Sacsayhuamán on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sacsayhuamán ( ; ) or Saksaywaman (from Quechua , , ) is a
 Vince Lee is an author, architect and explorer who has been consulted on various ancient sites that moved large megaliths. He theorized that the blocks were put into place by carving them first and then lowering them into place. This would have involved doing precise carving ahead of time to create the tight joints that are made to fit into prepared pockets existing in the wall. Then they would be towed up a ramp and above the wall where they would be placed on top of a stack of logs. Then the logs would be removed 1 at a time to lower the stones into place carefully. An experiment was done to see if this would work on a small scale; this accomplished limited success. In the event that they were unable to obtain the tight joints the first time the Incas would also have been able to lift the stones back up to correct their mistakes. They were not able to obtain as much precision as the Incas but they theorized that with more practice they could have accomplished more precise joints and done it with larger stones.
They also did several experiments in nearby Ollantaytambo to tow megalithic stones. This also led to limited success. They conducted one experiment where they tried to lower a 1 ton stone down a mountain. They lost control of this stone and it rolled down on its own. This is probably not the way the Incas did it since they would have wanted to control the transportation and this could have led to a lot of accidents. They concluded that although they had gravity on their side they had to practice to maintain control of the descent. They also did an experiment towing a megalith that may have been close to 10 tons on cobblestones. They had about 12 people behind the megalith pushing it while well over 100 people were pulling on several ropes to tow it. They succeeded in towing it at a fairly quick pace. The ancient Incas built a large road system that included 25,000 km of roads. Some of these roads were embellished with stone pavings. Additional experiments were done at other locations to move large megaliths some of which are listed here; these experiments were not adequate to replicate the successful efforts Pedro Cieza de León claimed to witness in the 16th century, and the largest megaliths currently there were more than twice his estimates of the largest
megaliths in his time.
Vince Lee is an author, architect and explorer who has been consulted on various ancient sites that moved large megaliths. He theorized that the blocks were put into place by carving them first and then lowering them into place. This would have involved doing precise carving ahead of time to create the tight joints that are made to fit into prepared pockets existing in the wall. Then they would be towed up a ramp and above the wall where they would be placed on top of a stack of logs. Then the logs would be removed 1 at a time to lower the stones into place carefully. An experiment was done to see if this would work on a small scale; this accomplished limited success. In the event that they were unable to obtain the tight joints the first time the Incas would also have been able to lift the stones back up to correct their mistakes. They were not able to obtain as much precision as the Incas but they theorized that with more practice they could have accomplished more precise joints and done it with larger stones.
They also did several experiments in nearby Ollantaytambo to tow megalithic stones. This also led to limited success. They conducted one experiment where they tried to lower a 1 ton stone down a mountain. They lost control of this stone and it rolled down on its own. This is probably not the way the Incas did it since they would have wanted to control the transportation and this could have led to a lot of accidents. They concluded that although they had gravity on their side they had to practice to maintain control of the descent. They also did an experiment towing a megalith that may have been close to 10 tons on cobblestones. They had about 12 people behind the megalith pushing it while well over 100 people were pulling on several ropes to tow it. They succeeded in towing it at a fairly quick pace. The ancient Incas built a large road system that included 25,000 km of roads. Some of these roads were embellished with stone pavings. Additional experiments were done at other locations to move large megaliths some of which are listed here; these experiments were not adequate to replicate the successful efforts Pedro Cieza de León claimed to witness in the 16th century, and the largest megaliths currently there were more than twice his estimates of the largest
megaliths in his time.
mincetur.gob.pe
"Fiesta del Warachikuy" (in Spanish), accessed 26 February 2014 Some people from Cusco use the large field within the walls of the complex for jogging,
File:Sacsayhuamán in 1877 by Ephraim George Squier.jpg, Sacsayhuamán in 1877 by
New Discoveries at Sacsayhuamán
*World's Greatest Riddle
Mystery of Sacsayhuamán
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sacsayhuamán Lost ancient cities and towns Buildings and structures in Cusco Ruins in Peru Inca Esoteric anthropogenesis Archaeological sites in Peru Archaeological sites in the Department of Cusco Tourist attractions in the Department of Cusco Forts in Peru Polygonal masonry
citadel
A citadel is the most fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of ''city'', meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
...
on the northern outskirts of the city of Cusco
Cusco or Cuzco (; or , ) is a city in southeastern Peru, near the Sacred Valley of the Andes mountain range and the Huatanay river. It is the capital of the eponymous Cusco Province, province and Cusco Region, department.
