Rideau Hall on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rideau Hall (officially Government House) is the
 The site of Rideau Hall and the original structure were chosen and built by stonemason
The site of Rideau Hall and the original structure were chosen and built by stonemason
 In 1864, Rideau Hall was leased by the Crown from the McKay family for $4,000 per year and was intended to serve only as a temporary home for the
In 1864, Rideau Hall was leased by the Crown from the McKay family for $4,000 per year and was intended to serve only as a temporary home for the  Still, despite the popularity of the events that took place in the building, negative first impressions of Rideau Hall itself were a theme until the early part of the 20th century. Upon arrival there in 1872, the Countess of Dufferin said in her journal: "We have been so very enthusiastic about everything hitherto that the first sight of Rideau Hall did lower our spirits just a little!" In 1893, Lady Stanley, wife of Governor General the Lord Stanley of Preston, said "you will find the furniture in the rooms very old-fashioned & not very pretty... The red drawing room... had no furniture except chairs & tables... The walls are absolutely bare... The room which has always been the wife of the G.G.'s sitting room is very empty... There are no lamps in the house at all. No cushions, no table cloths, in fact none of the small things that make a room pretty & comfortable." Echoing these earlier comments, the Marchioness of Aberdeen and Temair said upon her departure from Ottawa that Rideau Hall was a "shabby old Government House put away amongst its clump of bushes..."
Various improvements were undertaken over the decades, seeing the first gas chandeliers and a telegraph wire put in, as well as the construction of the ballroom in the same year. By the time Rideau Hall was to live up to its role as a royal home, when its first royal residents— the Marquess of Lorne and his wife, Princess Louise—moved in at the beginning of 1878, many upgrades had been completed. Lorne stated of the hall: "Here we are settling down in this big and comfortable House, which I tell Louise is much superior to Kensington, for the walls are thick, the rooms are
Still, despite the popularity of the events that took place in the building, negative first impressions of Rideau Hall itself were a theme until the early part of the 20th century. Upon arrival there in 1872, the Countess of Dufferin said in her journal: "We have been so very enthusiastic about everything hitherto that the first sight of Rideau Hall did lower our spirits just a little!" In 1893, Lady Stanley, wife of Governor General the Lord Stanley of Preston, said "you will find the furniture in the rooms very old-fashioned & not very pretty... The red drawing room... had no furniture except chairs & tables... The walls are absolutely bare... The room which has always been the wife of the G.G.'s sitting room is very empty... There are no lamps in the house at all. No cushions, no table cloths, in fact none of the small things that make a room pretty & comfortable." Echoing these earlier comments, the Marchioness of Aberdeen and Temair said upon her departure from Ottawa that Rideau Hall was a "shabby old Government House put away amongst its clump of bushes..."
Various improvements were undertaken over the decades, seeing the first gas chandeliers and a telegraph wire put in, as well as the construction of the ballroom in the same year. By the time Rideau Hall was to live up to its role as a royal home, when its first royal residents— the Marquess of Lorne and his wife, Princess Louise—moved in at the beginning of 1878, many upgrades had been completed. Lorne stated of the hall: "Here we are settling down in this big and comfortable House, which I tell Louise is much superior to Kensington, for the walls are thick, the rooms are
 When King George VI and his
When King George VI and his
 With the death of the King only a month following Churchill's 1952 visit, the front of Rideau Hall was covered with black bunting as a sign of
With the death of the King only a month following Churchill's 1952 visit, the front of Rideau Hall was covered with black bunting as a sign of  This caused controversy not only because Sauvé had contradicted her earlier statement about Rideau Hall, wherein she said: "oh yes, definitely, it has to be open," but also because it denied Ottawa residents the use of the grounds. One group formed under the name ''Canada Unlock the Gate Group'' and asserted the closure was more due to Sauvé's selfish desire for privacy than any real security risks; ''
This caused controversy not only because Sauvé had contradicted her earlier statement about Rideau Hall, wherein she said: "oh yes, definitely, it has to be open," but also because it denied Ottawa residents the use of the grounds. One group formed under the name ''Canada Unlock the Gate Group'' and asserted the closure was more due to Sauvé's selfish desire for privacy than any real security risks; ''
 Rideau Hall's main purpose is to house the offices of the Governor General of Canada and his or her household, including the
Rideau Hall's main purpose is to house the offices of the Governor General of Canada and his or her household, including the
 The original 1838 structure was relatively small; only two storeys tall with a full-height, central, curved bay, and an accordingly curved
The original 1838 structure was relatively small; only two storeys tall with a full-height, central, curved bay, and an accordingly curved  In 1872, during the tenure of the Earl of Dufferin, the indoor
In 1872, during the tenure of the Earl of Dufferin, the indoor  An accessible entrance—opened by
An accessible entrance—opened by
 Today the rooms are furnished both with elements from the history of the residence as well as art and other objects that showcase contemporary Canadian culture, including pieces by the
Today the rooms are furnished both with elements from the history of the residence as well as art and other objects that showcase contemporary Canadian culture, including pieces by the
 The sole remaining part of the original McKay villa is the reception room on the ground floor and the royal suite directly above. The former was created in 1913 by removing the interior partitions of the villa; the baseboards, mouldings, and trims date from that era. It is where small ceremonies and presentations take place, while the latter is an oval room that was previously the drawing room of the original McKay villa and was subsequently used as a ballroom, a studio, and a study before becoming the monarch's bedroom. Some signs of the McKay house are still visible, notably in the now blanked window on the north wall of the reception room and the ornate plaster ceiling in the royal suite.
Directly west of these rooms is the
The sole remaining part of the original McKay villa is the reception room on the ground floor and the royal suite directly above. The former was created in 1913 by removing the interior partitions of the villa; the baseboards, mouldings, and trims date from that era. It is where small ceremonies and presentations take place, while the latter is an oval room that was previously the drawing room of the original McKay villa and was subsequently used as a ballroom, a studio, and a study before becoming the monarch's bedroom. Some signs of the McKay house are still visible, notably in the now blanked window on the north wall of the reception room and the ornate plaster ceiling in the royal suite.
Directly west of these rooms is the
 Within the Monck Wing, built between 1865 and 1866, are other living quarters and drawing and dining rooms generally for non-state affairs, such as the Pauline Vanier Room, a small sitting room where informal meetings are held with visiting heads of state and other officials. The room was originally created in the 1960s by Pauline Vanier out of an old aide-de-camp smoking room, giving the space
Within the Monck Wing, built between 1865 and 1866, are other living quarters and drawing and dining rooms generally for non-state affairs, such as the Pauline Vanier Room, a small sitting room where informal meetings are held with visiting heads of state and other officials. The room was originally created in the 1960s by Pauline Vanier out of an old aide-de-camp smoking room, giving the space  The governor general's study sits at the far east end of the Monck Wing's ground floor, next to another study allocated for the viceroy's consort. The former is panelled in carved wood that was installed when the room was constructed in 1906, with the names of each governor general applied in succession around the room, below the
The governor general's study sits at the far east end of the Monck Wing's ground floor, next to another study allocated for the viceroy's consort. The former is panelled in carved wood that was installed when the room was constructed in 1906, with the names of each governor general applied in succession around the room, below the
