Rimini219 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rimini ( , ; rgn, Rémin; la, Ariminum) is a city in the
 The area was inhabited by
The area was inhabited by
 When the
When the
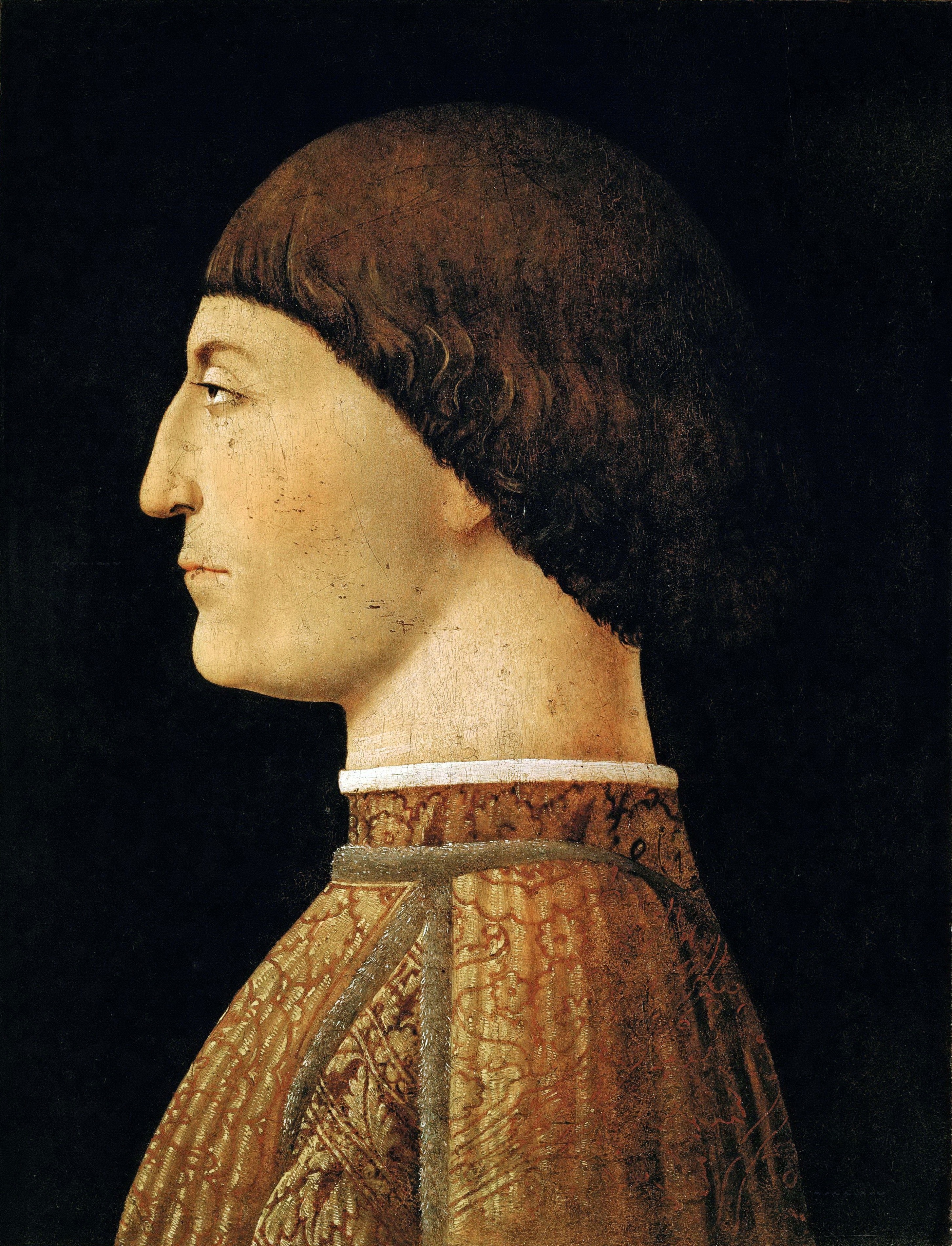
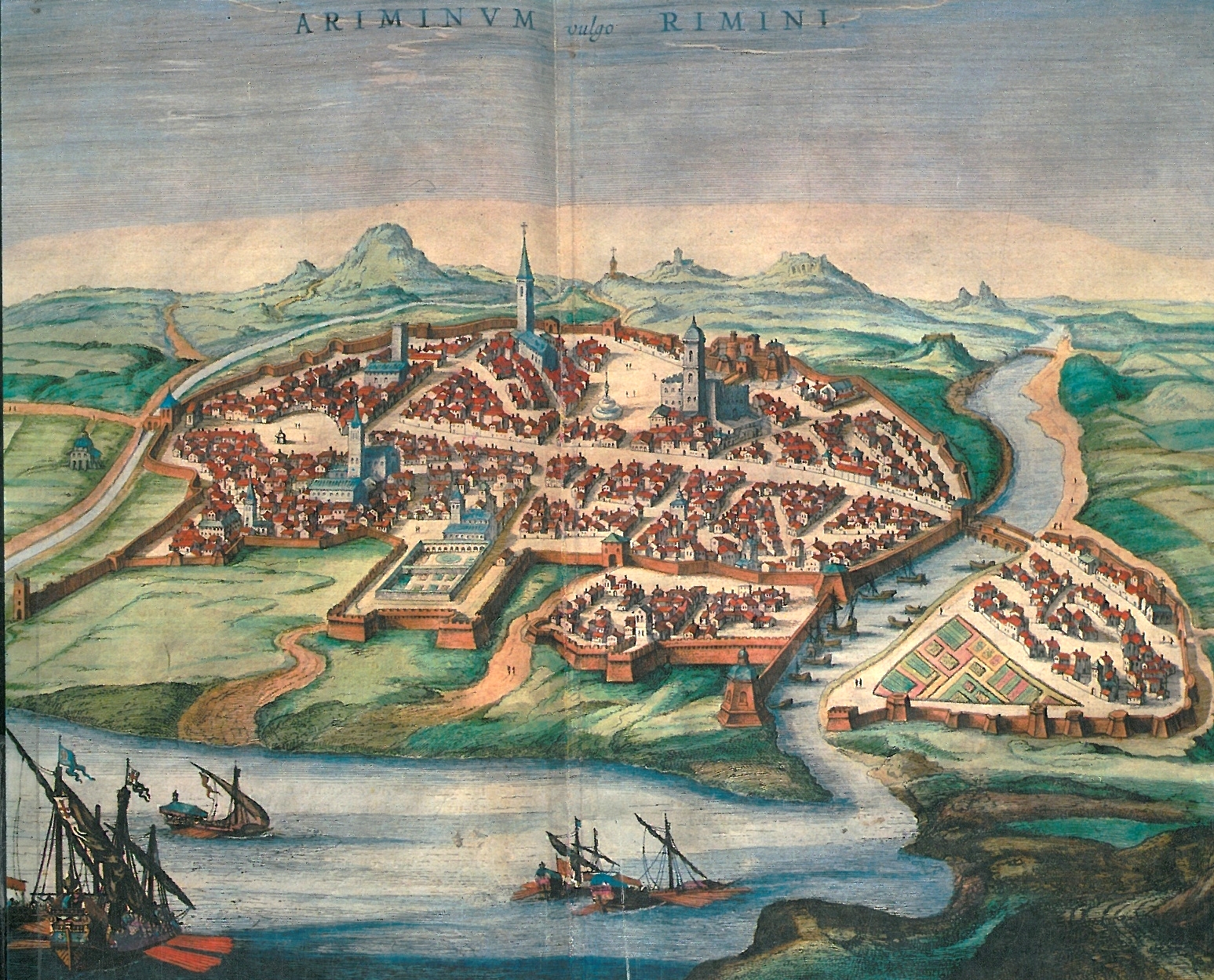 At the beginning of the 16th century, Rimini, now a secondary town of the Papal States, was ruled by an
At the beginning of the 16th century, Rimini, now a secondary town of the Papal States, was ruled by an
 On 30 March 1815,
On 30 March 1815,
 Rimini is situated at 44°03′00″
Rimini is situated at 44°03′00″
File:Rimini dall'alto (ottobre 2013).jpg, Aerial view of Rimini
File:Beach of Rimini (14-07-2012).jpg, Rimini beach
File:San Giuliano Mare and Rivabella (14-07-2012).jpg, View of Rimini Marina, San Giuliano Mare
File:Rimini-via01.jpg, Street in Borgo S. Giuliano
 Rimini is a major international tourist destination and seaside resort, among the most well known in
Rimini is a major international tourist destination and seaside resort, among the most well known in 
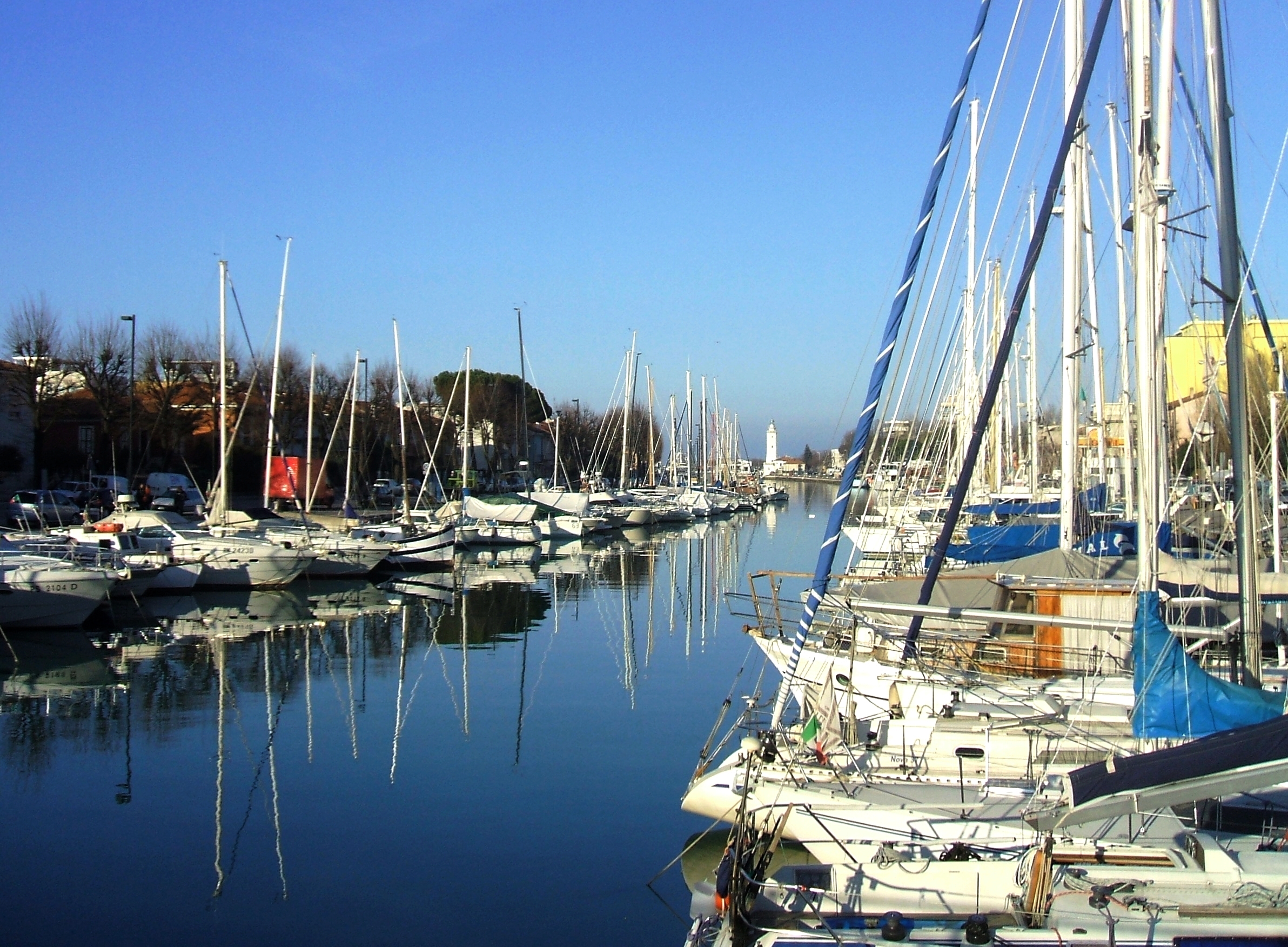
 Tourism in Rimini started as therapeutic stay (thalassotherapy, hydrotherapy and heliotherapy), evolving into elite vacation in the late 19th century, into middle-class tourism during the fascist era and finally into mass tourism in the postwar period.
On summer nights, there is a festival called "La Notte Rosa".
Rimini concentrates about a quarter of
Tourism in Rimini started as therapeutic stay (thalassotherapy, hydrotherapy and heliotherapy), evolving into elite vacation in the late 19th century, into middle-class tourism during the fascist era and finally into mass tourism in the postwar period.
On summer nights, there is a festival called "La Notte Rosa".
