Roman Invasion Of Britain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of
 The main invasion force under Aulus Plautius crossed in three divisions. The port of departure is usually taken to have been Bononia (
The main invasion force under Aulus Plautius crossed in three divisions. The port of departure is usually taken to have been Bononia (
17
it does not necessarily follow that the entire invasion force did. Richborough has a large natural harbour which would have been suitable, and archaeology shows Roman military occupation at about the right time. However, Dio says the Romans sailed east to west, and a journey from Boulogne to Richborough is south to north. Some historians suggest a sailing from Boulogne to the
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
by occupying Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Stanegate
The Stanegate (meaning "stone road" in Northumbrian dialect) was an important Roman road built in what is now northern England. It linked many forts including two that guarded important river crossings: Corstopitum (Corbridge) on the River Tyn ...
was established. Conquest of the far north and Scotland took longer with fluctuating success.
The Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
was generally recruited in Italia
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania ...
, and Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
. To control the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
they used the newly formed fleet
Fleet may refer to:
Vehicles
*Fishing fleet
*Naval fleet
*Fleet vehicles, a pool of motor vehicles
*Fleet Aircraft, the aircraft manufacturing company
Places
Canada
* Fleet, Alberta, Canada, a hamlet
England
* The Fleet Lagoon, at Chesil Beach ...
.
The Romans under their general Aulus Plautius
Aulus Plautius was a Roman politician and general of the mid-1st century. He began the Roman conquest of Britain in 43, and became the first governor of the new province, serving from 43 to 46 CE.
Career
Little is known of Aulus Plautius's e ...
first forced their way inland in several battles against British tribes
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point the ...
, including the Battle of the Medway
The Battle of the Medway took place in 43 AD, probably on the River Medway in the lands of the Iron Age tribe of the Cantiaci, now the English county of Kent. Other locations for the battle have been suggested but are less likely. This was an ...
, the Battle of the Thames, and in later years Caratacus's last battle
The final battle in Caratacus's resistance to Roman rule was fought in 50 AD. The Romans under Publius Ostorius Scapula defeated the Britons and in the aftermath captured Caratacus himself, since 43 the leader of armed opposition to the Roman ...
and the Roman conquest of Anglesey. Following a widespread uprising
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
in AD 60 in which Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh as ()), was a queen of the ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She ...
sacked Camulodunum
Camulodunum (; la, ), the Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important castrum and city in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. A temporary "strapline" in the 1960s identifying it as the "oldest re ...
, Verulamium
Verulamium was a town in Roman Britain. It was sited southwest of the modern city of St Albans in Hertfordshire, England. A large portion of the Roman city remains unexcavated, being now park and agricultural land, though much has been built upon ...
Churchill, ''A History of the English-Speaking Peoples'', p. 7 and Londinium
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. It was originally a settlement established on the current site of the City of London around AD 47–50. It sat at a key cross ...
, the Romans suppressed the rebellion in the Defeat of Boudica
The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic tribes against the Roman Empire. It took place c. 60–61 AD in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' ...
. They went on eventually to push as far north as central Caledonia in the Battle of Mons Graupius
The Battle of Mons Graupius was, according to Tacitus, a Roman Empire, Roman military victory in what is now Scotland, taking place in AD 83 or, less probably, 84. The exact location of the battle is a matter of debate. Historians have long que ...
. Even after Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
was established as the border, tribes in Scotland and northern England repeatedly rebelled against Roman rule and forts continued to be maintained across northern Britain to protect against these attacks.
Background
In common with other regions on the edge of the empire, Britain had enjoyed diplomatic and trading links with the Romans in the century sinceJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
's expeditions in 55 and 54 BC, and Roman economic and cultural influence was a significant part of the British late pre-Roman Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, especially in the south.
Between 55 BC and the 40s AD, the ''status quo'' of tribute, hostages, and client states
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
without direct military occupation, begun by Caesar's invasions of Britain
In the course of his Gallic Wars, Julius Caesar invaded Great Britain, Britain twice: in 55 and 54 BC. On the first occasion Caesar took with him only two legions, and achieved little beyond a landing on the coast of Kent. The second invasion co ...
, largely remained intact. Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
prepared invasions in 34 BC, 27 BC and 25 BC. The first and third were called off due to revolts elsewhere in the empire, the second because the Britons seemed ready to come to terms. According to Augustus's '' Res Gestae'', two British kings, Dubnovellaunus Dubnovellaunus or Dumnovellaunus was the name of at least one, and possibly several kings of south-eastern Britain in the late 1st century BC/early 1st century AD, known from coin legends and from a mention in the ''Res Gestae Divi Augusti''.
*Dubn ...
and Tincomarus
Tincomarus (a dithematic name form typical of insular and continental Celtic onomastics, analysable as ''tinco-'', perhaps a sort of fish f Latin ''tinca'', English ''tench''+ ''maro-'', "big") was a king of the Iron Age Belgic tribe of the Atreba ...
, fled to Rome as supplicants during his reign, and Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
's ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (Ancient Greek: Γεωγραφικά ''Geōgraphiká''), or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Ancient Greek, Greek and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen ...
'', written during this period, says Britain paid more in customs and duties than could be raised by taxation if the island were conquered.
By the 40s AD, the political situation within Britain was in ferment. The Catuvellauni
The Catuvellauni (Common Brittonic: *''Catu-wellaunī'', "war-chiefs") were a Celtic tribe or state of southeastern Britain before the Roman conquest, attested by inscriptions into the 4th century.
The fortunes of the Catuvellauni and their ...
had displaced the Trinovantes
The Trinovantēs (Common Brittonic: *''Trinowantī'') or Trinobantes were one of the Celtic tribes of Pre-Roman Britain. Their territory was on the north side of the Thames estuary in current Essex, Hertfordshire and Suffolk, and included land ...
as the most powerful kingdom in south-eastern Britain, taking over the former Trinovantian capital of Camulodunum
Camulodunum (; la, ), the Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important castrum and city in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. A temporary "strapline" in the 1960s identifying it as the "oldest re ...
(Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colches ...
). The Atrebates
The Atrebates (Gaulish: *''Atrebatis'', 'dwellers, land-owners, possessors of the soil') were a Belgic tribe of the Iron Age and the Roman period, originally dwelling in the Artois region.
After the tribes of Gallia Belgica were defeated by Caes ...
tribe whose capital was at Calleva Atrebatum ( Silchester) had friendly trade and diplomatic links with Rome and Verica
Verica (early 1st century AD) was a British client king of the Roman Empire in the years preceding the Claudian invasion of 43 AD.
From his coinage, he appears to have been king of the, probably Belgic, Atrebates tribe and a son of Commius. Th ...
was recognised by Rome as their king, but Caratacus
Caratacus ( Brythonic ''*Caratācos'', Middle Welsh ''Caratawc''; Welsh ''Caradog''; Breton ''Karadeg''; Greek ''Καράτακος''; variants Latin ''Caractacus'', Greek ''Καρτάκης'') was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the C ...
' Catuvellauni
The Catuvellauni (Common Brittonic: *''Catu-wellaunī'', "war-chiefs") were a Celtic tribe or state of southeastern Britain before the Roman conquest, attested by inscriptions into the 4th century.
