San Juan Boundary Dispute on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the
The Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the

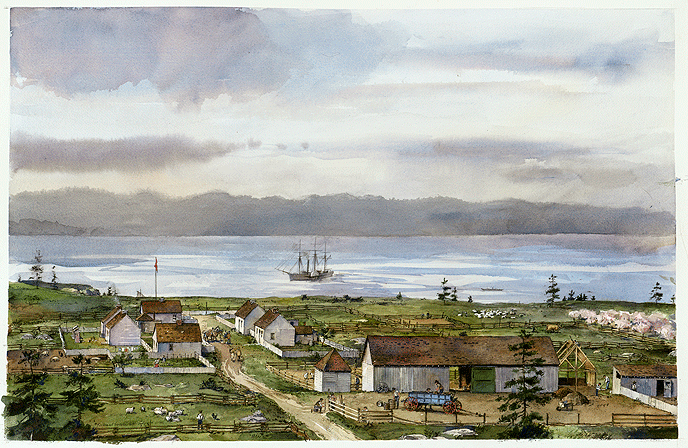
 On June 15, 1859, exactly 13 years after the adoption of the Oregon Treaty, the ambiguity led to direct conflict. Lyman Cutlar, an American farmer who had moved onto
On June 15, 1859, exactly 13 years after the adoption of the Oregon Treaty, the ambiguity led to direct conflict. Lyman Cutlar, an American farmer who had moved onto

 When news about the crisis reached Washington and London, officials from both nations were shocked and took action to calm the potentially explosive international incident.
In September,
When news about the crisis reached Washington and London, officials from both nations were shocked and took action to calm the potentially explosive international incident.
In September,
File:The redoubt commanding view of SJI southern tip and approach from Griffin Bay and Strait of Juan de Fuca.jpg, The redoubt had a commanding view of San Juan Island's southern tip and the water approaches to the prairie from Griffin bay (left) and the Strait of Juan de Fuca
File:Building the redoubt.jpg, Watercolor of US Army building Roberts Redoubt on San Juan Island
File:American Camp painting.gif, Water color of American camp, San Juan Island
File:American Camp today.jpg, American camp as it exists today
File:San Juan Island NHP Eng Camp.JPG, Union Jack at the British camp in San Juan Island National Historical Park
File:British troops evacuate San Juan Island, Washington Terr, 1872 - Restored.jpg, British troops evacuate San Juan Island
The Pig War
National Park Service
San Juan Island Pig War – Part 1
HistoryLink.org
Lyman Cutlar touches off Pig War between U.S. and Great Britain on June 15, 1859
HistoryLink.org * {{Coord, 48, 27, 42, N, 123, 00, 24, W, region:US-WA_type:event, display=title Canada–United States border disputes Battles and conflicts without fatalities Diplomatic incidents Conflicts in 1859 George Pickett Pre-Confederation British Columbia History of Washington (state) Military history of Canada History of the Pacific Northwest Conflicts in Canada Coast of British Columbia Arbitration cases United Kingdom–United States military relations Presidency of James Buchanan
 The Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the
The Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
over the British–U.S. border in the San Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of ...
, between Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian Provinces and territories of Canada, province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are o ...
(present-day Canada) and the State of Washington
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first U.S. president—the state was formed from the western part of the Washington ...
. The Pig War, so called because it was triggered by the shooting of a pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus s ...
, is also called the Pig Episode, the Pig and Potato War, the San Juan Boundary Dispute, and the Northwestern Boundary Dispute. Despite being referred to as a "war" there were no casualties on either side, aside from the pig.
Background
Border ambiguity
TheOregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to t ...
of June 15, 1846, resolved the Oregon boundary dispute
The Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations in ...
by dividing the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
/Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur trading
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold ...
between the United States and Britain "along the forty-ninth parallel of north latitude to the middle of the channel which separates the continent from Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian Provinces and territories of Canada, province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are o ...
, and thence southerly through the middle of the said channel, and of the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
, to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
."
