S5-DOS MT on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
CP/M-86 was a version of the
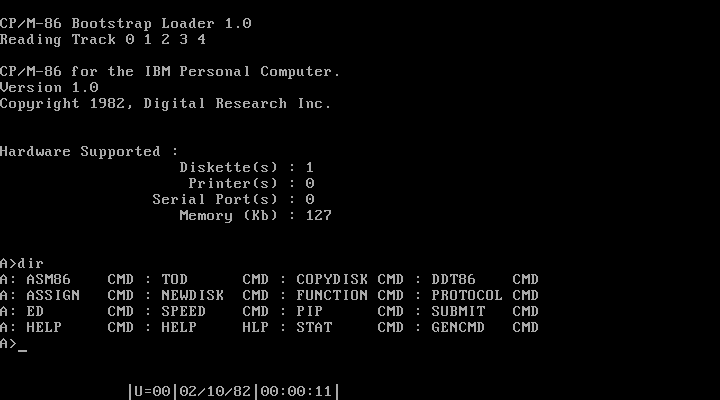 The IBM PC was announced on 12 August 1981, and the first machines began shipping in October the same year, ahead of schedule. CP/M-86 was one of three operating systems available from IBM, with PC DOS and
The IBM PC was announced on 12 August 1981, and the first machines began shipping in October the same year, ahead of schedule. CP/M-86 was one of three operating systems available from IBM, with PC DOS and
The Unofficial CP/M Website
which has a licence from the copyright holder to distribute original Digital Research software.
The comp.os.cpm FAQ
Intel iPDS-100 Using CP/M-Video
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cp M-86 CP/M variants IBM PC compatibles Microcomputer software Digital Research operating systems Discontinued operating systems Floppy disk-based operating systems Free software operating systems X86 operating systems 1981 software
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initial ...
operating system that Digital Research (DR) made for the Intel 8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit data bus (allowi ...
and Intel 8088. The system commands are the same as in CP/M-80. Executable files used the relocatable .CMD file format. Digital Research also produced a multi-user multitasking operating system compatible with CP/M-86, MP/M-86
MP/M (Multi-Programming Monitor Control Program) is a discontinued multi-user version of the CP/M operating system, created by Digital Research developer Tom Rolander in 1979. It allowed multiple users to connect to a single computer, each u ...
, which later evolved into Concurrent CP/M-86. When an emulator was added to provide PC DOS compatibility, the system was renamed Concurrent DOS
Multiuser DOS is a Real-time operating system, real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
An evolution of the older Concurrent CP/M-86, Concurrent DOS and Concurrent DOS 386 ...
, which later became Multiuser DOS, of which REAL/32 is the latest incarnation. The FlexOS, DOS Plus, and DR DOS families of operating systems started as derivations of Concurrent DOS as well.
History
Digital Research's CP/M-86 was originally announced to be released in November 1979, but was delayed repeatedly. When IBM contacted other companies to obtain components for theIBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
, the as-yet unreleased CP/M-86 was its first choice for an operating system because CP/M had the most applications at the time. Negotiations between Digital Research and IBM quickly deteriorated over IBM's non-disclosure agreement
A non-disclosure agreement (NDA) is a legal contract or part of a contract between at least two parties that outlines confidential material, knowledge, or information that the parties wish to share with one another for certain purposes, but wish ...
and its insistence on a one-time fee rather than DRI's usual royalty
Royalty may refer to:
* Any individual monarch, such as a king, queen, emperor, empress, etc.
* Royal family, the immediate family of a king or queen regnant, and sometimes his or her extended family
* Royalty payment for use of such things as int ...
licensing plan.
After discussions with Microsoft, IBM decided to use 86-DOS
86-DOS (known internally as QDOS, for Quick and Dirty Operating System) is a discontinued operating system developed and marketed by Seattle Computer Products (SCP) for its Intel 8086-based computer kit.
86-DOS shared a few of its commands wit ...