The fortunes of the Catuvellauni and their ...
conquered the entire kingdom some time after AD 40 and Verica was expelled from Britain.
Caligula
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), better known by his nickname Caligula (), was the third Roman emperor, ruling from 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the popular Roman general Germanicu ...
may have planned a campaign against the Britons in AD 40, but its execution was unclear: according to Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; c. AD 69 – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire.
His most important surviving work is a set of biographies ...
' ''The Twelve Caesars
''De vita Caesarum'' (Latin; "About the Life of the Caesars"), commonly known as ''The Twelve Caesars'', is a set of twelve biographies of Julius Caesar and the first 11 emperors of the Roman Empire written by Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus. The g ...
'', he drew up his troops in battle formation facing the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
and, once his forces had become quite confused, ordered them to gather seashell
A seashell or sea shell, also known simply as a shell, is a hard, protective outer layer usually created by an animal or organism that lives in the sea. The shell is part of the body of the animal. Empty seashells are often found washe ...
s, referring to them as "plunder from the ocean due to the Capitol
A capitol, named after the Capitoline Hill in Rome, is usually a legislative building where a legislature meets and makes laws for its respective political entity.
Specific capitols include:
* United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.
* Numerous ...
and the Palace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
". Alternatively, he may have actually told them to gather "huts", since the word ''musculi'' was also soldier's slang
Slang is vocabulary (words, phrases, and linguistic usages) of an informal register, common in spoken conversation but avoided in formal writing. It also sometimes refers to the language generally exclusive to the members of particular in-gro ...
for engineers' huts and Caligula himself was very familiar with the Empire's soldiers. In any case this readied the troops and facilities that would make Claudius' invasion possible three years later. For example, Caligula built a lighthouse at Bononia (modern Boulogne-sur-Mer
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
), the ''Tour d'Ordre'', that provided a model for the one built soon after at Dubris
Dubris, also known as Portus Dubris and Dubrae, was a port in Roman Britain on the site of present-day Dover, Kent, England.
As the closest point to continental Europe and the site of the estuary of the Dour, the site chosen for Dover was ideal ...
(Dover).
Claudian preparations
In 43, possibly by reassembling Caligula's troops from 40,Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
mounted an invasion force under overall charge of Aulus Plautius
Aulus Plautius was a Roman politician and general of the mid-1st century. He began the Roman conquest of Britain in 43, and became the first governor of the new province, serving from 43 to 46 CE.
Career
Little is known of Aulus Plautius's e ...
, a distinguished senator. A pretext of the invasion was to reinstate Verica
Verica (early 1st century AD) was a British client king of the Roman Empire in the years preceding the Claudian invasion of 43 AD.
From his coinage, he appears to have been king of the, probably Belgic, Atrebates tribe and a son of Commius. Th ...
, the exiled king of the Atrebates
The Atrebates (Gaulish: *''Atrebatis'', 'dwellers, land-owners, possessors of the soil') were a Belgic tribe of the Iron Age and the Roman period, originally dwelling in the Artois region.
After the tribes of Gallia Belgica were defeated by Caes ...
.
It is unclear how many legions were sent as only the ', commanded by future emperor Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
, was directly attested to have taken part.
The ', the ' (later styled ') and the ' (later styled ') are known to have served during the Boudican revolt
The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic tribes against the Roman Empire. It took place c. 60–61 AD in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' ...
of 60–61, and were probably there since the initial invasion, but the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
was flexible, with cohorts and auxiliary units being moved around whenever necessary.
Three other men of appropriate rank to command legions are known from the sources to have been involved in the invasion. Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
mentions Gnaeus Hosidius Geta
Gaius or Gnaeus Hosidius Geta ( ; c. 20 – after 95 AD) was a Roman Senator and general who lived in the 1st century. Geta was a praetor some time before 42. In the latter year, commanding a legion, probably the '' Legio IX Hispana'' in the Afr ...
, who probably led the ''IX Hispana'', and Vespasian's brother Titus Flavius Sabinus the Younger. He wrote that Sabinus was Vespasian's lieutenant, but as Sabinus was the older brother and preceded Vespasian into public life, he could hardly have been a military tribune
A military tribune (Latin ''tribunus militum'', "tribune of the soldiers") was an officer of the Roman army who ranked below the legate and above the centurion. Young men of Equestrian rank often served as military tribune as a stepping stone to ...
. Eutropius mentions Gnaeus Sentius Saturninus, although as a former consul he may have been too senior, and perhaps accompanied Claudius later.
Crossing and landing
 The main invasion force under Aulus Plautius crossed in three divisions. The port of departure is usually taken to have been Bononia (
The main invasion force under Aulus Plautius crossed in three divisions. The port of departure is usually taken to have been Bononia (Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
), and the main landing at Rutupiae
Richborough Castle is a Roman Saxon Shore fort better known as Richborough Roman Fort. It is situated in Richborough near Sandwich, Kent. Substantial remains of the massive fort walls still stand to a height of several metres.
It is p ...
(Richborough
Richborough () is a settlement north of Sandwich on the east coast of the county of Kent, England. Richborough lies close to the Isle of Thanet. The population of the settlement is included in the civil parish of Ash.
Although now some dist ...
, on the east coast of Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
). Neither of these locations is certain. Dio does not mention the port of departure, and although Suetonius says that the secondary force under Claudius sailed from Boulogne,Suetonius, ''Claudius'17
it does not necessarily follow that the entire invasion force did. Richborough has a large natural harbour which would have been suitable, and archaeology shows Roman military occupation at about the right time. However, Dio says the Romans sailed east to west, and a journey from Boulogne to Richborough is south to north. Some historians suggest a sailing from Boulogne to the
Solent
The Solent ( ) is a strait between the Isle of Wight and Great Britain. It is about long and varies in width between , although the Hurst Spit which projects into the Solent narrows the sea crossing between Hurst Castle and Colwell Bay to ...
, landing in the vicinity of Noviomagus (Chichester
Chichester () is a cathedral city and civil parish in West Sussex, England.OS Explorer map 120: Chichester, South Harting and Selsey Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton B2 edition. Publishing Date:2009. It is the only ci ...
) or Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
, in territory formerly ruled by Verica.
River battles
British resistance was led byTogodumnus
Togodumnus (died AD 43) was king of the British Catuvellauni tribe, whose capital was at St. Albans, at the time of the Roman conquest. He can probably be identified with the legendary British king Guiderius.
He is usually thought to have led t ...
and Caratacus
Caratacus ( Brythonic ''*Caratācos'', Middle Welsh ''Caratawc''; Welsh ''Caradog''; Breton ''Karadeg''; Greek ''Καράτακος''; variants Latin ''Caractacus'', Greek ''Καρτάκης'') was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the C ...