Rimini concentrates about a quarter of
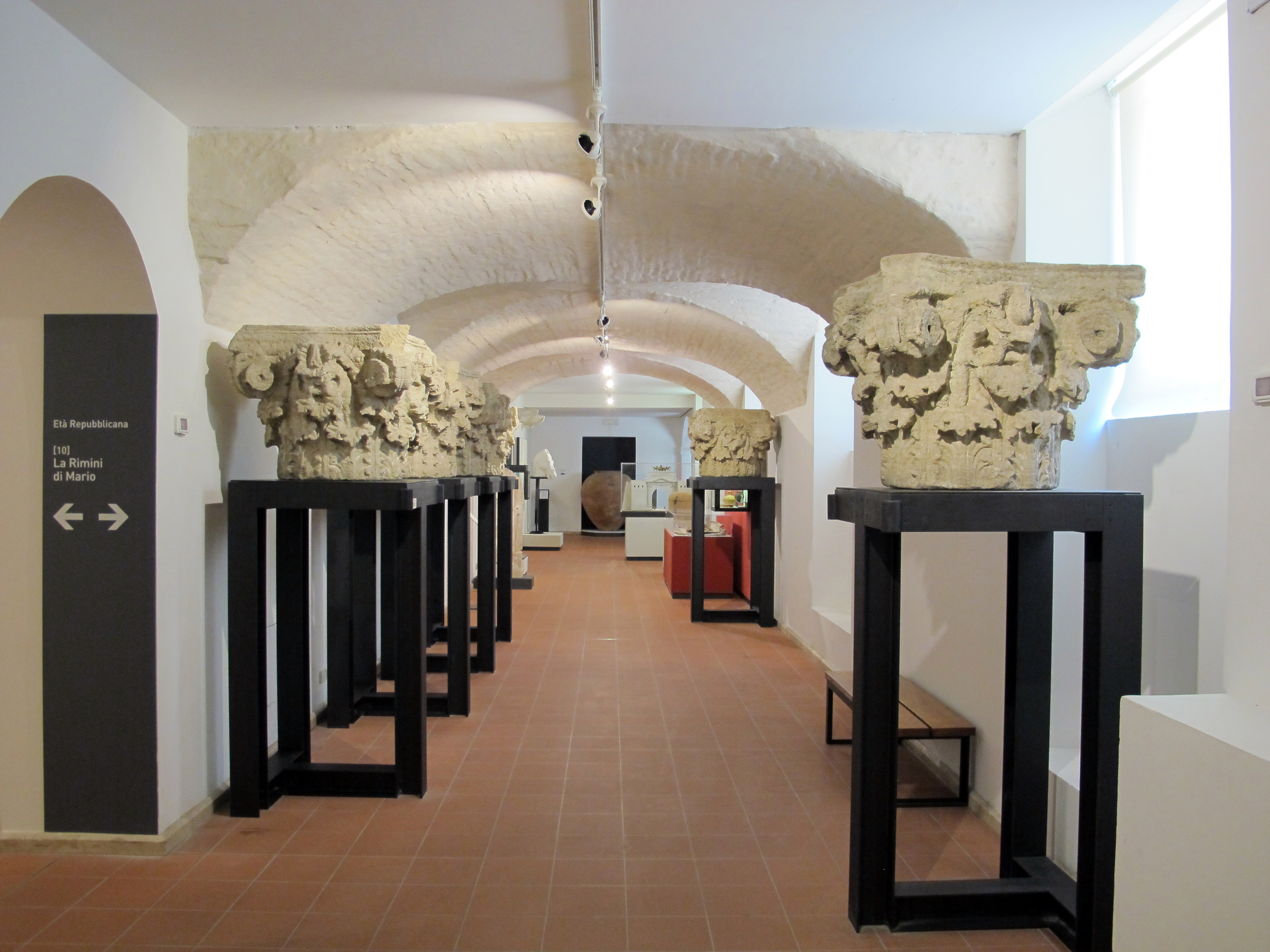 The ''City Museum'' (Museo della Città), main museal institution of Rimini, was inaugurated as "Archaeology Gallery", at the ground floor of Palazzo Gambalunga in 1872, thanks to Riminese historian Luigi Tonini, active in researching and studying the local archaeological heritage. The Archaeology Gallery was the first museum of the city and was conceived as a collection of Etruscan civilization and Ancient Rome, Roman antiquities, found in Rimini and in the surrounding countryside.
The civic museum was arranged in San Francesco monastery in 1923 and in 1938 was enlarged with a section of Medieval Art. The objects avoided the destructions of
The ''City Museum'' (Museo della Città), main museal institution of Rimini, was inaugurated as "Archaeology Gallery", at the ground floor of Palazzo Gambalunga in 1872, thanks to Riminese historian Luigi Tonini, active in researching and studying the local archaeological heritage. The Archaeology Gallery was the first museum of the city and was conceived as a collection of Etruscan civilization and Ancient Rome, Roman antiquities, found in Rimini and in the surrounding countryside.
The civic museum was arranged in San Francesco monastery in 1923 and in 1938 was enlarged with a section of Medieval Art. The objects avoided the destructions of  In the Archaeological department are exhibited grave goods from Villanovian civilization, Villanovian tombs of
In the Archaeological department are exhibited grave goods from Villanovian civilization, Villanovian tombs of
 The Gambalunghiana Library, historic institution founded in 1617 by jurist Alessandro Gambalunga, plays a leading role in the city's cultural life. The library has over 280,000 books, including 60,000 ancient books, 1,350 manuscripts, 6,000 prints and 80,000 photographs. Among the incunables, dated back from the 15th century, stand out ''De mulieribus claris, De Claris mulieribus'' (1497) by Giacomo Filippo Foresti and ''De re militari'' by Roberto Valturio. The collection of illuminated manuscripts, coming from different cultural and linguistic European boundaries, includes the ''Regalis Historia'' by Frate Leonardo and ''De Civitate Dei'' by Augustine of Hippo, Saint Augustine.
The Gambalunghiana Library, historic institution founded in 1617 by jurist Alessandro Gambalunga, plays a leading role in the city's cultural life. The library has over 280,000 books, including 60,000 ancient books, 1,350 manuscripts, 6,000 prints and 80,000 photographs. Among the incunables, dated back from the 15th century, stand out ''De mulieribus claris, De Claris mulieribus'' (1497) by Giacomo Filippo Foresti and ''De re militari'' by Roberto Valturio. The collection of illuminated manuscripts, coming from different cultural and linguistic European boundaries, includes the ''Regalis Historia'' by Frate Leonardo and ''De Civitate Dei'' by Augustine of Hippo, Saint Augustine.
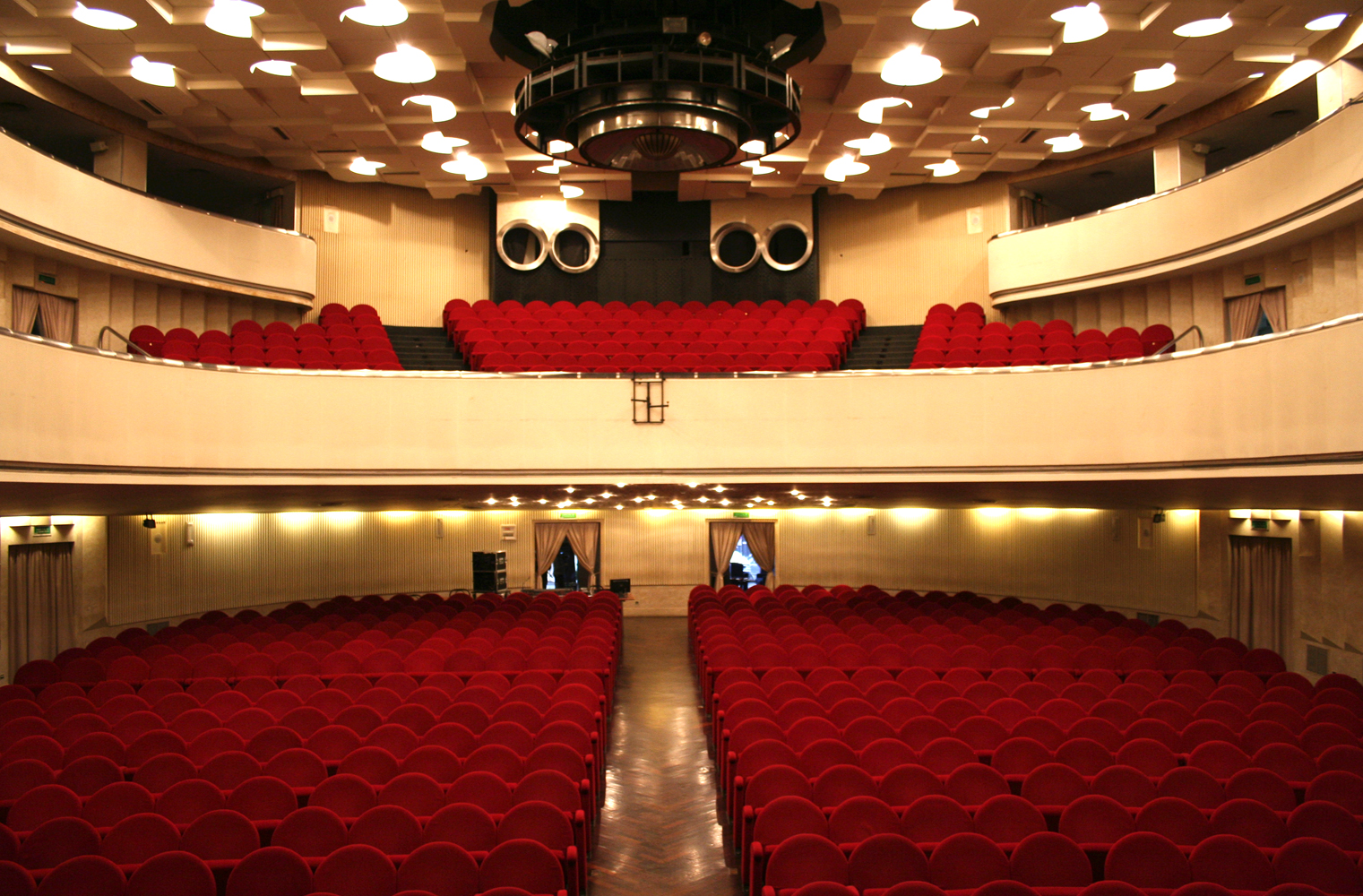 The first stable theatre in Rimini is documented since 1681, when the city council decided on the transformation of the Arengo's main hall into a large theatre hall, hosting shows of amateur dramatics companies and the young Carlo Goldoni, who was studying philosophy in the city at that time.
Between 1842 and 1857 the great Municipal Theatre Vittorio Emanuele II was built, designed in Neoclassical style by the architect Luigi Poletti (architect), Luigi Poletti, according to the traditional canons of the 19th-century Italian theatre. The theatre was inaugurated by Giuseppe Verdi, who directed "L'Aroldo", and hosted prestigious opera seasons until its destruction in 1943 due to aerial bombings. Since 1947, it has been called Amintore Galli Theatre. Since its closure, theatre shows has been hosted in the modern Teatro Ermete Novelli in Marina Centro.
Rimini appeared on the movie screen for the first time in some early footages, such as the documentary "Rimini l'Ostenda d'Italia" (1912), and in various Istituto Luce's newsreels in the Thirties. The film director
The first stable theatre in Rimini is documented since 1681, when the city council decided on the transformation of the Arengo's main hall into a large theatre hall, hosting shows of amateur dramatics companies and the young Carlo Goldoni, who was studying philosophy in the city at that time.
Between 1842 and 1857 the great Municipal Theatre Vittorio Emanuele II was built, designed in Neoclassical style by the architect Luigi Poletti (architect), Luigi Poletti, according to the traditional canons of the 19th-century Italian theatre. The theatre was inaugurated by Giuseppe Verdi, who directed "L'Aroldo", and hosted prestigious opera seasons until its destruction in 1943 due to aerial bombings. Since 1947, it has been called Amintore Galli Theatre. Since its closure, theatre shows has been hosted in the modern Teatro Ermete Novelli in Marina Centro.
