Rus (region) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ;
Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavic, Norse, and Finnic, it was ruled by the
 During its existence, Kievan Rusʹ was known as the "land of the Rus" ( orv, ро́усьскаѧ землѧ, from the ethnonym ;
During its existence, Kievan Rusʹ was known as the "land of the Rus" ( orv, ро́усьскаѧ землѧ, from the ethnonym ;
Глава I
/
Древняя Русь на международных путях: Междисциплинарные очерки культурных, торговых, политических связей IX—XII вв.
— М.: Языки русской культуры, 2001. — c. 40, 42—45, 49—50. — . Various
The Viking World
', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4-10 (pp. 6–7). The name ''Rusʹ'' would then have the same origin as the Finnish and
 There was once controversy over whether the Rusʹ were
There was once controversy over whether the Rusʹ were
A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the war in Chechnya
' (2006), pp. 2–3. Nevertheless, the close connection between the Rusʹ and the Norse is confirmed both by extensive Scandinavian settlement in Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine and by Slavic influences in the Swedish language. Though the debate over the origin of the Rusʹ remains politically charged, there is broad agreement that if the proto-Rusʹ were indeed originally Norse, they were quickly nativized, adopting Slavic languages and other cultural practices. This position, roughly representing a scholarly consensus (at least outside of nationalist historiography), was summarized by the historian, F. Donald Logan, "in 839, the Rus were
 According to the ''Primary Chronicle'', the territories of the East Slavs in the 9th century were divided between the Varangians and the Khazars. The Varangians are first mentioned imposing tribute from Slavic and Finnic tribes in 859. In 862, the Finnic and Slavic tribes in the area of
According to the ''Primary Chronicle'', the territories of the East Slavs in the 9th century were divided between the Varangians and the Khazars. The Varangians are first mentioned imposing tribute from Slavic and Finnic tribes in 859. In 862, the Finnic and Slavic tribes in the area of
"The First East Slavic State"
''A Companion to Russian History'' (Abbott Gleason, ed., 2009), p. 37Primary Chronicle
, p.8. The Chronicle reports that Askold and Dir continued to Constantinople with a navy to attack the city in 863–66, catching the Byzantines by surprise and ravaging the surrounding area, though other accounts date the attack in 860. Patriarch Photius vividly describes the "universal" devastation of the suburbs and nearby islands, and another account further details the destruction and slaughter of the invasion. The Rusʹ turned back before attacking the city itself, due either to a storm dispersing their boats, the return of the Emperor, or in a later account, due to a miracle after a ceremonial appeal by the Patriarch and the Emperor to the Virgin. The attack was the first encounter between the Rusʹ and Byzantines and led the Patriarch to send missionaries north to engage and attempt to convert the Rusʹ and the Slavs.Majeska (2009)
p.52
Dimitri Obolensky, ''Byzantium and the Slavs'' (1994)
p.245

 Rurik led the Rusʹ until his death in about 879, bequeathing his kingdom to his kinsman, Prince Oleg, as regent for his young son,
Rurik led the Rusʹ until his death in about 879, bequeathing his kingdom to his kinsman, Prince Oleg, as regent for his young son,
p. 37
and because it controlled three main trade routes of
p. 47
Trade from the Baltic also moved south on a network of rivers and short portages along the Dnieper known as the "
pp. 40, 47. Kiev was a central outpost along the Dnieper route and a hub with the east–west overland trade route between the Khazars and the Germanic lands of Central Europe. and may have been a staging post for Radhanite Jewish traders between Western Europe, Itil and China. These commercial connections enriched Rusʹ merchants and princes, funding military forces and the construction of churches, palaces, fortifications, and further towns. Demand for luxury goods fostered production of expensive jewelry and religious wares, allowing their export, and an advanced credit and money-lending system may have also been in place.
p. 62
Magocsi (2010)
p.66
The Khazars dominated trade from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus during the 8th century during an era historians call the ' The Byzantine Empire was able to take advantage of the turmoil to expand its political influence and commercial relationships, first with the Khazars and later with the Rusʹ and other steppe groups. The Byzantines established the Theme of Cherson, formally known as Klimata, in the Crimea in the 830s to defend against raids by the Rusʹ and to protect vital grain shipments supplying Constantinople. Cherson also served as a key diplomatic link with the Khazars and others on the steppe, and it became the centre of Black Sea commerce. The Byzantines also helped the Khazars build a fortress at
The Byzantine Empire was able to take advantage of the turmoil to expand its political influence and commercial relationships, first with the Khazars and later with the Rusʹ and other steppe groups. The Byzantines established the Theme of Cherson, formally known as Klimata, in the Crimea in the 830s to defend against raids by the Rusʹ and to protect vital grain shipments supplying Constantinople. Cherson also served as a key diplomatic link with the Khazars and others on the steppe, and it became the centre of Black Sea commerce. The Byzantines also helped the Khazars build a fortress at
pp. 138–139
Spanei (2009)
pp. 66, 70
Boxed in, the Magyars were forced to migrate further west across the
p. 17
The lucrative Rusʹ trade with the Byzantine Empire had to pass through Pecheneg-controlled territory, so the need for generally peaceful relations was essential. Nevertheless, while the Primary Chronicle reports the Pechenegs entering Rusʹ territory in 915 and then making peace, they were waging war with one another again in 920.Magocsi (2010)
p. 67
Pechenegs are reported assisting the Rusʹ in later campaigns against the Byzantines, yet allied with the Byzantines against the Rusʹ at other times.
 After the Rusʹ attack on Constantinople in 860, the Byzantine Patriarch Photius sent missionaries north to convert the Rusʹ and the Slavs to Christianity. Prince
After the Rusʹ attack on Constantinople in 860, the Byzantine Patriarch Photius sent missionaries north to convert the Rusʹ and the Slavs to Christianity. Prince
p.22
The importance of this trade relationship led to military action when disputes arose. The Primary Chronicle reports that the Rusʹ attacked Constantinople again in 907, probably to secure trade access. The Chronicle glorifies the military prowess and shrewdness of Oleg, an account imbued with legendary detail. Byzantine sources do not mention the attack, but a pair of treaties in In 941, Igor led another major Rusʹ attack on Constantinople, probably over trading rights again. A navy of 10,000 vessels, including Pecheneg allies, landed on the
In 941, Igor led another major Rusʹ attack on Constantinople, probably over trading rights again. A navy of 10,000 vessels, including Pecheneg allies, landed on the
 Following the death of Grand Prince Igor in 945, his wife
Following the death of Grand Prince Igor in 945, his wife
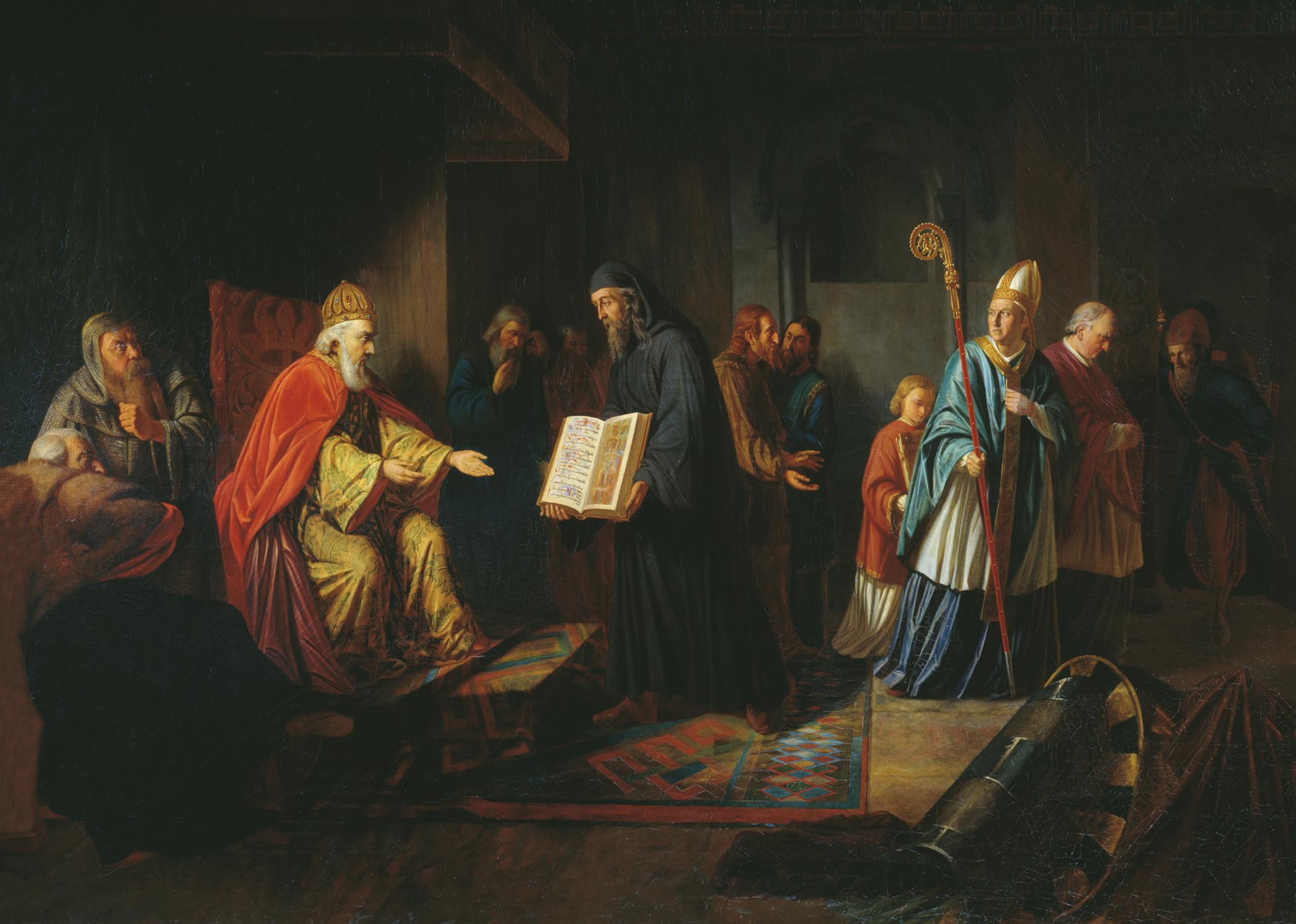 Vladimir's choice of Eastern Christianity may also have reflected his close personal ties with Constantinople, which dominated the Black Sea and hence trade on Kiev's most vital commercial route, the
Vladimir's choice of Eastern Christianity may also have reflected his close personal ties with Constantinople, which dominated the Black Sea and hence trade on Kiev's most vital commercial route, the
 Yaroslav the Wise, Yaroslav, known as "the Wise", struggled for power with his brothers. A son of
Yaroslav the Wise, Yaroslav, known as "the Wise", struggled for power with his brothers. A son of
 The gradual disintegration of the Kievan Rusʹ began in the 11th century, after the death of
The gradual disintegration of the Kievan Rusʹ began in the 11th century, after the death of  The most prominent struggle for power was the conflict that erupted after the death of Yaroslav the Wise. The rival Principality of Polotsk was contesting the power of the Grand Prince by occupying Novgorod, while Rostislav of Tmutarakan, Rostislav Vladimirovich was fighting for the Black Sea port of Tmutarakan belonging to Chernigov. Three of Yaroslav's sons that first allied together found themselves fighting each other especially after their defeat to the Cuman forces in 1068 at the Battle of the Alta River. At the same time, an uprising took place in Kiev, bringing to power Vseslav of Polotsk who supported the traditional Slavic paganism.
The ruling Grand Prince Iziaslav fled to Poland asking for support and in couple of years returned to establish the order. The affairs became even more complicated by the end of the 11th century driving the state into chaos and constant warfare. On the initiative of Vladimir II Monomakh in 1097 the first Council of Liubech, federal council of Kievan Rusʹ took place near Chernigov in the city of Liubech with the main intention to find an understanding among the fighting sides. However, even though that did not really stop the fighting, it certainly cooled things off.
By 1130, all descendants of Vseslav the Seer had been exiled to the Byzantine Empire by Mstislav the Great. The most fierce resistance to the Monomakhs was posed by the Olegovichi when the izgoi Vsevolod II of Kiev, Vsevolod II managed to become the Grand Prince of Kiev. The Volodar of Peremyshl, Rostislavichi who had initially established in Halych lands by 1189 were defeated by the Monomakh-Piast descendant Roman the Great.
The decline of Constantinople—a main trading partner of Kievan Rusʹ—played a significant role in the decline of the Kievan Rusʹ. The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, along which the goods were moving from the Black Sea (mainly Byzantine) through eastern Europe to the Baltic, was a cornerstone of Kievan wealth and prosperity. These trading routes became less important as the Byzantine Empire declined in power and Western Europe created new trade routes to Asia and the Near East. As people relied less on passing through Kievan Rusʹ territories for trade, the Kievan Rusʹ economy suffered.
The last ruler to maintain a united state was Mstislav the Great. After his death in 1132, the Kievan Rusʹ fell into recession and a rapid decline, and Mstislav's successor Yaropolk II of Kiev, instead of focusing on the external threat of the Cumans, was embroiled in conflicts with the growing power of the Novgorod Republic. In March 1169, a coalition of native princes led by Andrei Bogolyubsky of Vladimir sacked Kiev. This changed the perception of Kiev and was evidence of the fragmentation of the Kievan Rusʹ. By the end of the 12th century, the Kievan state fragmented even further, into roughly twelve different principalities.