, sons of the late king of the Catuvellauni, Cunobeline
Cunobeline (or Cunobelin, from Latin , derived from Common Brittonic ''*Cunobelinos'' "Strong as a Dog", "Strong Dog") was a king in pre-Roman Britain from about AD 9 until about AD 40.Malcolm Todd (2004)"Cunobelinus_

 Late in 47 the new governor of Britain,
Late in 47 the new governor of Britain,


 The new governor was Agricola, returning to Britain, and made famous through the highly laudatory biography of him written by his son-in-law, Tacitus. Arriving in mid-summer of 78, Agricola completed the conquest of Wales in defeating the Ordovices who had destroyed a cavalry
The new governor was Agricola, returning to Britain, and made famous through the highly laudatory biography of him written by his son-in-law, Tacitus. Arriving in mid-summer of 78, Agricola completed the conquest of Wales in defeating the Ordovices who had destroyed a cavalry
 The years 87–117 were of consolidation and only a few sites north of the Stanegate line were maintained, while the signs are that an orderly withdrawal to the Solway-Tyne line was made. There does not seem to have been any rout caused as a result of battles with various tribes.
Modifications to the Stanegate line, with the reduction in the size of the forts and the addition of fortlets and watchtowers between them, seem to have taken place from the mid-90s onwards. Apart from the Stanegate line, other forts existed along the Solway Coast at Beckfoot,
The years 87–117 were of consolidation and only a few sites north of the Stanegate line were maintained, while the signs are that an orderly withdrawal to the Solway-Tyne line was made. There does not seem to have been any rout caused as a result of battles with various tribes.
Modifications to the Stanegate line, with the reduction in the size of the forts and the addition of fortlets and watchtowers between them, seem to have taken place from the mid-90s onwards. Apart from the Stanegate line, other forts existed along the Solway Coast at Beckfoot,
 Under
Under
 *
*
Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
on the River Medway. The Battle of the Medway
The Battle of the Medway took place in 43 AD, probably on the River Medway in the lands of the Iron Age tribe of the Cantiaci, now the English county of Kent. Other locations for the battle have been suggested but are less likely. This was an ...
raged for two days. Gnaeus Hosidius Geta
Gaius or Gnaeus Hosidius Geta ( ; c. 20 – after 95 AD) was a Roman Senator and general who lived in the 1st century. Geta was a praetor some time before 42. In the latter year, commanding a legion, probably the '' Legio IX Hispana'' in the Afr ...
was almost captured, but recovered and turned the battle so decisively that he was awarded the Roman triumph
The Roman triumph (') was a civil religion, civil ceremony and Religion in ancient Rome, religious rite of ancient Rome, held to publicly celebrate and sanctify the success of a military commander who had led Roman forces to victory in the servi ...
. At least one division of auxiliary Batavian troops swam across the river as a separate force.
The British were pushed back to the Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
. They were pursued by the Romans across the river, causing some Roman losses in the marshes of Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G ...
. Whether the Romans made use of an existing bridge for this purpose or built a temporary one is uncertain.
Togodumnus died shortly after the battle on the Thames. Plautius halted and sent word for Claudius to join him for the final push. Cassius Dio presents this as Plautius needing the emperor's assistance to defeat the resurgent British, who were determined to avenge Togodumnus. However, Claudius was no military man. The Praetorian cohorts accompanied Emperor Claudius to Britain in AD 43. The Arch of Claudius in Rome says he received the surrender of eleven British kings with no losses, and Suetonius' ''The Twelve Caesars'' says that Claudius received the surrender of the Britons without battle or bloodshed. It is likely that the Catuvellauni were already as good as beaten, allowing the emperor to appear as conqueror on the final march on Camulodunum. Cassius Dio relates that he brought war elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant ...
s and heavy armaments which would have overawed any remaining native resistance. Eleven tribes of South East Britain surrendered to Claudius and the Romans prepared to move further west and north. The Romans established their new capital at Camulodunum and Claudius returned to Rome to celebrate his victory. Caratacus escaped with his family, retainers, and treasure, to continue his resistance further west.
After the invasion, Verica may have been restored as king of the Atrebates although by this time he would have been very elderly. In any case a new ruler for their region, Cogidubnus
Tiberius Claudius Cogidubnus (or Togidubnus, Togidumnus or similar; see naming difficulties) was a 1st-century king of the Regni or Regnenses tribe in early Roman Britain.
Chichester and the nearby Roman villa at Fishbourne, believed by some t ...
, soon appeared as his heir and as king of a number of territories following the first stage of the conquest as a reward as a Roman ally.
AD 44–60

Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
took a force westwards, subduing tribes and capturing ''oppida
An ''oppidum'' (plural ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretch ...
'' settlements as he went. The force proceeded at least as far as Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
, which became a base for the Roman legion, Legio II Augusta, from 55 until 75. Legio IX Hispana
Legio IX Hispana ("9th Spanish Legion"), also written Legio VIIII Hispana, was a legion of the Imperial Roman army that existed from the 1st century BC until at least 120 AD. The legion fought in various provinces of the late Roman Re ...
was sent north towards Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincol ...
( la, Lindum Colonia) and by 47 it is likely that an area south of a line from the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between th ...
to the Severn Estuary
The Severn Estuary ( cy, Aber Hafren) is the estuary of the River Severn, flowing into the Bristol Channel between South West England and South Wales. Its high tidal range, approximately , means that it has been at the centre of discussions in t ...
was under Roman control. That this line is followed by the Roman road of the Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia (Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis ( Bath), Corini ...
has led many historians to debate the route's role as a convenient frontier during the early occupation. It is unlikely that the border between Roman and Iron Age Britain was fixed with modern precision during this period.
 Late in 47 the new governor of Britain,
Late in 47 the new governor of Britain, Publius Ostorius Scapula
Publius Ostorius Scapula standing at the terrace of the Roman Baths (Bath)
Publius Ostorius Scapula (died 52) was a Roman statesman and general who governed Britain from 47 until his death, and was responsible for the defeat and capture of Ca ...
, began a campaign against the tribes of modern-day Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, and the Cheshire Gap. The Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobunn ...
of southeast Wales caused considerable problems to Ostorius and fiercely defended the Welsh border country. Caratacus himself led this guerilla campaign but was defeated when he finally chose to offer a decisive battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
; he fled to the Roman client tribe of the Brigantes who occupied the Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commo ...
. Their queen Cartimandua
Cartimandua or Cartismandua (reigned ) was a 1st-century queen of the Brigantes, a Celtic people living in what is now northern England. She came to power around the time of the Roman conquest of Britain, and formed a large tribal agglomeration ...
was unable or unwilling to protect him however, given her own accommodation with the Romans, and handed him over to the invaders. Ostorius died and was replaced by Aulus Didius Gallus
Aulus Didius Gallus was a Roman general and politician of the 1st century AD. He was governor of Britain between 52 and 57 AD.
Career
The career of Aulus Didius Gallus up to 51 can be partly reconstructed from an inscription from Olympia. He ...
who brought the Welsh borders under control but did not move further north or west, probably because Claudius was keen to avoid what he considered a difficult and drawn-out war for little material gain in the mountainous terrain of upland Britain. When Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
became emperor in 54, he seems to have decided to continue the invasion and appointed Quintus Veranius
Quintus Veranius (died AD 57) was a distinguished Roman general around the mid-first century CE. He was ''III vir monetalis'', tribune of Legio IV ''Scythica'' and quaestor under Tiberius. He was appointed tribune of the plebs in 41 and praetor i ...
as governor, a man experienced in dealing with the troublesome hill tribes of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. Veranius and his successor Gaius Suetonius Paulinus
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus (fl. AD 41–69) was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated the rebellion of Boudica.
