Santa Fe Trail (short Subjects) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central

 The Santa Fe Trail was a transportation route opened by the Indians as well as European trappers and traders in the second half of the 18th century. It was later used extensively by people from the United States in the 19th century after the Louisiana Purchase. Traders and settlers crossed the southwest of North America by the route connecting Independence, Missouri, with
The Santa Fe Trail was a transportation route opened by the Indians as well as European trappers and traders in the second half of the 18th century. It was later used extensively by people from the United States in the 19th century after the Louisiana Purchase. Traders and settlers crossed the southwest of North America by the route connecting Independence, Missouri, with
 In 1825, the merchant Manuel Escudero of Chihuahua was commissioned by New Mexico governor
In 1825, the merchant Manuel Escudero of Chihuahua was commissioned by New Mexico governor
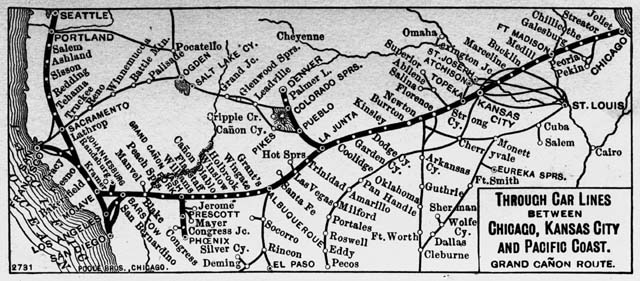 In 1863, with all the political bickering over railroad legislation, entrepreneurs opened their pockets and set their sights on the American Southwest leading to the gradual construction east to west of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway; the name eponymously reflecting the intentions of the founders, the expected eastern terminus to be in Atchison, Kansas.
Inside Kansas, the AT&SF roadbed roughly paralleled the Santa Fe Trail west of Topeka as it expanded between 1868 and 1874. When a railroad bridge was built across the Missouri River to connect eastern markets to the Dodge City cattle trail and Colorado coal mines, the railroad spurred the growth of
In 1863, with all the political bickering over railroad legislation, entrepreneurs opened their pockets and set their sights on the American Southwest leading to the gradual construction east to west of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway; the name eponymously reflecting the intentions of the founders, the expected eastern terminus to be in Atchison, Kansas.
Inside Kansas, the AT&SF roadbed roughly paralleled the Santa Fe Trail west of Topeka as it expanded between 1868 and 1874. When a railroad bridge was built across the Missouri River to connect eastern markets to the Dodge City cattle trail and Colorado coal mines, the railroad spurred the growth of

 The eastern end of the trail was in the central Missouri town of Franklin on the north bank of the Missouri River. The route across Missouri first used by Becknell followed portions of the existing
The eastern end of the trail was in the central Missouri town of Franklin on the north bank of the Missouri River. The route across Missouri first used by Becknell followed portions of the existing
 Travelers faced many hardships along the Santa Fe Trail. The trail was a challenging of dangerous plains, hot deserts, and steep and rocky mountains. The natural weather was and is continental: very hot and dry summers, coupled with long and bitterly cold winters. Fresh water was scarce, and the high steppe-like plains are nearly treeless. Water flows in the Pecos, Arkansas, Cimarron, and Canadian rivers that drain the region vary by 90 or more percent in their flows during an average year. Also on this trail, unlike the Oregon Trail, there was a serious danger of Indian attacks, for neither the
Travelers faced many hardships along the Santa Fe Trail. The trail was a challenging of dangerous plains, hot deserts, and steep and rocky mountains. The natural weather was and is continental: very hot and dry summers, coupled with long and bitterly cold winters. Fresh water was scarce, and the high steppe-like plains are nearly treeless. Water flows in the Pecos, Arkansas, Cimarron, and Canadian rivers that drain the region vary by 90 or more percent in their flows during an average year. Also on this trail, unlike the Oregon Trail, there was a serious danger of Indian attacks, for neither the


 ;MissouriSanta Fe trail, Official Map and Guide; National Park Service; Harpers Ferry, West Virginia; 1997
* Arrow Rock (Arrow Rock Landing, Santa Fe Spring, Huston Tavern)
* Harvey Spring/Weinrich Ruts
* Independence (Santa Fe trail Ruts, Lower Independence (Blue Mills) Landing, Upper Independence (Wayne City) Landing.
