Roman Mesopotamia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Mesopotamia was the name of a
Mesopotamia was the name of a
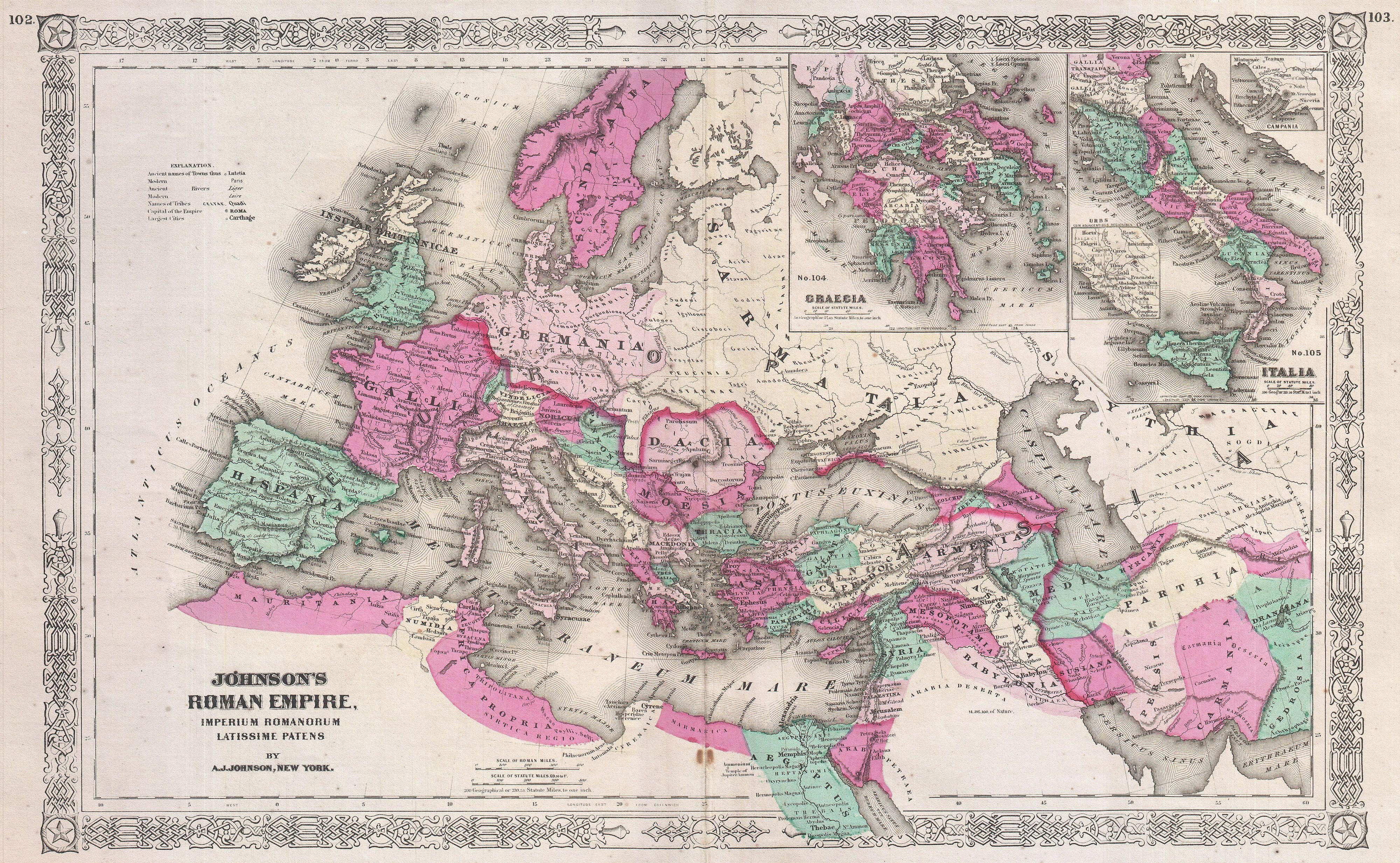 For the remainder of its existence, the new province would remain a bone of contention between the Romans and their eastern neighbors, suffering heavily in the recurrent
For the remainder of its existence, the new province would remain a bone of contention between the Romans and their eastern neighbors, suffering heavily in the recurrent

 Mesopotamia was the name of a
Mesopotamia was the name of a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
, initially a short-lived creation of the Roman emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
in 116‚Äď117 and then re-established by Emperor Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 ‚Äď 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
in c. 198. Control of the province was subsequently fought over between the Roman and the Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
empires until the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, ōßŔĄŔíŔĀŔŹō™ŔŹŔąō≠Ŕéōßō™ŔŹ ōßŔĄō•ō≥ŔíŔĄŔéōßŔÖŔźŔäŔéŔĎō©, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
of the 7th century.