The Crusades brought a shift in European trade routes that accelerated the decline of Kievan Rusʹ. In 1204, the forces of the Fourth Crusade sacked Constantinople, making the
The most prominent struggle for power was the conflict that erupted after the death of Yaroslav the Wise. The rival Principality of Polotsk was contesting the power of the Grand Prince by occupying Novgorod, while Rostislav of Tmutarakan, Rostislav Vladimirovich was fighting for the Black Sea port of Tmutarakan belonging to Chernigov. Three of Yaroslav's sons that first allied together found themselves fighting each other especially after their defeat to the Cuman forces in 1068 at the Battle of the Alta River. At the same time, an uprising took place in Kiev, bringing to power Vseslav of Polotsk who supported the traditional Slavic paganism.
The ruling Grand Prince Iziaslav fled to Poland asking for support and in couple of years returned to establish the order. The affairs became even more complicated by the end of the 11th century driving the state into chaos and constant warfare. On the initiative of Vladimir II Monomakh in 1097 the first Council of Liubech, federal council of Kievan Rusʹ took place near Chernigov in the city of Liubech with the main intention to find an understanding among the fighting sides. However, even though that did not really stop the fighting, it certainly cooled things off.
By 1130, all descendants of Vseslav the Seer had been exiled to the Byzantine Empire by Mstislav the Great. The most fierce resistance to the Monomakhs was posed by the Olegovichi when the izgoi Vsevolod II of Kiev, Vsevolod II managed to become the Grand Prince of Kiev. The Volodar of Peremyshl, Rostislavichi who had initially established in Halych lands by 1189 were defeated by the Monomakh-Piast descendant Roman the Great.
The decline of Constantinople—a main trading partner of Kievan Rusʹ—played a significant role in the decline of the Kievan Rusʹ. The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, along which the goods were moving from the Black Sea (mainly Byzantine) through eastern Europe to the Baltic, was a cornerstone of Kievan wealth and prosperity. These trading routes became less important as the Byzantine Empire declined in power and Western Europe created new trade routes to Asia and the Near East. As people relied less on passing through Kievan Rusʹ territories for trade, the Kievan Rusʹ economy suffered.
The last ruler to maintain a united state was Mstislav the Great. After his death in 1132, the Kievan Rusʹ fell into recession and a rapid decline, and Mstislav's successor Yaropolk II of Kiev, instead of focusing on the external threat of the Cumans, was embroiled in conflicts with the growing power of the Novgorod Republic. In March 1169, a coalition of native princes led by Andrei Bogolyubsky of Vladimir sacked Kiev. This changed the perception of Kiev and was evidence of the fragmentation of the Kievan Rusʹ. By the end of the 12th century, the Kievan state fragmented even further, into roughly twelve different principalities.
The Crusades brought a shift in European trade routes that accelerated the decline of Kievan Rusʹ. In 1204, the forces of the Fourth Crusade sacked Constantinople, making the
 In the northeast, Slavs from the Kievan region colonized the territory that later would become the Grand Duchy of Moscow by subjugating and merging with the Finnic tribes already occupying the area. The city of Rostov, the oldest centre of the northeast, was supplanted first by Suzdal and then by the city of Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir, which become the capital of Vladimir-Suzdal. The combined principality of Vladimir-Suzdal asserted itself as a major power in Kievan Rusʹ in the late 12th century.
In 1169, Prince Andrey Bogolyubskiy of Vladimir-Suzdal sacked the city of Kiev and took over the title of the grand prince to claim primacy in Rusʹ. Prince Andrey then installed his younger brother, who ruled briefly in Kiev while Andrey continued to rule his realm from Suzdal. In 1299, in the wake of the
In the northeast, Slavs from the Kievan region colonized the territory that later would become the Grand Duchy of Moscow by subjugating and merging with the Finnic tribes already occupying the area. The city of Rostov, the oldest centre of the northeast, was supplanted first by Suzdal and then by the city of Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir, which become the capital of Vladimir-Suzdal. The combined principality of Vladimir-Suzdal asserted itself as a major power in Kievan Rusʹ in the late 12th century.
In 1169, Prince Andrey Bogolyubskiy of Vladimir-Suzdal sacked the city of Kiev and took over the title of the grand prince to claim primacy in Rusʹ. Prince Andrey then installed his younger brother, who ruled briefly in Kiev while Andrey continued to rule his realm from Suzdal. In 1299, in the wake of the
 Following the Mongol invasion of Cumania (or the Kipchaks), in which case many Cuman rulers fled to Rusʹ, such as Köten, the state finally disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of Rusʹ, fragmenting it into successor principalities who paid tribute to the Golden Horde (the so-called Tatar Yoke). In the late 15th century, the Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Grand Dukes began taking over former Kievan territories and proclaimed themselves the sole legal successors of the Kievan principality according to the protocols of the medieval theory of translatio imperii.
On the western periphery, Kievan Rusʹ was succeeded by the Principality of Galicia-Volhynia. Later, as these territories, now part of modern central
Following the Mongol invasion of Cumania (or the Kipchaks), in which case many Cuman rulers fled to Rusʹ, such as Köten, the state finally disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of Rusʹ, fragmenting it into successor principalities who paid tribute to the Golden Horde (the so-called Tatar Yoke). In the late 15th century, the Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Grand Dukes began taking over former Kievan territories and proclaimed themselves the sole legal successors of the Kievan principality according to the protocols of the medieval theory of translatio imperii.
On the western periphery, Kievan Rusʹ was succeeded by the Principality of Galicia-Volhynia. Later, as these territories, now part of modern central

 Due to the expansion of trade and its geographical proximity, Kiev became the most important trade centre and chief among the communes; therefore the leader of Kiev gained political "control" over the surrounding areas. This princedom emerged from a coalition of traditional patriarchic family communes banded together in an effort to increase the applicable workforce and expand the productivity of the land. This union developed the first major cities in the Rusʹ and was the first notable form of self-government. As these communes became larger, the emphasis was taken off the family holdings and placed on the territory that surrounded. This shift in ideology became known as the ''vervʹ''.
In the 11th and the 12th centuries, the princes and their retinues, which were a mixture of Slavs, Slavic and
Due to the expansion of trade and its geographical proximity, Kiev became the most important trade centre and chief among the communes; therefore the leader of Kiev gained political "control" over the surrounding areas. This princedom emerged from a coalition of traditional patriarchic family communes banded together in an effort to increase the applicable workforce and expand the productivity of the land. This union developed the first major cities in the Rusʹ and was the first notable form of self-government. As these communes became larger, the emphasis was taken off the family holdings and placed on the territory that surrounded. This shift in ideology became known as the ''vervʹ''.
In the 11th and the 12th centuries, the princes and their retinues, which were a mixture of Slavs, Slavic and
 Kievan Rusʹ, although sparsely populated compared to Western Europe, was not only the largest contemporary European state in terms of area but also culturally advanced.
Literacy in Kiev, Novgorod and other large cities was high; as birch bark documents attest, inhabitants exchanged love letters and prepared cheat sheets for schools. Novgorod had a sewage system and road surface, wood pavement not often found in other cities at the time. The
Kievan Rusʹ, although sparsely populated compared to Western Europe, was not only the largest contemporary European state in terms of area but also culturally advanced.
Literacy in Kiev, Novgorod and other large cities was high; as birch bark documents attest, inhabitants exchanged love letters and prepared cheat sheets for schools. Novgorod had a sewage system and road surface, wood pavement not often found in other cities at the time. The
 The Mongol Empire invaded Kievan Rusʹ in the 13th century, destroying numerous cities, including Ryazan, Kolomna, Moscow, Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir and Kiev. Giovanni de Plano Carpini, the Pope's envoy to the Mongol Great Khan, traveled through Kiev in February 1246 and wrote:
The Mongol Empire invaded Kievan Rusʹ in the 13th century, destroying numerous cities, including Ryazan, Kolomna, Moscow, Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir and Kiev. Giovanni de Plano Carpini, the Pope's envoy to the Mongol Great Khan, traveled through Kiev in February 1246 and wrote:
 Byzantium quickly became the main Route from the Varangians to the Greeks, trading and cultural partner for Kiev, but relations were not always friendly. The most serious conflict between the two powers was the Sviatoslav I#Campaigns in the Balkans, war of 968–971 in Bulgaria, but several Rusʹ raiding expeditions against the Byzantine cities of the Black Sea coast and Constantinople itself are also recorded. Although most were repulsed, they were concluded by Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria, trade treaties that were generally favourable to the Rusʹ.
Rusʹ-Byzantine relations became closer following the marriage of the ''porphyrogenita'' Anna Porphyrogenita, Anna to
Byzantium quickly became the main Route from the Varangians to the Greeks, trading and cultural partner for Kiev, but relations were not always friendly. The most serious conflict between the two powers was the Sviatoslav I#Campaigns in the Balkans, war of 968–971 in Bulgaria, but several Rusʹ raiding expeditions against the Byzantine cities of the Black Sea coast and Constantinople itself are also recorded. Although most were repulsed, they were concluded by Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria, trade treaties that were generally favourable to the Rusʹ.
Rusʹ-Byzantine relations became closer following the marriage of the ''porphyrogenita'' Anna Porphyrogenita, Anna to


 In 988, the Christian Church in Rusʹ territorially fell under the jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople after it was officially adopted as the state religion. According to several chronicles after that date the predominant cult of Slavic paganism was persecuted.
The exact date of creation of the Kiev Metropolis is uncertain, as well as its first church leader. It is generally considered that the first head was Michael I of Kiev (metropolitan), Michael I of Kiev; however, some sources claim it to be Leontiy, who is often placed after Michael or Anastas Chersonesos, who became the first bishop of the Church of the Tithes. The first metropolitan to be confirmed by historical sources is Theopemp, who was appointed by Patriarch Alexius of Constantinople in 1038. Before 1015 there were five dioceses: Kiev, Chernihiv, Bilhorod, Volodymyr, Novgorod, and soon thereafter Bila Tserkva, Yuriy-upon-Ros. The Kiev Metropolitan sent his own delegation to the Council of Bari in 1098.
After the sacking of Kiev in 1169, part of the Kiev metropolis started to move to Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir-upon-Klyazma, concluding the move sometime after 1240 when Kiev was taken by Batu Khan. Metropolitan Maxim was the first metropolitan who chose Vladimir-upon-Klyazma as his official residence in 1299. As a result, in 1303, Lev I of Galicia petitioned Patriarch Athanasius I of Constantinople for the creation of a new Halych metropolis; however, it only existed until 1347.
The Church of the Tithes was chosen as the first Cathedral Temple. In 1037, the cathedral was transferred to the newly built Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kiev. Upon the transferring of the metropolitan seat in 1299, the Dormition Cathedral, Vladimir was chosen as the new cathedral.
By the mid-13th century, the dioceses of Kiev Metropolis (988) were as follows: Kiev (988), Pereyaslav, Chernihiv (991), Volodymyr-Volynsky (992), Turov (1005), Polotsk (1104), Novgorod (~990s), Smolensk (1137), Murom (1198), Peremyshl (1120), Halych (1134), Vladimir-upon-Klyazma (1215), Rostov (991), Bilhorod, Yuriy (1032), Chełm (1235) and Tver (1271). There also were dioceses in Carpathian Ruthenia, Zakarpattia and Tmutarakan. In 1261 the Sarai-Batu diocese was established.
In 988, the Christian Church in Rusʹ territorially fell under the jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople after it was officially adopted as the state religion. According to several chronicles after that date the predominant cult of Slavic paganism was persecuted.
The exact date of creation of the Kiev Metropolis is uncertain, as well as its first church leader. It is generally considered that the first head was Michael I of Kiev (metropolitan), Michael I of Kiev; however, some sources claim it to be Leontiy, who is often placed after Michael or Anastas Chersonesos, who became the first bishop of the Church of the Tithes. The first metropolitan to be confirmed by historical sources is Theopemp, who was appointed by Patriarch Alexius of Constantinople in 1038. Before 1015 there were five dioceses: Kiev, Chernihiv, Bilhorod, Volodymyr, Novgorod, and soon thereafter Bila Tserkva, Yuriy-upon-Ros. The Kiev Metropolitan sent his own delegation to the Council of Bari in 1098.
After the sacking of Kiev in 1169, part of the Kiev metropolis started to move to Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir-upon-Klyazma, concluding the move sometime after 1240 when Kiev was taken by Batu Khan. Metropolitan Maxim was the first metropolitan who chose Vladimir-upon-Klyazma as his official residence in 1299. As a result, in 1303, Lev I of Galicia petitioned Patriarch Athanasius I of Constantinople for the creation of a new Halych metropolis; however, it only existed until 1347.
The Church of the Tithes was chosen as the first Cathedral Temple. In 1037, the cathedral was transferred to the newly built Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kiev. Upon the transferring of the metropolitan seat in 1299, the Dormition Cathedral, Vladimir was chosen as the new cathedral.
By the mid-13th century, the dioceses of Kiev Metropolis (988) were as follows: Kiev (988), Pereyaslav, Chernihiv (991), Volodymyr-Volynsky (992), Turov (1005), Polotsk (1104), Novgorod (~990s), Smolensk (1137), Murom (1198), Peremyshl (1120), Halych (1134), Vladimir-upon-Klyazma (1215), Rostov (991), Bilhorod, Yuriy (1032), Chełm (1235) and Tver (1271). There also were dioceses in Carpathian Ruthenia, Zakarpattia and Tmutarakan. In 1261 the Sarai-Batu diocese was established.
