SEALAB II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
SEALAB I, II, and III were experimental
 SEALAB I was commanded by Captain Bond, who became known as "Papa Topside". SEALAB I proved that saturation diving in the open ocean was viable for extended periods. The experiment also offered information about habitat placement, habitat umbilicals, humidity, and helium speech descrambling.
SEALAB I was lowered off the coast of
SEALAB I was commanded by Captain Bond, who became known as "Papa Topside". SEALAB I proved that saturation diving in the open ocean was viable for extended periods. The experiment also offered information about habitat placement, habitat umbilicals, humidity, and helium speech descrambling.
SEALAB I was lowered off the coast of
p. 173. A sidenote from SEALAB II was a congratulatory
 According to
According to
Office of Naval Research
Photos from the 2002 High Performance Wireless Research and Education Network expedition to the SEALAB II/III habitat.
(One screen shot o
current habitat
* * * {{Authority control United States Navy in the 20th century Underwater habitats Scott Carpenter
underwater habitat
Underwater habitats are underwater structures in which people can live for extended periods and carry out most of the basic human functions of a 24-hour day, such as working, resting, eating, attending to personal hygiene, and sleeping. In thi ...
s developed by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
in the 1960s to prove the viability of saturation diving
Saturation diving is diving for periods long enough to bring all tissues into equilibrium with the partial pressures of the inert components of the breathing gas used. It is a diving mode that reduces the number of decompressions divers working ...
and humans living in isolation for extended periods of time. The knowledge gained from the SEALAB expeditions helped advance the science of deep sea diving
Underwater diving, as a human activity, is the practice of descending below the water's surface to interact with the environment. It is also often referred to as diving, an ambiguous term with several possible meanings, depending on contex ...
and rescue, and contributed to the understanding of the psychological and physiological strains humans can endure.
United States Navy Genesis Project
Preliminary research work was undertaken byGeorge F. Bond
Captain George Foote Bond (November 14, 1915 – January 3, 1983) was a United States Navy physician who was known as a leader in the field of undersea and hyperbaric medicine and the "Father of Saturation Diving".
While serving as Officer-in- ...
. Bond began investigations in 1957 to develop theories about saturation diving
Saturation diving is diving for periods long enough to bring all tissues into equilibrium with the partial pressures of the inert components of the breathing gas used. It is a diving mode that reduces the number of decompressions divers working ...
. Bond's team exposed rats, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s, monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomple ...
s, and human beings to various gas mixtures at different pressures. By 1963 they had collected enough data to test the first SEALAB habitat.
SEALAB I
 SEALAB I was commanded by Captain Bond, who became known as "Papa Topside". SEALAB I proved that saturation diving in the open ocean was viable for extended periods. The experiment also offered information about habitat placement, habitat umbilicals, humidity, and helium speech descrambling.
SEALAB I was lowered off the coast of
SEALAB I was commanded by Captain Bond, who became known as "Papa Topside". SEALAB I proved that saturation diving in the open ocean was viable for extended periods. The experiment also offered information about habitat placement, habitat umbilicals, humidity, and helium speech descrambling.
SEALAB I was lowered off the coast of Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = " Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, e ...
on July 20, 1964 to a depth of below the ocean surface. It was constructed from two converted floats and held in place with axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearing ...
s from railroad car
A railroad car, railcar (American and Canadian English), railway wagon, railway carriage, railway truck, railwagon, railcarriage or railtruck (British English and UIC), also called a train car, train wagon, train carriage or train truck, is a ...
s. The experiment involved four divers (LCDR Robert Thompson Robert or Bob Thompson may refer to:
Entertainment
* Bobby Thompson (comedian) (1911–1988), English comedian
* Bob Thompson (musician) (1924–2013), American orchestra leader, arranger, composer
* Robert E. Thompson (screenwriter) (1924–2004 ...
, MC; Gunners Mate First Class Lester Anderson
Lester is an ancient Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon surname and given name. Notable people and characters with the name include:
People
Given name
* Lester Bangs (1948–1982), American music critic
* Lester W. Bentley (1908–1972), American arti ...
, Chief Quartermaster Robert A. Barth, and Chief Hospital Corpsman Sanders Manning), who were to stay submerged for three weeks. The experiment was halted after 11 days due to an approaching tropical storm
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
. SEALAB I demonstrated problems with high humidity, temperature control, and verbal communication in the helium atmosphere.
The astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally r ...
and second American to orbit the Earth, Scott Carpenter
Malcolm Scott Carpenter (May 1, 1925 – October 10, 2013) was an American naval officer and aviator, test pilot, aeronautical engineer, astronaut, and aquanaut. He was one of the Mercury Seven astronauts selected for NASA's Project Mercury ...
, was scheduled to be the fifth aquanaut in the habitat. Carpenter was trained by Robert A. Barth. Shortly before the experiment took place, Carpenter had a scooter accident on Bermuda and broke a few bones. The crash ruined his chances of making the dive.
SEALAB I is on display at the Museum of Man in the Sea, in Panama City Beach, Florida
Panama City Beach is a resort town in Bay County, Florida, Bay County, Florida, United States, on the Gulf of Mexico coast. As of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census it had a population of 12,018. The city is often referred to under the u ...
, near where it was initially tested offshore before being deployed. It is on outdoor display. Its metal hull is largely intact, though the paint faded to a brick red over the years. The habitat's exterior was restored as part of its 50th anniversary, and now sports its original colors.
SEALAB II
SEALAB II was launched in 1965. It was nearly twice as large as SEALAB I with heating coils installed in the deck to ward off the constant helium-induced chill, and air conditioning to reduce the oppressive humidity. Facilities included hot showers, a built-in toilet, laboratory equipment, eleven viewing ports, two exits, andrefrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, ht ...
. It was placed in the La Jolla Canyon
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figur ...
off the coast of Scripps Institution of Oceanography
The Scripps Institution of Oceanography (sometimes referred to as SIO, Scripps Oceanography, or Scripps) in San Diego, California, US founded in 1903, is one of the oldest and largest centers for oceanography, ocean and Earth science research ...
/UCSD, in La Jolla, California
La Jolla ( , ) is a hilly, seaside neighborhood within the city of San Diego, California, United States, occupying of curving coastline along the Pacific Ocean. The population reported in the 2010 census was 46,781.
La Jolla is surrounded on ...
, at a depth of . On August 28, 1965, the first of three teams of divers moved into what became known as the "Tilton Hilton" (Tiltin' Hilton, because of the slope of the landing site). The support ship ''Berkone'' hovered on the surface above, within sight of the Scripps pier. Helium diffused through glass ruining watches and electronic instruments. The helium atmosphere conducted heat away from the divers bodies so quickly temperatures were raised to to ward off chill.
Each team spent 15 days in the habitat, but aquanaut/former astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally r ...
Scott Carpenter
Malcolm Scott Carpenter (May 1, 1925 – October 10, 2013) was an American naval officer and aviator, test pilot, aeronautical engineer, astronaut, and aquanaut. He was one of the Mercury Seven astronauts selected for NASA's Project Mercury ...
remained below for a record 30 days. In addition to physiological testing, the 28 divers tested new tools, methods of salvage, and an electrically heated drysuit. They were aided by a bottlenose dolphin
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the common ...
named Tuffy from the United States Navy Marine Mammal Program
The U.S. Navy Marine Mammal Program (NMMP) is a program administered by the U.S. Navy which studies the military use of marine mammals - principally bottlenose dolphins and California sea lions - and trains animals to perform tasks such as ship an ...
. Aquanauts and Navy trainers attempted, with mixed results, to teach Tuffy to ferry supplies from the surface to SEALAB or from one diver to another, and to come to the rescue of an aquanaut in distress. When the SEALAB II mission ended on 10 October 1965, there were plans for Tuffy also to take part in SEALAB III.Hellwarthp. 173. A sidenote from SEALAB II was a congratulatory
telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
call that was arranged for Carpenter and President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
. Carpenter was calling from a decompression chamber
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of ...
with helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
gas replacing nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, so Carpenter sounded unintelligible to operators. The tape of the call circulated for years among Navy divers before it was aired on National Public Radio
National Public Radio (NPR, stylized in all lowercase) is an American privately and state funded nonprofit media organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It differs from other n ...
in 1999.
In 2002, a group of researchers from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography's High Performance Wireless Research and Education Network
The High Performance Wireless Research and Education Network (HPWREN) is a network research program, funded by the National Science Foundation. The program includes the creation, demonstration, and evaluation of a non-commercial, prototype, high-pe ...
boarded the and used a Scorpio ROV
The Scorpio (Submersible Craft for Ocean Repair, Position, Inspection and Observation) is a brand of underwater submersible Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) manufactured by Perry Tritech used by sub-sea industries such as the oil industry for gen ...
to find the site of the SEALAB habitat. This expedition was the first return to the site since the habitat was moved.