*
;MissouriSanta Fe trail, Official Map and Guide; National Park Service; Harpers Ferry, West Virginia; 1997
* Arrow Rock (Arrow Rock Landing, Santa Fe Spring, Huston Tavern)
* Harvey Spring/Weinrich Ruts
* Independence (Santa Fe trail Ruts, Lower Independence (Blue Mills) Landing, Upper Independence (Wayne City) Landing.
*
The Great Prairie Highway
(National Park Service)
at Pecos National Park (National Park Service)
Santa Fe Trail Center
Santa Fe Trail Research
* ttp://www.kansasmemory.org/locate.php?categories=362-367&/ Access documents, photographs, and other primary sources on Kansas Memory, the Kansas State Historical Society's digital portal
New Mexico Santa Fe Trail National Scenic Byway
* ttp://www.kansasheritage.org/werner/ Pioneer Trails from US Land Surveys
Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory
{{Authority control Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Colorado Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Missouri Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in New Mexico Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Oklahoma Historic trails and roads in New Mexico Historic trails and roads in Colorado Historic trails and roads in Kansas Historic trails and roads in Missouri Historic trails and roads in Oklahoma Native American trails in the United States Trails and roads in the American Old West Colorado Territory Jefferson Territory New Mexico Territory New Mexico Scenic and Historic Byways 1822 establishments in the United States National Historic Trails of the United States Native American history of Colorado Native American history of New Mexico Native American history of Kansas Native American history of Missouri Native American history of Oklahoma
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell
William Becknell (1787 or 1788 – April 30, 1865) was an American soldier, politician, and freight operator who is credited by Americans with opening the Santa Fe Trail in 1821. He found a trail for part of the route that was wide enough for w ...
, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, the trail served as a vital commercial highway until 1880, when the railroad arrived in Santa Fe. Santa Fe was near the end of El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro which carried trade from Mexico City. The trail was later incorporated into parts of the National Old Trails Road and U.S. Route 66.
The route skirted the northern edge and crossed the north-western corner of Comancheria, the territory of the Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
. Realizing the value, they demanded compensation for granting passage to the trail. American traders envisioned them as another market. Comanche raiding farther south in Mexico isolated New Mexico, making it more dependent on the American trade. They raided to gain a steady supply of horses to sell. By the 1840s, trail traffic through the Arkansas Valley was so numerous that bison herds were cut off from important seasonal grazing land. This habitat disruption
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, on top of overhunting, contributed to the collapse of the species. Comanche power declined in the region when they lost their most important game.
In 1846, during the Mexican–American War, the United States Army used the Santa Fe Trail to invade New Mexico.
After the U.S. acquisition of the Southwest that ended the war, the trail was integral to the U.S. opening the region to economic development and settlement. It played a vital role in the westward expansion of the U.S. into these new lands. The road route is commemorated today by the National Park Service as the Santa Fe National Historic Trail. A highway route that roughly follows the trail's path, through the entire length of Kansas, the southeast corner of Colorado and northern New Mexico, has been designated as the Santa Fe Trail National Scenic Byway
A National Scenic Byway is a road recognized by the United States Department of Transportation for one or more of six "intrinsic qualities": archeological, cultural, historic, natural, recreational, and scenic. The program was established by Co ...
.
History

Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe ( ; , Spanish for 'Holy Faith'; tew, Oghá P'o'oge, Tewa for 'white shell water place'; tiw, Hulp'ó'ona, label=Tiwa language, Northern Tiwa; nv, Yootó, Navajo for 'bead + water place') is the capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico. ...
. Its major market in Missouri was St. Louis, with its port on the Mississippi River.
In 1719, the French officer Claude Charles Du Tisne was tasked by french authorities to establish a route to trade with the Spanish colony of Santa Fe in New Mexico. This first expedition, which started in Kaskaskia, Illinois
Kaskaskia is a village in Randolph County, Illinois. Having been inhabited by indigenous peoples, it was settled by France as part of the Illinois Country. It was named for the Kaskaskia people. Its population peaked at about 7,000 in the 18th c ...
