Road Racing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Road racing is a form of
Road racing is a form of
 The first organized automobile race was held on July 22, 1894, from
The first organized automobile race was held on July 22, 1894, from
 Road racing traditions in Europe, South America, Great Britain and the British Commonwealth nations grew around races held on paved, public roads such as the
Road racing traditions in Europe, South America, Great Britain and the British Commonwealth nations grew around races held on paved, public roads such as the
 Another motorcycle racing incident occurred at Monza during the 1973 Italian motorcycle Grand Prix when a racing accident claimed the lives of world champion Jarno Saarinen and
Another motorcycle racing incident occurred at Monza during the 1973 Italian motorcycle Grand Prix when a racing accident claimed the lives of world champion Jarno Saarinen and
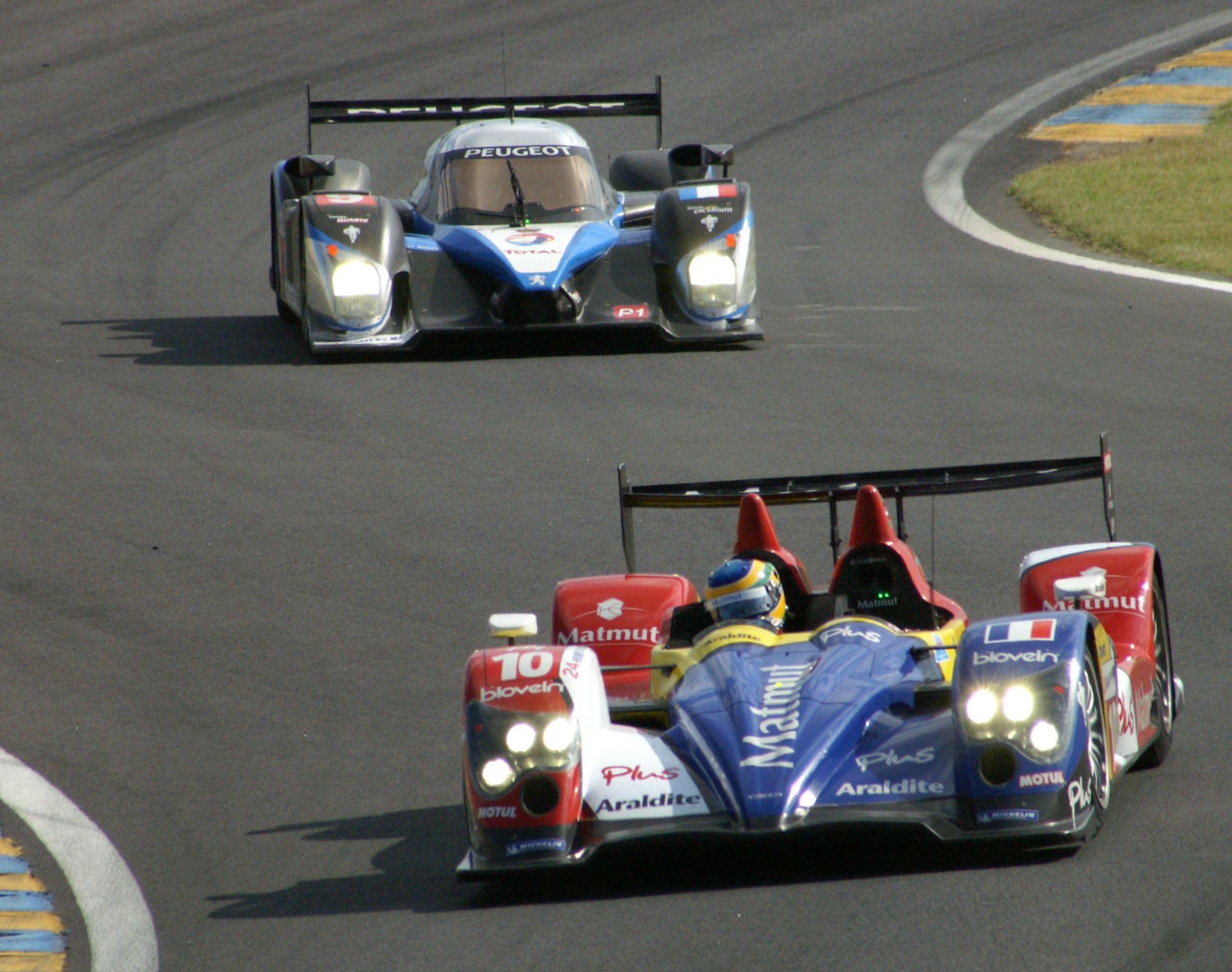

 The popularity of Formula One and motorcycle Grand Prix racing led to the formation of road racing world championships for other types of vehicles. In 1953, the FIA sanctioned a world championship for sports car racing which combined the Le Mans 24 Hours, the Mille Miglia, the 12 Hours of Sebring, the 24 Hours of Spa and the 1000km of the Nurburgring.
