Ringtail (sail) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A ringtail a 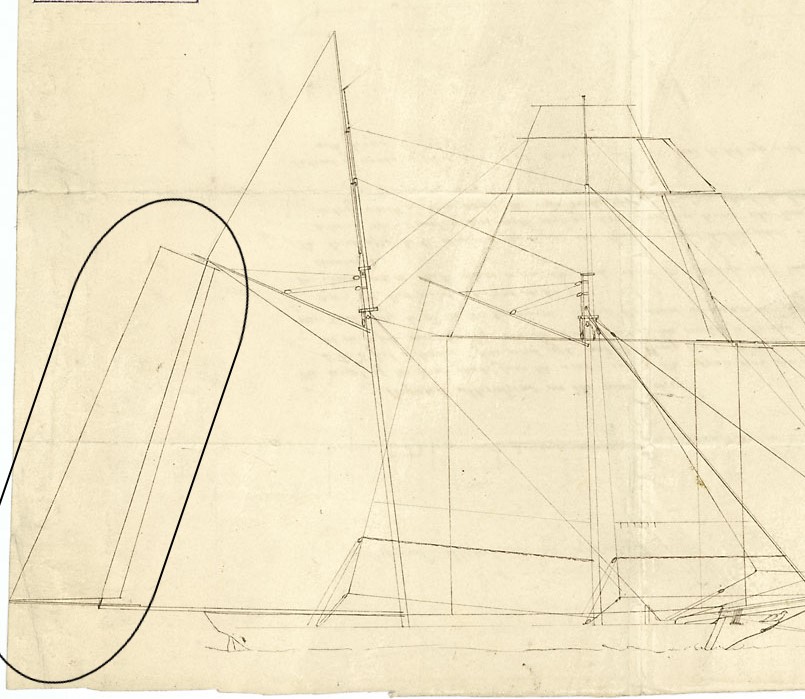
Article with image of topsail-type of triangular ringtail.
{{Sail Types Sailing rigs and rigging
sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may ...
which is set abaft (behind) a fore-and-aft
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel.
Description
Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, ga ...
sail to increase the total sail area of a sailing vessel in light winds. It may be three or four-sided.

Description
A ringtail sail may be quadrilateral or triangular in shape.Quadrilateral
The older and more common type is a quadrilateral sail set on spars which extend the gaff and boom of agaff sail
Gaff rig is a sailing rig (configuration of sails, mast and stays) in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the ''gaff''. Because of the size and sha ...
. The effect is as if the gaff sail were larger in size, with the extra sail cloth of the ringtail continuing the plane in which the gaff sail is set.
Triangular
The triangular ringtail is set both above and behind a triangular working sail on the mizzen mast, providing extra sail area with minimal crew input, typically on late 19th-century schooners on the American West Coast. The head of the ringtail is hoisted to the top of the topmast, and the clew is sheeted down to the end of the boom of the working sail. The luff runs parallel to the topmast, to which it is usually laced. The foot approximately follows the line of the luff of the working sail with which it is set.References
External links
Article with image of topsail-type of triangular ringtail.
{{Sail Types Sailing rigs and rigging