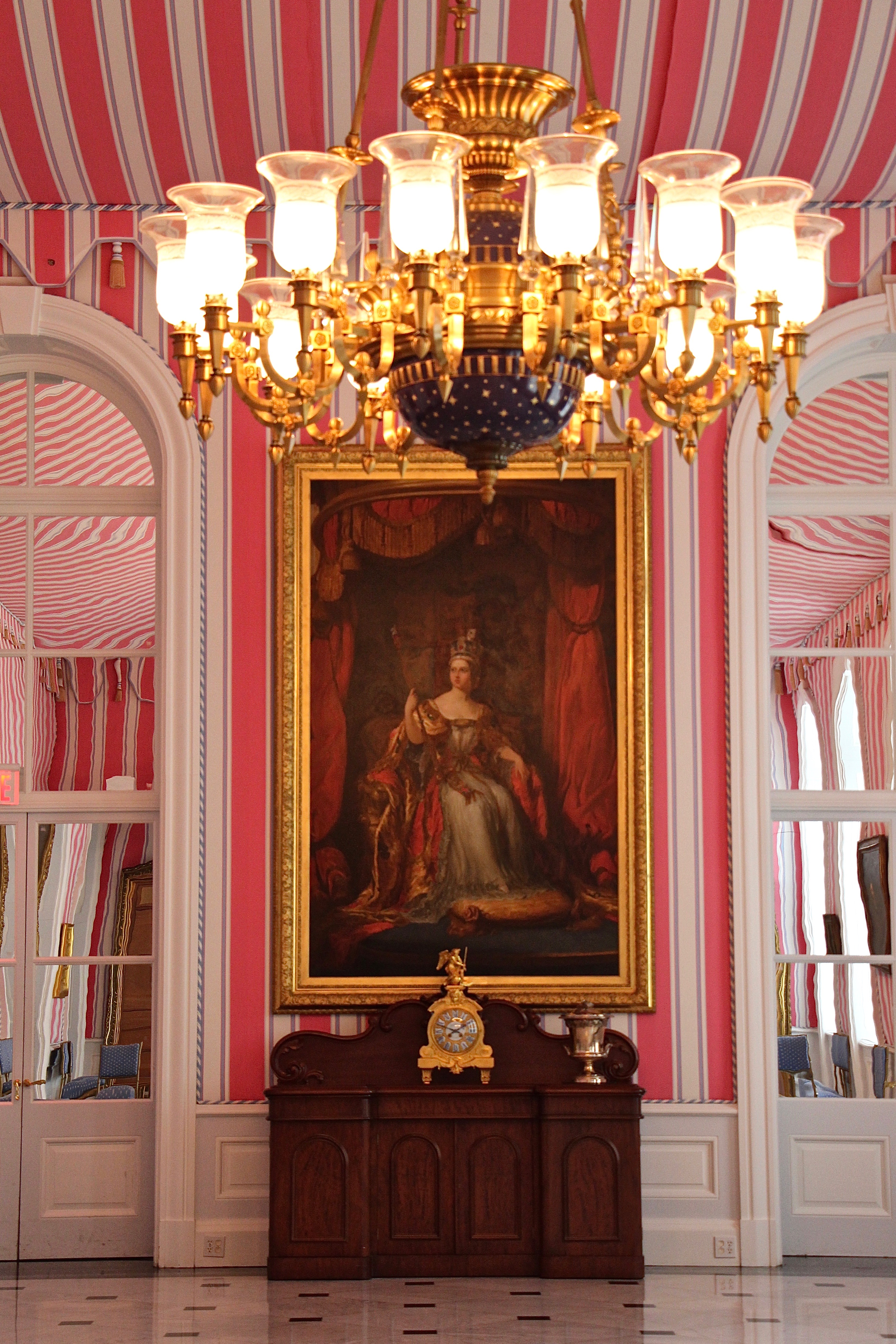 Originally, most of the art in Rideau Hall was the personal property of the incumbent governor general and, as with much of the furnishings, was removed upon the end of the viceroy's commission. Starting in the 20th century, however, more and more pieces were added to the dedicated Crown Collection for Government House, either through gifts or purchases; for instance, in 1946, Sir James Dunn presented the Crown with two paintings by Johann Zoffany. Today the collection of furnishing, art, and artifacts at Rideau Hall is composed of private gifts from the Canada Fund (a foundation created by the government of Canada) and the Friends of Rideau Hall. The pieces, though predominantly Canadian in origin, also represent the Far East, Europe, and other regions, and can be arranged thematically, such as the Asian influenced pieces in the Long Gallery, the portraits of Canadian governors general in the reception room. The Crown Collection works on display are also usually augmented with approximately 100 art pieces and antiques on loan from various museums, galleries, and private collections; this continues a tradition started in the 1930s, when the National Gallery lent pieces to the viceroy at the time, the Earl of Bessborough.
Additionally, since the time of Clarkson's appointment, themed artistic exhibitions have been mounted at Rideau Hall, such as that during the tenure of Michaëlle Jean wherein the show "Body and Land" featured select
Originally, most of the art in Rideau Hall was the personal property of the incumbent governor general and, as with much of the furnishings, was removed upon the end of the viceroy's commission. Starting in the 20th century, however, more and more pieces were added to the dedicated Crown Collection for Government House, either through gifts or purchases; for instance, in 1946, Sir James Dunn presented the Crown with two paintings by Johann Zoffany. Today the collection of furnishing, art, and artifacts at Rideau Hall is composed of private gifts from the Canada Fund (a foundation created by the government of Canada) and the Friends of Rideau Hall. The pieces, though predominantly Canadian in origin, also represent the Far East, Europe, and other regions, and can be arranged thematically, such as the Asian influenced pieces in the Long Gallery, the portraits of Canadian governors general in the reception room. The Crown Collection works on display are also usually augmented with approximately 100 art pieces and antiques on loan from various museums, galleries, and private collections; this continues a tradition started in the 1930s, when the National Gallery lent pieces to the viceroy at the time, the Earl of Bessborough.
Additionally, since the time of Clarkson's appointment, themed artistic exhibitions have been mounted at Rideau Hall, such as that during the tenure of Michaëlle Jean wherein the show "Body and Land" featured select
File:10 Rideau Hall P1350154.jpg, Entrance to the grounds in the cast iron and stone fence that surrounds the entire property
File:Inukshuk at Rideau Hall.jpg, An
As with the house that sits on them, the grounds too were transformed throughout the decades: Lady Byng created the existing rock garden, with a reflecting pool and wild corner for growing
Governor General of Canada: Rideau Hall
Ottawa Tourism and Convention Authority: Rideau Hall
CPAC's interactive Rideau Hall: Inside Canada's House
YouTube: Government House, Ottawa
YouTube: Tour of Rideau Hall Monck Wing with Governor General David Johnston and Sharon Johnston
CBC Digital Archives: The Schreyers’ new life at Rideau Hall
YouTube: Gate Posting at the Governor Generals House in Ottawa
Toronto Public Library: Historic images of Rideau Hall
Order-in-Council 1868-0718 for purchase of Rideau Hall
Property record for Rideau Hall in the Directory of Federal Real Property
{{ Official Government residences in North America and the Caribbean Houses completed in 1838 Houses completed in 1914 Federal government buildings in Ottawa Monarchy in Canada Houses in Ottawa + Canadian heraldry Cricket grounds in Ontario Museums in Ottawa Historic house museums in Ontario Palaces in Canada Estate gardens in Canada National Historic Sites in Ontario Royal residences in Canada Sussex Drive
official residence
An official residence is the residence of a head of state, head of government, governor, religious leader, leaders of international organizations, or other senior figure. It may be the same place where they conduct their work-related functions. ...
in Ottawa of both the Canadian monarch
The monarchy of Canada is Canada's form of government embodied by the Canadian sovereign and head of state. It is at the core of Canada's constitutional Canadian federalism, federal structure and Westminster system, Westminster-style Parliamentar ...
and their representative, the governor general of Canada
The governor general of Canada (french: gouverneure générale du Canada) is the federal viceregal representative of the . The is head of state of Canada and the 14 other Commonwealth realms, but resides in oldest and most populous realm, ...
. It stands in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
's capital on a estate at 1 Sussex Drive
Sussex Drive (french: Promenade Sussex), also known as Ottawa Regional Road93, is an arterial road in Ottawa, Ontario, the capital of Canada. It is one of the city's main ceremonial and institutional routes. Travelling roughly parallel to the Ot ...
, with the main building consisting of approximately 175 rooms across , and 27 outbuildings around the grounds. Rideau Hall's site lies outside the centre of Ottawa. It is one of two official royal residences maintained by the federal Crown, the other being the Citadelle of Quebec
The Citadelle of Quebec (french: Citadelle de Québec), also known as ''La Citadelle'', is an active military installation and the secondary official residence of both the Canadian monarch and the governor general of Canada. It is located atop C ...
.
Most of Rideau Hall is used for state affairs, only of its area being dedicated to private living quarters, while additional areas serve as the offices of the Canadian Heraldic Authority
The Canadian Heraldic Authority (CHA; french: Autorité héraldique du Canada) is part of the Canadian honours system under the Canadian monarch, whose authority is exercised by the Governor General of Canada. The authority is responsible for t ...
and the principal workplace of the governor general and their staff; either the term ''Rideau Hall'', as a metonym, or the formal idiom ''Government House'' is employed to refer to this bureaucratic branch. Officially received at the palace are foreign heads of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and ...
, both incoming and outgoing ambassadors and high commissioners to Canada, and Canadian Crown ministers for audiences
An audience is a group of people who participate in a show or encounter a work of art, literature (in which they are called "readers"), theatre, music (in which they are called "listeners"), video games (in which they are called "players"), or ...
with either the viceroy or the sovereign, should the latter be in residence. Rideau Hall is likewise the location of many Canadian award presentations and investitures, where prime ministers
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is no ...
and other members of the federal Cabinet are sworn in, and where federal writs of election are " dropped", among other ceremonial and constitutional functions.
Rideau Hall and the surrounding grounds were designated as a National Historic Site of Canada in 1977. The house is open to the public for guided tours throughout the year; approximately 200,000 visitors tour Rideau Hall annually. Since 1934, the Federal District Commission (now the National Capital Commission) has managed the grounds.
Name
The name ''Rideau Hall'' was chosen by Thomas McKay for his villa, drawing inspiration from the Rideau Canal which he had helped construct, though the house was also known colloquially as ''McKay's Castle''. Once the house became the official residence of the governor general, it was termed formally as ''Government House''. But, Rideau Hall stuck as the informal name and the existence of two names for the building led to some issue: in 1889 the viceregal consort, the Lady Stanley of Preston, was rebuked by Queen Victoria for calling the house Rideau Hall; it was to be Government House, as in all other Empire capitals. Today, however, Rideau Hall is the commonly accepted term for the house, with Government House remaining only in use for very formal or legal affairs; for example,royal proclamation
A proclamation (Lat. ''proclamare'', to make public by announcement) is an official declaration issued by a person of authority to make certain announcements known. Proclamations are currently used within the governing framework of some nations ...
s will finish with the phrase: "At Our Government House, in Our City of Ottawa..."
