Russian-Ottoman War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European history. Except for the war of 1710–11 and the
 The first
The first
 After the Russians had defeated the Swedes and the pro- Swedish Empire Ukrainian Cossacks led by
After the Russians had defeated the Swedes and the pro- Swedish Empire Ukrainian Cossacks led by  Russia entered into another war with the Ottoman Empire in 1736, prompted by raids on Ukraine by Crimean Tatars and the military campaign of the Crimean khan in the Caucasus. In May 1736, the Russian army launched an invasion of the Crimean peninsula and burned the capital of the Crimean Khanate
Russia entered into another war with the Ottoman Empire in 1736, prompted by raids on Ukraine by Crimean Tatars and the military campaign of the Crimean khan in the Caucasus. In May 1736, the Russian army launched an invasion of the Crimean peninsula and burned the capital of the Crimean Khanate
 The Polish opposition was defeated by
The Polish opposition was defeated by
 Gábor Ágoston attributes the decline of Ottoman power relative to Russia to the reactionary
Gábor Ágoston attributes the decline of Ottoman power relative to Russia to the reactionary  When in 1853 Russia destroyed the entire Ottoman fleet at
When in 1853 Russia destroyed the entire Ottoman fleet at  Soon the Balkan rebellions were beginning to falter. In Europe, papers were filled with reports of Ottoman soldiers killing thousands of Slavs. Even in Great Britain
Soon the Balkan rebellions were beginning to falter. In Europe, papers were filled with reports of Ottoman soldiers killing thousands of Slavs. Even in Great Britain Bulgarian Horrors and the Question of the East, 5 September 1876
/ref> Soon, a new Russo-Turkish war had begun. Despite fighting better than they ever had before, the advanced Ottoman armies still were not equal to the Russian forces. This time there was no help from abroad; in truth, many European nations supported the Russian war, as long as it did not get too close to Istanbul. Ten and a half months later when the war had ended the age of Ottoman domination over the Balkans was over. In the Balkans, the Russian army, having crossed the Danube, captured the Shipka Pass. The Turkish army of Osman Pasha, after a stubborn struggle, surrendered to Plevna. After that, the Russian army crossed the Balkan Mountains, defeated the remaining Turkish troops and reached the approaches to Constantinople. In the Caucasus, the Turkish army held back the Russian offensive, but after the defeat at Aladzha, retreated to In response to the Russian proximity to the straits the British, against the wishes of the Sultan, intervened in the war. A large task force representing British naval supremacy entered the straits of Marmara and anchored in view of both the royal palace and the Russian army. The British may have saved the Ottoman Empire once again, but it ended the rosy relations between the two powers that had endured since the Crimean War. Looking at the prospect of a British entry into the war the Russians decided to settle the dispute. The
In response to the Russian proximity to the straits the British, against the wishes of the Sultan, intervened in the war. A large task force representing British naval supremacy entered the straits of Marmara and anchored in view of both the royal palace and the Russian army. The British may have saved the Ottoman Empire once again, but it ended the rosy relations between the two powers that had endured since the Crimean War. Looking at the prospect of a British entry into the war the Russians decided to settle the dispute. The
 There were two main movements for the west side. The first one was performed while Ottomans were dealing with the Greek uprising, see Greek War of Independence.
The Greeks' independence war led to the Russian forces advancing into
There were two main movements for the west side. The first one was performed while Ottomans were dealing with the Greek uprising, see Greek War of Independence.
The Greeks' independence war led to the Russian forces advancing into
 During the early months of World War I,
During the early months of World War I,
online
* *
online
* Allen, William and Paul Muratoff. ''Caucasian Battlefields: A History Of The Wars On The Turco-Caucasian Border 1828-1921'' (2011) , * * Dupuy, R. Ernest and Trevor N. Dupuy. ''The Encyclopedia of Military History from 3500 B.C. to the Present'' (1986 and other editions), passim and 1461–1464. * * Jelavich, Barbara. ''St. Petersburg and Moscow: Tsarist and Soviet Foreign Policy, 1814–1974'' (1974) * Kagan, Frederick, and Robin Higham, eds. ''The Military History of Tsarist Russia'' (2008) * Topal, Ali E. "The effects of German Military Commission and Balkan wars on the reorganization and modernization of the Ottoman Army" (Naval Postgraduate School 2013
online
{{DEFAULTSORT:Russo-Turkish Wars * Geopolitical rivalry Wars involving the Russian Empire Wars involving Russia Military history of Ukraine History of Moldavia Bessarabia Governorate History of Wallachia Kingdom of Romania Modern history of Bulgaria Early Modern history of Georgia (country) Military operations involving the Crimean Khanate Invasions of Europe
Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
, which is often treated as a separate event, the conflicts ended disastrously for the Ottoman Empire; conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of Russia as a European power after the modernization efforts of Peter the Great in the early 18th century.
History
Conflict begins (1568–1739)
Before Peter the Great
 The first
The first Russo-Turkish War (1568–1570)
The Russo-Turkish War (1568–1570) or Don-Volga-Astrakhan campaign of 1569 (referred to in Ottoman sources as the ''Astrakhan Expedition'') was a war between the Tsardom of Russia and the Ottoman Empire over the Astrakhan Khanate. It was the fir ...
occurred after the conquest of Kazan
The siege of Kazan in 1552 was the final battle of the Russo-Kazan Wars and led to the fall of the Khanate of Kazan. Conflict continued after the fall of Kazan, however, as rebel governments formed in Çalım and Mişätamaq, and a new khan w ...
and Astrakhan by the Russian tsar Ivan the Terrible. The Ottoman sultan Selim II
Selim II (Ottoman Turkish: سليم ثانى ''Selīm-i sānī'', tr, II. Selim; 28 May 1524 – 15 December 1574), also known as Selim the Blond ( tr, Sarı Selim) or Selim the Drunk ( tr, Sarhoş Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire f ...
tried to squeeze the Russians out of the lower Volga by sending a military expedition to Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the C ...
in 1569. The Turkish expedition ended in disaster for the Ottoman army, which could not take Astrakhan and almost completely perished in the steppes, while the Ottoman fleet was wrecked in the Sea of Azov. The peace treaty between the two sides cemented Russia's conquests on the Volga, but allowed the Ottoman Empire to obtain a number of commercial benefits. Ottoman vassal the Crimean Khanate continued its expansion against the Russian Tsardom, but was defeated at the Battle of Molodi
The Battle of Molodi ( Russian: Би́тва при Мóлодях) was one of the key battles of Ivan the Terrible's reign. It was fought near the village of Molodi, south of Moscow, in July–August 1572 between the 40,000–60,000-strong''� ...
in 1572.
