Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3 or Global Goal 3), regarding "
Good Health
''Good Health'' is the first studio album by Pretty Girls Make Graves. Originally released in 2002 by Lookout Records, it was re-released by Matador Records with an additional 4 songs made up of the band's first self-titled EP. This album is oft ...
and
Well-being
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
", is one of the 17
Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
established by the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
in 2015. The official wording is: "To ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages''.''"
[United Nations (2015) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 25th September 2015, Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/70/1
The targets of SDG 3 cover and focus on various aspects of healthy life and healthy lifestyle. Progress towards the targets is measured using twenty-one indicators.
SDG 3 has 13 targets and 28 indicators to measure progress toward targets. The first nine targets are "outcome targets". Those are: reduction of
maternal mortality; ending all preventable
deaths under five years of age; fight
communicable diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
; ensure reduction of mortality from
non-communicable diseases and promote
mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental health ...
; prevent and treat
substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
; reduce
road injuries and deaths; grant universal access to
sexual and reproductive care,
family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marita ...
and education; achieve
universal health coverage
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
; and reduce illnesses and deaths from
hazardous chemicals
Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials ( syllabi ...
and
pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
. The four "means to achieving" SDG 3 targets are: implement the
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control; support research, development and universal access to affordable
vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifie ...
s and medicines; increase health financing and support
health workforce
Health human resources (HHR) – also known as human resources for health (HRH) or health workforce – is defined as "all people engaged in actions whose primary intent is to enhance positive health outcomes", according to World Health Organizati ...
in
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
; and improve early warning systems for global health risks.
[Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina (2018)]
Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
" (SDG 3) ''SDG-Tracker.org, website''
SDG 3 aims to achieve
universal health coverage
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
, that seeks equitable access of healthcare services to all men and women. It proposes to end the preventable death of newborns, infants and children under five (
child mortality
Child mortality is the mortality of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate, also under-five mortality rate, refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It en ...
) and end
epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics ...
s.
Good health is essential to
sustainable development
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The des ...
and the
2030 Agenda
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
. It focuses on broader
economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
and
social inequalities,
urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
,
climate crisis, continuing burden of HIV and other
infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
, not forgetting emerging challenges such as
non-communicable diseases.
Considering the global pandemic of
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, there is a need to give significant attention towards the realization of good health and well being on a global scale.
Background

Ensuring that every child survives and thrives depends on a combination of high-impact interventions – including quality
antenatal, delivery and
postnatal care for mothers and their newborns, prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV,
immunisation
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the immunogen).
When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ''non-sel ...
to protect children from infectious diseases and access to adequate and nutritious food.
The
UNDP
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
reports that "every 2 seconds, someone aged 30 to 70 years dies prematurely from noncommunicable diseases -
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
,
chronic respiratory disease,
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
or
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
."
According to statistics, globally, "2.4 million children died in the first month of life in 2019 – approximately 6,700
neonatal
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
deaths every day – with about a third of all neonatal deaths occurring within the first day after birth, and close to three-quarters occurring within the first week of life".
Lack of access to quality healthcare is one of the major factors behind the figures and regional data revealing that
neonatal mortality
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion o ...
was highest in
sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
which post 27 and 25 deaths per 1,000 live births, respectively, in 2019.
Significant steps have been made in increasing
life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
and reducing some of the common causes of
child
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger ...
and
maternal mortality. Between 2000 and 2016, the worldwide under-five mortality rate decreased by 47% (from 78 deaths per 1,000 live births to 41 deaths per 1,000 live births).
Still, the number of children dying under age five is extremely high: 5.6 million in 2016 alone.
New-borns account for a growing number of these deaths, and poorer children are at the greatest risk of under-five
mortality
Mortality is the state of being mortal, or susceptible to death; the opposite of immortality.
Mortality may also refer to:
* Fish mortality, a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock throug ...
due to a number of factors.