The city was the cap ...
, Peru, the historic capital of the Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
. The site is at an altitude of .
The complex was built by the Incas in the 15th century, particularly under Sapa Inca Pachacuti
Pachacuti Inca Yupanqui, also called Pachacútec (), was the ninth Sapa Inca of the Chiefdom of Cusco, which he transformed into the Inca Empire (). Most archaeologists now believe that the famous Inca site of Machu Picchu was built as an ...
and his successors. Dry stone
Dry stone, sometimes called drystack or, in Scotland, drystane, is a building method by which structures are constructed from stones without any mortar to bind them together. A certain amount of binding is obtained through the use of carefully ...
walls constructed of huge stones were built on the site, with the workers carefully cutting the boulders to fit them together tightly.
In 1983, Cusco and Sacsayhuamán together were designated as sites on the UNESCO World Heritage List
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
, for international recognition and protection. The archeological site is now a tourist destination.
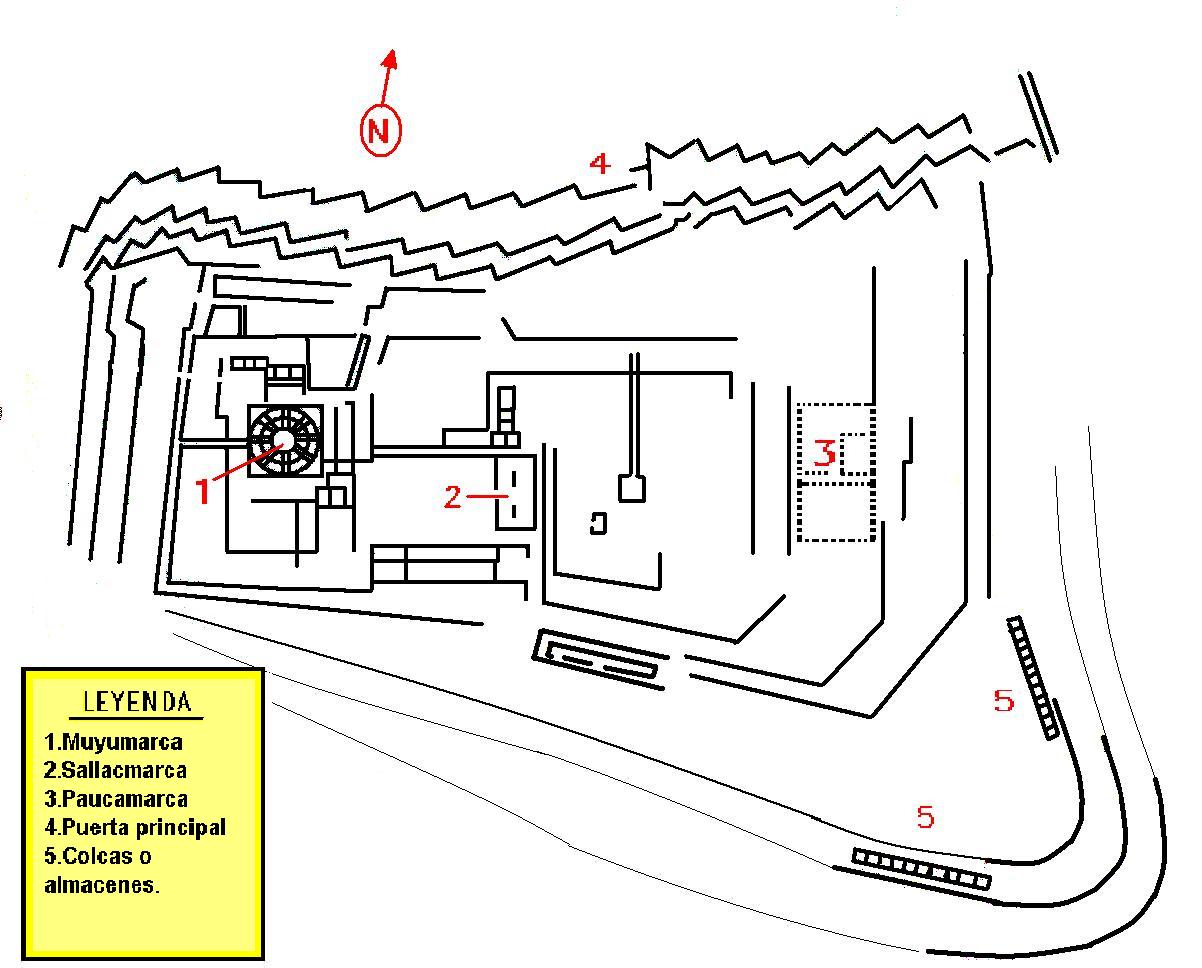