(QDOS), a CP/M-like operating system that Microsoft bought from Seattle Computer Products
Seattle Computer Products (SCP) was a Tukwila, Washington, microcomputer hardware company which was one of the first manufacturers of computer systems based on the 16-bit Intel 8086 processor. SCP began shipping its first S-100 bus 8086 CPU bo ...
renaming it MS-DOS. Microsoft adapted it for PC, and licensed it to IBM. It was sold by IBM under the name of PC DOS. After learning about the deal, Digital Research founder Gary Kildall threatened to sue IBM for infringing DRI's intellectual property, and IBM agreed to offer CP/M-86 as an alternative operating system on the PC to settle the claim. Most of the BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the ...
drivers for CP/M-86 for the IBM PC were written by Andy Johnson-Laird.
 The IBM PC was announced on 12 August 1981, and the first machines began shipping in October the same year, ahead of schedule. CP/M-86 was one of three operating systems available from IBM, with PC DOS and
The IBM PC was announced on 12 August 1981, and the first machines began shipping in October the same year, ahead of schedule. CP/M-86 was one of three operating systems available from IBM, with PC DOS and UCSD p-System
UCSD Pascal is a Pascal programming language system that runs on the UCSD p-System, a portable, highly machine-independent operating system. UCSD Pascal was first released in 1977. It was developed at the University of California, San Diego (UCS ...
. Digital Research's adaptation of CP/M-86 for the IBM PC was released six months after PC DOS in spring 1982, and porting applications from CP/M-80 to either operating system was about equally difficult. In November 1981, Digital Research also released a version for the proprietary IBM Displaywriter
The IBM 6580 Displaywriter System is a 16-bit microcomputer that was marketed and sold by IBM's Office Products Division primarily as a word processor. Announced in June 1980 and effectively withdrawn from marketing in July 1986, the system was s ...
.
On some dual-processor 8-bit/16-bit computers special versions of CP/M-86 could natively run CP/M-86 and CP/M-80 applications. A version for the DEC Rainbow was named CP/M-86/80, whereas the version for the was named CP/M 8-16 (see also: MP/M 8-16). The version of CP/M-86 for the 8085/8088-based Zenith Z-100 supported running programs for both processors as well.
When PC clones came about, Microsoft licensed MS-DOS to other companies as well. Experts found that the two operating systems were technically comparable, with CP/M-86 having better memory management but DOS being faster. '' BYTE'' speculated that Microsoft reserving multitasking for Xenix "appears to leave a big opening" for Concurrent CP/M-86.
On the IBM PC, however, at per copy for IBM's version, CP/M-86 sold poorly compared to the PC DOS; one survey found that 96.3% of IBM PCs were ordered with DOS, compared to 3.4% with CP/M-86 or Concurrent CP/M-86. In mid-1982 Lifeboat Associates
Lifeboat Associates was a New York City company that was one of the largest microcomputer software distributors in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Lifeboat acted as an independent software broker marketing software to major hardware vendors suc ...
, perhaps the largest CP/M software vendor, announced its support for DOS over CP/M-86 on the IBM PC. ''BYTE'' warned that IBM, Microsoft, and Lifeboat's support for DOS "poses a serious threat to" CP/M-86, and Jerry Pournelle stated in the magazine that "it is clear that Digital Research made some terrible mistakes in the marketing".
By early 1983 DRI began selling CP/M-86 1.1 to end users for . Advertisements called CP/M-86 a "terrific value", with "instant access to the largest collection of applications software in existence … hundreds of proven, professional software programs for every business and education need"; it also included Graphics System Extension
GEM (for Graphics Environment Manager) is an operating environment released by Digital Research (DRI) in 1985 for use with the DOS operating system on Intel 8088 and Motorola 68000 microprocessors.
GEM is known primarily as the graphical user i ...
(GSX), formerly . In May 1983 the company announced that it would offer DOS versions of all of its languages and utilities. It stated that "obviously, PC DOS has made great market penetration on the IBM PC; we have to admit that", but claimed that "the fact that CP/M-86 has not done as well as DRI had hoped has nothing to do with our decision". By early 1984 DRI gave free copies of Concurrent CP/M-86 to those who purchased two CP/M-86 applications as a limited time offer, and advertisements stated that the applications were booters, which did not require loading CP/M-86 first. In January 1984, DRI also announced Kanji CP/M-86, a Japanese version of CP/M-86, for nine Japanese companies including Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
, established on 15 January 1921, is a Japanese multinational electronics and electrical equipment manufacturing company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is one of the core companies of Mitsubishi. The products from MELCO include elevators an ...
, Sanyo Electric Co. Ltd.