The popularity of Formula One and motorcycle Grand Prix racing led to the formation of road racing world championships for other types of vehicles. In 1953, the FIA sanctioned a world championship for sports car racing which combined the Le Mans 24 Hours, the Mille Miglia, the 12 Hours of Sebring, the 24 Hours of Spa and the 1000km of the Nurburgring.
motorsport
Motorsport, motorsports or motor sport is a global term used to encompass the group of competitive sporting events which primarily involve the use of motorized vehicles. The terminology can also be used to describe forms of competition of t ...
racing
In sport, racing is a competition of speed, in which competitors try to complete a given task in the shortest amount of time. Typically this involves traversing some distance, but it can be any other task involving speed to reach a specific go ...
held on a paved road surface
A road surface (British English), or pavement (American English), is the durable surface material laid down on an area intended to sustain vehicular or foot traffic, such as a road or walkway. In the past, gravel road surfaces, hoggin, cob ...
. The races can be held either on a closed circuit
Closed circuit can refer to:
*Closed-circuit television
*Closed-circuit radio
*Rebreather – breathing sets
* ''Closed Circuit'' (1978 film), a 1978 Italian film
* ''Closed Circuit'' (2013 film), a 2013 British thriller film
*An electric circuit
...
or on a street circuit
A street circuit is a motorsport racing circuit composed of temporarily closed-off public roads of a city, town or village, used in motor races. Airport runways and taxiways are also sometimes part of street circuits. Facilities such as ...
utilizing temporarily closed public road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types o ...
s. Originally, road races were held almost entirely on public roads. However, public safety concerns eventually led to most races being held on purpose-built racing circuits.
Road racing's origins were centered in Western Europe and Great Britain as motor vehicles became more common in the early 20th century. After the Second World War, automobile road races were organized into a series called the Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, ...
world championship sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile
The Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA; en, International Automobile Federation) is an association established on 20 June 1904 to represent the interests of motoring organisations and motor car users. It is the governing body for ...
(FIA), while motorcycle road races were organized into the Grand Prix motorcycle racing
Grand Prix motorcycle racing is the premier class of motorcycle road racing events held on road circuits sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme (FIM). Independent motorcycle racing events have been held since the start ...
series and sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme (FIM). The success and popularity of road racing has seen the sport spread across the globe with Grand Prix road races having been held on six continents. Other variations of road racing include; open-wheel racing
Formula racing (known as open-wheel racing in North America) is any of several forms of open-wheeled single-seater motorsport. The origin of the term lies in the nomenclature that was adopted by the FIA for all of its post- World War II single ...
, sports car racing, touring car racing
Touring car racing is a motorsport road racing competition with heavily modified road-going cars. It has both similarities to and significant differences from stock car racing, which is popular in the United States.
While the cars do not mov ...
, stock car racing, superbike racing, truck racing
Truck racing is a form of motorsport road racing which involves modified versions of heavy tractor units on road racing or oval track circuits.
History
The sport started in the United States at the Atlanta Motor Speedway on June 17, 1979 and ...
, kart racing and endurance racing.
History of road racing
Early road racing
 The first organized automobile race was held on July 22, 1894, from
The first organized automobile race was held on July 22, 1894, from Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
to Rouen, France. The first held in the United States was a 54-mile competition from Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
to Evanston, Illinois and return, held on November 27, 1895. By 1905, the Gordon Bennett Cup, organized by the Automobile Club de France, was considered the most important race in the world. In 1904, the ''Association Internationale des Automobiles Clubs Reconnus'' was formed by several European automobile clubs. In 1904 the FIM created the international cup for motorcycles. The first international motorcycle road race took place in 1905 at Dourdan, France.
