Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=
Austro-Bavarian
Bavarian (german: Bairisch , Bavarian: ''Boarisch'') or alternately Austro-Bavarian, is a West Germanic language, part of the Upper German family, together with Alemannic and East Franconian.
Bavarian is spoken by approximately 12 million peop ...
) is the
fourth-largest city in
Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded as an
episcopal see
An episcopal see is, in a practical use of the phrase, the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, mak ...
in 696 and became a
seat of the archbishop in 798. Its main sources of income were salt extraction, trade, and gold mining. The fortress of
Hohensalzburg
Hohensalzburg Fortress (german: Festung Hohensalzburg, lit=High Salzburg Fortress) is a large medieval fortress in the city of Salzburg, Austria. It sits atop the Festungsberg at an altitude of 506 m. It was erected at the behest of the Prince-Ar ...
, one of the largest medieval fortresses in Europe, dates from the 11th century. In the 17th century, Salzburg became a center of the
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
, with monasteries and numerous Baroque churches built.
Salzburg's historic center (
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Altstadt'') is renowned for its
Baroque architecture and is one of the best-preserved city centers north of the Alps. The historic center was enlisted as a
UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. The city has three universities and a large population of students. Tourists also visit Salzburg to tour the historic center and the scenic
Alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National Pa ...
surroundings.
History
Antiquity to the High Middle Ages
Traces of
human settlements have been found in the area, dating to the
Neolithic Age. The first settlements in Salzburg continuous with the present were apparently by the
Celts around the 5th century BC.
Around 15 BC the
Roman Empire merged the settlements into one city. At this time, the city was called "Juvavum" and was awarded the status of a Roman ''
municipium'' in 45
AD. Juvavum developed into an important town of the
Roman province of
Noricum. After the Norican frontier's collapse, Juvavum declined so sharply that by the late 7th century it nearly became a ruin.
The ''Life of
Saint Rupert'' credits the 8th-century saint with the city's rebirth. When
Theodo of Bavaria asked Rupert to become
bishop c. 700, Rupert reconnoitered the river for the site of his
basilica. Rupert chose Juvavum, ordained priests, and annexed the manor of Piding. Rupert named the city "Salzburg". He travelled to
evangelise
In Christianity, evangelism (or witnessing) is the act of preaching the gospel with the intention of sharing the message and teachings of Jesus Christ.
Christians who specialize in evangelism are often known as evangelists, whether they are i ...
among
pagans Pagans may refer to:
* Paganism, a group of pre-Christian religions practiced in the Roman Empire
* Modern Paganism, a group of contemporary religious practices
* Order of the Vine, a druidic faction in the ''Thief'' video game series
* Pagan's ...
.
The name Salzburg means "Salt-Castle" (
Latin: ''Salis Burgium''). The name derives from the barges carrying salt on the River
Salzach, which were subject to a toll in the 8th century as was customary for many communities and cities on European rivers.
Hohensalzburg Fortress, the city's
fortress
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, was built in 1077 by Archbishop Gebhard, who made it his residence. It was greatly expanded during the following centuries.
Independence
Independence from
Bavaria was secured in the late 14th century. Salzburg was the seat of the
Archbishopric of Salzburg
The Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg (german: Fürsterzbistum Salzburg; Erzstift Salzburg; Erzbistum Salzburg) was an ecclesiastical principality and state of the Holy Roman Empire. It comprised the secular territory ruled by the archbishops of ...
, a
prince-bishopric of the
Holy Roman Empire. As the Reformation movement gained steam, riots broke out among peasants in the areas in and around Salzburg. The city was occupied during the
German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
, and the Archbishop had to flee to the safety of the fortress. It was besieged for three months in 1525.
Eventually, tensions were quelled, and the city's independence led to an increase in wealth and prosperity, culminating in the late 16th to 18th centuries under the Prince Archbishops
Wolf Dietrich von Raitenau,
Markus Sittikus, and
Paris Lodron
Paris Lodron or Paris of Lodron (''German'': Paris Graf von Lodron), 13 February 1586 - 15 December 1653, was the Prince-Archbishop of the Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg from 1619-1653.
Early life
He was born 13 February 1586 in the Castel ...
. It was in the 17th century that Italian architects (and Austrians who had studied the Baroque style) rebuilt the city center as it is today along with many palaces.
Modern era
Religious conflict
On 31 October 1731, the 214th anniversary of
the 95 Theses
The ''Ninety-five Theses'' or ''Disputation on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences''-The title comes from the 1517 Basel pamphlet printing. The first printings of the ''Theses'' use an incipit rather than a title which summarizes the conten ...
,
Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
Count
Leopold Anton von Firmian
Leopold Anton Eleutherius Freiherr von Firmian (11 March 1679 – 22 October 1744) was Bishop of Lavant 1718–24, Bishop of Seckau 1724–27 and Prince-Archbishop of Salzburg from 1727 until his death.
Early life
He was born in Munich, on his f ...
signed an Edict of Expulsion, the ''Emigrationspatent'', directing all
Protestant citizens to recant their non-Catholic beliefs. 21,475 citizens refused to recant their beliefs and were expelled from Salzburg. Most of them accepted an offer by King
Friedrich Wilhelm I of
Prussia, travelling the length and breadth of Germany to their new homes in East Prussia.
[Frank L. Perry Jr.]
Catholics Cleanse Salzburg of Protestants
, The Georgia Salzburger Society. The rest settled in other Protestant states in Europe and the British colonies in America.
Illuminism
In 1772–1803, under archbishop
Hieronymus Graf von Colloredo
Hieronymus Joseph Franz de Paula Graf Colloredo von Wallsee und Melz (Jérôme Joseph Franz de Paula, Count of Colloredo-Wallsee and Mels; ) was Prince-Bishop of Gurk from 1761 to 1772 and Prince-Archbishop of Salzburg from 1772 until 1803, whe ...
, Salzburg was a center of late
Illuminism
The Illuminati (; plural of Latin ''illuminatus'', 'enlightened') is a name given to several groups, both real and fictitious. Historically, the name usually refers to the Bavarian Illuminati, an Enlightenment-era secret society founded on ...
. Colloredo is known for being one of the main employers of
Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his ra ...
. He often had arguments with Mozart and he dismissed him by saying, "Soll er doch gehen, ich brauche ihn nicht!" (may he leave; I don't need him!). Mozart would leave Salzburg for Vienna in 1781 with his family, though his father Leopold stayed back as he had a close relationship with Colloredo.
Electorate of Salzburg
In 1803, the archbishopric was secularised by Emperor
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
; he transferred the territory to
Ferdinando III of Tuscany, former Grand Duke of
Tuscany, as the
Electorate of Salzburg.
Austrian annexation of Salzburg
In 1805, Salzburg was annexed to the
Austrian Empire, along with the
Berchtesgaden Provostry.
Salzburg under Bavarian rule
In 1809, the territory of Salzburg was transferred to the
Kingdom of Bavaria after Austria's defeat at
Wagram.
Division of Salzburg and annexation by Austria and Bavaria
After the
Congress of Vienna with the
Treaty of Munich (1816), Salzburg was definitively returned to Austria, but without Rupertigau and Berchtesgaden, which remained with
Bavaria. Salzburg was integrated into the Province of Salzach and Salzburgerland was ruled from
Linz.
In 1850, Salzburg's status was restored as the capital of the
Duchy of Salzburg, a
crownland of the
Austrian Empire. The city became part of
Austria-Hungary in 1866 as the capital of a crownland of the Austrian Empire. The nostalgia of the
Romantic Era led to increased tourism. In 1892, a
funicular was installed to facilitate tourism to
Hohensalzburg Fortress.

20th century
First Republic
Following
World War I and the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, Salzburg, as the capital of one of the
Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
territories, became part of the new
German Austria. In 1918, it represented the residual
German-speaking
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a ...
territories of the Austrian heartlands. This was replaced by the
First Austrian Republic
The First Austrian Republic (german: Erste Österreichische Republik), officially the Republic of Austria, was created after the signing of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye on 10 September 1919—the settlement after the end of World War I w ...
in 1919, after the
Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919).
