Saturnalia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saturnalia is an ancient Roman festival and
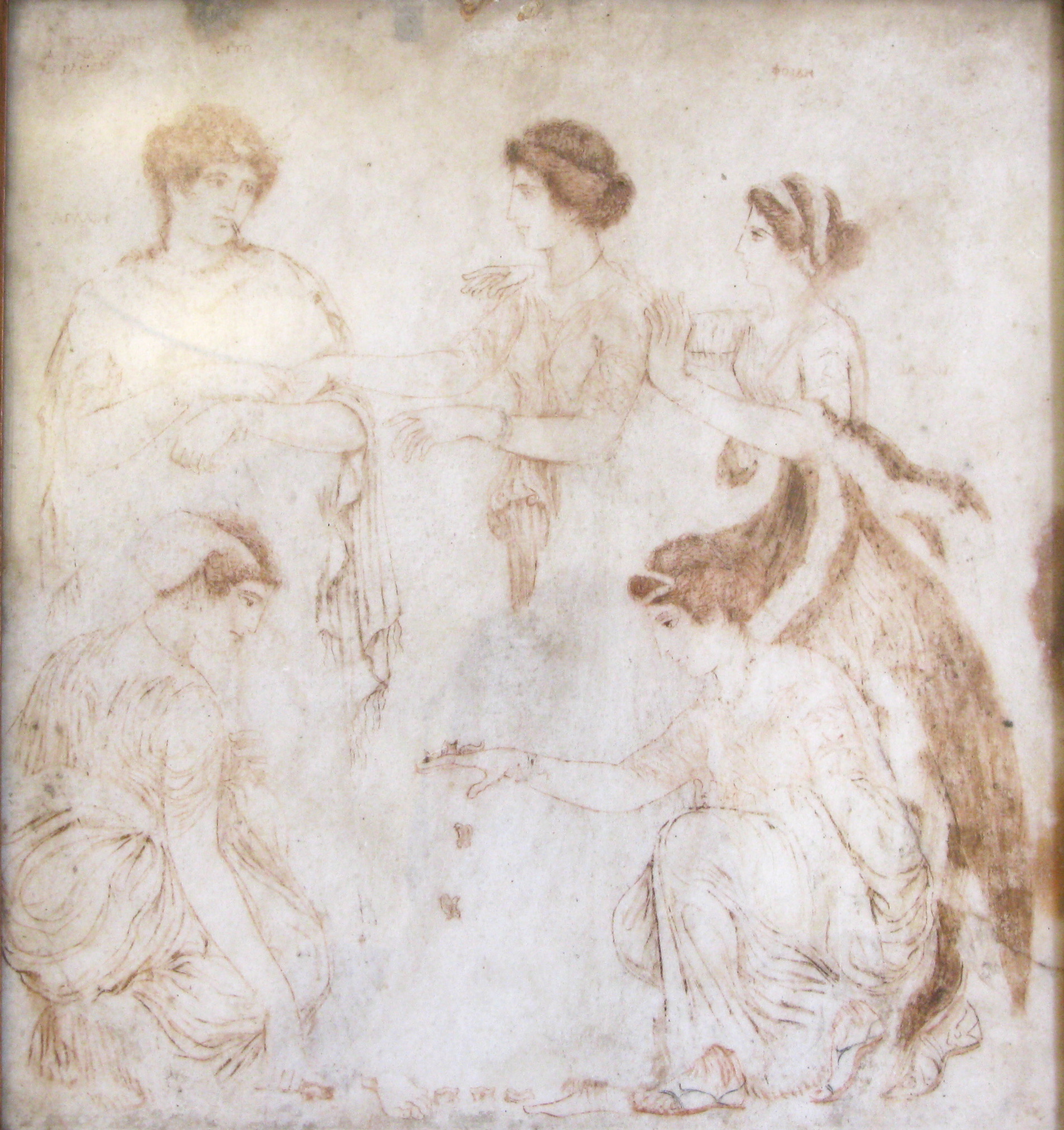 In
In
 The statue of Saturn at his main temple normally had its feet bound in wool, which was removed for the holiday as an act of liberation. The official rituals were carried out according to "Greek rite" ''( ritus graecus)''. The sacrifice was officiated by a priest, whose head was uncovered; in Roman rite, priests sacrificed ''
The statue of Saturn at his main temple normally had its feet bound in wool, which was removed for the holiday as an act of liberation. The official rituals were carried out according to "Greek rite" ''( ritus graecus)''. The sacrifice was officiated by a priest, whose head was uncovered; in Roman rite, priests sacrificed ''
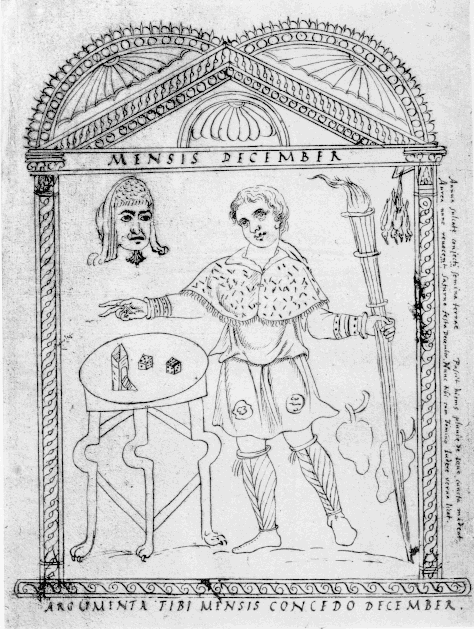
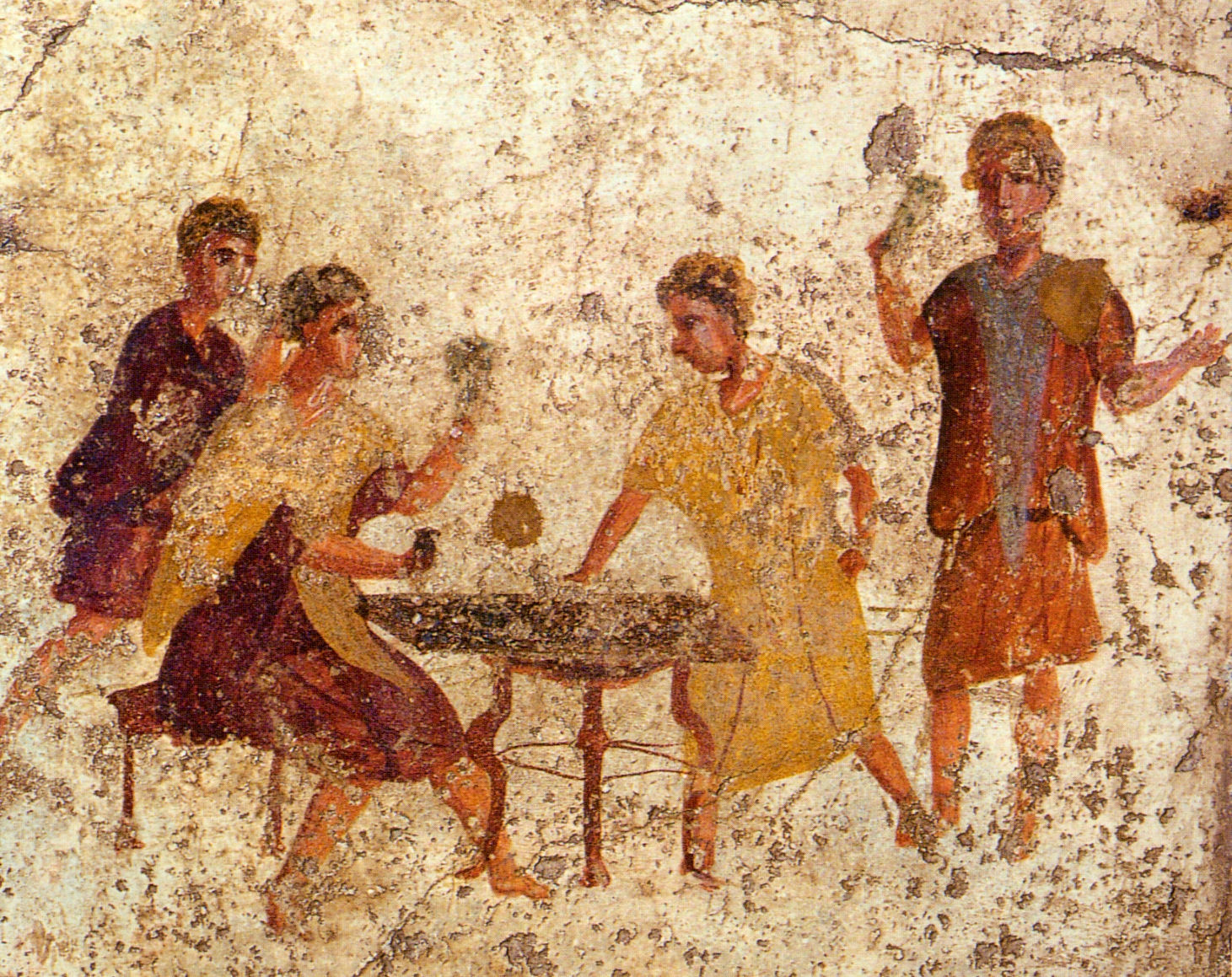 Gambling and dice-playing, normally prohibited or at least frowned upon, were permitted for all, even slaves. Coins and nuts were the stakes. On the
Gambling and dice-playing, normally prohibited or at least frowned upon, were permitted for all, even slaves. Coins and nuts were the stakes. On the

 As an observance of state religion, Saturnalia was supposed to have been held "''...quarto decimo Kalendarum Ianuariarum''", on the fourteenth day before the
As an observance of state religion, Saturnalia was supposed to have been held "''...quarto decimo Kalendarum Ianuariarum''", on the fourteenth day before the
 The Saturnalia reflects the contradictory nature of the deity Saturn himself: "There are joyful and utopian aspects of careless well-being side by side with disquieting elements of threat and danger."
As a deity of agricultural bounty, Saturn embodied prosperity and wealth in general. The name of his consort
The Saturnalia reflects the contradictory nature of the deity Saturn himself: "There are joyful and utopian aspects of careless well-being side by side with disquieting elements of threat and danger."
As a deity of agricultural bounty, Saturn embodied prosperity and wealth in general. The name of his consort  The third century Neoplatonic philosopher Porphyry took an allegorical view of the Saturnalia. He saw the festival's theme of liberation and dissolution as representing the "freeing of souls into immortality"—an interpretation that Mithraists may also have followed, since they included many slaves and freedmen. According to Porphyry, the Saturnalia occurred near the
The third century Neoplatonic philosopher Porphyry took an allegorical view of the Saturnalia. He saw the festival's theme of liberation and dissolution as representing the "freeing of souls into immortality"—an interpretation that Mithraists may also have followed, since they included many slaves and freedmen. According to Porphyry, the Saturnalia occurred near the