After disagreeing with Bennett Cup organizers over regulations limiting the number of entrants, the French automobile manufacturers responded in 1906 by organizing the first French Grand Prix race held at Le Mans. During the 1910s, the Elgin National Road Races held on public roads around Elgin, Illinois
Elgin ( ) is a city in Cook and Kane counties in the northern part of the U.S. state of Illinois. Elgin is located northwest of Chicago, along the Fox River. As of the 2020 Census, the city had a population of 114,797, the seventh-larg ...
attracted competitors from around the country and drew large crowds of spectators. The first 24 Hours of Le Mans
The 24 Hours of Le Mans (french: link=no, 24 Heures du Mans) is an endurance-focused sports car race held annually near the town of Le Mans, France. It is the world's oldest active endurance racing event. Unlike fixed-distance races whose ...
endurance race was held in 1923. The Automobile Racing Club of America was founded in 1933 and became the Sports Car Club of America
The Sports Car Club of America (SCCA) is a non-profit American automobile club and sanctioning body supporting road racing, rallying, and autocross in the United States. Formed in 1944, it runs many programs for both amateur and professional ...
in 1944.
Race course evolution
The great majority of road races were run over a lengthy circuit of closed public roads, not purpose-built racing circuits. This was true of the Le Mans circuit of the 1906 French Grand Prix, as well as the Targa Florio (run on of Sicilian roads), the GermanKaiserpreis The Kaiserpreis (german: Emperor's Prize) auto race, named after Emperor Wilhelm II, was held in 1907. Like his brother's Prinz-Heinrich-Fahrt held from 1908 to 1911, it was a precursor to the German Grand Prix.
As Camille Jenatzy had won the Gor ...
circuit in the Taunus
The Taunus is a mountain range in Hesse, Germany, located north of Frankfurt. The tallest peak in the range is '' Großer Feldberg'' at 878 m; other notable peaks are '' Kleiner Feldberg'' (825 m) and '' Altkönig'' (798 m).
The Taunus range spa ...
mountains, the French circuit at Dieppe, used for the 1907 Grand Prix and, the Isle of Man TT motorcycle road circuit first used in 1907. The exceptions were the steeply banked egg-shaped near oval circuit of Brooklands
Brooklands was a motor racing circuit and aerodrome built near Weybridge in Surrey, England, United Kingdom. It opened in 1907 and was the world's first purpose-built 'banked' motor racing circuit as well as one of Britain's first airfields ...
in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, completed in 1906, the Indianapolis Motor Speedway
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is an automobile racing circuit located in Speedway, Indiana, an enclave suburb of Indianapolis, Indiana. It is the home of the Indianapolis 500 and the Verizon 200, and and formerly the home of the United Sta ...
, and the oval, banked speedways constructed in Europe at Monza in 1922 and at Montlhéry
Montlhéry () is a commune in the Essonne department in Île-de-France in northern France. It is located from Paris.
History
Montlhéry lay on the strategically important road from Paris to Orléans. Under the Merovingians, it was owned by ...
in 1924.
Road racing on public roads was banned in Great Britain in 1925 when a spectator was injured at the Kop Hill Climb
The Kop Hill Climb is a hillclimb in Princes Risborough, Buckinghamshire. The climb was originally established in 1910 but due to a minor accident involving a spectator on the public road that formed the hillclimb, the last competitive event was ...
event. The Royal Automobile Club (R.A.C.) and the Auto-Cycle Union (A.C.U.) stopped issuing permits for races on public roads, a policy that has not changed to this day. Donington Park was the first permanent park circuit in the United Kingdom and held its first motorcycle race in 1931. As automobile and motorcycle technology improved, racers began to achieve higher speeds that caused an increasing number of accidents on roads not designed for motorized vehicles. Public safety concerns ultimately caused the number of road racing events on public roads in Europe to decrease over the years. Notable exceptions are the Mille Miglia
The Mille Miglia (, ''Thousand Miles'') was an open-road, motorsport endurance race established in 1927 by the young Counts Francesco Mazzotti and Aymo Maggi, which took place in Italy twenty-four times from 1927 to 1957 (thirteen before World ...
which was allowed to continue until 1957 and, the Pau Grand Prix which has been held on the city streets of Pau, France since 1933.
After the First World War, automobile and motorcycle road racing competitions in Europe and in North America went in different directions. Automobile and motorcycle racing in the United States was typically oval track racing
Oval track racing is a form of closed-circuit motorsport that is contested on an oval-shaped race track. An oval track differs from a Road racing, road course in that the layout resembles an oval with turns in only one direction, and the directi ...
on paved tracks such as the Indianapolis Motor Speedway and the Milwaukee Mile
The Milwaukee Mile is a oval race track in the central United States, located on the grounds of the Wisconsin State Fair Park in West Allis, Wisconsin, a suburb west of Milwaukee. Its grandstand and bleachers seats approximately 37,000 specta ...
track, or on dirt tracks using widely available horse racing circuits. Automobile dirt track racing would develop into stock car racing. American racing also branched out into drag racing.