Rimini appeared on the movie screen for the first time in some early footages, such as the documentary "Rimini l'Ostenda d'Italia" (1912), and in various Istituto Luce's newsreels in the Thirties. The film director

 Rimini's cuisine is simple and characterized by intense flavours and it is indissolubly related to the traditions of rural culture, influenced by the city's location—between the sea and the hills and near the border between
Rimini's cuisine is simple and characterized by intense flavours and it is indissolubly related to the traditions of rural culture, influenced by the city's location—between the sea and the hills and near the border between
File:Rimini Piazza Cavour.JPG, Piazza Cavour
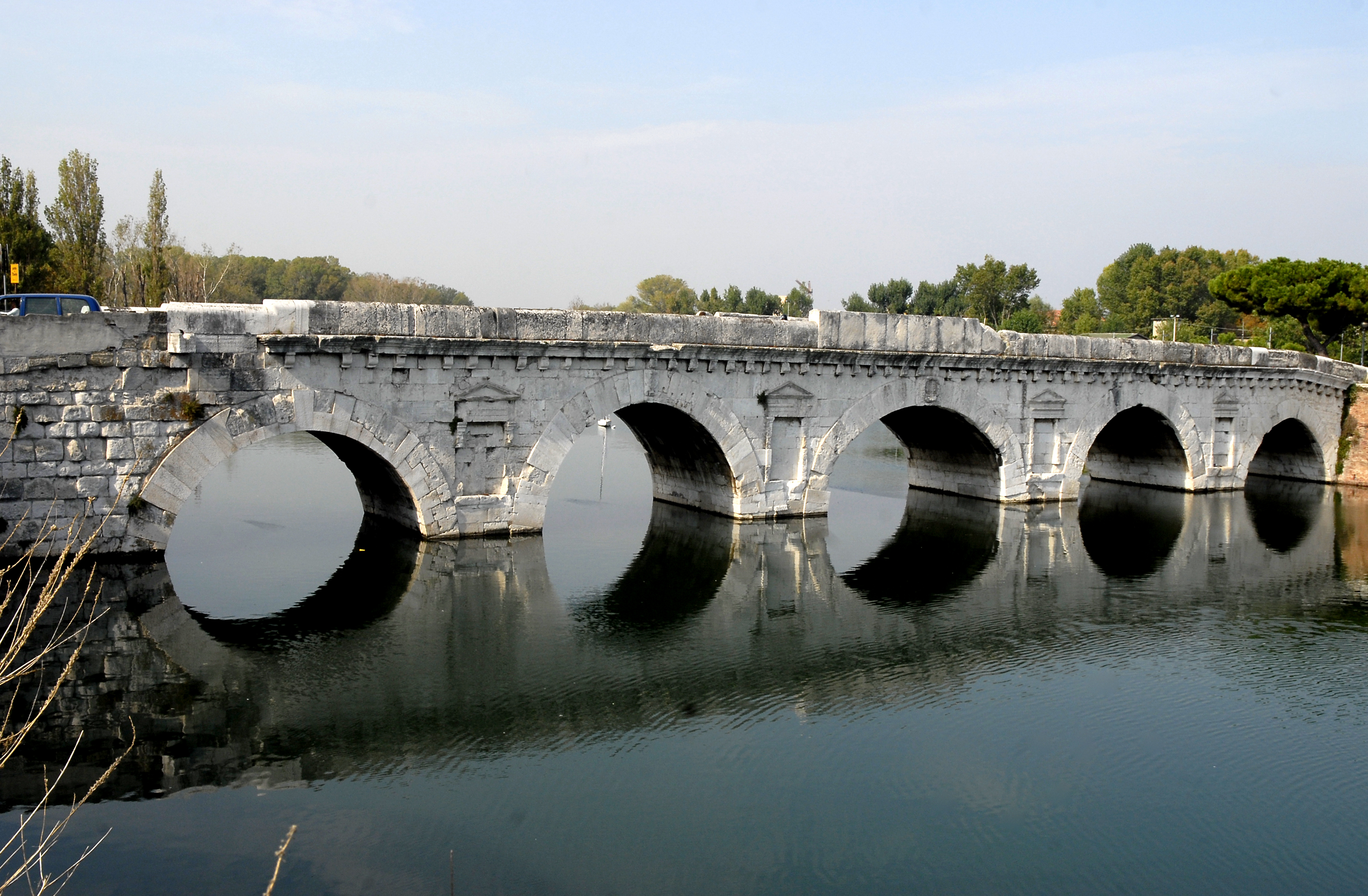
File:P71226-155652.jpg, The Tiberius Bridge
File:Rimini Piazza Tre Martiri 2.JPG, Piazza Tre Martiri







File:Rimini Parco XXV Aprile.JPG, XXV Aprile Park
File:Rimini Parco Giovanni Paolo II.JPG, Giovanni Paolo II Park
File:Rimini Parco Cervi.JPG, Alcide Cervi Park
File:Autostrada A14.jpg, Autostrada A14 (Italy), The A14 Adriatic Motorway
File:Stazione FS di Rimini (maggio 2011).jpg, Rimini railway station, Rimini Station
File:Aeroporto Rimini-Miramare.jpg, Federico Fellini International Airport
 The main football team of the city is Rimini Calcio. It played for nine years (between 1976 and 2009) in Serie B, the second-highest division in the Italian football league system. Its better positioning was the fifth place of the 2006–07 Serie B, 2006–07 season (when Rimini was also undefeated in both games against Juventus F.C., Juventus).
Rimini has also a notable basketball team, the Basket Rimini Crabs, which played for several years in Serie A and two times in the European FIBA Korać Cup, Korać Cup. About baseball, Rimini Baseball Club won 12 national championships and it was also European champion three times.
Rimini is the site of the annual Paganello event, one of the world's premier Beach Ultimate tournaments.
The main football team of the city is Rimini Calcio. It played for nine years (between 1976 and 2009) in Serie B, the second-highest division in the Italian football league system. Its better positioning was the fifth place of the 2006–07 Serie B, 2006–07 season (when Rimini was also undefeated in both games against Juventus F.C., Juventus).
Rimini has also a notable basketball team, the Basket Rimini Crabs, which played for several years in Serie A and two times in the European FIBA Korać Cup, Korać Cup. About baseball, Rimini Baseball Club won 12 national championships and it was also European champion three times.
Rimini is the site of the annual Paganello event, one of the world's premier Beach Ultimate tournaments.
 * Ancient Bards (founded 2006), symphonic metal band
* Enea Bastianini (born 1997), motorcycle racer
* Samuele Bersani (born 1970), singer-songwriter
* Marco Bezzecchi (born 1998), motorcycle racer
* Pier Paolo Bianchi (born 1952), Grand Prix motorcycle road racer
* Rosetta Boninsegna (1926–1972), painter
* Matteo Brighi (born 1981), football player
* Claudio Maria Celli (born 1941), titular archbishop
* Gregorio Celli (1225–1343), Roman Catholic priest, professed member of the Order of Saint Augustine, beatified by Pope Clement XIV on 6 September 1769
* Roberto Paci Dalò (born 1962), composer, director, visual artist
* Patrizia Deitos (born 1975), supermodel and singer
* Mattia Drudi (born 1998), racing driver
*
* Ancient Bards (founded 2006), symphonic metal band
* Enea Bastianini (born 1997), motorcycle racer
* Samuele Bersani (born 1970), singer-songwriter
* Marco Bezzecchi (born 1998), motorcycle racer
* Pier Paolo Bianchi (born 1952), Grand Prix motorcycle road racer
* Rosetta Boninsegna (1926–1972), painter
* Matteo Brighi (born 1981), football player
* Claudio Maria Celli (born 1941), titular archbishop
* Gregorio Celli (1225–1343), Roman Catholic priest, professed member of the Order of Saint Augustine, beatified by Pope Clement XIV on 6 September 1769
* Roberto Paci Dalò (born 1962), composer, director, visual artist
* Patrizia Deitos (born 1975), supermodel and singer
* Mattia Drudi (born 1998), racing driver
*
 Rimini is twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:
* Fort Lauderdale, Florida, Fort Lauderdale, United States
* Saint-Maur-des-Fossés, France
* Seraing, Belgium
* Sochi, Russia
* Yangzhou, China
* Ziguinchor, Senegal
Rimini is twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:
* Fort Lauderdale, Florida, Fort Lauderdale, United States
* Saint-Maur-des-Fossés, France
* Seraing, Belgium
* Sochi, Russia
* Yangzhou, China
* Ziguinchor, Senegal
Province of Rimini
Rimini Comune (Town Council)
Official Tourist Information site of Rimini (Town Council)
Rimini Travel Guide in Dutch
{{Authority control Rimini, 260s BC establishments 268 BC Populated places established in the 3rd century BC 3rd-century BC establishments in Italy Cities and towns in Emilia-Romagna Duchy of the Pentapolis Papal States Roman amphitheatres in Italy Roman sites of Emilia-Romagna Seaside resorts in Italy
Emilia-Romagna
egl, Emigliàn (man) egl, Emiglièna (woman) rgn, Rumagnòl (man) rgn, Rumagnòla (woman) it, Emiliano (man) it, Emiliana (woman) or it, Romagnolo (man) it, Romagnola (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title ...
region of northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
and capital city of the Province of Rimini
The province of Rimini ( it, provincia di Rimini) is a province in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy. The provincial capital is the eponymous city of Rimini. The province borders the independent Republic of San Marino. As of 2019, the province ...
. It sprawls along the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, on the coast between the rivers Marecchia
The Marecchia () is a river in eastern Italy. In ancient times it was known as the ''Ariminus'' which was from the Greek ''Aríminos'' (, which is also the ancient name of Rimini). The source of the river is near Monte dei Frati which is east of P ...
(the ancient ''Ariminus'') and Ausa (ancient ''Aprusa''). It is one of the most notable seaside resorts in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
with revenue from both internal and international tourism forming a significant portion of the city's economy. It is also near San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
, a small nation within Italy. The first bathing establishment opened in 1843. Rimini is an art city with ancient Roman and Renaissance monuments, and is also the birthplace of the film director Federico Fellini
Federico Fellini (; 20 January 1920 – 31 October 1993) was an Italian film director and screenwriter known for his distinctive style, which blends fantasy and baroque images with earthiness. He is recognized as one of the greatest and most i ...
.
The city was founded by the Romans in 268 BC. Throughout Roman times, Rimini was a key communications link between the north and south of the peninsula. On its soil, Roman emperors erected monuments such as the Arch of Augustus and the Tiberius Bridge to mark the beginning and the end of the Decumanus of Rimini. During the Renaissance, the city benefited from the court of the House of Malatesta )
, type= Noble house
, country=ItalySan Marino, estates= Castel Sismondo (Rimini) Rocca Malatestiana (Cesena)
, titles=, founded=, founder=Malatesta da Verucchio, final ruler=Pandolfo IV Malatesta, deposition=, dissolution=
The House of Malatesta ...
, which hosted artists like Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
and produced works such as the Tempio Malatestiano
The Tempio Malatestiano ( it, House of Malatesta, Malatesta Temple) is the Unfinished building, unfinished cathedral church of Rimini, Italy. Officially named for Francis of Assisi, St. Francis, it takes the popular name from Sigismondo Pandolfo ...
. The main monuments in Rimini are the Tiberius Bridge and the Arch of Augustus.
In the 19th century, Rimini was one of the most active cities on the revolutionary front, hosting many of the movements seeking to achieve Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
. In the course of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the city was the scene of numerous clashes and bombings, but also of a fierce partisan resistance that earned it the honour of a gold medal for civic valour. In recent years it has become one of the most important sites for trade fairs and conferences in Italy.
As of 31 December 2019, Rimini's urban area was home to 151,200 people, with approximately 325,000 living in the eponymous province, making it the twenty-eighth largest city in Italy. The city is located near the independent republic of San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
and the Misano race track.
History
Ancient history
 The area was inhabited by
The area was inhabited by Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
until the arrival of the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, who held it from the 6th century BC until their defeat by the Umbri in 283 BC. In 268 BC at the mouth of the Ariminus (now called the Marecchia), the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
founded the ''colonia'' of Ariminum.
Ariminum was seen as a bastion against invaders from Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
and also as a springboard for conquering the Padana plain. The city was involved in the civil wars of the first century, aligned with the popular party and its leaders, first Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important refor ...
, and then Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
. After crossing the Rubicon
The Rubicon ( la, Rubico; it, Rubicone ; rgn, Rubicôn ) is a shallow river in northeastern Italy, just north of Rimini.
It was known as Fiumicino until 1933, when it was identified with the ancient river Rubicon, famously crossed by Julius Ca ...
, the latter made his legendary appeal to the legions in the Forum of Rimini.
As the terminus of the Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia or Flaminian Way was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to ''Ariminum'' (Rimini) on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had ...
, which ended in the town at the surviving prestigious Arch of Augustus (erected 27 BC), Rimini was a road junction connecting central and northern Italy by the Via Aemilia
The ( it, Via Emilia; en, Aemilian Way) was a trunk Roman road in the north Italian plain, running from ''Ariminum'' (Rimini), on the Adriatic coast, to ''Placentia'' (Piacenza) on the river ''Padus'' ( Po). It was completed in 187 BC. The ' ...
that led to Piacenza
Piacenza (; egl, label= Piacentino, Piaṡëinsa ; ) is a city and in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy, and the capital of the eponymous province. As of 2022, Piacenza is the ninth largest city in the region by population, with over ...
and the Via Popilia __NOTOC__
The Via Popilia is the name of two different ancient Roman roads begun in the consulship of Publius Popilius Laenas. One was in southern Italy and the other was in north-eastern Italy.
Road in southern Italy
The road in southern Italy ...
that extended northwards; it also opened up trade by sea and river.
Remains of the amphitheatre that could seat 12,000 people, and a five-arched bridge of Istrian stone
Istrian stone, ''pietra d'Istria'', the characteristic group of building stones in the architecture of Venice, Istria and Dalmatia, is a dense type of impermeable limestones that was quarried in Istria, nowadays Croatia; between Portorož and Pu ...
completed by Tiberius (21 AD), are still visible. Later Galla Placidia
Galla Placidia (388–89/392–93 – 27 November 450), daughter of the Roman emperor Theodosius I, was a mother, tutor, and advisor to emperor Valentinian III, and a major force in Roman politics for most of her life. She was List of Visigothi ...
built the church of Santo Stefano.
The evidence that Rimini is of Roman origins is illustrated by the city being divided by two main streets, the Cardo and the Decumanus.
The end of Roman rule was marked by destruction caused by invasions and wars, but also by the establishment of the palaces of the Imperial officers and the first churches, the symbol of the spread of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
that held the important Council of Ariminum
The Council of Ariminum, also known after the city's modern name as the Council of Rimini, was an early Christian church synod.
In 358, the Roman Emperor Constantius II requested two councils, one of the western bishops at Ariminum and one of ...
in the city in 359.
Middle Ages
 When the
When the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the larg ...
conquered Rimini in 493, Odoacer
Odoacer ( ; – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a soldier and statesman of barbarian background, who deposed the child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became Rex/Dux (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustul ...
, besieged in Ravenna, had to capitulate. During the Gothic War (535–554)
The Gothic War between the Eastern Roman Empire during the reign of Emperor Justinian I and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy took place from 535 to 554 in the Italian Peninsula, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It was one of the last o ...