History
McKay villa
 The site of Rideau Hall and the original structure were chosen and built by stonemason
The site of Rideau Hall and the original structure were chosen and built by stonemason Thomas McKay
Thomas McKay (1 September 1792 – 9 October 1855) was a Canadian businessman who was one of the founders of the city of Ottawa, Ontario.
Biography
McKay was born in Perth, Scotland and became a skilled stonemason. He emigrated to the C ...
, who immigrated from Perth, Scotland, to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, Lower Canada, in 1817 and later became the main contractor involved in the construction of the Rideau Canal. Following the completion of the canal, McKay built mills at Rideau Falls, making him the founder of New Edinburgh, the original settlement of Ottawa. With his newly acquired wealth, McKay purchased the 100 acre site overlooking both the Ottawa and Rideau Rivers and built a stone villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
where he and his family lived until 1855 and which became the root of the present day Rideau Hall. Locals referred to the structure as ''McKay's Castle''.
Even before the building became a royal residence, the hall received noted visitors, including three Governors General of the Province of Canada: the Lord Sydenham, the Earl of Elgin, and Sir Edmund Head. It was said that the watercolours of Barrack Hill (now Parliament Hill
Parliament Hill (french: Colline du Parlement, colloquially known as The Hill, is an area of Crown land on the southern banks of the Ottawa River in downtown Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Its Gothic revival suite of buildings, and their archit ...
) painted by the latter governor's wife, Lady Head, while she was visiting Rideau Hall, had influenced Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previo ...
to choose Bytown (now Ottawa) as the national capital. Also, on 2 September 1860, the day after he laid the cornerstone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure.
Over tim ...
of the parliament buildings, Prince Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria and ...
), drove through the grounds of Rideau Hall as part of his tour of the region.
Royal and viceroyal home
After Bytown was chosen as the capital of the Province of Canada, a design competition was launched in 1859 for a new parliamentary campus. The Centre Block, departmental buildings, and a residence for the governor general were each awarded separately. The winning scheme for Government House was aSecond Empire Second Empire may refer to:
* Second British Empire, used by some historians to describe the British Empire after 1783
* Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396)
* Second French Empire (1852–1870)
** Second Empire architecture, an architectural styl ...
design by Toronto architects Cumberland & Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of the natural environment or the atmosphere of an astronomical body. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, tornadoes, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm), ...
. However, it was never built, owing to cost overruns on the construction of the parliament buildings.
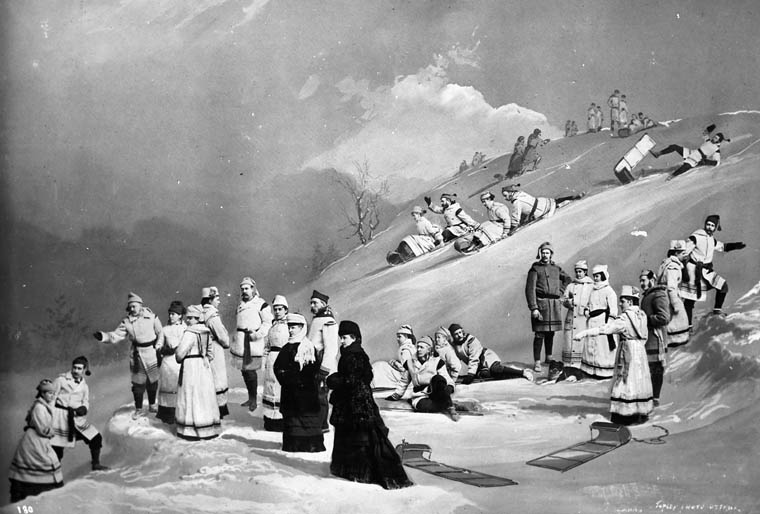
 In 1864, Rideau Hall was leased by the Crown from the McKay family for $4,000 per year and was intended to serve only as a temporary home for the
In 1864, Rideau Hall was leased by the Crown from the McKay family for $4,000 per year and was intended to serve only as a temporary home for the viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
until a proper government house could be constructed. The next year, Frederick Preston Rubidge oversaw the refinishing of the original villa and designed additions to accommodate the new functions. It was enlarged to three or four times the original size, mostly by way of a new 49-room wing, and, once complete, the first Governor General of Canada, the Viscount Monck, took residence. These additions were opposed by George Brown, who claimed that "the governor general's residence is a miserable little house, and the grounds those of an ambitious country squire." Prime Minister John A. Macdonald
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (January 10 or 11, 1815 – June 6, 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 to 1891. The dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, he had a political career that sp ...
agreed, complaining that more had been spent on patching up Rideau Hall than could have been used to construct a new royal palace. Nonetheless, the gatehouse was enhanced by Rubidge and the entire property purchased outright in 1868 for the sum of $82,000.
Thereafter, the house became the social centre of Ottawa—even Canada—hosting foreign visitors (the first being Grand Duke Alexis, son of Emperor Alexander II of Russia), investitures, swearing-in ceremonies, balls, dinners, garden parties, children's parties, and theatrical productions in the ballroom (initiated by the Earl
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
and Countess of Dufferin), in which members of the household and viceregal family would participate. Probably the largest event held in the ballroom was a fancy dress ball hosted by the Dufferins on the evening of 23 February 1876, which approximately 1,500 guests attended.
 Still, despite the popularity of the events that took place in the building, negative first impressions of Rideau Hall itself were a theme until the early part of the 20th century. Upon arrival there in 1872, the Countess of Dufferin said in her journal: "We have been so very enthusiastic about everything hitherto that the first sight of Rideau Hall did lower our spirits just a little!" In 1893, Lady Stanley, wife of Governor General the Lord Stanley of Preston, said "you will find the furniture in the rooms very old-fashioned & not very pretty... The red drawing room... had no furniture except chairs & tables... The walls are absolutely bare... The room which has always been the wife of the G.G.'s sitting room is very empty... There are no lamps in the house at all. No cushions, no table cloths, in fact none of the small things that make a room pretty & comfortable." Echoing these earlier comments, the Marchioness of Aberdeen and Temair said upon her departure from Ottawa that Rideau Hall was a "shabby old Government House put away amongst its clump of bushes..."
Various improvements were undertaken over the decades, seeing the first gas chandeliers and a telegraph wire put in, as well as the construction of the ballroom in the same year. By the time Rideau Hall was to live up to its role as a royal home, when its first royal residents— the Marquess of Lorne and his wife, Princess Louise—moved in at the beginning of 1878, many upgrades had been completed. Lorne stated of the hall: "Here we are settling down in this big and comfortable House, which I tell Louise is much superior to Kensington, for the walls are thick, the rooms are
Still, despite the popularity of the events that took place in the building, negative first impressions of Rideau Hall itself were a theme until the early part of the 20th century. Upon arrival there in 1872, the Countess of Dufferin said in her journal: "We have been so very enthusiastic about everything hitherto that the first sight of Rideau Hall did lower our spirits just a little!" In 1893, Lady Stanley, wife of Governor General the Lord Stanley of Preston, said "you will find the furniture in the rooms very old-fashioned & not very pretty... The red drawing room... had no furniture except chairs & tables... The walls are absolutely bare... The room which has always been the wife of the G.G.'s sitting room is very empty... There are no lamps in the house at all. No cushions, no table cloths, in fact none of the small things that make a room pretty & comfortable." Echoing these earlier comments, the Marchioness of Aberdeen and Temair said upon her departure from Ottawa that Rideau Hall was a "shabby old Government House put away amongst its clump of bushes..."
Various improvements were undertaken over the decades, seeing the first gas chandeliers and a telegraph wire put in, as well as the construction of the ballroom in the same year. By the time Rideau Hall was to live up to its role as a royal home, when its first royal residents— the Marquess of Lorne and his wife, Princess Louise—moved in at the beginning of 1878, many upgrades had been completed. Lorne stated of the hall: "Here we are settling down in this big and comfortable House, which I tell Louise is much superior to Kensington, for the walls are thick, the rooms are lath
A lath or slat is a thin, narrow strip of straight-wood grain, grained wood used under roof shingles or tiles, on lath and plaster walls and ceilings to hold plaster, and in Latticework, lattice and Trellis (architecture), trellis work.
''Lath ...
ed and plastered (which they are not at Kensington) and there is an abundant supply of heat and light." The princess was not long in Rideau Hall before Fenian
The word ''Fenian'' () served as an umbrella term for the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) and their affiliate in the United States, the Fenian Brotherhood, secret political organisations in the late 19th and early 20th centuries dedicated ...
s posed themselves as a threat to her life and she was ushered back to the UK for both rest and protection. When she returned in 1880, with the Queen greatly concerned for her daughter's safety, it was felt necessary to post extra guards around the grounds of the hall.
Thereafter, members of the royal family would stay periodically at Rideau Hall, if not as governor general then as guests of
the Crown, so that the palace played host to Prince Leopold (later also Duke of Albany) in 1880; Prince George (later King George V) in 1882, 1901, and 1908; Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught
Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn (Arthur William Patrick Albert; 1 May 185016 January 1942), was the seventh child and third son of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He served as Go ...