 Unlike several Roman religious festivals which were particular to cult sites in the city, the prolonged seasonal celebration of Saturnalia at home could be held anywhere in the Empire. Saturnalia continued as a secular celebration long after it was removed from the official calendar. As
Unlike several Roman religious festivals which were particular to cult sites in the city, the prolonged seasonal celebration of Saturnalia at home could be held anywhere in the Empire. Saturnalia continued as a secular celebration long after it was removed from the official calendar. As
2.7.4
* Justinus
Epitome of Pompeius Trogus
' *
Saturnalia
' * Pliny the Younger
Letters
'
Saturnalia – World History Encyclopedia
A longer article by James Grout {{Roman religion (festival) Saturn (mythology) Ancient Roman festivals December observances Winter festivals Religious festivals in Italy
holiday
A holiday is a day set aside by custom or by law on which normal activities, especially business or work including school, are suspended or reduced. Generally, holidays are intended to allow individuals to celebrate or commemorate an event or t ...
in honour of the god
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; ...
, held on 17 December of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematics, Greek mathematicians and Ancient Greek astronomy, as ...
and later expanded with festivities through to 23 December. The holiday was celebrated with a sacrifice at the Temple of Saturn
The Temple of Saturn (Latin: ''Templum Saturni'' or ''Aedes Saturni''; it, Tempio di Saturno) was an ancient Roman temple to the god Saturn, in what is now Rome, Italy. Its ruins stand at the foot of the Capitoline Hill at the western end of th ...
, in the Roman Forum, and a public banquet, followed by private gift-giving, continual partying, and a carnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival ...
atmosphere that overturned Roman social norms: gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of Value (economics), value ("the stakes") on a Event (probability theory), random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy (ga ...
was permitted, and masters provided table service for their slaves as it was seen as a time of liberty for both slaves and freedmen alike. A common custom was the election of a "King of the Saturnalia", who gave orders to people, which were followed and presided over the merrymaking. The gifts exchanged were usually gag gifts or small figurines made of wax or pottery known as ''sigillaria
''Sigillaria'' is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate '' Lepidodendron''.
Fossil ...
''. The poet Catullus
Gaius Valerius Catullus (; 84 - 54 BCE), often referred to simply as Catullus (, ), was a Latin poetry, Latin poet of the late Roman Republic who wrote chiefly in the neoteric style of poetry, focusing on personal life rather than classical h ...
called it "the best of days".