The next conflict between Russia and Turkey began 100 years later as part of the struggle for the territory of Ukraine. While Russia conquered the Left-bank Ukraine
Left-bank Ukraine ( uk, Лівобережна Україна, translit=Livoberezhna Ukrayina; russian: Левобережная Украина, translit=Levoberezhnaya Ukraina; pl, Lewobrzeżna Ukraina) is a historic name of the part of Ukrai ...
after the Russo-Polish War (1654-1667)
Armed conflicts between Poland (including the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) and Russia (including the Soviet Union) include:
Originally a Polish civil war that Russia, among others, became involved in.
Originally a Hungarian revolution ...
, Ottoman Empire in the course of the Polish–Ottoman War (1672–1676)
Polish–Ottoman War (1672–1676) was a conflict between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Ottoman Empire, as a precursor of the Great Turkish War. It ended in 1676 with the Treaty of Żurawno and the Commonwealth ceding control of m ...
, spread its rule over all of the Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb p ...
with the support of its vassal, Petro Doroshenko
Petro Doroshenko ( uk, Петро Дорофійович Дорошенко, russian: Пётр Дорофе́евич Дороше́нко, pl, Piotr Doroszenko; 1627–1698) was a Cossack political and military leader, Hetman of Right-bank Ukr ...
(1665–1672). The latter's pro-Ottoman policy caused discontent among many Ukrainian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
, who would elect Ivan Samoilovich
Ivan Samoylovych (, , ; died 1690) was the Hetman of Left-bank Ukraine from 1672 to 1687. His term in office was marked by further incorporation of the Cossack Hetmanate into the Tsardom of Russia and by attempts to win Right-bank Ukraine from ...
as a sole Hetman of all Ukraine in 1674. In 1676, Russian troops captured Chigirin
Chyhyryn ( uk, Чигирин, ) is a city and historic site located in Cherkasy Raion of Cherkasy Oblast of central Ukraine. From 1648 to 1669 the city was a Hetman residence. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see ...
and overthrew Doroshenko, who was exiled to Russia. In 1677, the Ottoman army tried to retake Chigirin, but was defeated. In 1678, the Ottoman army was finally able to take Chigirin after a bloody assault. But on this the Ottoman expansion to the northeast was stopped. In 1679–80, the Russians repelled the attacks of the Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
and signed the Treaty of Bakhchisarai
The Treaty of Bakhchisarai or Treaty of Radzin, (russian: Бахчисарайский мирный договор; tr, Bahçesaray Antlaşması) was signed in Bakhchisaray, which ended the Russo-Turkish War (1676–1681), on 3 January 1681 by R ...
on January 13, 1681, which would establish the Russo-Turkish border by the Dnieper River.
Peter the Great and further
Russia joined the European Holy League (Austria, Poland, Venice) in 1686. During the war, the Russian army organized theCrimean campaigns of 1687 and 1689
The Crimean campaigns of 1687 and 1689 (russian: Крымские походы, ) were two military campaigns of the Tsardom of Russia against the Crimean Khanate. They were a part of the Russo-Turkish War (1686–1700) and Russo-Crimean Wars. Th ...
and the Azov campaigns (1695–96). In the light of Russia's preparations for the war with Sweden and other countries' signing the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by ...
with Turkey in 1699, the Russian government signed the Treaty of Constantinople with the Ottoman Empire in 1700. Following the results of peace, Russia managed to annex Azov
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mout ...
and get access to the Sea of Azov.
 After the Russians had defeated the Swedes and the pro- Swedish Empire Ukrainian Cossacks led by
After the Russians had defeated the Swedes and the pro- Swedish Empire Ukrainian Cossacks led by Ivan Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (also spelled Mazeppa; uk, Іван Степанович Мазепа, pl, Jan Mazepa Kołodyński; ) was a Ukrainian military, political, and civic leader who served as the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host in 1687–1708. ...
in the Battle of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava; russian: Полта́вская би́тва; uk, Полта́вська би́тва (8 July 1709) was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. A Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeate ...
in 1709, Charles XII of Sweden
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII ( sv, Karl XII) or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 O.S.), was King of Sweden (including current Finland) from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of ...
managed to persuade the Ottoman Sultan Ahmed III
Ahmed III ( ota, احمد ثالث, ''Aḥmed-i sālis'') was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire and a son of Sultan Mehmed IV (r. 1648–1687). His mother was Gülnuş Sultan, originally named Evmania Voria, who was an ethnic Greek. He was born at H ...
to declare war on Russia on November 20, 1710. The Prut campaign
The Russo-Ottoman War of 1710—1711, also known as the Pruth River Campaign, was a brief military conflict between the Tsardom of Russia and the Ottoman Empire. The main battle took place during 18-22 July 1711 in the basin of the Pruth riv ...
of Peter the Great ended very unsuccessfully for Russia. The Russian army, led by the tsar, was surrounded by a superior Turkish-Tatar army and was forced to agree to unfavorable peace conditions, according to which it returned the previously captured Azov to the Ottoman Empire.
By the late 17th century, the Iranian Safavid dynasty, which neighbored both empires and had been one of the greatest rivals for Turkey for centuries (16th–19th centuries), had been heavily declining. Taking advantage of the situation, Russia and the Ottoman Empire conquered swaths of its territory comprising contemporary Dagestan, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
, and Northern Iran, which was taken by Peter I in the Russo-Persian War (1722–1723)
The Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723, known in Russian historiography as the Persian campaign of Peter the Great, was a war between the Russian Empire and Safavid Iran, triggered by the tsar's attempt to expand Russian influence in the Caspian ...