File:CHODZKO(1861) CARTE DES PAYS SLAVO-POLONAIS AUX VIII ET IX SIECLE.jpg, Map of 8th- to 9th-century Rusʹ by Leonard Chodzko (1861)
File:Polska Rosja Skandynawia w IX w.jpg, Map of 9th-century Rusʹ by Antoine Philippe Houze (1844)
File:LEROY-BEAULIEU(1893) p1.097 RUSSIA IN THE 9th CENTURY.jpg, Map of 9th-century Rusʹ by F. S. Weller (1893)
File:Europe 1000.jpg, Map of Rusʹ in Europe in 1000 (1911)
File:Shepherd-c-066-067.jpg, Map of Rusʹ in 1097 (1911)
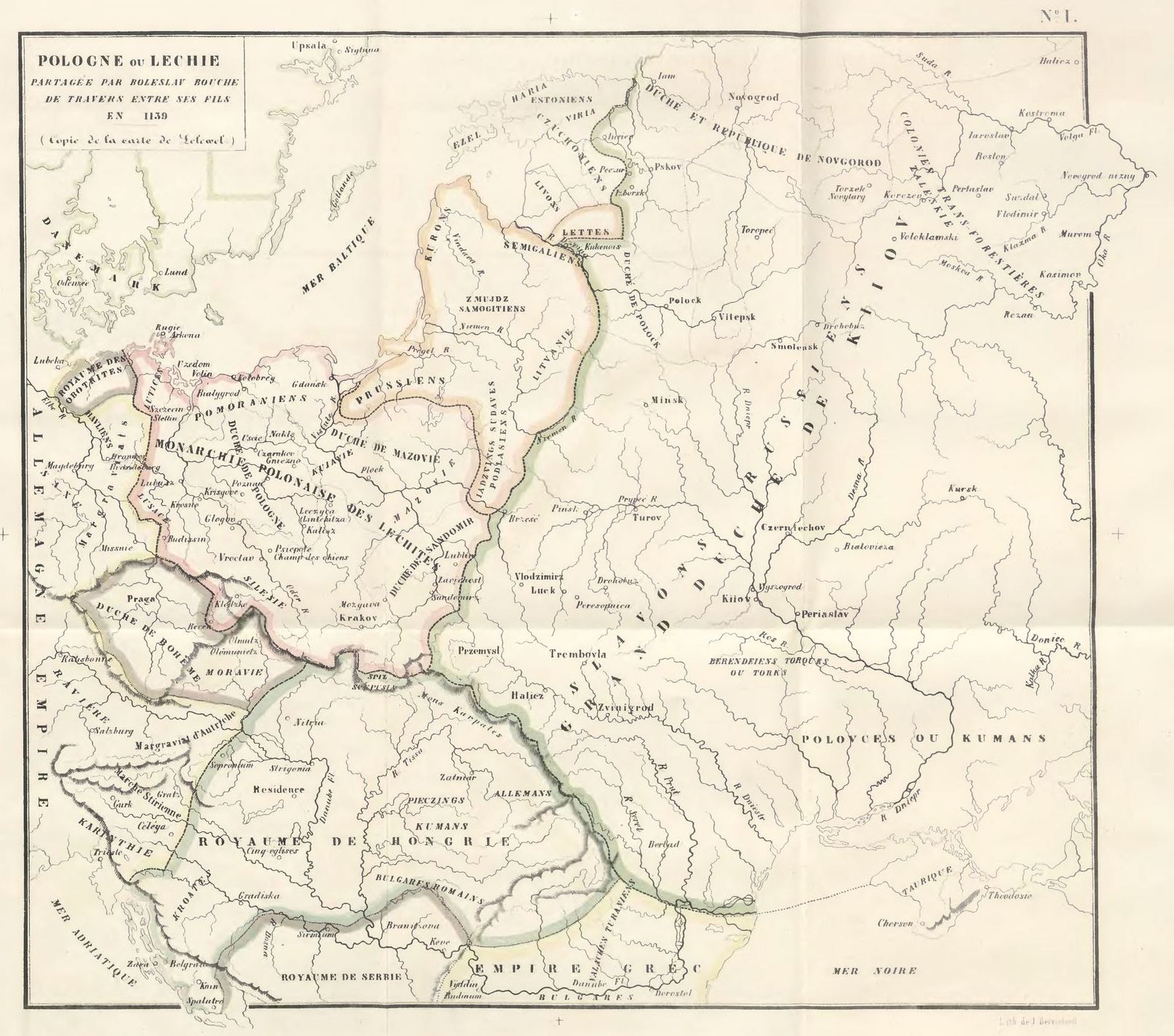
File:Europe-1139.jpg, Map of 1139 by Joachim Lelewel (1865)
File:Центры Руси по Идриси.jpg, Fragment of the 1154 Tabula Rogeriana by Muhammad al-Idrisi
Russia
Stephen Velychenko. New Wine Old Bottle. Ukrainian History, Muscovite /Russian Imperial Myths and the Cambridge History of Russia
*
Ancient Rus: trade and crafts
Chronology of Kievan Rusʹ 859–1240.
{{Authority control Kievan Rus', States and territories established in the 870s States and territories disestablished in 1240 882 establishments 1240 disestablishments in Europe Former countries in Europe Former Slavic countries Medieval Belarus Medieval Russia Medieval Ukraine 9th-century establishments in Russia Historical regions Former countries
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors ...
from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16.Kievan RusEncyclopædia Britannica Online. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavic, Norse, and Finnic, it was ruled by the
Rurik dynasty
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was ...
, founded by the Varangian
The Varangians (; non, Væringjar; gkm, Βάραγγοι, ''Várangoi'';Varangian
" Online Etymo ...
prince " Online Etymo ...
Rurik
Rurik (also Ryurik; orv, Рюрикъ, Rjurikŭ, from Old Norse '' Hrøríkʀ''; russian: Рюрик; died 879); be, Рурык, Ruryk was a semi-legendary Varangian chieftain of the Rus' who in the year 862 was invited to reign in Novgor ...
. The modern nations of Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
all claim Kievan Rusʹ as their cultural ancestor, with Belarus and Russia deriving their names from it. At its greatest extent in the mid-11th century, Kievan Rusʹ stretched from the White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is s ...
in the north to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
in the south and from the headwaters
The headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.
Definition
The ...
of the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
in the west to the Taman Peninsula
The Taman Peninsula (russian: Тама́нский полуо́стров, ''Tamanskiy poluostrov'') is a peninsula in the present-day Krasnodar Krai of Russia, which borders the Sea of Azov to the North, the Strait of Kerch to the West and the ...
in the east, uniting the East Slavic tribes.
According to the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'', the first ruler to start uniting East Slavic lands into what would become Kievan Rusʹ was Prince Oleg (879–912). He extended his control from Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ...
south along the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
river valley to protect trade from Khazar
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
incursions from the east, and took control of the city of Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
. Sviatoslav I (943–972) achieved the first major territorial expansion of the state, fighting a war of conquest against the Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
. Vladimir the Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych ( orv, Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь, ''Volodiměrъ Svętoslavičь'';, ''Uladzimir'', russian: Владимир, ''Vladimir'', uk, Володимир, ''Volodymyr''. Se ...
(980–1015) introduced Christianity with his own baptism and, by decree, extended it to all inhabitants of Kiev and beyond. Kievan Rusʹ reached its greatest extent under Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
(1019–1054); his sons assembled and issued its first written legal code, the ''Russkaya Pravda
The ''Russkaya Pravda'' (Rus' Justice, Rus' Truth, or Russian Justice; orv, Правда роусьскаꙗ, ''Pravda Rusĭskaya'' (13th century, 1280), Правда Руськая, ''Pravda Rus'kaya'' (second half of the 15th century); russian: ...
'', shortly after his death.Bushkovitch, Paul. ''A Concise History of Russia''. Cambridge University Press. 2011.
The state began to decline in the late 11th century, gradually disintegrating into various rival regional powers throughout the 12th century. It was further weakened by external factors, such as the decline of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire experienced several cycles of growth and decay over the course of nearly a thousand years, including major losses during the Early Muslim conquests of the 7th century. However, modern historians generally agree that the star ...
, its major economic partner, and the accompanying diminution of trade routes
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
through its territory. It finally fell to the Mongol invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
in the mid-13th century, though the Rurik dynasty would continue to rule until the death of Feodor I of Russia
Fyodor I Ivanovich (russian: Фёдор I Иванович) or Feodor I Ioannovich (russian: Феодор I Иоаннович; 31 May 1557 – 17 January (NS) 1598), also known as Feodor the Bellringer (russian: Феодор Звонарь), ...
in 1598.
Name
 During its existence, Kievan Rusʹ was known as the "land of the Rus" ( orv, ро́усьскаѧ землѧ, from the ethnonym ;
During its existence, Kievan Rusʹ was known as the "land of the Rus" ( orv, ро́усьскаѧ землѧ, from the ethnonym ; Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: ; Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
: '), in Greek as , in Old French as , in Latin as or (with local German spelling variants ''Ruscia'' and ''Ruzzia''), and from the 12th century also as or . ''Назаренко А. В.'Глава I
/
Древняя Русь на международных путях: Междисциплинарные очерки культурных, торговых, политических связей IX—XII вв.
— М.: Языки русской культуры, 2001. — c. 40, 42—45, 49—50. — . Various
etymologies
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words a ...
have been proposed, including , the Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
designation for Sweden or ''Ros'', a tribe from the middle Dnieper valley region.
According to the prevalent theory, the name ''Rusʹ'', like the Proto-Finnic name for Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
(''*rootsi''), is derived from an Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
term for 'men who row' (''rods-'') because rowing was the main method of navigating the rivers of Eastern Europe, and could be linked to the Swedish coastal area of Roslagen
Roslagen is the name of the coastal areas of Uppland province in Sweden, which also constitutes the northern part of the Stockholm archipelago.
Historically, it was the name for all the coastal areas of the Baltic Sea, including the eastern p ...
(''Rus-law'') or ''Roden'', as it was known in earlier times.Stefan Brink, 'Who were the Vikings?', in The Viking World
', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4-10 (pp. 6–7). The name ''Rusʹ'' would then have the same origin as the Finnish and
Estonian
Estonian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Estonia, a country in the Baltic region in northern Europe
* Estonians, people from Estonia, or of Estonian descent
* Estonian language
* Estonian cuisine
* Estonian culture
See also
*
...
names for Sweden: ''Ruotsi'' and ''Rootsi''."Russ, adj. and n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, June 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/169069. Accessed 12 January 2021.
The term ''Kievan Rusʹ'' (russian: Ки́евская Русь, translit=Kiyevskaya Rus) was coined in the 19th century in Russian historiography
This list of Russian historians includes the famous historians, as well as archaeologists, paleographers, genealogists and other representatives of auxiliary historical disciplines from the Russian Federation, the Soviet Union, the Russian Empire ...
to refer to the period when the centre was in Kiev. In the 19th century it also appeared in uk, Ки́ївська Русь, translit=Kyivska Rus, translit-std=ungegn. In English, the term was introduced in the early 20th century, when it was found in the 1913 English translation of Vasily Klyuchevsky's ''A History of Russia'', to distinguish the early polity from successor states, which were also named ''Rusʹ''. The variant ''Kyivan Rusʹ'' appeared in English-language scholarship by the 1950s. Later, the Russian term was rendered into be, Кіеўская Русь, translit=Kiyewskaya Rus’, translit-std=bgn/pcgn or and rue, Київска Русь, translit=Kyïvska Rus′, translit-std=ala-lc.
The historically accurate but rare spelling ''Kyevan Rusʹ'', based on Old East Slavic
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Old Russian; be, старажытнаруская мова; russian: древнерусский язык; uk, давньоруська мова) was a language used during the 9th–15th centuries by East ...
() 'Kyiv', is also occasionally seen.
History
Origin
Prior to the emergence of Kievan Rusʹ in the 9th century, most of the area north of theBlack Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, which roughly overlaps with modern-day Ukraine and Belarus, was primarily populated by eastern Slavic tribes. In the northern region around Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ...
were the Ilmen Slavs
The Novgorod Slavs, Ilmen Slavs (russian: Ильменские слове́не, ''Il'menskiye slovene''), or Slovenes (not to be confused with the Slovenian Slovenes) were the northernmost tribe of the Early Slavs, and inhabited the shores of L ...
and neighboring Krivichi
The Krivichs (Kryvichs) ( be, крывічы, kryvičý, ; rus, кри́вичи, p='krʲivʲɪtɕɪ, kríviči) were a tribal union of Early East Slavs between the 6th and the 12th centuries. It is suggested that originally the Krivichi were nat ...
, who occupied territories surrounding the headwaters of the West Dvina, Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
and Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catch ...
rivers. To their north, in the Ladoga and Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance fo ...
regions, were the Finnic Chud
Chud or Chude ( orv, чудь, in Finnic languages: tšuudi, čuđit) is a term historically applied in the early East Slavic annals to several Finnic peoples in the area of what is now Estonia, Karelia and Northwestern Russia.