Saturnalia was the Roman equivalent to the earlier Greek holiday of Kronia
The Kronia ( grc, Κρόνια) was an Athenian festival held in honor of Kronos ( Cronus) on the 12th day of Hekatombaion, the first month of the Attic calendar, and roughly equivalent to the latter part of July and first part of August.
Th ...
, which was celebrated during the Attic month of Hekatombaion in late midsummer. It held theological importance for some Romans, who saw it as a restoration of the ancient Golden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the '' Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the Go ...
, when the world was ruled by Saturn. The Neoplatonist
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some i ...
philosopher Porphyry interpreted the freedom associated with Saturnalia as symbolizing the "freeing of souls into immortality". Saturnalia may have influenced some of the customs associated with later celebrations in western Europe occurring in midwinter, particularly traditions associated with Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
, the Feast of the Holy Innocents, and Epiphany. In particular, the historical western European Christmas custom of electing a "Lord of Misrule
In England, the Lord of Misrule – known in Scotland as the Abbot of Unreason and in France as the ''Prince des Sots'' – was an officer appointed by lot during Christmastide to preside over the Feast of Fools. The Lord of Misrul ...
" may have its roots in Saturnalia celebrations.
Origins
Roman mythology
Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans. One of a wide variety of genres of Roman folklore, ''Roman mythology'' may also refer to the modern study of these represent ...
, Saturn was an agricultural deity who was said to have reigned over the world in the Golden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the '' Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the Go ...
, when humans enjoyed the spontaneous bounty of the earth without labour in a state of innocence
Innocence is a lack of guilt, with respect to any kind of crime, or wrongdoing. In a legal context, innocence is to the lack of legal guilt of an individual, with respect to a crime. In other contexts, it is a lack of experience.
In relatio ...
. The revelries of Saturnalia were supposed to reflect the conditions of the lost mythical age. The Greek equivalent was the Kronia
The Kronia ( grc, Κρόνια) was an Athenian festival held in honor of Kronos ( Cronus) on the 12th day of Hekatombaion, the first month of the Attic calendar, and roughly equivalent to the latter part of July and first part of August.
Th ...
, which was celebrated on the twelfth day of the month of Hekatombaion, which occurred from around mid-July to mid-August on the Attic calendar
The Attic calendar or Athenian calendar is the lunisolar calendar beginning in midsummer with the lunar month of Hekatombaion, in use in ancient Attica, the ancestral territory of the Athenian polis. It is sometimes called the Greek calendar be ...
. The Greek writer Athenaeus
Athenaeus of Naucratis (; grc, Ἀθήναιος ὁ Nαυκρατίτης or Nαυκράτιος, ''Athēnaios Naukratitēs'' or ''Naukratios''; la, Athenaeus Naucratita) was a Greek rhetorician and grammarian, flourishing about the end of t ...
also cites numerous other examples of similar festivals celebrated throughout the Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were dir ...
, including the Cretan
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
festival of Hermaia in honor of Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orato ...
, an unnamed festival from Troezen
Troezen (; ancient Greek: Τροιζήν, modern Greek: Τροιζήνα ) is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern Peloponnese, Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the munic ...
in honor of Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a ch ...
, the Thessalian
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thess ...
festival of Peloria in honor of Zeus Pelorios, and an unnamed festival from Babylon. He also mentions that the custom of masters dining with their slaves was associated with the Athenian festival of Anthesteria
The Anthesteria (; grc, Ἀνθεστήρια ) was one of the four Athenian festivals in honor of Dionysus. It was held each year from the 11th to the 13th of the month of Anthesterion, around the time of the January or February full moon. The ...
and the Spartan festival of Hyacinthia
The death of Hyacinthus was celebrated at Amyclae by the second most important of Spartan festivals, the Hyacinthia (Ancient Greek / ''Hyakínthia'')
in the Spartan month Hyacinthius in early summer.
Proceedings of Hyacinthia
The Hyacinthia last ...
. The Argive festival of Hybristica Hybristica was a solemn feast among the Greeks of ancient Argos, with sacrifices and other ceremonies, at which either sex appeared in the dress of the other to do honor to Aphrodite in quality of a god, a goddess, or both. The Hybristica was celebr ...
, though not directly related to the Saturnalia, involved a similar reversal of roles in which women would dress as men and men would dress as women.
The ancient Roman historian Justinus credits Saturn with being a historical king of the pre-Roman inhabitants of Italy:
Although probably the best-known Roman holiday, Saturnalia as a whole is not described from beginning to end in any single ancient source. Modern understanding of the festival is pieced together from several accounts dealing with various aspects. The Saturnalia was the dramatic setting of the multivolume work of that name by Macrobius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was ...
, a Latin writer from late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
who is the major source for information about the holiday. Macrobius describes the reign of Justinus' "king Saturn" as "a time of great happiness, both on account of the universal plenty that prevailed and because as yet there was no division into bond and free – as one may gather from the complete license enjoyed by slaves at the Saturnalia." In Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridiculed superstiti ...
's ''Saturnalia'' it is Chronos
Chronos (; grc-gre, Χρόνος, , "time"), also spelled Khronos or Chronus, is a personification of time in pre-Socratic philosophy
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrat ...
himself who proclaims a "festive season, when 'tis lawful to be drunken, and slaves have license to revile their lords".
In one of the interpretations in Macrobius's work, Saturnalia is a festival of light leading to the winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winte ...
, with the abundant presence of candles symbolizing the quest for knowledge and truth. The renewal of light and the coming of the new year
New Year is the time or day currently at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count increments by one. Many cultures celebrate the event in some manner. In the Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system to ...
was celebrated in the later Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
at the '' Dies Natalis Solis Invicti'', the "Birthday of the Unconquerable Sun", on 25 December.
The popularity of Saturnalia continued into the 3rd and 4th centuries AD, and as the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
came under Christian rule, many of its customs were recast into or at least influenced the seasonal celebrations surrounding Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
and the New Year
New Year is the time or day currently at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count increments by one. Many cultures celebrate the event in some manner. In the Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system to ...
.
Historical context
Saturnalia underwent a major reform in 217 BC, after theBattle of Lake Trasimene
The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. It took place on the north shore of Lake Trasimene, to the ...
, when the Romans suffered one of their most crushing defeats by Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the clas ...
during the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
. Until that time, they had celebrated the holiday according to Roman custom ''( more Romano)''. It was after a consultation of the Sibylline Books
The ''Sibylline Books'' ( la, Libri Sibyllini) were a collection of oracular utterances, set out in Greek hexameters, that, according to tradition, were purchased from a sibyl by the last king of Rome, Tarquinius Superbus, and were consulted a ...
that they adopted "Greek rite", introducing sacrifices carried out in the Greek manner, the public banquet, and the continual shouts of ''io Saturnalia'' that became characteristic of the celebration. Cato the Elder
Marcus Porcius Cato (; 234–149 BC), also known as Cato the Censor ( la, Censorius), the Elder and the Wise, was a Roman soldier, Roman Senate, senator, and Roman historiography, historian known for his conservatism and opposition to Hellenizati ...