However, two straits could be called the middle of the channel: Haro Strait
The Haro Strait is one of the main channels connecting the Strait of Georgia to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, separating Vancouver Island and the Gulf Islands in British Columbia, Canada from the San Juan Islands of Washington (state), Washington sta ...
, along the west side of the San Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of ...
; and Rosario Strait
Rosario Strait is a strait in northern Washington state, separating San Juan County and Skagit and Whatcom Counties. It extends from the Strait of Juan de Fuca about north to the Strait of Georgia. The USGS defines its southern boundary as a ...
, along the east side.
In 1846, there was still some uncertainty about the region's geography. The most commonly available maps were those of George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what a ...
, published in 1798, and of Charles Wilkes
Charles Wilkes (April 3, 1798 – February 8, 1877) was an American naval officer, ship's captain, and explorer. He led the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–1842).
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), he commanded ' during the ...
, published in 1845. In both cases, the maps are unclear in the vicinity of the southeastern coast of Vancouver Island and the Gulf Islands
The Gulf Islands are a group of islands in the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the mainland coast of British Columbia.
Etymology
The name "Gulf Islands" comes from "Gulf of Georgia," the original term used by George Vancouver in his ma ...
. As a result, Haro Strait is not fully clear either.
In 1856, the US and Britain set up a Boundary Commission to resolve several issues regarding the international boundary, including the water boundary from the Strait of Georgia
The Strait of Georgia (french: Détroit de Géorgie) or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada and the extreme northwestern mainland coast ...
to the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
. The British appointed James Charles Prevost
James Charles Prevost (1810–1891) was an admiral in the British Empire, British Royal Navy.
He was born in Bedhampton, Hampshire, England, the son of Rear-Admiral James Prevost and his first wife France née Haultain, and joined the navy in 1 ...
First Commissioner, George Henry Richards
Sir George Henry Richards (13 January 1820 –14 November 1896) was Hydrographer of the Royal Navy from 1863 to 1874.
Biography
Richards was born in Antony, Cornwall, the son of Captain G. S. Richards, and joined the Royal Navy in 1832. ...
Second Commissioner, and William A. G. Young Secretary. The US appointed Archibald Campbell First Commissioner, John Parke
John Grubb Parke (September 22, 1827 – December 16, 1900) was a United States Army engineer and a Union general in the American Civil War. Parke's Civil War service was closely associated with Ambrose E. Burnside, often serving him as chi ...
Second Commissioner, and William J. Warren Secretary. On June 27, 1857, the American and British commissioners met for the first time on board the British ship HMS ''Satellite'', anchored in Esquimalt Harbour
Esquimalt Harbour is a natural harbour in Greater Victoria on the southern tip of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. The entrance to Esquimalt Harbour is from the south off the Strait of Juan de Fuca through a narrow channel known as R ...
. The two sides met several more times in 1857 in Esquimalt Harbour
Esquimalt Harbour is a natural harbour in Greater Victoria on the southern tip of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. The entrance to Esquimalt Harbour is from the south off the Strait of Juan de Fuca through a narrow channel known as R ...
and Nanaimo
Nanaimo ( ) is a city on the east coast of Vancouver Island, in British Columbia, Canada. As of the Canada 2021 Census, 2021 census, it had a population of 99,863, and it is known as "The Harbour City." The city was previously known as the "H ...
Harbour, and corresponded by letter between meetings. The water boundary was discussed from October to December. From the start, Prevost maintained that Rosario Strait was required by the treaty's wording and was intended by the treaty framers, while Campbell had the same opinion for Haro Strait.
Prevost held that the channel specified in the treaty must have three essential qualities:
* it must separate the continent from Vancouver Island
* it must carry the boundary in a southerly direction
* it must be navigable
Only Rosario fulfilled these requirements, he wrote. Campbell countered that the expression "southerly", in the treaty, was to be understood in a general sense, that Rosario Strait did not separate the continent from Vancouver Island, but the San Juan Islands from Lummi Island
Lummi Island lies at the southwest corner of Whatcom County, Washington, United States, between the mainland part of the county and offshore San Juan County. The Lummi Indian Reservation is situated on a peninsula east of the island, but it d ...