SDG 3 aims to reduce under-five mortality to as low as 25 per 1,000 live births. But if current trends continue, more than 60 countries will miss the SDG
neonatal
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
mortality target for 2030. About half of these countries would not reach the target even by 2050.
Between 2000 and 2016, the worldwide under-five death rate decreased by 47 percent (from 78 deaths per 1,000 live births to 41 deaths per 1,000 live births).
As mentioned earlier, the number of children dying under age five is extremely high: 5.6 million in 2016 alone.
Reports by
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Devel ...
,
WHO, the
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
and
UNDESA
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Econ ...
indicate that sixty million children under five will die between 2017 and 2030 despite the fact that the number of children dying in 2016 was low (5.6m) compared to 2000 (9.9m). SDG 3 also aims to reduce maternal mortality to less than 70 deaths per 100,000 live births.
Though the maternal mortality ratio declined by 37 per cent between 2000 and 2015, there were approximately 303,000 maternal deaths worldwide in 2015, most from preventable causes.
Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to clean water and sanitation and on reducing
malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
,
tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
,
polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe s ...
and the spread of
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
.
Advances in technologies such as the internet have enabled the digitization of health records and easier access to online medical resources for doctors and health workers, leading to improvements in patient treatment and outcomes.
Targets, indicators, and progress
The UN has defined 13 Targets and 28 Indicators for SDG 3. The main data source and maps for the indicators for SDG 3 come from
Our World in Data's SDG Tracker.
[Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina (2018)]
Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
" (SDG 3) ''SDG-Tracker.org, website'' The targets of SDG 3 cover a wide range of issues including reduction of maternal mortality (Target 3.1), ending all
preventable deaths
Preventable causes of death are causes of death related to risk factors which could have been avoided. The World Health Organization has traditionally classified death according to the primary type of disease or injury. However, causes of death ...
under five years of age (Target 3.2), fight
communicable diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
(Target 3.3), ensure a reduction of mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote
mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental health ...
(Target 3.4), prevent and treat
substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
(Target 3.5), reduce road injuries and deaths (Target 3.6), grant universal access to
sexual and reproductive health care,
family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marita ...
and education (Target 3.7), achieve
universal health coverage
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
(Target 3.8), reduce illnesses and deaths from
hazardous chemicals
Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials ( syllabi ...
and
pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
(Target 3.9), implement the
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (Target 3.a), support research, development and universal access to affordable
vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifie ...
s and medicines (Target 3.b), increase health financing and support
health workforce
Health human resources (HHR) – also known as human resources for health (HRH) or health workforce – is defined as "all people engaged in actions whose primary intent is to enhance positive health outcomes", according to World Health Organizati ...
in developing countries (Target 3.c) and improve
early warning systems for global health risks (Target 3.d).
Target 3.1: Reduce maternal mortality

The full text of Target 3.1 is: "By 2030, reduce the global
maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births".
[United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/71/313
* Indicator 3.1.1:
Maternal mortality ratio
The maternal mortality ratio is a key performance indicator (KPI) for efforts to improve the health and safety of mothers before, during, and after childbirth per country worldwide. Often referred to as MMR, it is the annual number of female death ...
. The maternal mortality ratio refers to the number of women who die from pregnancy-related causes while pregnant or within 42 days of pregnancy termination per 100,000 live births.
* Indicator 3.1.2: Percentage of births attended by personnel trained to give the necessary supervision, care, and advice to women during pregnancy, labour, and the postpartum period; to conduct deliveries on their own; and to care for newborns
The unequal status of women and girls, lack of decision-making powers, knowledge and finances remain underlying causes for the inability or delay in seeking
health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
which ends up increasing maternal mortality rates.
[United Nations (2017]
HLPF Thematic Review of SDG3
New York,
Target 3.1 aims to reduce maternal mortality to less than 70 deaths per 100,000 live births.
Though the maternal mortality ratio declined by 37 percent between 2000 and 2015, there were approximately 303,000 maternal deaths worldwide in 2015, most from preventable causes.
In 2015,
maternal health conditions were also the leading cause of death among girls aged 15–19.