, Rimini was taken and retaken many times. In its vicinity the Byzantine general Narses
, image=Narses.jpg
, image_size=250
, caption=Man traditionally identified as Narses, from the mosaic depicting Justinian and his entourage in the Basilica of San Vitale, Ravenna
, birth_date=478 or 480
, death_date=566 or 573 (aged 86/95)
, allegi ...
overthrew (553) the Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
. Under the Byzantine rule, it belonged to the Duchy of the Pentapolis
In the Byzantine Empire, the Duchy of the Pentapolis was a duchy (Latin: ''ducatus''), a territory ruled by a duke (''dux'') appointed by and under the Exarch of Ravenna. The Pentapolis (from the Greek term ''πεντάπολις'', "five cities") ...
, part of the Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna ( la, Exarchatus Ravennatis; el, Εξαρχάτο της Ραβέννας) or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the ...
.
In 728, it was taken with many other cities by Liutprand, King of the Lombards
Liutprand was the king of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his multiple phases of law-giving, in fifteen separate sessions from 713 to 735 inclusive, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mos ...
but returned to the Byzantines about 735. Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
gave it to the Holy See, but during the wars of the popes and the Italian cities against the emperors, Rimini sided with the latter.
In the 13th century, it suffered from the discords of the Gambacari and Ansidei families. The city became a municipality in the 14th century, and with the arrival of the religious orders, numerous convents and churches were built, providing work for many illustrious artists. In fact, Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/Proto-Renaissance period. Giot ...
inspired the 14th-century School of Rimini, which was the expression of original cultural ferment.
The House of Malatesta )
, type= Noble house
, country=ItalySan Marino, estates= Castel Sismondo (Rimini) Rocca Malatestiana (Cesena)
, titles=, founded=, founder=Malatesta da Verucchio, final ruler=Pandolfo IV Malatesta, deposition=, dissolution=
The House of Malatesta ...
emerged from the struggles between municipal factions with Malatesta da Verucchio
Malatesta da Verucchio (1212–1312) was the founder of the powerful Italian Malatesta family and a notable '' condottiero.'' He was born in Verucchio. He was the son of Malatesta della Penna (1183-1248).
He was the leader of the Guelphs in Romag ...
, who in 1239 was named podestà
Podestà (, English: Potestate, Podesta) was the name given to the holder of the highest civil office in the government of the cities of Central and Northern Italy during the Late Middle Ages. Sometimes, it meant the chief magistrate of a city ...
(chief magistrate) of the city. Despite interruptions, his family held authority until 1528. In 1312 he was succeeded by Malatestino Malatesta Malatestino Malatesta (also known as ''Malatesta I'' (or ''II'') ''Malatesta'', nicknamed ''Il Guercio'' (English: the War-ish; the Warlike) or ''dell'Occhio'' (English: "of the Eye"); died 14 October 1317) was the lord of Rimini from 1312 until hi ...
, first ''signore'' (lord) of the city and Pandolfo I Malatesta
Pandolfo I Malatesta (c. 1267 – 6 April 1326), son of Malatesta da Verucchio, was an Italian condottiero and Lord of Rimini from 1317.
In 1304, at the death of Pope Boniface VIII, he captured Pesaro, Fano, Senigallia and Fossombrone, whi ...
, the latter's brother, named by Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328.
Louis' election as king of Germany in ...
, as imperial vicar
An imperial vicar (german: Reichsvikar) was a prince charged with administering all or part of the Holy Roman Empire on behalf of the emperor. Later, an imperial vicar was invariably one of two princes charged by the Golden Bull with administering ...
of Romagna
Romagna ( rgn, Rumâgna) is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to t ...
.
Ferrantino, son of Malatesta II (1335), was opposed by his cousin Ramberto and by Cardinal Bertrand du Pouget
Bertrand du Pouget (Italian ''Bertrando del Poggetto'') (1280 – 3 February 1352) was a French papal diplomat and Cardinal.
Bertrand was born in Castelnau-Montratier. He may have been a nephew of Pope John XXII. As cardinal he was closely ...
(1331), legate of Pope John XXII
Pope John XXII ( la, Ioannes PP. XXII; 1244 – 4 December 1334), born Jacques Duèze (or d'Euse), was head of the Catholic Church from 7 August 1316 to his death in December 1334.
He was the second and longest-reigning Avignon Pope, elected by ...
. Malatesta II was also lord of Pesaro
Pesaro () is a city and ''comune'' in the Italian region of Marche, capital of the Province of Pesaro e Urbino, on the Adriatic Sea. According to the 2011 census, its population was 95,011, making it the second most populous city in the Marche, ...
. He was succeeded by Malatesta Ungaro
Ungaro Malatesta (June 1327 – July 1372), born Galeotto Malatesta, was an Italian condottiero and lord of Jesi.
He was the son of Malatesta Guastafamiglia, lord of Pesaro and Rimini. He changed his name to Ungaro when King Louis I of Hungary ...
(1373) and Galeotto I Malatesta
Galeotto I Malatesta (1299–1385) was an Italian condottiero, who was lord of Rimini, Fano, Ascoli Piceno, Cesena and Fossombrone.
Biography
Born in Rimini, he was the son of Pandolfo I Malatesta and the brother of Malatesta II Malatesta. In 133 ...
, uncle of the former (1385), lord also of Fano
Fano is a town and ''comune'' of the province of Pesaro and Urbino in the Marche region of Italy. It is a beach resort southeast of Pesaro, located where the ''Via Flaminia'' reaches the Adriatic Sea. It is the third city in the region by popula ...
(from 1340), Pesaro, and Cesena (1378).
His son, Carlo I Malatesta
Carlo I Malatesta (June 1368 – 13 September 1429) (also Carlo of Rimini) was an Italian condottiero during the Wars in Lombardy and lord of Rimini, Fano, Cesena and Pesaro. He was a member of the powerful House of Malatesta. Carlo's wife was ...
, one of the most respected condottieri
''Condottieri'' (; singular ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian captains in command of mercenary companies during the Middle Ages and of multinational armies during the early modern period. They notably served popes and other Europ ...
of the time, enlarged the Riminese possessions and restored the port. Carlo died childless in 1429, and the lordship was divided into three parts, Rimini going to Galeotto Roberto Malatesta, a Catholic zealot inadequate for the position.
The Pesarese line of the Malatestas tried, in fact, to take advantage of his weakness and to capture the city, but Sigismondo Pandolfo Malatesta
Sigismondo Pandolfo Malatesta (19 June 1417 – 7 October 1468) was an Italian condottiero and nobleman, a member of the House of Malatesta and lord of Rimini and Fano from 1432. He was widely considered by his contemporaries as one of the mo ...
, Carlo's nephew, who was only 14 at the time, intervened to save it. Galeotto retired to a convent, and Sigismondo obtained the rule of Rimini.
Sigismondo Pandolfo was the most famous lord of Rimini. In 1433, Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 – 9 December 1437) was a monarch as King of Hungary and Croatia ('' jure uxoris'') from 1387, King of Germany from 1410, King of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in ...
, sojourned in the city and for a while he was the commander-in-chief of the Papal armies. A skilled general, Sigismondo often acted as ''condottiero'' for other states to gain money to embellish it (he was also a dilettante poet). He had the famous Tempio Malatestiano
The Tempio Malatestiano ( it, House of Malatesta, Malatesta Temple) is the Unfinished building, unfinished cathedral church of Rimini, Italy. Officially named for Francis of Assisi, St. Francis, it takes the popular name from Sigismondo Pandolfo ...
rebuilt by Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. H ...
. However, after the rise of Pope Pius II
Pope Pius II ( la, Pius PP. II, it, Pio II), born Enea Silvio Bartolomeo Piccolomini ( la, Aeneas Silvius Bartholomeus, links=no; 18 October 1405 – 14 August 1464), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 August ...
, he had to fight constantly for the independence of the city.
In 1463, he was forced to submit to Pius II, who left him only Rimini and little more; Roberto Malatesta
Roberto Malatesta (c. 1441/42 – 10 Septembe1482) was an Italian condottiero, or mercenary captain, lord of Rimini, and a member of the House of Malatesta.
Early life
Born at Fano, Roberto was an illegitimate son of Sigismondo Pandolfo an ...
, his son (1482), under Pope Paul II
Pope Paul II ( la, Paulus II; it, Paolo II; 23 February 1417 – 26 July 1471), born Pietro Barbo, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States
from 30 August 1464 to his death in July 1471. When his maternal uncle Eugene IV ...
, nearly lost his state, but under Pope Sixtus IV
Pope Sixtus IV ( it, Sisto IV: 21 July 1414 – 12 August 1484), born Francesco della Rovere, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 August 1471 to his death in August 1484. His accomplishments as pope include ...
, became the commanding officer of the pontifical army against Ferdinand of Naples. Sigismondo was, however, defeated by Neapolitan forces in the battle of Campomorto
The Battle of Campomorto was a battle fought near Frosinone, in the Lazio (Italy) on August 21, 1482, in the course of the War of Ferrara.
It saw the Papal army, led by the condottiero Roberto Malatesta, face King Ferdinand I of Naples's army, ...
(1482). Pandolfo IV, his son (1500), lost Rimini to Cesare Borgia
Cesare Borgia (; ca-valencia, Cèsar Borja ; es, link=no, César Borja ; 13 September 1475 – 12 March 1507) was an Italian ex- cardinal and '' condottiero'' (mercenary leader) of Aragonese (Spanish) origin, whose fight for power was a major ...
, after whose overthrow it fell to Venice (1503–1509), but it was later retaken by Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or th ...
and incorporated into the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
.
After the death of Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X ( it, Leone X; born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, 11 December 14751 December 1521) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 March 1513 to his death in December 1521.
Born into the prominent political an ...
, Pandolfo returned for several months, and with his son Sigismondo Malatesta
Sigismondo Malatesta (November 1498 – December 1553) was an Italian condottiero.
Biography
The son of Pandolfaccio Malatesta, Sigismondo strove for his whole life to reconquer the ancestral seat of the Malatesta seignory, Rimini, annexed by t ...
held a rule which looked tyrannous even for the time. Pope Adrian VI
Pope Adrian VI ( la, Hadrianus VI; it, Adriano VI; nl, Adrianus/Adriaan VI), born Adriaan Florensz Boeyens (2 March 1459 – 14 September 1523), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 January 1522 until his d ...
expelled him again and gave Rimini to the Duke of Urbino
The Duchy of Urbino was an independent duchy in early modern central Italy, corresponding to the northern half of the modern region of Marche. It was directly annexed by the Papal States in 1625.
It was bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the eas ...
, the pope's vicar in Romagna.
In 1527, Sigismondo managed to regain the city, but in the following year the Malatesta dominion died forever.
Renaissance and Enlightenment
 At the beginning of the 16th century, Rimini, now a secondary town of the Papal States, was ruled by an
At the beginning of the 16th century, Rimini, now a secondary town of the Papal States, was ruled by an Apostolic Legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title ''legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic ...
. Towards the end of the 16th century, the municipal square (now Piazza Cavour), which had been closed off on a site where the Poletti Theatre was subsequently built, was redesigned. The statue of Pope Paul V
Pope Paul V ( la, Paulus V; it, Paolo V) (17 September 1550 – 28 January 1621), born Camillo Borghese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 16 May 1605 to his death in January 1621. In 1611, he honored ...
has stood in the centre of the square next to the fountain since 1614.
In the 16th century, the 'grand square' (now the Piazza Tre Martiri in honor of three civilians hanged by the retreating Nazis at the end of World War II), which was where markets and tournaments were held, underwent various changes. A small temple dedicated to Saint Anthony of Padua
Anthony of Padua ( it, Antonio di Padova) or Anthony of Lisbon ( pt, António/Antônio de Lisboa; born Fernando Martins de Bulhões; 15 August 1195 – 13 June 1231) was a Portuguese Catholic priest and friar of the Franciscan Order. He was bor ...
and a clock tower were built there, giving the square its present shape and size.
Until the 18th century raiding armies, earthquakes, famines, floods and pirate attacks ravaged the city. In this gloomy situation and due to a weakened local economy, fishing took on great importance, a fact testified by the construction of structures such as the fish market and the lighthouse.
In 1797, Rimini, along with the rest of Romagna
Romagna ( rgn, Rumâgna) is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to t ...
, was affected by the passage of the Napoleonic army
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
and became part of the Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic ( it, Repubblica Cisalpina) was a sister republic of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organized t ...
. Napoleonic policy suppressed the monastic orders, confiscating their property and thus dispersing a substantial heritage, and demolished many churches including the ancient cathedral of Santa Colomba.
Modern history
 On 30 March 1815,
On 30 March 1815, Joachim Murat
Joachim Murat ( , also , ; it, Gioacchino Murati; 25 March 1767 – 13 October 1815) was a French military commander and statesman who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Under the French Empire he received the ...
launched his Rimini Proclamation to the Italian people from here, hoping to incite them to unity and independence. In 1845, a band of adventurers commanded by Ribbotti entered the city and proclaimed a constitution which was soon abolished. In 1860, Rimini and Romagna were incorporated into the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
.
The city was transformed after the 1843 founding of the first bathing establishment and the Kursaal, a building constructed to host sumptuous social events, became the symbol of Rimini's status as a tourist resort.
In just a few years, the seafront underwent considerable development work making Rimini 'the city of small villas'. At the beginning of the 20th century, The Grand Hotel A grand hotel is a large and luxurious hotel, especially one housed in a building with traditional architectural style. It began to flourish in the 1800s in Europe and North America.