; the Ottomans took the territory to the west, comprising modern day Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, parts of Eastern Anatolia, as well as western Iran. The gains by both were confirmed in the Treaty of Constantinople (1724)
The Treaty of Constantinople (russian: Константинопольский договор,) Russo-Ottoman Treaty or Treaty of the Partition of Persia (''Iran Mukasemenamesi'') was a treaty concluded on 24 June 1724 between the Ottoman Empire an ...
. For a few years, they bordered each other along a large territory in the Caucasus, which caused further frictions.
Russia managed to secure a favourable international situation by signing treaties with Persia in 1732
Events
January–March
* January 21 – Russia and Persia sign the Treaty of Riascha at Resht. Based on the terms of the agreement, Russia will no longer establish claims over Persian territories.
* February 9 – The Swedis ...
and 1735
Events
January–March
* January 2 – Alexander Pope's poem ''Epistle to Dr Arbuthnot'' is published in London.
* January 8 – George Frideric Handel's opera ''Ariodante'' is premièred at the Royal Opera House in Covent G ...
. These returned all Iranian territories gained since 1722 in the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' is ...
and South Caucasus and Northern Iran, and avoided war with the emerging leader of Persia, Nader Shah. The treaties had other diplomatically favourable aspects as they established a Russo-Iranian alliance against Turkey, as Persia was at war with the Ottoman Empire. In the meantime Russia was also supporting the accession to the Polish throne of Augustus III
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Augu ...
in the War of the Polish Succession (1733–35), over the French-nominated Stanisław Leszczyński. Austria had been Russia's ally since 1726.
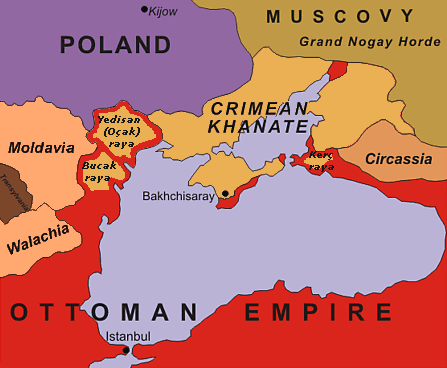
 Russia entered into another war with the Ottoman Empire in 1736, prompted by raids on Ukraine by Crimean Tatars and the military campaign of the Crimean khan in the Caucasus. In May 1736, the Russian army launched an invasion of the Crimean peninsula and burned the capital of the Crimean Khanate
Russia entered into another war with the Ottoman Empire in 1736, prompted by raids on Ukraine by Crimean Tatars and the military campaign of the Crimean khan in the Caucasus. In May 1736, the Russian army launched an invasion of the Crimean peninsula and burned the capital of the Crimean Khanate Bakhchisarai
Bakhchysarai ( crh, Bağçasaray, italic=yes; russian: Бахчисара́й; ua, Бахчисара́й; tr, Bahçesaray) is a town in Crimea, a territory recognized by a majority of countries as part of Ukraine and annexed by Russia as the ...
. On June 19, the Russian Don army under the command of General Peter Lacy captured Azov. In July 1737, the Münnich army took by storm the Ottoman fortress of Ochakov
Ochakiv, also known as Ochakov ( uk, Оча́ків, ; russian: Очаков; crh, Özü; ro, Oceacov and ''Vozia'', and Alektor ( in Greek), is a small city in Mykolaiv Raion, Mykolaiv Oblast (region) of southern Ukraine. It hosts the admini ...
. The Lacy army (now 40,000 strong) marched into the Crimea the same month, inflicting a number of defeats on the army of the Crimean khan and capturing Karasubazar
Bilohirsk (until 1944 – Karasubazar, uk, Білогірськ, translit=Bilohirsk; russian: Белого́рск, translit=Belogorsk, crh, Qarasuvbazar/Къарасувбазар) is a town and the administrative centre in Belohirsk Raion, o ...
. Lacy and his soldiers had to leave the Crimea, however, due to lack of supplies.
Austria entered the war against Turkey in July 1737 but was defeated a number of times. In August, Russia, Austria and Turkey began negotiations in Nemirov
Nemyriv ( uk, Немирів, russian: Немирoв, pl, Niemirów) is a historic town in Vinnytsia Oblast (province) in Ukraine, located in the historical region of Podolia. It was the administrative center of former Nemyriv Raion (district) ...
, which would turn out to be fruitless. There were no significant military operations in 1738. The Russian army had to leave Ochakov and Kinburn due to a plague outbreak. In 1739, the Münnich army crossed the Dnieper, defeated the Ottoman Empire at Stavuchany, and occupied the fortress of Khotin
Khotyn ( uk, Хотин, ; ro, Hotin, ; see other names) is a city in Dnistrovskyi Raion, Chernivtsi Oblast of western Ukraine and is located south-west of Kamianets-Podilskyi. It hosts the administration of Khotyn urban hromada, one of the ...
and Iaşi. However, Austria was defeated by the Ottoman Empire once again and signed a separate peace treaty on August 21. This, coupled with the imminent threat of Swedish invasion, forced Russia to sign the Treaty of Belgrade with Turkey on September 18, ending the war.
Gradual defeat of the Ottoman Empire (1768–1878)
Catherine the Great
Following a border incident at Balta, Sultan Mustafa III declared war on Russia on September 25, 1768. The Turks formed an alliance with the Polish opposition forces of theBar Confederation
The Bar Confederation ( pl, Konfederacja barska; 1768–1772) was an association of Polish nobles ( szlachta) formed at the fortress of Bar in Podolia (now part of Ukraine) in 1768 to defend the internal and external independence of the Poli ...
, while Russia was supported by Great Britain, which offered naval advisers to the Russian navy.
 The Polish opposition was defeated by
The Polish opposition was defeated by Alexander Suvorov
Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov (russian: Алекса́ндр Васи́льевич Суво́ров, Aleksándr Vasíl'yevich Suvórov; or 1730) was a Russian general in service of the Russian Empire. He was Count of Rymnik, Count of the Holy ...
