east to participate in the election of a new Grand Khan (leader).
Between 1289 and 1292, Bohemian king Wenceslaus II became ''suzerain'' of some of the Upper Silesian duchies. Polish monarchs had not renounced their hereditary rights to Silesia until 1335. The province became part of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, Bohemian Crown which was part of the Holy Roman Empire, however, a number of duchies remained under the rule of the Polish dukes from the houses of Piast, Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellon and House of Sobieski, Sobieski as formal Bohemian fiefdoms, some until the 17th–18th centuries. In 1469 sovereignty over the region passed to Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, and in 1490 it returned to Bohemia. In 1526 Silesia passed with the Bohemian Crown to the Habsburg monarchy.
In the 15th century, several changes were made to Silesia's borders. Parts of the territories which had been transferred to the Silesian Piasts in 1178 were bought by the Monarchs of Poland, Polish kings in the second half of the 15th century (the Duchy of Oświęcim in 1457; the Duchy of Zator in 1494). The Bytom area remained in the possession of the Silesian Piasts, though it was a part of the Diocese of Kraków. The Duchy of Krosno Odrzańskie (''Crossen'') was inherited by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1476, and with the renunciation of King Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I and the estates of Bohemia in 1538, became an integral part of Brandenburg. From 1645 until 1666, the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz was held in pawn by the Polish House of Vasa as dowry of the Polish queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, Cecylia Renata.
In the fourth century BC from the south, through the Kłodzko Valley, the Celts entered Silesia, and settled around Mount Ślęża near modern Wrocław, Oława and Strzelin.
Germanic peoples, Germanic Lugii tribes were first recorded within Silesia in the 1st century. West Slavs and Lechites arrived in the region around the 7th century, and by the early ninth century, their settlements had stabilized. Local West Slavs started to erect boundary structures like the Silesian Przesieka and the Silesia Walls. The eastern border of Silesian tribes, Silesian settlement was situated to the west of the Bytom, and east from Racibórz and Cieszyn. East of this line dwelt a closely related Lechitic tribe, the Vistulans. Their northern border was in the valley of the Barycz (river), Barycz River, north of which lived the Polans (western), Western Polans tribe who gave Name of Poland, Poland its name.R. Żerelik(in:) M. Czpliński (red.) Historia Śląska, Wrocław 2007, s. 21–22
The first known states in Silesia were Greater Moravia and Duchy of Bohemia, Bohemia. In the 10th century, the Polish ruler Mieszko I of the Piast dynasty incorporated Silesia into the newly established Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polish state. In 1000, the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Wrocław, Diocese of Wrocław was established as the oldest Catholic diocese in the region, and one of the oldest dioceses in Poland, subjugated to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Gniezno. Poland repulsed German invasions of Silesia in 1017 at Siege of Niemcza, Niemcza and in 1109 at Siege of Głogów, Głogów. During the History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Fragmentation of Poland, Silesia and the rest of the country were divided into Duchies of Silesia, many smaller duchies ruled by various Silesian Dukes of Silesia, dukes. During this time, German cultural and ethnic Germanization, influence increased as a result of Ostsiedlung, immigration from German-speaking states of the Holy Roman Empire. In 1178, parts of the Duchy of Kraków around Bytom, Oświęcim, Chrzanów, and Siewierz were transferred to the Silesian Piasts, although their population was primarily Vistulan and not of Silesian descent.
In 1241, the Mongol Empire, Mongols conducted their First Mongol invasion of Poland, first invasion of Poland, causing widespread panic and mass flight. They looted much of the region and defeated the combined Polish, Moravian and German forces led by Duke Henry II the Pious at the Battle of Legnica, which took place at Legnickie Pole near the Silesian city of Legnica. Upon the death of Orda Khan, the Mongols chose not to press forward further into Europe, but returned east to participate in the election of a new Grand Khan (leader).
Between 1289 and 1292, Bohemian king Wenceslaus II became ''suzerain'' of some of the Upper Silesian duchies. Polish monarchs had not renounced their hereditary rights to Silesia until 1335. The province became part of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, Bohemian Crown which was part of the Holy Roman Empire, however, a number of duchies remained under the rule of the Polish dukes from the houses of Piast, Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellon and House of Sobieski, Sobieski as formal Bohemian fiefdoms, some until the 17th–18th centuries. In 1469 sovereignty over the region passed to Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, and in 1490 it returned to Bohemia. In 1526 Silesia passed with the Bohemian Crown to the Habsburg monarchy.
In the 15th century, several changes were made to Silesia's borders. Parts of the territories which had been transferred to the Silesian Piasts in 1178 were bought by the Monarchs of Poland, Polish kings in the second half of the 15th century (the Duchy of Oświęcim in 1457; the Duchy of Zator in 1494). The Bytom area remained in the possession of the Silesian Piasts, though it was a part of the Diocese of Kraków. The Duchy of Krosno Odrzańskie (''Crossen'') was inherited by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1476, and with the renunciation of King Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I and the estates of Bohemia in 1538, became an integral part of Brandenburg. From 1645 until 1666, the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz was held in pawn by the Polish House of Vasa as dowry of the Polish queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, Cecylia Renata.
 In 1742, most of Silesia was seized by King Frederick II of Prussia, Frederick the Great of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in the War of the Austrian Succession, eventually becoming the Prussian Province of Silesia in 1815; consequently, Silesia became part of the German Empire when it was proclaimed in 1871.
After World War I, a part of Silesia, Upper Silesia, was contested by Germany and the newly independent Second Polish Republic. The League of Nations organized a Upper Silesia plebiscite, plebiscite to decide the issue in 1921. It resulted in 60% of votes being cast for Germany and 40% for Poland. Following the third Silesian uprising (1921), however, the easternmost portion of Upper Silesia (including Katowice), with a majority ethnic Polish population, was awarded to Poland, becoming the Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Silesian Voivodeship. The Prussian Province of Silesia within Germany was then divided into the provinces of Province of Lower Silesia, Lower Silesia and Province of Upper Silesia, Upper Silesia. Meanwhile, Austrian Silesia, the small portion of Silesia retained by Austria after the Silesian Wars, was mostly awarded to the new Czechoslovakia (becoming known as Czech Silesia and Zaolzie), although most of Cieszyn and territory to the east of it went to Poland.
In 1742, most of Silesia was seized by King Frederick II of Prussia, Frederick the Great of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in the War of the Austrian Succession, eventually becoming the Prussian Province of Silesia in 1815; consequently, Silesia became part of the German Empire when it was proclaimed in 1871.
After World War I, a part of Silesia, Upper Silesia, was contested by Germany and the newly independent Second Polish Republic. The League of Nations organized a Upper Silesia plebiscite, plebiscite to decide the issue in 1921. It resulted in 60% of votes being cast for Germany and 40% for Poland. Following the third Silesian uprising (1921), however, the easternmost portion of Upper Silesia (including Katowice), with a majority ethnic Polish population, was awarded to Poland, becoming the Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Silesian Voivodeship. The Prussian Province of Silesia within Germany was then divided into the provinces of Province of Lower Silesia, Lower Silesia and Province of Upper Silesia, Upper Silesia. Meanwhile, Austrian Silesia, the small portion of Silesia retained by Austria after the Silesian Wars, was mostly awarded to the new Czechoslovakia (becoming known as Czech Silesia and Zaolzie), although most of Cieszyn and territory to the east of it went to Poland.
 Polish Silesia was among the first regions invaded during Germany's 1939 invasion of Poland, attack on Poland, which started World War II. One of the claimed goals of Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Nazi German occupation, particularly in Upper Silesia, was the extermination of those whom Nazis viewed as "Untermensch, subhuman", namely Jews and ethnic Poles. The Polish and Jewish population of the then Polish part of Silesia was subjected to genocide involving Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany, expulsions, mass murder and deportation to Nazi concentration camps and Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, while Germans were settled in pursuit of ''Lebensraum''. Two thousand Polish intellectuals, politicians, and businessmen were murdered in the ''Intelligenzaktion, Intelligenzaktion Schlesien'' in 1940 as part of a Germanisation in Poland (1939–1945), Poland-wide Germanization program. Silesia also housed one of the two main wartime centers where medical experiments were conducted on Kidnapping of children by Nazi Germany, kidnapped Polish children by Nazis. Czech Silesia was German occupation of Czechoslovakia, occupied by Germany as part of so-called Sudetenland. In Silesia, Nazi Germany operated the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, several German prisoner-of-war camps in World War II, prisoner-of-war camps for Allies of World War II, Allied POWs (incl. the major Stalag VIII-A, Stalag VIII-B, Stalag VIII-C camps), numerous Nazi prisons and thousands of Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, including a network of forced labour camps solely for Poles (''Polenlager''), Subcamp (SS), subcamps of prisons, POW camps and of the Gross-Rosen and Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz concentration camps.