Data for girls of greatest concern – those aged between 10 and 14 years is currently unavailable. Key strategies for meeting SDG 3 will be to reduce
adolescent pregnancy (which is strongly linked to
gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
), provide better data for all women and girls, and achieve universal coverage of skilled birth attendants.
Target 3.2: End all preventable deaths under five years of age

The full text of Target 3.2 is: "By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age, with all countries aiming to reduce
neonatal mortality
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion o ...
to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under‑5 mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births."
* Indicator 3.2.1:
Under-5 mortality rate. The under-5 mortality rate measures the number of children per 1,000 live births who die before their fifth birthday.
* Indicator 3.2.2: Neonatal mortality rate. The neonatal mortality rate is defined as the share of newborns per 1,000 live births in a given year who die before reaching 28 days of age.
Globally, the risk for children dying before age five was reduced by 44 per cent since 2000, reaching 43 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2015. Still, a large number of preventable deaths remain, with about 16,000 children under the age of five dying every day in 2015.
The neonatal mortality rate declined from 31 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2000 to 19 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2015. Though neonatal mortality is decreasing, the proportion of the global under-five mortality is increasing, signalling a need to ramp up focus on antenatal care programs.
The
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
in 2020 results in fewer women and their babies having access to lifesaving care.
This is because many healthcare facilities are even more short-staffed and under-equipped than usual. This can negatively impact the under-five mortality rate as well as the neonatal mortality rate.
[BMGF (2020]
Covid-19 A Global Perspective - 2020 Goalkeepers Report
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Seattle, USA
Target 3.3: Fight communicable diseases

The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
, tuberculosis, malaria and
neglected tropical diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical disease, tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in Developing country, developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety ...
and combat
hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pa ...
, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases."
* Indicator 3.3.1: Number of new HIV infections per 1,000 uninfected population
* Indicator 3.3.2:
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
per 100,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.3:
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
incidence per 1,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.4:
Hepatitis B incidence per 100,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.5: Number of people requiring interventions against neglected
tropical disease
Tropical diseases are Infectious disease, diseases that are prevalent in or unique to tropics, tropical and subtropics, subtropical regions. The diseases are less prevalent in temperate climates, due in part to the occurrence of a cold season, whic ...
Target 3.3 proposes to end the preventable death of newborns and children under five and to end
epidemics
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious d ...
such as
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
, tuberculosis, malaria, and
water-borne diseases, for example.

Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to
clean water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ag ...
and sanitation and on reducing malaria, tuberculosis,
polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe s ...
, and the spread of HIV/AIDS. From 2000 to 2016, new HIV infections declined by 66 percent for children under 15 and by 45 percent among adolescents aged 15–19.
However, current trends mean that 1 out of 4 countries still will not meet the SDG target to end AIDS among children under 5, and 3 out of 4 will not meet the target to end AIDS among adolescents.
Overall, AIDS remains the leading cause of death among women aged between 15 and 49 years as approximately 1800 young people being newly infected with HIV every day. This underscores]the importance of ensuring that young people can fully exercise their rights to access
sexual and reproductive health and HIV information.
In 2015, there were an estimated 10.4 million new Tuberculosis cases (1 million of which were under age 15), corresponding to 142 cases per 100,000 population, the malaria incidence rate was 91 per 1000 persons at risk, representing a 41% decrease globally between while deaths attributed to hepatitis are estimated to be around 1.3 million.
With regards to HIV infections, people living with HIV are at increased risk of death due to
Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19 in the year 2020. Also, disruptions to health services can result in people not getting
antiretroviral therapy (ART), which would result in more deaths.
Target 3.4: Reduce mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote mental health
The full text of Target 3.4 is: "By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from
non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and
well-being
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
."
* Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
,
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
,
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
or
chronic respiratory disease
* Indicator 3.4.2:
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
mortality rate
Deaths caused by the four main
NCDs were 17.7 million from cardiovascular diseases, 8.8 million from
cancers, 3.9 million from chronic respiratory diseases, and 1.6 million from
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
. The risk of dying from the four main NCDs between ages 30 and 70 decreased from 23% in 2000 to 19% in 2015
Target 3.5: Prevent and treat substance abuse
The full text of Target 3.5 is: "Strengthen the prevention and treatment of
substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
, including
narcotic
The term narcotic (, from ancient Greek ναρκῶ ''narkō'', "to make numb") originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates ...
drug abuse and
harmful use of alcohol."
* Indicator 3.5.1: Coverage of treatment interventions (
pharmacological,
psychosocial and
rehabilitation
Rehabilitation or Rehab may refer to:
Health
* Rehabilitation (neuropsychology), therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
* Rehabilitation (wildlife), treatment of injured wildlife so they can be retur ...
and aftercare services) for substance use disorders
* Indicator 3.5.2: Harmful use of alcohol, defined according to the national context as alcohol
per capita consumption (aged 15 years and older) within a calendar year in litres of pure alcohol.
In 2016, worldwide consumption of alcohol was projected to be 6.4 litres per person aged 15 and older. Consumption is increasing in the Western
Pacific and
South-East Asia Regions, while remaining relatively stable in others. The available data is inadequate and much further work is needed to improve the measurement of treatment coverage for alcohol and drug use disorders.

Target 3.6: Reduce road injuries and deaths
The full text of Target 3.6 is: "By 2020, halve (50% less) the number of global deaths and injuries from
road traffic accidents."
Target 3.6 has only one Indicator: Indicator 3.6.1 is the Death rate due to road traffic injuries.
The need for improvements in safer infrastructure and government regulation continues. In countries with great success, such as Sweden that boasts a 66% reduction in injury and deaths from 1990 to 2015, tough government regulation has been key.
In November 2009, at the request of the
UN General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
, the first Global Ministerial Conference on
road safety was hosted by the
Government of the Russian Federation
The Government of Russia exercises executive power in the Russia, Russian Federation. The members of the government are the Prime Minister of Russia, prime minister, the Deputy Chairman of the Government, deputy prime ministers, and the federa ...
. Following the success of the conference, the
Decade of Action for Road Safety 2011-2020
A decade () is a period of ten years. Decades may describe any ten-year period, such as those of a person's life, or refer to specific groupings of calendar years.
Usage
Any period of ten years is a "decade". For example, the statement that "du ...
declared in March 2010 by the United Nations General Assembly. In February 2020, the third global ministerial conference on Road Safety was held in
Stockholm, Sweden
Stockholm () is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropoli ...
. The outcome of the conference was the Stockholm Declaration that set a global target of reducing road
traffic deaths
Worldwide it was estimated that 1.25 million people were killed and many millions more were injured in motor vehicle collisions in 2013. This makes motor vehicle collisions the leading cause of death among young adults of 15–29 years of age ...
and
injuries by 50% by 2030. In August 2020, the United Nations ratified the Stockholm Declaration declaring 2021-2030 the Second Decade of action for Road Safety.

Target 3.7: Universal access to sexual and reproductive care, family planning and education
The full text of Target 3.7 is: "By 2030, ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services, including for
family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marita ...
, information and education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programs."
* Indicator 3.7.1: Percentage of married women ages 15–49 years whose need for family planning is satisfied with modern methods of contraception.
* Indicator 3.7.2: Adolescent birth rate (aged 10–14 years; aged 15–19 years) per 1,000 women in that age group.
Half of the women in developing countries have received the health care they need, and the need for family planning is increasing exponentially as the population grows. While needs are being addressed gradually, more than 225 million women have an unmet need for
contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
. There is a slight increase in the proportion of women of reproductive age who were married or in-union who had access to modern family planning methods, from 74.5% in 2000 to 76.7% in 2017.
In 2017, an estimated 13 million births will be to girls under age 20 with almost 1.8 billion adolescents and youth globally, investing in their health and well-being is essential to achieving the 2030 agenda.