, failed, as it was stopped by Indian tribes in Kansas. Then, at the time of the Louisiana regime, under French and then Spanish sovereignty, the French traders Pierre Antoine and Paul Mallet made a first trip in 1739 and 1740, starting also from Kaskaskia, Illinois
Kaskaskia is a village in Randolph County, Illinois. Having been inhabited by indigenous peoples, it was settled by France as part of the Illinois Country. It was named for the Kaskaskia people. Its population peaked at about 7,000 in the 18th c ...
, reaching Santa Fe and returning. They made other expeditions in 1741 and 1750, which faced various challenges from Indians and Spaniards. Then, the French explorer Pierre Vial
Pierre Vial (born 25 December 1942) is an academic medievalist tied to the Jean Moulin University Lyon 3. A Nouvelle Droite leader, he is the founder of the Identitarian association Terre et Peuple.
Biography
Pierre Vial was born on 25 Decembe ...
made another pioneering trip on the route in 1792, and French traders and trappers from St. Louis gained progressively a fur trading dominance from the Spanish in Santa Fe as well as with the Indian tribes living in this vast region. Other French traders and trappers made trips on the trail from St. Louis, such as Auguste Pierre Chouteau
Auguste Pierre Chouteau (9 May 1786 – 25 December 1838) was a member of the Chouteau fur-trading family who established trading posts in what is now the U.S. state of Oklahoma.
Chouteau was born in St. Louis, then part of Spanish colonia ...
and Jules de Mun
Jules is the French form of the Latin "Julius" (e.g. Jules César, the French name for Julius Caesar). It is the given name of:
People with the name
*Jules Aarons (1921–2008), American space physicist and photographer
*Jules Abadie (1876–195 ...
in 1815, who were arrested by Spanish authorities in Santa Fe.
After Louisiana was sold to the United States in 1803 (Louisiana Purchase), Americans improved and publicized the Santa Fe Trail beginning in 1822, in order to take advantage of new trade opportunities with Mexico which had just won independence from Spain in the Mexican War of Independence. Manufactured goods were hauled from Missouri to Santa Fe, which was then in the northern Mexican state of '' Nuevo Mexico''.
Settlers seeking the opportunity to hold free land used wagon trains to follow various emigrant trail
In the history of the American frontier, overland trails were built by pioneers throughout the 19th century and especially between 1829 and 1870 as an alternative to sea and railroad transport. These immigrants began to settle much of North Ame ...
s that branched off to points west. The political philosophy of manifest destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
There were three basic tenets to the concept:
* The special vir ...
, the idea that the U.S. should extend from one coast to another, dominated national political discussions. The trail connected interior port cities along the Mississippi and Missouri and their wagon train outfitters to western destinations. The trail was used to carry products from the central plains to the trail head towns St. Joseph and Independence, Missouri.
In the 1820s–1830s, it was also sporadically important in the reverse trade, used by traders to transport foods and supplies to the fur trappers and mountain men opening the remote Northwest, especially in the interior Northwest: Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, and Montana. A mule trail (trapper's trails) led to points north to supply the lucrative overland fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
in ports on the Pacific Coast.
North–South trade
Santa Fe was near the northern terminus of El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro, which led overland between Mexico City to San Juan Pueblo, New Mexico. Cargo mule trains were run fromFort Bernard Fort Bernard was a small trading post in Wyoming, along the North Platte River on the Oregon Trail. It was established in 1845 on the site of an older fort established in the late 1830s. It was located about 8 miles southeast of Fort Laramie, and h ...
in Wyoming to the Santa Fe Trail at Fort Bent
Bent's Old Fort is an 1833 fort located in Otero County in southeastern Colorado, United States. A company owned by Charles Bent and William Bent and Ceran St. Vrain built the fort to trade with Southern Cheyenne and Arapaho Plains Indians and ...
in Colorado .