The Potsdam Conference of 1945 defined the Oder-Neisse line as the border between Germany and Poland, pending a final peace conference with Germany which eventually never took place. At the end of WWII, Germans in Silesia fled from the battle ground, assuming they would be able to return when the war was over. However, they could not return, and those who had stayed were expelled and a new Polish population, including people displaced from Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, former Eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union and from Central Poland, joined the surviving native Polish inhabitants of the region. After 1945 and in 1946, nearly all of the 4.5 million Silesians of German descent fled, or were interned in camps and expelled, including some thousand German Jews who survived the Holocaust and had returned to Silesia.
The newly formed Polish United Workers' Party created a Recovered Territories, Ministry of the Recovered Territories that claimed half of the available arable land for state-run collectivized farms. Many of the new Polish Silesians who resented the Germans for their invasion in 1939 and brutality in occupation now resented the newly formed Polish communist government for their population shifting and interference in agricultural and industrial affairs.
The administrative division of Silesia within Poland has changed several times since 1945. Since 1999, it has been divided between Lubusz Voivodeship, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Opole Voivodeship, and Silesian Voivodeship. Czech Silesia is now part of the Czech Republic, forming the Moravian-Silesian Region and the northern part of the Olomouc Region. Germany retains the Silesia-Lusatia region (''Niederschlesien-Oberlausitz'' or ''Schlesische Oberlausitz'') west of the Lusatian Neisse, Neisse, which is part of the federal state of Saxony.
The region was affected by the 1997 Central European flood.
Polish Silesia was among the first regions invaded during Germany's 1939 invasion of Poland, attack on Poland, which started World War II. One of the claimed goals of Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Nazi German occupation, particularly in Upper Silesia, was the extermination of those whom Nazis viewed as "Untermensch, subhuman", namely Jews and ethnic Poles. The Polish and Jewish population of the then Polish part of Silesia was subjected to genocide involving Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany, expulsions, mass murder and deportation to Nazi concentration camps and Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, while Germans were settled in pursuit of ''Lebensraum''. Two thousand Polish intellectuals, politicians, and businessmen were murdered in the ''Intelligenzaktion, Intelligenzaktion Schlesien'' in 1940 as part of a Germanisation in Poland (1939–1945), Poland-wide Germanization program. Silesia also housed one of the two main wartime centers where medical experiments were conducted on Kidnapping of children by Nazi Germany, kidnapped Polish children by Nazis. Czech Silesia was German occupation of Czechoslovakia, occupied by Germany as part of so-called Sudetenland. In Silesia, Nazi Germany operated the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, several German prisoner-of-war camps in World War II, prisoner-of-war camps for Allies of World War II, Allied POWs (incl. the major Stalag VIII-A, Stalag VIII-B, Stalag VIII-C camps), numerous Nazi prisons and thousands of Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, including a network of forced labour camps solely for Poles (''Polenlager''), Subcamp (SS), subcamps of prisons, POW camps and of the Gross-Rosen and Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz concentration camps.
The Potsdam Conference of 1945 defined the Oder-Neisse line as the border between Germany and Poland, pending a final peace conference with Germany which eventually never took place. At the end of WWII, Germans in Silesia fled from the battle ground, assuming they would be able to return when the war was over. However, they could not return, and those who had stayed were expelled and a new Polish population, including people displaced from Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, former Eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union and from Central Poland, joined the surviving native Polish inhabitants of the region. After 1945 and in 1946, nearly all of the 4.5 million Silesians of German descent fled, or were interned in camps and expelled, including some thousand German Jews who survived the Holocaust and had returned to Silesia.
The newly formed Polish United Workers' Party created a Recovered Territories, Ministry of the Recovered Territories that claimed half of the available arable land for state-run collectivized farms. Many of the new Polish Silesians who resented the Germans for their invasion in 1939 and brutality in occupation now resented the newly formed Polish communist government for their population shifting and interference in agricultural and industrial affairs.
The administrative division of Silesia within Poland has changed several times since 1945. Since 1999, it has been divided between Lubusz Voivodeship, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Opole Voivodeship, and Silesian Voivodeship. Czech Silesia is now part of the Czech Republic, forming the Moravian-Silesian Region and the northern part of the Olomouc Region. Germany retains the Silesia-Lusatia region (''Niederschlesien-Oberlausitz'' or ''Schlesische Oberlausitz'') west of the Lusatian Neisse, Neisse, which is part of the federal state of Saxony.
The region was affected by the 1997 Central European flood.
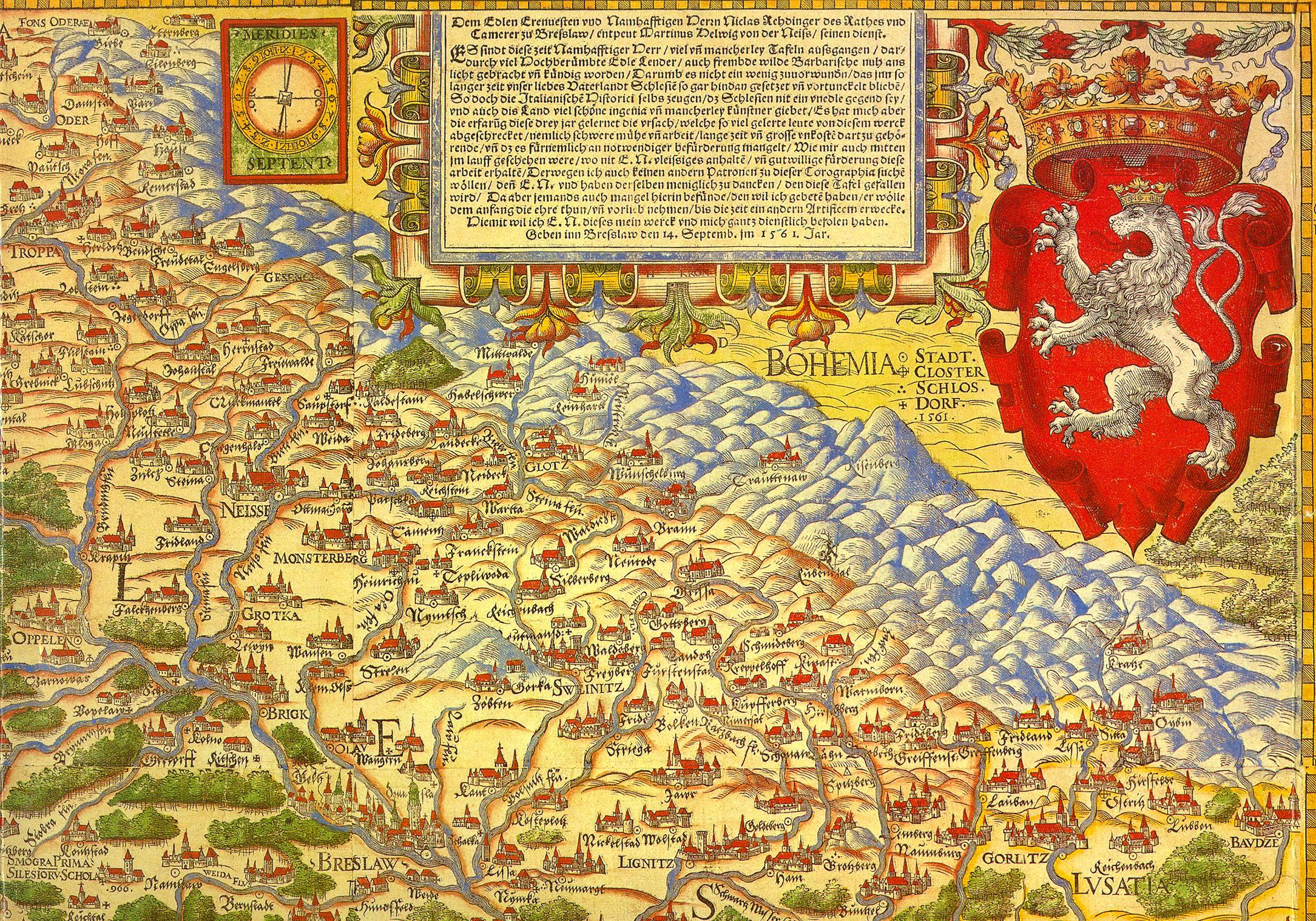 Most of Silesia is relatively flat, although its southern border is generally mountainous. It is primarily located in a swath running along both banks of the upper and middle Oder River, Oder (Odra) River, but it extends eastwards to the upper Vistula River. The region also includes many tributaries of the Oder, including the Bóbr (and its tributary the Kwisa), the Barycz (river), Barycz and the Nysa Kłodzka. The
Most of Silesia is relatively flat, although its southern border is generally mountainous. It is primarily located in a swath running along both banks of the upper and middle Oder River, Oder (Odra) River, but it extends eastwards to the upper Vistula River. The region also includes many tributaries of the Oder, including the Bóbr (and its tributary the Kwisa), the Barycz (river), Barycz and the Nysa Kłodzka. The
 The 41 coal mines in Silesia are mostly part of the Upper Silesian Coal Basin, which lies in the Silesian Upland. The coalfield has an area of about . Deposits in Lower Silesia have proven to be difficult to exploit and the area's unprofitable mines were closed in 2000. In 2008, an estimated 35 billion tonnes of lignite reserves were found near Legnica, making them some of the largest in the world.