Annexation by the Third Reich

The
Anschluss (the occupation and annexation of Austria, including Salzburg, into the
Third Reich) took place on 12 March 1938, one day before a scheduled
referendum on Austria's independence. German troops moved into the city. Political opponents,
Jewish citizens and
other minorities were subsequently arrested and
deported to concentration camps. The
synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worshi ...
was destroyed. After Germany invaded the Soviet Union, several
POW camps for prisoners from the
Soviet Union and other enemy nations were organized in the city.
During the Nazi occupation, a
Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
camp was built in Salzburg-Maxglan. It was an Arbeitserziehungslager (work 'education' camp), which provided slave labor to local industry. It also operated as a Zwischenlager (transit camp), holding Roma before their deportation to German camps or ghettos in German-occupied territories in eastern Europe.
World War II
Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
bombing destroyed 7,600 houses and killed 550 inhabitants. Fifteen air strikes destroyed 46 percent of the city's buildings, especially those around Salzburg railway station. Although the town's bridges and the dome of the
cathedral were destroyed, much of its Baroque architecture remained intact. As a result, Salzburg is one of the few remaining examples of a town of its style.
American troops
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
entered the city on 5 May 1945 and it became the centre of the
American-occupied area in Austria. Several
displaced persons camp
A refugee camp is a temporary Human settlement, settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced people who have fled their home country, but camps are also made for interna ...
s were established in Salzburgamong them Riedenburg, Camp Herzl (Franz-Josefs-Kaserne), Camp Mülln, Bet Bialik, Bet Trumpeldor, and New Palestine.
Today
After World War II, Salzburg became the capital city of the Federal
State of Salzburg (''Land Salzburg'') and saw the Americans leave the area once Austria had signed a
1955 treaty re-establishing the country as a democratic and independent nation and subsequently
declared its perpetual neutrality. In the 1960s, the city became the shooting and setting of the family musical film ''
The Sound of Music''. On 27 January 2006, the 250th anniversary of the birth of
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, all 35 churches of Salzburg rang their bells after 8:00 p.m. (local time) to celebrate the occasion. Major celebrations took place throughout the year.
As of 2017 Salzburg had a GDP per capita of €46,100, which was greater than the average for Austria and most European countries.
Geography
Salzburg is on the banks of the River
Salzach, at the northern boundary of the
Alps. The mountains to Salzburg's south contrast with the rolling plains to the north. The closest alpine peak, the 1,972‑metre-high
Untersberg, is less than from the city center. The ''Altstadt'', or "old town", is dominated by its
baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
towers and churches and the massive
Hohensalzburg Fortress. This area is flanked by two smaller hills, the
Mönchsberg and
Kapuzinerberg, which offer green relief within the city. Salzburg is approximately east of
Munich, northwest of
Ljubljana,
Slovenia, and west of
Vienna. Salzburg has about the same latitude as
Seattle.
Due to its proximity to the Austrian-German border, the greater Salzburg urban area has sometimes been regarded as, unofficially, including contiguous parts of Germany, including
Freilassing (until 1923 known as Salzburghofen),
Ainring and
Piding
Piding is an approved climatic spa in Bavaria near to the border of Austria close to Bad Reichenhall and Freilassing.
Geography
Geographical position
Piding is located in the middle of the ''Landkreis'' Berchtesgadener Land.
The municipal area ...
.
Climate
Salzburg is part of the
temperate zone. The
Köppen climate classification specifies the climate as a
humid continental climate (Dfb). However, with the isotherm for the coldest month, Salzburg can be classified as having four-season
oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
with significant temperature differences between seasons. Due to the location at the northern rim of the Alps, the amount of precipitation is comparatively high, mainly in the summer months. The specific
drizzle is called ''Schnürlregen'' in the local dialect. In winter and spring, pronounced
foehn winds regularly occur.
Population
Salzburg's official population significantly increased in 1935 when the city absorbed adjacent
municipalities. After
World War II, numerous
refugees
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution. found a new home in the city. New residential space was constructed for American soldiers of the postwar occupation and could be used for
refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution. s when they left. Around 1950, Salzburg passed the mark of 100,000 citizens, and in 2016, it reached the mark of 150000 citizens.
Salzburg is home to large German, Bosnian, Serbian, and Romanian communities.
Largest groups of immigrants by 1 January 2021 :
Architecture

Romanesque and Gothic
The
Romanesque and
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
churches, the
monasteries and the early carcass houses dominated the
medieval city for a long time. The Cathedral of
Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
Conrad of Wittelsbach was the largest
basilica north of the
Alps. The choir of the
Franciscan Church, construction was begun by
Hans von Burghausen
Hans von Burghausen (1350s in Burghausen, Bavaria10 August 1432) was a German architect. He designed the Church of St Martin, Landshut, and completed it in 1498.
Bibliography
* Friedrich Kobler, 1985: ''Hanns von Burghausen, Steinmetz – Übe ...
and completed by
Stephan Krumenauer, is one of the most prestigious religious gothic constructions of southern Germany. At the end of the Gothic era
Nonnberg Abbey, the Margaret Chapel in
St Peter's Abbey, St George's Chapel, and the stately halls of the "Hoher Stock" in
Hohensalzburg Fortress were constructed.
Renaissance and baroque
Inspired by
Vincenzo Scamozzi, Prince-Archbishop
Wolf Dietrich von Raitenau began to transform the medieval town to the architectural ideals of the late
Renaissance. Plans for a massive cathedral by Scamozzi failed to materialize upon the fall of the archbishop. A second cathedral planned by
Santino Solari rose as the first early
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
church in Salzburg. It served as an example for many other churches in Southern
Germany and
Austria.
Markus Sittikus and
Paris von Lodron
Paris Lodron or Paris of Lodron (''German'': Paris Graf von Lodron), 13 February 1586 - 15 December 1653, was the Prince-Archbishop of the Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg from 1619-1653.
Early life
He was born 13 February 1586 in the Castel ...
continued to rebuild the city with major projects such as
Hellbrunn Palace, the prince archbishop's residence, the university buildings, fortifications, and many other buildings. Giovanni Antonio Daria managed by order of Prince Archbishop Guido von Thun the construction of the residential well. Giovanni
Gaspare Zuccalli, by order of the same archbishop, created the Erhard and the Kajetan church in the south of the town. The city's redesign was completed with buildings designed by
Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach, donated by Prince Archbishop Johann Ernst von Thun.
After the era of Ernst von Thun, the city's expansion came to a halt, which is the reason why there are no churches built in the
Rococo style.
Sigismund von Schrattenbach continued with the construction of "Sigmundstor" and the statue of holy Maria on the cathedral square. With the fall and division of the former "Fürsterzbistum Salzburg" (Archbishopric) to
Upper Austria,
Bavaria (Rupertigau) and
Tyrol (Zillertal Matrei) began a long period of urban stagnancy. This era didn't end before the period of promoterism (''
Gründerzeit'') brought new life into urban development. The builder dynasty
Jakob Ceconi and
Carl Freiherr von Schwarz filled major positions in shaping the city in this era.
Classical modernism and post-war modernism
Buildings of classical
modernism and in particular, post-war modernism is frequently encountered in Salzburg. Examples are the Zahnwurzen house (a house in the Linzergasse 22 in the right center of the old town), the "Lepi" (public baths in ''Leopoldskron'') (built 1964), and the original 1957 constructed congress-center of Salzburg, which was replaced by a new building in 2001. An important and famous example of the architecture of this era is the 1960 opening of the
Großes Festspielhaus
The ''Großes Festspielhaus'' (Large Festival House), in its current form, was designed by architect Clemens Holzmeister in 1956 for the Salzburg Festival in
Austria. It was inaugurated on 26 July 1960 with a performance of Richard Strauss' ''D ...
by
Clemens Holzmeister.