Description
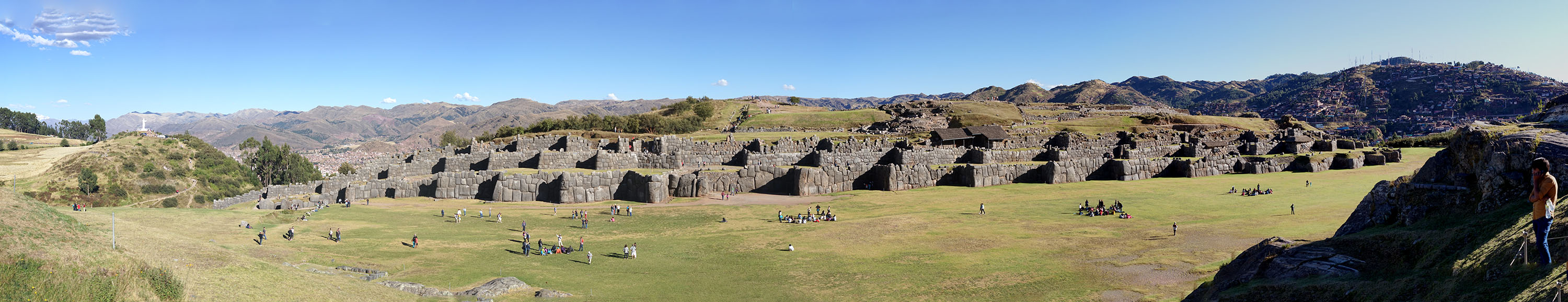
Located on a steep hill that overlooks the city, the fortified complex has a wide view of the valley to the southeast. Archeological studies of surface collections of pottery at Sacsayhuamán indicate that the earliest occupation of the hilltop dates to about 900 CE. According to Inca oral history, Tupac Inca"remembered that his fatherThe Inca decided the "best head would be to make a fortress on a high plateau to the north of the city."de Gamboa, P.S., (2015), ''History of the Incas'', Lexington, During the 15th century, the Imperial Inca expanded on this settlement, building dry stone walls constructed of huge stones. Spanish Chronicler Pedro Cieza de León wrote in 1553:Pachacuti Pachacuti Inca Yupanqui, also called Pachacútec (), was the ninth Sapa Inca of the Chiefdom of Cusco, which he transformed into the Inca Empire (). Most archaeologists now believe that the famous Inca site of Machu Picchu was built as an ...had called city of Cuzco the lion city. He said that the tail was where the two rivers unite which flow through it, that the body was the great square and the houses round it, and that the head was wanting."