From the fourth century BC, iron ore has been mined in the upland areas of Silesia. The same period had lead, copper, silver, and gold mining. Zinc, cadmium, arsenic, and uranium have also been mined in the region. Lower Silesia features large copper mining and processing between the cities of Legnica, Głogów, Lubin, and Polkowice.
The region is known for stone quarrying to produce limestone, marl, marble, and basalt.
The region also has a thriving agricultural sector, which produces cereals (wheat, rye, barley, oats, corn), potatoes, rapeseed, sugar beets and others. Milk production is well developed. The Opole Silesia has for decades occupied the top spot in Poland for their indices of effectiveness of agricultural land use.
Mountainous parts of southern Silesia feature many significant and attractive tourism destinations (e.g., Karpacz, Szczyrk, Wisła). Silesia is generally well forested. This is because greenness is generally highly desirable by the local population, particularly in the highly industrialized parts of Silesia.
The 41 coal mines in Silesia are mostly part of the Upper Silesian Coal Basin, which lies in the Silesian Upland. The coalfield has an area of about . Deposits in Lower Silesia have proven to be difficult to exploit and the area's unprofitable mines were closed in 2000. In 2008, an estimated 35 billion tonnes of lignite reserves were found near Legnica, making them some of the largest in the world.
From the fourth century BC, iron ore has been mined in the upland areas of Silesia. The same period had lead, copper, silver, and gold mining. Zinc, cadmium, arsenic, and uranium have also been mined in the region. Lower Silesia features large copper mining and processing between the cities of Legnica, Głogów, Lubin, and Polkowice.
The region is known for stone quarrying to produce limestone, marl, marble, and basalt.
The region also has a thriving agricultural sector, which produces cereals (wheat, rye, barley, oats, corn), potatoes, rapeseed, sugar beets and others. Milk production is well developed. The Opole Silesia has for decades occupied the top spot in Poland for their indices of effectiveness of agricultural land use.
Mountainous parts of southern Silesia feature many significant and attractive tourism destinations (e.g., Karpacz, Szczyrk, Wisła). Silesia is generally well forested. This is because greenness is generally highly desirable by the local population, particularly in the highly industrialized parts of Silesia.
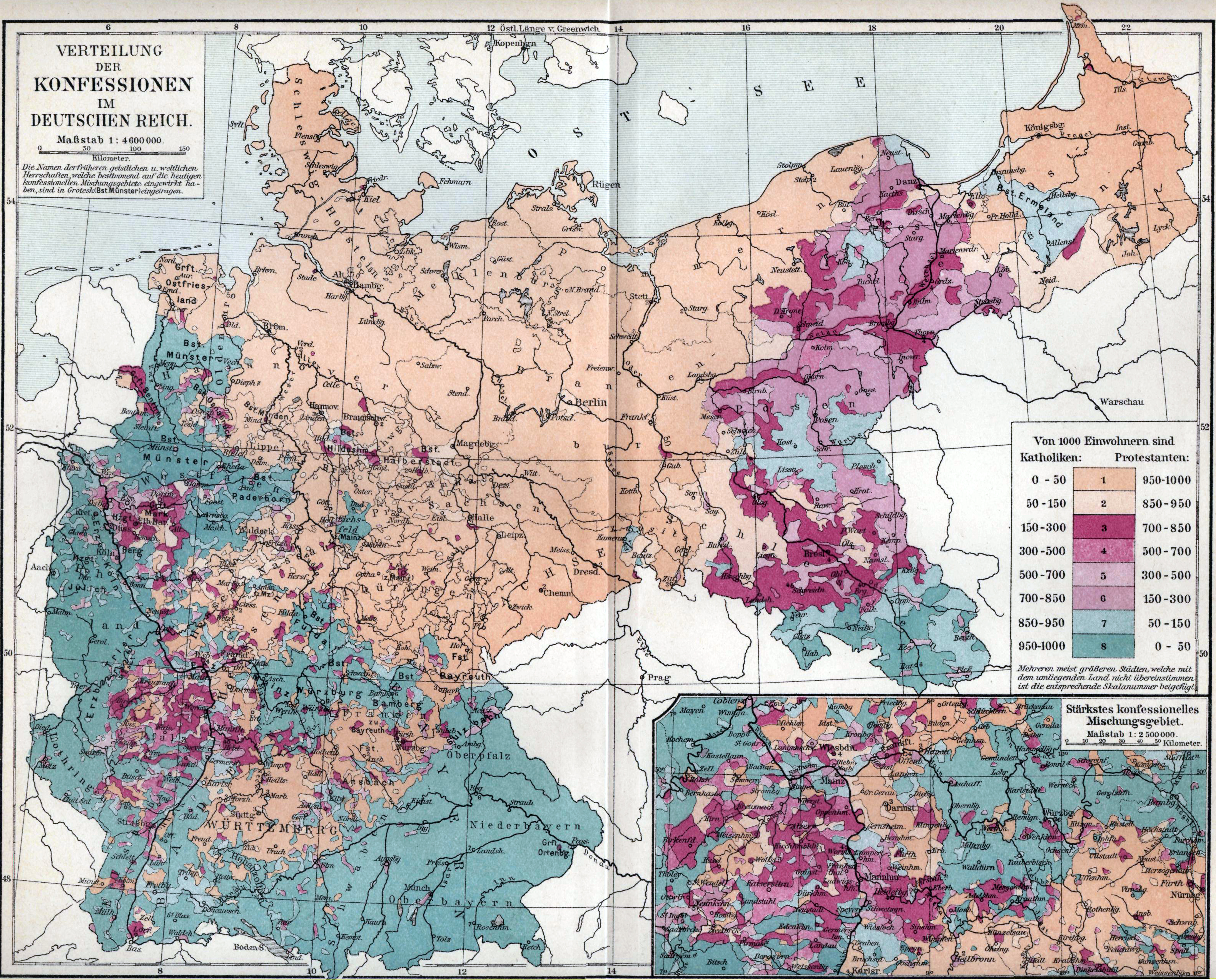 Historically, Silesia was about equally split between Protestants (overwhelmingly Lutherans) and Roman Catholics. In an 1890 census taken in the German part, Roman Catholics made up a slight majority of 53%, while the remaining 47% were almost entirely Lutheran. Geographically speaking, Lower Silesia was mostly Lutheran except for the Kłodzko Land, Glatzer Land (now Kłodzko County). Upper Silesia was mostly Roman Catholic except for some of its northwestern parts, which were predominantly Lutheran. Generally speaking, the population was mostly Protestant in the western parts, and it tended to be more Roman Catholic the further east one went. In Upper Silesia, Protestants were concentrated in larger cities and often identified as German. After World War II, the religious demographics changed drastically as Germans, who constituted the bulk of the Protestant population, Flight and expulsion of Germans, were forcibly expelled. Poles, who were mostly Roman Catholic, were resettled in their place. Today, Silesia remains predominantly Roman Catholic.
