Satmodem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A satellite modem or satmodem is a
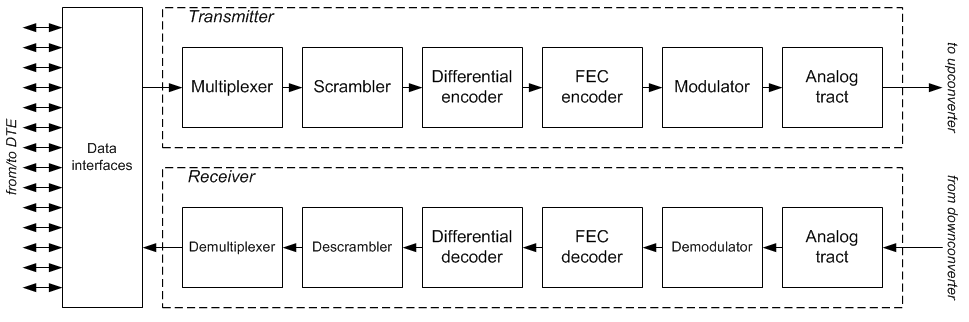 Probably the best way of understanding how a modem works is to look at its internal structure. A block diagram of a generic satellite modem is shown on the image.
Probably the best way of understanding how a modem works is to look at its internal structure. A block diagram of a generic satellite modem is shown on the image.

 Satellite modems are often used for home internet access.
There are two different types, both employing the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard as their basis:
* One-way satmodems (DVB-IP modems) use a return channel not based on communication with the satellite, such as
Satellite modems are often used for home internet access.
There are two different types, both employing the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard as their basis:
* One-way satmodems (DVB-IP modems) use a return channel not based on communication with the satellite, such as
modem
A modulator-demodulator or modem is a computer hardware device that converts data from a digital format into a format suitable for an analog transmission medium such as telephone or radio. A modem transmits data by Modulation#Digital modulati ...
used to establish data transfer
Data transmission and data reception or, more broadly, data communication or digital communications is the transfer and reception of data in the form of a digital bitstream or a digitized analog signal transmitted over a point-to-point or ...
s using a communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth ...
as a relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
. A satellite modem's main function is to transform an input bitstream to a radio signal and vice versa.
There are some devices that include only a demodulator (and no modulator, thus only allowing data to be downloaded by satellite) that are also referred to as "satellite modems." These devices are used in satellite Internet access (in this case uploaded data is transferred through a conventional PSTN
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) provides infrastructure and services for public telecommunication. The PSTN is the aggregate of the world's circuit-switched telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local teleph ...
modem or an ADSL
Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) technology, a data communications technology that enables faster data transmission over copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem can provide. ...
modem).
Satellite link
A satellite modem is not the only device needed to establish a communication channel. Other equipment that is essential for creating a satellite link include satellite antennas and frequency converters. Data to be transmitted are transferred to a modem fromdata terminal equipment
Data terminal equipment (DTE) is an end instrument that converts user information into signals or reconverts received signals. These can also be called tail circuits. A DTE device communicates with the data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) ...
(e.g. a computer). The modem usually has intermediate frequency (IF) output (that is, 50-200 MHz), however, sometimes the signal is modulated directly to L band
The L band is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) designation for the range of frequencies in the radio spectrum from 1 to 2 gigahertz (GHz). This is at the top end of the ultra high frequency (UHF) band, at the lower en ...
. In most cases, frequency has to be converted using an upconverter before amplification and transmission.
A modulated signal is a sequence of ''symbols'', pieces of data represented by a corresponding signal state, e.g. a bit or a few bits, depending upon the modulation scheme being used. Recovering a symbol clock (making a local symbol clock generator synchronous with the remote one) is one of the most important tasks of a demodulator.
Similarly, a signal received from a satellite is firstly downconverted (this is done by a Low-noise block converter
A low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is the receiving device mounted on satellite dishes used for satellite TV reception, which collects the radio waves from the dish and converts them to a signal which is sent through a cable to the receiver ...
- LNB), then demodulated by a modem, and at last handled by data terminal equipment. The LNB is usually powered by the modem through the signal cable with 13 or 18 V DC.
Features
The main functions of a satellite modem are modulation and demodulation. Satellite communication standards also define error correction codes and framing formats. Popular modulation types being used for satellite communications: * Binary phase-shift keying (BPSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at ...
);
* Quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at ...
);
* Offset quadrature phase-shift keying ( OQPSK);
* 8PSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at ...
;
* Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signa ...
(QAM), especially 16QAM.
The popular satellite error correction codes include:
* Convolutional code
In telecommunication, a convolutional code is a type of error-correcting code that generates parity symbols via the sliding application of a boolean polynomial function to a data stream. The sliding application represents the 'convolution' of t ...
s:
** with constraint length
In telecommunication, a convolutional code is a type of error-correcting code that generates parity symbols via the sliding application of a boolean polynomial function to a data stream. The sliding application represents the 'convolution' of t ...
less than 10, usually decoded using a Viterbi algorithm
The Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for obtaining the maximum a posteriori probability estimate of the most likely sequence of hidden states—called the Viterbi path—that results in a sequence of observed events, especiall ...