Arguably, th ...
tribe. In the south, in the area around Kiev, were the Poliane, a group of Slavicized tribes with Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
origins, the Drevliane to the west of the Dnieper, and the Severiane to the east. To their north and east were the Vyatichi, and to their south was forested land settled by Slav farmers, giving way to steppelands populated by nomadic herdsmen.
 There was once controversy over whether the Rusʹ were
There was once controversy over whether the Rusʹ were Varangians
The Varangians (; non, Væringjar; gkm, Βάραγγοι, ''Várangoi'';Varangian
" Online Etymo ...
or Slavs, however, more recently scholarly attention has focused more on debating how quickly an ancestrally Norse people assimilated into Slavic culture. "The controversies over the nature of the Rus and the origins of the Russian state have bedevilled Viking studies, and indeed Russian history, for well over a century. It is historically certain that the Rus were Swedes. The evidence is incontrovertible, and that a debate still lingers at some levels of historical writing is clear evidence of the holding power of received notions. The debate over this issue – futile, embittered, tendentious, doctrinaire – served to obscure the most serious and genuine historical problem which remains: the assimilation of these Viking Rus into the Slavic people among whom they lived. The principal historical question is not whether the Rus were Scandinavians or Slavs, but, rather, how quickly these Scandinavian Rus became absorbed into Slavic life and culture." This uncertainty is due largely to a paucity of contemporary sources. Attempts to address this question instead rely on archaeological evidence, the accounts of foreign observers, and legends and literature from centuries later. To some extent the controversy is related to the foundation myths of modern states in the region. This often unfruitful debate over origins has periodically devolved into competing nationalist narratives of dubious scholarly value being promoted directly by various government bodies, in a number of states. This was seen in the Stalinist period, when Soviet historiography sought to distance the Rusʹ from any connection to Germanic tribes, in an effort to dispel Nazi propaganda claiming the Russian state owed its existence and origins to the supposedly racially superior Norse tribes. More recently, in the context of resurgent nationalism in post-Soviet states, Anglophone scholarship has analyzed renewed efforts to use this debate to create ethno-nationalist foundation stories, with governments sometimes directly involved in the project. Conferences and publications questioning the Norse origins of the Rusʹ have been supported directly by state policy in some cases, and the resultant foundation myths have been included in some school textbooks in Russia.
While Varangians were Norse traders and " Online Etymo ...
Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
, some Russian and Ukrainian nationalist historians argue that the Rusʹ were themselves Slavs (see Anti-Normanism
Anti-Normanism is a movement of historical revisionism in opposition to the mainstream narrative of the Viking Age in Eastern Europe, and concerns the origin of Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and their historic predecessor, Kievan Rus'. At the c ...
). Normanist theories focus on the earliest written source for the East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert ...
, the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'', which was produced in the 12th century. Nationalist accounts on the other hand have suggested that the Rusʹ were present before the arrival of the Varangians, noting that only a handful of Scandinavian words can be found in Russian and that Scandinavian names in the early chronicles were soon replaced by Slavic names.David R. Stone
David Russell Stone (born 1968) is an American military historian and the William Eldridge Odom Professor of Russian Studies in the Strategy and Policy Department at the U.S. Naval War College.
Stone received a Bachelor of Arts degree in histo ...
, A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the war in Chechnya
' (2006), pp. 2–3. Nevertheless, the close connection between the Rusʹ and the Norse is confirmed both by extensive Scandinavian settlement in Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine and by Slavic influences in the Swedish language. Though the debate over the origin of the Rusʹ remains politically charged, there is broad agreement that if the proto-Rusʹ were indeed originally Norse, they were quickly nativized, adopting Slavic languages and other cultural practices. This position, roughly representing a scholarly consensus (at least outside of nationalist historiography), was summarized by the historian, F. Donald Logan, "in 839, the Rus were
Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
; in 1043 the Rus were Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
". Recent scholarship has attempted to move past the narrow and politicized debate on origins, to focus on how and why assimilation took place so quickly. Some modern DNA testing also points to Viking origins, not only of some of the early Rusʹ princely family and/or their retinues, but also links to possible brethren from neighboring countries like Sviatopolk I of Kiev
Sviatopolk I Vladimirovich (''Sviatopolk the Accursed'', the ''Accursed Prince''; orv, Свѧтоплъкъ, translit=Svętoplŭkŭ; russian: Святополк Окаянный; uk, Святополк Окаянний; c. 980 – 1019) was the ...
.
Ahmad ibn Fadlan
Aḥmad ibn Faḍlān ibn al-ʿAbbās ibn Rāšid ibn Ḥammād, ( ar, أحمد بن فضلان بن العباس بن راشد بن حماد; ) commonly known as Ahmad ibn Fadlan, was a 10th-century Muslim traveler, famous for his account of hi ...
, an Arab traveler during the 10th century, provided one of the earliest written descriptions of the Rusʹ: "They are as tall as a date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
, blond and ruddy, so that they do not need to wear a tunic nor a cloak; rather the men among them wear garments that only cover half of his body and leaves one of his hands free." Liutprand of Cremona
Liutprand, also Liudprand, Liuprand, Lioutio, Liucius, Liuzo, and Lioutsios (c. 920 – 972),"LIUTPRAND OF CREMONA" in '' The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'', Oxford University Press, New York & Oxford, 1991, p. 1241. was a historian, diplomat, ...
, who was twice an envoy to the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
court (949 and 968), identifies the "Russi" with the Norse ("the Russi, whom we call Norsemen by another name") but explains the name as a Greek term referring to their physical traits ("A certain people made up of a part of the Norse, whom the Greeks call ..the Russi on account of their physical features, we designate as Norsemen because of the location of their origin."). Leo the Deacon, a 10th-century Byzantine historian and chronicler, refers to the Rusʹ as "Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
" and notes that they tended to adopt Greek rituals and customs. But 'Scythians' in Greek parlance is used predominantly as a generic term for nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
s.
Invitation of the Varangians
 According to the ''Primary Chronicle'', the territories of the East Slavs in the 9th century were divided between the Varangians and the Khazars. The Varangians are first mentioned imposing tribute from Slavic and Finnic tribes in 859. In 862, the Finnic and Slavic tribes in the area of
According to the ''Primary Chronicle'', the territories of the East Slavs in the 9th century were divided between the Varangians and the Khazars. The Varangians are first mentioned imposing tribute from Slavic and Finnic tribes in 859. In 862, the Finnic and Slavic tribes in the area of Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ...
rebelled against the Varangians, driving them "back beyond the sea and, refusing them further tribute, set out to govern themselves." The tribes had no laws, however, and soon began to make war with one another, prompting them to invite the Varangians back to rule them and bring peace to the region:
The three brothers—Rurik
Rurik (also Ryurik; orv, Рюрикъ, Rjurikŭ, from Old Norse '' Hrøríkʀ''; russian: Рюрик; died 879); be, Рурык, Ruryk was a semi-legendary Varangian chieftain of the Rus' who in the year 862 was invited to reign in Novgor ...
, Sineus and Truvor
Sineus and Truvor were the brothers of Rurik, a chieftain of the Varangian Rus tribe considered to be the founder of the Rurik dynasty, which ruled the Kievan Rus'.
Description
According to the 12th-century Kievan ''Primary Chronicle'', a gr ...
—established themselves in Novgorod, Beloozero
Belozersk (russian: Белозе́рск), known as Beloozero (russian: Белоозеро, label=none) until 1777, is a town and the administrative center of Belozersky District in Vologda Oblast, Russia, located on the southern bank of Lake B ...
and Izborsk
Izborsk (russian: Избо́рск; et, Irboska; vro, Irbosk, Irbuska, label=Seto) is a rural locality ( village) in Pechorsky District of Pskov Oblast, Russia. It contains one of the most ancient and impressive fortresses of Western Russia. T ...
, respectively. Two of the brothers died, and Rurik became the sole ruler of the territory and progenitor of the Rurik dynasty
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was ...
. A short time later, two of Rurik's men, Askold and Dir
Askold and Dir (''Haskuldr'' or ''Hǫskuldr'' and ''Dyr'' or ''Djur'' in Old Norse; died in 882), mentioned in both the Primary Chronicle and the Nikon Chronicle, were the earliest known ''purportedly Norse'' rulers of Kiev.
Primary Chronicle ...
, asked him for permission to go to Tsargrad (Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
). On their way south, they discovered "a small city on a hill," Kiev, captured it and the surrounding country from the Khazars, populated the region with more Varangians, and "established their dominion over the country of the Polyanians."Janet Martin"The First East Slavic State"
''A Companion to Russian History'' (Abbott Gleason, ed., 2009), p. 37Primary Chronicle
, p.8. The Chronicle reports that Askold and Dir continued to Constantinople with a navy to attack the city in 863–66, catching the Byzantines by surprise and ravaging the surrounding area, though other accounts date the attack in 860. Patriarch Photius vividly describes the "universal" devastation of the suburbs and nearby islands, and another account further details the destruction and slaughter of the invasion. The Rusʹ turned back before attacking the city itself, due either to a storm dispersing their boats, the return of the Emperor, or in a later account, due to a miracle after a ceremonial appeal by the Patriarch and the Emperor to the Virgin. The attack was the first encounter between the Rusʹ and Byzantines and led the Patriarch to send missionaries north to engage and attempt to convert the Rusʹ and the Slavs.Majeska (2009)
p.52
Dimitri Obolensky, ''Byzantium and the Slavs'' (1994)
p.245
Foundation of the Kievan state

 Rurik led the Rusʹ until his death in about 879, bequeathing his kingdom to his kinsman, Prince Oleg, as regent for his young son,
Rurik led the Rusʹ until his death in about 879, bequeathing his kingdom to his kinsman, Prince Oleg, as regent for his young son, Igor
Igor may refer to:
People
* Igor (given name), an East Slavic given name and a list of people with the name
* Mighty Igor (1931–2002), former American professional wrestler
* Igor Volkoff, a professional wrestler from NWA All-Star Wrestling
* ...
. In 880–82, Oleg led a military force south along the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
river, capturing Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ...
and Lyubech
Liubech ( uk, Любеч, russian: Любеч, pl, Lubecz) is an urban-type settlement, previously a small ancient town (first mentioned in 882) connected with many important events in the Principality of Chernigov since the times of Kievan Rus'. ...
before reaching Kiev, where he deposed and killed Askold and Dir, proclaimed himself prince, and declared Kiev the " mother of Rusʹ cities." Oleg set about consolidating his power over the surrounding region and the riverways north to Novgorod, imposing tribute on the East Slav tribes.
In 883, he conquered the Drevlians
The Drevlians ( uk, Древляни, Drevliany, russian: Древля́не, Drevlyane) were a tribe of Early East Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries, which inhabited the territories of Polesia and right-bank Ukraine, west of the ea ...
, imposing a fur tribute on them. By 885 he had subjugated the Poliane, Severiane, Vyatichi, and Radimichs
The Radimichs (also Radimichi) ( be, Радзiмiчы, russian: Радимичи, uk, Радимичі and pl, Radymicze) were an East Slavic tribe of the last several centuries of the 1st millennium, which inhabited upper east parts of the ...
, forbidding them to pay further tribute to the Khazars. Oleg continued to develop and expand a network of Rusʹ forts in Slav lands, begun by Rurik in the north.
The new Kievan state prospered due to its abundant supply of furs, beeswax
Beeswax (''cera alba'') is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus ''Apis''. The wax is formed into scales by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in or at the hive. The hive work ...
, honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
and slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
for export,Walter Moss, A History of Russia: To 1917 (2005)p. 37
and because it controlled three main trade routes of
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
. In the north, Novgorod served as a commercial link between the Baltic Sea and the Volga trade route
In the Middle Ages, the Volga trade route connected Northern Europe and Northwestern Russia with the Caspian Sea and the Sasanian Empire, via the Volga River. The Rus used this route to trade with Muslim countries on the southern shores of the ...
to the lands of the Volga Bulgars
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria, was a historic Bulgar state that existed between the 7th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now European Russia. Volga Bulgaria was a multi-ethnic state ...
, the Khazars, and across the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
as far as Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, providing access to markets and products from Central Asia and the Middle East.Martin (2009)p. 47
Trade from the Baltic also moved south on a network of rivers and short portages along the Dnieper known as the "
route from the Varangians to the Greeks
The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks was a medieval trade route that connected Scandinavia, Kievan Rus' and the Eastern Roman Empire. The route allowed merchants along its length to establish a direct prosperous trade with the Empir ...
," continuing to the Black Sea and on to Constantinople.Martin (2009)pp. 40, 47. Kiev was a central outpost along the Dnieper route and a hub with the east–west overland trade route between the Khazars and the Germanic lands of Central Europe. and may have been a staging post for Radhanite Jewish traders between Western Europe, Itil and China. These commercial connections enriched Rusʹ merchants and princes, funding military forces and the construction of churches, palaces, fortifications, and further towns. Demand for luxury goods fostered production of expensive jewelry and religious wares, allowing their export, and an advanced credit and money-lending system may have also been in place.
Early foreign relations
Volatile steppe politics
The rapid expansion of the Rusʹ to the south led to conflict and volatile relationships with the Khazars and other neighbors on the Pontic steppe.Magocsi (2010)p. 62
Magocsi (2010)
p.66
The Khazars dominated trade from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus during the 8th century during an era historians call the '
Pax Khazarica
Pax Khazarica (Latin for "Khazar Peace") is a historiographical term, modeled after the original phrase ''Pax Romana'', applied to the period (roughly 700–950 AD) during which the Khazar Khaganate dominated the Pontic steppe and the Caucasus M ...
