Saint-Ouen Abbey, Rouen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saint-Ouen Abbey, () is a large Gothic 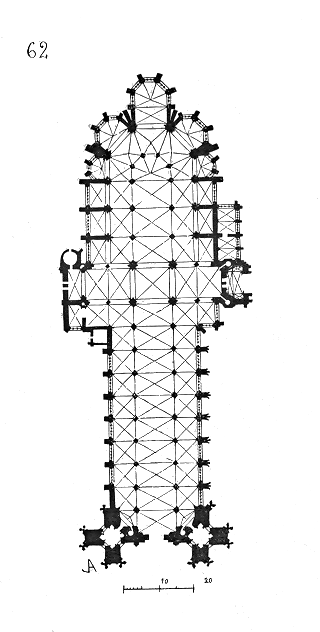
 The current church building was originally built as the abbey church of Saint-Ouen for the Benedictine Order, beginning in 1318 and interrupted by the
The current church building was originally built as the abbey church of Saint-Ouen for the Benedictine Order, beginning in 1318 and interrupted by the
File:Abbatiale Saint-Ouen de Rouen - Portail des Marmousets - 1.jpg, The ''Portail des Marmousets'' after restoration.
File:Abbatiale Saint-Ouen de Rouen - Portail des Marmousets - Statue de Saint Ouen.jpg, Statue of Saint Owen on the trumeau of the ''Portail des Marmousets'' after restoration.
File:Abbatiale Saint-Ouen de Rouen - Tour sur la croisée du transept - gros plan.jpg, The Crossing Tower.
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, 1910. (2787320269).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, 1910. (2787322649).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, 1910. (2788174178).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, 1910. (2788174286).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, 1910(?). (2788175980).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, n.d.. (2787320553).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, n.d.. (2787320663).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, n.d.. (2788174684).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, n.d.. (2788174728).jpg
File:St. Ouen, Rouen, France, n.d.. (2788174600).jpg
File:Sant-Ouen de Rouen.jpg
Gallery of St. Ouen de Rouen
in
Description of the church and organ
{{DEFAULTSORT:Church of Saint Ouen, Rouen 15th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in France Roman Catholic churches completed in 1851 Benedictine monasteries in France Gothic architecture in France Roman Catholic churches in Rouen 19th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in France
Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
church and former Benedictine
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, th ...
monastic
Monasticism (; ), also called monachism or monkhood, is a religious way of life in which one renounces worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual activities. Monastic life plays an important role in many Christian churches, especially ...
church in Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine, in northwestern France. It is in the prefecture of Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one ...
. It is named for Audoin
Alduin (Langobardic: ''Aldwin'' or ''Hildwin'', ; also called Auduin or Audoin) was List of kings of the Lombards, king of the Lombards from 547 to 560.
Life
Audoin was of the Gausian dynasty, Gausi, a prominent Lombard ruling clan, and accordin ...
(, ), 7th-century bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
of Rouen in modern Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. The church's name is sometimes anglicized
Anglicisation or anglicization is a form of cultural assimilation whereby something non-English becomes assimilated into or influenced by the culture of England. It can be sociocultural, in which a non-English place adopts the English language ...
as St Owen's. Built on a similar scale to nearby Rouen Cathedral
Rouen Cathedral () is a Catholic church architecture, church in Rouen, Normandy, France. It is the Episcopal see, see of the Archbishop of Rouen, Primate of Normandy. It is famous for its three towers, each in a different style. The cathedral, b ...
, the abbey is famous for both its architecture and its large, unaltered Cavaillé-Coll organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
, which was described by Charles-Marie Widor
Charles-Marie-Jean-Albert Widor (21 February 1844 – 12 March 1937) was a French organist, composer and teacher of the late Romantic era. As a composer he is known for his ten organ symphonies, especially the toccata of his fifth organ sympho ...
as "a Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (6March 147518February 1564), known mononymously as Michelangelo, was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was inspir ...
of an organ". With the cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
and the Church of Saint-Maclou
The Church of Saint-Maclou, () is a Roman Catholic church in Rouen, France, named after the Saint Malo, which is considered one of the best examples of the Flamboyant style of Gothic architecture in France.
Saint-Maclou, along with Rouen Cathedr ...
, Saint-Ouen is one of the principal French Gothic
French Gothic architecture is an architectural style which emerged in France in 1140, and was dominant until the mid-16th century. The most notable examples are the great Gothic cathedrals of France, including Notre-Dame Cathedral, Reims Cathed ...
monuments of the city.

The Abbey
 The current church building was originally built as the abbey church of Saint-Ouen for the Benedictine Order, beginning in 1318 and interrupted by the
The current church building was originally built as the abbey church of Saint-Ouen for the Benedictine Order, beginning in 1318 and interrupted by the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
and sacked and badly damaged during the Harelle
The Harelle (; from ''haro'') was a revolt that occurred in the French city of Rouen in 1382, followed by an uprising a few days later in Paris, as well as numerous other revolts across France in the subsequent week. France was in the midst of t ...
. It was completed in the 15th century in the Flamboyant
Flamboyant () is a lavishly-decorated style of Gothic architecture that appeared in France and Spain in the 15th century, and lasted until the mid-sixteenth century and the beginning of the Renaissance.Encyclopedia Britannica, "Flamboyant style ...
style.
The foundation of Saint-Ouen Abbey has been variously credited, among others, to Chlothar I
Chlothar I, sometime called "the Old" (French: le Vieux), (died December 561) also anglicised as Clotaire from the original French version, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I.
With his eldes ...
and to Clotilde
Clotilde ( 474 – 3 June 545 in Burgundy, France) (also known as Clotilda (Fr.), Chlothilde (Ger.) Chlothieldis, Chlotichilda, Clodechildis, Croctild, Crote-hild, Hlotild, Rhotild, and many other forms), is a saint and was a Queen of the Fran ...