Early life
Little is known of Suetonius' family, but it likely came from Pisaurum (modern Pesaro), a town on the Adri ...
mounted a successful campaign across North Wales, famously killing many druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. Whi ...
s when he invaded the island of Anglesey in 60. Final occupation of Wales was postponed however when the rebellion of Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh as ()), was a queen of the ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She ...
forced the Romans to return to the south east in 60 or 61.
AD 60–78
Following the successfulsuppression
Suppression may refer to:
Laws
* Suppression of Communism Act
*Suppression order a type of censorship where a court rules that certain information cannot be published
* Tohunga Suppression Act 1907, an Act of the Parliament of New Zealand aimed ...
of Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh as ()), was a queen of the ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She ...
's uprising in 60 or 61, a number of new Roman governors continued the conquest by edging north.
The leader of the Brigantes was queen Cartimandua
Cartimandua or Cartismandua (reigned ) was a 1st-century queen of the Brigantes, a Celtic people living in what is now northern England. She came to power around the time of the Roman conquest of Britain, and formed a large tribal agglomeration ...
. Her husband was Venutius
Venutius was a 1st-century king of the Brigantes in northern Britain at the time of the Roman conquest. Some have suggested he may have belonged to the Carvetii, a tribe that probably formed part of the Brigantes confederation.
History first b ...
; one speculation is that he might have been a Carvetian and may therefore have been responsible for the incorporation of Cumbria into a Brigantian federation whose territory straddled Britain along the Solway- Tyne line. Cartimandua may have ruled the Brigantian peoples east of the Pennines (possibly with a centre at Stanwick), while Venutius was the chief of the Brigantes (or Carvetii) west of the Pennines in Cumbria (with a possible centre based at Clifton Dykes
Clifton is a small linear village and civil parish in Cumbria, England. Historically part of Westmorland, it lies south east of Penrith.
Geography
The civil parish of Clifton has its western boundary defined by the River Lowther, to the north ...
.) Cartimandua was forced to ask for Roman aid following a rebellion by Venutius in 69. The Romans evacuated Cartimandua leaving Venutius in power.
Tacitus says that in 71 Quintus Petillius Cerialis
Quintus Petillius Cerialis Caesius Rufus ( AD 30 — after AD 83), otherwise known as Quintus Petillius Cerialis, was a Roman general and administrator who served in Britain during Boudica's rebellion and went on to participate in the civil wars af ...
(governor AD 71–74) waged a successful war against the Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geogr ...
. Tacitus praises both Cerialis and his successor Julius Frontinus
Sextus Julius Frontinus (c. 40 – 103 AD) was a prominent Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube ...
(governor 75–78).
Much of the conquest of the north may have been achieved under the governorships of Vettius Bolanus (governor AD 69–71), and of Cerialis. From other sources, it seems that Bolanus had possibly dealt with Venutius and penetrated into Scotland, and evidence from the carbon-dating of the gateway timbers of the Roman fort at Carlisle (Luguvalium
Luguvalium was a Roman town in northern Britain in antiquity. It was located within present-day Carlisle, Cumbria, and may have been the capital of the 4th-century province of Valentia.
Name
The Romans called the settlement at what is today ...
) suggest that they were felled in AD 72, during the governorship of Cerialis. Lead ingots from Deva Victrix
Deva Victrix, or simply Deva, was a legionary fortress and town in the Roman province of Britannia on the site of the modern city of Chester. The fortress was built by the Legio II ''Adiutrix'' in the 70s AD as the Roman army advanced north ag ...
, the Roman fortress at Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
, indicate that construction there was probably under way by AD 74. Nevertheless, Gnaeus Julius Agricola
Gnaeus Julius Agricola (; 13 June 40 – 23 August 93) was a Roman general and politician responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. Born to a political family of senatorial rank, Agricola began his military career as a military tribun ...
played his part in the west as commander of the legion XX Valeria Victrix (71–73), while Cerialis led the IX Hispania
Legio IX Hispana ("9th Spanish Legion"), also written Legio VIIII Hispana, was a legion of the Imperial Roman army that existed from the 1st century BC until at least 120 AD. The legion fought in various provinces of the late Roman Re ...
in the east. In addition, the Legio II Adiutrix
Legio II Adiutrix ("Second Legion, the Rescuer"), was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 70 by the emperor Vespasian (r. 69–79), originally composed of Roman navy marines of the '' classis Ravennatis''. There are still records ...
sailed from Chester up river estuaries to cause surprise to the enemy.
The western thrust was started from Lancaster, where there is evidence of a Cerialian foundation, and followed the line of the Lune and Eden river valleys through Low Borrow Bridge and Brougham
Brougham may refer to:
Transport
* Brougham (carriage), a light four-wheeled horse-drawn carriage
* Brougham (car body), an automobile with a similar style
Automobile models
* Cadillac Brougham, 1987–1992
* Chrysler New Yorker Brougham, c. 1 ...
(Brocavum
Brocavum is the Latin name of a Roman fort at Brougham near Penrith, Cumbria. The fort survives as earthworks, but no excavation of these has been carried out so far.
Location and date
With the rivers Eamont and Lowther flowing nearby and me ...
). On the Cumbrian coast, Ravenglass
Ravenglass is a coastal village in the Copeland District in Cumbria, England. It is between Barrow-in-Furness and Whitehaven. Historically in Cumberland, it is the only coastal village in the Lake District National Park. It is located at the es ...
and Blennerhasset were probably involved from evidence of one of the earliest Roman occupations in Cumbria. Beckfoot
Beckfoot is a hamlet in the civil parish of Holme St Cuthbert in Cumbria, England. It is located on the B5300 coast road, three miles south of Silloth-on-Solway and two miles north of the village of Mawbray. The county town of Carlisle is twe ...
and Maryport
Maryport is a town and civil parish in the Allerdale borough of Cumbria, England, historically in Cumberland.
The town is situated just outside the Lake District National Park, at the northern end of the former Cumberland Coalfield.
Locatio ...
may also have featured early on. At some point between 72 and 73, part of Cerialis's force moved across the Stainmore Pass from Corbridge westwards to join Agricola, as evidenced by campaign camps (which may have been previously set up by Bolanus) at Rey Cross
Rey Cross is the remains of a stone cross at Stainmore. It is also known as Rere Cross and is a Grade II* listed structure and a scheduled monument. It is located towards the western edge of County Durham, approximately east of the border with ...
, Crackenthorpe, Kirkby Thore
Kirkby Thore is a small village and civil parish in Cumbria, England (), in the historic county of Westmorland. It is close to the Lake District national park and the Cumbrian Pennines. It includes the areas of Bridge End, in the southwest by t ...
and Plumpton Head. Signal- or watch-towers are also in evidence across the Stainmore area - Maiden Castle, Bowes Moor and Roper Castle, for example. The two forces then moved up from the vicinity of Penrith to Carlisle, establishing the fort there in AD 72–73.
Frontinus
Sextus Julius Frontinus (c. 40 – 103 AD) was a prominent Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube ...
was sent into Roman Britain in 74 to succeed Cerialis as governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
.