Contemporary architecture
Adding
contemporary architecture to Salzburg's old town without risking its UNESCO World Heritage status is problematic. Nevertheless, some new structures have been added: the
Mozarteum at the Baroque
Mirabell Garden (Architecture Robert Rechenauer), the 2001 Congress House (Architecture: Freemasons), the 2011 Unipark Nonntal (Architecture: Storch Ehlers Partners), the 2001 "Makartsteg" bridge (Architecture: HALLE1), and the "Residential and Studio House" of the architects
Christine
Christine may refer to:
People
* Christine (name), a female given name
Film
* ''Christine'' (1958 film), based on Schnitzler's play ''Liebelei''
* ''Christine'' (1983 film), based on King's novel of the same name
* ''Christine'' (1987 fil ...
and
Horst Lechner in the middle of Salzburg's old town (winner of the
architecture award of Salzburg 2010). Other examples of contemporary architecture lie outside the old town: the Faculty of Science building (Universität Salzburg – Architecture
Willhelm Holzbauer) built on the edge of free green space, the
blob architecture
Blobitecture (from blob architecture), blobism and blobismus are terms for a movement in architecture in which buildings have an organic, amoeba-shaped, building form. Though the term ''blob architecture'' was in vogue already in the mid-1990s, t ...
of Red Bull
Hangar-7 (Architecture: Volkmar Burgstaller) at Salzburg Airport, home to
Dietrich Mateschitz's Flying Bulls and the Europark Shopping Centre. (Architecture:
Massimiliano Fuksas)
Districts
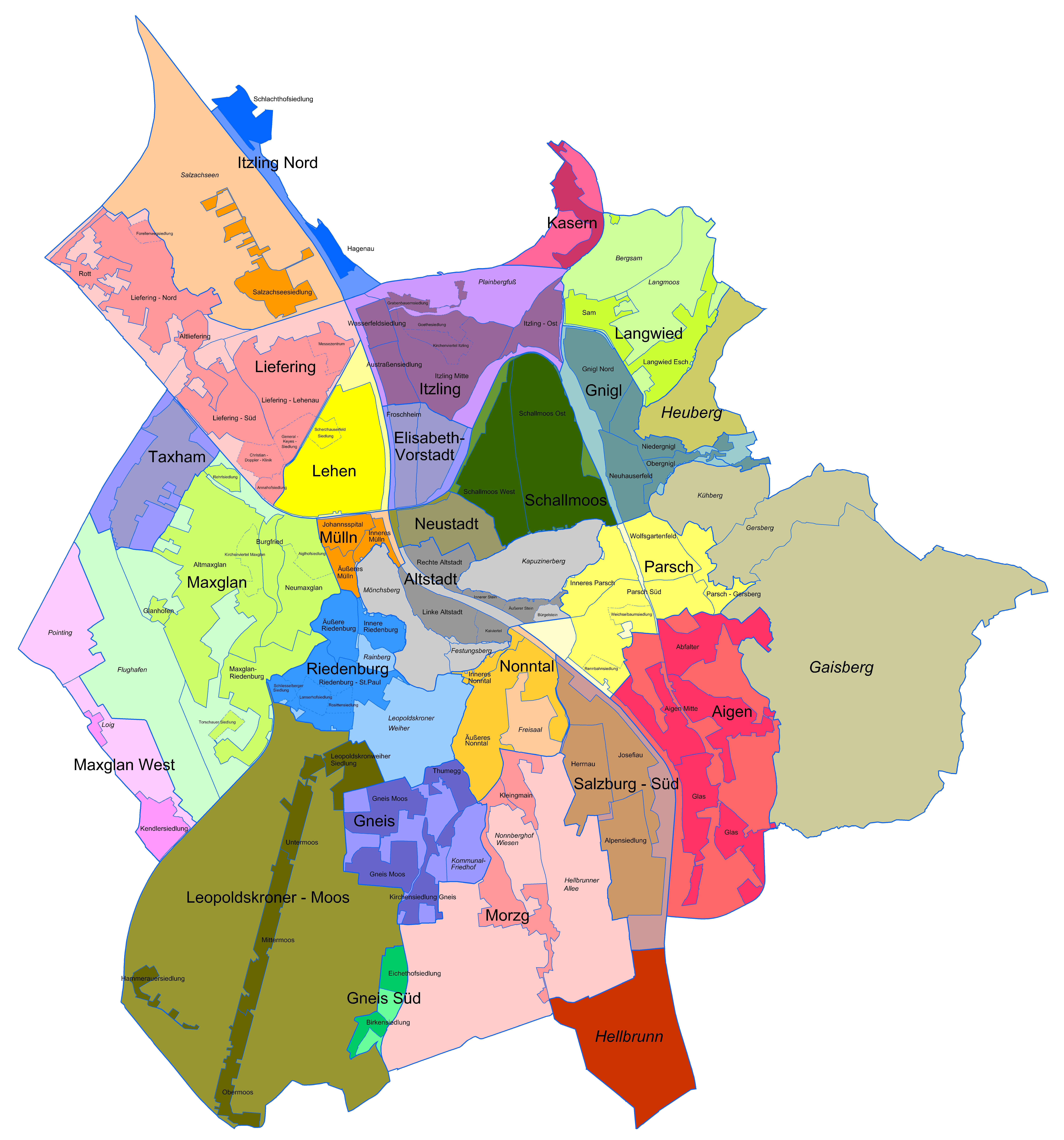
Salzburg has twenty-four urban districts and three extra-urban populations.
Urban districts (''Stadtteile''):
*
Aigen
*
Altstadt
''Altstadt'' is the German language word for "old town", and generally refers to the historical town or city centre within the old town or city wall, in contrast to younger suburbs outside. '' Neustadt'' (new town), the logical opposite of ''Alt ...
*Elisabeth-Vorstadt
*Gneis
*Gneis-Süd
*Gnigl
*Itzling
*Itzling-Nord
*Kasern
*Langwied
*Lehen
*Leopoldskron-Moos
*Liefering
*Maxglan
*Maxglan-West
*Morzg
*
Mülln
Mülln (Bavarian: "Mijn" or "Mün") is a small neighborhood in Salzburg, Austria surrounded by the Salzach River and neighborhoods , Riedenburg and Maxglan. The northern border is formed by the Westbahnlinie (West Train Line), Aiglhofstraße f ...