, who was then transferred to the Ottoman theatre of operations, where in 1773 and 1774 he won several minor and major battles following the previous grand successes of the Russian Field-Marshal Pyotr Rumyantsev at Larga and Kagul
Also called tagutok (Maranao), bantula or tagungtung (Bukidnon) and kuratung ( Banuwaen).
The kagul is a type of Philippine bamboo scraper gong/ slit drum of the Maguindanaon and Visayans with a jagged edge on one side, played with two beaters ...
.
Naval operations of the Russian Baltic Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Baltic fleet.svg
, image_size = 150
, caption = Baltic Fleet Great ensign
, dates = 18 May 1703 – present
, country =
, allegiance = (1703–1721) (1721–1917) (1917–1922) (1922–1991)(1991–present)
...
in the Mediterranean yielded victories under the command of Aleksei Orlov. In 1771, Egypt and Syria rebelled against the Ottoman rule, while the Russian fleet totally destroyed the Ottoman Navy at the battle of Chesma
The naval Battle of Chesme took place on 5–7 July 1770 during the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774) near and in Çeşme (Chesme or Chesma) Bay, in the area between the western tip of Anatolia and the island of Chios, which was the site of a num ...
.
On July 21, 1774, the Ottoman Empire signed the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca, which formally granted independence to the Crimean Khanate, but in reality it became dependent on Russia. Russia received 4.5 million rubles and two key seaports allowing the direct access to the Black Sea. It also marked the first time that a foreign power directly interfered in the affairs of the Ottoman Porte, as the treaty gave Russia protector status over Turkey's Orthodox Christian subjects.
In 1783, Russia annexed the Crimean Khanate. In the same year, Russia established its protectorate over Eastern Georgia according to the Treaty of Georgievsk
The Treaty of Georgievsk (russian: Георгиевский трактат, Georgievskiy traktat; ka, გეორგიევსკის ტრაქტატი, tr) was a bilateral treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and the east G ...
. In 1787, Empress Catherine II
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
made a triumphant trip across the Crimea, accompanied by representatives of foreign courts and her ally, Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II
Joseph II (German: Josef Benedikt Anton Michael Adam; English: ''Joseph Benedict Anthony Michael Adam''; 13 March 1741 – 20 February 1790) was Holy Roman Emperor from August 1765 and sole ruler of the Habsburg lands from November 29, 1780 un ...
. These events and the friction caused by mutual complaints of infringements of the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca, which had closed the previous war, stirred up public opinion in Istanbul, and the British ambassador lent his support to the war party.
In 1787 the Ottomans demanded that Russia vacate the Crimea. Russia declared war, but Ottoman preparations were inadequate and the moment was ill-chosen, now that Russia and Austria were in alliance, a fact that came to light only after events were already in motion. The Turks drove back the Austrians from Mehadia
Mehadia ( hu, Mehádia; german: Mehadia; tr, Mehadiye) is a small market town and commune in Caraș-Severin County, Banat, Romania. It lies on the European route E70, in the Cerna River valley. The town is located on the site of the ancient R ...
and overran the Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of ...
(1789); but in Moldavia Field-Marshal Pyotr Rumyantsev was successful and captured Iaşi and Khotyn. Ottoman generals were incompetent and the army mutinous; expeditions for the relief of Bender and Akkerman
Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi ( uk, Бі́лгород-Дністро́вський, Bílhorod-Dnistróvskyy, ; ro, Cetatea Albă), historically known as Akkerman ( tr, Akkerman) or under different names, is a city, municipality and port situated on ...
failed, Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 m ...
was taken by the Austrians, The Russian army under the command of Alexander Suvorov
Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov (russian: Алекса́ндр Васи́льевич Суво́ров, Aleksándr Vasíl'yevich Suvórov; or 1730) was a Russian general in service of the Russian Empire. He was Count of Rymnik, Count of the Holy ...
defeated the Turks in the battle of Rymnik
The Battle of Rymnik ( tr, Boze Savaşı) on September 22, 1789 took place in Wallachia, near Râmnicu Sărat (now in Romania), during the Russo-Turkish War of 1787–1792. The Russian general Alexander Suvorov, acting together with the Habsb ...
and captured Izmail. The fall of Anapa
Anapa (russian: Ана́па, ) is a town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located on the northern coast of the Black Sea near the Sea of Azov. Population:
History
The area around Anapa was settled in antiquity. It was originally a major seaport ...
completed the series of Ottoman disasters. The Russian Black Sea Fleet
Chernomorskiy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet
, dates = May 13, ...
, created just a few years earlier, under the command of Admiral Ushakov
Fyodor Fyodorovich Ushakov ( rus, Фёдор Фёдорович Ушако́в, p=ʊʂɐˈkof; – ) was an 18th century Russian naval commander and admiral. He is notable for winning every engagement he participated in as the Admiral of ...
, inflicted a series of defeats on the Turkish Fleet and seized the initiative in the Black Sea.
Sultan Selim III was anxious to restore his country's prestige by a victory before making peace, but the condition of his troops rendered this hope unavailing. Turkey signed an assistance pact with Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
on 31 January 1790, but received no help during the war. Accordingly, the Treaty of Jassy was signed with Russia on 9 January 1792, by which the Crimea and Ochakov were left to Russia, the Dniester was made the frontier in Europe, and the Asiatic frontier remained unchanged.
Conflicts in 19th century
 Gábor Ágoston attributes the decline of Ottoman power relative to Russia to the reactionary
Gábor Ágoston attributes the decline of Ottoman power relative to Russia to the reactionary Janissaries
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ...
:
:Despite all these treatises and efforts at modernization, the Janissaries and their allies managed to derail Sultan Selim III's Western-style military, bureaucratic, and financial reforms, even killing the "infidel sultan" himself. It was not until the 1830s that fundamental reforms could be started under Mahmud II, who destroyed the Janissaries in 1826, a century and a quarter after Peter the Great's liquidation of the '' strel'tsy.''