Existing since the 12th century, Silesia's Jewish community was concentrated around Wrocław and Upper Silesia, and numbered 48,003 (1.1% of the population) in 1890, decreasing to 44,985 persons (0.9%) by 1910. In Polish East Upper Silesia, the number of Jews was around 90,000–100,000. Historically the community had suffered a number of localised expulsions such as their 1453 expulsion from Wrocław. From 1712 to 1820 a succession of men held the title Chief Rabbi of Silesia ("Landesrabbiner"): Naphtali ha-Kohen (1712–16); Samuel ben Naphtali (1716–22); Ḥayyim Jonah Te'omim (1722–1727); Baruch b. Reuben Gomperz (1733–54); Joseph Jonas Fränkel (1754–93); Jeremiah Löw Berliner (1793–99); Lewin Saul Fränkel (1800–7); Aaron Karfunkel (1807–16); and Abraham ben Gedaliah Tiktin (1816–20).
Historically, Silesia was about equally split between Protestants (overwhelmingly Lutherans) and Roman Catholics. In an 1890 census taken in the German part, Roman Catholics made up a slight majority of 53%, while the remaining 47% were almost entirely Lutheran. Geographically speaking, Lower Silesia was mostly Lutheran except for the Kłodzko Land, Glatzer Land (now Kłodzko County). Upper Silesia was mostly Roman Catholic except for some of its northwestern parts, which were predominantly Lutheran. Generally speaking, the population was mostly Protestant in the western parts, and it tended to be more Roman Catholic the further east one went. In Upper Silesia, Protestants were concentrated in larger cities and often identified as German. After World War II, the religious demographics changed drastically as Germans, who constituted the bulk of the Protestant population, Flight and expulsion of Germans, were forcibly expelled. Poles, who were mostly Roman Catholic, were resettled in their place. Today, Silesia remains predominantly Roman Catholic.
Existing since the 12th century, Silesia's Jewish community was concentrated around Wrocław and Upper Silesia, and numbered 48,003 (1.1% of the population) in 1890, decreasing to 44,985 persons (0.9%) by 1910. In Polish East Upper Silesia, the number of Jews was around 90,000–100,000. Historically the community had suffered a number of localised expulsions such as their 1453 expulsion from Wrocław. From 1712 to 1820 a succession of men held the title Chief Rabbi of Silesia ("Landesrabbiner"): Naphtali ha-Kohen (1712–16); Samuel ben Naphtali (1716–22); Ḥayyim Jonah Te'omim (1722–1727); Baruch b. Reuben Gomperz (1733–54); Joseph Jonas Fränkel (1754–93); Jeremiah Löw Berliner (1793–99); Lewin Saul Fränkel (1800–7); Aaron Karfunkel (1807–16); and Abraham ben Gedaliah Tiktin (1816–20).
File:DEU Oberschlesien 1926-1945 COA.svg, Coat of arms of the Prussian province of Upper Silesia (1919–1938 and 1941–1945)
File:POL województwo śląskie COA.svg, Coat of arms of the Silesian Voivodeship
File:POL województwo opolskie COA.svg, coat of arms of the Opole Voivodeship, The coat of arms of the Opolskie Voivodeship
File:Henryk I Probus herb.png, Henryk IV's Probus coat of arms
File:Wappen Herzogtum Schlesien.png, Coat of arms of Austrian Silesia (1742–1918)
File:Wappen Provinz Niederschlesien.png, Prussian province of Lower Silesia (1919–1938 and 1941–1945)
File:POL województwo dolnośląskie COA.svg, Coat of arms of the Lower Silesia Voivodeship
File:Silesia.svg, Coat of arms of Czech Silesia
Flags with their colors refer to the coat of arms of Silesia.
File:Flagge Preußen - Provinz Oberschlesien.svg, Flag of Upper Silesia, Flag of Prussian Upper Silesia province (1919–1938 and 1941–1945)
File:POL województwo śląskie flag.svg, Flag of Silesia Voivodeship
File:Flag of Czech Silesia.svg, Flag of the Austrian Silesia (1742–1918), and Czech Silesia
File:Flagge Preußen - Provinz Schlesien.svg, Flag of Silesia and Lower Silesia, Flag of Prussian Lower Silesia province (1919–1938 and 1941–1945)
File:POL województwo dolnośląskie flag.svg, Flag of Lower Silesia Voivodeship
File:Swidnica- Kosciol Pokoju 02.jpg, Churches of Peace, Świdnica and Jawor
File:Wrocław - Jahrhunderthalle5.jpg, Hala Stulecia (Wrocław), Centennial Hall, Wrocław
File:SZTOLNIA GŁĘBOKA FRYDERYK - część trasy turystycznej pn. Sztolnia Czarnego Pastrąga.jpg, Historic Silver Mine in Tarnowskie Gory, Historic Silver Mine, Tarnowskie Góry
File:Das Neue Schloss im Park.jpg, Muskau Park, Łęknica and Bad MuskauŁęknica and Bad Muskau were considered part of Silesia in years 1815–1945.
Map of Silesia in 1763
* [http://culture.pl/en/article/what-is-silesia What is Silesia?] {{Authority control Silesia, Czech geographic history Divided regions Geography of Central Europe Historical regions in Germany Historical regions in Poland Historical regions
cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
, traditions, and the Silesian language
Silesian
* Polish: ''etnolekt śląski'', ''język śląski'', ''gwara śląska'', ''śląszczyzna''
* german: link=no, Schlonsakisch, Wasserpolnisch or Upper Silesian is a West Slavic ethnolect of either the Lechitic group or the Czech� ...
(minority in Upper Silesia).
Silesia is along the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows thr ...
River, with the Sudeten Mountains
The Sudetes ( ; pl, Sudety; german: Sudeten; cs, Krkonošsko-jesenická subprovincie), commonly known as the Sudeten Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince in Central Europe, shared by Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic. They consis ...
extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. The largest city and Lower Silesia's capital is Wrocław; the historic capital of Upper Silesia is Opole. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrava and the German city of Görlitz are within Silesia's borders.
Silesia's borders and national affiliation have changed over time, both when it was a hereditary possession of feudalism, noble houses and after the rise of modern nation-states, resulting in an abundance of List of castles in Poland, castles, especially in the List of castles and palaces in Jelenia Góra valley, Jelenia Góra valley. The first known states to hold power in Silesia were probably those of Greater Moravia at the end of the 9th century and Duchy of Bohemia, Bohemia early in the 10th century. In the 10th century, Silesia was incorporated into the early Polish state, and after its fragmentation in the 12th century it formed the Duchy of Silesia, a provincial duchy of Poland. As a result of further fragmentation, Silesia was divided into many Duchies of Silesia, duchies, ruled by various lines of the Polish Piast dynasty. In the 14th century, it became a constituent part of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, Bohemian Crown Lands under the Holy Roman Empire, which passed to the Austrian Habsburg monarchy in 1526, however, a number of duchies remained under the rule of Polish dukes from the houses of Piast, Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellon and House of Sobieski, Sobieski as formal Bohemian fiefdoms, some until the 17th–18th centuries. As a result of the Silesian Wars, the region was annexed by the German state of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in 1742.
After World War I, when the Poles and Czechs regained their independence, the easternmost part of Upper Silesia became again part of Poland by the decision of the Triple Entente, Entente Powers after Silesian Uprisings, insurrections by Poles and the Upper Silesian plebiscite, while the Austrian Silesia, remaining former Austrian parts of Silesia were divided between Czechoslovakia and Poland. During World War II, as a result of German occupation the entire region was under control of Nazi Germany. In 1945, after World War II, most of the German-held Silesia was transferred to Polish jurisdiction by the Potsdam Agreement between the victorious Allies of World War II, Allies and became again part of Poland, although with a Soviet Union, Soviet-installed Polish People's Republic, communist regime. The small Lusatian strip west of the Oder–Neisse line, which had belonged to Silesia since 1815, became part of East Germany.