, and Princess Louise, Duchess of Connaught (later also the Duke and Duchess of Strathearn), in 1890 and as the viceregal couple from 1906 to 1912; Princess Louise in 1900; Princess Patricia with her parents from 1906 to 1912; Prince Albert (later King George VI) in 1910 and 1913; Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VIII), in 1919, 1923, 1924, and 1927; Prince George (later also Duke of Kent) in 1926 and 1927; and Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester, in 1929.
A member of the royal family, Alastair Windsor, 2nd Duke of Connaught and Strathearn, lost his life on the grounds of Rideau hall. Theo Aronson
Theodore Ian Wilson Aronson (13 November 1929 – 13 May 2003) was a royal biographer whose easy manner enabled him to earn the trust of his subjects.
He was the son of a Latvian Jewish storekeeper, born at Kirkwood, South Africa and educated ...
, in his 1981 biography of Princess Alice, Countess of Athlone, simply stated that the Duke "was found dead on the floor of his room at Rideau Hall on the morning of 26 April 1943. He had died, apparently, from hypothermia." The diaries of Sir Alan Lascelles, King George VI's private secretary, published in 2006, recorded that both the regiment and Athlone had rejected him as incompetent, and he fell out of a window when drunk and perished of hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
overnight.
Second World War
 When King George VI and his
When King George VI and his consort __NOTOC__
Consort may refer to:
Music
* "The Consort" (Rufus Wainwright song), from the 2000 album ''Poses''
* Consort of instruments, term for instrumental ensembles
* Consort song (musical), a characteristic English song form, late 16th–earl ...
, Queen Elizabeth, arrived at Rideau Hall on 19 May 1939, during their first royal tour of Canada, official royal tour historian Gustave Lanctot
Gustave Lanctot , also spelled Gustave Lanctôt, (5 July 1883 – 2 February 1975) was a Canadian historian and archivist.
Born in Saint-Constant, Quebec, he studied law at Université de Montréal and was called to the Quebec Bar in 1907. A ...
stated: "When Their Majesties walked into their Canadian residence, the Statute of Westminster had assumed full reality: the King of Canada had come home." The King, while there, became the first monarch of Canada to personally receive the credentials of an ambassador, that being Daniel Calhoun Roper as the representative of the United States. It was thought for a time, after the outbreak of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, that the King, Queen, and their two daughters— Princesses Elizabeth and Margaret—would move permanently to Canada for the duration of the conflict in Europe; though, Hatley Castle, in Colwood, British Columbia, was purchased by the King in Right of Canada for this purpose, instead of using Rideau Hall. However, it was decided that the royal family leaving the United Kingdom at a time of war would be a major blow to morale and they remained in Britain.
During the war, the palace became the home in exile of a number of royals displaced by the invasions of their respective countries back in Europe. Among the royal guests were Crown Prince Olav (later King Olav V) and Crown Princess Märtha
''Crown Princess Märtha'' is a bronze statue of Crown Princess Märtha of Norway, by Kirsten Kokkin.
It is located at the Norwegian residence at Massachusetts Avenue and 34th Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. It was unveiled 18 September 2005. ...
of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
, Grand Duchess Charlotte
Charlotte (Charlotte Adelgonde Elisabeth Marie Wilhelmine; 23 January 1896 – 9 July 1985) reigned as Grand Duchess of Luxembourg from 14 January 1919 until her abdication on 12 November 1964.
She acceded to the throne on 14 January 1919 foll ...
and Prince Felix of Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, King Peter II of Yugoslavia, King George II of Greece, Empress Zita of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and her daughters, as well as Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands, her daughter, Princess Juliana (later Queen Juliana), and granddaughters, Princesses Beatrix
Beatrix is a Latin feminine given name, most likely derived from ''Viatrix'', a feminine form of the Late Latin name ''Viator'' which meant "voyager, traveller" and later influenced in spelling by association with the Latin word ''beatus'' or "bles ...
(later Queen Beatrix), Irene and Margriet. Though the resident governor general's wife, Princess Alice, Countess of Athlone, could do little to add her personal touch to Rideau Hall, due to rationing and scarce supplies, she put many of the other royal ladies to work making clothing for those who had lost their homes in the Blitz
The Blitz was a German bombing campaign against the United Kingdom in 1940 and 1941, during the Second World War. The term was first used by the British press and originated from the term , the German word meaning 'lightning war'.
The Germa ...
. It was then in 1940 that the governor general's office in the East Block
The East Block (officially the Eastern Departmental Building; french: Édifice administratif de l'est) is one of the three buildings on Canada's Parliament Hill, in Ottawa, Ontario, containing offices for parliamentarians, as well as some preser ...
of Parliament Hill was closed and moved to Rideau Hall. In December 1941, Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
arrived at the hall, where he presided over British Cabinet
The Cabinet of the United Kingdom is the senior decision-making body of His Majesty's Government. A committee of the Privy Council, it is chaired by the prime minister and its members include secretaries of state and other senior ministers. ...
meetings via telephone from his bed.
Canadian viceregal residents
At the end of the global war, the first peacetime ball at Rideau Hall was held forPresident of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
, after which life within the household returned to normal. The transition from war to peace was marked by the appointment as governor general of the Viscount Alexander, whose son, Brian, reportedly used the portraits of former governors general throughout the hall as targets for his water pistol. During Alexander's tenure, Government House's first post-war Canadian royal visitors were the heiress presumptive to the throne, Princess Elizabeth, Duchess of Edinburgh (later Queen Elizabeth II), and her husband, Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh (born Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark, later Philip Mountbatten; 10 June 1921 – 9 April 2021) was the husband of Queen Elizabeth II. As such, he served as the consort of the British monarch from E ...
, who came in late 1951 and, amongst other activities, took part in a square dance in the ballroom (replete with checked shirts). Churchill, once again Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, returned to Rideau Hall in January of the next year, where, sprawled on a sofa with a cigar in one hand and a brandy in the other, he persuaded Alexander to join the British Cabinet.
 With the death of the King only a month following Churchill's 1952 visit, the front of Rideau Hall was covered with black bunting as a sign of
With the death of the King only a month following Churchill's 1952 visit, the front of Rideau Hall was covered with black bunting as a sign of mourning
Mourning is the expression of an experience that is the consequence of an event in life involving loss, causing grief, occurring as a result of someone's death, specifically someone who was loved although loss from death is not exclusively ...
. As one of his last acts as king of Canada, George VI appointed Vincent Massey
Charles Vincent Massey (February 20, 1887December 30, 1967) was a Canadian lawyer and diplomat who served as Governor General of Canada, the 18th since Confederation. Massey was the first governor general of Canada who was born in Canada after ...
as not only the first Canadian-born viceregal resident of his Canadian home, but also the first who was single, with Massey having been widowed
A widow (female) or widower (male) is a person whose spouse has died.
Terminology
The state of having lost one's spouse to death is termed ''widowhood''. An archaic term for a widow is "relict," literally "someone left over". This word can so ...
two years prior to his installation; his daughter-in-law, Lilias, thus acted as Chatelaine of Rideau Hall
The viceregal consort of Canada is the spouse of the serving governor general of Canada, assisting the viceroy with ceremonial and charitable work, accompanying him or her to official state occasions, and occasionally undertaking philanthropic work ...
. Massey spoke of Rideau Hall as "a piece of architecture that might be regarded as possessing a certain lovable eccentricity," in spite of "some of the most regrettable pieces of furniture I have ever seen."
The number of formal occasions at Rideau Hall increased through the 1950s and 1960s, as Canada's diplomatic corps increased and the country gained greater international standing; visitors during Massey's tenure included Queen Juliana, President Eisenhower, Emperor Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia
Haile Selassie I ( gez, ቀዳማዊ ኀይለ ሥላሴ, Qädamawi Häylä Səllasé, ; born Tafari Makonnen; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as Ethiopian aristocratic and court titles ...
, Jawaharlal Nehru
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru (; ; ; 14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat—
*
*
*
* and author who was a central figure in India during the middle of the 20t ...
, and the presidents of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. With the greater ease of travel, more members of Canada's royal family visited as well, including the Queen Mother; Princess Mary, Princess Royal; Katharine, Duchess of Kent
Katharine, Duchess of Kent, (born Katharine Lucy Mary Worsley, 22 February 1933) is a member of the British royal family. She is married to Prince Edward, Duke of Kent, a grandson of King George V.
The Duchess of Kent converted to Roman Ca ...
; Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon; Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh; and, in 1957, Elizabeth was again in residence, though for the first time as queen. The Queen also stayed in her Ottawa government house and held audience with an influx of 53 foreign heads of state and government during Expo 67, held in Montreal, and Canada's centennial celebrations.
Darker days fell on Rideau Hall during the October Crisis of 1970, when, under threat from the '' Front de libération du Québec'', who had planted bombs and conducted kidnappings in Quebec, the palace was heavily guarded for a number of weeks. The relatively free access to the grounds, which had been traditionally allowed since 1921 and enjoyed by tourists and local neighbours alike, ceased during Jeanne Sauvé
Jeanne Mathilde Sauvé (; April 26, 1922 – January 26, 1993) was a Canadian politician and journalist who served as Governor General of Canada, the 23rd since Canadian Confederation.