', trading and frequently allying with the Byzantine Empire against Persians and Arabs. In the late 8th century, the collapse of the Göktürk Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of Bumi ...
led the Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic ...
and the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
, Ugrians
Historically, the Ugrians or Ugors were the ancestors of the Hungarians of Central Europe, and the Khanty and Mansi people of the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug of Russia. The name is sometimes also used in a modern context as a cover term for th ...
and Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
from Central Asia, to migrate west into the steppe region, leading to military conflict, disruption of trade, and instability within the Khazar Khaganate. The Rusʹ and Slavs had earlier allied with the Khazars against Arab raids on the Caucasus, but they increasingly worked against them to secure control of the trade routes.
 The Byzantine Empire was able to take advantage of the turmoil to expand its political influence and commercial relationships, first with the Khazars and later with the Rusʹ and other steppe groups. The Byzantines established the Theme of Cherson, formally known as Klimata, in the Crimea in the 830s to defend against raids by the Rusʹ and to protect vital grain shipments supplying Constantinople. Cherson also served as a key diplomatic link with the Khazars and others on the steppe, and it became the centre of Black Sea commerce. The Byzantines also helped the Khazars build a fortress at
The Byzantine Empire was able to take advantage of the turmoil to expand its political influence and commercial relationships, first with the Khazars and later with the Rusʹ and other steppe groups. The Byzantines established the Theme of Cherson, formally known as Klimata, in the Crimea in the 830s to defend against raids by the Rusʹ and to protect vital grain shipments supplying Constantinople. Cherson also served as a key diplomatic link with the Khazars and others on the steppe, and it became the centre of Black Sea commerce. The Byzantines also helped the Khazars build a fortress at Sarkel
Sarkel (or Šarkel, literally ''white house'' in the Khazar language was a large limestone-and-brick fortress in the present-day Rostov Oblast of Russia, on the left bank of the lower Don River.
It was built by the Khazars with Byzantine as ...
on the Don river to protect their northwest frontier against incursions by the Turkic migrants and the Rusʹ, and to control caravan trade routes and the portage between the Don and Volga rivers.
The expansion of the Rusʹ put further military and economic pressure on the Khazars, depriving them of territory, tributaries and trade. In around 890, Oleg waged an indecisive war in the lands of the lower Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and t ...
and Dnieper rivers with the Tivertsi and the Ulichs, who were likely acting as vassals of the Magyars, blocking Rusʹ access to the Black Sea. In 894, the Magyars and Pechenegs were drawn into the wars
''The Wars'' is a 1977 novel by Timothy Findley that follows Robert Ross, a nineteen-year-old Canadian who enlists in World War I after the death of his beloved older sister in an attempt to escape both his grief and the social norms of oppressi ...
between the Byzantines and the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
. The Byzantines arranged for the Magyars to attack Bulgarian territory from the north, and Bulgaria in turn persuaded the Pechenegs to attack the Magyars from their rear.John V. A. Fine, ''The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century'' (1991)pp. 138–139
Spanei (2009)
pp. 66, 70
Boxed in, the Magyars were forced to migrate further west across the
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretche ...
into the Hungarian plain, depriving the Khazars of an important ally and a buffer from the Rusʹ. The migration of the Magyars allowed Rusʹ access to the Black Sea, and they soon launched excursions into Khazar territory along the sea coast, up the Don river, and into the lower Volga region. The Rusʹ were raiding and plundering into the Caspian Sea region from 864, with the first large-scale expedition in 913, when they extensively raided Baku, Gilan, Mazandaran and penetrated into the Caucasus.
As the 10th century progressed, the Khazars were no longer able to command tribute from the Volga Bulgars, and their relationship with the Byzantines deteriorated, as Byzantium increasingly allied with the Pechenegs against them. The Pechenegs were thus secure to raid the lands of the Khazars from their base between the Volga and Don rivers, allowing them to expand to the west. Rusʹ relations with the Pechenegs were complex, as the groups alternately formed alliances with and against one another. The Pechenegs were nomads roaming the steppe raising livestock which they traded with the Rusʹ for agricultural goods and other products.Martin (2003)p. 17
The lucrative Rusʹ trade with the Byzantine Empire had to pass through Pecheneg-controlled territory, so the need for generally peaceful relations was essential. Nevertheless, while the Primary Chronicle reports the Pechenegs entering Rusʹ territory in 915 and then making peace, they were waging war with one another again in 920.Magocsi (2010)
p. 67
Pechenegs are reported assisting the Rusʹ in later campaigns against the Byzantines, yet allied with the Byzantines against the Rusʹ at other times.
Rusʹ–Byzantine relations
 After the Rusʹ attack on Constantinople in 860, the Byzantine Patriarch Photius sent missionaries north to convert the Rusʹ and the Slavs to Christianity. Prince
After the Rusʹ attack on Constantinople in 860, the Byzantine Patriarch Photius sent missionaries north to convert the Rusʹ and the Slavs to Christianity. Prince Rastislav of Moravia
Rastislav or Rostislav, also known as St. Rastislav, (Latin: ''Rastiz'', Greek: Ῥασισθλάβος / ''Rhasisthlábos'') was the second known ruler of Moravia (846–870).Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 20. Although he started his reign as vass ...
had requested the Emperor to provide teachers to interpret the holy scriptures, so in 863 the brothers Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (815–885) were two brothers and Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are credited w ...
were sent as missionaries, due to their knowledge of the Slavonic language. The Slavs had no written language, so the brothers devised the Glagolitic alphabet
The Glagolitic script (, , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed to have been created in the 9th century by Saint Cyril, a monk from Thessalonica. He and his brother Saint Methodius were sent by the Byzan ...
, later replaced by Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
(developed in the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Eur ...
) and standardized the language of the Slavs, later known as Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic () was the first Slavic literary language.
Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with standardizing the language and using it in translating the Bible and othe ...
. They translated portions of the Bible and drafted the first Slavic civil code and other documents, and the language and texts spread throughout Slavic territories, including Kievan Rusʹ. The mission of Cyril and Methodius served both evangelical and diplomatic purposes, spreading Byzantine cultural influence in support of imperial foreign policy. In 867 the Patriarch announced that the Rusʹ had accepted a bishop, and in 874 he speaks of an "Archbishop of the Rusʹ."
Relations between the Rusʹ and Byzantines became more complex after Oleg took control over Kiev, reflecting commercial, cultural, and military concerns. The wealth and income of the Rusʹ depended heavily upon trade with Byzantium. Constantine Porphyrogenitus
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Ka ...
described the annual course of the princes of Kiev, collecting tribute from client tribes, assembling the product into a flotilla of hundreds of boats, conducting them down the Dnieper to the Black Sea, and sailing to the estuary of the Dniester, the Danube delta, and on to Constantinople. On their return trip they would carry silk fabrics, spices, wine, and fruit.Vernadsky (1976)p.22
The importance of this trade relationship led to military action when disputes arose. The Primary Chronicle reports that the Rusʹ attacked Constantinople again in 907, probably to secure trade access. The Chronicle glorifies the military prowess and shrewdness of Oleg, an account imbued with legendary detail. Byzantine sources do not mention the attack, but a pair of treaties in
907
__NOTOC__
Year 907 ( CMVII) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
* Rus'–Byzantine War: Varangian prince Oleg of Novgorod leads the K ...
and 911
911 or 9/11 may refer to:
Dates
* AD 911
* 911 BC
* September 11
** 9/11, the September 11 attacks of 2001
** 11 de Septiembre, Chilean coup d'état in 1973 that outed the democratically elected Salvador Allende
* November 9
Numbers
* 911 ...
set forth a trade agreement with the Rusʹ, the terms suggesting pressure on the Byzantines, who granted the Rusʹ quarters and supplies for their merchants and tax-free trading privileges in Constantinople.
The Chronicle provides a mythic tale of Oleg's death. A sorcerer prophesies that the death of the Grand Prince
Grand prince or great prince (feminine: grand princess or great princess) ( la, magnus princeps; Greek: ''megas archon''; russian: великий князь, velikiy knyaz) is a title of nobility ranked in honour below emperor, equal of king ...
would be associated with a certain horse. Oleg has the horse sequestered, and it later dies. Oleg goes to visit the horse and stands over the carcass, gloating that he had outlived the threat, when a snake strikes him from among the bones, and he soon becomes ill and dies. The Chronicle reports that Prince Igor succeeded Oleg in 913, and after some brief conflicts with the Drevlians and the Pechenegs, a period of peace ensued for over twenty years.
 In 941, Igor led another major Rusʹ attack on Constantinople, probably over trading rights again. A navy of 10,000 vessels, including Pecheneg allies, landed on the
In 941, Igor led another major Rusʹ attack on Constantinople, probably over trading rights again. A navy of 10,000 vessels, including Pecheneg allies, landed on the Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
n coast and devastated the Asiatic shore of the Bosphorus.Ostrogorski, p.277 The attack was well timed, perhaps due to intelligence, as the Byzantine fleet was occupied with the Arabs in the Mediterranean, and the bulk of its army was stationed in the east. The Rusʹ burned towns, churches and monasteries, butchering the people and amassing booty. The emperor arranged for a small group of retired ships to be outfitted with Greek fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon used by the Eastern Roman Empire beginning . Used to set fire to enemy ships, it consisted of a combustible compound emitted by a flame-throwing weapon. Some historians believe it could be ignited on contact w ...
throwers and sent them out to meet the Rusʹ, luring them into surrounding the contingent before unleashing the Greek fire.Logan, p.193.
Liutprand of Cremona
Liutprand, also Liudprand, Liuprand, Lioutio, Liucius, Liuzo, and Lioutsios (c. 920 – 972),"LIUTPRAND OF CREMONA" in '' The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'', Oxford University Press, New York & Oxford, 1991, p. 1241. was a historian, diplomat, ...
wrote that "the Rusʹ, seeing the flames, jumped overboard, preferring water to fire. Some sank, weighed down by the weight of their breastplates and helmets; others caught fire." Those captured were beheaded. The ploy dispelled the Rusʹ fleet, but their attacks continued into the hinterland as far as Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
, with many atrocities reported as victims were crucified and set up for use as targets. At last a Byzantine army arrived from the Balkans to drive the Rusʹ back, and a naval contingent reportedly destroyed much of the Rusʹ fleet on its return voyage (possibly an exaggeration since the Rusʹ soon mounted another attack). The outcome indicates increased military might by Byzantium since 911, suggesting a shift in the balance of power.
Igor returned to Kiev keen for revenge. He assembled a large force of warriors from among neighboring Slavs and Pecheneg allies, and sent for reinforcements of Varangians from "beyond the sea." In 944 the Rusʹ force advanced again on the Greeks, by land and sea, and a Byzantine force from Cherson responded. The Emperor sent gifts and offered tribute in lieu of war, and the Rusʹ accepted. Envoys were sent between the Rusʹ, the Byzantines, and the Bulgarians in 945, and a peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surre ...
was completed. The agreement again focused on trade, but this time with terms less favorable to the Rusʹ, including stringent regulations on the conduct of Rusʹ merchants in Cherson and Constantinople and specific punishments for violations of the law. The Byzantines may have been motivated to enter the treaty out of concern of a prolonged alliance of the Rusʹ, Pechenegs, and Bulgarians against them, though the more favorable terms further suggest a shift in power.
Sviatoslav
 Following the death of Grand Prince Igor in 945, his wife
Following the death of Grand Prince Igor in 945, his wife Olga
Olga may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Olga (name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters named Olga or Olha
* Michael Algar (born 1962), English singer also known as "Olga"
Places
Russia
* Olga, Russia, ...
ruled as regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
in Kiev until their son Sviatoslav
Sviatoslav (russian: Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ; uk, Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ) is a Russian and Ukrainian given name of Slavic origin. Cognates include Svetoslav, Svatoslav, , Svetislav. It has a Pre-Christian pagan characte ...
reached maturity (c. 963). His decade-long reign over Rusʹ was marked by rapid expansion through the conquest of the Khazars of the Pontic steppe and the invasion of the Balkans. By the end of his short life, Sviatoslav carved out for himself the largest state in Europe, eventually moving his capital from Kiev to Pereyaslavets
Pereyaslavets ( East Slavic: ) or Preslavets ( bg, Преславец) was a trade city located near mouths of the Danube. The city's name is derived from that of the Bulgarian capital of the time, Preslav, and means Little Preslav (). In Greek ...
on the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
in 969.
In contrast with his mother's conversion to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
, Sviatoslav, like his druzhina
In the medieval history of Kievan Rus' and Early Poland, a druzhina, drużyna, or družyna ( Slovak and cz, družina; pl, drużyna; ; , ''druzhýna'' literally a "fellowship") was a retinue in service of a Slavic chieftain, also called ''knyaz ...
, remained a staunch pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. I ...
. Due to his abrupt death in an ambush in 972, Sviatoslav's conquests, for the most part, were not consolidated into a functioning empire, while his failure to establish a stable succession led to a fratricidal
Fratricide (, from the Latin words ' "brother" and the assimilated root of ' "to kill, to cut down") is the act of killing one's own brother.
It can either be done directly or via the use of either a hired or an indoctrinated intermediary (a ...
feud among his sons, which resulted in two of his three sons being killed.