Importance of Santa Fe
Bartolome Baca Bartolome is a Tagalog surname and may refer to:
* Donnalyn Bartolome (1994), Filipina internet personality, vlogger, singer, songwriter and rapper
* Heber Bartolome (1948–2021), Filipino folk and rock singer, songwriter, composer, poet, guitaris ...
to negotiate in Washington, D.C. for opening U.S. borders to traders from Mexico. Beginning in 1826, prominent aristocratic families of New Mexicans, such as the Chávezes, Armijos, Pereas, and Oteros, entered into the commerce along the trail. By 1843, traders from New Mexico and Chihuahua had become the majority of traders involved in the traffic of goods over the Santa Fe Trail.Marc Simmons, ''Murder on the Santa Fe Trail: an International Incident, 1843'', El Paso, Texas: The University of Texas El Paso (1987)
In 1835, Mexico City had sent Albino Pérez to govern the department of New Mexico as ''Jefe Politico'' (political chief or governor) and as commanding military officer. In 1837, the forces of ''Rio Arriba'' (the upper Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
, i.e., northern New Mexico) rebelled against Pérez's enforcement of the recent Mexican constitution, new revenue laws taxing Santa Fe commerce and entertainment, and the large grants of New Mexico land to wealthy Mexicans. New Mexicans appreciated the relative freedoms of a frontier, remote from Mexico City. The rebels defeated and executed governor Albino Perez, but were later ousted by the forces of ''Rio Abajo'' (the lower Rio Grande, or southern New Mexico) led by Manuel Armijo.
Conflict between Texas and Mexico
TheRepublic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
competed with Mexico in claiming Santa Fe, as part of the territory north and east of the Rio Grande which both nations claimed following Texas's secession from Mexico in 1836.
In 1841, a small military and trading expedition departed from Austin, Texas for Santa Fe. They represented the Republic of Texas and its president Mirabeau B. Lamar. Their intention was to persuade the people of Santa Fe and New Mexico to relinquish control over the territory under dispute with Mexico, and over associated Santa Fe Trail commerce. Knowing about recent political disturbances there, they hoped for a welcome by the rebellious faction in New Mexico. What was known as the Texan Santa Fe Expedition encountered many difficulties. The party was captured by governor Armijo's Mexican army under less than honest negotiations. They were subjected to harsh and austere treatment during a tortuous forced march to Mexico City, where they were tried, convicted and imprisoned for their insurgent activities.
In 1842, Colonel William A. Christy wrote Sam Houston
Samuel Houston (, ; March 2, 1793 – July 26, 1863) was an American general and statesman who played an important role in the Texas Revolution. He served as the first and third president of the Republic of Texas and was one of the first two i ...
, president of Texas, requesting support for an overthrow scheme by Charles Warfield dependent on armed forces. He proposed deposing the governments in the Mexican provinces of New Mexico and Chihuahua and returning half of the spoils to the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
. Houston agreed, provided the operation be conducted under the strictest secrecy.
He commissioned Warfield as a colonel, who attempted to raise volunteers in Texas, St. Louis, Missouri; and the southern Rockies for a Warfield Expedition. He recruited John McDaniel and a small band of men in the proximate vicinity of St. Louis, giving McDaniel the rank of a Texas captain. After Warfield headed toward the Rockies with a companion, McDaniel led a robbery in April 1843 (in present-day Rice County, Kansas) of a lightly defended Santa Fe Trail trading caravan. This resulted in the murder of its leader Antonio José Chávez, the son of a former governor of New Mexico, Francisco Xavier Chávez.
Warfield was reportedly unaware of the crime. McDaniel and one accomplice were tried, convicted and executed. Other participating suspects arrested by the U.S. were convicted and imprisoned. The newspapers reported that Americans and Mexicans were outraged by the crime. Local merchants and citizens at the U.S. end of the Santa Fe Trail demanded justice and a return to the stable commerce which their economy depended on.
After the murder of Chávez, Warfield began limited military hostilities in the region using recruits from the southern Rockies. He made an unprovoked attack on Mexican troops outside Mora, New Mexico, leaving five dead. Warfield lost his horses after an encounter in Wagon Mound, where the Mexican forces had made chase. After Warfield's men reached Bent's Fort on foot, they disbanded.
In February 1843, Colonel Jacob Snively had received a commission to intercept Mexican caravans along the Santa Fe Trail, similar to that received by Warfield the year prior. After disbanding the volunteers under his command, Warfield located and joined the 190-man, Texas "Battalion of Invincibles," under the command of Snively. New Mexico Governor Manuel Armijo led Mexican troops out of Santa Fe to protect incoming caravans. But, after the Invincibles destroyed much of an advance party led by Captain Ventura Lovato, the governor retreated. Following this battle, many Americans resigned and Snively's force was reduced to little over 100 men. Snively planned to plunder Mexican merchant caravans on territory claimed by Texas, in retaliation for recent Texian executions and Mexican invasions, but his battalion was quickly arrested and disarmed by the US troops escorting the caravans. After disarming these men, Captain Philip St. George Cooke
Philip St. George Cooke (June 13, 1809 – March 20, 1895) was a career United States Army cavalry officer who served as a Union General in the American Civil War. He is noted for his authorship of an Army cavalry manual, and is sometimes called ...
allowed them to return to Texas.