The Inca ordered that the provinces should provide 20,000 men and that the villages should send the necessary provisions. If any fell sick, another labourer was to supply his place, and he was to return to his home. But these Indians were not kept constantly at a work in progress. They laboured for a limited time, and were then relieved by others, so that they did not feel the demand on their services. There were 4,000 labourers whose duty it was to quarry and get out the stones; 6,000 conveyed them by means of great cables of leather and of cabuya 02to the works. The rest opened the ground and prepared the foundations, some being told off to cut the posts and beams for the wood-work. For their greater convenience, these labourers made their dwelling-huts, each lineage apart, near the place where the works were progressing. To this day most of the walls of these lodgings may be seen. Overseers were stationed to superintend, and there were great masters of the art of building who had been well instructed. Thus on the highest part of a hill to the north of the city, and little more than an arquebus-shot from it, this fortress was built which the natives called the House of the Sun, but which we named the Fortress. The living rock was excavated for the foundation, which was prepared with such solidity that it will endure as long as the world itself. The work had, according to my estimate, a length of 330 paces, 03and a width of 200. Its walls were so strong that there is no artillery which could breach them. The principal entrance was a thing worthy of contemplation, to see how well it was built, and how the walls were arranged so that one commanded the other. And in these walls there were stones so large and mighty that it tired the judgment to conceive how they could have been conveyed and placed, and who could have had sufficient power to shape them, seeing that among these people there are so few tools. Some of these stones are of a width of twelve feet and more than twenty long, others are thicker than a bullock. 04All the stones are laid and joined with such delicacy that a rial could not be put in between two of them. I went to see this edifice twice. On one occasion I was accompanied by Tomas Vasquez, 05a conqueror, and on the other I found Hernando de Guzman there, he who was present at the siege, 06and Juan de la Haya. 07Those who read this should believe that I relate nothing that I did not see. As I walked about, observing what was to be seen, I beheld, near the fortress, a stone which measured 260 of my palmos in circuit, and so high that it looked as if it was in its original position. All the Indians say that the stone got tired at this point, and that they were unable to move it further. 08Assuredly if I had not myself seen that the stone had been hewn and shaped I should not have believed, however much it might have been asserted, that the force of man would have sufficed to bring it to where it now is. There it remains, as a testimony of what manner of men those were who conceived so good a work. The Spaniards have so pillaged and ruined it, that I should be sorry to have been guilty of the fault of those in power who have permitted so magnificent a work to be so ruined. They have not considered the time to come, for it would have been better to have preserved the edifice and to have put a guard over it. 09 There were many buildings within the fortress, some small, one over the other, and others, which were large, were underground. They made two blocks of buildings, one larger than the other, wide and so well-built, that I know not how I can exaggerate the art with which the stones are laid and worked; and they say that the subterranean edifices are even better. Other things were told me, which I do not repeat, because I am not certain of their accuracy. This fortress was commenced in the time of Ynca Yupanqui. His son, Tupac Inca, as well as Huayna Ccapac and Huascar, worked much at it, and although it is still worthy of admiration, it was formerly without comparison grander. When the Spaniards entered Cuzco, the Indians of Quizquiz had already collected great treasure; but some was still found, and it is believed that there is a great quantity in the vicinity. It would be well to give orders for the preservation of what is left of this fortress, and of that of Huarcu, 10as memorials of the grandeur of this people, and even for utility, as they could be made serviceable at so little cost.After ambushing Atahualpa during the Spanish Conquest of Peru,
Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro, Marquess of the Atabillos (; ; – 26 June 1541) was a Spanish ''conquistador'', best known for his expeditions that led to the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire.
Born in Trujillo, Cáceres, Trujillo, Spain, to a poor fam ...
sent Martin Bueno and two other Spaniards to help transport gold and silver from the Temple of Coricancha in Cusco to Cajamarca, where the Spaniards were based.Leon, P., 1998, ''The Discovery and Conquest of Peru, Chronicles of the New World Encounter,'' edited and translated by Cook and Cook, Durham: Duke University Press, They found the Temple of the Sun "covered with plates of gold", which the Spanish supposedly ordered removed as payment for Atahualpa
Atahualpa (), also Atawallpa or Ataw Wallpa ( Quechua) ( 150226 July 1533), was the last effective Inca emperor, reigning from April 1532 until his capture and execution in July of the following year, as part of the Spanish conquest of the In ...
's ransom
Ransom refers to the practice of holding a prisoner or item to extort money or property to secure their release. It also refers to the sum of money paid by the other party to secure a captive's freedom.
When ransom means "payment", the word ...
. Seven hundred plates were removed, and added to two hundred ''cargas'' of gold transported back to Cajamarca.
After Francisco Pizarro finally entered Cuzco, Pedro Pizarro described what they found,
"on top of a hill they he Incahad a very strong fort surrounded with masonry walls of stones and having two very high round towers. And in the lower part of this wall there were stones so large and thick that it seemed impossible that human hands could have set them in place...they were so close together, and so well fitted, that the point of a pin could not have been inserted in one of the joints. The whole fortress was built up in terraces and flat spaces." The numerous rooms were "filled with arms, lances, arrows, darts, clubs,The large plaza, capable of holding thousands of people, was designed for communal ceremonial activities. Several of the large structures at the site may also have been used during rituals. A similar relationship to that between Cuzco and Sacsayhuamán was replicated by the Inca in their distant colony wherebuckler A buckler (French ''bouclier'' 'shield', from Old French ''bocle, boucle'' ' boss') is a small shield, up to 45 cm (up to 18 in) in diameter, gripped in the fist with a central handle behind the boss. It became more common as a companio ...s and large oblong shields...there were many morions...there were also...certain stretchers in which the Lords travelled, as in litters."Pizzaro, P., 1571, ''Relation of the Discovery and Conquest of the Kingdoms of Peru,'' Vol. 1–2, New York: Cortes Society, RareBooksClub.com, Pedro Pizarro described in detail storage rooms that were within the complex and filled with military equipment.