In 1806, the Ottoman Empire incited by Napoleonic France started a new war. The long six-year war for Russia took place in parallel with the Russo-Persian War, the Russo-Swedish War and the War of the Fourth Coalition
The Fourth Coalition fought against Napoleon's French Empire and were defeated in a war spanning 1806–1807. The main coalition partners were Prussia and Russia with Saxony, Sweden, and Great Britain also contributing. Excluding Prussia, ...
. Despite this, in the decisive campaign of 1811, the Russian army of Kutuzov
Prince Mikhail Illarionovich Golenishchev-Kutuzov ( rus, Князь Михаи́л Илларио́нович Голени́щев-Куту́зов, Knyaz' Mikhaíl Illariónovich Goleníshchev-Kutúzov; german: Mikhail Illarion Golenishchev-Kut ...
defeated the Ottoman army on the Danube, which made it possible to conclude a peace treaty beneficial for Russia, according to which Russia get Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds o ...
.
The Ottoman Empire had maintained military parity with Russia until the second half of the eighteenth century, but by the 1820s the Ottoman armies were unable to put down the Greek War of Independence in southern Greece
Southern Greece ( el, Νότια Ελλάδα) is a loosely defined geographical term, usually encompassing the Peloponnese peninsula and varying parts of Continental Greece (Attica is usually included), as well as the islands of the Cyclades, ...
. The great powers of Europe decided to intervene and assist Greece with its independence. After the Battle of Navarino
The Battle of Navarino was a naval battle fought on 20 October (O. S. 8 October) 1827, during the Greek War of Independence (1821–29), in Navarino Bay (modern Pylos), on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. Allied f ...
and the Russo-Turkish War (1828–29)
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histor ...
, in which the Russian army first crossed the Balkan Mountains
The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border be ...
and took Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
, Turkey recognized the independence of Greece and the transition of the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus to Russia. Thus Greece became the first independent country created out of a section of the Ottoman Empire. Russian Empire aspirations for a section of the empire and bases on Russia's southern flank provoked British fears over naval domination of the Mediterranean and control of the land route to the Indian Subcontinent.David R. Stone
David Russell Stone (born 1968) is an American military historian and the William Eldridge Odom Professor of Russian Studies in the Strategy and Policy Department at the U.S. Naval War College.
Stone received a Bachelor of Arts degree in histo ...
, ''A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the War in Chechnya'' (Greenwood Publishing, 2006)
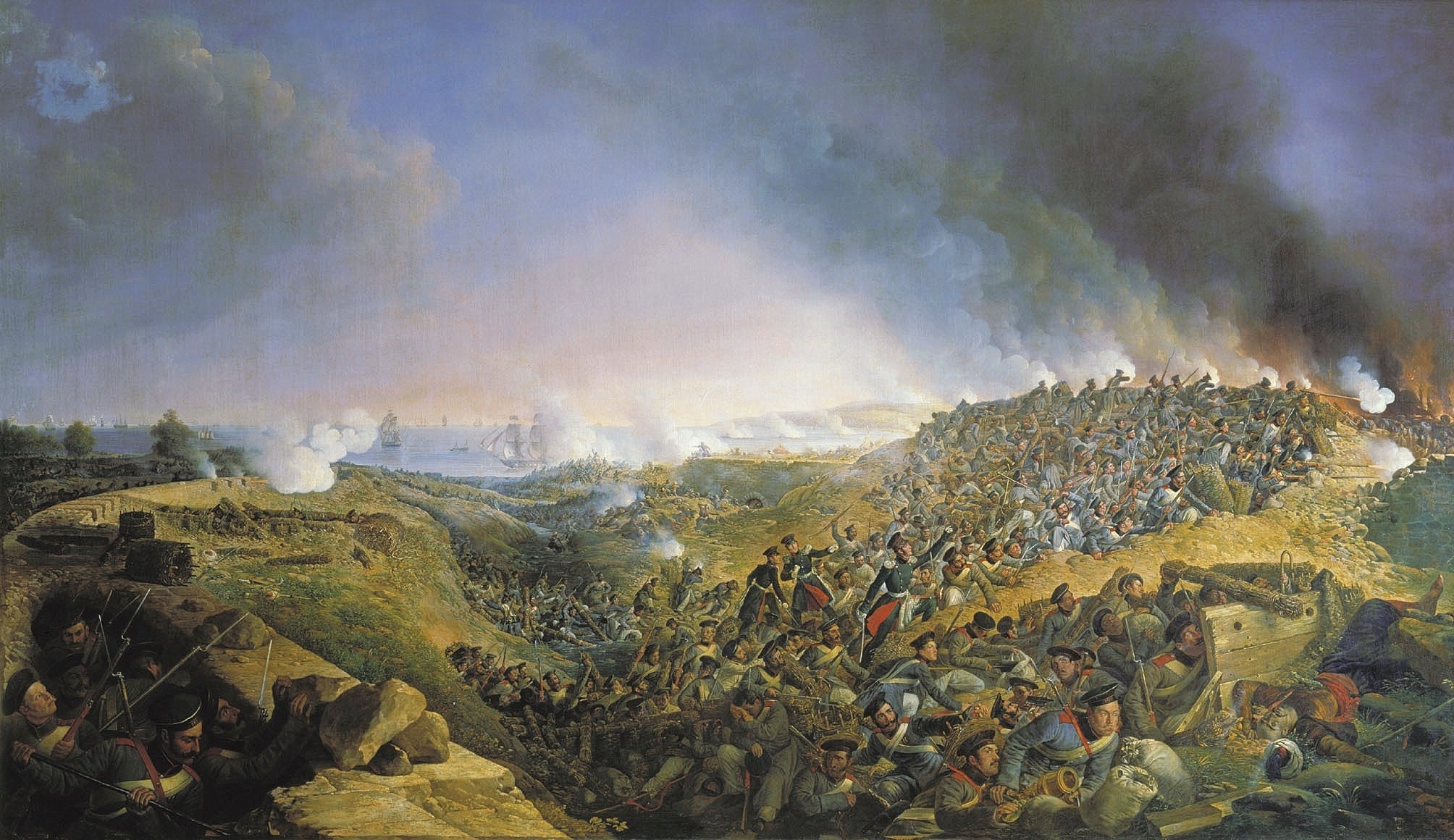
 When in 1853 Russia destroyed the entire Ottoman fleet at
When in 1853 Russia destroyed the entire Ottoman fleet at Sinop Sinop can refer to:
* Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea
** Sinop Nuclear Power Plant, was planned in 2013, but cancelled in 2018
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*** Russian ship ''Sinop'', Russian ships named after the ...