*Neustadt
*Nonntal
*Parsch
*Riedenburg
*Salzburg-Süd
*Taxham
*Schallmoos
Extra-urban populations (''Landschaftsräume''):
*Gaisberg
*
Hellbrunn
*Heuberg
Main sights
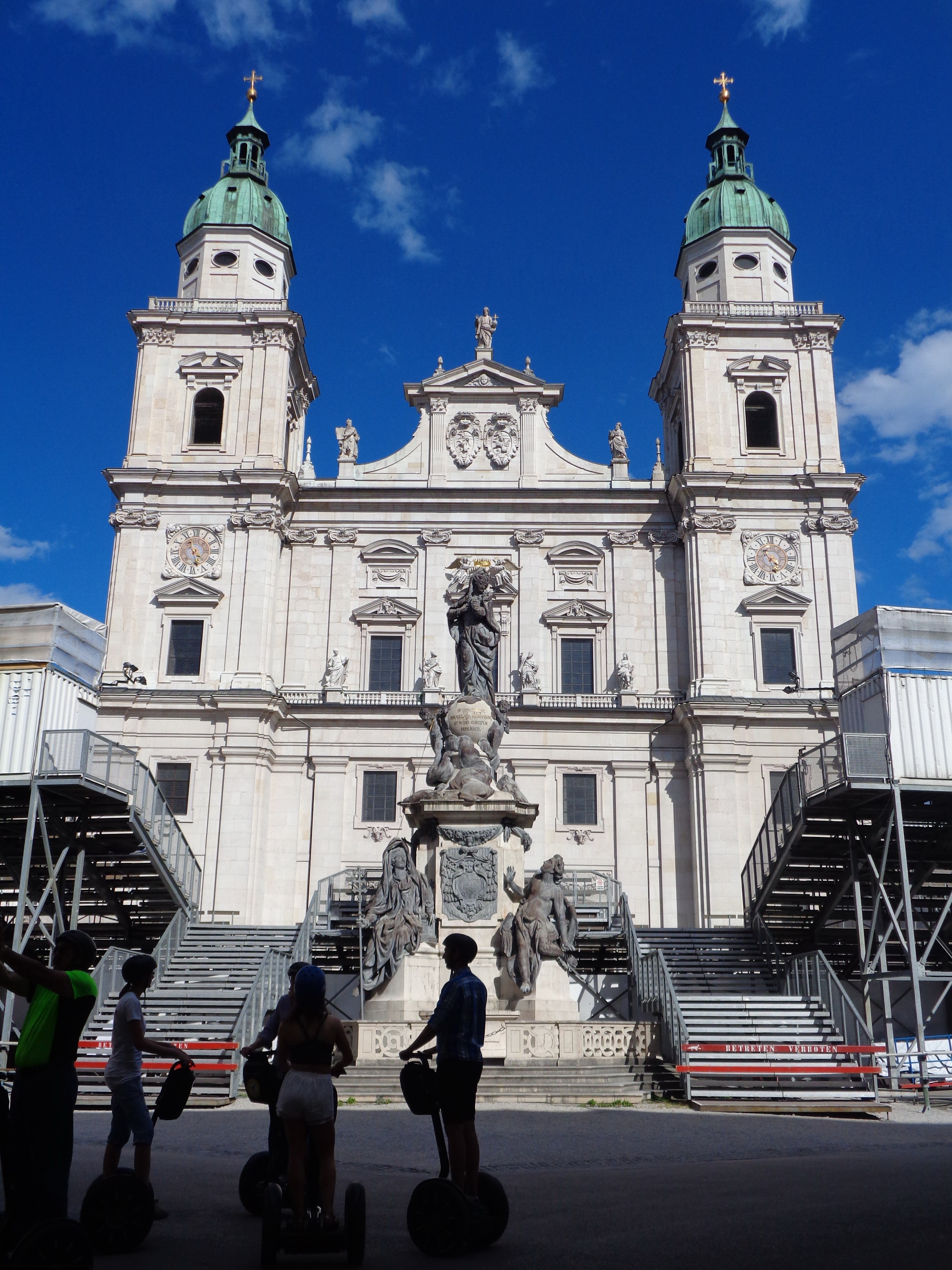
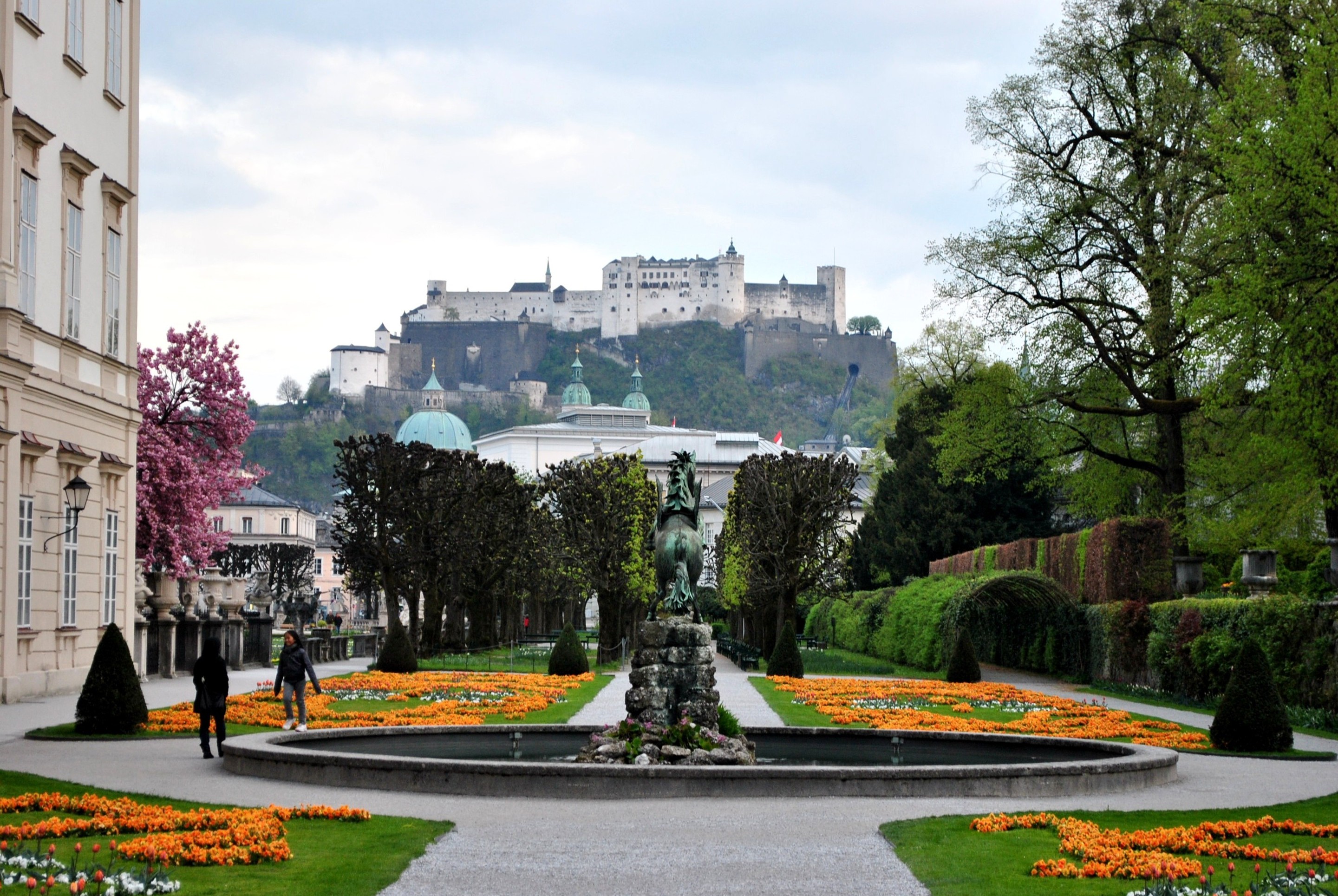


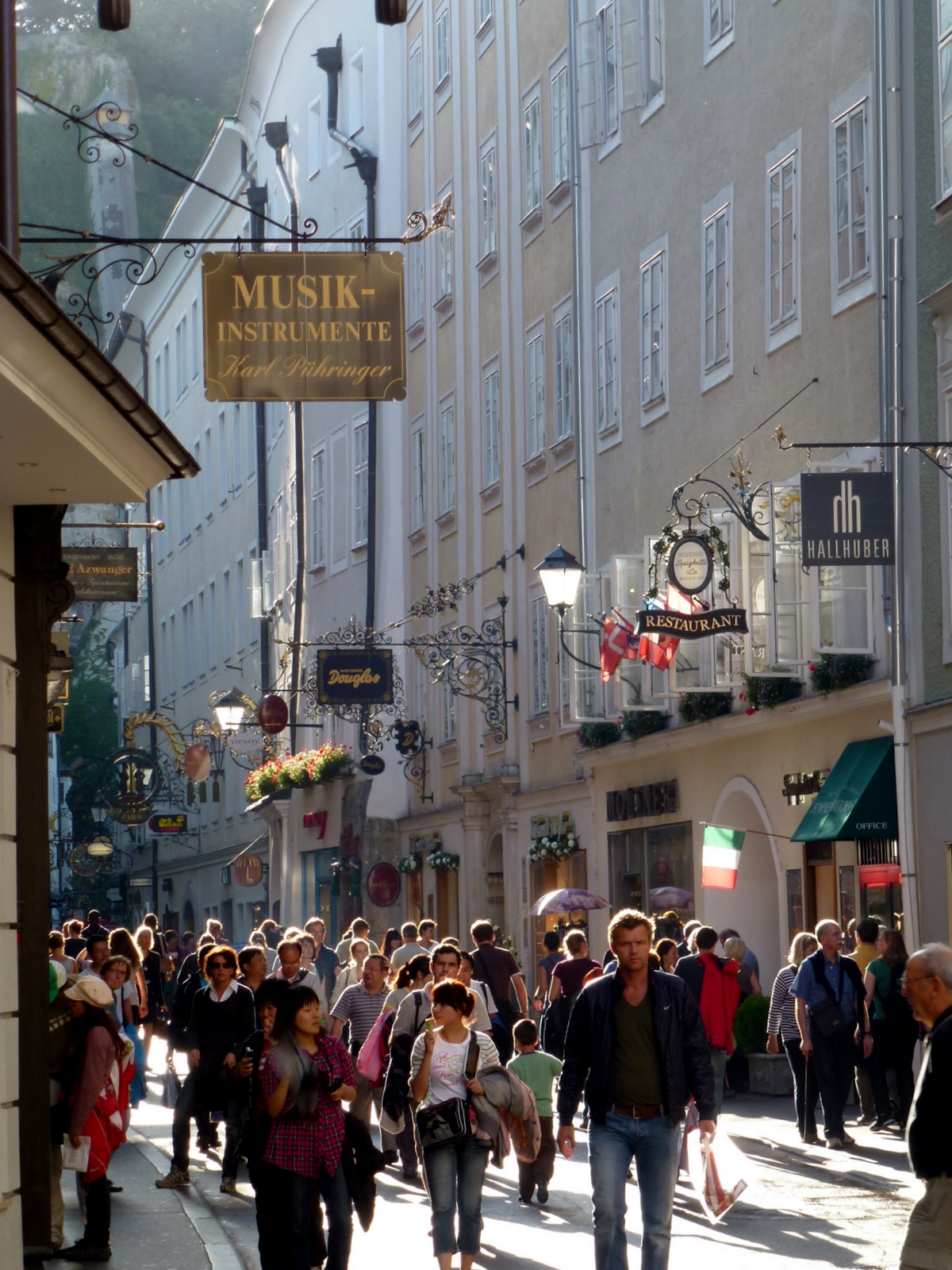

Salzburg is a
tourist favorite, with the number of visitors outnumbering locals by a large margin in peak times. In addition to Mozart's birthplace noted above, other notable places include:
Old Town
*
Historic center of the city of Salzburg
The Historic Center of the City of Salzburg, also known as the Altstadt, is a district of Salzburg, Austria, recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1996. It corresponds with the historic city center, situated on the left and right banks o ...