As the result of the Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950), forced population shifts of 1945–48, today's inhabitants of Silesia speak the national languages of their respective countries. Previously German-speaking Lower Silesia had developed a new mixed Polish dialect and novel costumes. There is ongoing debate about whether the Silesian language
Silesian
* Polish: ''etnolekt śląski'', ''język śląski'', ''gwara śląska'', ''śląszczyzna''
* german: link=no, Schlonsakisch, Wasserpolnisch or Upper Silesian is a West Slavic ethnolect of either the Lechitic group or the Czech� ...
should be considered a dialect of Polish language, Polish or a separate language. The Lower Silesian language, Lower Silesian German dialect is nearing extinction due to its speakers' expulsion.
Etymology
The names of Silesia in different languages most likely share their etymology— pl, Śląsk ; german: link=no, Schlesien ; cs, Slezsko ; sli, Schläsing; szl, Ślōnsk ; dsb, Šlazyńska; hsb, Šleska; Latin, Spanish and English: ''Silesia''; french: link=no, Silésie; nl, Silezië; it, Slesia; sk, Sliezsko; csb, Sląsk. The names all relate to the name of a river (now Ślęza) and mountain (Mount Ślęża) in mid-southern Silesia, which served as a place of cult for pagans before Christianization. ''Ślęża'' is listed as one of the numerous Pre-Indo-European languages, Pre-Indo-European topographic names in the region (see old European hydronymy). According to some Polish language, Polonists, the name ''Ślęża'' or ''Ślęż'' is directly related to the Old Polish words ''ślęg'' or ''śląg'' , which means dampness, moisture, or humidity. They disagree with the hypothesis of an origin for the name ''Śląsk'' from the name of the Silingi, Silings tribe, an etymology preferred by some German authors. In Polish common usage, "Śląsk" refers to traditionally Polish Upper Silesia and today's Silesian Voivodeship, but less to Lower Silesia, which is different from Upper Silesia in many respects as its population was predominantly German-speaking until 1945–48.History
 In the fourth century BC from the south, through the Kłodzko Valley, the Celts entered Silesia, and settled around Mount Ślęża near modern Wrocław, Oława and Strzelin.
Germanic peoples, Germanic Lugii tribes were first recorded within Silesia in the 1st century. West Slavs and Lechites arrived in the region around the 7th century, and by the early ninth century, their settlements had stabilized. Local West Slavs started to erect boundary structures like the Silesian Przesieka and the Silesia Walls. The eastern border of Silesian tribes, Silesian settlement was situated to the west of the Bytom, and east from Racibórz and Cieszyn. East of this line dwelt a closely related Lechitic tribe, the Vistulans. Their northern border was in the valley of the Barycz (river), Barycz River, north of which lived the Polans (western), Western Polans tribe who gave Name of Poland, Poland its name.R. Żerelik(in:) M. Czpliński (red.) Historia Śląska, Wrocław 2007, s. 21–22
The first known states in Silesia were Greater Moravia and Duchy of Bohemia, Bohemia. In the 10th century, the Polish ruler Mieszko I of the Piast dynasty incorporated Silesia into the newly established Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polish state. In 1000, the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Wrocław, Diocese of Wrocław was established as the oldest Catholic diocese in the region, and one of the oldest dioceses in Poland, subjugated to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Gniezno. Poland repulsed German invasions of Silesia in 1017 at Siege of Niemcza, Niemcza and in 1109 at Siege of Głogów, Głogów. During the History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Fragmentation of Poland, Silesia and the rest of the country were divided into Duchies of Silesia, many smaller duchies ruled by various Silesian Dukes of Silesia, dukes. During this time, German cultural and ethnic Germanization, influence increased as a result of Ostsiedlung, immigration from German-speaking states of the Holy Roman Empire. In 1178, parts of the Duchy of Kraków around Bytom, Oświęcim, Chrzanów, and Siewierz were transferred to the Silesian Piasts, although their population was primarily Vistulan and not of Silesian descent.
In 1241, the Mongol Empire, Mongols conducted their First Mongol invasion of Poland, first invasion of Poland, causing widespread panic and mass flight. They looted much of the region and defeated the combined Polish, Moravian and German forces led by Duke Henry II the Pious at the Battle of Legnica, which took place at Legnickie Pole near the Silesian city of Legnica. Upon the death of Orda Khan, the Mongols chose not to press forward further into Europe, but returned east to participate in the election of a new Grand Khan (leader).
Between 1289 and 1292, Bohemian king Wenceslaus II became ''suzerain'' of some of the Upper Silesian duchies. Polish monarchs had not renounced their hereditary rights to Silesia until 1335. The province became part of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, Bohemian Crown which was part of the Holy Roman Empire, however, a number of duchies remained under the rule of the Polish dukes from the houses of Piast, Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellon and House of Sobieski, Sobieski as formal Bohemian fiefdoms, some until the 17th–18th centuries. In 1469 sovereignty over the region passed to Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, and in 1490 it returned to Bohemia. In 1526 Silesia passed with the Bohemian Crown to the Habsburg monarchy.
In the 15th century, several changes were made to Silesia's borders. Parts of the territories which had been transferred to the Silesian Piasts in 1178 were bought by the Monarchs of Poland, Polish kings in the second half of the 15th century (the Duchy of Oświęcim in 1457; the Duchy of Zator in 1494). The Bytom area remained in the possession of the Silesian Piasts, though it was a part of the Diocese of Kraków. The Duchy of Krosno Odrzańskie (''Crossen'') was inherited by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1476, and with the renunciation of King Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I and the estates of Bohemia in 1538, became an integral part of Brandenburg. From 1645 until 1666, the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz was held in pawn by the Polish House of Vasa as dowry of the Polish queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, Cecylia Renata.
In the fourth century BC from the south, through the Kłodzko Valley, the Celts entered Silesia, and settled around Mount Ślęża near modern Wrocław, Oława and Strzelin.
Germanic peoples, Germanic Lugii tribes were first recorded within Silesia in the 1st century. West Slavs and Lechites arrived in the region around the 7th century, and by the early ninth century, their settlements had stabilized. Local West Slavs started to erect boundary structures like the Silesian Przesieka and the Silesia Walls. The eastern border of Silesian tribes, Silesian settlement was situated to the west of the Bytom, and east from Racibórz and Cieszyn. East of this line dwelt a closely related Lechitic tribe, the Vistulans. Their northern border was in the valley of the Barycz (river), Barycz River, north of which lived the Polans (western), Western Polans tribe who gave Name of Poland, Poland its name.R. Żerelik(in:) M. Czpliński (red.) Historia Śląska, Wrocław 2007, s. 21–22
The first known states in Silesia were Greater Moravia and Duchy of Bohemia, Bohemia. In the 10th century, the Polish ruler Mieszko I of the Piast dynasty incorporated Silesia into the newly established Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polish state. In 1000, the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Wrocław, Diocese of Wrocław was established as the oldest Catholic diocese in the region, and one of the oldest dioceses in Poland, subjugated to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Gniezno. Poland repulsed German invasions of Silesia in 1017 at Siege of Niemcza, Niemcza and in 1109 at Siege of Głogów, Głogów. During the History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Fragmentation of Poland, Silesia and the rest of the country were divided into Duchies of Silesia, many smaller duchies ruled by various Silesian Dukes of Silesia, dukes. During this time, German cultural and ethnic Germanization, influence increased as a result of Ostsiedlung, immigration from German-speaking states of the Holy Roman Empire. In 1178, parts of the Duchy of Kraków around Bytom, Oświęcim, Chrzanów, and Siewierz were transferred to the Silesian Piasts, although their population was primarily Vistulan and not of Silesian descent.
In 1241, the Mongol Empire, Mongols conducted their First Mongol invasion of Poland, first invasion of Poland, causing widespread panic and mass flight. They looted much of the region and defeated the combined Polish, Moravian and German forces led by Duke Henry II the Pious at the Battle of Legnica, which took place at Legnickie Pole near the Silesian city of Legnica. Upon the death of Orda Khan, the Mongols chose not to press forward further into Europe, but returned east to participate in the election of a new Grand Khan (leader).