(234–149 BC) remembered a time before the so-called "Greek" elements had been added to the Roman Saturnalia.
It was not unusual for the Romans to offer cult ''(cultus Cultus may refer to:
*Cult (religious practice)
* ''Cultus'' (stonefly), a genus of stoneflies
*Cultus Bay, a bay in Washington
*Cultus Lake (disambiguation) Cultus Lake may refer to:
*Cultus Lake, British Columbia, Canada
*Cultus Lake (Oregon), Un ...
)'' to the deities of other nations in the hope of redirecting their favour (see ''evocatio
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence on ...
''), and the Second Punic War in particular created pressures on Roman society that led to a number of religious innovations and reforms. Robert E.A. Palmer has argued that the introduction of new rites at this time was in part an effort to appease Ba'al Hammon, the Carthaginian god who was regarded as the counterpart of the Roman Saturn and Greek Cronus. The table service that masters offered their slaves thus would have extended to Carthaginian or African war captives.
Public religious observance
Rite at the temple of Saturn
 The statue of Saturn at his main temple normally had its feet bound in wool, which was removed for the holiday as an act of liberation. The official rituals were carried out according to "Greek rite" ''( ritus graecus)''. The sacrifice was officiated by a priest, whose head was uncovered; in Roman rite, priests sacrificed ''
The statue of Saturn at his main temple normally had its feet bound in wool, which was removed for the holiday as an act of liberation. The official rituals were carried out according to "Greek rite" ''( ritus graecus)''. The sacrifice was officiated by a priest, whose head was uncovered; in Roman rite, priests sacrificed ''capite velato
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence on ...
'', with head covered by a special fold of the toga
The toga (, ), a distinctive garment of ancient Rome, was a roughly semicircular cloth, between in length, draped over the shoulders and around the body. It was usually woven from white wool, and was worn over a tunic. In Roman historical tr ...
. This procedure is usually explained by Saturn's assimilation with his Greek counterpart Cronus, since the Romans often adopted and reinterpreted Greek myths
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of d ...
, iconography, and even religious practices for their own deities, but the uncovering of the priest's head may also be one of the Saturnalian reversals, the opposite of what was normal.
Following the sacrifice the Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in ...
arranged a '' lectisternium'', a ritual of Greek origin that typically involved placing a deity's image on a sumptuous couch, as if he were present and actively participating in the festivities. A public banquet followed ''( convivium publicum)''.
The day was supposed to be a holiday from all forms of work. Schools were closed, and exercise regimens were suspended. Courts were not in session, so no justice was administered, and no declaration of war could be made. After the public rituals, observances continued at home. On 18 and 19 December, which were also holidays from public business, families conducted domestic rituals. They bathed early, and those with means sacrificed a suckling pig
A suckling pig is a piglet fed on its mother's milk (i.e., a piglet which is still a "suckling"). In culinary contexts, a suckling pig is slaughtered between the ages of two and six weeks. It is traditionally cooked whole, often roasted, in va ...
, a traditional offering to an earth deity.
Human offerings
Saturn also had a less benevolent aspect. One of his consorts wasLua
Lua or LUA may refer to:
Science and technology
* Lua (programming language)
* Latvia University of Agriculture
* Last universal ancestor, in evolution
Ethnicity and language
* Lua people, of Laos
* Lawa people, of Thailand sometimes referred t ...
, sometimes called ''Lua Saturni'' ("Saturn's Lua") and identified with Lua Mater, "Mother Destruction", a goddess in whose honor the weapons of enemies killed in war were burned, perhaps in expiation. Saturn's chthonic
The word chthonic (), or chthonian, is derived from the Ancient Greek word ''χθών, "khthon"'', meaning earth or soil. It translates more directly from χθόνιος or "in, under, or beneath the earth" which can be differentiated from Γῆ ...
nature connected him to the underworld and its ruler Dīs Pater
Dīs Pater (; ; genitive ''Dītis Patris''), otherwise known as Rex Infernus or Pluto, is a Roman god of the underworld. Dis was originally associated with fertile agricultural land and mineral wealth, and since those minerals came from undergro ...
, the Roman equivalent of Greek Plouton
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Pluto ( gr, Πλούτων, ') was the ruler of the Greek underworld. The earlier name for the god was Hades, which became more common as the name of the underworld itself. Pluto represents a more posi ...
(Pluto in Latin) who was also a god of hidden wealth. In sources of the third century AD and later, Saturn is recorded as receiving dead gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
s as offerings (''munera'') during or near the Saturnalia. These gladiatorial events, ten days in all throughout December, were presented mainly by the quaestor
A ( , , ; "investigator") was a public official in Ancient Rome. There were various types of quaestors, with the title used to describe greatly different offices at different times.
In the Roman Republic, quaestors were elected officials who ...
s and sponsored with funds from the treasury of Saturn.
The practice of gladiator ''munera'' was criticized by Christian apologists
Christian apologetics ( grc, ἀπολογία, "verbal defense, speech in defense") is a branch of Christian theology that defends Christianity.
Christian apologetics has taken many forms over the centuries, starting with Paul the Apostle in ...
as a form of human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherei ...
. Although there is no evidence of this practice during the Republic, the offering of gladiators led to later theories that the primeval Saturn had demanded human victims. Macrobius says that Dīs Pater was placated with human heads and Saturn with sacrificial victims consisting of men (''virorum victimis''). In mythic lore, during the visit of Hercules to Italy, the civilizing demigod insisted that the practice be halted and the ritual reinterpreted. Instead of heads to Dīs Pater, the Romans were to offer effigies or masks ''(oscilla :For the genus of marine molluscs, see ''Oscilla'' (gastropod).
''Oscilla'' is a word applied in Latin usage to small figures, most commonly masks or faces, which were hung up as offerings to various deities, either for propitiation or expiation, ...
)''; a mask appears in the representation of Saturnalia in the Calendar of Filocalus
The ''Chronograph of 354'' (or "Chronography"), also known as the ''Calendar of 354'', is a compilation of chronological and calendrical texts produced in 354 AD for a wealthy Roman Christian named Valentinus by the calligrapher and illustrator ...
. Since the Greek word ''phota'' meant both 'man' and 'lights', candles were a substitute offering to Saturn for the light of life. The figurines that were exchanged as gifts (''sigillaria
''Sigillaria'' is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate '' Lepidodendron''.