Mother of the railroad
 In 1863, with all the political bickering over railroad legislation, entrepreneurs opened their pockets and set their sights on the American Southwest leading to the gradual construction east to west of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway; the name eponymously reflecting the intentions of the founders, the expected eastern terminus to be in Atchison, Kansas.
Inside Kansas, the AT&SF roadbed roughly paralleled the Santa Fe Trail west of Topeka as it expanded between 1868 and 1874. When a railroad bridge was built across the Missouri River to connect eastern markets to the Dodge City cattle trail and Colorado coal mines, the railroad spurred the growth of
In 1863, with all the political bickering over railroad legislation, entrepreneurs opened their pockets and set their sights on the American Southwest leading to the gradual construction east to west of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway; the name eponymously reflecting the intentions of the founders, the expected eastern terminus to be in Atchison, Kansas.
Inside Kansas, the AT&SF roadbed roughly paralleled the Santa Fe Trail west of Topeka as it expanded between 1868 and 1874. When a railroad bridge was built across the Missouri River to connect eastern markets to the Dodge City cattle trail and Colorado coal mines, the railroad spurred the growth of Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City (abbreviated KC or KCMO) is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central ...
. Building the railway so that it extended westwards to destinations in and beyond the New Mexico border was delayed and kept the fledgling railroad gasping for cash. In a move to bootstrap their own base market, the railway began offering packaged "Shopping Excursion deals" to potential buyers desiring to look over a real estate parcel. The railroad began to discount such trips to visit its land offices and gave back the ticket price as part of the purchase price, if a sale was concluded.
The railroad's sale of its land granted by congress fostered growth of new towns and businesses along its route, which generated railway traffic and revenues. With this financial base, the railway extended west, gradually adding new connections through rougher west country along the western Trail. With the development of rail transport, traffic on the Trail soon dropped to merely local trade. In a sense, after World War I the trail was reborn; by the 1920s it gradually became paved automobile roads.
Route
 The eastern end of the trail was in the central Missouri town of Franklin on the north bank of the Missouri River. The route across Missouri first used by Becknell followed portions of the existing
The eastern end of the trail was in the central Missouri town of Franklin on the north bank of the Missouri River. The route across Missouri first used by Becknell followed portions of the existing Osage Trace
The Great Osage Trail, also known as the Osage Trace or the Kaw Trace, was one of the more well-known Native American trails through the countryside of what are today called the Midwest and Plains States of the U.S., pathways originally created ...
and the Medicine Trails. West of Franklin, the trail crossed the Missouri near Arrow Rock, after which it followed roughly the route of present-day U.S. Route 24. It passed north of Marshall, through Lexington to Fort Osage, then to Independence. Independence was also one of the historic "jumping off points" for the Oregon and California Trail
The California Trail was an emigrant trail of about across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California. After it was established, the first half of the California Trail f ...
s.
West of Independence, it roughly followed the route of U.S. Route 56
U.S. Route 56 (US 56) is an east–west United States highway that runs for approximately in the Midwestern United States. US 56's western terminus is at Interstate 25 Business (I-25 Bus.), US 412 and New Mexico State Road 21 (NM 21) in Springe ...
from near the town of Olathe
Olathe ( ) is the county seat of Johnson County, Kansas, United States. It is the fourth-most populous city in both the Kansas City metropolitan area and the state of Kansas, with a 2020 population of 141,290.
History 19th century
Olathe was ...
to the western border of Kansas. It enters Colorado, cutting across the southeast corner of the state before entering New Mexico. The section of the trail between Independence and Olathe was also used by immigrants on the California and Oregon Trails, which branched off to the northwest near Gardner, Kansas.
From Olathe, the trail passed through the towns of Baldwin City
Baldwin City is a city in Douglas County, Kansas, United States, about south of Lawrence. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 4,826. The city is home to Baker University, the state's oldest four-year university.