Between 1289 and 1292, Bohemian king Wenceslaus II became ''suzerain'' of some of the Upper Silesian duchies. Polish monarchs had not renounced their hereditary rights to Silesia until 1335. The province became part of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, Bohemian Crown which was part of the Holy Roman Empire, however, a number of duchies remained under the rule of the Polish dukes from the houses of Piast, Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellon and House of Sobieski, Sobieski as formal Bohemian fiefdoms, some until the 17th–18th centuries. In 1469 sovereignty over the region passed to Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, and in 1490 it returned to Bohemia. In 1526 Silesia passed with the Bohemian Crown to the Habsburg monarchy.
In the 15th century, several changes were made to Silesia's borders. Parts of the territories which had been transferred to the Silesian Piasts in 1178 were bought by the Monarchs of Poland, Polish kings in the second half of the 15th century (the Duchy of Oświęcim in 1457; the Duchy of Zator in 1494). The Bytom area remained in the possession of the Silesian Piasts, though it was a part of the Diocese of Kraków. The Duchy of Krosno Odrzańskie (''Crossen'') was inherited by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1476, and with the renunciation of King Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I and the estates of Bohemia in 1538, became an integral part of Brandenburg. From 1645 until 1666, the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz was held in pawn by the Polish House of Vasa as dowry of the Polish queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, Cecylia Renata.
 In 1742, most of Silesia was seized by King Frederick II of Prussia, Frederick the Great of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in the War of the Austrian Succession, eventually becoming the Prussian Province of Silesia in 1815; consequently, Silesia became part of the German Empire when it was proclaimed in 1871.
After World War I, a part of Silesia, Upper Silesia, was contested by Germany and the newly independent Second Polish Republic. The League of Nations organized a Upper Silesia plebiscite, plebiscite to decide the issue in 1921. It resulted in 60% of votes being cast for Germany and 40% for Poland. Following the third Silesian uprising (1921), however, the easternmost portion of Upper Silesia (including Katowice), with a majority ethnic Polish population, was awarded to Poland, becoming the Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Silesian Voivodeship. The Prussian Province of Silesia within Germany was then divided into the provinces of Province of Lower Silesia, Lower Silesia and Province of Upper Silesia, Upper Silesia. Meanwhile, Austrian Silesia, the small portion of Silesia retained by Austria after the Silesian Wars, was mostly awarded to the new Czechoslovakia (becoming known as Czech Silesia and Zaolzie), although most of Cieszyn and territory to the east of it went to Poland.
In 1742, most of Silesia was seized by King Frederick II of Prussia, Frederick the Great of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in the War of the Austrian Succession, eventually becoming the Prussian Province of Silesia in 1815; consequently, Silesia became part of the German Empire when it was proclaimed in 1871.
After World War I, a part of Silesia, Upper Silesia, was contested by Germany and the newly independent Second Polish Republic. The League of Nations organized a Upper Silesia plebiscite, plebiscite to decide the issue in 1921. It resulted in 60% of votes being cast for Germany and 40% for Poland. Following the third Silesian uprising (1921), however, the easternmost portion of Upper Silesia (including Katowice), with a majority ethnic Polish population, was awarded to Poland, becoming the Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Silesian Voivodeship. The Prussian Province of Silesia within Germany was then divided into the provinces of Province of Lower Silesia, Lower Silesia and Province of Upper Silesia, Upper Silesia. Meanwhile, Austrian Silesia, the small portion of Silesia retained by Austria after the Silesian Wars, was mostly awarded to the new Czechoslovakia (becoming known as Czech Silesia and Zaolzie), although most of Cieszyn and territory to the east of it went to Poland.
 Polish Silesia was among the first regions invaded during Germany's 1939 invasion of Poland, attack on Poland, which started World War II. One of the claimed goals of Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Nazi German occupation, particularly in Upper Silesia, was the extermination of those whom Nazis viewed as "Untermensch, subhuman", namely Jews and ethnic Poles. The Polish and Jewish population of the then Polish part of Silesia was subjected to genocide involving Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany, expulsions, mass murder and deportation to Nazi concentration camps and Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, while Germans were settled in pursuit of ''Lebensraum''. Two thousand Polish intellectuals, politicians, and businessmen were murdered in the ''Intelligenzaktion, Intelligenzaktion Schlesien'' in 1940 as part of a Germanisation in Poland (1939–1945), Poland-wide Germanization program. Silesia also housed one of the two main wartime centers where medical experiments were conducted on Kidnapping of children by Nazi Germany, kidnapped Polish children by Nazis. Czech Silesia was German occupation of Czechoslovakia, occupied by Germany as part of so-called Sudetenland. In Silesia, Nazi Germany operated the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, several German prisoner-of-war camps in World War II, prisoner-of-war camps for Allies of World War II, Allied POWs (incl. the major Stalag VIII-A, Stalag VIII-B, Stalag VIII-C camps), numerous Nazi prisons and thousands of Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, including a network of forced labour camps solely for Poles (''Polenlager''), Subcamp (SS), subcamps of prisons, POW camps and of the Gross-Rosen and Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz concentration camps.
The Potsdam Conference of 1945 defined the Oder-Neisse line as the border between Germany and Poland, pending a final peace conference with Germany which eventually never took place. At the end of WWII, Germans in Silesia fled from the battle ground, assuming they would be able to return when the war was over. However, they could not return, and those who had stayed were expelled and a new Polish population, including people displaced from Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, former Eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union and from Central Poland, joined the surviving native Polish inhabitants of the region. After 1945 and in 1946, nearly all of the 4.5 million Silesians of German descent fled, or were interned in camps and expelled, including some thousand German Jews who survived the Holocaust and had returned to Silesia.
The newly formed Polish United Workers' Party created a Recovered Territories, Ministry of the Recovered Territories that claimed half of the available arable land for state-run collectivized farms. Many of the new Polish Silesians who resented the Germans for their invasion in 1939 and brutality in occupation now resented the newly formed Polish communist government for their population shifting and interference in agricultural and industrial affairs.
The administrative division of Silesia within Poland has changed several times since 1945. Since 1999, it has been divided between Lubusz Voivodeship, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Opole Voivodeship, and Silesian Voivodeship. Czech Silesia is now part of the Czech Republic, forming the Moravian-Silesian Region and the northern part of the Olomouc Region. Germany retains the Silesia-Lusatia region (''Niederschlesien-Oberlausitz'' or ''Schlesische Oberlausitz'') west of the Lusatian Neisse, Neisse, which is part of the federal state of Saxony.
The region was affected by the 1997 Central European flood.
Polish Silesia was among the first regions invaded during Germany's 1939 invasion of Poland, attack on Poland, which started World War II. One of the claimed goals of Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Nazi German occupation, particularly in Upper Silesia, was the extermination of those whom Nazis viewed as "Untermensch, subhuman", namely Jews and ethnic Poles. The Polish and Jewish population of the then Polish part of Silesia was subjected to genocide involving Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany, expulsions, mass murder and deportation to Nazi concentration camps and Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, while Germans were settled in pursuit of ''Lebensraum''. Two thousand Polish intellectuals, politicians, and businessmen were murdered in the ''Intelligenzaktion, Intelligenzaktion Schlesien'' in 1940 as part of a Germanisation in Poland (1939–1945), Poland-wide Germanization program. Silesia also housed one of the two main wartime centers where medical experiments were conducted on Kidnapping of children by Nazi Germany, kidnapped Polish children by Nazis. Czech Silesia was German occupation of Czechoslovakia, occupied by Germany as part of so-called Sudetenland. In Silesia, Nazi Germany operated the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, several German prisoner-of-war camps in World War II, prisoner-of-war camps for Allies of World War II, Allied POWs (incl. the major Stalag VIII-A, Stalag VIII-B, Stalag VIII-C camps), numerous Nazi prisons and thousands of Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, including a network of forced labour camps solely for Poles (''Polenlager''), Subcamp (SS), subcamps of prisons, POW camps and of the Gross-Rosen and Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz concentration camps.