, stylized as SANYO, is a Japanese electronics company and formerly a member of the ''Fortune'' Global 500 whose headquarters was located in Moriguchi, Osaka prefecture, Japan. Sanyo had over 230 subsidiaries and affiliates, and was founded by ...
, Sord Computer Corp. In December 1984 Fujitsu
is a Japanese multinational information and communications technology equipment and services corporation, established in 1935 and headquartered in Tokyo. Fujitsu is the world's sixth-largest IT services provider by annual revenue, and the la ...
announced a number of FM-16
The Fujitsu Micro 16s was a business personal computer from Fujitsu that was launched in 1983, around the same time as the launch of the original IBM PC/XT. The Micro 16s used a plug in microprocessor board, and two models were offered, ...
-based machines using Kanji CP/M-86.
CP/M-86 and DOS had very similar functionality, but were not compatible because the system calls for the same functions and program file
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program i ...
formats were different, so two versions of the same software had to be produced and marketed to run under both operating systems. The command interface again had similar functionality but different syntax; where CP/M-86 (and CP/M) copied file SOURCE to TARGET with the command PIP TARGET=SOURCE, DOS used COPY SOURCE TARGET.
Initially MS-DOS and CP/M-86 also ran on computers not necessarily hardware-compatible with the IBM PC such as the Apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus ''Prunus''.
Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also ...
and Sirius, the intention being that software would be independent of hardware by making standardised operating system calls to a version of the operating system custom tailored to the particular hardware. However, writers of software which required fast performance accessed the IBM PC hardware directly instead of going through the operating system, resulting in PC-specific software which performed better than other MS-DOS and CP/M-86 versions; for example, games would display fast by writing to video memory directly instead of suffering the delay of making a call to the operating system, which would then write to a hardware-dependent memory location. Non-PC-compatible computers were soon replaced by models with hardware which behaved identically to the PC's. A consequence of the universal adoption of detailed PC architecture was that no more than 640 kilobytes of memory were supported; early machines running MS-DOS and CP/M-86 did not suffer from this restriction, and some could make use of nearly one megabyte of RAM.
Reception
''PC Magazine
''PC Magazine'' (shortened as ''PCMag'') is an American computer magazine published by Ziff Davis. A print edition was published from 1982 to January 2009. Publication of online editions started in late 1994 and have continued to the present d ...
'' wrote that CP/M-86 "in several ways seems better fitted to the PC" than DOS; however, for those who did not plan to program in assembly language, because it cost six times more "CP/M seems a less compelling purchase". It stated that CP/M-86 was strong in areas where DOS was weak, and vice versa, and that the level of application support for each operating system would be most important, although CP/M-86's lack of a run-time version for applications was a weakness.
Versions
A given version of CP/M-86 has two version numbers. One applies to the whole system and is usually displayed at startup; the other applies to theBDOS
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initiall ...
kernel. Versions known to exist include:
All known Personal CP/M-86 versions contain references to CP/M-86 Plus, suggesting that they are derived from the CP/M-86 Plus codebase.
A number of 16-bit CP/M-86 derivatives existed in the former East-bloc under the names SCP1700 (), CP/K, and K8918-OS. They were produced by the East-German VEB Robotron Dresden and Berlin.
Legacy
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
permitted the redistribution and modification of all original Digital Research files, including source code, related to the CP/M family through Tim Olmstead's "The Unofficial CP/M Web site" since 1997. After Olmstead's death on 12 September 2001, the free distribution license was refreshed and expanded by Lineo
Lineo was a thin client and embedded systems company spun out of Caldera Thin Clients by 20 July 1999.
History
Caldera Thin Clients, Inc., had been created as a subsidiary of Caldera, Inc., on 2 September 1998. Caldera Thin Clients' original ...
, who had meanwhile become the owner of those Digital Research assets, on 19 October 2001.
See also
*History of computing hardware (1960s-present)
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
* SpeedStart CP/M-86
* DOS Plus
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
The Unofficial CP/M Website
which has a licence from the copyright holder to distribute original Digital Research software.
The comp.os.cpm FAQ
Intel iPDS-100 Using CP/M-Video
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cp M-86 CP/M variants IBM PC compatibles Microcomputer software Digital Research operating systems Discontinued operating systems Floppy disk-based operating systems Free software operating systems X86 operating systems 1981 software