Grand Hotel may refer to:
Hotels Africa
* Grande Hotel Beir ...
, the city's first major accommodation facility, was built near the beach.
During the first World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Rimini and its surrounding infrastructure was one of the primary targets of the Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
Navy. After Italy's declaration of war on 15 May 1915, the Austro-Hungarian fleet left its harbours the same day and started its assault on the Adriatic coast between Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
and Barletta
Barletta () is a city, ''comune'' of Apulia, in south eastern Italy. Barletta is the capoluogo, together with Andria and Trani, of the Province of Barletta-Andria-Trani. It has a population of around 94,700 citizens.
The city's territory belong ...
.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the city was torn apart by heavy bombardments and by the passage of the front over the Gothic Line
The Gothic Line (german: Gotenstellung; it, Linea Gotica) was a German Defense line, defensive line of the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Campaign of World War II. It formed Generalfeldmarschall, Field Marshal Albert Kesselring's la ...
during the Battle of Rimini and was eventually captured by Greek and Canadian forces. Following its liberation on 21 September 1944, reconstruction work began, culminating in huge development of the tourist industry in the city.
Geography
Topography

north
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and 12°34′00″ east
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
, along the coast of the Adriatic sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, at the southeastern edge of Emilia-Romagna
egl, Emigliàn (man) egl, Emiglièna (woman) rgn, Rumagnòl (man) rgn, Rumagnòla (woman) it, Emiliano (man) it, Emiliana (woman) or it, Romagnolo (man) it, Romagnola (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title ...
, at a short distance from Montefeltro
Montefeltro is a historical and geographical region in Marche, which was historically part of Romagna. It gave its name to the House of Montefeltro, Montefeltro family, who ruled in the area during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance.
Regions of I ...
and Marche
Marche ( , ) is one of the twenty regions of Italy. In English, the region is sometimes referred to as The Marches ( ). The region is located in the central area of the country, bordered by Emilia-Romagna and the republic of San Marino to the ...
. Rimini extends for 135.71 square km and borders the municipalities of Bellaria-Igea Marina, San Mauro Pascoli
San Mauro Pascoli ( rgn, San Mevar) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Forlì-Cesena in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about southeast of Forlì. It is at some from the sea, the ''frazio ...
, and Santarcangelo di Romagna
Santarcangelo di Romagna ( rgn, Santarcànzul) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Rimini, Emilia-Romagna, Italy, on the Via Emilia. As of 2009, it had a population of some 21,300. It is crossed by two rivers, the Uso and the Marecchia
...
towards NW, Verucchio
Verucchio ( rgn, Vròcc) is a ''comune ''in the province of Rimini, region of Emilia-Romagna, Italy. It has a population of about 9,300 and is from Rimini, on a spur overlooking the valley of the Marecchia river.
History
Traces of a 12th-9th ce ...
and Serravalle, San Marino
Serravalle is a ''castello'' in northern San Marino. With a population of 10,878 inhabitants (of which 2,000 are of foreign origin) and an area of 10.53 km2, it is not only the most densely populated municipality in San Marino, but it also con ...
towards SW, Coriano
Coriano ( rgn, Curién) is a ''comune'' in the province of Rimini. This town is known for being the city of the Motorcycle World Champion, in 250cc class, Marco Simoncelli.
History
Coriano's origins are ancient: it was an Umbrian, Etruscan civi ...
towards S, and Riccione
Riccione (; rgn, Arciôn ) is a ''comune'' in the Province of Rimini, Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy. As of 2018, Riccione had an estimated population of 35,003.
History
The oldest archaeological findings in Riccione's area date to the 2nd cen ...
towards SE. The city is also located at the intersection of three Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
s: Via Emilia
The ( it, Via Emilia; en, Aemilian Way) was a trunk Roman road in the north Italian plain, running from ''Ariminum'' (Rimini), on the Adriatic coast, to ''Placentia'' (Piacenza) on the river ''Padus'' ( Po). It was completed in 187 BC. The ' ...
, Via Popilia __NOTOC__
The Via Popilia is the name of two different ancient Roman roads begun in the consulship of Publius Popilius Laenas. One was in southern Italy and the other was in north-eastern Italy.
Road in southern Italy
The road in southern Italy ...
, and Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia or Flaminian Way was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to ''Ariminum'' (Rimini) on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had ...
. Viserba is the most important of Rimini's northern districts, with 8,556 inhabitants.
Rimini is located in a historically strategic position, at the extreme southern edge of the Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
, at the junction point of Northern and Central Italy.
It is surrounded towards southwest by the gently rolling hills of Covignano (153 metres high), Vergiano (81 m), San Martino Monte l'Abbate (57 m) and San Lorenzo in Correggiano (60 m), widely cultivated, with vineyards, olive groves and orchards, and dominated by ancient mansions. These hills, mostly made of clay and sand, connect the plains, created by the Marecchia
The Marecchia () is a river in eastern Italy. In ancient times it was known as the ''Ariminus'' which was from the Greek ''Aríminos'' (, which is also the ancient name of Rimini). The source of the river is near Monte dei Frati which is east of P ...
and Ausa, the two most important rivers of Rimini territory, to the higher hills of the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
.
The Marecchia river runs through its valley and the plain in a very large riverbed and, after confluence with the Ausa, it flows into the Adriatic sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
through a deviator between San Giuliano Mare and Rivabella, while the ancient riverbed is used in its last section as the city's harbour.
The Marecchia, usually with little water flow, was subjected to periodic, destructive floods near its mouth, where the riverbed became narrow after various bends: for this reason it was deviated north. Ausa creek, which was the eastern limit of Rimini for many centuries, was deviated as well after World War II, and its original riverbed was filled and turned into an urban park.
The coastal strip, made of recent marine deposits, is edged by a fine sandy beach, 15 km long and up to 200 metres wide, interrupted only by the mouth of the rivers and gently shelving towards the sea. Along the coastline there is a low sandy cliff, created by sea rise around 4000 B.C., partly conserved north of Rimini, between Rivabella and Bellaria-Igea Marina, at a distance of about 1,300 metres from the coast.
Rimini's territory, for its geographical position and its climatic features, is situated on the edge between the mediterranean and the central European phytoclimatic zones, and thus it represents an environment of notable naturalistic value.
Districts
Rimini is the main centre of a long coastalconurbation
A conurbation is a region comprising a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ca ...
, which extends from Cervia
Cervia ( rgn, Zirvia) is a seaside resort town in the province of Ravenna, located in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna.
Cervia is a major seaside resort in Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Its population was 28,700 at the 2018 census.
...
to Gabicce Mare
Gabicce Mare, also named Gabicce (Romagnol dialect, Romagnol: ''Gabéc''), is a town and ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Pesaro e Urbino, in Italy, region Marche. It is located about northwest of Ancona, north of Pesaro, and is close ...
, including the seaside resort
A seaside resort is a resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, suc ...
s of Cesenatico
Cesenatico ( rgn, Ziznàtic) is a port town with about 26,000 inhabitants on the Adriatic coast of Italy. It is located in the province of Forlì-Cesena in the region of Emilia-Romagna, about south of Ravenna. Cesenatico's port canal was surv ...
, Gatteo a Mare, Bellaria-Igea Marina, Riccione
Riccione (; rgn, Arciôn ) is a ''comune'' in the Province of Rimini, Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy. As of 2018, Riccione had an estimated population of 35,003.
History
The oldest archaeological findings in Riccione's area date to the 2nd cen ...
, Misano Adriatico
Misano Adriatico ( rgn, Misên) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Rimini in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about southeast of Rimini.
Misano Adriatico borders the following municipaliti ...
and Cattolica
Cattolica (; rgn, Catòlga) is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Rimini, Italy, with 16,233 inhabitants as of 2007.
History
Archaeological excavations show that the area was already settled in ancient Rome, Roman times.
Cattolica rose a ...
. The conurbation
A conurbation is a region comprising a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ca ...
has about 300,000 inhabitants and originated around the mid-20th century due to urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
following intensive tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
development.
The city of Rimini includes the seaside localities and districts of Torre Pedrera, Viserbella, Viserba, Rivabella, San Giuliano Mare towards north and Bellariva, Marebello, Rivazzurra, Miramare di Rimini, Miramare towards south. These districts are important to tourism in Rimini.
The city proper includes the historic centre, the four ancient boroughs of S. Giuliano, S. Giovanni, S. Andrea and Marina, the seaside district of Marina Centro and various modern districts—Celle, Marecchiese, INA Casa, V PEEP, Colonnella, Lagomaggio—and outer suburbs such as Padulli, Spadarolo, Covignano, Grottarossa and Villaggio 1° Maggio, located outside of the Adriatic Highway beltline. More outer suburbs are S. Giustina, S. Vito, Spadarolo, Vergiano, Corpolò and Gaiofana.
The historic centre of Rimini, surrounded by the city walls built by House of Malatesta, Malatesta, and formerly bounded by the Marecchia and Ausa rivers, has a distinctive, regular urban structure of Roman origins. It was divided since the Middle Ages in four districts (Rioni): Cittadella, Clodio, Pomposo and Montecavallo.Giorgio Conti and Pier Giorgio Pasini, ''Rimini Città come Storia'', Rimini, Giusti, 1982, p. 215. The boundaries of these districts are not known, but it is assumed that they followed the current Corso d'Augusto, Via Garibaldi, and Via Gambalunga. Additionally, the ancient coastline was situated much farther inland than today's; it gradually shifted outward over centuries and the new land was developed throughout the 20th century.
Rione Cittadella, in the western area of the centre, was the most important district of the city and included the Municipal palaces, Castel Sismondo and the Cathedral of Santa Colomba. Rione Clodio, towards the north, was popular and a peculiar urban structure tied with the near Marecchia river. Rione Pomposo, the widest district of the city, included large orchards and convents. Rione Montecavallo, on the southern part of the historical centre, is characterized by bowed, irregular streets of medieval origins, by the Fossa Patara creek and a small hill called "Montirone".
Outside of the city walls, there are four boroughs (Borghi), which were entirely incorporated to the city by the urban sprawl in the early 20th century.Giorgio Conti and Pier Giorgio Pasini, ''Rimini Città come Storia'', Rimini, Giusti, 1982, p. 251.
Borgo S. Giuliano, along Via Emilia
The ( it, Via Emilia; en, Aemilian Way) was a trunk Roman road in the north Italian plain, running from ''Ariminum'' (Rimini), on the Adriatic coast, to ''Placentia'' (Piacenza) on the river ''Padus'' ( Po). It was completed in 187 BC. The ' ...
, dates back to the 11th century and was originally a fishermen's settlement. Dominated by the Church of San Giuliano, it is one of the most picturesque spots of the city, with narrow streets and squares, colourful small houses and many frescoes representing characters and places of Federico Fellini
Federico Fellini (; 20 January 1920 – 31 October 1993) was an Italian film director and screenwriter known for his distinctive style, which blends fantasy and baroque images with earthiness. He is recognized as one of the greatest and most i ...
's films.
Borgo S. Giovanni, on both sides of Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia or Flaminian Way was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to ''Ariminum'' (Rimini) on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had ...
, was populated by artisans and middle-class; Borgo S. Andrea, located outside of Porta Montanara, along Via Covignano, Via Montefeltro and Via Monte Titano, was strictly tied with agriculture and commerce of cows. Both these two boroughs were developed in the 15th century; then they burned in a fire in 1469 and were rebuilt in the 19th century, relocating small industries and manufactures, including a brick factory and a phosphorus matches factory.
Borgo Marina, situated on the right bank of the Marecchia, was a portal borough, heavily transformed by Fascist demolitions and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
bombings, which hit this area due to its proximity to the bridges and railway station of the city.
Climate
Rimini has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen: Cfa) moderated by the influence of theAdriatic sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, featuring autumn and winter mean temperatures and annual low temperatures among the very highest in Emilia-Romagna
egl, Emigliàn (man) egl, Emiglièna (woman) rgn, Rumagnòl (man) rgn, Rumagnòla (woman) it, Emiliano (man) it, Emiliana (woman) or it, Romagnolo (man) it, Romagnola (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title ...
.
Precipitations are equally distributed during the year, with a peak in October (75 mm) and two slight minimums, in January (42 mm) and July (43 mm). In spring, autumn and winter precipitations mainly come from oceanic fronts, while in summer they are brought by thunderstorms, coming from the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
or the Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
.
Humidity is high all year round, averaging a minimum of 72% in June and July and a maximum of 84% in November and December. Prevailing winds blow from W, S, E and NE. Southwesterly winds, known as libeccio or garbino, are foehn winds, which may bring warm temperatures in each season. On average, there are over 2,040 sunshine hours per year.
Demographics
Population
, Rimini has 150,951 inhabitants, with a density of about 1,100 inhabitants per square kilometre within the city limits. In 1861, by the time of the first Italian census, the population was around 28,000; in 1931 it was more than double, 57,000. With the increasing tourism development, population rapidly grew between 1951 and 1981, the fastest growing period for Rimini in the 20th century, when the city's population grew from 77,000 to over 128,000. During the 20th century, two former districts of Rimini got administrative autonomy, causing two distinct temporary drops in population totals:Riccione
Riccione (; rgn, Arciôn ) is a ''comune'' in the Province of Rimini, Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy. As of 2018, Riccione had an estimated population of 35,003.
History
The oldest archaeological findings in Riccione's area date to the 2nd cen ...
in 1922 and Bellaria-Igea Marina in 1956.