He returned to the conquest of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
interrupted years before and with steady and successful progress finally subdued the Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobunn ...
in circa 76 and other hostile tribes, establishing a new base at Caerleon
Caerleon (; cy, Caerllion) is a town and community in Newport, Wales. Situated on the River Usk, it lies northeast of Newport city centre, and southeast of Cwmbran. Caerleon is of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Roman ...
for Legio II ''Augusta'' (Isca Augusta
Isca, variously specified as Isca Augusta or Isca Silurum, was the site of a Roman legionary fortress and settlement or ''vicus'', the remains of which lie beneath parts of the present-day suburban village of Caerleon in the north of the city of ...
) in 75 and a network of smaller forts fifteen to twenty kilometres apart for his auxiliary units. During his tenure, he probably established the fort at Pumsaint
Pumsaint is a village in Carmarthenshire, Wales, halfway between Llanwrda and Lampeter on the A482 in the valley of the Afon Cothi. It forms part of the extensive estate of Dolaucothi, which is owned by the National Trust.
The name is Welsh fo ...
in west Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, largely to exploit the gold deposits at Dolaucothi
The Dolaucothi Gold Mines (; cy, Mwynfeydd Aur Dolaucothi) (), also known as the Ogofau Gold Mine, are ancient Roman surface and underground mines located in the valley of the River Cothi, near Pumsaint, Carmarthenshire, Wales. The gold min ...
. He left the post in 78, and later he was appointed water commissioner in Rome.
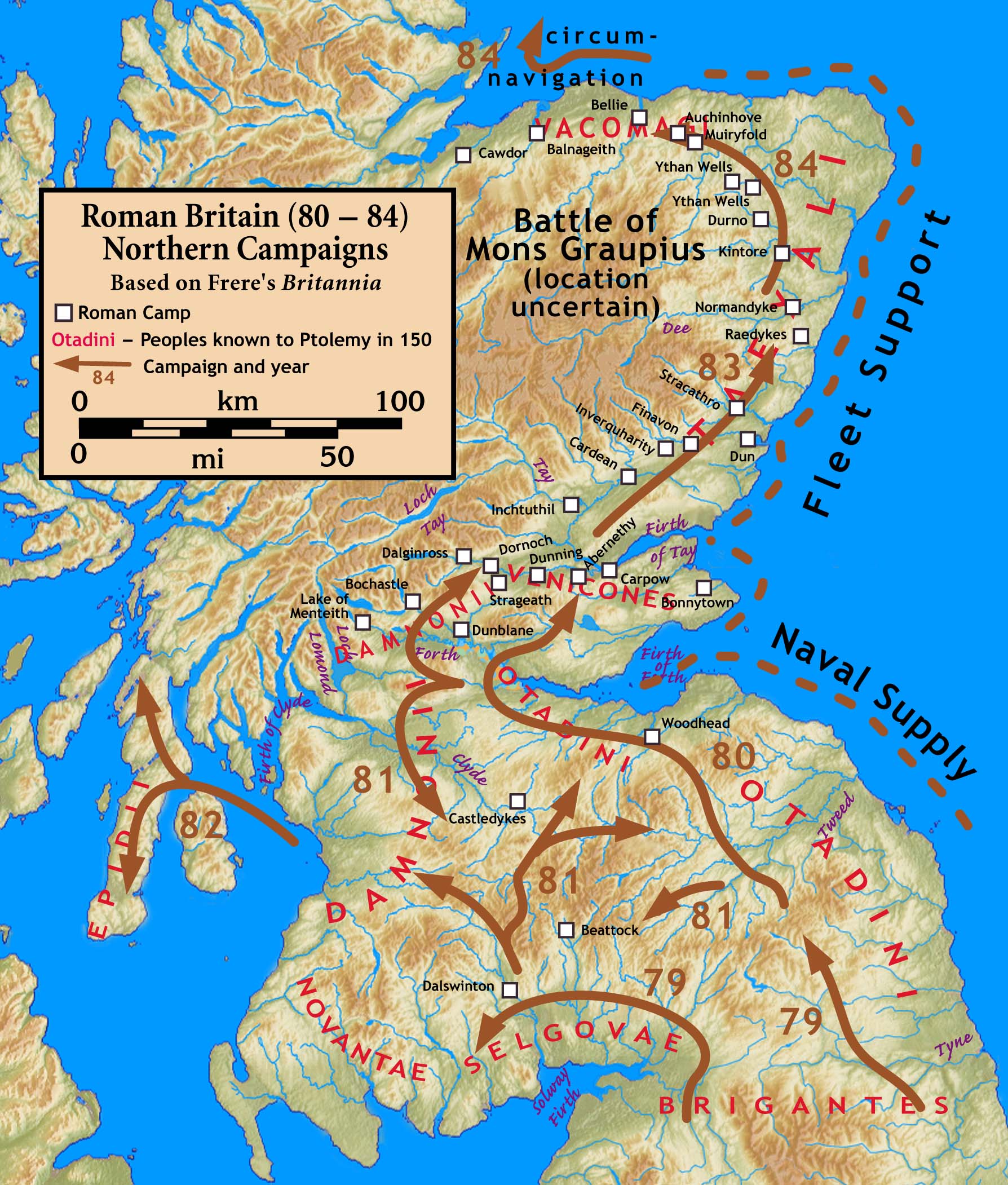
Campaigns of Agricola (AD 78–84)



 The new governor was Agricola, returning to Britain, and made famous through the highly laudatory biography of him written by his son-in-law, Tacitus. Arriving in mid-summer of 78, Agricola completed the conquest of Wales in defeating the Ordovices who had destroyed a cavalry
The new governor was Agricola, returning to Britain, and made famous through the highly laudatory biography of him written by his son-in-law, Tacitus. Arriving in mid-summer of 78, Agricola completed the conquest of Wales in defeating the Ordovices who had destroyed a cavalry ala Ala, ALA, Alaa or Alae may refer to:
Places
* Ala, Hiiu County, Estonia, a village
* Ala, Valga County, Estonia, a village
* Ala, Alappuzha, Kerala, India, a village
* Ala, Iran, a village in Semnan Province
* Ala, Gotland, Sweden
* Alad, S ...
of Roman auxiliaries stationed in their territory. Knowing the terrain from his prior military service in Britain, he was able to move quickly to subdue them. He then invaded Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
, forcing the inhabitants to sue for peace.
The following year he moved against the Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geogr ...
of northern England and the Selgovae
The Selgovae (Common Brittonic: *''Selgowī'') were a Celtic tribe of the late 2nd century AD who lived in what is now the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright and Dumfriesshire, on the southern coast of Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ' ...
along the southern coast of Scotland, using overwhelming military power to establish Roman control.
Agricola in Caledonia
Tacitus says that after a combination of force and diplomacy quieted discontent among the Britons who had been conquered previously, Agricola built forts in their territories in 79. In 80, he marched to theFirth of Tay
The Firth of Tay (; gd, Linne Tatha) is a firth on the east coast of Scotland, into which the River Tay (Scotland's largest river in terms of flow) empties. The firth is surrounded by four council areas: Fife, Perth and Kinross, City of Du ...