, Britain and France concluded that armed intervention on the side of the Ottomans was the only way to halt a massive Russian expansion. Even though Ottomans and Russians were on opposing sides, the roots of the ensuing Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
lay in the rivalry between the British and the Russians. The war ended unfavorably for the Russians, with the Paris peace of 1856.
The war brought a decline in Ottoman morale and a feeling of helplessness, illustrating that modern technology and superior weaponry were the most important part of a modern army, and a part that the Ottoman Empire was sorely lacking. While fighting alongside the British, French, and even the Piedmontese
Piedmontese (; autonym: or , in it, piemontese) is a language spoken by some 2,000,000 people mostly in Piedmont, northwestern region of Italy. Although considered by most linguists a separate language, in Italy it is often mistakenly regard ...
, the Ottomans could see how far they had fallen behind. Things began to change after the Crimean War.
One of these changes arose as Europeans began to see commercial opportunity in the country and the money entering via trade dramatically increased. The government also received a great deal of extra money from a uniform tax system with little corruption. The Sultan managed to get a tighter grip on the provincial bey
Bey ( ota, بك, beğ, script=Arab, tr, bey, az, bəy, tk, beg, uz, бек, kz, би/бек, tt-Cyrl, бәк, translit=bäk, cjs, пий/пек, sq, beu/bej, sh, beg, fa, بیگ, beyg/, tg, бек, ar, بك, bak, gr, μπέης) is ...
s and increased the tribute they had to pay. However, Abdülaziz
Abdulaziz ( ota, عبد العزيز, ʿAbdü'l-ʿAzîz; tr, Abdülaziz; 8 February 18304 June 1876) was the 32nd Sultan of the Ottoman Empire and reigned from 25 June 1861 to 30 May 1876, when he was overthrown in a government coup. He was a ...
, the Sultan at the time, used much of this money on furnishing and creating great palaces to rival the great ones in England and France, which he had visited. The Empire was undergoing a revolution, and throughout Anatolia a new Ottoman nationalism was appearing. It seemed as though it might be possible for the Empire to turn its decline around.
The monetary and governmental collapse combined with a new threat from Russia began the final stages of the Empire's collapse. Russia had been forced by the Crimean War to give up its ambitions of conquering the Ottoman capital of Constantinople and taking control of the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
. Instead it decided to focus on gaining power in the Balkans. The population of much of the Balkans were Slavs, as were the Russians. They also mainly followed the Eastern Orthodox Church, as did the Russians. When new movements in Russia, such as that of the Slavophile
Slavophilia (russian: Славянофильство) was an intellectual movement originating from the 19th century that wanted the Russian Empire to be developed on the basis of values and institutions derived from Russia's early history. Slavop ...
s, started to enter the area, it became agitated and prone to revolution. When the government in Constantinople tried to initiate measures to prevent an economic collapse throughout the empire, it touched off a revolt in Herzegovina in 1875. The revolt in Herzegovina quickly spread to Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
and then Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
. Soon Serbian armies also entered the war against the Turks. These revolts were the first test of the new Ottoman armies. Even though they were not up to western European standards, the army fought effectively and brutally; during the war, the Ottomans carried out the Batak massacre
The Batak massacre was a massacre of Bulgarians in Batak by Ottoman irregular cavalry troops in 1876 at the beginning of the April Uprising. The estimate for the number of victims ranges from 1,200 to 8,000, depending on the source.
Uprising ...
in 1876. Januarius MacGahan
Januarius Aloysius MacGahan əˈɡæn(June 12, 1844 – June 9, 1878) was an American journalist and war correspondent working for the ''New York Herald'' and the London '' Daily News''. His articles describing the massacre of Bulgarian civilia ...
, a journalist of the New York Herald and the London '' Daily News'' wrote of the terrible happenings after his visitation to Batak with Eugene Schuyler
Eugene Schuyler (February 26, 1840 – July 16, 1890) was a nineteenth-century American scholar, writer, explorer and diplomat. Schuyler was one of the first three Americans to earn a Ph.D. from an American university; and the first American tr ...
. According to most sources, around 5,000 people were massacred in Batak alone. The total number of victims in the April uprising according to most estimates around 15,000, which is supported by Eugene Schuyler
Eugene Schuyler (February 26, 1840 – July 16, 1890) was a nineteenth-century American scholar, writer, explorer and diplomat. Schuyler was one of the first three Americans to earn a Ph.D. from an American university; and the first American tr ...
's report, published in '' Daily News'', according to which at least 15,000 persons were killed during the April Uprising in addition to 36 villages in three districts being buried. According to Donald Quataert Donald George Quataert (September 10, 1941 – February 10, 2011) was a historian at Binghamton University. He taught courses on Middle East/Ottoman history, with an interest in labor, social and economics, during the early and modern periods. H ...
around 1,000 Muslims were killed by Christian Bulgarians and consequently 3,700 Christians were killed by Muslims.Quataert, Donald. ''The Ottoman Empire 1700–1922'', Cambridge University Press 2005, pp.69
William Ewart Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-conse ...
published his account of Ottoman atrocities in his ''Bulgarian Horrors and the Question of the East''./ref> Soon, a new Russo-Turkish war had begun. Despite fighting better than they ever had before, the advanced Ottoman armies still were not equal to the Russian forces. This time there was no help from abroad; in truth, many European nations supported the Russian war, as long as it did not get too close to Istanbul. Ten and a half months later when the war had ended the age of Ottoman domination over the Balkans was over. In the Balkans, the Russian army, having crossed the Danube, captured the Shipka Pass. The Turkish army of Osman Pasha, after a stubborn struggle, surrendered to Plevna. After that, the Russian army crossed the Balkan Mountains, defeated the remaining Turkish troops and reached the approaches to Constantinople. In the Caucasus, the Turkish army held back the Russian offensive, but after the defeat at Aladzha, retreated to
Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
, after which the Russians took Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of K ...
