SMS Freya on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
SMS was a
 was
was
 On 1 August 1910, departed for her next major voyage overseas; unlike previous years that included numerous stops while on the way, the ship steamed directly to Mexico with a special envoy aboard. There, she met the
On 1 August 1910, departed for her next major voyage overseas; unlike previous years that included numerous stops while on the way, the ship steamed directly to Mexico with a special envoy aboard. There, she met the
protected cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers re ...
of the , built for the German Imperial Navy () in the 1890s, along with her sister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They often share a ...
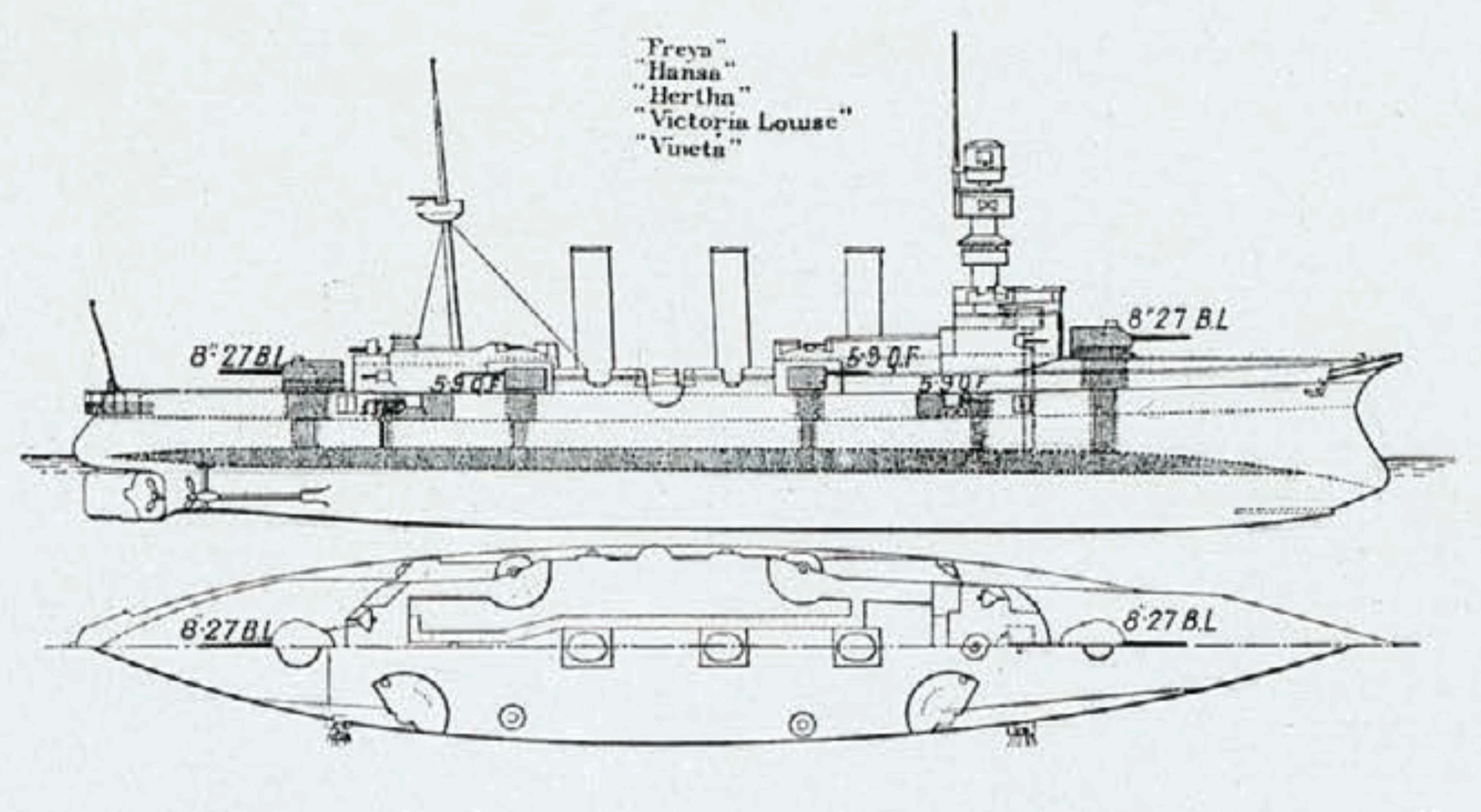
s , , , and . was laid down at the Imperial Dockyard in Danzig in 1895, launched in April 1897, and commissioned into the Navy in October 1898. The ship was armed with a battery of two 21 cm guns and eight 15 cm guns and had a top speed of .
served in the German fleet for the initial years of her career, unlike her sister ships, all of which served abroad on foreign stations. As a result, she led a fairly uneventful career in the fleet. After a modernization in 1905–1907, was used as a school ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house classr ...
for cadets. At the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, was mobilized into V Scouting Group, but served in front-line duty only briefly. She was used as a barracks ship
A barracks ship or barracks barge or berthing barge, or in civilian use accommodation vessel or accommodation ship, is a ship or a non-self-propelled barge containing a superstructure of a type suitable for use as a temporary barracks for sai ...
after 1915, and ultimately sold for scrapping in 1921.