, Cypress Island
Cypress Island is the westernmost part of Skagit County, Washington and is about halfway between the mainland and offshore San Juan County. It is separated from Blakely Island to the west by Rosario Strait and from Guemes Island to the east by ...
, Fidalgo Island
Fidalgo Island is an island in Skagit County, Washington, located about north of Seattle. To the east, it is separated from the mainland by the Swinomish Channel, and from Whidbey Island to the south by Deception Pass. The island is named after ...
, and others, and that navigability was not germane to the issue, but even if it was, Haro Strait was the wider and more direct passage. Finally, he challenged Prevost to produce any evidence showing that the treaty framers had intended Rosario Strait. Prevost responded to the challenge by referring to American maps showing the boundary running through Rosario Strait, including one by John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont or Fremont (January 21, 1813July 13, 1890) was an American explorer, military officer, and politician. He was a U.S. Senator from California and was the first Republican nominee for president of the United States in 1856 ...
, produced for and published by the US government, and another by John B. Preston, Surveyor General
A surveyor general is an official responsible for government surveying in a specific country or territory. Historically, this would often have been a military appointment, but it is now more likely to be a civilian post.
The following surveyor ge ...
of Oregon in 1852. To the other points, Prevost repeated his statements about Rosario Strait's navigability—the channels between Lummi, Cypress, and Fidalgo islands not being navigable—and that a line through Rosario would be southerly. At the same time, one through Haro would have to be drawn westerly. The two continued to discuss the issue into December 1857, until it was clear what each side's argument was and that neither would be convinced of the other. Prevost made a final offer at the sixth meeting, on December 3. He suggested a compromise line through San Juan Channel, which would give the US all the main islands except San Juan Island. This offer was rejected and the commission adjourned, agreeing to report back to their respective governments. Thus ambiguity over the water boundary remained.
Because of this ambiguity, both the United States and Britain claimed sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
over the San Juan Islands. During this period of disputed sovereignty, Britain's Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
established operations on San Juan and turned the island into a sheep ranch. Meanwhile, by mid-1859, twenty-five to twenty-nine American settlers had arrived.
San Juan Island held significance not for its size, but as a military strategic point. While the British held Fort Victoria on Vancouver Island to the west, overlooking the Strait of Juan de Fuca, the entry point to Haro Strait, leading to the Strait of Georgia, the nation that held the San Juan Islands would be able to dominate all the straits connecting the Strait of Juan de Fuca with the Strait of Georgia.
Political context
GeneralGeorge B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 – October 29, 1885) was an American soldier, Civil War Union general, civil engineer, railroad executive, and politician who served as the 24th governor of New Jersey. A graduate of West Point, McCl ...
, George Pickett
George Edward Pickett (January 16,Military records cited by Eicher, p. 428, and Warner, p. 239, list January 28. The memorial that marks his gravesite in Hollywood Cemetery lists his birthday as January 25. Thclaims to have accessed the baptism ...
’s West Point classmate and lifelong friend, claimed that General William S. Harney and Pickett conspired with a cabal, to start a war with Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, creating a common enemy, to head off a north–south confrontation. However, General Granville O. Haller debunked McClellan's theory. He said they had wanted to start a war, but with hope of distracting the north so that the south could secede from the union.
The theories are given credence when it is noted that Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Silas Casey
Silas Casey (July 12, 1807 – January 22, 1882) was a career United States Army officer who rose to the rank of major general during the American Civil War.
Early life and military career
Casey was born in East Greenwich, Rhode Island. He gradua ...