Trajan's province
In 113, the Roman emperorTrajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
(r. 98‚Äď117) launched a war against Rome's long-time eastern rival, the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
. In 114, he conquered Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
, which was made into a province, and by the end of 115, he had conquered northern Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotam√≠ńĀ''; ar, ō®ŔźŔĄŔéōßōĮ ŔĪŔĄōĪŔéŔĎōßŔĀŔźōĮŔéŔäŔíŔÜ or ; syc, ‹ź‹™‹° ‹Ę‹ó‹™Őą‹Ě‹Ę, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris‚ÄďEuphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
. This too was organized as a province in early 116, when coins were minted to celebrate the fact.
Later in the same year, Trajan marched into central and southern Mesopotamia (enlarging and completing the province of Mesopotamia) and across the river Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
to Adiabene
Adiabene was an ancient kingdom in northern Mesopotamia, corresponding to the northwestern part of ancient Assyria. The size of the kingdom varied over time; initially encompassing an area between the Zab Rivers, it eventually gained control of N ...
, which he annexed into another Roman province, Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''mńĀt AŇ°Ň°ur''; syc, ‹ź‹¨‹ė‹™, ĺńĀthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
. But he did not stop there. In the last months of 116, he captured the Persian city of Susa and deposed the Parthian king Osroes I, putting his own puppet ruler Parthamaspates on the Parthian throne. Never again would the Roman Empire advance so far to the east.
As soon as Trajan died, however, his successor Hadrian (r. 117‚Äď138) relinquished his conquests east of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
river, which became again the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, őíőĪŌÉőĻőĽőĶőĮőĪ ŌĄŠŅ∂őĹ ŠŅ¨ŌČőľőĪőĮŌČőĹ, Basile√≠a t√īn RhŇćma√≠Ňćn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
's eastern boundary.
Severus's province
Lucius Verus's campaign
Northern Mesopotamia, includingOsroene
Osroene or Osrhoene (; grc-gre, ŠĹąŌÉŌĀőŅő∑őĹőģ) was an ancient region and state in Upper Mesopotamia. The ''Kingdom of Osroene'', also known as the "Kingdom of Edessa" ( syc, ‹°‹†‹ü‹ė‹¨‹ź ‹ē‹í‹Ě‹¨ ‹ź‹ė‹™‹ó‹Ě / "Kingdom of Urhay"), according to ...
, came again under Roman control in the expedition of Lucius Verus in 161‚Äď166, but were not formally organized into provinces; instead, they were left under local vassal rulers, although Roman garrisons were maintained, notably at Nisibis
Nusaybin (; '; ar, ŔÜŔŹōĶŔéŔäŔíō®ŔźŔäŔíŔÜ, translit=NuŠĻ£aybńęn; syr, ‹Ę‹®‹Ě‹í‹Ě‹Ę, translit=NŠĻ£ńębńęn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is ...
.
Year of the Five Emperors
This control was threatened in 195, during the civil war betweenSeptimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 ‚Äď 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
(r. 193‚Äď211) and the usurper Pescennius Niger, when rebellions broke out in the area, and Nisibis was besieged. Severus quickly restored order and organized Osroene as a full province.
Reconquest by Severus
Next, Severus embarked on a war against Parthia, which he concluded successfully with the sack of the Parthian capital Ctesiphon. In emulation of Trajan, he re-established a province of Mesopotamia in 198, with Nisibis, elevated to the status of a full '' colonia'', as its capital. Unlike Trajan's province, which encompassed the whole of Roman-occupied Mesopotamia between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, the new province was limited between the province ofOsroene
Osroene or Osrhoene (; grc-gre, ŠĹąŌÉŌĀőŅő∑őĹőģ) was an ancient region and state in Upper Mesopotamia. The ''Kingdom of Osroene'', also known as the "Kingdom of Edessa" ( syc, ‹°‹†‹ü‹ė‹¨‹ź ‹ē‹í‹Ě‹¨ ‹ź‹ė‹™‹ó‹Ě / "Kingdom of Urhay"), according to ...
to the south, the Euphrates and Tigris to the north, and the river Chaboras (modern Khabur) to the east.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1348
Warzone
 For the remainder of its existence, the new province would remain a bone of contention between the Romans and their eastern neighbors, suffering heavily in the recurrent
For the remainder of its existence, the new province would remain a bone of contention between the Romans and their eastern neighbors, suffering heavily in the recurrent Roman‚ÄďPersian Wars
The Roman‚ÄďPersian Wars, also known as the Roman‚ÄďIranian Wars, were a series of conflicts between states of the Greco-Roman world and two successive Iranian empires: the Parthian and the Sasanian. Battles between the Parthian Empire and the ...