Design
In the early 1890s, elements in the German naval command structure grappled with what type of cruiser ought to be built to fulfill the various needs of the fleet. The (RMA—Imperial Navy Office) preferred to build a combination of large cruisers of around along the lines of and significantly smaller vessels of about to support them, while the (Naval High Command) argued that a uniform force of cruisers was preferable. In the event, the RMA carried the day and three 6,000-ton cruisers were authorized in 1895. They resembled the larger s, designed at the same time, albeit at reduced scale. was
was long overall
__NOTOC__
Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, an ...
and had a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of and a draft
Draft, The Draft, or Draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a vessel ...
of forward. As designed, she displaced , and at full load
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into wei ...
, her displacement rose to . Her propulsion system consisted of three vertical 4-cylinder triple-expansion steam engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages.
A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up he ...
s, each driving a single screw propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
, with steam provided by twelve coal-fired Niclausse boiler
A Field-tube boiler (also known as a bayonet tube)
is a form of water-tube boiler where the water tubes are single-ended. The tubes are closed at one end, and they contain a concentric inner tube. Flow is thus separated into the colder inner flow ...
s. Her engines were rated for , and provided a top speed of . The ship had a range of approximately at . She had a crew of 31 officers and 446 enlisted men.
The ship was armed with a main battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a gun or group of guns, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted ...
of two SK L/40 guns in single gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechani ...
s, one forward and one aft. The guns were supplied with 58 rounds of ammunition each. They had a range of . also carried a secondary battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prima ...
of eight SK L/40 guns. Four were mounted in turrets amidships and the other four were placed in casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, th ...
s, two abreast the conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
and the others abreast the mainmast
The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the centre-line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, and giving necessary height to a navigation ligh ...
. These guns had a range of . She also carried ten SK L/35 guns for defense against torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of se ...
s. The gun armament was rounded out by ten Maxim machine cannon. She was also equipped with three torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s with eight torpedoes, two launchers were mounted on the broadside
Broadside or broadsides may refer to:
Naval
* Broadside (naval), terminology for the side of a ship, the battery of cannon on one side of a warship, or their near simultaneous fire on naval warfare
Printing and literature
* Broadside (comic ...
and the third was in the bow, all below the waterline.
In 1916, all of the ships of the class were disarmed, with the exception of , which was re-equipped with a single 15 cm gun, four 10.5 cm SK L/45 guns, and fourteen 8.8 cm guns of both the L/30 and L/35 versions, for use as a gunnery training ship.
The ship was protected with Krupp armor
Krupp armour was a type of steel naval armour used in the construction of capital ships starting shortly before the end of the nineteenth century. It was developed by Germany's Krupp Arms Works in 1893 and quickly replaced Harvey armour as the p ...
; their deck was on the horizontal with sloped sides that were thick. Her main and secondary battery turrets had 10 cm thick sides and the secondary casemates had the same level of protection. The conning tower had 15 cm thick sides.
Service history
Construction and fleet service
was ordered under the contract name " " and waslaid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
at the (Imperial Shipyard) in Danzig on 2 January 1896. She was launched on 27 April 1897; Prince Heinrich of Prussia
A prince is a Monarch, male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary title, hereditary, in s ...
gave a speech at the ceremony and Queen Charlotte
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and of Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until the union of the two kingdoms ...
christened the ship. After completing fitting-out
Fitting out, or outfitting, is the process in shipbuilding that follows the float-out/launching of a vessel and precedes sea trials. It is the period when all the remaining construction of the ship is completed and readied for delivery to her o ...
work, she began builder's sea trials
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a "shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and i ...
, which revealed significant problems with her boilers, prompting the navy to issue a formal complaint to the manufacturer, Friedrich Krupp Germaniawerft Friedrich may refer to:
Names
*Friedrich (surname), people with the surname ''Friedrich''
*Friedrich (given name), people with the given name ''Friedrich''
Other
*Friedrich (board game), a board game about Frederick the Great and the Seven Years' ...