 Road racing traditions in Europe, South America, Great Britain and the British Commonwealth nations grew around races held on paved, public roads such as the
Road racing traditions in Europe, South America, Great Britain and the British Commonwealth nations grew around races held on paved, public roads such as the Circuit de la Sarthe
The Circuit des 24 Heures du Mans, also known as Circuit de la Sarthe (after the 1906 French Grand Prix triangle circuit) located in Le Mans, Sarthe, France, is a semi-permanent motorsport race course, chiefly known as the venue for the 24 H ...
circuit near the town of Le Mans
Le Mans (, ) is a city in northwestern France on the Sarthe River where it meets the Huisne. Traditionally the capital of the province of Maine, it is now the capital of the Sarthe department and the seat of the Roman Catholic diocese of Le ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, the Spa-Francorchamps
The Circuit de Spa-Francorchamps (), frequently referred to as ''Spa'', is a motor-racing circuit located in Stavelot, Belgium. It is the current venue of the Formula One Belgian Grand Prix, hosting its first Grand Prix in 1925, and has he ...
Circuit in Belgium and the Mount Panorama Circuit in Australia. Certain European race circuits were situated in mountainous regions where the topography meant that the roads featured numerous curves and elevation changes, allowing the creation of sinuous and undulating race courses such as the Nürburgring in the Eifel mountains of Germany and the Circuit de Charade in the Chaîne des Puys
The Chaîne des Puys () is a north-south oriented chain of cinder cones, lava domes, and maars in the Massif Central of France. The chain is about 40 km (25 mi) long, and the identified volcanic features, which constitute a volcanic ...
in the Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.
Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,0 ...
of France. These circuits presented such a challenge that they were both feared and respected by racers. The long Nurburgring with more than 300 metres (1,000 feet) of elevation change from its lowest to highest points, was nicknamed "The Green Hell" by Jackie Stewart, due to its challenging nature. The sinuous track layout of the Charade circuit caused some drivers like Jochen Rindt in the 1969 French Grand Prix
The 1969 French Grand Prix was a Formula One motor race held at the Charade Circuit on 6 July 1969. It was race 5 of 11 in both the 1969 World Championship of Drivers and the 1969 International Cup for Formula One Manufacturers. There were only t ...
to complain of motion sickness, and wore open face helmets just in case.
Post-war era
In 1949 the FIM introduced the Grand Prix motorcycle racing world championship with the 1949 Isle of Man TT being the inaugural event. With the exception of the Monza circuit, all the Grand Prix races were held onstreet circuit
A street circuit is a motorsport racing circuit composed of temporarily closed-off public roads of a city, town or village, used in motor races. Airport runways and taxiways are also sometimes part of street circuits. Facilities such as ...
s. The Association Internationale des Automobiles Clubs Reconnus was renamed the Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile in 1946 and, plans were developed for a road racing world championship. In 1950, the FIA created the Formula One world championship, a competition of seven rounds that included the Indianapolis 500.World Championship of Drivers, 1974 FIA Yearbook, Grey section, pages 118 & 119 A Formula I manufacturers' championship was begun in 1955.
The success of American racers such as Phil Hill
Philip Toll Hill Jr. (April 20, 1927 – August 28, 2008) was an American automobile racing driver. He was one of two American drivers to win the Formula One World Drivers' Championship, and the only one who was born in the United States ( ...
and Dan Gurney in Formula One in the late 1950s sparked to a renewal of interest in road racing in the United States and, led to the construction of new road racing circuits such as Riverside International Raceway, Road America and Laguna Seca. The 1964 United States motorcycle Grand Prix
The United States motorcycle Grand Prix was a round of the FIM Grand Prix motorcycle racing World Championship.
History
The first United States Grand Prix was held in 1961 as a non-championship race at the Daytona International Speedway on the ...
was held at the Daytona International Speedway
Daytona International Speedway is a race track in Daytona Beach, Florida, United States. Since opening in 1959, it has been the home of the Daytona 500, the most prestigious race in NASCAR as well as its season opening event. In addition to NASC ...
and led to increased international prominence for the Daytona 200
The Daytona 200 is an annual motorcycle road racing competition held in early spring at the Daytona International Speedway in Daytona Beach, Florida. The race was founded in 1937 when it was sanctioned by the American Motorcyclist Associat ...
road race which peaked in 1974 with the victory by 15-time world champion Giacomo Agostini.