Fossil ...
'') may also have represented token substitutes.
Private festivities
Role reversal
Saturnalia was characterized by role reversals and behavioral license. Slaves were treated to a banquet of the kind usually enjoyed by their masters. Ancient sources differ on the circumstances: some suggest that master and slave dined together, while others indicate that the slaves feasted first, or that the masters actually served the food. The practice might have varied over time. Saturnalian license also permitted slaves to disrespect their masters without the threat of a punishment. It was a time forfree speech
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The right to freedom of expression has been recogn ...
: the Augustan poet Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his ...
calls it "December liberty". In two satires set during the Saturnalia, Horace has a slave offer sharp criticism to his master. Everyone knew, however, that the leveling of the social hierarchy
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on Socioeconomic status, socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, Race (human categorization), race, education, ethnicity, gender, Job, occupation, socia ...
was temporary and had limits; no social norms were ultimately threatened, because the holiday would end.
The toga
The toga (, ), a distinctive garment of ancient Rome, was a roughly semicircular cloth, between in length, draped over the shoulders and around the body. It was usually woven from white wool, and was worn over a tunic. In Roman historical tr ...
, the characteristic garment of the male Roman citizen, was set aside in favor of the Greek ''synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
'', colourful "dinner clothes" otherwise considered in poor taste for daytime wear. Romans of citizen status normally went about bare-headed, but for the Saturnalia donned the ''pilleus
Pileus may refer to:
* Pileus (hat), a brimless cap
* Pileus (mycology), the "cap" of a mushroom
* Pileus (meteorology), a cloud formation
*the crown of a bird's head
*the scales on the top of lizard and snake heads
See also
*
* Jewish hat, ...
'', the conical felt cap that was the usual mark of a freedman. Slaves, who ordinarily were not entitled to wear the ''pilleus'', wore it as well, so that everyone was "pilleated" without distinction.
The participation of freeborn Roman women is implied by sources that name gifts for women, but their presence at banquets may have depended on the custom of their time; from the late Republic onward, women mingled socially with men more freely than they had in earlier times. Female entertainers were certainly present at some otherwise all-male gatherings. Role-playing was implicit in the Saturnalia's status reversals, and there are hints of mask-wearing or "guising
Trick-or-treating is a traditional Halloween custom for children and adults in some countries. During the evening of Halloween, on October 31, people in costumes travel from house to house, asking for treats with the phrase "trick or treat". The ...
". No theatrical events are mentioned in connection with the festivities, but the classicist Erich Segal
Erich Wolf Segal (June 16, 1937January 17, 2010) was an American author, screenwriter, educator, and classicist who wrote the bestselling novel ''Love Story'' (1970) and its hit film adaptation.
Early life and education
Born and raised in a ...
saw Roman comedy
The architectural form of theatre in Rome has been linked to later, more well-known examples from the 1st century BC to the 3rd Century AD. The theatre of ancient Rome referred to as a period of time in which theatrical practice and performance t ...
, with its cast of impudent, free-wheeling slaves and libertine seniors, as imbued with the Saturnalian spirit.
Gambling
 Gambling and dice-playing, normally prohibited or at least frowned upon, were permitted for all, even slaves. Coins and nuts were the stakes. On the
Gambling and dice-playing, normally prohibited or at least frowned upon, were permitted for all, even slaves. Coins and nuts were the stakes. On the Calendar of Philocalus
The ''Chronograph of 354'' (or "Chronography"), also known as the ''Calendar of 354'', is a compilation of chronological and calendrical texts produced in 354 AD for a wealthy Roman Christian named Valentinus by the calligrapher and illustrator ...
, the Saturnalia is represented by a man wearing a fur-trimmed coat next to a table with dice, and a caption reading: "Now you have license, slave, to game with your master." Rampant overeating and drunkenness became the rule, and a sober person the exception.
Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
looked forward to the holiday, if somewhat tentatively, in a letter to a friend:
"It is now the month of December, when the greatest part of the city is in a bustle. Loose reins are given to public dissipation; everywhere you may hear the sound of great preparations, as if there were some real difference between the days devoted to Saturn and those for transacting business. … Were you here, I would willingly confer with you as to the plan of our conduct; whether we should eve in our usual way, or, to avoid singularity, both take a better supper and throw off the toga."Some Romans found it all a bit much. Pliny describes a secluded suite of rooms in his Laurentine
villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
, which he used as a retreat: "...especially during the Saturnalia when the rest of the house is noisy with the licence of the holiday and festive cries. This way I don't hamper the games of my people and they don't hinder my work or studies."
Gift-giving
The Sigillaria on 19 December was a day of gift-giving. Because gifts of value would mark social status contrary to the spirit of the season, these were often thepottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and po ...
or wax figurines called ''sigillaria
''Sigillaria'' is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate '' Lepidodendron''.
Fossil ...
'' made specially for the day, candles, or " gag gifts", of which Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
was particularly fond. Children received toys as gifts. In his many poems about the Saturnalia, Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 an ...
names both expensive and quite cheap gifts, including writing tablets, dice, knucklebones
Knucklebones, also known as scatter jacks, snobs, astragalus, tali, dibs, fivestones, jacks, or jackstones, among many other names, is a game of dexterity played with a number of small objects that are thrown up, caught, and manipulated in var ...
, moneyboxes, combs, toothpicks, a hat, a hunting knife, an axe, various lamps, balls, perfume
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. ...
s, pipes, a pig, a sausage, a parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittaco ...
, tables, cups, spoons, items of clothing, statues, masks, books, and pets. Gifts might be as costly as a slave or exotic animal, but Martial suggests that token gifts of low intrinsic value inversely measure the high quality of a friendship. Patrons
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
or "bosses" might pass along a gratuity ''(sigillaricium)'' to their poorer clients or dependents to help them buy gifts. Some emperors
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother (em ...
were noted for their devoted observance of the Sigillaria.
In a practice that might be compared to modern greeting card
A greeting card is a piece of card stock, usually with an illustration or photo, made of high quality paper featuring an expression of friendship or other sentiment. Although greeting cards are usually given on special occasions such as birthda ...
s, verses sometimes accompanied the gifts. Martial has a collection of poems written as if to be attached to gifts. Catullus received a book of bad poems by "the worst poet of all time" as a joke from a friend.
Gift-giving was not confined to the day of the Sigillaria. In some households, guests and family members received gifts after the feast in which slaves had shared.