, which was forced to provide replacements. Additional problems led the navy to turn to the British Thornycroft boiler
Three-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, a ...
, which the design staff of the ''RMA'' developed further, leading to what would become the Marine-type boiler. These would be used on most German warships thereafter. was commissioned on 20 October 1898 for additional sea trials, conducted by the navy. During this period, she was officially assigned to II Division of I Battle Squadron
The I Battle Squadron was a unit of the German Imperial Navy before and during World War I. Being part of the High Seas Fleet, the squadron saw action throughout the war, including the Battle of Jutland on 31 May – 1 June 1916, where it for ...
, replacing the old ironclad warship
An ironclad is a steam-propelled warship protected by iron or steel armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. T ...
, though she was not yet ready for active service. In March 1899, was lightly damaged in a collision with a vessel under construction for the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, after the latter vessel broke free from her moorings. The ship's first commander, (''KzS''—Captain at Sea) Hugo Westphal, arrived aboard the ship in October 1900. occasionally took part in training exercises with other elements of the fleet through mid-1901, though she remained on trials until 8 June, when she was decommissioned.
In the interest of developing the capabilities of the fleet's gunners, the navy established the Artillery Testing Command on 14 December 1901, and on 3 May 1902, was recommissioned to join the new establishment. (Frigate Captain) Hermann Jacobsen took command of the vessel at that time. She began training activities on 15 May, based in Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the J ...
. Later that year, she was allocated to the training fleet for use as a scout for the annual large-scale maneuvers held every August and September. During the exercises, suffered damage to her boilers that necessitated repairs that were completed on 15 September. She thereafter resumed her gunnery training duties, along with her tender, the old armored gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.
History Pre-steam ...
. The two vessels accidentally collided on 13 November but suffered no significant damage. The year 1903 passed much the same as the previous one, with gunnery training interrupted only by the fleet maneuvers in August and September. On 11 January 1904, was again decommissioned in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsha ...
.
Cadet training ship
By this time, the naval command had decided to convert the -class ships into dedicatedtraining ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house classr ...
s for naval cadets and apprentice seamen, as they were no longer suitable for front-line service. They would replace the old screw corvette
Steam frigates (including screw frigates) and the smaller steam corvettes, steam sloops, steam gunboats and steam schooners, were steam-powered warships that were not meant to stand in the line of battle. There were some exceptions like for exam ...
s that had been in use for that purpose for some time and were by then badly worn out. In 1905, went into drydock at the in Wilhelmshaven for modernization. During the refit she was re-boilered; unlike her sister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They often share a ...
s, which had their original three funnels reduced to two, kept her original funnels. The refit was finished in early 1907, and she was recommissioned on 4 April, now under the command of ''KzS'' Franz von Holleben Franz may refer to:
People
* Franz (given name)
* Franz (surname)
Places
* Franz (crater), a lunar crater
* Franz, Ontario, a railway junction and unorganized town in Canada
* Franz Lake, in the state of Washington, United States – see ...
. She completed a short trials period, operating from Wilhelmshaven and then Kiel, before embarking her first class of trainees in early May. then went on a short cruise in the western Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
before participating in the Kiel Week
The Kiel Week (german: Kieler Woche) or Kiel Regatta is an annual sailing event in Kiel, the capital of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the largest sailing event in Europe, and also one of the largest Volksfeste in Germany, attracting ...
regatta
Boat racing is a sport in which boats, or other types of watercraft, race on water. Boat racing powered by oars is recorded as having occurred in ancient Egypt, and it is likely that people have engaged in races involving boats and other wate ...
.
next embarked on a major training cruise on 19 July that included visits to Norway, various ports on the Atlantic coast of Europe, and the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
before entering the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. There, visited a number of cities, including Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, Italy, Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
in the Ottoman Empire, and Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
in the Khedivate of Egypt
The Khedivate of Egypt ( or , ; ota, خدیویت مصر ') was an autonomous tributary state of the Ottoman Empire, established and ruled by the Muhammad Ali Dynasty following the defeat and expulsion of Napoleon Bonaparte's forces which brou ...