Racing hazards and safety
The dangers associated with the increasing speeds at road races were highlighted by the1955 Le Mans disaster
The 1955 Le Mans disaster was a major crash that occurred on 11 June 1955 during the 24 Hours of Le Mans motor race at Circuit de la Sarthe in Le Mans, Sarthe, France. Large pieces of debris flew into the crowd, killing 83 spectators and Frenc ...
. With spectators seated near the edges of the circuit, two race cars came into contact causing one of the vehicles to crash into the embankment, where it exploded in a ball of flames and then plowed through the crowd of spectators. In addition to the driver of the race car, 83 spectators were killed and 120 were injured. Auto racing was temporarily banned in several countries after the Le Mans disaster until safety was improved for spectators. Switzerland would not allow circuit racing until the Zürich ePrix in 2018.
The Formula One championship experienced its worst tragedy during the 1961 Italian Grand Prix
The 1961 Italian Grand Prix was a Formula One motor race held on 10 September 1961 at Monza. It was race 7 of 8 in both the 1961 World Championship of Drivers and the 1961 International Cup for Formula One Manufacturers.
The race was marked b ...
at Monza, when driver Wolfgang von Trips lost control of his Ferrari
Ferrari S.p.A. (; ) is an Italian luxury sports car manufacturer based in Maranello, Italy. Founded by Enzo Ferrari (1898–1988) in 1939 from the Alfa Romeo racing division as ''Auto Avio Costruzioni'', the company built its first car in ...
and crashed into a stand full of spectators, killing 15 and himself. In 1970, Jochen Rindt won the Formula One drivers' championship
Formula One, abbreviated to F1, is the highest class of open-wheeled auto racing defined by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA), motorsport's world governing body. The "formula" in the name refers to a set of rules to which ...
posthumously, the only man to do so, underlining the continuing risks associated with road racing. The tragedies highlighted the need for improved safety standards for both drivers and spectators; safety would continue to be an issue throughout the 1960s and 1970s.
When motorcycle racer Gilberto Parlotti was killed while competing in the 1972 Isle of Man TT, it sparked a rider's boycott of the event led by multi-time world champion, Giacomo Agostini, a close friend of Parlotti. Once the most prestigious race of the year, the event was increasingly boycotted by the top riders, and in 1976, the Isle of Man TT finally succumbed to pressure for increased safety in racing events and had its world championship status revoked by the FIM.
Renzo Pasolini
Renzo Pasolini (18 July 1938 – 20 May 1973), nicknamed "Paso", was an Italian professional motorcycle road racer. He competed in the FIM Grand Prix motorcycle racing world championships from 1964 to 1972.
Although he never won a world champ ...
. After the von Trips accident in 1961, the Monza Circuit had been lined with steel barriers as a result of demands by automobile racers. Most auto racers believed steel barriers would improve safety for auto racers and spectators, but they had the opposite effect for motorcyclists and proved fatal for Saarinen and Pasolini.
The dangers of street circuits was further exposed at the 1975 Spanish Grand Prix held on the twisty, tree-lined Montjuich circuit in Barcelona. The racing drivers found that the circuit's safety barriers had been shoddily installed and threatened to strike if the barriers were not brought up to standard. Under pressure from race organizers, the race was started only to be stopped after 29 laps when the car of Rolf Stommelen plowed into the crowd, killing four spectators.
Safety improvements
By the late 1970s, the popularity of Grand Prix road racing attracted corporate sponsors and lucrative television contracts which, led to an increased level of professionalism. Road racers organized to demand that stricter safety regulations be adopted by sanctioning bodies in relation to race track safety and race organizers requirements. Race circuits that had originally been public roads were widened and modified to include chicanes and run-off areas while, some circuits were shortened to reduce the amount of safety personnel required. These changes saw a dramatic decrease in deaths and accidents.Modern road racing on public roads
By the 1980s, motorcycle Grand Prix and the Formula One races were held on purpose built race circuits with the exception of theMonaco Grand Prix
The Monaco Grand Prix (french: Grand Prix de Monaco) is a Formula One motor racing event held annually on the Circuit de Monaco, in late May or early June. Run since 1929, it is widely considered to be one of the most important and prestigio ...
held on the city streets of Monaco. Street circuits such as the Montjuïc circuit and the Opatija Circuit with their numerous unmovable roadside obstacles, such as trees, stone walls, lampposts and buildings, were gradually removed from world championship competition.