(some historians hold that he stopped along the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meani ...
in that year), not returning south until 81, at which time he consolidated his gains in the new lands that he had conquered, and in the rebellious lands that he had re-conquered. In 82, he sailed to either Kintyre
Kintyre ( gd, Cinn Tìre, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to East and West Loch Tarbert in the north. The region immediately north ...
or the shores of Argyll
Argyll (; archaically Argyle, in modern Gaelic, ), sometimes called Argyllshire, is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland.
Argyll is of ancient origin, and corresponds to most of the part of the ancient kingdom of ...
, or to both. In 83 and 84, he moved north along Scotland's eastern and northern coasts using both land and naval forces, campaigning successfully against the inhabitants and winning a significant victory over the northern British peoples led by Calgacus at the Battle of Mons Graupius
The Battle of Mons Graupius was, according to Tacitus, a Roman Empire, Roman military victory in what is now Scotland, taking place in AD 83 or, less probably, 84. The exact location of the battle is a matter of debate. Historians have long que ...
. Archaeology has shown the Romans built military camps in the north along Gask Ridge
The Gask Ridge is the modern name given to an early series of fortifications, built by the Romans in Scotland, close to the Highland Line. Modern excavation and interpretation has been pioneered by the Roman Gask Project, with Birgitta Hoffmann ...
, controlling the glens that provided access to and from the Scottish Highlands
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Sco ...
, and also throughout the Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( sco, Lallans or ; gd, a' Ghalldachd, , place of the foreigners, ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Lowlands and the Highlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowl ...
in northeastern Scotland.
Agricola built a network of military roads and forts to secure the Roman occupation. Existing forts were strengthened and new ones planted in northeastern Scotland along the Highland Line, consolidating control of the glens that provided access to and from the Scottish Highlands
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Sco ...
. The line of military communication and supply along southeastern Scotland and northeastern England (i.e., Dere Street
Dere Street or Deere Street is a modern designation of a Roman road which ran north from Eboracum (York), crossing the Stanegate at Corbridge (Hadrian's Wall was crossed at the Portgate, just to the north) and continuing beyond into what is n ...
) was well-fortified. In southernmost Caledonia, the lands of the Selgovae
The Selgovae (Common Brittonic: *''Selgowī'') were a Celtic tribe of the late 2nd century AD who lived in what is now the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright and Dumfriesshire, on the southern coast of Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ' ...
(approximating to modern Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries (''Siorrachd Dhùn Phris'' in Gaelic) is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.
I ...
and the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county ...
) were heavily planted with forts, not only establishing effective control there, but also completing a military enclosure of south-central Scotland (most of the Southern Uplands
The Southern Uplands ( gd, Na Monaidhean a Deas) are the southernmost and least populous of mainland Scotland's three major geographic areas (the other two being the Central Lowlands and the Grampian Mountains and the Highlands, as illustrated ...
, Teviotdale
Roxburghshire or the County of Roxburgh ( gd, Siorrachd Rosbroig) is a historic county and registration county in the Southern Uplands of Scotland. It borders Dumfriesshire to the west, Selkirkshire and Midlothian to the north-west, and Berw ...
, and western Tweeddale
Tweeddale (Scottish Gaelic: ''Srath Thuaidh/Tuaidhdail'') is a committee area and lieutenancy area in the Scottish Borders council area in south-eastern Scotland. It had also been a province in the Middle Ages. From 1975 to 1996 it was a local gov ...
). In contrast to Roman actions against the Selgovae, the territories of the Novantae
The Novantae were a people of the late 2nd century who lived in what is now Galloway and Carrick, in southwesternmost Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (written c. 150), and there is no other historical record of th ...
, Damnonii
The Damnonii (also referred to as Damnii) were a Brittonic people of the late 2nd century who lived in what became the Kingdom of Strathclyde by the Early Middle Ages, and is now southern Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geo ...
, and Votadini
The Votadini, also known as the ''Uotadini'', ''Wotādīni'', ''Votādīni'', or ''Otadini'' were a Brittonic people of the Iron Age in Great Britain. Their territory was in what is now south-east Scotland and north-east England, extending fro ...
were not planted with forts, and there is nothing to indicate that the Romans were at war with them. Agricola was recalled to Rome in 84.
Findings
In 2019, GUARD Archaeology team led by Iraia Arabaolaza uncovered a marching camp dating to the 1st century AD, used by Roman legions during the invasion of Roman general Agricola. According to Arabaolaza, the fire pits were split 30 metres apart into two parallel lines. The findings also included clay-domed ovens and 26 fire pits dated to between AD 77 and 86 and AD 90 loaded with burn and charcoal contents. Archaeologists suggested that this site had been chosen as a strategic location for the Roman conquest ofAyrshire
Ayrshire ( gd, Siorrachd Inbhir Àir, ) is a historic county and registration county in south-west Scotland, located on the shores of the Firth of Clyde. Its principal towns include Ayr, Kilmarnock and Irvine and it borders the counties of Re ...
.
AD 84–117
Agricola's successors are not named in any surviving source, but it seems they were unable or unwilling to further subdue the far north. The fortress atInchtuthil
Inchtuthil is the site of a Roman legionary fortress situated on a natural platform overlooking the north bank of the River Tay southwest of Blairgowrie, Perth and Kinross, Scotland (Roman Caledonia).
It was built in AD 82 or 83 as the advan ...
was dismantled before its completion and the other fortifications of the Gask Ridge
The Gask Ridge is the modern name given to an early series of fortifications, built by the Romans in Scotland, close to the Highland Line. Modern excavation and interpretation has been pioneered by the Roman Gask Project, with Birgitta Hoffmann ...
in Perthshire
Perthshire (locally: ; gd, Siorrachd Pheairt), officially the County of Perth, is a historic county and registration county in central Scotland. Geographically it extends from Strathmore in the east, to the Pass of Drumochter in the north, ...
, erected to consolidate the Roman presence in Scotland in the aftermath of Mons Graupius
The Battle of Mons Graupius was, according to Tacitus, a Roman military victory in what is now Scotland, taking place in AD 83 or, less probably, 84. The exact location of the battle is a matter of debate. Historians have long questioned some ...
, were abandoned within the space of a few years. It is equally likely that the costs of a drawn-out war outweighed any economic or political benefit and it was more profitable to leave the Caledonians alone and only under ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' submission.
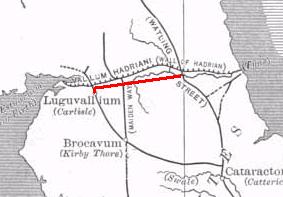
With the decline of imperial ambitions in Scotland (and Ireland) by AD 87 (the withdrawal of the XX legion), consolidation based on the line of the Stanegate
The Stanegate (meaning "stone road" in Northumbrian dialect) was an important Roman road built in what is now northern England. It linked many forts including two that guarded important river crossings: Corstopitum (Corbridge) on the River Tyn ...
road (between Carlisle and Corbridge) was settled upon. Carlisle was the seat of a ''centurio regionarius'' (or district commissioner). When the Stanegate became the new frontier it was augmented by large forts as at Vindolanda
Vindolanda was a Roman auxiliary fort ('' castrum'') just south of Hadrian's Wall in northern England, which it originally pre-dated.British windo- 'fair, white, blessed', landa 'enclosure/meadow/prairie/grassy plain' (the modern Welsh word ...
and additional forts at half-day marching intervals were built at Newbrough
Newbrough is a village in Northumberland, England, on the north bank of the River South Tyne about north-west of Hexham.