, a
World Heritage Site
*Baroque architecture, including many churches
*''
Felsenreitschule'', an open-air theatre built in the quarry used for the construction of Salzburg Cathedral
*''
Franziskanerkirche'', one of Salzburg's oldest buildings, dating from 1208 and used by the
Franciscans since 1642
*''
Getreidegasse'', a busy narrow shopping street characterized by numerous high townhouses
*''
Großes Festspielhaus
The ''Großes Festspielhaus'' (Large Festival House), in its current form, was designed by architect Clemens Holzmeister in 1956 for the Salzburg Festival in
Austria. It was inaugurated on 26 July 1960 with a performance of Richard Strauss' ''D ...
'', an opera house and concert hall dating from 1960 and built for the annual
Salzburg Festival
*''
Haus für Mozart
The Haus für Mozart, or House for Mozart, is a 1,500-seat theatre of the Salzburg Festival in the city of that name in Austria. It was established in 1925 when horse stables were converted into a venue for the mystery plays that were a main facet ...
'', formerly the ''Kleines Festspielhaus'', an opera house and concert hall dating from 1925
*
Hohensalzburg Fortress (''Festung Hohensalzburg''), overlooking the Old Town, one of the largest castles in Europe
*
Holy Trinity Church Holy Trinity Church may refer to:
Albania
* Holy Trinity Church (Berat), Berat County
* Holy Trinity Church, Lavdar, Opar, Korçë County
Armenia
* Holy Trinity Church, Yerevan
Australia
* Garrison Church, Sydney, South Wales, also known as ''H ...
(''Dreifaltigkeitskirche''), dating from 1694
*
Hotel Goldener Hirsch, a five-star hotel located in a building on ''Getreidegasse'' dating back to at least 1407
*''
Kollegienkirche'', the
Baroque style church of the
University of Salzburg
*
Mirabell Palace (''Schloss Mirabell''), a pleasure palace built in 1606 with wide gardens and a marble hall
*''
Museum der Moderne Salzburg'', a modern art museum with locations in the old city and on the Mönchsberg
*''
Mozartplatz
''Mozartplatz'', formerly known as ''Michaelsplatz'', is a square in the historic centre (''Altstadt'') of Salzburg in Austria. In the centre of the square is a statue in memory of the composer Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, who was born in the city an ...
'', a historic square with monument to
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
*
Mozart's birthplace
Mozart's birthplace (German: or ) was the birthplace of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart at No. 9 Getreidegasse in Salzburg, Austria. The Mozart family resided on the third floor from 1747 to 1773. Mozart himself was born here on 27 January 1756. He was ...
(''Mozarts Geburtshaus''), a house in ''Getreidegasse'' that is now a museum dedicated to Mozart
*
Nonnberg Abbey (''Stift Nonnberg''), a
Benedictine monastery founded c.712/715
*''
Residenz
Residenz () is a German word for "place of living", now obsolete except in the formal sense of an official residence. A related term, Residenzstadt, denotes a city where a sovereign ruler resided, therefore carrying a similar meaning as the modern ...
'', the former residence of the
Prince-Archbishops
*''
Residenzgalerie
The Residenzgalerie is an art gallery in the Alte Residenz, Salzburg, Austria. Its collection includes works by Rembrandt, Carel Fabritius, Carlo Saraceni and Hieronymus Francken II.
History
The state-owned Residenzgalerie provides a cross-se ...
'', an art museum in the Residenz
*''
Residenzplatz
''Residenzplatz'' is a large, stately square in the historic centre (''Altstadt'') of Salzburg in Austria. Originally named ''Hauptplatz'', it is now named after the ''Alte Residenz
The Salzburg Residenz, also known as the Alte Residenz or Old R ...
'', a large square outside the Residenz with a large and ornate fountain
*
Salzburg Cathedral (''Salzburger Dom'')
*''
Salzburger Landestheater'', a theatre and venue for opera, theatre, and dance, with resident companies of actors, singers, and dancers
*''
Salzburger Marionettentheater Salzburg Marionette Theatre was established in 1913 and is one of the oldest continuing marionette theatres in the world. It is based in the city of Salzburg, Austria. Original productions featured live actors and musicians. Today soundtracks are r ...
'', a
marionette theatre
A marionette (; french: marionnette, ) is a puppet controlled from above using wires or strings depending on regional variations. A marionette's puppeteer is called a marionettist. Marionettes are operated with the puppeteer hidden or revealed ...
established in 1912
*
Salzburg Museum, a museum of the artistic and cultural history of the city and region of Salzburg
*''
Sigmundstor
The Sigmundstor, often still known as the Neutor, is a road tunnel in Salzburg that also forms one of the city gates of the historic Altstadt Salzburg, Altstadt. It connects the Altstadt with the Riedenburg quarter through the Mönchsberg mountain ...
'', an eighteenth-century tunnel connecting the Altstadt with the Riedenburg quarter through the Mönchsberg
*, a sculpture of a man on a golden sphere (Stephan Balkenhol, 2007)
*
St Peter's Abbey (''Stift Sankt Peter''), a
Benedictine monastery founded 696 with
a well-known cemetery
* (''Sebastianskirche''), a church consecrated in 1511
Outside the Old Town
*
Schloss Leopoldskron
Schloss Leopoldskron is a rococo palace and a national historic monument in Leopoldskron-Moos, a southern district of the city of Salzburg, Austria. The palace, and its surrounding seven hectare park, is located on the lake ''Leopoldskroner Weiher ...
, a rococo palace and national historic monument in Leopoldskron-Moos, a southern district of Salzburg
*
Hellbrunn with its parks and castles
*''
The Sound of Music'' tour companies who operate tours of film locations
*
Hangar-7, a multifunctional building owned by
Red Bull
Red Bull is a brand of energy drinks of Austria, Austrian company Red Bull GmbH. With 38% market share, it is the most popular energy drink brand as of 2019. Since its launch in 1987, more than 100 billion cans of Red Bull have been sold worldwid ...