, then a lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colone ...
and deputy commander of the 9th Infantry Regiment, was reduced to a support role for Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
George Pickett who was given independent jurisdiction over a vast area by Harney, then a brevet
Brevet may refer to:
Military
* Brevet (military), higher rank that rewards merit or gallantry, but without higher pay
* Brevet d'état-major, a military distinction in France and Belgium awarded to officers passing military staff college
* Aircre ...
major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
, and was also passed over by Harney in favor of Pickett when given this choice command.
On the other hand, it can be said that Lieutenant Colonel Casey had not been reduced, for he was given command over the USS ''Massachusetts'' and Major Haller to protect and supervise the water of Puget Sound. He was given discretion to deviate from his orders, based on his military experience. (His textbook on infantry tactics was used at West Point during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
.)
The pig incident

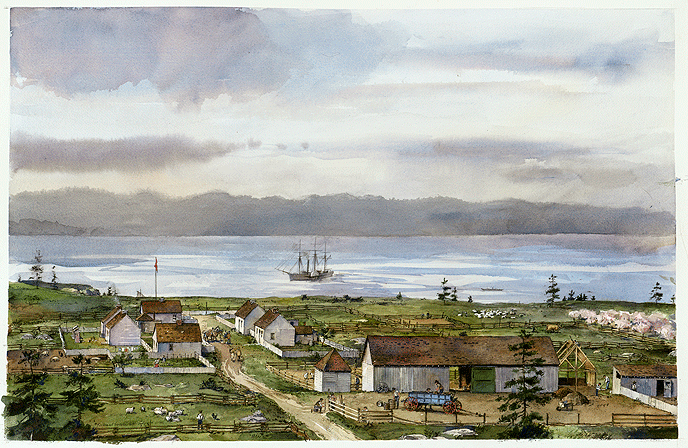
 On June 15, 1859, exactly 13 years after the adoption of the Oregon Treaty, the ambiguity led to direct conflict. Lyman Cutlar, an American farmer who had moved onto
On June 15, 1859, exactly 13 years after the adoption of the Oregon Treaty, the ambiguity led to direct conflict. Lyman Cutlar, an American farmer who had moved onto San Juan Island
San Juan Island is the second-largest and most populous of the San Juan Islands in northwestern Washington (state), Washington, United States. It has a land area of 142.59 km2 (55.053 sq mi) and a population of 6,822 as of the United States ...
claiming rights to live there under the Donation Land Claim Act
The Donation Land Claim Act of 1850, sometimes known as the Donation Land Act, was a statute enacted by the United States Congress in late 1850, intended to promote homestead settlements in the Oregon Territory. It followed the Distribution-Preem ...
, found a pig rooting in his garden and eating his tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure used as storage organs for nutrients in some plants. They are used for the plant's perennation (survival of the winter or dry months), to provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growing ...
s. This was not the first occurrence and as a result Cutlar shot the pig, killing it. It turned out that the pig was owned by an Irishman, Charles Griffin, who was employed by the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
to run the sheep ranch on the island. He also owned several pigs that he allowed to roam freely. The two had lived in peace until this incident. Cutlar offered $10 () to Griffin to compensate for the pig, but Griffin was unsatisfied with this offer and demanded $100 (). Following this reply, Cutlar believed he should not have to pay for the pig because the pig had been trespassing on his land. One likely apocryphal account has Cutlar saying to Griffin, "It was eating my potatoes"; and Griffin replying, "It is up to you to keep your potatoes out of my pig." When British authorities threatened to arrest Cutlar, American settlers called for military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
protection.