In West Africa, the number of women using contraceptives more than doubled between 2011 and 2020.
Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage
The full text of Target 3.8 is: "Achieve
universal health coverage
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
, including
financial risk
Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financial ...
protection, access to quality
essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable
essential medicines and vaccines for all."
* Indicator 3.8.1: Coverage of essential health services.
* Indicator 3.8.2: Proportion of population with large household expenditures on health as a share of total household expenditure or income
Through the lens of leaving no one behind, Universal Health Coverage (UHC) includes migrants and
refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution. s, many of whom may not have legal status or are unaccounted, in financial risk protection schemes and access to equitable health services.
(PHC) is the most important pathway to achieve universal health coverage.
This because it can address more than 80 percent of a person's health needs and is accessible and affordable. In 2020, the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
resulted in a reduction in the "Universal Health Coverage Effective Coverage Index" (an index which assesses whether people in a country have access to essential health services).
Target 3.9: Reduce illnesses and deaths from hazardous chemicals and pollution
The full text of Target 3.9 is: "By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination."
* Indicator 3.9.1: Mortality rate attributed to the household (indoor) and ambient (outdoor) air pollution.
* Indicator 3.9.2: Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, sanitation, and lack of hygiene.
* Indicator 3.9.3: Mortality rate attributed to unintentional
poisoning.
Household air pollution is estimated to cause half of all pneumonia deaths among children under age five. The global mortality rate from unintentional poisonings decreased by 33% between the years 2000 and 2015 but still causes 108,000 deaths annually.

Target 3.a: Implement the WHO framework convention on tobacco control
The full text of Target 3.a is: "Strengthen the implementation of the
in all countries, as appropriate."
Target 3.a has only one Indicator: Indicator 3.a.1 is the "age-standardized
prevalence of current tobacco use among persons aged 15 years and older".
The
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control has been ratified by 180 Parties representing 90% of the global population. More than 80% of Parties have either adopted new or strengthened their existing tobacco control laws and regulations.
In 2019 the global average value for the "age-standardized smoking prevalence among ages 15 and older" was 17%, down from nearly 25% in 1990, which is a positive development.
The COVID-19 pandemic might accelerate this trend because people might stop buying tobacco if their income drops. Also, people have learned that smokers are more likely to get seriously ill or die from
Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19, which might cause them to smoke less.
Target 3.b: Support research, development and universal access to affordable vaccines and medicines

The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the
Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health The Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health was adopted by the WTO Ministerial Conference of 2001 in Doha on November 14, 2001. It reaffirmed flexibility of TRIPS member states in circumventing patent rights for better access to es ...
, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the
regarding flexibilities to protect public health, and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all."
* Indicator 3.b.1: Proportion of the target population covered by all vaccines included in their national program.
* Indicator 3.b.2: Total net
official development assistance (ODA) to medical research and basic health sectors.
* Indicator 3.b.3: Proportion of health facilities that have a core set of relevant essential medicines available and affordable on a sustainable basis.
The current landscape of health research and development (R&D) is insufficiently aligned with global health demands and needs. As little as 1% of all funding for health R&D is allocated to diseases that are predominantly incident in developing countries.
SDG 3 aims to achieve universal health coverage, including access to essential medicines and vaccines.
2016 rates for the third dose of the
pertussis vaccine
Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough (pertussis). There are two main types: whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78% effective while the acellular vaccine is 71–85% effectiv ...
(DTP3) and the first dose of the
measles vaccine (MCV1) reached 86 per cent and 85 per cent, respectively. Yet about 20 million children did not receive DTP3 and about 21 million did not receive MCV1.
Around two in five countries will need to accelerate progress in order to reach SDG targets for immunization.
Immunization averts an estimated 2 million-3 million deaths every year. In 2016, global coverage rates for the third dose of the
diphtheria, tetanus-pertussis vaccine (DTP3) and the first dose of measles-containing vaccine (MCV1) reached 86 per cent and 85 per cent, respectively, up from 72 per cent for each in 2000. Despite this increased coverage, about 20 million children did not receive three doses of DTP and about 21 million missed the first dose of MCV.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the gradual progress made in the past years with immunization, faces a huge decline. With highly contagious diseases like
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, this poses a bigger risk to the world's children.