History
Newbrough is the site of one of the line of Roman forts along the original northern frontier of the Roman Stanega ...
, Magnis (Carvoran) and Brampton Old Church.
 The years 87–117 were of consolidation and only a few sites north of the Stanegate line were maintained, while the signs are that an orderly withdrawal to the Solway-Tyne line was made. There does not seem to have been any rout caused as a result of battles with various tribes.
Modifications to the Stanegate line, with the reduction in the size of the forts and the addition of fortlets and watchtowers between them, seem to have taken place from the mid-90s onwards. Apart from the Stanegate line, other forts existed along the Solway Coast at Beckfoot,
The years 87–117 were of consolidation and only a few sites north of the Stanegate line were maintained, while the signs are that an orderly withdrawal to the Solway-Tyne line was made. There does not seem to have been any rout caused as a result of battles with various tribes.
Modifications to the Stanegate line, with the reduction in the size of the forts and the addition of fortlets and watchtowers between them, seem to have taken place from the mid-90s onwards. Apart from the Stanegate line, other forts existed along the Solway Coast at Beckfoot, Maryport
Maryport is a town and civil parish in the Allerdale borough of Cumbria, England, historically in Cumberland.
The town is situated just outside the Lake District National Park, at the northern end of the former Cumberland Coalfield.
Locatio ...
, Burrow Walls (near to the present town of Workington) and Moresby (near to Whitehaven). Other forts in the region were built to consolidate Roman presence (Beckfoot, for example may date from the late 1st century). A fort at Troutbeck may have been established from the period of Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
(98–117) onwards. Other forts that may have been established during this period include Ambleside (Galava
Ambleside Roman Fort is the modern name given to the remains of a fort of the Roman province of Britannia. The ruins have been tentatively identified as Galava, mentioned in the Antonine Itinerary. Dating to the 1st or 2nd century AD, its ruins ...
), positioned to take advantage of ship-borne supply to the forts of the Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
. From here, a road was constructed during the Trajanic period to Hardknott Roman Fort
Hardknott Roman Fort is an archeological site, the remains of the Roman fort ''Mediobogdum'', located on the western side of the Hardknott Pass in the English county of Cumbria. The fort was built between 120 and 138 on a rocky spur, and was ini ...
. A road between Ambleside to Old Penrith and/or Brougham, going over High Street
High Street is a common street name for the primary business street of a city, town, or village, especially in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. It implies that it is the focal point for business, especially shopping. It is also a metonym fo ...
, may also date from this period.
From AD 117
 Under
Under Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
(117–138), Roman occupation was withdrawn to a defendable frontier in the River Tyne
The River Tyne is a river in North East England. Its length (excluding tributaries) is . It is formed by the North Tyne and the South Tyne, which converge at Warden Rock near Hexham in Northumberland at a place dubbed 'The Meeting of the Wate ...
-Solway Firth
The Solway Firth ( gd, Tràchd Romhra) is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in ...
frontier area by the construction of Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
from around 122.
When Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius (Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatoria ...
rose to the throne, he moved quickly to reverse the empire limit system put in place by his predecessor. Following his defeat of the Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geogr ...
in 139 AD, Quintus Lollius Urbicus
Quintus Lollius Urbicus was a Numidian Berber governor of Roman Britain between the years 139 and 142, during the reign of the Emperor Antoninus Pius. He is named in the ''Historia Augusta'', although it is not entirely historical, and his name ...
, the Roman Governor of Britannia, was ordered by Antoninus Pius to march north of Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
to conquer the Caledonian Lowlands
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.
Definitions
Upland and lowland are portions of p ...
which were settled by the Otadini, Selgovae
The Selgovae (Common Brittonic: *''Selgowī'') were a Celtic tribe of the late 2nd century AD who lived in what is now the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright and Dumfriesshire, on the southern coast of Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ' ...
, Damnonii
The Damnonii (also referred to as Damnii) were a Brittonic people of the late 2nd century who lived in what became the Kingdom of Strathclyde by the Early Middle Ages, and is now southern Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geo ...
and the Novantae
The Novantae were a people of the late 2nd century who lived in what is now Galloway and Carrick, in southwesternmost Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (written c. 150), and there is no other historical record of th ...
, and to push the frontier further north. Lollius Urbicus moved three legions into position initially establishing his supply routes from Coria and Bremenium
Bremenium is an ancient Roman fort (castrum) located at Rochester, Northumberland, England. The fort is one of the defensive structures built along Dere Street, a Roman road running from York to Corbridge and onwards to Melrose. Significa ...
and moved three legions, the Legio II Augusta
Legio II Augusta ( Second Legion "Augustus'") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army that was founded during the late Roman republic. Its emblems were the Capricornus, Pegasus, and Mars. It may have taken the name "''Augusta''" from a victory or ...
from Caerleon
Caerleon (; cy, Caerllion) is a town and community in Newport, Wales. Situated on the River Usk, it lies northeast of Newport city centre, and southeast of Cwmbran. Caerleon is of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Roman ...
, the Legio VI Victrix
Legio VI Victrix ("Victorious Sixth Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in 41 BC by the general Octavian (who, as Augustus, later became Rome's first emperor). It was the twin legion of VI ''Ferrata'' and perhaps held vete ...
from Eboracum
Eboracum () was a fort and later a city in the Roman province of Britannia. In its prime it was the largest town in northern Britain and a provincial capital. The site remained occupied after the decline of the Western Roman Empire and ultimate ...
, and the Legio XX Valeria Victrix
Legio XX Valeria Victrix, in English Twentieth Victorious Valeria Legion was a legion of the Imperial Roman army.
The origin of the Legion's name is unclear and there are various theories, but the legion may have gained its title ''Valeria ...
from Deva Victrix
Deva Victrix, or simply Deva, was a legionary fortress and town in the Roman province of Britannia on the site of the modern city of Chester. The fortress was built by the Legio II ''Adiutrix'' in the 70s AD as the Roman army advanced north ag ...
into the theatre between 139 and 140 AD, and thereafter moved his army, a force of at least 16,500 men, north of Hadrian's Wall.
The Selgovae
The Selgovae (Common Brittonic: *''Selgowī'') were a Celtic tribe of the late 2nd century AD who lived in what is now the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright and Dumfriesshire, on the southern coast of Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ' ...
, having settled in the regions of present-day Kirkcudbrightshire
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county ...
and Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries (''Siorrachd Dhùn Phris'' in Gaelic) is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.
I ...
immediately northwest of Hadrian's Wall, were amongst the first of the Caledonian tribes to face Lollius Urbicus's legions together with the Otadini. The Romans, who were well versed in warfare on hilly terrain since their founding, moved quickly to occupy strategic points and high ground, some of which had already been fortified by the Caledonians with hill forts
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
. One such was Burnswark Hill
Burnswark Hill, to the east of the A74(M) between Ecclefechan and Lockerbie in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, sits prominently in the landscape. Its rich history has been a consistent source of archaeological interpretation for generations. ...
which was strategically located commanding the western route north further into Caledonia and where significant evidence of the battle has been found.