King of the Saturnalia

Imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texas
...
sources refer to a ''Saturnalicius princeps'' ("Ruler of the Saturnalia"), who ruled as master of ceremonies for the proceedings. He was appointed by lot, and has been compared to the medieval Lord of Misrule
In England, the Lord of Misrule – known in Scotland as the Abbot of Unreason and in France as the ''Prince des Sots'' – was an officer appointed by lot during Christmastide to preside over the Feast of Fools. The Lord of Misrul ...
at the Feast of Fools
Feast of Fools
The Feast of Fools or Festival of Fools (Latin: ''festum fatuorum, festum stultorum'') was a feast day on January 1 celebrated by the clergy in Europe during the Middle Ages, initially in Southern France, but later more widely. D ...
. His capricious commands, such as "Sing naked!" or "Throw him into cold water!", had to be obeyed by the other guests at the ''convivium'': he creates and (mis)rules a chaotic and absurd world. The future emperor Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 unt ...
is recorded as playing the role in his youth.
Since this figure does not appear in accounts from the Republican period, the ''princeps'' of the Saturnalia may have developed as a satiric response to the new era of rule by a ''princeps
''Princeps'' (plural: ''principes'') is a Latin word meaning "first in time or order; the first, foremost, chief, the most eminent, distinguished, or noble; the first man, first person". As a title, ''princeps'' originated in the Roman Republic w ...
'', the title assumed by the first emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
to avoid the hated connotations of the word "king" ''(rex)''. Art and literature under Augustus celebrated his reign as a new Golden Age, but the Saturnalia makes a mockery of a world in which law is determined by one man and the traditional social and political networks are reduced to the power of the emperor over his subjects. In a poem about a lavish Saturnalia under Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavi ...
, Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the '' Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetr ...
makes it clear that the emperor, like Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandt ...
, still reigns during the temporary return of Saturn.
''Io Saturnalia''
The phrase ''io Saturnalia'' was the characteristic shout or salutation of the festival, originally commencing after the public banquet on the single day of 17 December. Theinterjection
An interjection is a word or expression that occurs as an utterance on its own and expresses a spontaneous feeling or reaction. It is a diverse category, encompassing many different parts of speech, such as exclamations ''(ouch!'', ''wow!''), curse ...
''io'' (Greek ''ἰώ'', ''ǐō'') is pronounced either with two syllables (a short ''i'' and a long ''o'') or as a single syllable (with the ''i'' becoming the Latin consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced ...
al ''j'' and pronounced ''yō''). It was a strongly emotive ritual exclamation or invocation, used for instance in announcing triumph or celebrating Bacchus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; grc, wikt:Διόνυσος, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstas ...
, but also to punctuate a joke.
On the calendar
 As an observance of state religion, Saturnalia was supposed to have been held "''...quarto decimo Kalendarum Ianuariarum''", on the fourteenth day before the
As an observance of state religion, Saturnalia was supposed to have been held "''...quarto decimo Kalendarum Ianuariarum''", on the fourteenth day before the Kalends
The calends or kalends ( la, kalendae) is the first day of every month in the Roman calendar. The English word "calendar" is derived from this word.
Use
The Romans called the first day of every month the ''calends'', signifying the start of a ...
of the pre-Julian, twenty-nine day December, on the oldest Roman religious calendar, which the Romans believed to have been established by the legendary founder Romulus
Romulus () was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of these ...
and his successor Numa Pompilius. It was a '' dies festus'', a legal holiday when no public business could be conducted. The day marked the dedication anniversary ''( dies natalis)'' of the Temple to Saturn in the Roman Forum in 497 BC. When Julius Caesar had the calendar reformed because it had fallen out of synchronization with the solar year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky of a celestial body of the Solar System such as the Earth, completing a full cycle of seasons; for example, the time ...
, two days were added to the month, and the date of Saturnalia then changed, still falling on the 17 December, but with this now being the sixteenth day before the Kalends, as per the Roman reckoning of dates of this time. It was felt, thus, that the original day had thus been moved by two days, and so Saturnalia was celebrated under Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
as a three-day official holiday encompassing both dates.
By the late Republic, the private festivities of Saturnalia had expanded to seven days, but during the Imperial period contracted variously to three to five days. Caligula
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), better known by his nickname Caligula (), was the third Roman emperor, ruling from 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the popular Roman general Germanic ...
extended official observances to five.
The date 17 December was the first day of the astrological sign Capricorn, the house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air ...
of Saturn, the planet named for the god. Its proximity to the winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winte ...
(21 to 23 December on the Julian calendar) was endowed with various meanings by both ancient and modern scholars: for instance, the widespread use of wax candles ''(cerei,'' singular ''cereus)'' could refer to "the returning power of the sun's light after the solstice".
Ancient theological and philosophical views
Roman
 The Saturnalia reflects the contradictory nature of the deity Saturn himself: "There are joyful and utopian aspects of careless well-being side by side with disquieting elements of threat and danger."
As a deity of agricultural bounty, Saturn embodied prosperity and wealth in general. The name of his consort
The Saturnalia reflects the contradictory nature of the deity Saturn himself: "There are joyful and utopian aspects of careless well-being side by side with disquieting elements of threat and danger."
As a deity of agricultural bounty, Saturn embodied prosperity and wealth in general. The name of his consort Ops
In ancient Roman religion, Ops or ''Opis'' (Latin: "Plenty") was a fertility deity and earth goddess of Sabine origin. Her equivalent in Greek mythology was Rhea.
Iconography
In Ops' statues and coins, she is figured sitting down, as Chthon ...
meant "wealth, resources". Her festival, Opalia
The Opiconsivia (or Opeconsiva or Opalia) was an ancient Roman religious festival held August 25 in honor of Ops ("Plenty"), also known as Opis, a goddess of agricultural resources and wealth. The festival marked the end of harvest, with a mirro ...
, was celebrated on 19 December. The Temple of Saturn
The Temple of Saturn (Latin: ''Templum Saturni'' or ''Aedes Saturni''; it, Tempio di Saturno) was an ancient Roman temple to the god Saturn, in what is now Rome, Italy. Its ruins stand at the foot of the Capitoline Hill at the western end of th ...
housed the state treasury (''aerarium Saturni
Aerarium, from ''aes'' (“bronze, money”) + -''ārium'' (“place for”), was the name given in Ancient Rome to the public treasury, and in a secondary sense to the public finances.
''Aerarium populi Romani''
The main ''aerarium'', that o ...
'') and was the administrative headquarters of the quaestor
A ( , , ; "investigator") was a public official in Ancient Rome. There were various types of quaestors, with the title used to describe greatly different offices at different times.
In the Roman Republic, quaestors were elected officials who ...
s, the public officials whose duties included oversight of the mint
MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaAE ...