. In the turmoil that followed the Year of the Six Emperors, in 239‚Äď243, Ardashir I (r. 224‚Äď241), the founder of the new Sassanid Empire which replaced the moribund Parthians, attacked and overran the area, but it was recovered by Timesitheus before his death in 243. In the 250s, the Persian shah Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; pal, ūź≠Īūź≠ßūź≠Įūź≠•ūź≠ßūź≠•ūź≠©, ҆ńĀbuhr ) was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardas ...
(r. ca. 240‚Äď270) attacked Mesopotamia, and fought with the Roman emperor Valerian (r. 253‚Äď260), whom he captured at Edessa in 260. In the next year, however, Shapur was heavily defeated by Odaenathus
Septimius Odaenathus ( Palmyrene Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; ar, ō£ōįŔäŔÜō©, translit=UŠłŹaina; 220 ‚Äď 267) was the founder king ( ''Mlk'') of the Palmyrene Kingdom who ruled from Palmyra, Syria. He elevated the status of his kingdom from a r ...
of Palmyra
Palmyra (; Palmyrene: () ''Tadmor''; ar, ō™ŔéōĮŔíŔÖŔŹōĪ ''Tadmur'') is an ancient city in present-day Homs Governorate, Syria. Archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early secon ...
and driven out of Mesopotamia.Mommsen, Dickson & Haverfield (2004), pp. 103‚Äď104
Diocletianic-Constantinian reorganization
Under the reforms of Diocletian (r. 284‚Äď305) andConstantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
(r. 306‚Äď337), it became part of the Diocese of the East
The Diocese of the East ( la, Dioecesis Orientis; el, ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the western Middle East, between the Mediterranean Sea and Mesopotamia. During late Antiquity, it was one of the majo ...
, which in turn was subordinated to the praetorian prefecture of the East
The praetorian prefecture of the East, or of the Orient ( la, praefectura praetorio Orientis, el, ŠľźŌÄőĪŌĀŌáŌĆŌĄő∑Ōā/ŠĹĎŌÄőĪŌĀŌáőĮőĪ ŌĄŠŅ∂őĹ ŌÄŌĀőĪőĻŌĄŌČŌĀőĮŌČőĹ ŌĄŠŅÜŌā ŠľÄőĹőĪŌĄőŅőĽŠŅÜŌā) was one of four large praetorian prefectures into whic ...
.

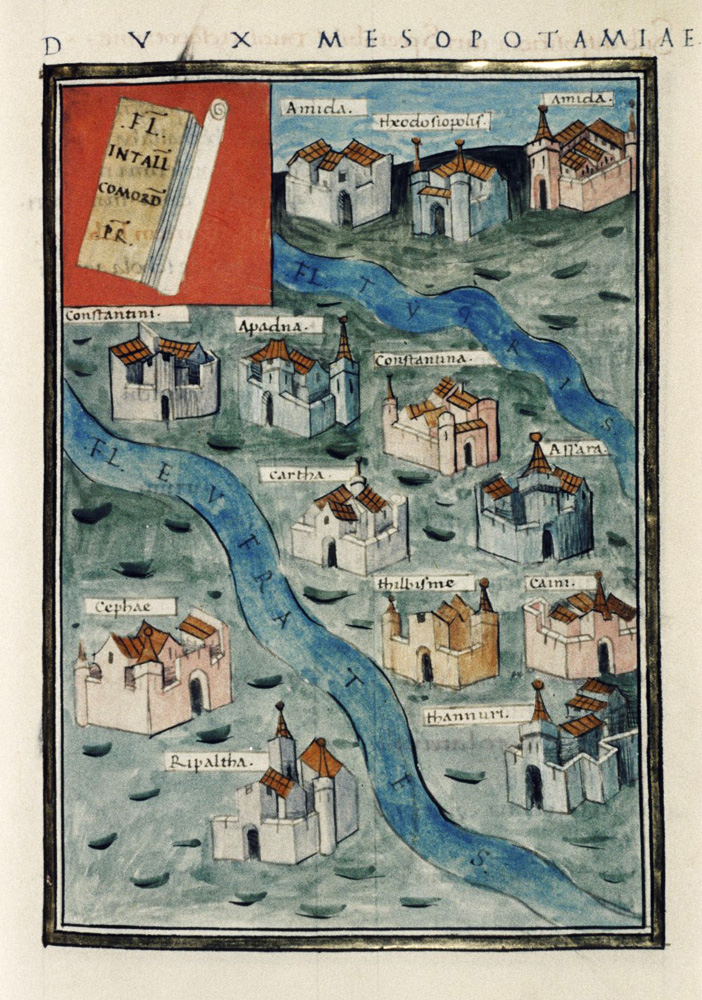
Nisibis
Nusaybin (; '; ar, ŔÜŔŹōĶŔéŔäŔíō®ŔźŔäŔíŔÜ, translit=NuŠĻ£aybńęn; syr, ‹Ę‹®‹Ě‹í‹Ě‹Ę, translit=NŠĻ£ńębńęn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is ...