However, some of the affected countries have already implemented measures to respond and combat this disruption. By combining health campaigns (for vaccines, deworming pills, bed nets, etc.) communities can receive several services all at the same time instead of one by one. This can increase coverage while minimizing exposure during the pandemic.
Another viable route to attain this Target is to accelerate COVID-19 vaccination opportunities to people who are often underserved by community vaccination programmes, for example prisoners. Experts have called for people in prisons to be prioritised for the national COVID-19 vaccination strategy, given their risk profile of underlying chronic conditions, age and living environment.

Target 3.c: Increase health financing and support health workforce in developing countries
The full text of Target 3.c is: "Substantially increase health financing and the recruitment, development, training and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in the least developed countries and small island developing states."
Target 3.c has only one Indicator: Indicator 3.c.1 is the Health worker density and distribution.
The joint
ITU
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
/
WHO initiative "Be Healthy Be Mobile" utilizes mobile technology to help countries combat growing burden of non-
communicable diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
by bringing mobile health services to scale within national
health system
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
s and providing technical expertise on implementing mobile health interventions.

Target 3.d: Improve early warning systems for global health risks
The full text of Target 3.d is: "Strengthen the capacity of all countries, in particular developing countries, for early warning,
risk reduction and management of national and global health risks."
* Indicator 3.d.1:
International Health Regulations (IHR) capacity and
health emergency preparedness
* Indicator 3.d.2: Percentage of bloodstream infections due to selected antimicrobial resistant organisms.
The 2016 IHR review process acknowledged the need to include migration and mobile populations in epidemic and
pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic (epidemiology), endemic disease wi ...
preparedness and response plans. Pandemic preparedness and
global health security require across the board upscaling of IHR implementation.
Custodian agencies
Custodian agencies are in charge of reporting on the following indicators:
* Indicators 3.1.1, 3.2.1, 3.2.2, 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.5.2, 3.6.1, 3.8.2, 3.9.1, 3.9.2, 3.9.3, 3.b.3, 3.c.1, 3.d.1 and 3.d.2:
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
(WHO).
* Indicator 3.1.2:
United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF)
* Indicator 3.3.1:
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS) (, ONUSIDA) is the main advocate for accelerated, comprehensive and coordinated global action on the HIV/AIDS pandemic.
The mission of UNAIDS is to lead, strengthen and support an e ...
* Indicators 3.3.2, 3.3.3, 3.3.4 and 3.3.5:
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Devel ...
.
* Indicator 3.5.1:
the World Health Organisation and
the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime.
* Indicators 3.7.1 and 3.7.2:
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Econ ...
.
* Indicators 3.8.1 and 3.b.1:
WHO and
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Devel ...
.
* Indicator 3.b.2:
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Monitoring
An annual report is prepared by the
Secretary-General of the United Nations evaluating the progress towards the
Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
.
[United Nations Economic and Social Council (2020]
Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020 In 2017, the
UN's High Level Political Forum published a thematic review of SDG 3.
Investing in
multi-stakeholder partnerships to remove barriers to equitable health services which are responsive to increasingly diverse population health needs, and to reach those most further behind first is essential for the
2030 Agenda
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
for Sustainable Development. Strong commitment by
UN Member States
The United Nations member states are the sovereign states that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the United Nations General Assembly, UN General Assembly. The UN is the world's largest international o ...
and the
international community
The international community is an imprecise phrase used in geopolitics and international relations to refer to a broad group of people and governments of the world.
As a rhetorical term
Aside from its use as a general descriptor, the term is ...
to ensuring good health and
wellbeing is achieved is therefore emphasised.