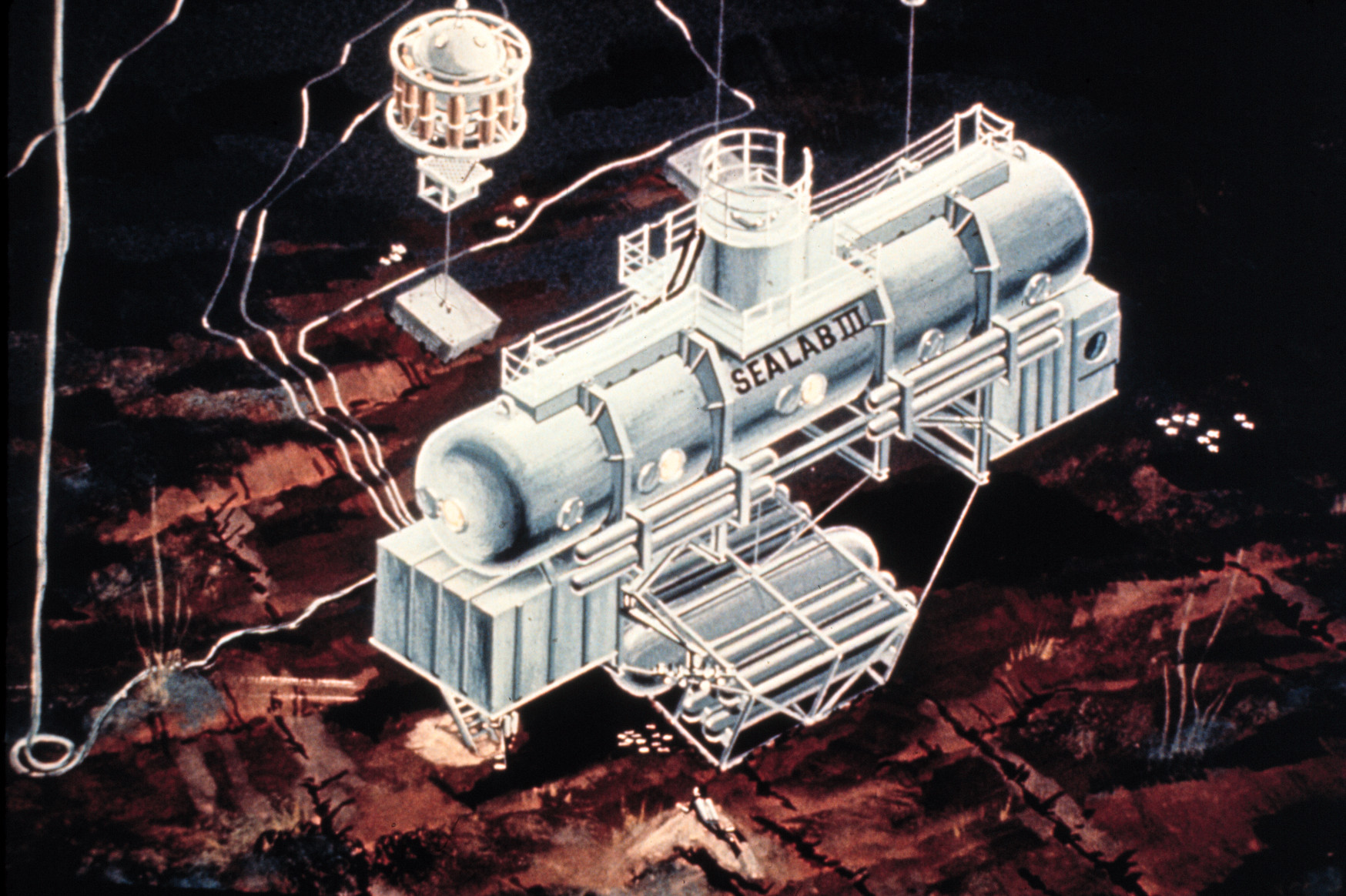
SEALAB III
With naval research funding constrained byVietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
combat requirements, it was four years later before SEALAB III used the refurbished SEALAB II habitat placed in water three times deeper. Five teams of nine divers
Diver or divers may refer to:
*Diving (sport), the sport of performing acrobatics while jumping or falling into water
*Practitioner of underwater diving, including:
**scuba diving,
**freediving,
**surface-supplied diving,
**saturation diving, a ...
were scheduled to spend 12 days each in the habitat, testing new salvage techniques and conducting oceanographic
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics ...
and fishery
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ...
studies. Preparations for such a deep dive were extensive. In addition to many biomedical
Biomedicine (also referred to as Western medicine, mainstream medicine or conventional medicine)
studies, work-up dives were conducted at the U.S. Navy Experimental Diving Unit at the Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, Navy Yard. These “dives” were not done in the open sea, but in a special hyperbaric chamber
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of ...
that could recreate the pressures at depths as great as of sea water.