History
...
, Burlingame, and Council Grove
Council Grove is a city and county seat in Morris County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 2,140. It was named after an agreement between American settlers and the Osage Nation allowing settlers' ...
, then swung west of McPherson to the town of Lyons
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of th ...
. West of Lyons the trail followed nearly the route of present-day Highway 56 to Great Bend. Ruts in the earth made from the trail are still visible in several locations (Ralph's Ruts are visible in aerial photos at (). At Great Bend, the trail encountered the Arkansas River. Branches of the trail followed both sides of the river upstream to Dodge City and Garden City.
West of Garden City in southwestern Kansas the trail splits into two branches. One of the branches, called the Mountain Route or the Upper Crossing follows the Purgatoire River from La Junta
La Junta is a home rule municipality in , the county seat of, and the most populous municipality of Otero County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 7,322 at the 2020 United States Census. La Junta is located on the Arkansa ...
upstream to Trinidad then south through the Raton Pass into New Mexico.
The other main branch, called the Cimarron Cutoff or Cimarron Crossing or Middle Crossing cut southwest across the Cimarron Desert (also known as the Waterscrape or ''La Jornada'') to the valley of the Cimarron River near the town of Ulysses and Elkhart then continued toward Boise City, Oklahoma, to Clayton, New Mexico
Clayton is a town and county seat of Union County, New Mexico, United States. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 2,980.
History
Early History
Native Americans were present in the area of Clayton for at least 10,000 years, as evi ...
, joining up with northern branch at Fort Union. This route was generally very hazardous because it had very little water. In fact, the Cimarron River was one of the only sources of water along this branch of the trail.
From Watrous, the reunited branches continued southward to Santa Fe. Part of this route has been designated a National Scenic Byway
A National Scenic Byway is a road recognized by the United States Department of Transportation for one or more of six "intrinsic qualities": archeological, cultural, historic, natural, recreational, and scenic. The program was established by Co ...
.
Challenges
Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
nor the Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño an ...
of the southern high plains tolerated trespassers. In 1825, Congress voted for federal protection for the Santa Fe Trail, even though much of it lay in the Mexican territory. Lack of food and water also made the trail very risky. Weather conditions, like huge lightning storms, gave the travelers even more difficulty. If a storm developed, there was often no place to take shelter and the livestock could get spooked. Rattlesnakes often posed a threat, and many people died due to snakebites. The caravan size increased later on to prevent Indian raids. The travelers also harnessed more oxen instead of mules—primarily for the greater hauling power of oxen but also because they were less valued by Indians and thus less risk of being raided.
Historic preservation
Segments of this trail in Missouri, Kansas,Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
, and New Mexico are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. In Missouri, this includes the 85th and Manchester "Three Trails" Trail Segment, Arrow Rock Ferry Landing, Santa Fe Trail – Grand Pass Trail Segments, and Santa Fe Trail – Saline County Trail Segments. The longest clearly identifiable section of the trail, Santa Fe Trail Remains, near Dodge City, Kansas, is listed as a National Historic Landmark. In Colorado, Santa Fe Trail Mountain Route – Bent's New Fort is included on the National Register.
Notable features

 ;MissouriSanta Fe trail, Official Map and Guide; National Park Service; Harpers Ferry, West Virginia; 1997
* Arrow Rock (Arrow Rock Landing, Santa Fe Spring, Huston Tavern)
* Harvey Spring/Weinrich Ruts
* Independence (Santa Fe trail Ruts, Lower Independence (Blue Mills) Landing, Upper Independence (Wayne City) Landing.
*
;MissouriSanta Fe trail, Official Map and Guide; National Park Service; Harpers Ferry, West Virginia; 1997
* Arrow Rock (Arrow Rock Landing, Santa Fe Spring, Huston Tavern)
* Harvey Spring/Weinrich Ruts
* Independence (Santa Fe trail Ruts, Lower Independence (Blue Mills) Landing, Upper Independence (Wayne City) Landing.
* Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
(Westport Landing)
;Kansas
* Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
(Shawnee Mission, Big Blue River Crossing)
* Council Grove
Council Grove is a city and county seat in Morris County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 2,140. It was named after an agreement between American settlers and the Osage Nation allowing settlers' ...