. It was among the oldest cult sites in Rome, and had been the location of "a very ancient" altar ''(ara
ARA may refer to:
Media and the arts
* American-Romanian Academy of Arts and Sciences
* '' Artistička Radna Akcija'', compilation album released in former Yugoslavia
* Associate of the Royal Academy, denoting membership in the British Royal Acad ...
)'' even before the building of the first temple in 497 BC.
The Romans regarded Saturn as the original and autochthonous
Autochthon, autochthons or autochthonous may refer to:
Fiction
* Autochthon (Atlantis), a character in Plato's myth of Atlantis
* Autochthons, characters in the novel ''The Divine Invasion'' by Philip K. Dick
* Autochthon, a Primordial in the ' ...
ruler of the Capitolium
A ''Capitolium'' (Latin) was an ancient Roman temple dedicated to the Capitoline Triad of gods Jupiter, Juno and Minerva. A capitolium was built on a prominent area in many cities in Italy and the Roman provinces, particularly during the Augu ...
, and the first king of Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil ( Old Latium) on ...
or even the whole of Italy. At the same time, there was a tradition that Saturn had been an immigrant deity, received by Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; la, Ianvs ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janu ...
after he was usurped by his son Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandt ...
(Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion, ...
) and expelled from Greece. His contradictions—a foreigner with one of Rome's oldest sanctuaries, and a god of liberation who is kept in fetters most of the year—indicate Saturn's capacity for obliterating social distinctions.
Roman mythology of the Golden Age of Saturn's reign differed from the Greek tradition. He arrived in Italy "dethroned and fugitive", but brought agriculture and civilization and became a king. As the Augustan poet Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
described it: " gathered together the unruly race f fauns and nymph">faun.html" ;"title="f faun">f fauns and nymphs">faun">f_faun<_a>s_and_nymph.html" ;"title="faun.html" ;"title="f faun">f fauns and nymph">faun.html" ;"title="f faun">f fauns and nymphsscattered over mountain heights, and gave them laws … . Under his reign were the golden ages men tell of: in such perfect peace he ruled the nations."
 The third century Neoplatonic philosopher Porphyry took an allegorical view of the Saturnalia. He saw the festival's theme of liberation and dissolution as representing the "freeing of souls into immortality"—an interpretation that Mithraists may also have followed, since they included many slaves and freedmen. According to Porphyry, the Saturnalia occurred near the
The third century Neoplatonic philosopher Porphyry took an allegorical view of the Saturnalia. He saw the festival's theme of liberation and dissolution as representing the "freeing of souls into immortality"—an interpretation that Mithraists may also have followed, since they included many slaves and freedmen. According to Porphyry, the Saturnalia occurred near the winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winte ...
because the sun enters Capricorn, the astrological house of Saturn, at that time. In the Saturnalia of Macrobius, the proximity of the Saturnalia to the winter solstice leads to an exposition of solar monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxf ...
, the belief that the Sun (see Sol Invictus
Sol Invictus (, "Unconquered Sun"), sometimes simply known as Helios, was long considered to be the official Solar deity, sun god of the later Roman Empire. In recent years, however, the scholarly community has become divided on Sol between tradi ...
) ultimately encompasses all divinities as one.
Jewish
M.Avodah Zarah
''Avodah Zarah'' ( Hebrew: , or "foreign worship", meaning "idolatry" or "strange service") is the name of a tractate of the Talmud, located in '' Nezikin'', the fourth Order of the Talmud dealing with damages. The main topic of the tractate ...
lists Saturnalia as a "festival of the gentiles," along with the Kalents of January and Kratesis. B. Avodah Zarah records that Ḥanan b. Rava said, "Kalends begins eight days after the intersolstice and Saturnura begins eight days before the inter
Inter may refer to:
Association football clubs
* Inter Milan, an Italian club
* SC Internacional, a Brazilian club
* Inter Miami CF, an American club
* FC Inter Sibiu, a Romanian club
* FC Inter Turku, a Finnish club
* FK Inter Bratislava, a forme ...
solstice". Ḥananel b. Ḥushiel, followed by Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki ( he, רבי שלמה יצחקי; la, Salomon Isaacides; french: Salomon de Troyes, 22 February 1040 – 13 July 1105), today generally known by the acronym Rashi (see below), was a medieval French rabbi and author of a compr ...
, claims: "Eight days before the solstice -- their festival was for all eight days," which slightly overstates the Saturnalia's historical six-day length, possibly to associate the holiday with Hanukkah
or English translation: 'Establishing' or 'Dedication' (of the Temple in Jerusalem)
, nickname =
, observedby = Jews
, begins = 25 Kislev
, ends = 2 Tevet or 3 Tevet
, celebrations = Lighting candles each nigh ...
.
In the Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud ( he, תַּלְמוּד יְרוּשַׁלְמִי, translit=Talmud Yerushalmi, often for short), also known as the Palestinian Talmud or Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century ...
, ''Avodah Zarah
''Avodah Zarah'' ( Hebrew: , or "foreign worship", meaning "idolatry" or "strange service") is the name of a tractate of the Talmud, located in '' Nezikin'', the fourth Order of the Talmud dealing with damages. The main topic of the tractate ...
'' claims the etymology of Saturnalia is שנאה טמונה ''śinʾâ ṭǝmûnâ'' "hidden hatred," and refers to the hatred Esau
Esau ''Ēsaû''; la, Hesau, Esau; ar, عِيسَوْ ''‘Īsaw''; meaning "hairy"Easton, M. ''Illustrated Bible Dictionary'', (, , 2006, p. 236 or "rough".Mandel, D. ''The Ultimate Who's Who in the Bible'', (.), 2007, p. 175 is the elder son o ...
, whom the Rabbis believed had fathered Rome, harbored for Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam ...
.
The Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
's ''Avodah Zarah'' ascribes the origins of Saturnalia (and Kalends) to Adam
Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as " ...
, who saw that the days were getting shorter and thought it was punishment for his sin:
In the Babylonian ''Avodah Zarah'', this etiology is attributed to the tannaim
''Tannaim'' ( Amoraic Hebrew: תנאים , singular , ''Tanna'' "repeaters", "teachers") were the rabbinic sages whose views are recorded in the Mishnah, from approximately 10–220 CE. The period of the ''Tannaim'', also referred to as the Mis ...
, but the story is suspiciously similar to the etiology of Kalends attributed by the Jerusalem Avodah Zarah to Abba Arikha
Abba Arikha (175–247 CE; Jewish Babylonian Aramaic: ; born: ''Rav Abba bar Aybo'', ), commonly known as Rav (), was a Jewish amora of the 3rd century. He was born and lived in Kafri, Asoristan, in the Sasanian Empire.
Abba Arikha establ ...
.