 According to
According to John Piña Craven
John Piña Craven (October 30, 1924 – February 12, 2015) was an American scientist who was known for his involvement with Bayesian search theory and the recovery of lost objects at sea. He was Chief Scientist of the Special Projects Offic ...
, the U.S. Navy's head of the Deep Submergence Systems Project of which SEALAB was a part, SEALAB III "was plagued with strange failures at the very start of operations". Craven, John Piña (2001). ''The Silent War: The Cold War Battle Beneath the Sea'', New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
: Simon & Schuster
Simon & Schuster () is an American publishing company and a subsidiary of Paramount Global. It was founded in New York City on January 2, 1924 by Richard L. Simon and M. Lincoln Schuster. As of 2016, Simon & Schuster was the third largest publ ...
. USS ''Elk River'' (IX-509) was specially fitted as a SEALAB operations support ship to replace ''Berkone''; but the project was 18 months late and three million dollars over budget when SEALAB III was lowered to off San Clemente Island
San Clemente Island (Tongva: ''Kinkipar''; Spanish: ''Isla de San Clemente'') is the southernmost of the Channel Islands of California. It is owned and operated by the United States Navy, and is a part of Los Angeles County. It is administered b ...
, California, on 15 February 1969. SEALAB team members were tense and frustrated by these delays, and began taking risks to make things work. When a poorly sized neoprene seal caused helium to leak from the habitat at an unacceptable rate, four divers volunteered to repair the leak in place rather than lifting the habitat to the surface. Their first attempt was unsuccessful, and the divers had been awake for twenty hours using amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
s to stay alert for a second attempt, during which aquanaut
An aquanaut is any person who remains underwater, breathing at the ambient pressure for long enough for the concentration of the inert components of the breathing gas dissolved in the body tissues to reach equilibrium, in a state known as satura ...
Berry L. Cannon
Berry Louis Cannon (March 22, 1935 – February 17, 1969) was an American aquanaut who served on the SEALAB II and III projects of the U.S. Navy. Cannon died of carbon dioxide poisoning while attempting to repair SEALAB III. It was later found ...
died. It was found that his rebreather
A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's breathing, exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. ...
was missing baralyme Baralyme is a mixture of 80% calcium hydroxide and 20% barium hydroxide compounds that is used as an alternative to soda lime
Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH and CaO chemicals, used in granular form in closed breathing environments, such as gener ...
, the chemical necessary to remove carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
. Surgeon commander John Rawlins, a Royal Navy medical officer assigned to the project, also suggested that hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe h ...
during the dive was a contributing factor to the problem not being recognized by the diver.
According to Craven, while the other divers were undergoing the week-long decompression, repeated attempts were made to sabotage their air supply by someone aboard the command barge. Eventually, a guard was posted on the decompression chamber and the men were recovered safely. A potentially unstable suspect was identified by the staff psychiatrist, but the culprit was never prosecuted. Craven suggests this may have been done to spare the Navy bad press so soon after the USS ''Pueblo'' incident.
The SEALAB program came to a halt, and although the SEALAB III habitat was retrieved, it was eventually scrapped. Aspects of the research continued, but no new habitats were built.
NCEL (now a part of Naval Facilities Engineering Service Center
NFESC, the Naval Facilities Engineering Service Center (Formerly NCEL, Naval Civil Engineering Laboratory) in Port Hueneme, California, provides engineering services, technology testing, specialized facilities, and expertise in these facilities. ...
) of Port Hueneme, California
Port Hueneme ( ; Chumash: ''Wene Me'') is a small beach city in Ventura County, California, surrounded by the city of Oxnard and the Santa Barbara Channel. Both the Port of Hueneme and Naval Base Ventura County lie within the city limits.
Port ...
, was responsible for the handling of several contracts involving life support systems used on SEALAB III.
See also
* * * *References
*This page incorporates text in thepublic domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work
A creative work is a manifestation of creative effort including fine artwork (sculpture, paintings, drawing, sketching, performance art), dance, writing (literature), filmmaking, ...
from thOffice of Naval Research
Bibliography
* * * * * (For children.)External links
*US Naval Undersea Museu(One screen shot o
current habitat
* * * {{Authority control United States Navy in the 20th century Underwater habitats Scott Carpenter