and Singara
Singara (, ''tà Síngara'') was a strongly fortified post at the northern extremity of Mesopotamia, which for a while, as it appears from coins minted there, was occupied by the Romans as an advanced colony against the Persians. It was the camp o ...
, along with the territory in Adiabene
Adiabene was an ancient kingdom in northern Mesopotamia, corresponding to the northwestern part of ancient Assyria. The size of the kingdom varied over time; initially encompassing an area between the Zab Rivers, it eventually gained control of N ...
conquered by Diocletian were lost after the debacle of Julian's Persian expedition in 363, and the capital was transferred to Amida, while the seat of the military commander, the ''dux Mesopotamiae'', was located at Constantina
Flavia Valeria Constantina (also sometimes called ''Constantia'' and ''Constantiana''; el, őöŌČőĹŌÉŌĄőĪőĹŌĄőĮőĹőĪ; b. after 307/before 317 ‚Äď d. 354), later known as Saint Constance, was the eldest daughter of Roman emperor Constantine the Great ...
. Other cities included Martyropolis and Kephas
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64‚Äď68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupation ...
.
Late Roman/Early Byzantine Mesopotamia
After the troubles Roman forces faced in theAnastasian War
The Anastasian War was fought from 502 to 506 between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire. It was the first major conflict between the two powers since 440, and would be the prelude to a long series of destructive conflicts between the t ...
of 502‚Äď506, the East Roman emperor Anastasius I (r. 491‚Äď518) built the fortress of Dara
Dara is a given name used for both males and females, with more than one origin. Dara is found in the Bible's Old Testament Books of Chronicles. Dara ď◊®◊Ęwas a descendant of Judah (son of Jacob). (The Bible. 1 Chronicles 2:6). Dara (also known ...
as a counter to Nisibis and as the new base of the ''dux Mesopotamiae''.
During the reforms of Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, ŠľłőŅŌÖŌÉŌĄőĻőĹőĻőĪőĹŌĆŌā ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
(r. 527‚Äď565), the province was split up: the northern districts with Martyropolis went to the new province of Armenia IV, while the remainder was divided into two civil and ecclesiastical districts, one (the region south of the Tigris) with capital at Amida and the other (the region of Tur Abdin
Tur Abdin ( syr, ‹õ‹Ĺ‹ė‹™ ‹•‹į‹í›ā‹ē‹ļ‹Ě‹Ę or ‹õ‹ė‹ľ‹™ ‹•‹≤‹í›ā‹ē‹Ě‹ľ‹Ę, ŠĻ¨Ňęr ŅAŠłádńęn) is a hilly region situated in southeast Turkey, including the eastern half of the Mardin Province, and ŇěńĪrnak Province west of the Tigris, on the borde ...
) with capital at Dara. The province suffered greatly during the near-constant wars with Persia in the 6th century. In 573, the Persians even took Dara, although the East Romans recovered it under the peace of 591. They lost it again to the Persians in the great war of 602‚Äď628, and regained it afterwards only to lose the entire region permanently to the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, ōßŔĄŔíŔĀŔŹō™ŔŹŔąō≠Ŕéōßō™ŔŹ ōßŔĄō•ō≥ŔíŔĄŔéōßŔÖŔźŔäŔéŔĎō©, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
in 633‚Äď640.
See also
* History of MesopotamiaReferences
Sources
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mesopotamia (Roman Province) States and territories established in the 110s States and territories disestablished in the 2nd century States and territories disestablished in the 7th century Provinces of the Byzantine Empire Late Roman provinces Near East in classical antiquity Ancient Upper Mesopotamia