(Kaw Mission, Neosho River Crossing, Hermit's Cave, Last Chance Store, Council Oak, Post Office Oak)
* Fort Larned National Historic Site
* Fort Dodge (Jackson's Grove and Island, Santa Fe Trail Ruts, Middle Crossing, Point of Rocks, Fort Atkinson Site)
''Mountain Route'' towards Colorado
* Arkansas River Crossing
;Colorado
''Mountain Route''
* Bent's Old Fort National Historic Site
* Raton Pass
''Cimarron Route'' thru Kansas towards Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
* Cimarron River
* Cimarron National Grassland
;New Mexico
''Mountain Route''
* Clifton House
* Cimarron (Aztec Mill, Cimarron Plaza and Well)
* Philmont Scout Ranch
''Cimarron Route''
* Kiowa National Grassland
''Joint route''
* Fort Union National Monument
* Pecos National Historical Park
Pecos National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in San Miguel and Santa Fe Counties, New Mexico. The park, operated by the National Park Service, encompasses thousands of acres of landscape infused with historical ...
* Santa Fe
* De Vargas Street House
The De Vargas Street House, often referred to as the Oldest House, is a historic building in Santa Fe, New Mexico, which is often said to be one of the oldest buildings in United States. The original date of construction is unknown but the maj ...
, Oldest House in the United States
* Northern Rio Grande National Heritage Area
See also
* MO: Jackson County Historic Places * KS: Johnson County Historic Places * OK: Cimarron County Historic Places * NM: Colfax County Historic Places * Oregon-California Trails Association *Pawnee Rock
Pawnee Rock, one of the most famous and beautiful landmarks on the Santa Fe Trail, is located in Pawnee Rock State Park, just north of Pawnee Rock, Kansas, United States. Originally over tall, railroad construction stripped it of some 15 to in ...
* Related National Park Units
** Fort Larned National Historic Site
** Bent's Old Fort National Historic Site
** Fort Union National Monument
* Santa Fe Trail Remains
* Santa Fe Trail Museum, part of the Trinidad History Museum
* Santa Fe Trail Historical Park
Santa Fe Trail Historical Park, also called Pioneer Park, is located on the bank of the Rio Hondo (California), Rio Hondo River in El Monte, California. The location was designated a California Historic Landmark (No. 975) on Aug. 13, 1987. T ...
in El Monte, California
* Trailside Center
The Trailside Center is a tourist center, museum, and community facility in Kansas City, Missouri. The center is located at the intersection of Holmes Road and East 99th Street. Items on display include exhibits of Civil War items related to the ...
museum in Kansas City, Missouri
* Scenic byways in the United States
* ''Tree in the Trail
''Tree in the Trail'' is a 1942 children's book, written and illustrated by American author and artist Holling C. Holling.
The book tells the story of a lone cottonwood tree encountered as a sapling by a Kansa Indian boy in 1610, on what became ...
''
References
Further reading
* 224 pages. * 208 pages. * 252 pages. * 272 pages. * 168 pages. * 162 pages. * 190 pages. * ;318 pages. * 320 pages. * 287 pages. ; Maps * 196 pages. * 121 pages. * 21 pages.External links
The Great Prairie Highway
(National Park Service)
at Pecos National Park (National Park Service)
Santa Fe Trail Center
Santa Fe Trail Research
* ttp://www.kansasmemory.org/locate.php?categories=362-367&/ Access documents, photographs, and other primary sources on Kansas Memory, the Kansas State Historical Society's digital portal
New Mexico Santa Fe Trail National Scenic Byway
* ttp://www.kansasheritage.org/werner/ Pioneer Trails from US Land Surveys
Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory
{{Authority control Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Colorado Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Missouri Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in New Mexico Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Oklahoma Historic trails and roads in New Mexico Historic trails and roads in Colorado Historic trails and roads in Kansas Historic trails and roads in Missouri Historic trails and roads in Oklahoma Native American trails in the United States Trails and roads in the American Old West Colorado Territory Jefferson Territory New Mexico Territory New Mexico Scenic and Historic Byways 1822 establishments in the United States National Historic Trails of the United States Native American history of Colorado Native American history of New Mexico Native American history of Kansas Native American history of Missouri Native American history of Oklahoma