Foreign population is 18,396, (12.5% of the total), mainly from Eastern Europe, East Asia and North Africa. Between 1992 and 2014, foreign population grew from around 1,800 to over 18,000 units.
The most important foreign communities are Albanians (3,479), Romanians (2,904), Ukrainians (2,409), Chinese (1,197) and Moldovans (1,023). Other notable foreign groups in the city are Senegalese, Moroccans, Macedonians, Tunisians, Russians, Bangladeshis and Peruvians.
Religion
Rimini's population is mostly Catholic. The city is the seat of the Diocese of Rimini, a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Ravenna-Cervia. The first cathedral of the diocese was the former Cathedral of Santa Colomba until 1798, when the title was transferred to the church of Sant'Agostino. Since 1809, Rimini's cathedral is theTempio Malatestiano
The Tempio Malatestiano ( it, House of Malatesta, Malatesta Temple) is the Unfinished building, unfinished cathedral church of Rimini, Italy. Officially named for Francis of Assisi, St. Francis, it takes the popular name from Sigismondo Pandolfo ...
.
Besides Roman Catholic churches, there are also Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox, Evangelical and Adventism, Adventist churches. Between the 13th and 14th century, Rimini had a flourishing Jewish community, which built three distinct synagogues, all destroyed, formerly located around the area of Piazza Cavour, Via Cairoli and Santa Colomba.
Government
Economy
 Rimini is a major international tourist destination and seaside resort, among the most well known in
Rimini is a major international tourist destination and seaside resort, among the most well known in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and the Mediterranean basin, thanks to a long sandy beach, well-equipped bathing establishments, theme parks and a number of opportunities for leisure and spare time. The economy of the city is mainly based on tourism, whose development started in the first half of the 19th century and increased after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Rimini's origins as a seaside resort
A seaside resort is a resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, suc ...
date back to 1843, when the first "Bathing Establishment" was founded, the oldest one of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
. The width of the beach, the gentle gradient of the sea bed, the equipment of bathing establishments, the luxurious hotels, the mildness of the climate, the richness of curative waters, the prestigious social events, made Rimini a renowned tourist destination among the Italian and European aristocracy during the Belle Époque.


Emilia-Romagna
egl, Emigliàn (man) egl, Emiglièna (woman) rgn, Rumagnòl (man) rgn, Rumagnòla (woman) it, Emiliano (man) it, Emiliana (woman) or it, Romagnolo (man) it, Romagnola (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title ...
's hotels, with over 1,000 hotels, more than 220 of which are open all year round, aside from apartment hotels, apartments, holiday homes, bed & breakfast and campings. Tourism is mainly based on seaside holidays, but also includes trade fairs and conventions, events, nightlife, culture, wellness, food and wine.
Rimini is a leading trade fair and convention site in Italy, with an important trade fair (Rimini Fiera) and a convention centre (Palacongressi di Rimini).
The city's other economic sectors, such as services, commerce, construction industry, have been influenced by the development of tourism. Commerce is one of the main economic sectors, thanks to the presence of a large wholesale center, two hypermarkets, department stores, supermarkets and hundreds of shops and boutiques. Industrial sector, Industry, less developed than tourism and services, includes various companies active in food industry, woodworking machineries, building constructions, furnishing, clothing and publishing. Notable companies are Bimota (motorcycles), SCM (woodworking machines), Trevi S.p.A. (electronic goods). Rimini is also seat of a historic railway works plant.
Agriculture and fishing were the city's main economic sources until the early 20th century. The most common crops, in terms of surface area, are alfalfa, wheat, durum wheat, grape vine, olive tree, barley and sorghum. Among fruit trees dominates apricot, peach and plum trees. Important are the traditional productions of wine (Sangiovese, Trebbiano, Rebola, Pagadebit, Albana wines) and extra virgin olive oil.
The fishing industry can count on a fleet of about 100 fishing boats, the most consistent of Rimini's fishing department, which includes the coast between Cattolica
Cattolica (; rgn, Catòlga) is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Rimini, Italy, with 16,233 inhabitants as of 2007.
History
Archaeological excavations show that the area was already settled in ancient Rome, Roman times.
Cattolica rose a ...
and Cesenatico
Cesenatico ( rgn, Ziznàtic) is a port town with about 26,000 inhabitants on the Adriatic coast of Italy. It is located in the province of Forlì-Cesena in the region of Emilia-Romagna, about south of Ravenna. Cesenatico's port canal was surv ...
.
Arts and culture
Museums
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, being moved between 1940 and 1943 to two different shelters in Spadarolo and Novafeltria. In 1964, the collections were moved to Palazzo Visconti and finally, from 1990, to the Collegio dei Gesuiti, a large Jesuit convent designed by bolognese architect Alfonso Torreggiani, built in 1749.
 In the Archaeological department are exhibited grave goods from Villanovian civilization, Villanovian tombs of
In the Archaeological department are exhibited grave goods from Villanovian civilization, Villanovian tombs of Verucchio
Verucchio ( rgn, Vròcc) is a ''comune ''in the province of Rimini, region of Emilia-Romagna, Italy. It has a population of about 9,300 and is from Rimini, on a spur overlooking the valley of the Marecchia river.
History
Traces of a 12th-9th ce ...
and Covignano, architectural pieces, sculptures, mosaics, ceramics, coins of Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial eras, and the exceptional medical kit from the Domus del Chirurgo. The collection of the Roman Lapidary, exhibited in the inner courtyard of the convent, has funerary monuments, epigraphies and milestones.
The Medieval and Modern Art departments include collections of paintings, sculptures and Work of art, art objects by artists from Romagna
Romagna ( rgn, Rumâgna) is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to t ...
(Giovanni da Rimini, Giuliano da Rimini, Guido Cagnacci), Emilia (region of Italy), Emilia (Guercino, Vittorio Maria Bigari), Tuscany (Domenico Ghirlandaio, Agostino di Duccio) and Veneto (Giovanni Bellini), from 14th to 19th century. The City Museum arranges temporary exhibitions and promotes researches, study and restoration activities of the city's historical and artistic heritage.
The ''Fellini Museum'' (Museo Fellini), dedicated to Federico Fellini
Federico Fellini (; 20 January 1920 – 31 October 1993) was an Italian film director and screenwriter known for his distinctive style, which blends fantasy and baroque images with earthiness. He is recognized as one of the greatest and most i ...
, houses temporary exhibitions of documents, drawings, scenography, scenographies and costumes related to the movie production of the film director.
The ''Museum of Glances'' (Museo degli Sguardi), housed in Villa Alvarado, on Covignano hill, was instituted in 2005 acquiring the objects of the former Museum of Extra European Cultures "Dinz Rialto", founded in Rimini in 1972 by explorer Delfino Dinz Rialto, the art pieces of the former Missionary Museum of the Grazie and other private collections. The museum has over 3,000 objects coming from China, Oceania, Africa and Pre-Columbian, pre-Columbian America, with paintings, sculptures, everyday objects, totems, masks, musical instruments and clothes illustrating how the Western world has looked at these territories' cultures through history.
The ''Museum of Small Fishing and Marine'' (Museo della Piccola Pesca e della Marineria), in Viserbella, shows the history of Rimini's Marine through a collection of boats, fishing tools, photographs and a large seashells collection, with pieces from all over the Mediterranean Sea.
In the municipality of Rimini there are also two private museums: the ''Aviation Museum'' (Museo dell'Aviazione) in Sant'Aquilina, close to the boundary of the Republic of San Marino, and the ''National Museum of Motorcycle'' (Museo Nazionale del Motociclo) in Casalecchio.
Libraries
 The Gambalunghiana Library, historic institution founded in 1617 by jurist Alessandro Gambalunga, plays a leading role in the city's cultural life. The library has over 280,000 books, including 60,000 ancient books, 1,350 manuscripts, 6,000 prints and 80,000 photographs. Among the incunables, dated back from the 15th century, stand out ''De mulieribus claris, De Claris mulieribus'' (1497) by Giacomo Filippo Foresti and ''De re militari'' by Roberto Valturio. The collection of illuminated manuscripts, coming from different cultural and linguistic European boundaries, includes the ''Regalis Historia'' by Frate Leonardo and ''De Civitate Dei'' by Augustine of Hippo, Saint Augustine.
The Gambalunghiana Library, historic institution founded in 1617 by jurist Alessandro Gambalunga, plays a leading role in the city's cultural life. The library has over 280,000 books, including 60,000 ancient books, 1,350 manuscripts, 6,000 prints and 80,000 photographs. Among the incunables, dated back from the 15th century, stand out ''De mulieribus claris, De Claris mulieribus'' (1497) by Giacomo Filippo Foresti and ''De re militari'' by Roberto Valturio. The collection of illuminated manuscripts, coming from different cultural and linguistic European boundaries, includes the ''Regalis Historia'' by Frate Leonardo and ''De Civitate Dei'' by Augustine of Hippo, Saint Augustine.
Theatre and Films
 The first stable theatre in Rimini is documented since 1681, when the city council decided on the transformation of the Arengo's main hall into a large theatre hall, hosting shows of amateur dramatics companies and the young Carlo Goldoni, who was studying philosophy in the city at that time.
Between 1842 and 1857 the great Municipal Theatre Vittorio Emanuele II was built, designed in Neoclassical style by the architect Luigi Poletti (architect), Luigi Poletti, according to the traditional canons of the 19th-century Italian theatre. The theatre was inaugurated by Giuseppe Verdi, who directed "L'Aroldo", and hosted prestigious opera seasons until its destruction in 1943 due to aerial bombings. Since 1947, it has been called Amintore Galli Theatre. Since its closure, theatre shows has been hosted in the modern Teatro Ermete Novelli in Marina Centro.
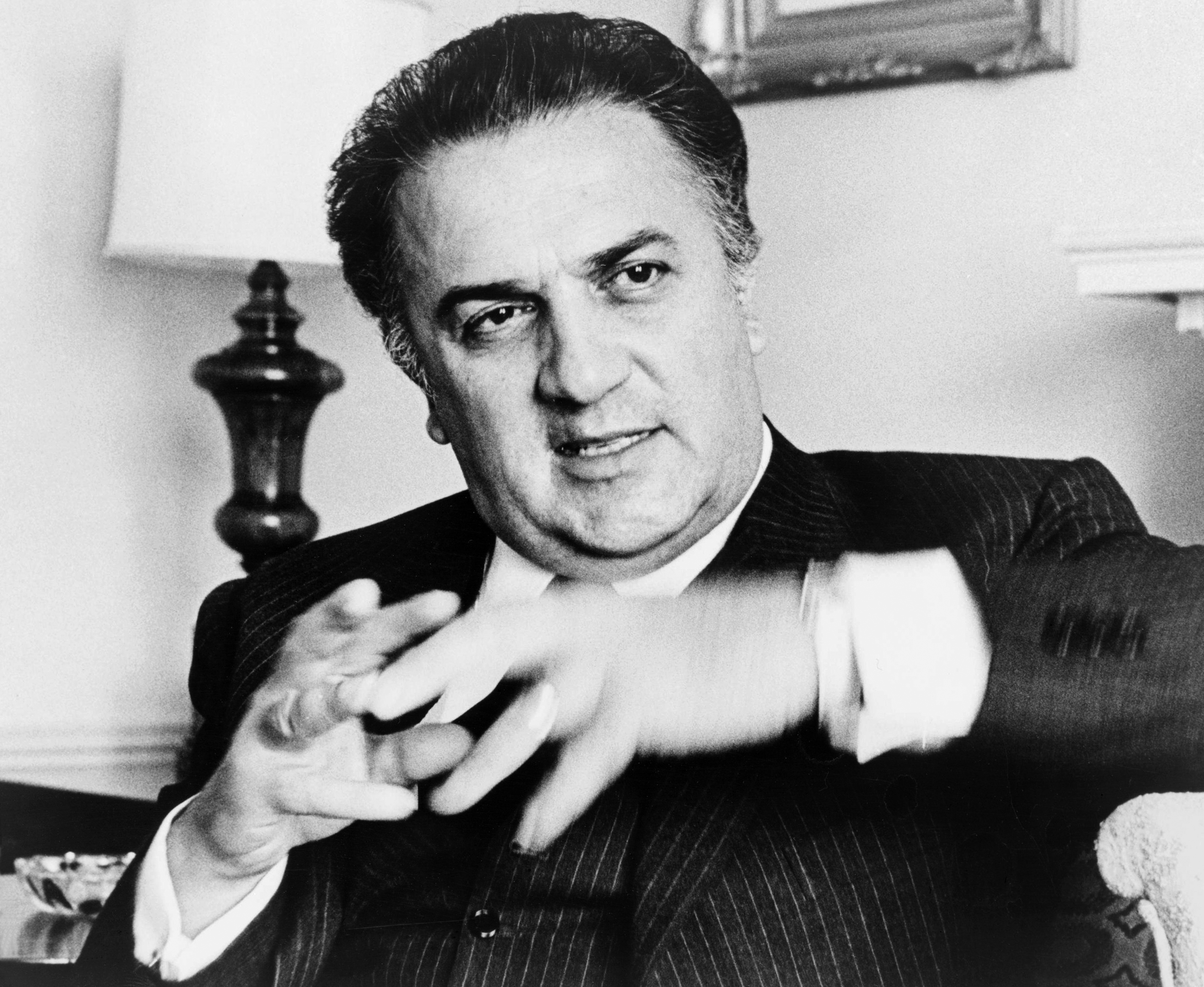
Rimini appeared on the movie screen for the first time in some early footages, such as the documentary "Rimini l'Ostenda d'Italia" (1912), and in various Istituto Luce's newsreels in the Thirties. The film director
The first stable theatre in Rimini is documented since 1681, when the city council decided on the transformation of the Arengo's main hall into a large theatre hall, hosting shows of amateur dramatics companies and the young Carlo Goldoni, who was studying philosophy in the city at that time.