Reign of Vladimir and Christianisation
It is not clearly documented when the title of the Grand Duke was first introduced, but the importance of the Kiev principality was recognized after the death of Sviatoslav I in 972 and the ensuing struggle betweenVladimir the Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych ( orv, Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь, ''Volodiměrъ Svętoslavičь'';, ''Uladzimir'', russian: Владимир, ''Vladimir'', uk, Володимир, ''Volodymyr''. Se ...
and Yaropolk I. The region of Kiev dominated the state of Kievan Rusʹ for the next two centuries. The grand prince
Grand prince or great prince (feminine: grand princess or great princess) ( la, magnus princeps; Greek: ''megas archon''; russian: великий князь, velikiy knyaz) is a title of nobility ranked in honour below emperor, equal of king ...
or grand duke ( be, вялікі князь, translit=vyaliki knyaz’, translit-std=bgn/pcgn or , russian: великий князь, translit=velikiy kniaz, rue, великый князь, translit=velykŷĭ kni͡az′, translit-std=ala-lc, uk, великий князь, translit=velykyi kniaz, translit-std=ungegn) of Kiev controlled the lands around the city, and his formally subordinate relatives ruled the other cities and paid him tribute. The zenith of the state's power came during the reigns of Vladimir the Great (980–1015) and Prince Yaroslav I the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
(1019–1054). Both rulers continued the steady expansion of Kievan Rusʹ that had begun under Oleg.
Vladimir had been prince of Novgorod The Prince of Novgorod (russian: Князь новгородский, ''knyaz novgorodskii'') was the chief executive of the Republic of Novgorod. The office was originally an appointed one until the late eleventh or early twelfth century, then bec ...
when his father Sviatoslav I died in 972. He was forced to flee to Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
in 976 after his half-brother Yaropolk had murdered his other brother Oleg
Oleg (russian: Олег), Oleh ( uk, Олег), or Aleh ( be, Алег) is an East Slavic given name. The name is very common in Russia, Ukraine and Belаrus. It derives from the Old Norse ''Helgi'' ( Helge), meaning "holy", "sacred", or "bless ...
and taken control of Rus. In Scandinavia, with the help of his relative Earl
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant " chieftain", particu ...
Håkon Sigurdsson, ruler of Norway, Vladimir assembled a Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
army and reconquered Novgorod and Kiev from Yaropolk.
As Prince of Kiev, Vladimir's most notable achievement was the Christianization of Kievan Rusʹ, a process that began in 988. The Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
states that when Vladimir had decided to accept a new faith instead of the traditional idol-worship (paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. I ...
) of the Slavs, he sent out some of his most valued advisors and warriors as emissaries to different parts of Europe. They visited the Christians of the Latin Rite
Latin liturgical rites, or Western liturgical rites, are Catholic rites of public worship employed by the Latin Church, the largest particular church '' sui iuris'' of the Catholic Church, that originated in Europe where the Latin language onc ...
, the Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
s, and the Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
before finally arriving in Constantinople. They rejected Islam because, among other things, it prohibited the consumption of alcohol, and Judaism because the god of the Jews had permitted his chosen people
Throughout history, various groups of people have considered themselves to be the chosen people of a deity, for a particular purpose. The phenomenon of a "chosen people" is well known among the Israelites and Jews, where the term ( he, עם ס� ...
to be deprived of their country.Janet Martin, Medieval Russia, 980–1584, (Cambridge, 1995), p. 6-7
They found the ceremonies in the Roman church to be dull. But at Constantinople, they were so astounded by the beauty of the cathedral of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
and the liturgical service held there that they made up their minds there and then about the faith they would like to follow. Upon their arrival home, they convinced Vladimir that the faith of the Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
The canonical hours a ...
was the best choice of all, upon which Vladimir made a journey to Constantinople and arranged to marry Princess Anna, the sister of Byzantine emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
.
 Vladimir's choice of Eastern Christianity may also have reflected his close personal ties with Constantinople, which dominated the Black Sea and hence trade on Kiev's most vital commercial route, the
Vladimir's choice of Eastern Christianity may also have reflected his close personal ties with Constantinople, which dominated the Black Sea and hence trade on Kiev's most vital commercial route, the Dnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
. Adherence to the Eastern Church
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and ...
had long-range political, cultural, and religious consequences. The church had a liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
written in Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
and a corpus of translations from Greek that had been produced for the Slavic peoples
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout ...
. This literature facilitated the conversion to Christianity of the Eastern Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert Hud ...
and introduced them to rudimentary Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC, marking the end of the Greek Dark Ages. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and the period in which Greece and most Greek-inhabited lands were part of the Roman Empi ...
, science, and historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians h ...
without the necessity of learning Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(there were some merchants who did business with Greeks and likely had an understanding of contemporary business Greek).
In contrast, educated people in medieval Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Europe learned Latin (language), Latin. Enjoying independence from the Roman authority and free from tenets of Latin learning, the East Slavs developed their own literature and fine arts, quite distinct from those of other Eastern Orthodox countries. (See Old East Slavic language and Architecture of Kievan Rus for details). Following the East–West Schism, Great Schism of 1054, the Rusʹ church maintained communion with both Rome and Constantinople for some time, but along with most of the Eastern churches it eventually split to follow the Eastern Orthodox. That being said, unlike other parts of the Greek world, Kievan Rusʹ did not have a strong hostility to the Western world.
Golden age
 Yaroslav the Wise, Yaroslav, known as "the Wise", struggled for power with his brothers. A son of
Yaroslav the Wise, Yaroslav, known as "the Wise", struggled for power with his brothers. A son of Vladimir the Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych ( orv, Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь, ''Volodiměrъ Svętoslavičь'';, ''Uladzimir'', russian: Владимир, ''Vladimir'', uk, Володимир, ''Volodymyr''. Se ...
, he was prince of Novgorod at the time of his father's death in 1015. Subsequently, his eldest surviving brother, Svyatopolk the Accursed, according to domestic but not foreign sources, killed three of his other brothers and seized power in Kiev. Yaroslav, with the active support of the Novgorodians and the help of Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
mercenaries, defeated Svyatopolk and became the grand prince of Kiev in 1019.
Although he first established his rule over Kiev in 1019, he did not have uncontested rule of all of Kievan Rusʹ until 1036. Like Vladimir, Yaroslav was eager to improve relations with the rest of Europe, especially the Byzantine Empire. Yaroslav's granddaughter, Eupraxia of Kiev, Eupraxia, the daughter of his son Vsevolod I, Prince of Kiev, was married to Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor. Yaroslav also arranged marriages for his sister and three daughters to the kings of Poland, France, Hungary and Norway.
Yaroslav promulgated the first East Slavic law code, ''Russkaya Pravda
The ''Russkaya Pravda'' (Rus' Justice, Rus' Truth, or Russian Justice; orv, Правда роусьскаꙗ, ''Pravda Rusĭskaya'' (13th century, 1280), Правда Руськая, ''Pravda Rus'kaya'' (second half of the 15th century); russian: ...
''; built Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kiev and Saint Sophia Cathedral in Novgorod; patronized local clergy and monasticism; and is said to have founded a school system. Yaroslav's sons developed the great Kiev Pechersk Lavra (monastery), which functioned in Kievan Rusʹ as an ecclesiastical academy.
In the centuries that followed the state's foundation, Rurik dynasty, Rurik's descendants shared power over Kievan Rusʹ. Princely succession moved from elder to younger brother and from uncle to nephew, as well as from father to son. Junior members of the dynasty usually began their official careers as rulers of a minor district, progressed to more lucrative principalities, and then competed for the coveted throne of Kiev.
Fragmentation and decline
 The gradual disintegration of the Kievan Rusʹ began in the 11th century, after the death of
The gradual disintegration of the Kievan Rusʹ began in the 11th century, after the death of Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
. The position of the Grand Prince of Kiev was weakened by the growing influence of regional clans.
An unconventional power succession system was established (rota system) whereby power was transferred to the eldest member of the ruling dynasty rather than from father to son, i.e. in most cases to the eldest brother of the ruler, fomenting constant hatred and rivalry within the royal family. Familicide was frequently deployed to obtain power and can be traced particularly during the time of the Yaroslavichi (sons of Yaroslav), when the established system was skipped in the establishment of Vladimir II Monomakh as the Grand Prince of Kiev, in turn creating major squabbles between Oleg I of Chernigov, Olegovichi from Chernigov, Monomakhs from Pereyaslav, Izyaslav I of Kiev, Izyaslavichi from Principality of Turov, Turov/Volhynia, and Principality of Polotsk, Polotsk Princes.
 The most prominent struggle for power was the conflict that erupted after the death of Yaroslav the Wise. The rival Principality of Polotsk was contesting the power of the Grand Prince by occupying Novgorod, while Rostislav of Tmutarakan, Rostislav Vladimirovich was fighting for the Black Sea port of Tmutarakan belonging to Chernigov. Three of Yaroslav's sons that first allied together found themselves fighting each other especially after their defeat to the Cuman forces in 1068 at the Battle of the Alta River. At the same time, an uprising took place in Kiev, bringing to power Vseslav of Polotsk who supported the traditional Slavic paganism.
The ruling Grand Prince Iziaslav fled to Poland asking for support and in couple of years returned to establish the order. The affairs became even more complicated by the end of the 11th century driving the state into chaos and constant warfare. On the initiative of Vladimir II Monomakh in 1097 the first Council of Liubech, federal council of Kievan Rusʹ took place near Chernigov in the city of Liubech with the main intention to find an understanding among the fighting sides. However, even though that did not really stop the fighting, it certainly cooled things off.
By 1130, all descendants of Vseslav the Seer had been exiled to the Byzantine Empire by Mstislav the Great. The most fierce resistance to the Monomakhs was posed by the Olegovichi when the izgoi Vsevolod II of Kiev, Vsevolod II managed to become the Grand Prince of Kiev. The Volodar of Peremyshl, Rostislavichi who had initially established in Halych lands by 1189 were defeated by the Monomakh-Piast descendant Roman the Great.
The decline of Constantinople—a main trading partner of Kievan Rusʹ—played a significant role in the decline of the Kievan Rusʹ. The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, along which the goods were moving from the Black Sea (mainly Byzantine) through eastern Europe to the Baltic, was a cornerstone of Kievan wealth and prosperity. These trading routes became less important as the Byzantine Empire declined in power and Western Europe created new trade routes to Asia and the Near East. As people relied less on passing through Kievan Rusʹ territories for trade, the Kievan Rusʹ economy suffered.
The last ruler to maintain a united state was Mstislav the Great. After his death in 1132, the Kievan Rusʹ fell into recession and a rapid decline, and Mstislav's successor Yaropolk II of Kiev, instead of focusing on the external threat of the Cumans, was embroiled in conflicts with the growing power of the Novgorod Republic. In March 1169, a coalition of native princes led by Andrei Bogolyubsky of Vladimir sacked Kiev. This changed the perception of Kiev and was evidence of the fragmentation of the Kievan Rusʹ. By the end of the 12th century, the Kievan state fragmented even further, into roughly twelve different principalities.
The Crusades brought a shift in European trade routes that accelerated the decline of Kievan Rusʹ. In 1204, the forces of the Fourth Crusade sacked Constantinople, making the
The most prominent struggle for power was the conflict that erupted after the death of Yaroslav the Wise. The rival Principality of Polotsk was contesting the power of the Grand Prince by occupying Novgorod, while Rostislav of Tmutarakan, Rostislav Vladimirovich was fighting for the Black Sea port of Tmutarakan belonging to Chernigov. Three of Yaroslav's sons that first allied together found themselves fighting each other especially after their defeat to the Cuman forces in 1068 at the Battle of the Alta River. At the same time, an uprising took place in Kiev, bringing to power Vseslav of Polotsk who supported the traditional Slavic paganism.
The ruling Grand Prince Iziaslav fled to Poland asking for support and in couple of years returned to establish the order. The affairs became even more complicated by the end of the 11th century driving the state into chaos and constant warfare. On the initiative of Vladimir II Monomakh in 1097 the first Council of Liubech, federal council of Kievan Rusʹ took place near Chernigov in the city of Liubech with the main intention to find an understanding among the fighting sides. However, even though that did not really stop the fighting, it certainly cooled things off.
By 1130, all descendants of Vseslav the Seer had been exiled to the Byzantine Empire by Mstislav the Great. The most fierce resistance to the Monomakhs was posed by the Olegovichi when the izgoi Vsevolod II of Kiev, Vsevolod II managed to become the Grand Prince of Kiev. The Volodar of Peremyshl, Rostislavichi who had initially established in Halych lands by 1189 were defeated by the Monomakh-Piast descendant Roman the Great.
The decline of Constantinople—a main trading partner of Kievan Rusʹ—played a significant role in the decline of the Kievan Rusʹ. The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, along which the goods were moving from the Black Sea (mainly Byzantine) through eastern Europe to the Baltic, was a cornerstone of Kievan wealth and prosperity. These trading routes became less important as the Byzantine Empire declined in power and Western Europe created new trade routes to Asia and the Near East. As people relied less on passing through Kievan Rusʹ territories for trade, the Kievan Rusʹ economy suffered.