Military escalation

Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
William S. Harney, commanding the Department of Oregon, initially dispatched Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
George Pickett
George Edward Pickett (January 16,Military records cited by Eicher, p. 428, and Warner, p. 239, list January 28. The memorial that marks his gravesite in Hollywood Cemetery lists his birthday as January 25. Thclaims to have accessed the baptism ...
and 66 American soldiers of the 9th Infantry Regiment under Pickett's command, to San Juan Island with orders to prevent the British from landing; the regiment sailed aboard . Concerned that a squatter population of Americans would begin to occupy San Juan Island if the Americans were not kept in check, the British sent three warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a state. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are usually faster a ...
s under the command of Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
Geoffrey Hornby
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Geoffrey Thomas Phipps Hornby GCB (10 February 1825 – 3 March 1895) was a Royal Navy officer. As a junior officer, he saw action at the capture of Acre in November 1840 during the Egyptian–Ottoman War. As a captai ...
to counter the Americans. Pickett was quoted as saying defiantly, "We'll make a Bunker Hill of it," placing him in the national limelight. Pickett sited his company and battery near the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
's Belle Vue sheep farm located near today's Cattle Point Light
Cattle Point Lighthouse is a lighthouse on the southeastern tip of San Juan Island overlooking the Strait of Juan de Fuca where the Haro Straits meet the San Juan Channel, in San Juan County, Washington. The light lies adjacent to the state's Ca ...
, and directly under the guns of HMS ''Satellite'', a British ship. When this tactical error was pointed out, Capt Pickett moved his battery of cannon a few miles north to high ground overlooking both Griffin Bay and the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
, and commenced to build a redoubt
A redoubt (historically redout) is a fort or fort system usually consisting of an enclosed defensive emplacement outside a larger fort, usually relying on earthworks, although some are constructed of stone or brick. It is meant to protect soldi ...
for his cannon.
Pickett established the American camp near the south end of San Juan Island, today one of two historical sites on the island, the other being the British camp, defended by the Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
on the north end of the island. The camp redoubt was built under the supervision of new West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known Metonymy, metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a f ...
graduate 2nd Lieutenant Henry Martyn Robert
Henry Martyn Robert (May 2, 1837 – May 11, 1923) was an American soldier, engineer, and author. In 1876, Robert published the first edition of his manual of parliamentary procedure, ''Robert's Rules of Order'', which remains today the most com ...
; Robert went on to become a general in the Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confedera ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
and author of ''Robert's Rules of Order
''Robert's Rules of Order'', often simply referred to as ''Robert's Rules'', is a manual of parliamentary procedure by U.S. Army officer Henry Martyn Robert.
"The object of Rules of Order is to assist an assembly to accomplish the work for which ...
''. Robert's Redoubt is considered the best-preserved fortification of its kind in the United States. (To the east is Jackle's Lagoon, named for George Jackle, a soldier stationed at the American camp.)
The situation continued to escalate. By August 10, 1859, 461 Americans with 14 cannons under Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
Silas Casey
Silas Casey (July 12, 1807 – January 22, 1882) was a career United States Army officer who rose to the rank of major general during the American Civil War.
Early life and military career
Casey was born in East Greenwich, Rhode Island. He gradua ...
were opposed by five British warships mounting 70 guns and carrying 2,140 men.
The governor of the Colony of Vancouver Island
The Colony of Vancouver Island, officially known as the Island of Vancouver and its Dependencies, was a Crown colony of British North America from 1849 to 1866, after which it was united with the mainland to form the Colony of British Columbia. ...
, James Douglas, had ordered Captain Hornby to dislodge the American troops, avoiding armed conflict if possible. At the time, the additional reinforcements sent by American General Harney had not yet arrived, and the island was occupied by only Pickett's 66 men. Hornby refused to take any action until British Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarde ...
Robert L. Baynes, who was in command of the British Navy in the Pacific, would arrive himself. When Baynes finally came and took stock of the situation, he told Governor Douglas that he would not escalate the conflict into a war between great nations "over a squabble about a pig".
Resolution
 When news about the crisis reached Washington and London, officials from both nations were shocked and took action to calm the potentially explosive international incident.
In September,
When news about the crisis reached Washington and London, officials from both nations were shocked and took action to calm the potentially explosive international incident.
In September, U.S. President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
James Buchanan
James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was an American lawyer, diplomat and politician who served as the 15th president of the United States from 1857 to 1861. He previously served as secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and repr ...
sent General Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
to negotiate with Governor Douglas and resolve the growing crisis. This was in the best interest of the United States, as sectionalist tensions within the country were increasing, soon to culminate in the Civil War. Scott had calmed two other border crises between the two nations in the late 1830s. He arrived in the San Juans in October and began negotiations with Douglas.