The Potsdam Conference of 1945 defined the Oder-Neisse line as the border between Germany and Poland, pending a final peace conference with Germany which eventually never took place. At the end of WWII, Germans in Silesia fled from the battle ground, assuming they would be able to return when the war was over. However, they could not return, and those who had stayed were expelled and a new Polish population, including people displaced from Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, former Eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union and from Central Poland, joined the surviving native Polish inhabitants of the region. After 1945 and in 1946, nearly all of the 4.5 million Silesians of German descent fled, or were interned in camps and expelled, including some thousand German Jews who survived the Holocaust and had returned to Silesia.
The newly formed Polish United Workers' Party created a Recovered Territories, Ministry of the Recovered Territories that claimed half of the available arable land for state-run collectivized farms. Many of the new Polish Silesians who resented the Germans for their invasion in 1939 and brutality in occupation now resented the newly formed Polish communist government for their population shifting and interference in agricultural and industrial affairs.
The administrative division of Silesia within Poland has changed several times since 1945. Since 1999, it has been divided between Lubusz Voivodeship, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Opole Voivodeship, and Silesian Voivodeship. Czech Silesia is now part of the Czech Republic, forming the Moravian-Silesian Region and the northern part of the Olomouc Region. Germany retains the Silesia-Lusatia region (''Niederschlesien-Oberlausitz'' or ''Schlesische Oberlausitz'') west of the Lusatian Neisse, Neisse, which is part of the federal state of Saxony.
The region was affected by the 1997 Central European flood.
Geography
 Most of Silesia is relatively flat, although its southern border is generally mountainous. It is primarily located in a swath running along both banks of the upper and middle Oder River, Oder (Odra) River, but it extends eastwards to the upper Vistula River. The region also includes many tributaries of the Oder, including the Bóbr (and its tributary the Kwisa), the Barycz (river), Barycz and the Nysa Kłodzka. The
Most of Silesia is relatively flat, although its southern border is generally mountainous. It is primarily located in a swath running along both banks of the upper and middle Oder River, Oder (Odra) River, but it extends eastwards to the upper Vistula River. The region also includes many tributaries of the Oder, including the Bóbr (and its tributary the Kwisa), the Barycz (river), Barycz and the Nysa Kłodzka. The Sudeten Mountains
The Sudetes ( ; pl, Sudety; german: Sudeten; cs, Krkonošsko-jesenická subprovincie), commonly known as the Sudeten Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince in Central Europe, shared by Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic. They consis ...
run along most of the southern edge of the region, though at its south-eastern extreme it reaches the Silesian Beskids and Moravian-Silesian Beskids, which belong to the Carpathian Mountains range.
Historically, Silesia was bounded to the west by the Kwisa and Bóbr Rivers, while the territory west of the Kwisa was in Upper Lusatia (earlier ''Milsko''). However, because part of Upper Lusatia was included in the Province of Silesia in 1815, in Germany Görlitz, Niederschlesischer Oberlausitzkreis and neighbouring areas are considered parts of historical Silesia. Those districts, along with Poland's Lower Silesian Voivodeship and parts of Lubusz Voivodeship, make up the geographic region of Lower Silesia.
Silesia has undergone a similar notional extension at its eastern extreme. Historically, it extended only as far as the Brynica River, which separates it from Zagłębie Dąbrowskie in the Lesser Poland region. However, to many Poles today, Silesia (''Śląsk'') is understood to cover all of the area around Katowice, including Zagłębie. This interpretation is given official sanction in the use of the name Silesian Voivodeship (''województwo śląskie'') for the province covering this area. In fact, the word ''Śląsk'' in Polish (when used without qualification) now commonly refers exclusively to this area (also called ''Górny Śląsk'' or Upper Silesia).
As well as the Katowice area, historical Upper Silesia also includes the Opole region (Poland's Opole Voivodeship) and Czech Silesia. Czech Silesia consists of a part of the Moravian-Silesian Region and the Jeseník District in the Olomouc Region.
Natural resources
Silesia is a resource-rich and populous region. Since the middle of the 18th century, coal has been mined. The industry had grown while Silesia was part of Germany, and peaked in the 1970s under the History of Poland (1945–1989), People's Republic of Poland. During this period, Silesia became one of the world's largest producers of coal, with a record tonnage in 1979. Coal mining declined during the next two decades, but has increased again following the end of Communist rule. The 41 coal mines in Silesia are mostly part of the Upper Silesian Coal Basin, which lies in the Silesian Upland. The coalfield has an area of about . Deposits in Lower Silesia have proven to be difficult to exploit and the area's unprofitable mines were closed in 2000. In 2008, an estimated 35 billion tonnes of lignite reserves were found near Legnica, making them some of the largest in the world.
From the fourth century BC, iron ore has been mined in the upland areas of Silesia. The same period had lead, copper, silver, and gold mining. Zinc, cadmium, arsenic, and uranium have also been mined in the region. Lower Silesia features large copper mining and processing between the cities of Legnica, Głogów, Lubin, and Polkowice.
The region is known for stone quarrying to produce limestone, marl, marble, and basalt.
The region also has a thriving agricultural sector, which produces cereals (wheat, rye, barley, oats, corn), potatoes, rapeseed, sugar beets and others. Milk production is well developed. The Opole Silesia has for decades occupied the top spot in Poland for their indices of effectiveness of agricultural land use.
Mountainous parts of southern Silesia feature many significant and attractive tourism destinations (e.g., Karpacz, Szczyrk, Wisła). Silesia is generally well forested. This is because greenness is generally highly desirable by the local population, particularly in the highly industrialized parts of Silesia.
The 41 coal mines in Silesia are mostly part of the Upper Silesian Coal Basin, which lies in the Silesian Upland. The coalfield has an area of about . Deposits in Lower Silesia have proven to be difficult to exploit and the area's unprofitable mines were closed in 2000. In 2008, an estimated 35 billion tonnes of lignite reserves were found near Legnica, making them some of the largest in the world.
From the fourth century BC, iron ore has been mined in the upland areas of Silesia. The same period had lead, copper, silver, and gold mining. Zinc, cadmium, arsenic, and uranium have also been mined in the region. Lower Silesia features large copper mining and processing between the cities of Legnica, Głogów, Lubin, and Polkowice.
The region is known for stone quarrying to produce limestone, marl, marble, and basalt.
The region also has a thriving agricultural sector, which produces cereals (wheat, rye, barley, oats, corn), potatoes, rapeseed, sugar beets and others. Milk production is well developed. The Opole Silesia has for decades occupied the top spot in Poland for their indices of effectiveness of agricultural land use.
Mountainous parts of southern Silesia feature many significant and attractive tourism destinations (e.g., Karpacz, Szczyrk, Wisła). Silesia is generally well forested. This is because greenness is generally highly desirable by the local population, particularly in the highly industrialized parts of Silesia.
Demographics
Silesia has been historically diverse in every aspect. Nowadays, the largest part of Silesia is located in Poland; it is often cited as one of the most diverse regions in that country. The United States Immigration Commission, in its ''Dictionary of Races or Peoples'' (published in 1911, during a period of intense immigration from Silesia to the United States), considered Silesian as a geographical (not ethnic) term, denoting the inhabitants of Silesia. It is also mentioned the existence of both Polish Silesian and German Silesian dialects in that region.Ethnicity
Modern Silesia is inhabited by Poles, Silesians, ethnic Germans, Germans, and Czechs. Germans first came to Silesia during the Late Middle Ages, Late Medieval Ostsiedlung. The last Polish census of 2011 showed that the Silesians are the largest ethnic or national minority in Poland, Germans being the second; both groups are located mostly in Upper Silesia. The Czech part of Silesia is inhabited by Czechs, Moravians (ethnic group), Moravians, Silesians, and Polish minority in the Czech Republic, Poles. In the early 19th century the population of the Province of Silesia, Prussian part of Silesia was between 2/3 and 3/4 German-speaking, between 1/5 and 1/3 Polish-speaking, with Sorbs, Czechs, Moravians and Jews forming other smaller minorities (see Table 1. below). Before the Second World War, Silesia was inhabited mostly by Germans, with Poles a large minority, forming a majority in Upper Silesia. Silesia was also the home of Czech and Jewish minorities. The German population tended to be based in the urban centres and in the rural areas to the north and west, whilst the Polish population was mostly rural and could be found in the east and in the south. Ethnic structure of Prussian Upper Silesia (Opole regency) during the 19th century and the early 20th century can be found in Table 2.: The Austrian Silesia, Austrian part of Silesia had a mixed German, Polish and Czech population, with Polish-speakers forming a majority in Cieszyn Silesia.Religion
 Historically, Silesia was about equally split between Protestants (overwhelmingly Lutherans) and Roman Catholics. In an 1890 census taken in the German part, Roman Catholics made up a slight majority of 53%, while the remaining 47% were almost entirely Lutheran. Geographically speaking, Lower Silesia was mostly Lutheran except for the Kłodzko Land, Glatzer Land (now Kłodzko County). Upper Silesia was mostly Roman Catholic except for some of its northwestern parts, which were predominantly Lutheran. Generally speaking, the population was mostly Protestant in the western parts, and it tended to be more Roman Catholic the further east one went. In Upper Silesia, Protestants were concentrated in larger cities and often identified as German. After World War II, the religious demographics changed drastically as Germans, who constituted the bulk of the Protestant population, Flight and expulsion of Germans, were forcibly expelled. Poles, who were mostly Roman Catholic, were resettled in their place. Today, Silesia remains predominantly Roman Catholic.