. On the Black Sea, the Ottoman fleet had a colossal advantage, since the Russian fleet did not recover after the Crimean War. Despite this, the hostilities on the Black Sea in this war were not important.
 In response to the Russian proximity to the straits the British, against the wishes of the Sultan, intervened in the war. A large task force representing British naval supremacy entered the straits of Marmara and anchored in view of both the royal palace and the Russian army. The British may have saved the Ottoman Empire once again, but it ended the rosy relations between the two powers that had endured since the Crimean War. Looking at the prospect of a British entry into the war the Russians decided to settle the dispute. The
In response to the Russian proximity to the straits the British, against the wishes of the Sultan, intervened in the war. A large task force representing British naval supremacy entered the straits of Marmara and anchored in view of both the royal palace and the Russian army. The British may have saved the Ottoman Empire once again, but it ended the rosy relations between the two powers that had endured since the Crimean War. Looking at the prospect of a British entry into the war the Russians decided to settle the dispute. The Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-187 ...
gave Romania and Montenegro their independence, Serbia and Russia each received extra territory, Austria was given control over Bosnia, and Bulgaria was given almost complete autonomy. The hope of the Sultan was that the other great powers would oppose such a one-sided resolution and a conference would be held to revise it. His desire became reality and in 1878 the Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at t ...
was held where Germany promised to be an "honest broker" in the treaty's revision. In the new treaty Bulgarian territory was decreased and the war indemnities were cancelled. The conference also again hurt Anglo-Ottoman relations by giving the British the island of Cyprus. While annoyed at British Prime Minister
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern p ...
Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield, (21 December 1804 – 19 April 1881) was a British statesman and Conservative politician who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a central role in the creation o ...
, the Sultan had nothing but praise for Otto von Bismarck who forced many of the major concessions upon Russia. These close Germano-Ottoman relations would persist until both empires' very end.
The Russian extension in this century developed with the main theme of supporting independence of Ottomans' former provinces and then bringing all of the Slav peoples of the Balkans under Bulgaria or using Armenians in the east sets the stage. At the end of the century from Russian perspective; Romania, Serbia and Montenegro and autonomy of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
was achieved. That alarmed the Great Powers. After the Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at t ...
the Russian expansion was controlled through stopping the expansion of Bulgaria. The Russian public felt that at the end of Congress of Berlin thousands of Russian soldiers had died for nothing.
The Balkans
 There were two main movements for the west side. The first one was performed while Ottomans were dealing with the Greek uprising, see Greek War of Independence.
The Greeks' independence war led to the Russian forces advancing into
There were two main movements for the west side. The first one was performed while Ottomans were dealing with the Greek uprising, see Greek War of Independence.
The Greeks' independence war led to the Russian forces advancing into Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
before the Turks sued for peace. The resulting Treaty of Adrianople (Edirne) on September 14, 1829, gave Russia most of the eastern shore of the Black Sea and the mouth of the Danube.
The second independence movement happened during the uprisings. See Bosnia and Herzegovina: 19th-20th centuries, Romanian War of Independence. An uprising
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
against Ottoman rule began in Herzegovina in July 1875. The Bulgarians organised the April Uprising
The April Uprising ( bg, Априлско въстание, Aprilsko vastanie) was an insurrection organised by the Bulgarians in the Ottoman Empire from April to May 1876. The regular Ottoman Army and irregular bashi-bazouk units brutally su ...
, which lasted from April to May 1876.
Serbia achieved autonomy and Russia was allowed to occupy Moldavia and Wallachia (guaranteeing their prosperity, and full "liberty of trade" for them) until Turkey had paid a large indemnity. The uprisings raised a chance for Russia ( Prince Gorchakov) and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1 ...
( Count Andrássy), who made the secret Reichstadt Agreement
The Reichstadt agreement was an agreement made between Austria-Hungary and Russia in July 1876, who were at that time in an alliance with each other and Germany in the League of the Three Emperors, or ''Dreikaiserbund''. Present were the Russian ...
on July 8, on partitioning the Balkan peninsula depending on the outcome.
During the Russo-Turkish war of 1877–1878, in February 1878 the Russian army had almost reached the Ottoman capital but, scared the city might fall, the British sent a fleet of battleships to intimidate Russia from entering the Ottoman capital. Under pressure from the British fleet to negotiate on the outcome of the war, Russia agreed a settlement under the Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-187 ...
on March 3, by which the Ottoman Empire recognized the independence of its former provinces Romania, Serbia and Montenegro and autonomy of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
. The Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at t ...
also allowed Austria to occupy Bosnia and Herzegovina and Great Britain to take over Cyprus.
The Caucasus
During the Greek uprising, the Russian empire reached the Ottoman borders in the Caucasus, which were located in the southwest of the region, as well as northeastern Anatolia. Under the terms of the Treaty of Adrianople, the Ottoman Empire recognized Russian sovereignty over westernGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, which was formerly under Ottoman suzerainty, and recognized Russian domination of present-day Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, which had been conquered a year earlier (1828) by the Russians from Qajar Iran
Qajar Iran (), also referred to as Qajar Persia, the Qajar Empire, '. Sublime State of Persia, officially the Sublime State of Iran ( fa, دولت علیّه ایران ') and also known then as the Guarded Domains of Iran ( fa, ممالک م ...
through the Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second o ...
. After the war of 1877-78, Russia also received Kars and Ardahan.
End of the Ottoman and Russian Empires (1914–23)
 During the early months of World War I,
During the early months of World War I, Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of K ...
was a key military objective for the Ottoman army. Ismail Enver
İsmail Enver, better known as Enver Pasha ( ota, اسماعیل انور پاشا; tr, İsmail Enver Paşa; 22 November 1881 – 4 August 1922) was an Ottoman military officer, revolutionary, and convicted war criminal who formed one-third o ...
who pushed the Ottoman Empire into World War I, needed a victory against the Russians to defend his position. He collected an army on the eastern border. The army was badly defeated under Enver's command at the Battle of Sarikamish
The Battle of Sarikamish (''Sarighamishi chakatamart''), russian: Сражение при Сарыкамыше; tr, Sarıkamış Harekatı, lit=''Operation Sarıkamış'' was an engagement between the Russian and Ottoman empires during World ...