(see Viterbi decoder);
** with constraint length
In telecommunication, a convolutional code is a type of error-correcting code that generates parity symbols via the sliding application of a boolean polynomial function to a data stream. The sliding application represents the 'convolution' of t ...
more than 10, usually decoded using a Fano algorithm Recognised by John Wozencraft, sequential decoding is a limited memory technique for decoding tree codes. Sequential decoding is mainly used as an approximate decoding algorithm for long constraint-length convolutional codes. This approach may ...
(see Sequential decoder Recognised by John Wozencraft, sequential decoding is a limited memory technique for decoding tree codes. Sequential decoding is mainly used as an approximate decoding algorithm for long constraint-length convolutional codes. This approach may ...
);
* Reed–Solomon codes usually concatenated with convolutional codes with an interleaving;
* New modems support superior error correction codes (turbo code
In information theory, turbo codes (originally in French ''Turbocodes'') are a class of high-performance forward error correction (FEC) codes developed around 1990–91, but first published in 1993. They were the first practical codes to closel ...
s and LDPC
In information theory, a low-density parity-check (LDPC) code is a linear error correcting code, a method of transmitting a message over a noisy transmission channel. An LDPC code is constructed using a sparse Tanner graph (subclass of the bip ...
codes).
Frame formats that are supported by various satellite modems include:
* Intelsat business service (IBS) framing
* Intermediate data rate (IDR) framing
* MPEG-2 transport framing (used in DVB
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) o ...
)
* E1 and T1 framing
High-end
In economics, a luxury good (or upmarket good) is a good for which demand increases more than what is proportional as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a greater proportion of overall spending. Luxury goods are in contrast t ...
modems also incorporate some additional features:
* Multiple data interfaces (like RS-232
In telecommunications, RS-232 or Recommended Standard 232 is a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a ''DTE'' (''data terminal equipment'') such ...
, RS-422
RS-422, also known as TIA/EIA-422, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. It was meant to be the foundation of a suite of standards that ...
, V.35, G.703, LVDS
Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS), also known as TIA/EIA-644, is a technical standard that specifies electrical characteristics of a differential, serial signaling standard. LVDS operates at low power and can run at very high speeds ...
, Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1 ...
);
* ''Embedded Distant-end Monitor and Control'' (EDMAC), allowing to control the distant-end modem;
* ''Automatic Uplink Power Control'' (AUPC), that is, adjusting the output power to maintain a constant signal to noise ratio at the remote end;
* Drop and insert feature for a multiplexed
In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource - a ...
stream, allowing to replace some channels in it.
Internal structure
 Probably the best way of understanding how a modem works is to look at its internal structure. A block diagram of a generic satellite modem is shown on the image.
Probably the best way of understanding how a modem works is to look at its internal structure. A block diagram of a generic satellite modem is shown on the image.
Analog tract
After adigital-to-analog conversion
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
There are several DAC archite ...
in the transmitter, the signal passes through a reconstruction filter
In a mixed-signal system ( analog and digital), a reconstruction filter, sometimes called an anti-imaging filter, is used to construct a smooth analog signal from a digital input, as in the case of a digital to analog converter ( DAC) or other samp ...
. Then, if needed, frequency conversion is performed.
The purpose of the analog tract in the receiver is to convert signal's frequency, to adjust its power via an automatic gain control circuit and to get its complex envelope
In mathematics and signal processing, an analytic signal is a complex-valued function that has no negative frequency components. The real and imaginary parts of an analytic signal are real-valued functions related to each other by the Hil ...
components.
The input signal for the analog tract is at the intermediate frequency, sometimes, in the L band
The L band is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) designation for the range of frequencies in the radio spectrum from 1 to 2 gigahertz (GHz). This is at the top end of the ultra high frequency (UHF) band, at the lower en ...
, in which case it must be converted to an IF. Then the signal is either sampled
Sample or samples may refer to:
Base meaning
* Sample (statistics), a subset of a population – complete data set
* Sample (signal), a digital discrete sample of a continuous analog signal
* Sample (material), a specimen or small quantity of so ...
or processed by the four-quadrant multiplier which produces the complex envelope components ('' I, Q'') through multiplying it by the heterodyne frequency (see superheterodyne receiver).
At last the signal passes through an anti-aliasing filter
An anti-aliasing filter (AAF) is a filter used before a signal sampler to restrict the bandwidth of a signal to satisfy the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem over the band of interest. Since the theorem states that unambiguous reconstruct ...
and is sampled
Sample or samples may refer to:
Base meaning
* Sample (statistics), a subset of a population – complete data set
* Sample (signal), a digital discrete sample of a continuous analog signal
* Sample (material), a specimen or small quantity of so ...
or (digitized).