, with a collection of historical airplanes, helicopters, and
Formula One racing cars
Greater Salzburg area
*Anif Castle, located south of the city in
Anif
*Shrine of Our Lady of Maria Plain, a late Baroque church on the northern edge of Salzburg
*Salzburger Freilichtmuseum Großgmain, an open-air museum containing old farmhouses from all over the state assembled in a historic setting
*
Schloss Klessheim
Schloss Klessheim is a Baroque palace located in Wals-Siezenheim, west of Salzburg, Austria. The palace was designed and constructed by Austrian architect Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach for Prince-Archbishop Johann Ernst von Thun in 1700. It ...
, a palace and casino, formerly used by
Adolf Hitler
*
Berghof, Hitler's mountain retreat near
Berchtesgaden
Berchtesgaden () is a municipality in the district Berchtesgadener Land, Bavaria, in southeastern Germany, near the border with Austria, south of Salzburg and southeast of Munich. It lies in the Berchtesgaden Alps, south of Berchtesgaden; the ...
*
Kehlsteinhaus, the only remnant of Hitler's Berghof
*
Salzkammergut, an area of lakes east of the city
*
Untersberg mountain, next to the city on the
Austria–Germany border, with panoramic views of Salzburg and the surrounding Alps
*
Skiing is an attraction during winter. Salzburg has no skiing facilities, but it is a gateway to skiing areas to the south. During the winter, its airport receives
charter flights from around Europe.
*
Salzburg Zoo, located south of the city in
Anif
Education
Salzburg is a center of education and home to three universities, as well as several professional colleges and
gymnasiums (high schools).
Universities and higher education institutions
*
Salzburg University of Applied Sciences
*
University of Salzburg, a federal public university
*
Paracelsus Medical University
The Paracelsus Medical University (german: Paracelsus Medizinische Privatuniversität) is a private university located in Salzburg municipality, Austria and Nuremberg, Germany.
Organization and financing
University management
* Wolfgang Spe ...
*
Mozarteum University Salzburg, a public music and dramatic arts university
*
Alma Mater Europaea
Alma Mater Europaea (Latin for "The European nourishing mother", i.e. university) is an international university based in the Austrian city of Salzburg, with campuses in several European cities. It was founded as an initiative by the European Ac ...
, a private university
*SEAD – Salzburg Experimental Academy of Dance
Notable citizens

*
Saint Liutberga Saint Liutberga (died c. 870), also called Liutbirg and Liutbirga, was an influential nun in Saxony in the 9th century, who ended her life as an anchoress in Windenhausen (or Wendhausen). Her life provides important evidence for female experiences o ...
(died c. 870).
*The composer
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, born and raised in Salzburg when it was part of the Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg within the Holy Roman Empire, was employed as a musician at the
archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
al court from 1773 to 1781. His house of birth and residence are tourist attractions. His family is buried in a small church graveyard in the old town, and there are many monuments to "Wolferl" in the city.
*The composer
Johann Michael Haydn
Johann Michael Haydn (; 14 September 173710 August 1806) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period, the younger brother of Joseph Haydn.
Life
Michael Haydn was born in 1737 in the Austrian village of Rohrau, near the Hungarian borde ...
, brother of the composer
Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( , ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
. His works were admired by
Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his ra ...
and
Schubert. He was also the teacher of
Carl Maria von Weber and
Anton Diabelli
Anton (or Antonio) Diabelli (5 September 17818 April 1858) was an Austrian music publisher, editor and composer. Best known in his time as a publisher, he is most familiar today as the composer of the waltz on which Ludwig van Beethoven wrote ...
and is known for his sacred music.
*
Christian Doppler, expert on
acoustic theory, was born in Salzburg. He is most known for his discovery of the
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who d ...
.
*
Josef Mohr, born in Salzburg. Together with
Franz Gruber, he composed and wrote the text for "
Silent Night". As a priest in neighboring
Oberndorf he performed the song for the first time on Christmas Eve 1818.
*King
Otto
Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', ''Odo'', ''Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity".
The name is recorded fro ...
of
Greece was born Prince Otto Friedrich Ludwig of Bavaria at the Palace of Mirabell, a few days before the city reverted from Bavarian to Austrian rule.
*Writer
Stefan Zweig
Stefan Zweig (; ; 28 November 1881 – 22 February 1942) was an Austrian novelist, playwright, journalist, and biographer. At the height of his literary career, in the 1920s and 1930s, he was one of the most widely translated and popular write ...
, lived in Salzburg for about 15 years, until 1934.
*The
Trapp Family
The Trapp Family (also known as the von Trapp Family) were a singing group formed from the family of former Austrian naval commander Georg von Trapp. The family achieved fame in their original singing career in their native Austria during the i ...
, including
Georg von Trapp,
Maria von Trapp, and their children lived in Salzburg until they fled to the United States following the Nazi takeover.
*Salzburg is the birthplace of
Hans Makart
Hans Makart (28 May 1840 – 3 October 1884) was a 19th-century Austrian academic history painter, designer, and decorator. Makart was a prolific painter whose ideas significantly influenced the development of visual art in Austria-Hungary, Germa ...
, a 19th-century Austrian painter-decorator and national celebrity. Makartplatz (''Makart Square'') is named in his honor.
*Writer
Thomas Bernhard
Nicolaas Thomas Bernhard (; 9 February 1931 – 12 February 1989) was an Austrian novelist, playwright and poet who explored death, social injustice, and human misery in controversial literature that was deeply pessimistic about modern civilizati ...
, raised in Salzburg, spent part of his life there.
*
Herbert von Karajan, notable orchestral conductor. He was born in Salzburg and died in 1989 in neighboring
Anif.
*
Roland Ratzenberger,
Formula One driver, was born in Salzburg. He died in practice for the
1994 San Marino Grand Prix
The 1994 San Marino Grand Prix (formally the 14º Gran Premio di San Marino) was a Formula One motor race held on 1 May 1994 at the Autodromo Enzo e Dino Ferrari, located in Imola, Italy. It was the third race of the 1994 Formula One World Ch ...
.
*
Joseph Leutgeb, a virtuoso on the French horn, was part of the archbishop's court.
*
Paracelsus
Paracelsus (; ; 1493 – 24 September 1541), born Theophrastus von Hohenheim (full name Philippus Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim), was a Swiss physician, alchemist, lay theologian, and philosopher of the German Renaissance.
He w ...
, Swiss physician, alchemist, and astrologer of the German Renaissance died in Salzburg.
*
Klaus Ager
Klaus Ager (born 10 May 1946) is an Austrian composer and conductor.
Born in Salzburg, Ager studied piano, composition, and conducting at the Mozarteum in Salzburg, and musicology at University of Salzburg, Salzburg University. He continued his ...
, the distinguished contemporary composer and Mozarteum professor, was born in Salzburg on 10 May 1946.
*
Alex Jesaulenko
Oleksandr "Alex" Jesaulenko ( ; uk, Олександр Васильович Єсауленко, Oleksandr Vasiliovych Yesaulenko, ; born 2 August 1945) is a former Australian rules footballer and who played for the Carlton Football Club and t ...
, former
Australian rules football-player for Carlton and
Australian Football Hall of Fame
The Australian Football Hall of Fame was established in 1996, the Centenary year of the Australian Football League, to help recognise the contributions made to the sport of Australian rules football by players, umpires, media personalities, coa ...
member with "Legend" status was born in Salzburg on 2 August 1945.
*
Barbara Thenn
Barbara Thenn (1519-1579) was an Austrian merchant and Münzmeister. August Stockhammer: In Salzburg geboren, Lebensbilder aus sieben Jahrhunderten, Salzburger Nachrichten Verlags GmbH. Erscheinungsjahr: 1973, 2. Auflage ISBN 3-85304-032-2
She w ...
(1519-1579), merchant and Münzmeister
*
Georg Trakl, one of the most important voices in German literature was born in Salzburg.