Influence
 Unlike several Roman religious festivals which were particular to cult sites in the city, the prolonged seasonal celebration of Saturnalia at home could be held anywhere in the Empire. Saturnalia continued as a secular celebration long after it was removed from the official calendar. As
Unlike several Roman religious festivals which were particular to cult sites in the city, the prolonged seasonal celebration of Saturnalia at home could be held anywhere in the Empire. Saturnalia continued as a secular celebration long after it was removed from the official calendar. As William Warde Fowler
William Warde Fowler (16 May 1847 – 15 June 1921) was an English historian and ornithologist, and tutor at Lincoln College, Oxford. He was best known for his works on ancient Roman religion.
Among his most influential works wa''The Roman ...
notes: " aturnaliahas left its traces and found its parallels in great numbers of medieval and modern customs, occurring about the time of the winter solstice."
The actual date of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
's birth is unknown. A spurious correspondence between Cyril of Jerusalem and Pope Julius I
Pope Julius I was the bishop of Rome from 6 February 337 to his death on 12 April 352. He is notable for asserting the authority of the pope over the Arian Eastern bishops, as well as a dubious claim that he set 25 December as the official birth ...
(337–352), quoted by John of Nikiu in the 9th century, is sometimes given as a source for a claim that, in the fourth century AD, Pope Julius I
Pope Julius I was the bishop of Rome from 6 February 337 to his death on 12 April 352. He is notable for asserting the authority of the pope over the Arian Eastern bishops, as well as a dubious claim that he set 25 December as the official birth ...
formalized that the nativity of Christ should be celebrated on 25 December. Some speculate that this is around the same time as the Saturnalia celebrations, and that part of the reason why he chose this date may have been because he was trying to create a Christian alternative to Saturnalia. Another reason for the decision may have been because, in 274 AD, the Roman emperor Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited ...
had declared 25 December the birthdate of Sol Invictus
Sol Invictus (, "Unconquered Sun"), sometimes simply known as Helios, was long considered to be the official Solar deity, sun god of the later Roman Empire. In recent years, however, the scholarly community has become divided on Sol between tradi ...
and Julius I may have thought that he could attract more converts to Christianity by allowing them to continue to celebrate on the same day. He may have also been influenced by the idea that Jesus had died on the anniversary of his conception; because Jesus died during Passover and, in the third century AD, Passover was celebrated on 25 March, he may have assumed that Jesus's birthday must have come nine months later, on 25 December. But in fact the correspondence is spurious.
As a result of the close proximity of dates, many Christians in western Europe continued to celebrate traditional Saturnalia customs in association with Christmas and the surrounding holidays. Like Saturnalia, Christmas during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
was a time of ruckus, drinking, gambling, and overeating. The tradition of the ''Saturnalicius princeps'' was particularly influential. In medieval France and Switzerland, a boy would be elected " bishop for a day" on 28 December (the Feast of the Holy Innocents) and would issue decrees much like the ''Saturnalicius princeps''. The boy bishop's tenure ended during the evening vespers
Vespers is a service of evening prayer, one of the canonical hours in Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic (both Latin and Eastern), Lutheran, and Anglican liturgies. The word for this fixed prayer time comes from the Latin , meani ...
. This custom was common across western Europe, but varied considerably by region; in some places, the boy bishop's orders could become quite rowdy and unrestrained, but, in others, his power was only ceremonial. In some parts of France, during the boy bishop's tenure, the actual clergy would wear masks or dress in women's clothing, a reversal of roles in line with the traditional character of Saturnalia.
During the late medieval period and early Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
, many towns in England elected a "Lord of Misrule
In England, the Lord of Misrule – known in Scotland as the Abbot of Unreason and in France as the ''Prince des Sots'' – was an officer appointed by lot during Christmastide to preside over the Feast of Fools. The Lord of Misrul ...
" at Christmas time to preside over the Feast of Fools
Feast of Fools
The Feast of Fools or Festival of Fools (Latin: ''festum fatuorum, festum stultorum'') was a feast day on January 1 celebrated by the clergy in Europe during the Middle Ages, initially in Southern France, but later more widely. D ...
. This custom was sometimes associated with the Twelfth Night
''Twelfth Night'', or ''What You Will'' is a romantic comedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written around 1601–1602 as a Twelfth Night's entertainment for the close of the Christmas season. The play centres on the twins V ...
or Epiphany. A common tradition in western Europe was to drop a bean, coin, or other small token into a cake or pudding; whoever found the object would become the "King (or Queen) of the Bean". During the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
, reformers sought to revise or even completely abolish such practices, which they regarded as "popish
The words Popery (adjective Popish) and Papism (adjective Papist, also used to refer to an individual) are mainly historical pejorative words in the English language for Roman Catholicism, once frequently used by Protestants and Eastern Orthodo ...
"; these efforts were largely successful. The Puritans banned the "Lord of Misrule" in England and the custom was largely forgotten shortly thereafter, though the bean in the pudding survived as a tradition of a small gift to the one finding a single almond hidden in the traditional Christmas porridge in Scandinavia.
Nonetheless, in the middle of the nineteenth century, some of the old ceremonies, such as gift-giving, were revived in English-speaking countries as part of a widespread "Christmas revival". During this revival, authors such as Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
sought to reform the "conscience of Christmas" and turn the formerly riotous holiday into a family-friendly occasion. Vestiges of the Saturnalia festivities may still be preserved in some of the traditions now associated with Christmas. The custom of gift-giving at Christmas time resembles the Roman tradition of giving ''sigillaria'' and the lighting of Advent candles resembles the Roman tradition of lighting torches and wax tapers. Likewise, Saturnalia and Christmas both share associations with eating, drinking, singing, and dancing.
See also
*Brumalia
The Brumalia ( la, Brumalia ) were a winter solstice festival celebrated in the eastern part of the Roman Empire. In Rome there had been the minor holiday of Bruma on November 24, which turned into large scale end of the year festivities in Const ...
* Yule
Yule, actually Yuletide ("Yule time") is a festival observed by the historical Germanic peoples, later undergoing Christianised reformulation resulting in the now better-known Christmastide. The earliest references to Yule are by way of indige ...
* Bacchanalia
The Bacchanalia were unofficial, privately funded popular Roman festivals of Bacchus, based on various ecstatic elements of the Greek Dionysia. They were almost certainly associated with Rome's native cult of Liber, and probably arrived in Ro ...
References
Bibliography
Ancient sources
*Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his ...
''Satire'2.7.4
* Justinus
Epitome of Pompeius Trogus
' *
Macrobius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was ...
Saturnalia
' * Pliny the Younger
Letters
'
Modern secondary sources
* * * * *External links
*Saturnalia – World History Encyclopedia
A longer article by James Grout {{Roman religion (festival) Saturn (mythology) Ancient Roman festivals December observances Winter festivals Religious festivals in Italy