Challenges
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
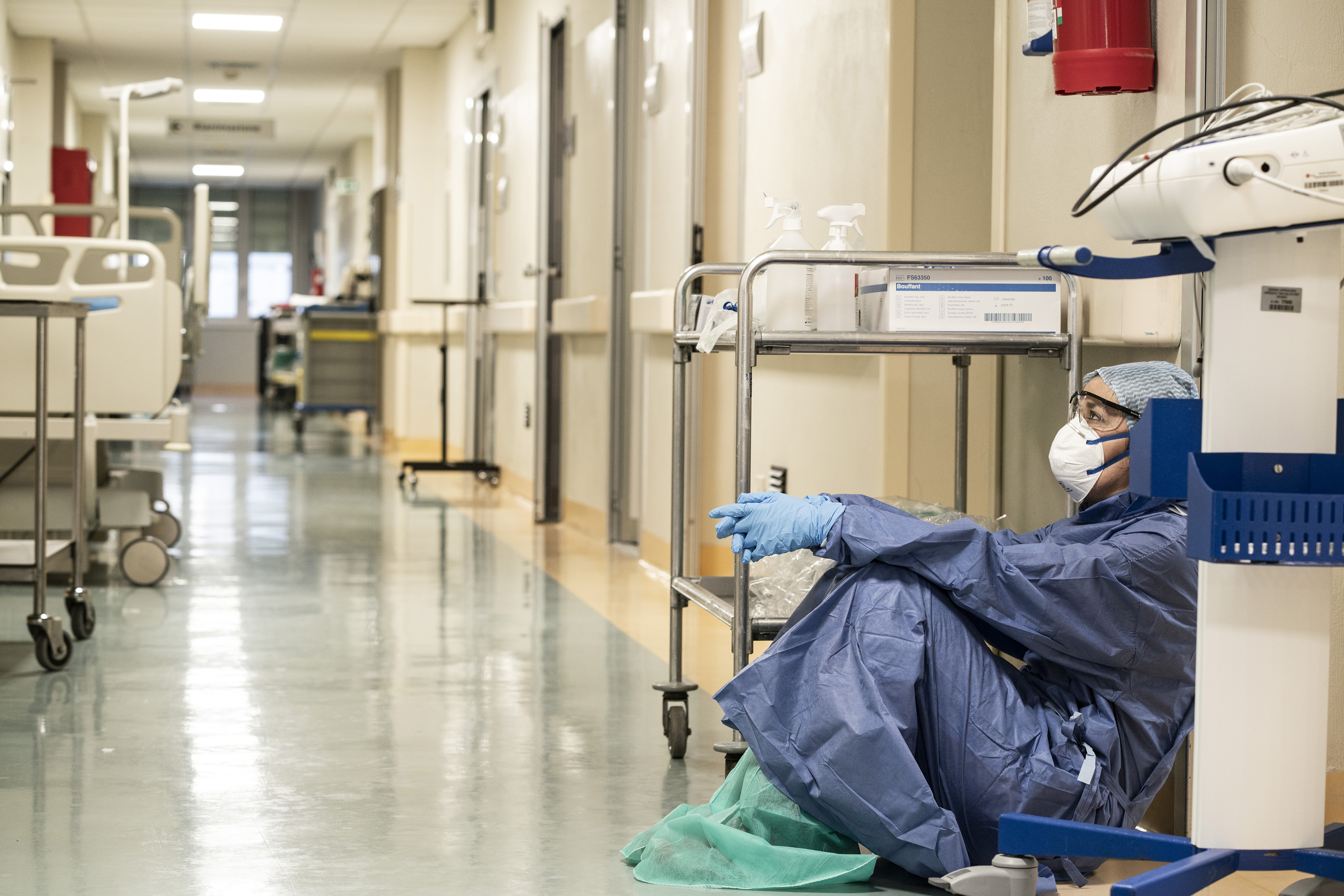

The
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
is a serious threat to the progress of SDG 3 aimed to ensure healthy lives and well-being for all. As the pandemic spread worldwide, the lockdown had over 70 countries putting a hold on various health services such as child vaccination, family planning, and cancer screening. The pandemic has also led to overloading and overcrowding of health facilities and many people became afraid of visiting for fear of being infected.