*
Irma von Troll-Borostyani
Irma Troll-Borostyáni (31 March 1847 – 10 February 1912) was an Austrian writer, journalist and campaigner for women's rights.
Biography
Troll-Borostyáni was born in Salzburg as Maria von Troll to Josephine von Appeltauer and Otto Ritter von ...
, an Austrian writer, journalist, and campaigner for women's rights.
*
Theodor Herzl, worked in the
courts in Salzburg during the year after he earned his
law degree
A law degree is an academic degree conferred for studies in law. Such degrees are generally preparation for legal careers. But while their curricula may be reviewed by legal authority, they do not confer a license themselves. A legal license is gra ...
in 1884.
*Skydiver and BASE Jumper
Felix Baumgartner, who set three world records during the
Red Bull Stratos project on 14 October 2012.
*
Hilda Crozzoli
Hilda Crozzoli was one of the first female architects and civil engineers in Austria.
Early life and education
Hilda Johana Crozzoli was born on 16 August 1900 in Salzburg, Austria. Her father was Ambrogio (Ambros) Crozzoli (1870-1925) and her ...
, Austria's first female architect and civil engineer.
*
Ferdinand Habsburg, racing driver and
heir apparent to the headship of the
House of Habsburg-Lorraine
Events
*The
Salzburg Festival is a famous music and theatre festival that attracts visitors during July and August each year. A smaller
Salzburg Easter Festival is held around Easter each year.
*The
Europrix multimedia award takes place in Salzburg.
*
Electric Love Festival takes place in Salzburg
Transport

 Salzburg Hauptbahnhof
Salzburg Hauptbahnhof is served by comprehensive rail connections, with frequent east-west trains serving
Vienna,
Munich,
Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
, and
Zürich, including daily high-speed
ICE services. North-south rail connections also serve popular destinations such as
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
and
Prague. The city acts as a hub for southbound trains through the Alps into
Italy.
Salzburg Airport has scheduled flights to European cities such as
Frankfurt,
Vienna,
London,
Rotterdam,
Amsterdam,
Brussels,
Düsseldorf, and
Zürich, as well as
Hamburg,
Edinburgh and
Dublin. In addition to these, there are numerous charter flights.
In the main city, there is the
Salzburg trolleybus system and bus system with a total of more than 20 lines, and service every 10 minutes. Salzburg has an
S-Bahn system with four Lines (S1, S2, S3, S11), trains depart from the main station every 30 minutes, and they are part of the
ÖBB network. Suburb line number S1 reaches the world-famous Silent Night chapel in
Oberndorf in about 25 minutes.
Popular culture
In the 1960s, ''
The Sound of Music'', based on the true story of
Maria von Trapp, who took up with an aristocratic family and fled the German
Anschluss, used locations in and around Salzburg and
the state of Salzburg as
filming location
A filming location is a place where some or all of a film or television series is produced, in addition to or instead of using sets constructed on a movie studio backlot or soundstage. In filmmaking, a location is any place where a film crew wil ...
s.
The city briefly appears on the map when Indiana Jones travels through the city in ''
Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade
''Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade'' is a 1989 American action film, action-adventure film directed by Steven Spielberg, from a story co-written by executive producer George Lucas. It is the third installment in the Indiana Jones, ''Indiana ...
''.
Salzburg is the setting for the Austrian crime series ''
Stockinger {{for, the surname, Stockinger (surname)
''Stockinger'' is an Austrian-made police procedural, police television drama, with fourteen 45-minute episodes first aired from 1996 to 1997.
The series is a spin-off (media), spin-off from the popular Ital ...
'' and an Austrian-German television crime drama series
Der Pass.
In the 2010 film ''
Knight & Day'', Salzburg serves as the backdrop for a large portion of the film.
Language
Austrian German is widely written and differs from Germany's standard variation only in some vocabulary and a few grammar points. Salzburg belongs to the region of
Austro-Bavarian
Bavarian (german: Bairisch , Bavarian: ''Boarisch'') or alternately Austro-Bavarian, is a West Germanic language, part of the Upper German family, together with Alemannic and East Franconian.
Bavarian is spoken by approximately 12 million peop ...
dialects, in particular
Central Bavarian. It is widely spoken by young and old alike although professors of linguistics from the Universität Salzburg, Irmgard Kaiser, and Hannes Scheutz, have seen over the past few years a reduction in the number of dialect speakers in the city. Although more and more school children are speaking standard German, Scheutz feels it has less to do with parental influence and more to do with media consumption.
Sports
Soccer

The former SV Austria Salzburg reached the
UEFA Cup final in
1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which Sinking of the MS Estonia, sank in ...
. On 6 April 2005
Red Bull
Red Bull is a brand of energy drinks of Austria, Austrian company Red Bull GmbH. With 38% market share, it is the most popular energy drink brand as of 2019. Since its launch in 1987, more than 100 billion cans of Red Bull have been sold worldwid ...
bought the club and changed its name to
FC Red Bull Salzburg
FC Red Bull Salzburg is an Austrian professional football club based in Wals-Siezenheim, that competes in the Austrian Bundesliga, the top flight of Austrian Football. Their home ground is the Red Bull Arena. Due to sponsorship restrictions, ...
. The home stadium of Red Bull Salzburg is the
Wals Siezenheim Stadium
Red Bull Arena (), known during the UEFA Euro 2008 as the EM-Stadion Wals-Siezenheim and during UEFA club football events as Stadion Salzburg, is a football stadium in Wals-Siezenheim, a municipality in the suburbs of Salzburg, Austria. It was ...
in a suburb in the agglomeration of Salzburg and was one of the venues for the
2008 European Football Championship
The 2008 UEFA European Football Championship, commonly referred to as UEFA Euro 2008 or simply Euro 2008, was the 13th UEFA European Championship, a quadrennial football tournament contested by the member nations of UEFA (the Union of European ...
. FC Red Bull Salzburg plays in the
Austrian Bundesliga
The Austrian Football Bundesliga (german: Österreichische Fußball-Bundesliga, italic=no , "Austrian Football Federal League"), also known as Admiral Bundesliga for sponsorship reasons, is the top level of the Austrian football league system. Th ...
.
After Red Bull had bought the SV Austria Salzburg and changed its name and team colors, some supporters of the club decided to leave and form a new club with the old name and old colors, wanting to preserve the traditions of their club. The reformed
SV Austria Salzburg was founded in 2005 and currently plays in the
Erste Liga, only one tier below the Bundesliga.
Ice-hockey
Red Bull also sponsors the local
ice hockey team, the
EC Salzburg Red Bulls. The team plays in the
Erste Bank Eishockey Liga, an Austria-headquartered cross-border league featuring the best teams from Austria, Hungary, Slovenia, Croatia, and Italy, as well as one Czech team.
Other sports
Salzburg was a candidate city for the
2010
File:2010 Events Collage New.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2010 Chile earthquake was one of the strongest recorded in history; The Eruption of Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland disrupts air travel in Europe; A scene from the opening ceremony of ...
and
2014 Winter Olympics
, ''Zharkie. Zimnie. Tvoi'')
, nations = 88
, events = 98 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, athletes = 2,873
, opening = 7 February 2014
, closing = 23 February 2014
, opened_by = President Vladimir Putin
, cauldron =
, stadium = Fisht Olympic ...
, but lost to
Vancouver and
Sochi
Sochi ( rus, Со́чи, p=ˈsotɕɪ, a=Ru-Сочи.ogg) is the largest resort city in Russia. The city is situated on the Sochi River, along the Black Sea in Southern Russia, with a population of 466,078 residents, up to 600,000 residents in ...
respectively.
International relations
Twin towns—sister cities
Salzburg is twinned with:
*
Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
,
Marne Marne can refer to:
Places France
*Marne (river), a tributary of the Seine
*Marne (department), a département in northeastern France named after the river
* La Marne, a commune in western France
*Marne, a legislative constituency (France)
Nethe ...