Between 1842 and 1857 the great Municipal Theatre Vittorio Emanuele II was built, designed in Neoclassical style by the architect Luigi Poletti (architect), Luigi Poletti, according to the traditional canons of the 19th-century Italian theatre. The theatre was inaugurated by Giuseppe Verdi, who directed "L'Aroldo", and hosted prestigious opera seasons until its destruction in 1943 due to aerial bombings. Since 1947, it has been called Amintore Galli Theatre. Since its closure, theatre shows has been hosted in the modern Teatro Ermete Novelli in Marina Centro.
Rimini appeared on the movie screen for the first time in some early footages, such as the documentary "Rimini l'Ostenda d'Italia" (1912), and in various Istituto Luce's newsreels in the Thirties. The film director Federico Fellini
Federico Fellini (; 20 January 1920 – 31 October 1993) was an Italian film director and screenwriter known for his distinctive style, which blends fantasy and baroque images with earthiness. He is recognized as one of the greatest and most i ...
, was born and raised in Rimini, portrayed characters, places and atmospheres of his hometown through his movies, which however were almost entirely shot in Cinecittà's studios in Rome: I Vitelloni, 8 e ½ (Oscar award in 1964), I clowns, Amarcord (Oscar award in 1975). Other Italian movies filmed in Rimini includes "La prima notte di quiete" by Valerio Zurlini, "Rimini Rimini" by Sergio Corbucci, "Abbronzatissimi" by Bruno Gaburro, "Sole negli occhi" by Andrea Porporati, "Da zero a dieci" by Luciano Ligabue and "Non pensarci" by Gianni Zanasi.
Music
The earliest musician from Rimini was Saint Arduino (10th century); a musical tradition of some distinction was witnessed in the following century by the presence of a music school, named "Scuola cantorum", at the Cathedral of Santa Colomba. French composer Guillaume Dufay stayed in Rimini, at Malatesta's court until 1427. In 1518 Pietro Aaron became the first choirmaster of the Cathedral's chapel. In 1690 Carlo Tessarini, violinist and composer, was born in Rimini. The city also gave birth to the musician Benedetto Neri, professor at the Academy of Music in Milan. Amintore Galli, illustrious musicologist and composer born in Talamello in 1845, attended the city's Classical Lyceum before moving to Milan, where he studied at the Academy of Music; in 1945 the Municipal Theatre of Rimini was dedicated to him. Between the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many social events and dance parties took place at the Bathing Establishment, hosting celebrities such as soprano Elena Bianchini-Cappelli and tenor Enrico Caruso. In recent years, the city inspired the homonymous music album by Fabrizio De André, released in 1978, and it is cited in various popular Italian and foreign songs by Fabrizio De André, Francesco Guccini, Nino Rota, Elvis Costello, Fred Buscaglione. Also born in Rimini were the songwriter Samuele Bersani and the composer and music producer Carlo Alberto Rossi, author of some of Mina (Italian singer), Mina's songs.Cuisine

 Rimini's cuisine is simple and characterized by intense flavours and it is indissolubly related to the traditions of rural culture, influenced by the city's location—between the sea and the hills and near the border between
Rimini's cuisine is simple and characterized by intense flavours and it is indissolubly related to the traditions of rural culture, influenced by the city's location—between the sea and the hills and near the border between Romagna
Romagna ( rgn, Rumâgna) is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to t ...
and Marche
Marche ( , ) is one of the twenty regions of Italy. In English, the region is sometimes referred to as The Marches ( ). The region is located in the central area of the country, bordered by Emilia-Romagna and the republic of San Marino to the ...
.
The traditional first course is pasta, which includes regular pasta, pasta in broth and baked pasta, prepared in many different shapes. Almost all pasta dishes require a base of "sfoglia", a dough of eggs and flour, handmade with a rolling pin. First courses include Cappelletti (pasta), cappelletti, passatelli in broth, lasagne, cannelloni, nidi di rondine, ravioli, tagliatelle, garganelli, maltagliati, gnocchi and strozzapreti, seasoned with bolognese sauce or a sauce, dressing of butter and Salvia officinalis, sage.
Second courses include meat dishes, such as pollo alla cacciatora, rabbit in porchetta, meat-filled zucchini, sausages and mixed grilled meats, and fish dishes, like barbecues of atlantic mackerels, sardines, rotisseries of oily fishes, sepia (genus), sepias with peas, fried squids and gianchetti (known here as "omini nudi").
Piadina, Piada is a flatbread of ancient traditions, thin and crumbly, obtained from a dough of flour, water, lard and salt, and baked on a scorching "testo" of terracotta or cast iron. It is often accompanied by grilled meats or fishes, sausages, gratinée vegetables, salami, prosciutto, fresh cheeses and country herbs. Cassoni are stuffed flatbreads similar to piadina, piada, with various fillings: country herbs, potatoes and sausages, tomato and mozzarella. Side dishes include mixed salads, gratinée vegetables, roasted potatoes, sautée bladder campion leaves, marinated olives with dill, garlic and orange zest.
Traditional desserts are ciambella, Carnevale's fried fiocchetti and castagnole, piada dei morti (a doughnut with walnuts, raisins, pinenuts and almonds, prepared in November), zuppa inglese (a rich dessert with custard, savoiardi and liqueurs), caramelized Common fig, figs, peaches in white wine and strawberry, strawberries in red wine.
Typical local products are ''squacquerone'' (a fresh cheese) and saba, a grape syrup used to prepare desserts. Quality extra virgin olive oil is traditionally produced in Rimini area since ancient times.
The wines include Sangiovese, Trebbiano, Pagadebit, Rebola (wine), Rebola, Cabernet Sauvignon and Albana (grape), Albana, a dessert wine of Roman origins.
Cityscape
Architecture
Rimini has a varied historical and artistic heritage which includes churches and monasteries, villas and palaces, fortifications, archaeological sites, streets and squares, as a result of the succession of various civilizations, dominations and historical events through its history, from the Roman Empire, Romans to the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines, the medieval ''comune'', the House of Malatesta, Malatesta seignory, the Venetian Republic and thePapal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
dominations.
The city has always been a key gate to the Orient and the southern areas of the Mediterranean for the Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
, thanks to its geographical position and its harbour, and a meeting point between cultures of Northern Italy, Northern and Central Italy.
Rimini has monuments of different eras, with important examples of architecture from the Roman age, such as the Arch of Augustus, the Tiberius Bridge, the Amphitheatre and the Domus del Chirurgo; from the Middle Ages, such as the Palazzo dell'Arengo, the church of Sant'Agostino and Castel Sismondo; from the Renaissance, with the Tempio Malatestiano
The Tempio Malatestiano ( it, House of Malatesta, Malatesta Temple) is the Unfinished building, unfinished cathedral church of Rimini, Italy. Officially named for Francis of Assisi, St. Francis, it takes the popular name from Sigismondo Pandolfo ...
, masterpiece of Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. H ...
.
Rimini's archaeological heritage includes some domus of Republican and Imperial age, characterized by polychrome or black and white mosaics, necropolis and sections of the pavement of the ancient Roman streets.
The city, along with its boroughs and the seaside district of Marina Centro, also preserves buildings from the Baroque, the Neoclassical and Art Nouveau periods, with churches, palaces, hotels and mansions which reveal its role of cultural and trading centre and seaside resort.
The city centre has a Roman structure, partly modified by following medieval transformations. Urban evolution, through the renovation of the House of Malatesta, Malatesta, earthquakes and the suppressions of monasteries, has led to a stratification of historic sites and buildings. The bombings of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
caused extensive destruction and damage, compromising the monumental heritage and the integrity of the city centre, which has been reconstructed and restored in order to valorize its historic places and buildings.
Main sights


Religious buildings
*Tempio Malatestiano
The Tempio Malatestiano ( it, House of Malatesta, Malatesta Temple) is the Unfinished building, unfinished cathedral church of Rimini, Italy. Officially named for Francis of Assisi, St. Francis, it takes the popular name from Sigismondo Pandolfo ...
: The original gothic architecture, gothic-style cathedral of San Francesco was built in the 13th century, but reconstructed into a Renaissance masterwork by the Florentine architect Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. H ...
, commissioned by Sigismondo Pandolfo Malatesta, hence the name. In the cathedral are the tombs of Sigismondo and his wife Isotta.
** ''Bell tower of the former Cathedral of Santa Colomba''.
* ''Sant'Agostino, Rimini, Sant'Agostino'': 13th-century Romanesque church
* ''Chiesa dei Teatini, Rimini, Chiesa dei Teatini'': 17th-century Baroque-style church
* ''San Fortunato, Rimini, San Fortunato'': This 1418 church houses the ''Adoration of the Magi'' painting (1547) by Giorgio Vasari.
* ''San Giovanni Battista, Rimini, San Giovanni Battista'': 12th-century church with single nave with rich stucco decoration from the 18th century.
* ''San Giuliano, Rimini, San Giuliano Martire'': 1553–1575 church houses ta painting by Paul Veronese (1588) depicting the martyrdom of that saint. The church also houses the polyptych (1409) by Bittino da Faenza (1357–1427) depicting episodes of this saint's life.
* ''Santa Maria dei Servi'': Church built in 1317 by the religious order of the Servants of Mary and entirely transformed in 1779 by architect Gaetano Stegani, which was buried here. The façade was completed in 1894 by Giuseppe Urbani. The interior has a single nave, adorned with coupled columns on each side and rich Baroque plasters.
* ''San Francesco Saverio, Rimini, Church of Suffragio'': Situated in Piazza Ferrari, was constructed by the Jesuites in 1721, designed by Giovan Francesco Buonamici. It features an unfinished brick façade. The interior, shaped in the form of the Latin Cross, has a single nave flanked by chapels and adorned by plain Baroque decorations and paintings by Guido Cagnacci.
* ''Tempietto of Sant'Antonio, Rimini, Tempietto of Sant'Antonio''
* ''Madonna della Scala, Rimini, Madonna della Scala''
Secular buildings
* ''Castel Sismondo'' or Rocca Malatestiana: This castle built by Sigismondo Pandolfo was later used as a prison. * ''Grand Hotel'': The Grand Hotel was built in Art Nouveau style by Swiss architect Paolito Somazzi between 1906 and 1908. and protected as "National monument" in 1994. The building is fronted by a wide elevated terrace and it has two central towers which were originally topped by moorish domes, with rich floreal decorations. The hotel has 117 bedrooms, a large atrium, a restaurant and several living rooms, ornamented by ancient furnitures and 18th-century Venetian chandeliers. The hotel hosted many illustrious people, sovereigns, nobles and exponents of the European bourgeoisie. * ''Palazzo dell'Arengo e del Podestà'' (1204): This building was the seat of the judiciary and civil administrations. On the short side, in the 14th century, the podestà residence was added. It was modified at the end of the 16th century. * ''Palazzo Garampi''. * Amintore Galli Theatre: This theater was originally dedicated to king Victor Emmanuel II and then renamed for the musician Amintore Galli; it was designed by architect Luigi Poletti (architect), Luigi Poletti. It was inaugurated in 1857 with an opera by Giuseppe Verdi (''Aroldo''). The theatre was bombed during World War II. Many projects were started to restore it; it reopened in 2019. * ''Villa Des Vergers'': It is the largest riminese villa, situated on the hills of San Lorenzo in Correggiano, about 6 km from the city centre. The villa was built in the 17th century for want of the Diotallevi family; in 1843 it was purchased by French historian and archaeologist Adolphe Noël des Vergers and entirely renovated between 1880 and 1890 by architect Arthur-Stanislas Diet. The palace is a typical example of Napoleon III Eclectic architecture, with a main building fronted by a pronaos and flanked by two lateral wings, and internal halls characterized by Neoclassical furnitures and decorations. The villa is surrounded by a 6 hectares park, which includes a water parterre, a formal giardino all'italiana and a landscape garden, with groups of evergreen oaks, pines and cypresses which frame the palace in scenographic perspectives.Monuments
* Arch of Augustus: This arch built in 27 BC has a single gate high and wide. Merlons were added in the Middle Ages. It was restored in the 18th century by Tommaso Temanza. * ''Fontana della Pigna''. * ''Fontana dei Quattro Cavalli'': The fountain is one of the symbols of Rimini as a seaside resort, built in 1928 by riminese sculptor Filogenio Fabbri. Demolished in 1954, was accurately reconstructed in 1983, recomposing the original parts. The fountain features a large circular basin, overlooked by four marine horses which sustain the superior basin. * ''Monument to Pope Paul V''. * Tiberius Bridge: This bridge on the riverMarecchia
The Marecchia () is a river in eastern Italy. In ancient times it was known as the ''Ariminus'' which was from the Greek ''Aríminos'' (, which is also the ancient name of Rimini). The source of the river is near Monte dei Frati which is east of P ...
was begun under Emperor Augustus in 14 AD, as the inscription on the internal parapets recalls, and completed under Tiberius in 21. The bridge still connects the city centre to Borgo San Giuliano and leads to the consular roads Via Emilia and Via Popilia that lead north. Built in Istria stone, the bridge consists of five arches that rest on massive pillars with breakwater spurs set at an oblique angle with respect to the bridge's axis in order to follow the current. The bridge's structure, on the other hand, rests on a practical system of wooden poles.