Santiago, Chile
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile (), is the capital and largest city of Chile and one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is located in the country's central valley and is the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Regi ...
developed. The Inca fortress there, known as Chena, predated the Spanish colonial city. It was a ceremonial ritual site known as Huaca de Chena.
The best-known zone of Sacsayhuamán includes its great plaza and its adjacent three massive terrace walls. The stones used in the construction of these terraces are among the largest used in any building in pre-Hispanic America. They display a precision of cutting and fitting that is unmatched in the Americas. The stones are so closely spaced that a single piece of paper will not fit between many of the stones. This precision, combined with the rounded corners of the blocks, the variety of their interlocking shapes, and the way the walls lean inward, is thought to have helped the ruins survive devastating earthquakes
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they c ...
in Cuzco. The longest of the three walls is about 400 meters. They are about 6 meters tall. The estimated volume of stone is over 6,000 cubic meters. Estimates for the weight of the largest Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
block vary from 128 tonnes to almost 200 tonnes. These stones were moved an estimated 35 km (22 miles) from Rumicolca.
Following the siege of Cusco, the Spaniards began to use Sacsayhuamán as a source of stones for building Spanish Cuzco; within a few years, they had taken apart and demolished much of the complex. The site was destroyed block by block to salvage materials with which to build the new Spanish governmental and religious buildings of the colonial city, as well as the houses of the wealthiest Spaniards. In the words of Garcilaso de la Vega (1966:471 609: Part 1, Book. Bk. 7, Ch. 29:
"to save themselves the expense, effort and delay with which the Indians worked the stone, they pulled down all the smooth masonry in the walls. There is indeed not a house in the city that has not been made of this stone, or at least the houses built by the Spaniards."Today, only the stones that were too large to be easily moved remain at the site. On 13 March 2008, archaeologists discovered additional ruins at the periphery of Sacsayhuamán. It has been theorized that the site was first built upon during the Killke period, which preceded the Inca. While appearing ceremonial in nature, the exact function remains unknown. In January 2010, parts of the site were damaged during periods of heavy rainfall in the region. Today's (2025) concrete or cement paving can have patterns made by prefabricated moulds. The moulding in Incan walls is similar.

Theories about constructing the megalithic walls
 Vince Lee is an author, architect and explorer who has been consulted on various ancient sites that moved large megaliths. He theorized that the blocks were put into place by carving them first and then lowering them into place. This would have involved doing precise carving ahead of time to create the tight joints that are made to fit into prepared pockets existing in the wall. Then they would be towed up a ramp and above the wall where they would be placed on top of a stack of logs. Then the logs would be removed 1 at a time to lower the stones into place carefully. An experiment was done to see if this would work on a small scale; this accomplished limited success. In the event that they were unable to obtain the tight joints the first time the Incas would also have been able to lift the stones back up to correct their mistakes. They were not able to obtain as much precision as the Incas but they theorized that with more practice they could have accomplished more precise joints and done it with larger stones.
They also did several experiments in nearby Ollantaytambo to tow megalithic stones. This also led to limited success. They conducted one experiment where they tried to lower a 1 ton stone down a mountain. They lost control of this stone and it rolled down on its own. This is probably not the way the Incas did it since they would have wanted to control the transportation and this could have led to a lot of accidents. They concluded that although they had gravity on their side they had to practice to maintain control of the descent. They also did an experiment towing a megalith that may have been close to 10 tons on cobblestones. They had about 12 people behind the megalith pushing it while well over 100 people were pulling on several ropes to tow it. They succeeded in towing it at a fairly quick pace. The ancient Incas built a large road system that included 25,000 km of roads. Some of these roads were embellished with stone pavings. Additional experiments were done at other locations to move large megaliths some of which are listed here; these experiments were not adequate to replicate the successful efforts Pedro Cieza de León claimed to witness in the 16th century, and the largest megaliths currently there were more than twice his estimates of the largest
megaliths in his time.