Modulator and demodulator
A digital modulator transforms a digital stream into a radio signal at the intermediate frequency (IF). A modulator is generally simpler than a demodulator because it doesn't have to recover symbol and carrier frequencies. A demodulator is one of the most important parts of the receiver. The exact structure of the demodulator is defined by a modulation type. However, the fundamental concepts are similar. Moreover, it is possible to develop a demodulator that can process signals with different modulation types. Digital demodulation implies that a ''symbol clock'' (and, in most cases, an intermediate frequency generator) at the receiving side has to be synchronous with those at the transmitting side. This is achieved by the following two circuits: * timing recovery circuit, determining the borders of symbols; * carrier recovery circuit, which determines the actual meaning of each symbol. There are modulation types (like frequency-shift keying) that can be demodulated without carrier recovery, however, this method, known as ''noncoherent demodulation'', is generally worse. There are also additional components in the demodulator such as theintersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference (ISI) is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have a similar effect as noise, thus making ...
equalizer.
If the analog signal was digitized without a four-quadrant multiplier, the complex envelope has to be calculated by a digital ''complex mixer''.
Sometimes a digital automatic gain control circuit is implemented in the demodulator.
FEC coding
Error correction techniques are essential for satellite communications, because, due to satellite's limited power asignal-to-noise
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal (electrical engineering), signal to the level of background Noise (signal processing), noise. SNR is defined as the ratio ...
ratio at the receiver is usually rather poor. Error correction works by adding an artificial redundancy to a data stream at the transmitting side and using this redundancy to correct errors caused by noise and interference. This is performed by an ''FEC encoder.'' The encoder applies an error correction code to the digital stream, thereby adding redundancy.
An ''FEC decoder'' decodes the Forward error correction code used within the signal. For example, the Digital Video Broadcasting standard defines a concatenated code consisting of inner convolutional (standard NASA code, punctured, with rates , , , , ), interleaving and outer Reed–Solomon code (block length: 204 bytes, information block: 188 bytes, can correct up to 8 bytes in the block).
Differential coding
There are several modulation types (such as PSK andQAM
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signa ...
) that have a phase ambiguity, that is, a carrier can be restored in different ways. Differential coding In digital communications, differential coding is a technique used to provide ''unambiguous'' signal reception when using some types of modulation. It makes data to be transmitted to depend not only on the current signal state (or symbol), but also ...
is used to resolve this ambiguity.
When differential coding is used, the data are deliberately made to depend not only on the current ''symbol'', but also on the previous one.
Scrambling
Scrambling
Scrambling is a mountaineering term for ascending steep terrain using one's hands to assist in holds and balance.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. It is also used to describe terrain that falls between hiking and rock climbing (as a “scrambl ...
is a technique used to randomize a data stream to eliminate long '0'-only and '1'-only sequences and to assure energy dispersal. Long '0'-only and '1'-only sequences create difficulties for timing recovery circuit. Scramblers and descramblers are usually based on linear-feedback shift register
In computing, a linear-feedback shift register (LFSR) is a shift register whose input bit is a linear function of its previous state.
The most commonly used linear function of single bits is exclusive-or (XOR). Thus, an LFSR is most often a ...
s.
A scrambler randomizes the transmitted data stream. A descrambler restores the original stream from the scrambled one.
Scrambling shouldn't be confused with encryption, since it doesn't protect information from intruders.
Multiplexing
Amultiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The sel ...
transforms several digital streams into one stream. This is often referred to as 'muxing.'
Generally, a demultiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The sel ...
is a device that transforms one multiplexed
In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource - a ...
data stream into several. Satellite modems don't have many outputs, so a ''demultiplexer'' here performs a drop operation, allowing to the modem to choose channels that will be transferred to the output.
A demultiplexer achieves this goal by maintaining ''frame synchronization''.
Applications

 Satellite modems are often used for home internet access.
There are two different types, both employing the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard as their basis:
* One-way satmodems (DVB-IP modems) use a return channel not based on communication with the satellite, such as
Satellite modems are often used for home internet access.
There are two different types, both employing the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard as their basis:
* One-way satmodems (DVB-IP modems) use a return channel not based on communication with the satellite, such as telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
or cable
Cable may refer to:
Mechanical
* Nautical cable, an assembly of three or more ropes woven against the weave of the ropes, rendering it virtually waterproof
* Wire rope, a type of rope that consists of several strands of metal wire laid into a hel ...
.
* Two-way satmodems ( DVB-RCS modems, also called astromodems) employ a satellite-based return channel as well; they do not need another connection. DVB-RCS is ETSI standard Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object th ...
EN 301 790.
There are also industrial satellite modems intended to provide a permanent link. They are used, for example, in the Steel shankar network.
See also
*Communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth ...
* Yahsat
Al Yah Satellite Communications Company P.J.S.C. (Yahsat) is a public company listed on thAbu Dhabi Securities Exchange (ADX)and a subsidiary of Mubadala Investment Company PJSC, offering multi-mission satellite services in more than 150 countries ...
* Intelsat
* Satellite Internet access
* VSAT
A very-small-aperture terminal (VSAT) is a two-way satellite ground station with a dish antenna that is smaller than 3.8 meters. The majority of VSAT antennas range from 75 cm to 1.2 m. Bit rates, in most cases, range from 4 kbit/s up to 1 ...
External links
{{Satcomm Satellite broadcasting Modems Telecommunications equipment Telecommunications infrastructure