, royal saint and wife of Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
, but evidence is scanty. It was dedicated at first to Saint Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the Jewish Christian#Jerusalem ekklēsia, e ...
; when the body of Audoin, Archbishop of Rouen
The Archdiocese of Rouen (Latin: ''Archidioecesis Rothomagensis''; French: ''Archidiocèse de Rouen'') is a Latin Church archdiocese of the Catholic Church in France. As one of the fifteen Archbishops of France, the Archbishop of Rouen's ecclesi ...
(d. 678), was buried there; the name of St Peter and St Ouen became common and finally St Ouen only.
The history of the abbey, on record from the 1000, is unremarkable; a list of abbots is in ''Gallia Christiana
The ''Gallia Christiana'', a type of work of which there have been several editions, is a documentary catalogue or list, with brief historical notices, of all the Catholic dioceses and abbeys of France from the earliest times, also of their occupa ...
'' XI, 140.
The fourth abbot, Nicolas
Nicolas or Nicolás may refer to:
People Given name
* Nicolas (given name)
Mononym
* Nicolas (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer
* Nicolas (footballer, born 2000), Brazilian footballer
Surname Nicolas
* Dafydd Nicolas (c.1705–1774), ...
(r. 1042–1092) was the first cousin of William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
, and supplied ships and men for the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
.
In 1660 the monastery was united to the Congregation of Saint Maur
The Congregation of St. Maur, often known as the Maurists, were a congregation of French Benedictines, established in 1621, and known for their high level of scholarship. The congregation and its members were named after Saint Maurus (died 565), a ...
, and when suppressed, in 1794, the community numbered twenty-four. The abbey buildings were confiscated at the time of the French Revolution and were subsequently occupied by the Town Hall of Rouen.
Architecture
The church is 137 m in length under 33 m high vaults. The central crossing is surmounted by an unusual lantern-style tower similar to that atEly Cathedral
Ely Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of the Holy and Undivided Trinity of Ely, is an Church of England, Anglican cathedral in the city of Ely, Cambridgeshire, England.
The cathedral can trace its origin to the abbey founded in Ely in 67 ...
in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
. The tower was completed in the Flamboyant
Flamboyant () is a lavishly-decorated style of Gothic architecture that appeared in France and Spain in the 15th century, and lasted until the mid-sixteenth century and the beginning of the Renaissance.Encyclopedia Britannica, "Flamboyant style ...
style.
The well-preserved stained glass
Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material or art and architectural works created from it. Although it is traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensio ...
of the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
dates to the 15th and 16th centuries, and features jewel tones among panels of clear and frosted white glass. These materials allow more light to filter into the nave, creating a brighter interior than is typical of Gothic churches. Despite the use of Flamboyant tracery in the aisle
An aisle is a linear space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, in buildings such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, parliaments, courtrooms, ...
s, triforium
A triforium is an interior Gallery (theatre), gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, o ...
, and clerestory
A clerestory ( ; , also clearstory, clearstorey, or overstorey; from Old French ''cler estor'') is a high section of wall that contains windows above eye-level. Its purpose is to admit light, fresh air, or both.
Historically, a ''clerestory' ...
, the nave maintains a conservative appearance through the use of compound pier
Compound pier or cluster pier is the architectural term given to a clustered column or pier which consists of a centre mass or newel, to which engaged or semi-detached shafts have been attached, in order to perform (or to suggest the performance o ...
s, trumpet bases, and capitals
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
which helps maintain harmony throughout the edifice.
The west façade was never completed during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. The present structure was constructed between 1846 and 1851 in a Neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half of the 19th century ...
style that bears little resemblance to the original Late Gothic designs.
Organ
The church contains a large four- manualpipe organ
The pipe organ is a musical instrument that produces sound by driving pressurised air (called ''wind'') through the organ pipes selected from a Musical keyboard, keyboard. Because each pipe produces a single tone and pitch, the pipes are provide ...
built in 1890 by Aristide Cavaillé-Coll
Aristide Cavaillé-Coll (; 4 February 1811 – 13 October 1899) was a French organ builder. He has the reputation of being the most distinguished organ builder of the 19th century. He pioneered innovations in the art and science of organ build ...
. This instrument is considered to be one of the most important organs in France, and is notable for its powerful 32' Contre-bombarde. The organ stands unaltered and thus is one of the few of his works to speak with its original voice.
* Couplers: Tirasse G.O., Tirasse Pos., Tirasse Réc., Appel G.O., Pos./G.O., Réc./G.O., Bomb./G.O., Pos./Réc., Bomb./Réc., Oct. gr. G.O., Oct. gr. Réc./G.O., Oct. gr. Réc., Oct. aiguë Réc., Anches Péd., Anches G.O., Anches Pos., Anches Réc., Anches Bomb., Trémolo Réc., Expression Réc.
Notes
Bibliography
* Davis, Michael T. and Linda Elaine Neagley. "Mechanics and Meaning in the Plan Designs of Saint-Urbain, Troyes and Saint-Ouen, Rouen," ''Gesta'' 39 (2000): 161-182. https://www.jstor.org/stable/767144External links
Gallery of St. Ouen de Rouen
in
Flickr
Flickr ( ) is an image hosting service, image and Online video platform, video hosting service, as well as an online community, founded in Canada and headquartered in the United States. It was created by Ludicorp in 2004 and was previously a co ...
Description of the church and organ
{{DEFAULTSORT:Church of Saint Ouen, Rouen 15th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in France Roman Catholic churches completed in 1851 Benedictine monasteries in France Gothic architecture in France Roman Catholic churches in Rouen 19th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in France