Most non-COVID-19 diseases have been either neglected or interrupted and healthcare systems are in turn stretched beyond their capacity and capabilities to provide adequate care. This is a great reverse in decades of improvement and has reiterated the need for governments to prioritize issues of healthy living and well-being and work towards the goal of SDG 3.
The governments of countries who already suffer from health workers shortage and other healthcare systems should take advantage of the lessons learnt during this crisis and build up resilience to combat future health pandemics and achieve progress towards Universal Health Coverage.
Links with other SDGs
SDG 3 is interwoven throughout the 2030 Agenda, with its targets directly linking to targets in other goals. Among these are targets of
SDG 2
Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2 or Global Goal 2) aims to achieve "zero hunger". It is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is: "End hunger, achieve food security and im ...
; 2.2 (end all forms of malnutrition),
SDG 4
Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4 or Global Goal 4) is about quality education and is among the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in September 2015.United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Asse ...
; 4.1 (free, equitable and good-quality secondary education), 4.2 (good-quality early childhood development), 4.7 (knowledge and skills for sustainable development),
SDG 5; 5.2 (eliminate all forms of violence against women and girls in the public and private spheres), 5.3 (eliminate all harmful practices, including
female genital mutilation
Female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision, is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the external female genitalia. The practice is found ...
), 5.6 (universal access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights),
SDG 6; 6.1(access to drinking water), 6.2 (access to sanitation),
SDG 7; 7.1 (access to modern energy services),
SDG 9
Sustainable Development Goal 9 (Goal 9 or SDG 9) is about "industry, innovation and infrastructure" and is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. SDG 9 aims to build resilient infrastruc ...
; 9.5 (enhance scientific research /increase number of R&D workers),
SDG 11; 11.6 (air quality and municipal waste),
SDG 13; 13.1 (resilience to natural disasters), and
SDG 16; 16.1 (reduce violence and related death rates).
Organizations
Organizations dedicated to good health and well-being include:
*
The Global Fund to Fight AIDS
* Joint United Nations Program on
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
(
UNAIDS)
*
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
*
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
(WHO)
*
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Devel ...
*
Department of Economic and Social Affairs
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Econ ...
(DESA)
*
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention by combining the ...
(UNODC)
*
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
*
UN Women
The United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women, also known as UN Women, is a United Nations entity working for gender equality and the empowerment of women. UN Women advocates for the rights of women and girls, and focu ...
*
Gavi the Vaccine Alliance
*
Vodafone Foundation
*
Doctors Without Borders
Red Cross InternationalMedical IMPACT*
Partners in Health
PanAfricareThe Global Health Network
US Based Organizations
In the US there are over seventy-two thousand tax-exempt organizations working on issues related to UN SDG 3, according to data filed with the
Internal Revenue Service –IRS and aggregated by X4Impact. X4Impact, with the support of the Rockefeller Foundation, Ford Foundation, Hewlett Foundation,
and Giving Tech Labs, created a free online interactive too
Health and Well-being in the US This online tool enables users to see health-related indicators nationally and by state, as well as relevant information for over seventy-two thousand tax-exempt organizations in the US working on issues related to UN SDG 3. The nonprofit data in the tool is updated every 15 days while the indicators are updated annually.
References
External links
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 3“Global Goals” Campaign - SDG 3SDG-Track.org - SDG 3UN SDG 3 in the US{{Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainable development
Sustainable Development Goals
 Ensuring that every child survives and thrives depends on a combination of high-impact interventions – including quality antenatal, delivery and postnatal care for mothers and their newborns, prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV,
Ensuring that every child survives and thrives depends on a combination of high-impact interventions – including quality antenatal, delivery and postnatal care for mothers and their newborns, prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV,  The full text of Target 3.1 is: "By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births".United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
The full text of Target 3.1 is: "By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births".United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
 The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of
The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of  Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to
Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to 

 The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the
The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the 

 The
The