,
Grand Est, France, since 1964
*
Verona,
Verona,
Veneto, Italy, since 1973
*
León, Nicaragua, since 1984
*
Singida
Singida is a town in central Tanzania. The town is the location of the regional headquarters of Singida Region as well as the district headquarters of Singida Urban District. The region and district are named after the town.
Transport
Road lin ...
, Tanzania, since 1984
*
Busseto,
Parma,
Emilia-Romagna, Italy, since 1988
*
Vilnius, Lithuania, since 1989
*
Dresden,
Saxony, Germany, since 1991
*
Kawasaki, Japan, since 1992
*
Meran,
South Tyrol,
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Italy, since 2000
*
Shanghai, China, since 2004
*
Jahrom, Iran, since 2019
Gallery
File:Mozart (5).JPG, Mozart's birthplace at Getreidegasse 9
File:Salzburg (night) - Mirabellgarten.jpg, View from Mirabellgarten at night
File:Fountain Mirabell.JPG, The famous fountain in Mirabell Gardens (seen in the "Do-Re-Mi" song from ''The Sound of Music'')
File:Salzburg Sunset by Horst Michael Lechner.jpg, The Sunset at the Staatsbrücke
File:Sigmund-Haffner-Gasse1.jpg, Sigmund Haffner Gasse – Rathaus
File:Wohn&Atelierhaus Lechner Gartengeschoß1.jpg, Residential and studio house Lechner in the old town
File:Untersberg (16).JPG, The Salzburg basin
File:Salzburg (16).JPG, The fortress (background), Salzburg Cathedral (middle), the Salzach (foreground)
File:Feb20532.JPG, ÖBB rail connection to Salzburg in Innsbruck
File:Feb20516.JPG, Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his ra ...
monument
File:salzburg.fountain.jpg, Fountain in the Residenzplatz
''Residenzplatz'' is a large, stately square in the historic centre (''Altstadt'') of Salzburg in Austria. Originally named ''Hauptplatz'', it is now named after the ''Alte Residenz
The Salzburg Residenz, also known as the Alte Residenz or Old R ...
File:Gardens at the Palace of Mirabell.JPG, Palace of Mirabell.
File:SalzburgerAltstadt02.JPG, View of the old town and fortress
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, seen from Kapuzinerberg
File:Salzburg - Panorama (nachts) cropped.jpg, Salzburg at night
See also
*
List of World Heritage Sites in Austria
Notes
References
Bibliography
External links
Salzburg, Austria – Travel guideat visit-salzburg.net
*
nbsp;– Informationen zum Outlet Salzburg
{{Authority control
Salzburg, Salzburg
15 BC establishments
Austrian state capitals
Cities and towns in Salzburg (state)
Displaced persons camps in the aftermath of World War II
Districts of Salzburg (state)
World Heritage Sites in Austria
Holocaust locations in Austria

 The Anschluss (the occupation and annexation of Austria, including Salzburg, into the Third Reich) took place on 12 March 1938, one day before a scheduled referendum on Austria's independence. German troops moved into the city. Political opponents, Jewish citizens and other minorities were subsequently arrested and deported to concentration camps. The
The Anschluss (the occupation and annexation of Austria, including Salzburg, into the Third Reich) took place on 12 March 1938, one day before a scheduled referendum on Austria's independence. German troops moved into the city. Political opponents, Jewish citizens and other minorities were subsequently arrested and deported to concentration camps. The 
 Salzburg has twenty-four urban districts and three extra-urban populations.
Urban districts (''Stadtteile''):
* Aigen
*
Salzburg has twenty-four urban districts and three extra-urban populations.
Urban districts (''Stadtteile''):
* Aigen
*

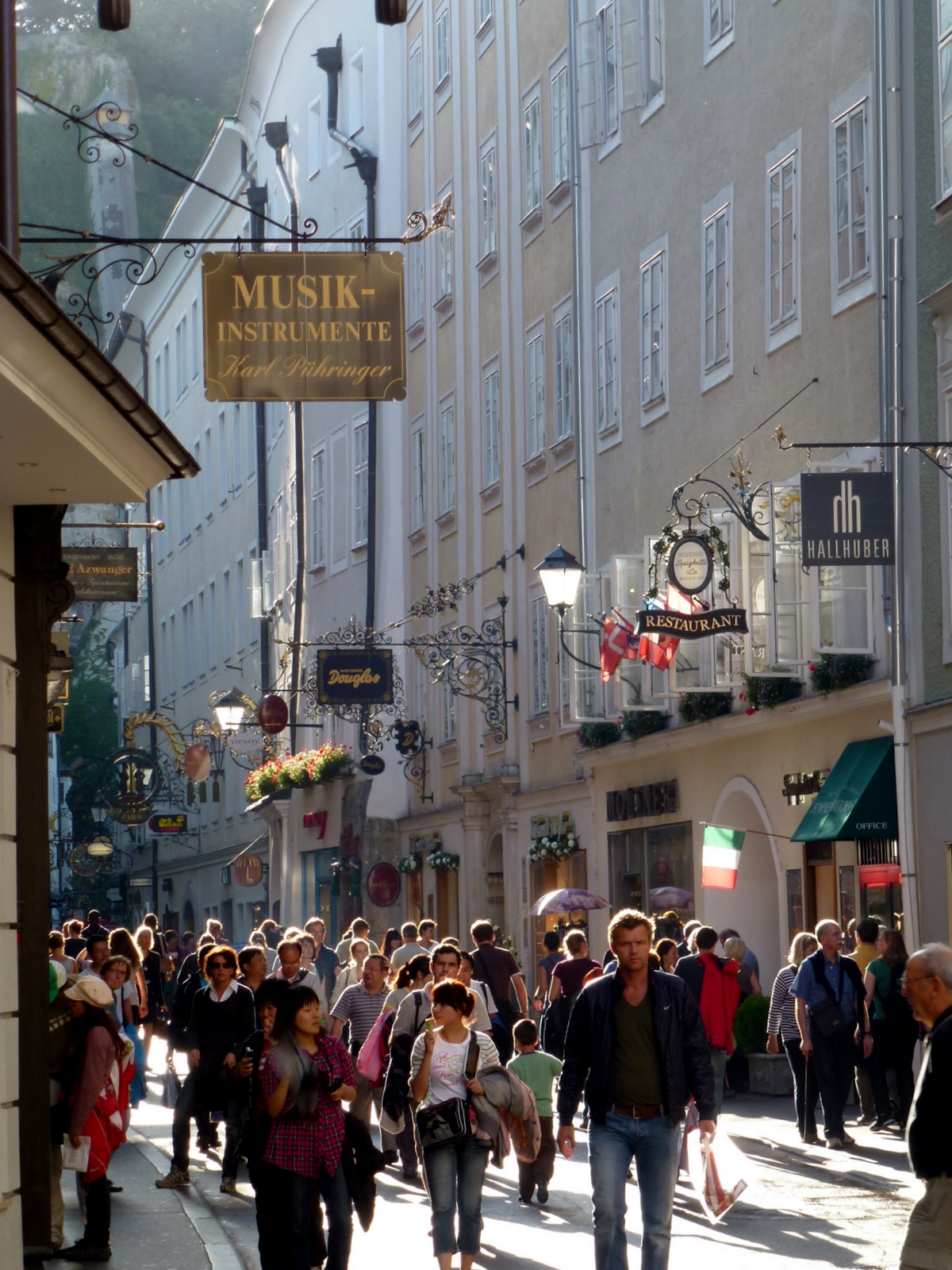
 Salzburg is a tourist favorite, with the number of visitors outnumbering locals by a large margin in peak times. In addition to Mozart's birthplace noted above, other notable places include:
Old Town
*
Salzburg is a tourist favorite, with the number of visitors outnumbering locals by a large margin in peak times. In addition to Mozart's birthplace noted above, other notable places include:
Old Town
* *
*
 Salzburg Hauptbahnhof is served by comprehensive rail connections, with frequent east-west trains serving Vienna, Munich,
Salzburg Hauptbahnhof is served by comprehensive rail connections, with frequent east-west trains serving Vienna, Munich,