Vince Lee is an author, architect and explorer who has been consulted on various ancient sites that moved large megaliths. He theorized that the blocks were put into place by carving them first and then lowering them into place. This would have involved doing precise carving ahead of time to create the tight joints that are made to fit into prepared pockets existing in the wall. Then they would be towed up a ramp and above the wall where they would be placed on top of a stack of logs. Then the logs would be removed 1 at a time to lower the stones into place carefully. An experiment was done to see if this would work on a small scale; this accomplished limited success. In the event that they were unable to obtain the tight joints the first time the Incas would also have been able to lift the stones back up to correct their mistakes. They were not able to obtain as much precision as the Incas but they theorized that with more practice they could have accomplished more precise joints and done it with larger stones.
They also did several experiments in nearby Ollantaytambo to tow megalithic stones. This also led to limited success. They conducted one experiment where they tried to lower a 1 ton stone down a mountain. They lost control of this stone and it rolled down on its own. This is probably not the way the Incas did it since they would have wanted to control the transportation and this could have led to a lot of accidents. They concluded that although they had gravity on their side they had to practice to maintain control of the descent. They also did an experiment towing a megalith that may have been close to 10 tons on cobblestones. They had about 12 people behind the megalith pushing it while well over 100 people were pulling on several ropes to tow it. They succeeded in towing it at a fairly quick pace. The ancient Incas built a large road system that included 25,000 km of roads. Some of these roads were embellished with stone pavings. Additional experiments were done at other locations to move large megaliths some of which are listed here; these experiments were not adequate to replicate the successful efforts Pedro Cieza de León claimed to witness in the 16th century, and the largest megaliths currently there were more than twice his estimates of the largest
megaliths in his time.
Modern-day use
Peruvians continue to celebrate ''Inti Raymi
The Inti Raymi (Quechua language, Quechua for "Inti festival") is a traditional religious ceremony of the Inca Empire in honor of the god Inti (Quechua for "sun"), the most venerated deity in Religion in the Inca Empire, Inca religion. It was t ...
'', the annual Inca festival of the winter solstice
The winter solstice, or hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's geographical pole, poles reaches its maximum axial tilt, tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern Hemisphere, Northern and So ...
and new year. It is held near Sacsayhuamán on 24 June. Another important festival is '' Warachikuy,'' held there annually on the third Sunday of September."Fiesta del Warachikuy" (in Spanish), accessed 26 February 2014 Some people from Cusco use the large field within the walls of the complex for jogging,
tai chi
is a Chinese martial art. Initially developed for combat and self-defense, for most practitioners it has evolved into a sport and form of exercise. As an exercise, tai chi is performed as gentle, low-impact movement in which practitioners ...
, and other athletic activities.
Ephraim George Squier
Ephraim George Squier (June 17, 1821 – April 17, 1888), usually cited as E. G. Squier, was an American archaeologist, history writer, painter and newspaper editor.
Biography
Squier was born in Bethlehem, New York, the son of a minister, Joel S ...
.
File:Sacsayhuamán 2 in 1877 by Ephraim George Squier.jpg, Sacsayhuamán in 1877 by Ephraim George Squier
Ephraim George Squier (June 17, 1821 – April 17, 1888), usually cited as E. G. Squier, was an American archaeologist, history writer, painter and newspaper editor.
Biography
Squier was born in Bethlehem, New York, the son of a minister, Joel S ...
.
See also
*List of megalithic sites
This is a list of monoliths organized according to the size of the largest block of stone on the site. A monolith is a large stone which has been used to build a structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. In this list at l ...
* Huaca de Chena
References
External links
*BBC ArticlNew Discoveries at Sacsayhuamán
*World's Greatest Riddle
Mystery of Sacsayhuamán
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sacsayhuamán Lost ancient cities and towns Buildings and structures in Cusco Ruins in Peru Inca Esoteric anthropogenesis Archaeological sites in Peru Archaeological sites in the Department of Cusco Tourist attractions in the Department of Cusco Forts in Peru Polygonal masonry