Sauvé was born in Prud'homme, Saskatchewan, and educate ...
's time as governor general; access was requested only through invitation, appointment, or pre-arranged tours on certain days. The decision to do so was based on concerns expressed by the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal police, federal and national police service of ...
and the National Capital Commission for the security of the vicereine and brought Rideau Hall in line with other official residences, including 24 Sussex Drive and Buckingham Palace, that did not allow public access. However, Sauvé was reported to have also been personally concerned for her safety, saying: "I'm worried about those crazy men out there."
 This caused controversy not only because Sauvé had contradicted her earlier statement about Rideau Hall, wherein she said: "oh yes, definitely, it has to be open," but also because it denied Ottawa residents the use of the grounds. One group formed under the name ''Canada Unlock the Gate Group'' and asserted the closure was more due to Sauvé's selfish desire for privacy than any real security risks; ''
This caused controversy not only because Sauvé had contradicted her earlier statement about Rideau Hall, wherein she said: "oh yes, definitely, it has to be open," but also because it denied Ottawa residents the use of the grounds. One group formed under the name ''Canada Unlock the Gate Group'' and asserted the closure was more due to Sauvé's selfish desire for privacy than any real security risks; ''The Globe and Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of approximately 2 million in 2015, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on weekdays and Saturdays, although it ...
'' reported in 1986 that the group planned to boycott the Governor General's annual garden party because of what they called her "bunker mentality". Sauvé's successor, Ray Hnatyshyn
Ramon John Hnatyshyn ( ; uk, Роман Іванович Гнатишин, Roman Ivanovych Hnatyshyn, ; March 16, 1934December 18, 2002) was a Canadian lawyer and statesman who served as governor general of Canada, the 24th since Canadian Co ...
, reopened Government House and its gardens to the public. Sauvé also entertained a plan suggested by management consultants Price Waterhouse
PricewaterhouseCoopers is an international professional services brand of firms, operating as partnerships under the PwC brand. It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is considered one of the Big Four accounting ...
to move from Rideau Hall into Rideau Cottage, both for privacy and cost savings.
21st century
Julie Payette did not take up residence in Rideau Hall during her tenure since, at the time of her appointment in October 2017, renovations that are part of a long-term plan toward 2067 were underway. In particular, the private apartments of the palace were being altered to provide a "sense of privacy and intimacy". Payette instead moved into 7 Rideau Gate, the residence, immediately outside the main entrance to the Rideau Hall grounds, normally reserved for dignitaries on official visits to Canada. Though the alterations to the viceregal family suite were complete by March 2018, further renovations to improve accessibility began immediately after. There was an intent for Payette to move to Rideau Hall in the summer of 2019, but she spent the summer at theCitadelle of Quebec
The Citadelle of Quebec (french: Citadelle de Québec), also known as ''La Citadelle'', is an active military installation and the secondary official residence of both the Canadian monarch and the governor general of Canada. It is located atop C ...
.
The grounds were again closed through much of 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
. During that period, on 2 July, a former Canadian soldier and businessman from Bowsman, Manitoba, drove his truck through Thomas Gate, a pedestrian entrance in the fence surrounding the park. He continued in his vehicle approximately 120 metres along the path beyond before proceeding further on foot, hiding in the rose garden for a few minutes and then moving on towards the greenhouses behind Rideau Hall itself. Groundskeepers noticed the intruder and the Royal Canadian Mounted Police were eventually called. The man, who the police noted was armed, was arrested without incident. Neither the Governor General nor the Prime Minister, who is using Rideau Cottage as a temporary residence while 24 Sussex Drive is under renovation, were on the Rideau Hall property at the time. According to a preliminary investigation by the RCMP, the man intended to have the prime minister "arrested" for recent policy decisions.
Function
 Rideau Hall's main purpose is to house the offices of the Governor General of Canada and his or her household, including the
Rideau Hall's main purpose is to house the offices of the Governor General of Canada and his or her household, including the Canadian Heraldic Authority
The Canadian Heraldic Authority (CHA; french: Autorité héraldique du Canada) is part of the Canadian honours system under the Canadian monarch, whose authority is exercised by the Governor General of Canada. The authority is responsible for t ...
. It is also the Ottawa residence of Canada's monarch. The majority of Rideau Hall's area is dedicated to affairs of state; only 500 m2 (5,400 sq ft) of the total 9,500 m2 (102,000 sq ft) being dedicated to private living quarters. Some 200 events are held at Rideau Hall every year, most being Canadian award presentations and investitures. In this way, the palace is where prime ministers
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is no ...
and other members of the federal Cabinet are sworn-in and federal writs of election are dropped, among other constitutional functions of the governor general. Heads of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and ...
, both incoming and outgoing ambassadors and high commissioners to Canada, and Canadian Crown ministers and loyal opposition
Loyal opposition in terms of politics, refers to specific political concepts that are related to the opposition parties of a particular political system. In many Westminster-style parliamentary systems of government, the loyal opposition indicate ...
leaders are received at Rideau Hall for audiences
An audience is a group of people who participate in a show or encounter a work of art, literature (in which they are called "readers"), theatre, music (in which they are called "listeners"), video games (in which they are called "players"), or ...
with either the viceroy or the sovereign, should the latter be in residence.
The residence is also open to the public, running a visitors' program and free tours of the state rooms throughout the year, as well as educational tours for students; it is the only one of the six official residences in the National Capital Region that is publicly accessible. A visitors' centre is located on the grounds, adjacent to the main gate. Rideau Hall takes part annually in Doors Open Ottawa and children may trick-or-treat at the house each Hallowe'en
Halloween or Hallowe'en (less commonly known as Allhalloween, All Hallows' Eve, or All Saints' Eve) is a celebration observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Saints' Day. It begins the observan ...
.
Architecture
 The original 1838 structure was relatively small; only two storeys tall with a full-height, central, curved bay, and an accordingly curved
The original 1838 structure was relatively small; only two storeys tall with a full-height, central, curved bay, and an accordingly curved pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape.
Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds.
A pedim ...
on top, the villa was designed by Thomas McKay (who had also designed and built Earnscliffe) in a Regency style, inspired by the work of architect Sir John Soane
Sir John Soane (; né Soan; 10 September 1753 – 20 January 1837) was an English architect who specialised in the Neo-Classical style. The son of a bricklayer, he rose to the top of his profession, becoming professor of architecture at the R ...
, who had himself designed a never realised government house for the then capital of Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of th ...
, York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
, in 1818. Unlike the present arrangement, the rooms of the McKay villa for entertaining, sleeping, and service were dispersed throughout the two floors of the structure, with the main parlour located on the second level, in an oval room behind the curved, south bay, which National Capital Commission Chief Architect David Scarlett said in 2014 was made in such a shape so as to display the advanced abilities of McKay's stonemasons. The main entrance to the house was on the west side and opened into a hall with stairs to the upper floor directly ahead. Along the south front were a library, a dining room, and a boudoir, all with French doors opening onto a narrow balcony
A balcony (from it, balcone, "scaffold") is a platform projecting from the wall of a building, supported by columns or console brackets, and enclosed with a balustrade, usually above the ground floor.
Types
The traditional Maltese balcony ...
; the dining room was served by three of these doors, one of which now opens into the Tent Room's antechamber, one into the Long Gallery, and one that still opens to the outside. The French door originally opening from the boudoir is today the window of the Pauline Vanier Room.
Initially rented from the McKay family as a temporary accommodation for the Canadian viceroy, the house has since been expanded numerous times. The Viscount Monck oversaw the first addition to the villa in 1865: a long wing extending to the east and built in a style that, while attempting to be harmonious with the original, was intended to resemble the governor general's residence in Quebec, Spencer Wood, which Monck greatly preferred over Rideau Hall. The extension was thus done in an overall Norman style of design that was typical in Quebec at the time, and had a similar long, covered verandah
A veranda or verandah is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch, attached to the outside of a building. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure.
Although the form ''vera ...
, a cross hall, and a new staircase capped by an ornate stained glass lantern. The exterior walls were clad in ashlar limestone masonry and the roof in cedar shingles until replaced by copper in 1913.
 In 1872, during the tenure of the Earl of Dufferin, the indoor
In 1872, during the tenure of the Earl of Dufferin, the indoor tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent ( singles) or between two teams of two players each ( doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball ...
court and the ballroom were added to the western end of the house, arranged to the south and north, respectively, of the main entrance. The ballroom is a structure of heavy timber framing
Timber framing (german: Holzfachwerk) and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and joined timbers with joints secured by large wooden ...
with brick infill and finished stone exterior. Then, when the Earl of Minto
Earl of Minto, in the County of Roxburgh, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created in 1813 for Gilbert Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 1st Baron Minto. The current earl is Gilbert Timothy George Lariston Elliot-Murray-Kynynm ...
arrived in 1898 with his large family and household, the Minto Wing was constructed on the east end of Rideau Hall and was completed in the following year, though this was again intended to only be a temporary measure until a proper government house could be built. Minto's successor, the Earl Grey, added the governor general's study to the far east end of the Monck Wing, thus symmetrically balancing out the curved bay and pediment of the original McKay villa to the west.