* ''Torre dell'Orologio'': The Clock tower was built in 1547 in Piazza Tre Martiri, replacing the ancient "beccherie" (public butcher's), and reconstructed in 1759 by Giovan Francesco Buonamici. In 1875, the top of the tower was ruined due to an earthquake, and it was restored in 1933. The clock, which dates back to 1562, overlooks a perpetual calendar assembled in 1750, decorated by terracotta panels depicting zodiacal signs, months and lunar phases. The central, blind arch of the porch houses the memorial of the victims of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Archaeological sites
* ''Roman amphitheater'' (2nd century): The amphitheater was erected alongside the ancient coast line, and had two orders of porticoes with 60 arcades. It had elliptical shape, with axes of . The arena measured , not much smaller than the greatest Roman amphitheatres: the edifice could house up to 15,000 spectators.Parks and recreation
Rimini has an extensive parks system, with 1.3 million square metres of parks and gardens inside the urban area and a total of 2.8 million square metres of green areas inside the city limits, including river parks, sport facilities and natural areas. The city's park system includes a series of large urban parks, created along the old riverbeds ofMarecchia
The Marecchia () is a river in eastern Italy. In ancient times it was known as the ''Ariminus'' which was from the Greek ''Aríminos'' (, which is also the ancient name of Rimini). The source of the river is near Monte dei Frati which is east of P ...
and Ausa, neighbourhood parks and gardens and tree-lined boulevards.
The main parks of the city are Liberation Day (Italy), XXV Aprile Park, Giovanni Paolo II Park, Alcide Cervi Park, Fabbri Park, Ghirlandetta Park, Federico Fellini Park, Pertini Park in Marebello and Briolini Park in San Giuliano Mare. Every Saturday, XXV Aprile Park hosts one of the Italy's thirteen (as of 2022) parkruns.
In Rimini there are about 42,000 public trees, belonging to 190 different species, predominantly linden, planes, maples, poplars, pines and oaks. 23 of these are old trees, protected as "monumental trees" for their age and their naturalistic value, such as the Platanus x acerifolia, plane of piazza Malatesta, the downy oak of Giovanni Paolo II Park, the Cupressus sempervirens, cypresses of Sant'Agostino, the elm of Viale Vespucci and the Tilia platyphyllos, linden trees of San Fortunato.
The city's cycling network is articulated inside the main parks and boulevards, linking the most important monuments, tourist attractions, beaches, meeting places, offering various opportunities to different use categories, including urban travels, mountain bike and cyclotourism.
The urban cycling network is connected, through XXV Aprile Park, to the cycle route which links Rimini and Saiano, along the river Marecchia
The Marecchia () is a river in eastern Italy. In ancient times it was known as the ''Ariminus'' which was from the Greek ''Aríminos'' (, which is also the ancient name of Rimini). The source of the river is near Monte dei Frati which is east of P ...
.
Education
Rimini is the seat of a Campus of University of Bologna, attended by 5,800 students, which include bachelors and masters belonging to eight Faculties: Economics, Statistical Sciences, Pharmacy, Literature and Philosophy, Industrial Chemistry, Sport Sciences, Medicine and Surgery. The city has public schools of all levels, including 13 nurseries, 12 kindergartens, 39 primary schools, 5 secondary schools and 11 high schools (4 Lyceums, 3 Technical Institutes, 3 Professional Institutes and an Institute of Musical Studies). The most ancient city's Lyceum, the Classical Lyceum "Giulio Cesare", founded in 1800, was attended by Giovanni Pascoli andFederico Fellini
Federico Fellini (; 20 January 1920 – 31 October 1993) was an Italian film director and screenwriter known for his distinctive style, which blends fantasy and baroque images with earthiness. He is recognized as one of the greatest and most i ...
.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Rimini is an important road and railway junction, thanks to its position at the intersection between the Adriatic coastal routes and thePo Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
ones and its proximity to the Republic of San Marino.
Roads
The Adriatic motorway (A14) connects Rimini to Bologna towards north and Taranto towards south, through the tolls of Rimini Nord and Rimini Sud. Rimini is a junction of three highways of Ancient Rome, Roman origins: theVia Emilia
The ( it, Via Emilia; en, Aemilian Way) was a trunk Roman road in the north Italian plain, running from ''Ariminum'' (Rimini), on the Adriatic coast, to ''Placentia'' (Piacenza) on the river ''Padus'' ( Po). It was completed in 187 BC. The ' ...
(SS 9) to Milan, the Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia or Flaminian Way was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to ''Ariminum'' (Rimini) on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had ...
(SS 16) to Rome and the Via Popilia __NOTOC__
The Via Popilia is the name of two different ancient Roman roads begun in the consulship of Publius Popilius Laenas. One was in southern Italy and the other was in north-eastern Italy.
Road in southern Italy
The road in southern Italy ...
(SS 16) to Padova.
The Rimini–San Marino Highway (SS 72) connects the Adriatic Riviera to the capital of the Republic of San Marino, entering the Sammarinese territory after the State limit at Dogana.
Via Marecchiese (SP 258), leading to Sansepolcro, passes through the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
at Viamaggio Pass and links Rimini to its hinterland, Tuscany and the Tiber Valley. Roads of local importance are the provincial roads to Coriano
Coriano ( rgn, Curién) is a ''comune'' in the province of Rimini. This town is known for being the city of the Motorcycle World Champion, in 250cc class, Marco Simoncelli.
History
Coriano's origins are ancient: it was an Umbrian, Etruscan civi ...
(SP 31), Montescudo (SP 41) and Santa Cristina (SP 69).
Railways
Rimini is a major junction of the regional railway network and it is one of the main stations of the Adriatic railway. Rimini Station is a junction of the railroad lines Bologna-Ancona and Ferrara-Ravenna-Rimini, and trains of all categories stop there, including Frecciarossa and Frecciabianca. It is also the ending point of long-distance railway services to Rome and of regional services to Bologna, Castelbolognese, Ancona and Ravenna. Rimini also has four minor railway stations: Miramare, Viserba, Torre Pedrera, served by regional services, and Rimini Fiera, periodically served by regional and intercity services in conjunction with the main trade fairs.Airways
The city is served by the Federico Fellini International Airport, at Miramare, the second largest airport inEmilia-Romagna
egl, Emigliàn (man) egl, Emiglièna (woman) rgn, Rumagnòl (man) rgn, Rumagnòla (woman) it, Emiliano (man) it, Emiliana (woman) or it, Romagnolo (man) it, Romagnola (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title ...
by passenger traffic. It has regular links to national and international hubs, low cost, charter and seasonal flights.
The closest major international airports are Bologna Guglielmo Marconi Airport, Bologna-Marconi, Venice Marco Polo Airport, Venice-Marco Polo and Milan-Malpensa Airport, Milan-Malpensa.
Urban transport
The network of urban transport, operated by START Romagna, includes 13 urban bus lines, nine suburban bus lines, as well as two lines connecting Rimini city centre with the nearby seaside resort ofRiccione
Riccione (; rgn, Arciôn ) is a ''comune'' in the Province of Rimini, Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy. As of 2018, Riccione had an estimated population of 35,003.
History
The oldest archaeological findings in Riccione's area date to the 2nd cen ...
: a Trolleybuses in Rimini, trolleybus line and since November 2019, the Metromare bus rapid transit line.
Utilities
Rimini is served by the sewage treatment, wastewater treatment plant of Rimini-Santa Giustina. To prevent most of the temporary sea bathing prohibitions occurring when wastewater is discharged into the sea in case of heavy rainfall or thunderstorms, in 2013 extensive work began to upgrade the sewage system, which is expected to be completed in 2024. The works done between 2013 and 2020 made it possible to eliminate nearly all temporary sea bathing prohibitions in Marina Centro, Viserba, in the southern parts of Viserbella and in the northern parts of both Rivabella and Torre Pedrera, in addition to coastal areas that were already not affected, such as northern Marina Centro, southern Bellariva, Marebello, northern Rivazzurra and central Torre Pedrera. Waste management is operated by the multi-utility company Hera Group. Waste sorting attained 71,8% in 2020.Sports
 The main football team of the city is Rimini Calcio. It played for nine years (between 1976 and 2009) in Serie B, the second-highest division in the Italian football league system. Its better positioning was the fifth place of the 2006–07 Serie B, 2006–07 season (when Rimini was also undefeated in both games against Juventus F.C., Juventus).
Rimini has also a notable basketball team, the Basket Rimini Crabs, which played for several years in Serie A and two times in the European FIBA Korać Cup, Korać Cup. About baseball, Rimini Baseball Club won 12 national championships and it was also European champion three times.
Rimini is the site of the annual Paganello event, one of the world's premier Beach Ultimate tournaments.
The main football team of the city is Rimini Calcio. It played for nine years (between 1976 and 2009) in Serie B, the second-highest division in the Italian football league system. Its better positioning was the fifth place of the 2006–07 Serie B, 2006–07 season (when Rimini was also undefeated in both games against Juventus F.C., Juventus).
Rimini has also a notable basketball team, the Basket Rimini Crabs, which played for several years in Serie A and two times in the European FIBA Korać Cup, Korać Cup. About baseball, Rimini Baseball Club won 12 national championships and it was also European champion three times.
Rimini is the site of the annual Paganello event, one of the world's premier Beach Ultimate tournaments.
Notable natives of Rimini and environs
 * Ancient Bards (founded 2006), symphonic metal band
* Enea Bastianini (born 1997), motorcycle racer
* Samuele Bersani (born 1970), singer-songwriter
* Marco Bezzecchi (born 1998), motorcycle racer
* Pier Paolo Bianchi (born 1952), Grand Prix motorcycle road racer
* Rosetta Boninsegna (1926–1972), painter
* Matteo Brighi (born 1981), football player
* Claudio Maria Celli (born 1941), titular archbishop
* Gregorio Celli (1225–1343), Roman Catholic priest, professed member of the Order of Saint Augustine, beatified by Pope Clement XIV on 6 September 1769
* Roberto Paci Dalò (born 1962), composer, director, visual artist
* Patrizia Deitos (born 1975), supermodel and singer
* Mattia Drudi (born 1998), racing driver
*
* Ancient Bards (founded 2006), symphonic metal band
* Enea Bastianini (born 1997), motorcycle racer
* Samuele Bersani (born 1970), singer-songwriter
* Marco Bezzecchi (born 1998), motorcycle racer
* Pier Paolo Bianchi (born 1952), Grand Prix motorcycle road racer
* Rosetta Boninsegna (1926–1972), painter
* Matteo Brighi (born 1981), football player
* Claudio Maria Celli (born 1941), titular archbishop
* Gregorio Celli (1225–1343), Roman Catholic priest, professed member of the Order of Saint Augustine, beatified by Pope Clement XIV on 6 September 1769
* Roberto Paci Dalò (born 1962), composer, director, visual artist
* Patrizia Deitos (born 1975), supermodel and singer
* Mattia Drudi (born 1998), racing driver
* Federico Fellini
Federico Fellini (; 20 January 1920 – 31 October 1993) was an Italian film director and screenwriter known for his distinctive style, which blends fantasy and baroque images with earthiness. He is recognized as one of the greatest and most i ...
(1920–1993), film director
* Alberto Marvelli (1918–1946), engineer, president of Azione Cattolica
* Carlton Myers (born 1971), basketball player
* Elio Pagliarani (1927–2012), poet and literary critic
* Renzo Pasolini (1938–1973), Grand Prix motorcycle road racer
* Alessandra Perilli (born 1988), shooter and first Olympic medalist for San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
* Hugo Pratt (1927–1995), comic book creator
* Giuliano da Rimini (c. 1307 – c. 1324), painter
* Michael Ruben Rinaldi (born 1995), motorcycle racer
* Delio Rossi (born 1960), football manager
* Loris Stecca (born 1960), former world champion boxer
* Massimo Tamburini (1943–2014), motorcycle designer
* Giovanni Urbinati (born 1946), ceramist and sculptor
* Roberto Valturio (1405–1475), engineer and writer
* Renato Zangheri (1925-2015), mayor of the city of Bologna from 1970 to 1983, historical and Italian scholar
* Carlotta Montanari (born 1981), actress and former TV host
Twin towns — sister cities
 Rimini is twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:
* Fort Lauderdale, Florida, Fort Lauderdale, United States
* Saint-Maur-des-Fossés, France
* Seraing, Belgium
* Sochi, Russia
* Yangzhou, China
* Ziguinchor, Senegal
Rimini is twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:
* Fort Lauderdale, Florida, Fort Lauderdale, United States
* Saint-Maur-des-Fossés, France
* Seraing, Belgium
* Sochi, Russia
* Yangzhou, China
* Ziguinchor, Senegal
See also
* Roman Catholic Diocese of Rimini * Battle of Rimini (1944) * The Grand Hotel Rimini * Rimini Calcio F.C., Rimini Calcio Football Club * Rimini LighthouseBibliography
*References
Sources and external links
Province of Rimini
Rimini Comune (Town Council)
Official Tourist Information site of Rimini (Town Council)
Rimini Travel Guide in Dutch
{{Authority control Rimini, 260s BC establishments 268 BC Populated places established in the 3rd century BC 3rd-century BC establishments in Italy Cities and towns in Emilia-Romagna Duchy of the Pentapolis Papal States Roman amphitheatres in Italy Roman sites of Emilia-Romagna Seaside resorts in Italy