January 2, 1915 against Nikolai Yudenich. This defeat was more due to the winter weather and bad planning, given the fact that Russians were actually preparing to evacuate Kars. With the loss of the eastern army, Ottoman defenses crumbled with further small battles and the Russian army succeeded in advancing as far west as Erzincan
Erzincan (; ku, Erzîngan), historically Yerznka ( hy, Երզնկա), is the capital of Erzincan Province in Eastern Turkey. Nearby cities include Erzurum, Sivas, Tunceli, Bingöl, Elazığ, Malatya, Gümüşhane, Bayburt, and Giresun. The ci ...
. The Ottoman army suffered the next heavy defeat in the Battle of Erzurum in 1916, after which the Russian army captured the whole of Western Armenia. After the 1916 campaign, the front remained stable until the Russian Revolution.
The collapse of the Russian army after the 1917 revolution left only thinly spread Armenian units to resist the inevitable Ottoman counter-attack. Before the end of World War I in 1918, the Ottoman army reformed with what was left from the middle-east branch and tried to build a line between whatever seemed to be left on their east border. The newly declared First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն), was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle ...
captured Kars in April 1918, which was eventually handed back by the future Soviet administration. That same year in March, the Baku Commune
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the List of capital cities by elevat ...
was established in the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic), or simply as Azerbaijan in Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920,''Bulletin d'Information de l'Azerbaidjan'', No. I, September 1, 1919, pp. 6–7''125 H.C.Debs.'', 58., February 24, 1920, p. 1467. Caucasian Az ...
. The commune later became the Centrocaspian Dictatorship
The Centro-Caspian Dictatorship, also known as the Central-Caspian Dictatorship (russian: Диктатура Центрокаспия, ''Diktatura Tsentrokaspiya'') ( Azerbaijani: Sentrokaspi Diktaturası), was a short-lived anti-Soviet administ ...
, in turn conquered by the Islamic Army of the Caucasus
The Islamic Army of the Caucasus ( az, Qafqaz İslam Ordusu; Turkish: ''Kafkas İslâm Ordusu'') (also translated as ''Caucasian Army of Islam'' in some sources) was a military unit of the Ottoman Empire formed on July 10, 1918. The Ottoman Min ...
, then shortly by the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French '' entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well a ...
and finally the Bolsheviks. Defeat on other fronts caused the Ottoman Empire to surrender and withdraw forces. Both the Armenian and Azerbaijani Republics ended up being part of the Soviet Union in 1920. The Soviet-Turkish border was established under the Treaty of Moscow (1921)
The Treaty of Moscow, or Treaty of Brotherhood ( tr, Moskova Antlaşması, russian: Московский договор) was an agreement between the Grand National Assembly of Turkey (TBMM), under the leadership of Mustafa Kemal, and Russia, u ...
.
List of conflicts
See also
* Ottoman wars in Europe *Battle of Sarikamish
The Battle of Sarikamish (''Sarighamishi chakatamart''), russian: Сражение при Сарыкамыше; tr, Sarıkamış Harekatı, lit=''Operation Sarıkamış'' was an engagement between the Russian and Ottoman empires during World ...
* Caucasian War
The Caucasian War (russian: Кавказская война; ''Kavkazskaya vojna'') or Caucasus War was a 19th century military conflict between the Russian Empire and various peoples of the North Caucasus who resisted subjugation during the R ...
* Crimean Khanate
* Crimean–Nogai slave raids in Eastern Europe
For over three centuries, the military of the Crimean Khanate and the Nogai Horde conducted slave raids primarily in lands controlled by Russia and Poland-Lithuania as well as other territories, often under the sponsorship of the Ottoman Empir ...
* Foreign policy of the Russian Empire
The foreign policy of the Russian Empire covers Russian foreign relations from their origins in the policies of the Tsardom of Russia (until 1721) down to the end of the Russian Empire in 1917. Under the system tsarist autocracy, the Emperors/Emp ...
* List of Serbian–Ottoman conflicts
* Russia–Turkey relations
* Russian conquest of the Caucasus
* Russo-Crimean Wars
* Russo-Persian Wars
The Russo-Persian Wars or Russo-Iranian Wars were a series of conflicts between 1651 and 1828, concerning Persia (Iran) and the Russian Empire. Russia and Persia fought these wars over disputed governance of territories and countries in the Cau ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * *Lewitter, Lucjan Ryszard. "The Russo-Polish Treaty of 1686 and Its Antecedents." ''Polish Review'' (1964): 5-2online
* *
Further reading
* Ágoston, Gábor "Military transformation in the Ottoman Empire and Russia, 1500–1800." ''Kritika: Explorations in Russian and Eurasian History'' 12.2 (2011): 281-31online
* Allen, William and Paul Muratoff. ''Caucasian Battlefields: A History Of The Wars On The Turco-Caucasian Border 1828-1921'' (2011) , * * Dupuy, R. Ernest and Trevor N. Dupuy. ''The Encyclopedia of Military History from 3500 B.C. to the Present'' (1986 and other editions), passim and 1461–1464. * * Jelavich, Barbara. ''St. Petersburg and Moscow: Tsarist and Soviet Foreign Policy, 1814–1974'' (1974) * Kagan, Frederick, and Robin Higham, eds. ''The Military History of Tsarist Russia'' (2008) * Topal, Ali E. "The effects of German Military Commission and Balkan wars on the reorganization and modernization of the Ottoman Army" (Naval Postgraduate School 2013
online
{{DEFAULTSORT:Russo-Turkish Wars * Geopolitical rivalry Wars involving the Russian Empire Wars involving Russia Military history of Ukraine History of Moldavia Bessarabia Governorate History of Wallachia Kingdom of Romania Modern history of Bulgaria Early Modern history of Georgia (country) Military operations involving the Crimean Khanate Invasions of Europe