. The ship arrived back in Kiel on 18 March 1908. After embarking a new contingent of cadets and a new captain, ''KzS'' Leberecht Maass
Leberecht Maass (or Maaß) (24 November 1863 – 28 August 1914) was the ''Konteradmiral'' who commanded the German naval forces at the first Battle of Heligoland Bight. He lost his life when his flagship, the light cruiser , was sunk by ...
in April, began the next training cruise, which started with maneuvers off Apenrade and in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
, before crossing the Atlantic to visit North America. In August, represented Germany at celebrations in Halifax, Canada, commemorating the 150th anniversary of the opening of the Canadian Parliament. While entering the port at around midnight on 9 August, she inadvertently rammed a schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoon ...
in heavy fog. Nine sailors were killed in the accident. thereafter steamed south to visit ports in the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
. She arrived back in Kiel on 8 March 1909, where ''KzS'' Carl Schaumann relieved Maass.
s third major cruise began on 2 June 1909, first with a visit to Norway, followed by a short return to Cuxhaven
Cuxhaven (; ) is an independent town and seat of the Cuxhaven district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town includes the northernmost point of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the shore of the North Sea at the mouth of the Elbe River. Cuxhaven has ...
and then Wilhelmshaven, to make preparations to go abroad. From Wilhelmshaven, she got underway for the Mediterranean, stopping in Funchal
Funchal () is the largest city, the municipal seat and the capital of Portugal's Madeira, Autonomous Region of Madeira, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean. The city has a population of 105,795, making it the sixth largest city in Portugal. Because of ...
in Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
and Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitants as of Janu ...
in the Canaries on the way. She steamed as far as the eastern Mediterranean, visiting Alexandria again, where she rendered assistance after a major fire in the city, along with ports in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
. arrived back in Wilhelmshaven on 28 March 1910, where she went into dry dock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
for an overhaul that lasted until 2 May. She then moved to Kiel, where she took on another crew of cadets for a short training cruise to Norwegian waters that ended in Wilhelmshaven on 20 July.
 On 1 August 1910, departed for her next major voyage overseas; unlike previous years that included numerous stops while on the way, the ship steamed directly to Mexico with a special envoy aboard. There, she met the
On 1 August 1910, departed for her next major voyage overseas; unlike previous years that included numerous stops while on the way, the ship steamed directly to Mexico with a special envoy aboard. There, she met the light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to thi ...
, which was cruising off the coast of South America. The two ships represented Germany at celebrations marking the 100th anniversary of Mexico's independence from Spain. disembarked the envoy in Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, Mexico, on 3 September; he went on to meet the President of Mexico
The president of Mexico ( es, link=no, Presidente de México), officially the president of the United Mexican States ( es, link=no, Presidente de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the head of state and head of government of Mexico. Under the Co ...
. On 16 September, the ship was present for the unveiling of a monument to Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, p ...
, a German explorer and geographer who had surveyed much of Mexico in 1803–1804. Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and List of monarchs of Prussia, King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until Abdication of Wilhelm II, his abdication on 9 ...
donated the monument to Mexico. got underway on 22 September for a cruise through the Caribbean before returning home, arriving in Kiel on 13 March 1911. She then proceeded to Danzig, where she was decommissioned on 28 March for another extensive modernization. This included replacing her troublesome Niclausse boilers with modern Marine-type boilers, and her third funnel was removed at this time. After completing the work in 1913, she was assigned to the reserve fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; a ...
, remaining out of commission.
World War I
Following the outbreak ofWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in July 1914, was mobilized
Mobilization is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the Prussian Army. Mobilization theories and ...
for active service, but she was initially only activated for use as a training ship for boiler room personnel. She was briefly commanded ''KzS'' Max Schlicht from 4 to 27 August, before being replaced by (Corvette Captain) Eduard Bartels. Following the reestablishment of the Training Inspectorate in April 1915, which had been closed at the start of the conflict, returned to her old training duties in the Baltic. At that time, she moved from Kiel to Flensburg
Flensburg (; Danish, Low Saxon: ''Flensborg''; North Frisian: ''Flansborj''; South Jutlandic: ''Flensborre'') is an independent town (''kreisfreie Stadt'') in the north of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. Flensburg is the centre of the ...
, where she remained through the end of the war. ''KzS'' Ernst-Oldwig von Natzmer took command of the vessel at that time, but he remained aboard only for four months, when he was replaced by ''KzS'' Wilhelm Goetze The old aviso
An ''aviso'' was originally a kind of dispatch boat or "advice boat", carrying orders before the development of effective remote communication.
The term, derived from the Portuguese and Spanish word for "advice", "notice" or "warning", an '' ...
became s tender starting in July. She was stricken on 25 January 1920 and used briefly as a barracks ship
A barracks ship or barracks barge or berthing barge, or in civilian use accommodation vessel or accommodation ship, is a ship or a non-self-propelled barge containing a superstructure of a type suitable for use as a temporary barracks for sai ...
for police in Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
. She was ultimately broken up for scrap in Harburg in 1921.
Notes
References
* * * * * *Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Freya Victoria Louise-class cruisers Ships built in Danzig 1897 ships World War I cruisers of Germany