One of the greatest alterations to the form of Rideau Hall came in 1913, with the construction of the Mappin Block as a link between the ballroom and Tent Room, along with a re-facing of the two latter structures to harmonise their windows, cornice heights, and cladding (in a limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
ashlar), all in an "adapted Florentine architectural style" designed by Chief Dominion Architect David Ewart. The block is three storeys in height, and its front is divided by pilaster
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wal ...
s into five bays, with the central one slightly wider than the equal other four. The windows on the main floor are each surrounded by smaller pilasters beneath a triangular pediment formed by keel moulding geison
{{other
Geison ( grc, γεῖσον – often interchangeable with somewhat broader term cornice) is an architectural term of relevance particularly to ancient Greek and Roman buildings, as well as archaeological publications of the same. The ge ...
s, while the second level windows are each simply framed by astragal
An astragal is a moulding profile composed of a half-round surface surrounded by two flat planes ( fillets). An astragal is sometimes referred to as a miniature torus. It can be an architectural element used at the top or base of a column, b ...
moulding broken at the top by a keystone. A heavy entablature separates the second and third levels, atop which sits less pronounced pilasters and simply framed windows, with the entire facade capped by a narrow cornice and a pediment with a tympanum that bears a bas relief of the Royal Arms of the United Kingdom (believed to be the largest rendition in the Commonwealth).
For formal arrivals at the main door, later called the King's Entrance, this addition also included a porte-cochère
A porte-cochère (; , late 17th century, literally 'coach gateway'; plural: porte-cochères, portes-cochères) is a doorway to a building or courtyard, "often very grand," through which vehicles can enter from the street or a covered porch-like ...
with three arched openings between columns resting on the foundations of posts that supported the McKay villa's porte-cochère. The centre opening is topped with a carved stone rendition of the shield of the Royal Arms of Canada
The Arms of Canada (french: Armoiries du Canada, links=no), also known as the Royal Coat of Arms of Canada (french: armoiries royales du Canada, links=no) or formally as the Arms of His Majesty the King in Right of Canada (french: Armoiries de Sa M ...
as it appeared between 1868 and 1870. All the arches can be fitted during the winter with fanlights and glass doors to provide an enclosed space in which to exit cars. Further projects that were completed by 1914 were the addition in 1912 of the Long Gallery to the east of the Tent Room, and the enlargement of the State Dining Room.
Off the Long Gallery is the Verandah, added in 1927. It is a simple, stucco-clad structure containing one room with large windows and French door
A door is a hinged or otherwise movable barrier that allows ingress (entry) into and egress (exit) from an enclosure. The created opening in the wall is a ''doorway'' or ''portal''. A door's essential and primary purpose is to provide security by ...
s overlooking the upper terrace lawn in the corner between the Dufferin and Monck Wings. Between the windows are half-round and flat classical pilasters. A set of stairs leads from the French doors to the upper terrace.
 An accessible entrance—opened by
An accessible entrance—opened by Anne, Princess Royal
Anne, Princess Royal (Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise; born 15 August 1950), is a member of the British royal family. She is the second child and only daughter of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the only sister of ...
, and named after her—was added in 1982 and the Minto Wing was eventually converted from residences to offices. Then, at the prompting of Governor General Michaëlle Jean
Michaëlle Jean (; born September 6, 1957) is a Canadian stateswoman and former journalist who served from 2005 to 2010 as governor general of Canada, the 27th since Canadian Confederation. She is the first Haitian Canadian and black person ...
, the main facade of Rideau Hall underwent a major renovation through 2006 and 2007, overseen by the National Capital Commission, which has been responsible for the maintenance and upkeep of the building and its grounds since 1986. Masonry was treated and restored, the original sash windows rehabilitated and stripped of their lead paint, and the copper roof of the Mappin Wing was repaired. This was the first time any considerable work had been done on the front façade since the 1960s. A project began in 2012 to replace the building's climate control system—consisting of three large external chiller
A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid coolant via a vapor-compression, adsorption refrigeration, or absorption refrigeration cycles. This liquid can then be circulated through a heat exchanger to cool equipment, or another p ...
s and multiple window-mounted air conditioners—with a geothermal heating
Geothermal heating is the direct use of geothermal energy for some heating applications. Humans have taken advantage of geothermal heat this way since the Paleolithic era. Approximately seventy countries made direct use of a total of 270 PJ of ...
and cooling system, expected to supply approximately half of the building's heating requirements during winter, until the geothermal system is expanded in future.
The hall was designated as a classified heritage property by the Federal Heritage Buildings Review Office in 1986, giving it the highest heritage significance in Canada.
Decor and furnishings
Rideau Hall has long been a collection point for Canadian art and cabinetry. As early as the first viceregal inhabitants, the hall has held pieces by prominent Canadian cabinet makers, such as Jaques & Hay ofToronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, James Thompson of Montreal, and William Drum of Quebec. Originally, the interior decoration was heavily Victorian, with many Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
influences. Renovations, however, have turned the interiors into predominantly Georgian spaces, with Adam and Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
elements. Until the 1960s, the contents and colours of the house changed with each successive royal and viceregal family; the consort typically seeing it as her duty to update Rideau Hall to suit both her personal and contemporary tastes. As there were few paintings in the palace's permanent collection, the National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
would provide works on loan; a relationship that continues into the present.
 Today the rooms are furnished both with elements from the history of the residence as well as art and other objects that showcase contemporary Canadian culture, including pieces by the
Today the rooms are furnished both with elements from the history of the residence as well as art and other objects that showcase contemporary Canadian culture, including pieces by the Group of Seven
The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated member". It is officiall ...
's Lawren Harris
Lawren Stewart Harris LL. D. (October 23, 1885 – January 29, 1970) was a Canadian painter, best known as a leading member of the Group of Seven. He played a key role as a catalyst in Canadian art and as a visionary in Canadian landscape art. ...
, Emily Carr, Jean Paul Lemieux, and Bill Reid
William Ronald Reid Jr. (12 January 1920 – 13 March 1998) (Haida) was a Canadian artist whose works include jewelry, sculpture, screen-printing, and paintings. Producing over one thousand original works during his fifty-year career, Reid ...
. The Long Gallery's Chinoiserie
(, ; loanword from French '' chinoiserie'', from '' chinois'', "Chinese"; ) is the European interpretation and imitation of Chinese and other East Asian artistic traditions, especially in the decorative arts, garden design, architecture, lite ...
decoration was restored in 1993 at the direction of Gerda Hnatyshyn, wife of Governor General Ray Hnatyshyn, putting back much of the furniture and artifacts that had been collected by the Machioness of Willingdon throughout her tour of China in 1926. The space, used to greet and host functions for ambassadors and high commissioners to Canada, now contains five carpets donated by the Hongkong and Shanghai Bank and a Steinway & Sons baby grand piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a keyboa ...
that belonged to Glenn Gould
Glenn Herbert Gould (; né Gold; September 25, 1932October 4, 1982) was a Canadian classical pianist. He was one of the most famous and celebrated pianists of the 20th century, and was renowned as an interpreter of the keyboard works of Johann ...
. Other consorts left their mark on Rideau Hall, such as Princess Louise's painted apple branches on a 6-panel Georgian door (into the room adjacent to the Pauline Vanier Room) in the first-floor corridor and Nora Michener's donated collection of Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
sculpture. Governor General Adrienne Clarkson
Adrienne Louise Clarkson (; ; born February 10, 1939) is a Hong Kong-born Canadian journalist who served from 1999 to 2005 as Governor General of Canada, the 26th since Canadian Confederation.
Clarkson arrived in Canada with her family in 19 ...
and her husband, John Ralston Saul
John Ralston Saul (born June 19, 1947) is a Canadian writer, political philosopher, and public intellectual. Saul is most widely known for his writings on the nature of individualism, citizenship and the Public good (economics), public good; t ...
, not only oversaw the extensive repainting of the state rooms from a consistent white to more historically accurate and polychrome palette, but also worked with Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
potter Bill Reddick to develop Rideau Hall's first Canadian porcelain state dinner service.
Since Vincent Massey's time as governor general, the viceroy has worked closely with the Department of Public Works and Government Services in repairing and refurbishing Rideau Hall; the department now provides a more systematic approach to the maintenance of the palace, with a full-time building manager in charge of the project. The National Capital Commission is charged with the decoration of the rooms; since 2004 the commission has undertaken a project to restore many of the salons and other state rooms to the period in which they were first built. Many pieces—objets d'art
In art history, the French term Objet d’art describes an ornamental work of art, and the term Objets d’art describes a range of works of art, usually small and three-dimensional, made of high-quality materials, and a finely-rendered finish th ...
, paintings, sculptures, books, furnishings, and rugs—are drawn from the Crown Collection, so that, in Adrienne Clarkson's words, "the mix of furniture and other objects here now reflects the country, the people who came and settled here, and became part of the Canadian story."
Centre block and Mappin Wing
 The sole remaining part of the original McKay villa is the reception room on the ground floor and the royal suite directly above. The former was created in 1913 by removing the interior partitions of the villa; the baseboards, mouldings, and trims date from that era. It is where small ceremonies and presentations take place, while the latter is an oval room that was previously the drawing room of the original McKay villa and was subsequently used as a ballroom, a studio, and a study before becoming the monarch's bedroom. Some signs of the McKay house are still visible, notably in the now blanked window on the north wall of the reception room and the ornate plaster ceiling in the royal suite.