As a result of the negotiations, both sides agreed to retain joint military occupation of the island until a final settlement could be reached, reducing their presence to a token force of no more than 100 men. The British camp was established on the north end of San Juan Island along the shoreline, for ease of supply and access; and the American camp was created on the south end on a high, windswept meadow, suitable for artillery barrages against shipping. Today the Union Jack
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Flag the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. ...
still flies above the British camp site, being raised and lowered daily by park rangers, making it one of the few places without diplomatic status where U.S. government employees regularly hoist the flag of another country, though this is only for commemorative purposes.
During the years of joint military occupation
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
, the small British and American units on San Juan Island had an amicable mutual social life, visiting one another's camps to celebrate their respective national holidays and holding various athletic competitions. Park rangers tell visitors the biggest threat to peace on the island during these years was "the large amounts of alcohol available".
This state of affairs continued for the next 12 years. The dispute was peacefully resolved after more than a decade of confrontation and military bluster, during which time local British authorities lobbied London to seize back the Puget Sound region
The Puget Sound region is a coastal area of the Pacific Northwest in the U.S. state of Washington, including Puget Sound, the Puget Sound lowlands, and the surrounding region roughly west of the Cascade Range and east of the Olympic Mountains. ...
while the Americans were busy elsewhere with the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. In 1866, the Colony of Vancouver Island was merged with the Colony of British Columbia The Colony of British Columbia refers to one of two colonies of British North America, located on the Pacific coast of modern-day Canada:
*Colony of British Columbia (1858–1866)
*Colony of British Columbia (1866–1871)
See also
*History of Br ...
to form an enlarged Colony of British Columbia. In 1871, the enlarged colony joined the newly formed Dominion of Canada
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the name of Canada, its origin is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word , meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. In 1535, indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec C ...
. That year, the United Kingdom and the United States signed the Treaty of Washington, which dealt with various differences between the two nations, including border issues involving the newly formed dominion. Among the results of the treaty was the decision to resolve the San Juan dispute by international arbitration, with German Emperor Wilhelm I
William I or Wilhelm I (german: Wilhelm Friedrich Ludwig; 22 March 1797 – 9 March 1888) was King of Prussia from 2 January 1861 and German Emperor from 18 January 1871 until his death in 1888. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he was the f ...
chosen to act as arbitrator, meaning that the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
would decide if the British or the Americans would officially own the San Juan Islands. Wilhelm referred the issue to a three-man arbitration commission which met in Geneva for nearly a year. On October 21, 1872, the commission decided in favor of the United States' offer. The arbitrators chose the American-preferred marine boundary via Haro Strait
The Haro Strait is one of the main channels connecting the Strait of Georgia to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, separating Vancouver Island and the Gulf Islands in British Columbia, Canada from the San Juan Islands of Washington (state), Washington sta ...
, to the west of the islands, over the British preference for Rosario Strait
Rosario Strait is a strait in northern Washington state, separating San Juan County and Skagit and Whatcom Counties. It extends from the Strait of Juan de Fuca about north to the Strait of Georgia. The USGS defines its southern boundary as a ...
which lay to their east.
On November 25, 1872, the British withdrew their Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
from the British camp. The Americans followed by July 1874.
The Pig War is commemorated in San Juan Island National Historical Park
San Juan Island National Historical Park, also known as American and English Camps, San Juan Island, is a U.S. National Historical Park owned and operated by the National Park Service on San Juan Island in the state of Washington. The park is ...
.
Key figures
*Henry Martyn Robert
Henry Martyn Robert (May 2, 1837 – May 11, 1923) was an American soldier, engineer, and author. In 1876, Robert published the first edition of his manual of parliamentary procedure, ''Robert's Rules of Order'', which remains today the most com ...
who later published ''Robert's Rules of Order
''Robert's Rules of Order'', often simply referred to as ''Robert's Rules'', is a manual of parliamentary procedure by U.S. Army officer Henry Martyn Robert.