The last ruler to maintain a united state was Mstislav the Great. After his death in 1132, the Kievan Rusʹ fell into recession and a rapid decline, and Mstislav's successor Yaropolk II of Kiev, instead of focusing on the external threat of the Cumans, was embroiled in conflicts with the growing power of the Novgorod Republic. In March 1169, a coalition of native princes led by Andrei Bogolyubsky of Vladimir sacked Kiev. This changed the perception of Kiev and was evidence of the fragmentation of the Kievan Rusʹ. By the end of the 12th century, the Kievan state fragmented even further, into roughly twelve different principalities.
The Crusades brought a shift in European trade routes that accelerated the decline of Kievan Rusʹ. In 1204, the forces of the Fourth Crusade sacked Constantinople, making the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
trade route marginal. At the same time, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword (of the Northern Crusades) were conquering the Baltic region, Baltic region and threatening the Lands of Novgorod. Concurrently with it, the Ruthenian Federation of Kievan Rusʹ started to disintegrate into smaller principalities as the Rurik dynasty grew. The local Orthodox Christianity of Kievan Rusʹ, while struggling to establish itself in the predominantly pagan state and losing its main base in Constantinople, was on the brink of extinction. Some of the main regional centres that developed later were Novgorod, Chernigov, Halych, Kiev, Ryazan, Vladimir-upon-Klyazma, Volodimer-Volyn and Polotsk.
Novgorod Republic
In the north, the Republic of Novgorod prospered because it controlled trade routes from the River Volga to the Baltic Sea. As Kievan Rusʹ declined, Novgorod became more independent. A local oligarchy ruled Novgorod; major government decisions were made by a town assembly, which also elected a prince as the city's military leader. In 1136, Novgorod revolted against Kiev, and became independent. Now an independent City-state, city republic, and referred to as "Lord Novgorod the Great" it would spread its "mercantile interest" to the west and the north; to the Baltic Sea and the low-populated forest regions, respectively. In 1169, Novgorod acquired its own Diocese of Novgorod, archbishop, named Ilya (Archbishop of Novgorod), Ilya, a sign of further increased importance and political independence. Novgorod enjoyed a wide degree of autonomy although being closely associated with the Kievan Rus.Northeast
 In the northeast, Slavs from the Kievan region colonized the territory that later would become the Grand Duchy of Moscow by subjugating and merging with the Finnic tribes already occupying the area. The city of Rostov, the oldest centre of the northeast, was supplanted first by Suzdal and then by the city of Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir, which become the capital of Vladimir-Suzdal. The combined principality of Vladimir-Suzdal asserted itself as a major power in Kievan Rusʹ in the late 12th century.
In 1169, Prince Andrey Bogolyubskiy of Vladimir-Suzdal sacked the city of Kiev and took over the title of the grand prince to claim primacy in Rusʹ. Prince Andrey then installed his younger brother, who ruled briefly in Kiev while Andrey continued to rule his realm from Suzdal. In 1299, in the wake of the
In the northeast, Slavs from the Kievan region colonized the territory that later would become the Grand Duchy of Moscow by subjugating and merging with the Finnic tribes already occupying the area. The city of Rostov, the oldest centre of the northeast, was supplanted first by Suzdal and then by the city of Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir, which become the capital of Vladimir-Suzdal. The combined principality of Vladimir-Suzdal asserted itself as a major power in Kievan Rusʹ in the late 12th century.
In 1169, Prince Andrey Bogolyubskiy of Vladimir-Suzdal sacked the city of Kiev and took over the title of the grand prince to claim primacy in Rusʹ. Prince Andrey then installed his younger brother, who ruled briefly in Kiev while Andrey continued to rule his realm from Suzdal. In 1299, in the wake of the Mongol invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
, the metropolitan bishop, metropolitan moved from Kiev to the city of Vladimir and Vladimir-Suzdal.
Southwest
To the southwest, the principality of Halych had developed trade relations with its Poland, Polish, Hungary, Hungarian and Lithuanian neighbours and emerged as the local successor to Kievan Rusʹ. In 1199, Roman the Great, Prince Roman Mstislavych united the two previously separate principalities of Halych and Volhynia, Volyn. In 1202 he conquered Kiev, and assumed the title of Knyaz of Kievan Rusʹ, which was held by the rulers of Vladimir-Suzdal since 1169. His son, Daniel of Galicia, Prince Daniel (r. 1238–1264) looked for support from the West. He accepted a crown as a "Rex Rusiae" ("King of Rus") from the Roman papacy, apparently doing so without breaking with Constantinople. In 1370, the patriarch of the Eastern Orthodox Church in Constantinople granted the King of Poland a metropolitan for his Ruthenian subjects. Lithuanian rulers also requested and received a metropolitan for Novagrudok shortly afterwards. Cyprian, Metropolitan of Kiev, Cyprian, a candidate pushed by the Lithuanian rulers, became Metropolitan of Kiev in 1375 and metropolitan of Moscow in 1382; this way the church in the territory of former Kievan Rusʹ was reunited for some time. In 1439, Kiev became the seat of a separate "Metropolitan of Kiev, Halych and all Rusʹ" for all Greek Orthodox Christians under Polish-Lithuanian rule. However, a long and unsuccessful struggle against the Mongols combined with internal opposition to the prince and foreign intervention weakened Galicia-Volhynia. With the end of the Mstislavich branch of the Rurikids in the mid-14th century, Galicia-Volhynia ceased to exist; Poland conquered Halych; Lithuania took Volhynia, including Kiev, conquered by Gediminas in 1321 Battle on the Irpin River, ending the rule of Rurikids in the city. Lithuanian rulers then assumed the title over Ruthenia.Final disintegration
 Following the Mongol invasion of Cumania (or the Kipchaks), in which case many Cuman rulers fled to Rusʹ, such as Köten, the state finally disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of Rusʹ, fragmenting it into successor principalities who paid tribute to the Golden Horde (the so-called Tatar Yoke). In the late 15th century, the Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Grand Dukes began taking over former Kievan territories and proclaimed themselves the sole legal successors of the Kievan principality according to the protocols of the medieval theory of translatio imperii.
On the western periphery, Kievan Rusʹ was succeeded by the Principality of Galicia-Volhynia. Later, as these territories, now part of modern central
Following the Mongol invasion of Cumania (or the Kipchaks), in which case many Cuman rulers fled to Rusʹ, such as Köten, the state finally disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of Rusʹ, fragmenting it into successor principalities who paid tribute to the Golden Horde (the so-called Tatar Yoke). In the late 15th century, the Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Grand Dukes began taking over former Kievan territories and proclaimed themselves the sole legal successors of the Kievan principality according to the protocols of the medieval theory of translatio imperii.
On the western periphery, Kievan Rusʹ was succeeded by the Principality of Galicia-Volhynia. Later, as these territories, now part of modern central Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, fell to the Gediminids, the powerful, largely Ruthenized Grand Duchy of Lithuania drew heavily on Rusʹ cultural and legal traditions. From 1398 until the Union of Lublin in 1569 its full name was the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Ruthenia and Samogitia. Due to the fact of the economic and cultural core of Rusʹ being located on the territory of modern Ukraine, Ukrainian historians and scholars consider Kievan Rusʹ to be a founding Ukrainian state. After the Union of Lublin, the southern parts of the Grand Duchy were joined to the remnants of Galicia-Volhynia, forming a split of Ruthenia in the Lesser Poland Province, Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. This would almost be the modern borders between northern and southern Ruthenia, or modern Ukraine and Belarus, which have historically been influenced by Poland and Lithuania respectively.
On the north-eastern periphery of Kievan Rusʹ, traditions were adapted in the Vladimir-Suzdal Principality that gradually gravitated towards Moscow. To the very north, the Novgorod Republic, Novgorod and Pskov Republic, Pskov Feudal Republics were less autocratic than Vladimir-Suzdal-Moscow until they were absorbed by the Grand Duchy of Moscow. Russian historians consider Kievan Rusʹ the first period of Russian history.
Economy
During the Kievan era, trade and transport depended largely on networks of rivers and portages. By this period, trade networks had expanded to cater to more than just local demand. This is evidenced by a survey of glassware found in over 30 sites ranging from Suzdal, Drutsk and Belozeroo, which found that a substantial majority was manufactured in Kiev. Kiev was the main depot and transit point for trade between itself, Byzantium and theBlack Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
region. Even though this trade network had already been existent, the volume of which had expanded rapidly in the 11th century. Kiev was also dominant in internal trade between the Rus towns; it held a monopoly on glassware products (glass vessels, glazed pottery and window glass) up until the early- to mid-12th century until which it lost its monopoly to the other Rus towns. Inlaid Enamelled glass, enamel production techniques was borrowed from Byzantine. Byzantine amphorae, wine and olive oil have been found along the middle Dnieper, suggesting trade between Kiev, along trade towns to Byzantium.
The peoples of Rusʹ experienced a period of great economic expansion, opening trade routes with the Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
to the north and west and with the Byzantine Greeks to the south and west; traders also began to travel south and east, eventually making contact with Persia and the peoples of Central Asia.
In winter, the ruler of Kiev went out on rounds, visiting Dregovichs, Krivichs, Drevlians
The Drevlians ( uk, Древляни, Drevliany, russian: Древля́не, Drevlyane) were a tribe of Early East Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries, which inhabited the territories of Polesia and right-bank Ukraine, west of the ea ...
, Severians, and other subordinated tribes. Some paid tribute in money, some in furs or other commodities, and some in slaves. This system was called poliudie.
Society

 Due to the expansion of trade and its geographical proximity, Kiev became the most important trade centre and chief among the communes; therefore the leader of Kiev gained political "control" over the surrounding areas. This princedom emerged from a coalition of traditional patriarchic family communes banded together in an effort to increase the applicable workforce and expand the productivity of the land. This union developed the first major cities in the Rusʹ and was the first notable form of self-government. As these communes became larger, the emphasis was taken off the family holdings and placed on the territory that surrounded. This shift in ideology became known as the ''vervʹ''.
In the 11th and the 12th centuries, the princes and their retinues, which were a mixture of Slavs, Slavic and
Due to the expansion of trade and its geographical proximity, Kiev became the most important trade centre and chief among the communes; therefore the leader of Kiev gained political "control" over the surrounding areas. This princedom emerged from a coalition of traditional patriarchic family communes banded together in an effort to increase the applicable workforce and expand the productivity of the land. This union developed the first major cities in the Rusʹ and was the first notable form of self-government. As these communes became larger, the emphasis was taken off the family holdings and placed on the territory that surrounded. This shift in ideology became known as the ''vervʹ''.
In the 11th and the 12th centuries, the princes and their retinues, which were a mixture of Slavs, Slavic and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
n elites, dominated the society of Kievan Rusʹ. Leading soldiers and officials received income and land from the princes in return for their political and military services. Kievan society lacked the class institutions and autonomous towns that were typical of Western European feudalism. Nevertheless, urban merchants, artisans and labourers sometimes exercised political influence through a city assembly, the ''veche'' (council), which included all the adult males in the population.
In some cases, the veche either made agreements with their rulers or expelled them and invited others to take their place. At the bottom of society was a stratum of slaves. More important was a class of tribute-paying peasants, who owed labour duty to the princes. The widespread personal serfdom characteristic of Western Europe did not exist in Kievan Rusʹ.
The change in political structure led to the inevitable development of the peasant class or smerd, ''smerds''. The smerdy were free un-landed people that found work by labouring for wages on the manors that began to develop around 1031 as the ''vervʹ'' began to dominate socio-political structure. The smerdy were initially given equality in the Kievian law code; they were theoretically equal to the prince; so they enjoyed as much freedom as can be expected of manual labourers. However, in the 13th century, they slowly began to lose their rights and became less equal in the eyes of the law.
Historical assessment
 Kievan Rusʹ, although sparsely populated compared to Western Europe, was not only the largest contemporary European state in terms of area but also culturally advanced.
Literacy in Kiev, Novgorod and other large cities was high; as birch bark documents attest, inhabitants exchanged love letters and prepared cheat sheets for schools. Novgorod had a sewage system and road surface, wood pavement not often found in other cities at the time. The
Kievan Rusʹ, although sparsely populated compared to Western Europe, was not only the largest contemporary European state in terms of area but also culturally advanced.
Literacy in Kiev, Novgorod and other large cities was high; as birch bark documents attest, inhabitants exchanged love letters and prepared cheat sheets for schools. Novgorod had a sewage system and road surface, wood pavement not often found in other cities at the time. The Russkaya Pravda
The ''Russkaya Pravda'' (Rus' Justice, Rus' Truth, or Russian Justice; orv, Правда роусьскаꙗ, ''Pravda Rusĭskaya'' (13th century, 1280), Правда Руськая, ''Pravda Rus'kaya'' (second half of the 15th century); russian: ...
confined punishments to fines and generally did not use capital punishment. Certain rights were accorded to women, such as property and inheritance rights.Janet Martin, ''Medieval Russia, 980–1584'', (Cambridge, 1995), p. 72
The economic development of Kievan Rus may be reflected in its demographics. Around 1200, Kiev had a population of 50,000, followed by Novgorod and Chernigov, which each had around 30,000;Janet Martin, ''Medieval Russia, 980–1584'', (Cambridge, 1995), p. 61 Constantinople, then one of the largest cities in the world, had a population of about 400,000 around 1180.J. Phillips, ''The Fourth Crusade and the Sack of Constantinople'' page 144 Soviet scholar Mikhail Tikhomirov calculated that Kievan Rusʹ had around 300 urban centres on the eve of the Mongol invasion.