Directly west of these rooms is the
The sole remaining part of the original McKay villa is the reception room on the ground floor and the royal suite directly above. The former was created in 1913 by removing the interior partitions of the villa; the baseboards, mouldings, and trims date from that era. It is where small ceremonies and presentations take place, while the latter is an oval room that was previously the drawing room of the original McKay villa and was subsequently used as a ballroom, a studio, and a study before becoming the monarch's bedroom. Some signs of the McKay house are still visible, notably in the now blanked window on the north wall of the reception room and the ornate plaster ceiling in the royal suite.
Directly west of these rooms is the Edwardian
The Edwardian era or Edwardian period of British history spanned the reign of King Edward VII, 1901 to 1910 and is sometimes extended to the start of the First World War. The death of Queen Victoria in January 1901 marked the end of the Victori ...
Mappin Wing, which contains the entrance hall. Its walls are partly panelled, partly clad in marble; the lower floor covered in mosaic tile and the upper with wood. The two levels are connected by a wide, white marble, central stair; to each side, at the upper landing, are marble guards with ornate, Neoclassical balustrades
A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its con ...
. Across from the top of the stair is a door (to the reception room) flanked with wood panels documenting the names and escutcheons of each of the governors general for New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
, British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
, and Canada. On the opposite wall, to the left of the entrance, is the Royal Window—a stained glass piece commemorating the 40th anniversary of the accession of Elizabeth II to the throne, displaying, between the Queen's Canadian royal standard above and the Great Seal of Canada below, the monarch's coat of arms for Canada surrounded by the shields of each of the provincial coats of arms. Additionally, in the top two corners are images of Elizabeth's royal cypher, balancing out representations of the Sovereign's badges for both the Order of Canada
The Order of Canada (french: Ordre du Canada; abbreviated as OC) is a Canadian state order and the second-highest honour for merit in the system of orders, decorations, and medals of Canada, after the Order of Merit.
To coincide with the cen ...
and the Order of Military Merit in the bottom two corners. Another stained glass window is found to the right of the entrance, marking the first appointment of a Canadian-born governor general; the viceregal position is symbolised by a crowned lion holding a maple leaf and surrounded by the shields of the arms of the first seven persons to hold the post. In 2012, bronze and glass handrails, funded by a private donation from Rouge Herald Extraordinary Roger Alexander Lindsay, were added to each side of the stair in commemoration of the Diamond Jubilee of Queen Elizabeth II
The year 2012 marked the Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II being the 60th anniversary of the accession of Queen Elizabeth II on 6 February 1952. The only diamond jubilee celebration for any of Elizabeth's predecessors was in 1897, for the 60th an ...
.
Book-ending the Mappin Wing are the Tent Room—used for slightly less formal gatherings—and the ballroom—the centre of state life at Rideau Hall. It is in the latter space that honours and awards ceremonies take place, members of the Cabinet are sworn in, ambassadors present their diplomatic credentials, and large-scale state dinners are held; as such, it is the second most photographed and televised room in Canada, preceded only by the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. A double-height space, it is lined with tall, arched windows between rectangular pilasters that are topped with gilt, acanthused capitals. Cable moulding trim surrounds most of the openings and, around the perimeter of the room, at the intersection of walls and ceiling, is a deep and ornate plaster crown moulding formed by a godroon textured frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor ...
and a heavy dentil
A dentil (from Lat. ''dens'', a tooth) is a small block used as a repeating ornament in the bedmould of a cornice. Dentils are found in ancient Greek and Roman architecture, and also in later styles such as Neoclassical, Federal, Georgian R ...
ed bed-mould between layers of talon and gorge mouldings. Above this is the Victorian, lacunar, clear span vaulted
In architecture, a vault (French ''voûte'', from Italian ''volta'') is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while ring ...
ceiling, from the centre of which hangs a Waterford Crystal
Waterford Crystal is a manufacturer of lead glass or "crystal", especially in cut glass, named after the city of Waterford, Ireland. In January 2009, the main Waterford Crystal manufacturing base on the edge of Waterford was closed due to the ...
chandelier, presented by the British government on Victoria Day in 1951 as a token of gratitude for Canada's role in World War II. Also, in an alcove to the south of the ballroom's main door is a stained glass window that celebrates the excellence of Canadian performing artists and the establishment of the Governor General's Performing Arts Awards.
The present decor in the ballroom—powder blue
__NOTOC__
Powder blue is a pale shade of blue.
As with most colours, there is no absolute definition of its exact hue. Originally, ''powder blue'', in the 1650s, was powdered smalt (cobalt glass) used in laundering and dyeing applications, an ...
walls with beige marbleised pilasters, cream
Cream is a dairy product composed of the higher-fat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, the fat, which is less dense, eventually rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream, this process ...
trim, and shades of peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-f ...
, cream, and Old Gold
Old gold is a dark yellow, which varies from light olive or olive brown to deep or strong yellow, generally on the darker side of this range.
The first recorded use of ''old gold'' as a color name in English was in the early 19th century (exact ...
on the ceiling, all with gilt highlights—was implemented by Adrienne Clarkson when she served as the Queen's representative between 1999 and 2005. By stripping away a more monochrome palette that had been applied to the room in the 1970s, this restored the ballroom to a scheme closer to the original that was in place when the room was first completed in 1872.
The appearance of the Tent Room is drawn from the original use of striped fabric draped on the walls and hung in swaths from the ceiling in order to temporarily transform what was normally the tennis court into a dining hall. The room today has a wall covering of vertically striped red and gold fabric with a padded backing, which rises to meet the same fabric hung in a swag fashion outwards from a single coffer
A coffer (or coffering) in architecture is a series of sunken panels in the shape of a square, rectangle, or octagon in a ceiling, soffit or vault.
A series of these sunken panels was often used as decoration for a ceiling or a vault, also ...
in the centre of the ceiling and trimmed around the perimeter of the room with a scallop edged valence of simple passementerie
Passementerie (, ) or passementarie is the art of making elaborate trimmings or edgings (in French, ) of applied braid, gold or silver cord, embroidery, colored silk, or beads for clothing or furnishings.
Styles of passementerie include the tas ...
and tassel
A tassel is a finishing feature in fabric and clothing decoration. It is a universal ornament that is seen in varying versions in many cultures around the globe.
History and use
In the Hebrew Bible, the Lord spoke to Moses instructing him to ...
s. This gives the space an overall resemblance to the interior of a large tent. The west wall of the room is broken by series of windows, each paired with a double door into the Long Gallery on the opposite wall, and between them a continuous frame and panel wainscoting
Panelling (or paneling in the U.S.) is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials.
Panelling was developed in antiquity to make ro ...
. All this woodwork, including the door frames and other trim, is painted in a gloss white to contrast with the textured and patterned wall fabric.
Monck Wing
 Within the Monck Wing, built between 1865 and 1866, are other living quarters and drawing and dining rooms generally for non-state affairs, such as the Pauline Vanier Room, a small sitting room where informal meetings are held with visiting heads of state and other officials. The room was originally created in the 1960s by Pauline Vanier out of an old aide-de-camp smoking room, giving the space
Within the Monck Wing, built between 1865 and 1866, are other living quarters and drawing and dining rooms generally for non-state affairs, such as the Pauline Vanier Room, a small sitting room where informal meetings are held with visiting heads of state and other officials. The room was originally created in the 1960s by Pauline Vanier out of an old aide-de-camp smoking room, giving the space pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
panelling and filling it with antique furnishings from Quebec. However, it was later again refurbished to remove the tongue and groove planks Vanier had installed and which were said to be reminiscent of suburban basement panelling popular in the 1970s. The Pauline Vanier Room today contains furniture and other cabinetry works by Canadian artisans, as well as works by Canadian artists such as Kenojuak Ashevak
Kenojuak Ashevak, (Inuktitut: ᕿᓐᓄᐊᔪᐊᖅ ᐋᓯᕙᒃ, Qinnuajuaq Aasivak), (October 3, 1927 – January 8, 2013) is celebrated as a leading figure of modern Inuit art.
Early life and family
Kenojuak Ashevak was born in an igloo ...
, Emily Carr, and Norval Morrisseau
Norval Morrisseau (March 14, 1932 – December 4, 2007), also known as Copper Thunderbird, was an Indigenous Canadian artist from the Bingwi Neyaashi Anishinaabek First Nation. Known as the "Picasso of the North", Morrisseau created works depic ...
.
For more formal gatherings both before and after state events, as well as for entertaining visiting heads of state and their party, the Large Drawing Room, on the south side of the Monck Wing, is used. Previously called the Red Salon, the space underwent thorough renovations in 1901, updating it to the Edwardian style that was popular at the time, giving it boiserie
Panelling (or paneling in the U.S.) is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials.
Panelling was developed in antiquity to make roo ...
panelling formed from plaster mouldings, a layered crown moulding, as well as windows and doors with chambranle
In architecture and joinery, the chambranle is the border, frame, or ornament, made of stone or wood, that is a component of the three sides round chamber doors, large windows, and chimneys.