Existing since the 12th century, Silesia's Jewish community was concentrated around Wrocław and Upper Silesia, and numbered 48,003 (1.1% of the population) in 1890, decreasing to 44,985 persons (0.9%) by 1910. In Polish East Upper Silesia, the number of Jews was around 90,000–100,000. Historically the community had suffered a number of localised expulsions such as their 1453 expulsion from Wrocław. From 1712 to 1820 a succession of men held the title Chief Rabbi of Silesia ("Landesrabbiner"): Naphtali ha-Kohen (1712–16); Samuel ben Naphtali (1716–22); Ḥayyim Jonah Te'omim (1722–1727); Baruch b. Reuben Gomperz (1733–54); Joseph Jonas Fränkel (1754–93); Jeremiah Löw Berliner (1793–99); Lewin Saul Fränkel (1800–7); Aaron Karfunkel (1807–16); and Abraham ben Gedaliah Tiktin (1816–20).
Historically, Silesia was about equally split between Protestants (overwhelmingly Lutherans) and Roman Catholics. In an 1890 census taken in the German part, Roman Catholics made up a slight majority of 53%, while the remaining 47% were almost entirely Lutheran. Geographically speaking, Lower Silesia was mostly Lutheran except for the Kłodzko Land, Glatzer Land (now Kłodzko County). Upper Silesia was mostly Roman Catholic except for some of its northwestern parts, which were predominantly Lutheran. Generally speaking, the population was mostly Protestant in the western parts, and it tended to be more Roman Catholic the further east one went. In Upper Silesia, Protestants were concentrated in larger cities and often identified as German. After World War II, the religious demographics changed drastically as Germans, who constituted the bulk of the Protestant population, Flight and expulsion of Germans, were forcibly expelled. Poles, who were mostly Roman Catholic, were resettled in their place. Today, Silesia remains predominantly Roman Catholic.
Existing since the 12th century, Silesia's Jewish community was concentrated around Wrocław and Upper Silesia, and numbered 48,003 (1.1% of the population) in 1890, decreasing to 44,985 persons (0.9%) by 1910. In Polish East Upper Silesia, the number of Jews was around 90,000–100,000. Historically the community had suffered a number of localised expulsions such as their 1453 expulsion from Wrocław. From 1712 to 1820 a succession of men held the title Chief Rabbi of Silesia ("Landesrabbiner"): Naphtali ha-Kohen (1712–16); Samuel ben Naphtali (1716–22); Ḥayyim Jonah Te'omim (1722–1727); Baruch b. Reuben Gomperz (1733–54); Joseph Jonas Fränkel (1754–93); Jeremiah Löw Berliner (1793–99); Lewin Saul Fränkel (1800–7); Aaron Karfunkel (1807–16); and Abraham ben Gedaliah Tiktin (1816–20).
Consequences of World War II
After the German invasion of Poland in 1939, following Racial policy of Nazi Germany, Nazi racial policy, the Jewish population of Silesia was subjected to Nazi genocide with executions performed by Einsatzgruppe z. B.V. led by Udo von Woyrsch and Einsatzgruppe I led by Bruno Streckenbach, imprisonment in ghettos and ethnic cleansing to the General Government. In their efforts to exterminate the Jews through murder and ethnic cleansing Nazi established in Silesia province the Auschwitz and Gross-Rosen camps. Expulsions were carried out openly and reported in the local press.Steinbacher, S. "In the Shadow of Auschwitz, The murder of the Jews of East Upper Silesia", in Cesarani, D. (2004) ''Holocaust: From the persecution of the Jews to mass murder,'' Routledge, P126 Those sent to ghettos would from 1942 be expelled to concentration and work camps.Steinbacher, S. "In the Shadow of Auschwitz, The murder of the Jews of East Upper Silesia", in Cesarani, D. (2004) ''Holocaust: From the persecution of the Jews to mass murder,'' Routledge, pp.110–138. Between 5 May and 17 June, 20,000 Silesian Jews were sent to Birkenau to gas chambers and during August 1942, 10,000 to 13,000 Silesian Jews were murdered by gassing at Auschwitz. Most Jews in Silesia were exterminated by the Nazis. After the war Silesia became a major centre for repatriation of the Jewish population in Poland which survived Nazi German extermination and in autumn 1945, 15,000 Jews were in Lower Silesia, mostly Polish Jews returned from territories now belonging to Soviet Union, rising in 1946 to seventy thousand as Jewish survivors from other regions in Poland were relocated.Kochavi, AJ (2001). ''Post-Holocaust politics: Britain, the United States & Jewish refugees, 1945–1948,'' University of North Carolina Press, p.176. The majority of Germans fled or were expelled from the present-day Polish and Czech parts of Silesia during and after World War II. From June 1945 to January 1947, 1.77 million Germans were expelled from Lower Silesia, and 310,000 from Upper Silesia. Today, most German Silesians and their descendants live in the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany, many of them in the Ruhr area working as miners, like their ancestors in Silesia. To smooth their integration into West German society after 1945, they were placed into officially recognized organizations, like the Landsmannschaft Schlesien, with financing from the federal West German budget. One of its most notable but controversial spokesmen was the Christian Democratic Union (Germany), Christian Democratic Union politician Herbert Hupka. The expulsion of Germans led to widespread underpopulation. The population of the town of Głogów fell from 33,500 to 5,000, and from 1939 to 1966 the population of Wrocław fell by 25%. Attempts to repopulate Silesia proved unsuccessful in the 1940s and 1950s, and Silesia's population did not reach pre-war levels until the late 1970s. The Polish settlers who repopulated Silesia were partly from the former Polish Kresy, Eastern Borderlands, which was annexed by the Soviet Union in 1939. Wrocław was partly repopulated with refugees from the formerly Polish city of Lviv, Lwów.Cities
The following table lists the cities in Silesia with a population greater than 20,000 (2015). * Only part in SilesiaFlags and coats of arms
The emblems of Lower Silesia and Upper Silesia originate from the emblems of the Piasts of Lower Silesia and Upper Silesia. The coat of arms of Upper Silesia depicts the golden eagle on the blue shield. The coat of arms of Lower Silesia depicts a black eagle on a golden (yellow) shield.World Heritage Sites
See also
* 257 Silesia * Expulsion of Poles by Germany * Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950) * List of people from Silesia * Silesian German * Silesian Interurbans * Slezak * Upper Silesian Industrial Region * Upper Silesian metropolitan area, Upper Silesian Metropolitan AreaFootnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * Procházka, Jiří: 1683, Vienna obsessa. Via Silesiaca.() Brno, Wien 2012, ITEMExternal links
*Map of Silesia in 1763
* [http://culture.pl/en/article/what-is-silesia What is Silesia?] {{Authority control Silesia, Czech geographic history Divided regions Geography of Central Europe Historical regions in Germany Historical regions in Poland Historical regions