"The object of Rules of Order is to assist an assembly to accomplish the work for which ...
'' was stationed on the island for much of the period.
* Captain George Pickett
George Edward Pickett (January 16,Military records cited by Eicher, p. 428, and Warner, p. 239, list January 28. The memorial that marks his gravesite in Hollywood Cemetery lists his birthday as January 25. Thclaims to have accessed the baptism ...
, later of Pickett's Charge
Pickett's Charge (July 3, 1863), also known as the Pickett–Pettigrew–Trimble Charge, was an infantry assault ordered by Confederate General Robert E. Lee against Major General George G. Meade's Union positions on the last day of the B ...
fame, was in charge of the initial American landing force.
* Captain Geoffrey Hornby
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Geoffrey Thomas Phipps Hornby GCB (10 February 1825 – 3 March 1895) was a Royal Navy officer. As a junior officer, he saw action at the capture of Acre in November 1840 during the Egyptian–Ottoman War. As a captai ...
, commander of the initial British naval force deployed, was later promoted to Admiral of the Fleet, the highest rank in the Royal Navy, and earned a reputation as a pre-eminent tactician and fleet commander.
Gallery
See also
*Aroostook War
The Aroostook War (sometimes called the Pork and Beans WarLe Duc, Thomas (1947). The Maine Frontier and the Northeastern Boundary Controversy. ''The American Historical Review'' Vol. 53, No. 1 (Oct., 1947), pp. 30–41), or the Madawaska War, wa ...
, the "Northeastern Boundary Dispute"
* List of conflicts in the United States
This is a list of conflicts in the United States. Conflicts are arranged chronologically from the late modern period to contemporary history. This list includes (but is not limited to) the following: Indian wars, skirmishes, wars of independe ...
* List of conflicts in Canada
List of conflicts in Canada is a timeline of events that includes wars, battles, skirmishes, major terrorist attacks, riots and other related items that have occurred in the country of Canada's current geographical area. A complete list of terror ...
* List of bloodless wars
* Military history of Canada
The military history of Canada comprises hundreds of years of armed actions in the territory encompassing modern Canada, and interventions by the Canadian Forces, Canadian military in conflicts and peacekeeping worldwide. For thousands of years, t ...
* Military history of the United Kingdom
The military history of the United Kingdom covers the period from the creation of the united Kingdom of Great Britain, with the political union of England and Scotland in 1707, to the present day.
From the 18th century onwards, with the expansio ...
* Military history of the United States
* The Great Rapprochement
The Great Rapprochement is a historical term referring to the convergence of diplomatic, political, military, and economic objectives of the United States and the British Empire from 1895 to 1915, the two decades before American entry into World W ...
, a convergence of goals between the United States and the British Empire in subsequent decades
* Point Roberts
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
* Points ...
* War of the Stray Dog
The Incident at Petrich, or War of the Stray Dog, was a Greek–Bulgarian crisis in 1925 that resulted in a brief invasion of Bulgaria by Greece near the border town of Petrich after the killing of a Greek captain and a sentry by Bulgarian soldi ...
, a brief war that began under similar circumstances.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
The Pig War
National Park Service
San Juan Island Pig War – Part 1
HistoryLink.org
Lyman Cutlar touches off Pig War between U.S. and Great Britain on June 15, 1859
HistoryLink.org * {{Coord, 48, 27, 42, N, 123, 00, 24, W, region:US-WA_type:event, display=title Canada–United States border disputes Battles and conflicts without fatalities Diplomatic incidents Conflicts in 1859 George Pickett Pre-Confederation British Columbia History of Washington (state) Military history of Canada History of the Pacific Northwest Conflicts in Canada Coast of British Columbia Arbitration cases United Kingdom–United States military relations Presidency of James Buchanan