Although events held on closed public roads such as the Isle of Man TT, lost their world championship status due to their considerable safety risk, their popularity continued to flourish leading to a branch of road racing known as Traditional Road Racing. Traditional road racing on closed public roads is popular in the United Kingdom, New Zealand and parts of Europe. The Duke Road Racing Rankings was established in 2002 to establish rider classifications in traditional road racing events such as the North West 200
The International North West 200 is a Northern Irish motorsport event established in 1929 for road racing motorcycles held on a street circuit known as ''the Triangle'' between the towns of Portstewart, Coleraine and Portrush in Causeway Coast ...
and the Ulster Grand Prix
The Ulster Grand Prix is a motorcycle race that takes place on the Dundrod Circuit made up entirely of closed-off public roads near Belfast, Northern Ireland. The first races took place in 1922 and in 1935 and 1948 the Fédération Internati ...
.
In Formula One, street circuits have made a comeback with the Melbourne Grand Prix Circuit and the Baku City Circuit joining the Circuit de Monaco as part of the world championship. There are no street circuits being used in MotoGP racing.. In North America, racing on public streets takes place at the Grand Prix of Long Beach, the Firestone Grand Prix of St. Petersburg
The Firestone Grand Prix of St. Petersburg is an IndyCar Series race held in St. Petersburg, Florida. In most years since 2009, the race has served as the season opener (or at minimum, the first race held on U.S. soil). The race is held annually ...
, the Detroit Grand Prix, and the Honda Indy Toronto.
Road racing proliferation

 The popularity of Formula One and motorcycle Grand Prix racing led to the formation of road racing world championships for other types of vehicles. In 1953, the FIA sanctioned a world championship for sports car racing which combined the Le Mans 24 Hours, the Mille Miglia, the 12 Hours of Sebring, the 24 Hours of Spa and the 1000km of the Nurburgring.
The popularity of Formula One and motorcycle Grand Prix racing led to the formation of road racing world championships for other types of vehicles. In 1953, the FIA sanctioned a world championship for sports car racing which combined the Le Mans 24 Hours, the Mille Miglia, the 12 Hours of Sebring, the 24 Hours of Spa and the 1000km of the Nurburgring. NASCAR
The National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing, LLC (NASCAR) is an American auto racing sanctioning and operating company that is best known for stock car racing. The privately owned company was founded by Bill France Sr. in 1948, and ...
held its first road race in 1957 at the Watkins Glen International circuit with Buddy Baker as the winner. The FIA launched the European Touring Car Championship in 1963.
The FIA created the International Karting Commission (CIK) in 1962 and, in 1964, the first CIK Karting World Championship was won by Guido Sala. Karting has become a significant step in the development of road racers including Formula One world champion Lewis Hamilton. The European Truck Racing Championship
The FIA European Truck Racing Championship is a motorsport truck road racing series for semi-tractors which is sanctioned to the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile
The Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA; en, Internati ...
was founded in 1985. A Superbike World Championship for road-going production motorcycles was created in 1988.
As road racing grew in popularity it eventually expanded across the globe with Grand Prix road races having been held on six continents. Expansion of the Formula One and MotoGP series has resulted in many dedicated tracks being built, like in Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
, Sepang in Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
, and Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the ...
in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
.
See also
* Drag racing *Formula racing
Formula racing (known as open-wheel racing in North America) is any of several forms of open-wheeled single-seater motorsport. The origin of the term lies in the nomenclature that was adopted by the FIA for all of its post-World War II single ...
* Hillclimbing
* Isle of Man TT
* List of Formula One circuits
Formula One, abbreviated to F1, is currently the highest class of open-wheeled auto racing defined by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA), motorsport's world governing body. The "formula" in the name refers to a set of rules ...
* List of Grand Prix motorcycle circuits
This is a list of circuits which have hosted a World Championship race from to .
In total, 73 different circuits have hosted World Championship races. The first to do so was the Snaefell Mountain Course, home of the Isle of Man TT, which also h ...
* Oval track racing
Oval track racing is a form of closed-circuit motorsport that is contested on an oval-shaped race track. An oval track differs from a Road racing, road course in that the layout resembles an oval with turns in only one direction, and the directi ...
* Street circuit
A street circuit is a motorsport racing circuit composed of temporarily closed-off public roads of a city, town or village, used in motor races. Airport runways and taxiways are also sometimes part of street circuits. Facilities such as ...
* Superkart
* Traditional Road Racing
* World Superbike Championship
References
{{Reflist Auto racing by type *