By 142 the Romans had pacified the entire area and had successfully moved the frontier north to the River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major cit ...
-River Forth
The River Forth is a major river in central Scotland, long, which drains into the North Sea on the east coast of the country. Its drainage basin covers much of Stirlingshire in Scotland's Central Belt. The Gaelic name for the upper reach of th ...
area when the Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as ''Vallum Antonini'', was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twe ...
was constructed. After two decades this was abandoned in 162 and only subsequently re-occupied on an occasional basis. Meanwhile, the Romans retreated to the earlier and stronger Hadrian's Wall.
Roman troops, however, penetrated far into the north of modern Scotland several more times. Indeed, there is a greater density of Roman marching camps in Scotland than anywhere else in Europe as a result of at least four major attempts to subdue the area.
3rd and 4th centuries
The most notable later expedition was in 209 when the emperorSeptimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced thro ...
, claiming to be provoked by the belligerence of the Maeatae
The Maeatae were a confederation of tribes that probably lived beyond the Antonine Wall in Roman Britain.
The historical sources are vague as to the exact region they inhabited, but an association is thought to be indicated in the names of two h ...
tribe, campaigned against the Caledonian Confederacy
The Caledonians (; la, Caledones or '; grc-gre, Καληδῶνες, ''Kalēdōnes'') or the Caledonian Confederacy were a Brittonic-speaking ( Celtic) tribal confederacy in what is now Scotland during the Iron Age and Roman eras.
The Gr ...
, a coalition of Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
Pictish
Pictish is the extinct language, extinct Brittonic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited num ...
tribes of the north of Britain. He used the three legions of the British garrison (augmented by the recently formed 2nd Parthica legion), 9000 imperial guards with cavalry support, and numerous auxiliaries supplied from the sea by the British fleet, the Rhine fleet and two fleets transferred from the Danube for the purpose. According to Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, he inflicted genocidal depredations on the natives and incurred the loss of 50,000 of his own men to the attrition of guerrilla tactics before having to withdraw to Hadrian's Wall. He repaired and reinforced the wall with a degree of thoroughness that led most subsequent Roman authors to attribute the construction of the wall to him. During the negotiations to purchase the truce necessary to secure the Roman retreat to the wall, Septimius Severus's wife, Julia Domna
Julia Domna (; – 217 AD) was Roman empress from 193 to 211 as the wife of Emperor Septimius Severus. She was the first empress of the Severan dynasty. Domna was born in Emesa (present-day Homs) in Roman Syria to an Arab family of priests of ...
, criticised the sexual morals of the Caledonian women; the wife of Argentocoxos, a Caledonian chief, replied: "We consort openly with the best of men while you allow yourselves to be debauched in private by the worst". This is the first recorded utterance confidently attributable to a native of the area now known as Scotland. The emperor Septimius Severus died at York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
while planning to renew hostilities, and these plans were abandoned by his son Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
.
Emperor Constantius came to Britain in 306, despite his poor health, with an army aiming to invade northern Britain, after the provincial defences had been rebuilt following the Carausian Revolt. Little is known of his campaigns with scant archaeological evidence, but fragmentary historical sources suggest he reached the far north of Britain and won a major battle in early summer before returning south. His son Constantine (later Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
) spent a year in northern Britain at his father's side, campaigning against the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
beyond Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
in the summer and autumn.Mattingly, 233–34; Southern, 170, 341.
Later excursions into Scotland by the Romans were generally limited to the scouting expeditions of ''exploratores'' in the buffer zone that developed between the walls, trading contacts, bribes to purchase truces from the natives, and eventually the spread of Christianity. The degree to which the Romans interacted with the Goidelic
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages ( ga, teangacha Gaelacha; gd, cànanan Goidhealach; gv, çhengaghyn Gaelgagh) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historically ...
-speaking island of Hibernia
''Hibernia'' () is the Classical Latin name for Ireland. The name ''Hibernia'' was taken from Greek geographical accounts. During his exploration of northwest Europe (c. 320 BC), Pytheas of Massalia called the island ''Iérnē'' (written ). ...
(modern Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
) is still unresolved amongst archaeologists in Ireland.
See also
 *
*Ancient Britain
Several species of humans have intermittently occupied Great Britain for almost a million years. The earliest evidence of human occupation around 900,000 years ago is at Happisburgh on the Norfolk coast, with stone tools and footprints prob ...
*British military history
The military history of the United Kingdom covers the period from the creation of the united Kingdom of Great Britain, with the political union of England and Scotland in 1707, to the present day.
From the 18th century onwards, with the expansio ...
*Roman governors of Britain
This is a partial list of governors of Roman Britain from 43 to 409. As the unified province "Britannia", Roman Britain was a consular province, meaning that its governors had to first serve as a consul in Rome before they could govern it. While th ...
* Roman mining
* Roman sites in Great Britain
*Itius Portus
Itius Portus or Portus Itius was the ancient Roman name for a sea port on the English Channel in what is now Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France, though its precise location is unknown. The main candidates have been Wissant and Boulogne (more usually called ...
*Pugnaces Britanniae Dogs of Roman Britain concerns the presence of dogs within Britain under Roman occupation. Through various excavations in the Province of Britannia, evidence for a variety of uses from dogs has been found. There has been presences of dog remains, f ...
Citations
References
* *Further reading
*The Great Invasion, Leonard Cottrell, Coward–McCann, New York, 1962, hardback. Was published in the UK in 1958. *Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
, '' Histories'', ''Annals
Annals ( la, annāles, from , "year") are a concise historical record in which events are arranged chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record.
Scope
The nature of the distinction between ann ...
'' and '' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae''
*''A.D. 43'', John Manley
John Paul Manley (born January 5, 1950) is a Canadian lawyer, businessman, and politician who served as the eighth deputy prime minister of Canada from 2002 to 2003. He served as Liberal Member of Parliament for Ottawa South from 1988 to 2 ...
, Tempus, 2002.
*''Roman Britain'', Peter Salway, Oxford, 1986
*Miles Russel – Ruling Britannia – History Today
''History Today'' is an illustrated history magazine. Published monthly in London since January 1951, it presents serious and authoritative history to as wide a public as possible. The magazine covers all periods and geographical regions and pub ...
8/2005 pp 5–6
*Francis Pryor
Francis Manning Marlborough Pryor (born 13 January 1945) is an English archaeologist specialising in the study of the Bronze and Iron Ages in Britain. He is best known for his discovery and excavation of Flag Fen, a Bronze Age archaeological s ...
. 2004. ''Britain BC''. New York: HarperPerennial.
*Francis Pryor. 2004. ''Britain AD''. New York: HarperCollins
HarperCollins Publishers LLC is one of the Big Five English-language publishing companies, alongside Penguin Random House, Simon & Schuster, Hachette, and Macmillan. The company is headquartered in New York City and is a subsidiary of News Cor ...
.
*George Shipway – Imperial Governor. 2002. London: Cassell Military Paperbacks.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Roman Conquest Of Britain
1st-century conflicts
1st century in Great Britain
1st century in the Roman Empire
43
Iron Age Britain
Military history of Roman Britain
Wars involving the Roman Empire
Invasions of England
Roman Britain