Kievan Rusʹ also played an important genealogical role in European politics. Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
, whose stepmother belonged to the Macedonian dynasty that ruled the Byzantine Empire from 867 to 1056, married the only legitimate daughter of the king who Christianized Sweden. His daughters became queens of Hungary, France and Norway; his sons married the daughters of a Polish king and Byzantine emperor, and a niece of the Pope; and his granddaughters were a German empress and (according to one theory) the queen of Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland. A grandson married the only daughter of the last Anglo-Saxon king of England. Thus the Rurikids were a well-connected royal family of the time.
Foreign relations
Turkic peoples
From the 9th century, the Pecheneg nomads began an uneasy relationship with Kievan Rusʹ. For over two centuries they launched sporadic raids into the lands of Rusʹ, which sometimes escalated into full-scale wars (such as the 920 war on the Pechenegs by Igor of Kiev reported in the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
''), but there were also temporary military alliances (e.g., the 943 Byzantine campaign by Igor). In 968, the Pechenegs Siege of Kiev (968), attacked and besieged the city of Kiev. Some speculation exists that the Pechenegs drove off the Tivertsi and the Ulichs to the regions of the upper Dniester river in Bukovina. The Byzantine Empire was known to support the Pechenegs in their military campaigns against the Eastern Slavic states.
Boniak was a Cuman Khan (title), khan who led a series of invasions on Kievan Rusʹ. In 1096, Boniak attacked Kiev, plundered the Kiev Monastery of the Caves, and burned down the prince's palace in Berestovo. He was defeated in 1107 by Vladimir Monomakh, Oleg, Sviatopolk and other Rusʹ princes.
Mongols
 The Mongol Empire invaded Kievan Rusʹ in the 13th century, destroying numerous cities, including Ryazan, Kolomna, Moscow, Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir and Kiev. Giovanni de Plano Carpini, the Pope's envoy to the Mongol Great Khan, traveled through Kiev in February 1246 and wrote:
The Mongol Empire invaded Kievan Rusʹ in the 13th century, destroying numerous cities, including Ryazan, Kolomna, Moscow, Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir and Kiev. Giovanni de Plano Carpini, the Pope's envoy to the Mongol Great Khan, traveled through Kiev in February 1246 and wrote:
When this was done, they [the Mongols, "''Tartari''")] marched against Rusʹ, and made great havoc in it, destroyed cities and forts, and killed people. They besieged Kyiv, the metropolis of Rusʹ, for a long time, and finally took it and killed its citizens. From there, while passing through that land, we found innumerable skulls and bones of dead men, lying on the ground. For the city had been very large and populous, but now it seems reduced to nothing: for hardly more than two hundred houses remain, whose inhabitants are also held in absolute servitude.
Byzantine Empire
 Byzantium quickly became the main Route from the Varangians to the Greeks, trading and cultural partner for Kiev, but relations were not always friendly. The most serious conflict between the two powers was the Sviatoslav I#Campaigns in the Balkans, war of 968–971 in Bulgaria, but several Rusʹ raiding expeditions against the Byzantine cities of the Black Sea coast and Constantinople itself are also recorded. Although most were repulsed, they were concluded by Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria, trade treaties that were generally favourable to the Rusʹ.
Rusʹ-Byzantine relations became closer following the marriage of the ''porphyrogenita'' Anna Porphyrogenita, Anna to
Byzantium quickly became the main Route from the Varangians to the Greeks, trading and cultural partner for Kiev, but relations were not always friendly. The most serious conflict between the two powers was the Sviatoslav I#Campaigns in the Balkans, war of 968–971 in Bulgaria, but several Rusʹ raiding expeditions against the Byzantine cities of the Black Sea coast and Constantinople itself are also recorded. Although most were repulsed, they were concluded by Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria, trade treaties that were generally favourable to the Rusʹ.
Rusʹ-Byzantine relations became closer following the marriage of the ''porphyrogenita'' Anna Porphyrogenita, Anna to Vladimir the Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych ( orv, Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь, ''Volodiměrъ Svętoslavičь'';, ''Uladzimir'', russian: Владимир, ''Vladimir'', uk, Володимир, ''Volodymyr''. Se ...
, and the subsequent Christianization of Kievan Rusʹ, Christianization of the Rusʹ: Byzantine priests, architects and artists were invited to work on numerous cathedrals and churches around Rusʹ, expanding Byzantine cultural influence even further. Numerous Rusʹ served in the Byzantine army as mercenaries, most notably as the famous Varangian Guard.
Military campaigns
* Caspian expeditions of the Rusʹ (864–1041) * Rusʹ–Byzantine War (disambiguation), Rusʹ–Byzantine Wars (830–1043) * Bolesław I's intervention in the Kievan succession crisis, 1018 Polish interventionAdministrative divisions
; 11th century * Novgorod Land 862–1478 the allied territory of Kievan Rusʹ; from 1136 the Novgorod Republic * Vladimir-Suzdal#Rostov-Suzdal, Principality of Rostov-Suzdal Rostov Principality until 1125; became Vladimir-Suzdal Principality in 1155 * Principality of Polotsk 9th century – 14th century (separatist territory, partial suzerainty under Kievan Rusʹ) ** Principality of Minsk * Principality of Smolensk from 1054 * Principality of Pereyaslavl * Principality of Volhynia * Principality of Kiev from 1132 to 1399 ** Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, Principality of Galicia ** Principality of Turov and Pinsk * Principality of Chernigov ** Murom-Ryazan Principality until 1078 ** Principality of Novgorod-Seversk * City of Tmutarakan from 988 until some time in the 12th century * Sarkel, Belaya Vezha from 965 until some time in the 12th century * Southern dependencies Oleshky, New Galich, Peresechen' * Drevlian territories annexed to Rusʹ by Oleg ?–884; 912–946 (vassal of Rusʹ from 914, Drevlians Uprising in 945)Principal cities
* Belgorod Kievsky, capital of Rusʹ under Rurik Rostislavich * Chernigov, capital along with Kiev from 1024 to 1036 (joint rule between Yaroslav and Mstislav) * Halych *Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
* Minsk, centre of Principality of Minsk
* Murom
* Pereyaslavets
Pereyaslavets ( East Slavic: ) or Preslavets ( bg, Преславец) was a trade city located near mouths of the Danube. The city's name is derived from that of the Bulgarian capital of the time, Preslav, and means Little Preslav (). In Greek ...
, capital of Rusʹ from 969 to 971 (in present-day Romania)
* Polotsk
* Rostov Veliky
* Ryazan
* Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ...
* Staraya Ladoga
* Suzdal
* Tmutarakan
* Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ...
* Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir
* Vyshhorod, Vyshgorod, princes' residence and royal library (at Mezhyhirya Monastery, Mezhyhirya)
Religion
 In 988, the Christian Church in Rusʹ territorially fell under the jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople after it was officially adopted as the state religion. According to several chronicles after that date the predominant cult of Slavic paganism was persecuted.
The exact date of creation of the Kiev Metropolis is uncertain, as well as its first church leader. It is generally considered that the first head was Michael I of Kiev (metropolitan), Michael I of Kiev; however, some sources claim it to be Leontiy, who is often placed after Michael or Anastas Chersonesos, who became the first bishop of the Church of the Tithes. The first metropolitan to be confirmed by historical sources is Theopemp, who was appointed by Patriarch Alexius of Constantinople in 1038. Before 1015 there were five dioceses: Kiev, Chernihiv, Bilhorod, Volodymyr, Novgorod, and soon thereafter Bila Tserkva, Yuriy-upon-Ros. The Kiev Metropolitan sent his own delegation to the Council of Bari in 1098.
After the sacking of Kiev in 1169, part of the Kiev metropolis started to move to Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir-upon-Klyazma, concluding the move sometime after 1240 when Kiev was taken by Batu Khan. Metropolitan Maxim was the first metropolitan who chose Vladimir-upon-Klyazma as his official residence in 1299. As a result, in 1303, Lev I of Galicia petitioned Patriarch Athanasius I of Constantinople for the creation of a new Halych metropolis; however, it only existed until 1347.
The Church of the Tithes was chosen as the first Cathedral Temple. In 1037, the cathedral was transferred to the newly built Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kiev. Upon the transferring of the metropolitan seat in 1299, the Dormition Cathedral, Vladimir was chosen as the new cathedral.
By the mid-13th century, the dioceses of Kiev Metropolis (988) were as follows: Kiev (988), Pereyaslav, Chernihiv (991), Volodymyr-Volynsky (992), Turov (1005), Polotsk (1104), Novgorod (~990s), Smolensk (1137), Murom (1198), Peremyshl (1120), Halych (1134), Vladimir-upon-Klyazma (1215), Rostov (991), Bilhorod, Yuriy (1032), Chełm (1235) and Tver (1271). There also were dioceses in Carpathian Ruthenia, Zakarpattia and Tmutarakan. In 1261 the Sarai-Batu diocese was established.
In 988, the Christian Church in Rusʹ territorially fell under the jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople after it was officially adopted as the state religion. According to several chronicles after that date the predominant cult of Slavic paganism was persecuted.
The exact date of creation of the Kiev Metropolis is uncertain, as well as its first church leader. It is generally considered that the first head was Michael I of Kiev (metropolitan), Michael I of Kiev; however, some sources claim it to be Leontiy, who is often placed after Michael or Anastas Chersonesos, who became the first bishop of the Church of the Tithes. The first metropolitan to be confirmed by historical sources is Theopemp, who was appointed by Patriarch Alexius of Constantinople in 1038. Before 1015 there were five dioceses: Kiev, Chernihiv, Bilhorod, Volodymyr, Novgorod, and soon thereafter Bila Tserkva, Yuriy-upon-Ros. The Kiev Metropolitan sent his own delegation to the Council of Bari in 1098.
After the sacking of Kiev in 1169, part of the Kiev metropolis started to move to Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir-upon-Klyazma, concluding the move sometime after 1240 when Kiev was taken by Batu Khan. Metropolitan Maxim was the first metropolitan who chose Vladimir-upon-Klyazma as his official residence in 1299. As a result, in 1303, Lev I of Galicia petitioned Patriarch Athanasius I of Constantinople for the creation of a new Halych metropolis; however, it only existed until 1347.
The Church of the Tithes was chosen as the first Cathedral Temple. In 1037, the cathedral was transferred to the newly built Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kiev. Upon the transferring of the metropolitan seat in 1299, the Dormition Cathedral, Vladimir was chosen as the new cathedral.
By the mid-13th century, the dioceses of Kiev Metropolis (988) were as follows: Kiev (988), Pereyaslav, Chernihiv (991), Volodymyr-Volynsky (992), Turov (1005), Polotsk (1104), Novgorod (~990s), Smolensk (1137), Murom (1198), Peremyshl (1120), Halych (1134), Vladimir-upon-Klyazma (1215), Rostov (991), Bilhorod, Yuriy (1032), Chełm (1235) and Tver (1271). There also were dioceses in Carpathian Ruthenia, Zakarpattia and Tmutarakan. In 1261 the Sarai-Batu diocese was established.
Collection of maps
See also
* History of Belarus * History of Russia * History of Ukraine * De Administrando Imperio * Kievan Rusʹ Park * Old Russian Chronicles * Slavic studies * Symbols of the Rurikids * European RussiaExplanatory notes
References
Citations
General sources
* * �Russia
Further reading
* David Christian (historian), Christian, David. ''A History of Russia, Mongolia and Central Asia''. Blackwell, 1999. * Franklin, Simon and Shepard, Jonathon, ''The Emergence of Rus, 750–1200''. (Longman History of Russia, general editor Harold Shukman.) Longman, London, 1996. * John Lister Illingworth Fennell, Fennell, John, ''The Crisis of Medieval Russia, 1200–1304''. (Longman History of Russia, general editor Harold Shukman.) Longman, London, 1983. * Gwyn Jones (author), Jones, Gwyn. ''A History of the Vikings''. 2nd ed. London: Oxford Univ. Press, 1984. * Martin, Janet, ''Medieval Russia 980–1584''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1993. * * Pritsak, Omeljan. ''The Origin of Rusʹ''. Cambridge Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1991. * Stang, Håkon. ''The Naming of Russia''. Meddelelser, Nr. 77. Oslo: University of Oslo Slavisk-baltisk Avelding, 1996. * Alexander F. Tsvirkun E-learning course. History of Ukraine. Journal Auditorium, Kiev, 2010. * Velychenko, Stephen, ''National history as cultural process: a survey of the interpretations of Ukraine's past in Polish, Russian, and Ukrainian historical writing from the earliest times to 1914''. Edmonton, 1992. * Velychenko, Stephen, "Nationalizing and Denationalizing the Past. Ukraine and Russia in Comparative Context", Ab Imperio 1 (2007). * Velychenko, Stephen "New wine old bottle. Ukrainian history Muscovite-Russian Imperial myths and the Cambridge-History of Russia,Stephen Velychenko. New Wine Old Bottle. Ukrainian History, Muscovite /Russian Imperial Myths and the Cambridge History of Russia
External links
*
Ancient Rus: trade and crafts
Chronology of Kievan Rusʹ 859–1240.
{{Authority control Kievan Rus', States and territories established in the 870s States and territories disestablished in 1240 882 establishments 1240 disestablishments in Europe Former countries in Europe Former Slavic countries Medieval Belarus Medieval Russia Medieval Ukraine 9th-century establishments in Russia Historical regions Former countries