When a chambranle is plain and without mouldings, it is ...
d montants, the latter openings also equipped with moulded, classical overdoor
An "overdoor" (or "Supraporte" as in German, or "sopraporte" as in Italian) is a painting, bas-relief or decorative panel, generally in a horizontal format, that is set, typically within ornamental mouldings, over a door, or was originally intend ...
s. On the walls of the drawing room are hung portraits depicting the viceregal consorts of previous governors general. Directly across the hall from the Large Drawing Room is the State Dining Room, which is reserved for state dinners for visiting heads of state with smaller parties, with the table seating a maximum of 42 guests. in 1909, the dining room too was renovated to a similar Edwardian look, but its present day layout did not emerge until the late 1940s, after various subsequent renovations. The sterling silver sets on display in this room are on loan from Buckingham Palace.
 The governor general's study sits at the far east end of the Monck Wing's ground floor, next to another study allocated for the viceroy's consort. The former is panelled in carved wood that was installed when the room was constructed in 1906, with the names of each governor general applied in succession around the room, below the
The governor general's study sits at the far east end of the Monck Wing's ground floor, next to another study allocated for the viceroy's consort. The former is panelled in carved wood that was installed when the room was constructed in 1906, with the names of each governor general applied in succession around the room, below the dado rail
A dado rail, also known as a chair rail or surbase, is a type of moulding fixed horizontally to the wall around the perimeter of a room.
The dado rail is traditionally part of the dado or wainscot and, although the purpose of the dado is main ...
and a rendition of the sovereign's arms for the United Kingdom as a focal piece above the fireplace (reflecting the era in which the room was fitted). When the prime minister arrives for an audience with the governor in the latter's study, he or she uses the dedicated Prime Minister's Entrance, which is situated on the north side of the Monck addition, and opens into the easternmost of the wing's two staircases, from which it is only a short walk to the viceroy's office. Across from the study, the library contains a complete collection of Governor General's Literary Award
The Governor General's Awards are a collection of annual awards presented by the Governor General of Canada, recognizing distinction in numerous academic, artistic, and social fields.
The first award was conceived and inaugurated in 1937 by the ...
winning works. This room began as a bedroom for Lady Monck, later becoming the governor general's office, a boudoir, the military secretary's office, a smoking room, a flower room, and a card room, before being assigned its current role in 1952.
Further, the Monck Wing houses another, smaller drawing room and a billiard room. The viceregal suite, consisting of a study/living room, a large bedroom, and a kitchenette, is at the far west end of the upper floor. Also on the second level is the royal suite (the bedroom being the former parlour of the McKay villa) and the other guest bedrooms, each being named for a former British governor. The descendants of these men were approached in the 1990s with a request for donations of historical memorabilia, to which, amongst others, the Devonshires—relations of the ninth Duke of Devonshire—responded with a Regency mirror that had been used at Chatsworth House
Chatsworth House is a stately home in the Derbyshire Dales, north-east of Bakewell and west of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, Chesterfield, England. The seat of the Duke of Devonshire, it has belonged to the House of Cavendish, Cavendish family sin ...
. On that floor is also a chapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common ty ...
, installed during the Michener period, and which was made ecumenical
Ecumenism (), also spelled oecumenism, is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjec ...
and opened on 2 July 1967, in the presence of Queen Elizabeth II, for both Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
and Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
services.
Art
 Originally, most of the art in Rideau Hall was the personal property of the incumbent governor general and, as with much of the furnishings, was removed upon the end of the viceroy's commission. Starting in the 20th century, however, more and more pieces were added to the dedicated Crown Collection for Government House, either through gifts or purchases; for instance, in 1946, Sir James Dunn presented the Crown with two paintings by Johann Zoffany. Today the collection of furnishing, art, and artifacts at Rideau Hall is composed of private gifts from the Canada Fund (a foundation created by the government of Canada) and the Friends of Rideau Hall. The pieces, though predominantly Canadian in origin, also represent the Far East, Europe, and other regions, and can be arranged thematically, such as the Asian influenced pieces in the Long Gallery, the portraits of Canadian governors general in the reception room. The Crown Collection works on display are also usually augmented with approximately 100 art pieces and antiques on loan from various museums, galleries, and private collections; this continues a tradition started in the 1930s, when the National Gallery lent pieces to the viceroy at the time, the Earl of Bessborough.
Additionally, since the time of Clarkson's appointment, themed artistic exhibitions have been mounted at Rideau Hall, such as that during the tenure of Michaëlle Jean wherein the show "Body and Land" featured select
Originally, most of the art in Rideau Hall was the personal property of the incumbent governor general and, as with much of the furnishings, was removed upon the end of the viceroy's commission. Starting in the 20th century, however, more and more pieces were added to the dedicated Crown Collection for Government House, either through gifts or purchases; for instance, in 1946, Sir James Dunn presented the Crown with two paintings by Johann Zoffany. Today the collection of furnishing, art, and artifacts at Rideau Hall is composed of private gifts from the Canada Fund (a foundation created by the government of Canada) and the Friends of Rideau Hall. The pieces, though predominantly Canadian in origin, also represent the Far East, Europe, and other regions, and can be arranged thematically, such as the Asian influenced pieces in the Long Gallery, the portraits of Canadian governors general in the reception room. The Crown Collection works on display are also usually augmented with approximately 100 art pieces and antiques on loan from various museums, galleries, and private collections; this continues a tradition started in the 1930s, when the National Gallery lent pieces to the viceroy at the time, the Earl of Bessborough.
Additionally, since the time of Clarkson's appointment, themed artistic exhibitions have been mounted at Rideau Hall, such as that during the tenure of Michaëlle Jean wherein the show "Body and Land" featured select silkscreen
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink (or dye) onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open me ...
prints from the artist's book '' The Journals of Susanna Moodie'' by author Margaret Atwood
Margaret Eleanor Atwood (born November 18, 1939) is a Canadian poet, novelist, literary critic, essayist, teacher, environmental activist, and inventor. Since 1961, she has published 18 books of poetry, 18 novels, 11 books of non-fiction, nin ...
and artist Charles Pachter. What had been praised during Clarkson's tenure, however, was soon critiqued when it was revealed that into Jean's appointment, Rideau Hall's interpretation and exhibition planner, Fabienne Fusade, was removing from sight the portraits of Canada's past and present sovereigns and other members of the royal family, in order to fulfill Jean's wish to make the royal residence a showcase for Canadian art and give "a strong image of Canada"; the portrait by Jean Paul Lemieux of Queen Elizabeth II and the Duke of Edinburgh that had for decades dominated the focal wall of the ballroom was shifted to the rear wall, thereby bumping the copy of George Hayter
Sir George Hayter (17 December 1792 – 18 January 1871) was an English painter, specialising in portraits and large works involving in some cases several hundred individual portraits. Queen Victoria appreciated his merits and appointed Hayter h ...
's state portrait of Queen Victoria that had hung there to the Tent Room, where the portraits of Canada's British governors general had been collected together. These moves and removals were criticized by the editorial board of the ''National Post
The ''National Post'' is a Canadian English-language broadsheet newspaper available in several cities in central and western Canada. The paper is the flagship publication of Postmedia Network and is published Mondays through Saturdays, with ...
'', as well as other journalists, as having "demoted and ghettoized" history in order to "siphon off the great symbolic power of the monarchy, to further he staff'sparticular tastes and agendas," noting that Rideau Hall should not be used "primarily san art gallery."
Grounds
Rideau Hall's property is surrounded by a long Victorian stylecast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
and cast stone
Cast stone or reconstructed stone is a highly refined building material, a form of precast concrete used as masonry intended to simulate natural-cut stone. It is used for architectural features: trim, or ornament; facing buildings or other st ...
fence
A fence is a structure that encloses an area, typically outdoors, and is usually constructed from posts that are connected by boards, wire, rails or netting. A fence differs from a wall in not having a solid foundation along its whole length.
...
put up in 1928 and contains uniquely Canadian landscapes designed in the natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
and formal styles, including broad lawns, groves of trees, and meandering roads and pathways. The entire site is divided into five distinct areas: the wooded entrance park (trees, groundcover, daffodil
''Narcissus'' is a genus of predominantly spring flowering perennial plants of the amaryllis family, Amaryllidaceae. Various common names including daffodil,The word "daffodil" is also applied to related genera such as '' Sternbergia'', ''Is ...
s, and lawn
A lawn is an area of soil-covered land planted with grasses and other durable plants such as clover which are maintained at a short height with a lawnmower (or sometimes grazing animals) and used for aesthetic and recreational purposes. L ...
), the open parkland (meadow
A meadow ( ) is an open habitat, or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non-woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows may be naturally occurring or artifi ...
), the sugar bush, the ornamental gardens, and the farm (out-buildings and open area). The last once included a herd of cattle and fields used to grow hay, but today the only remaining agricultural ventures are the working vegetable and herb gardens that have been present on the site since the time of the McKay family. From these fields, plants, fruits, and edible flowers are used in the palace kitchens, and a greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
and flower garden provide flowers for the hall and other government buildings in Ottawa. Further, during the early spring months, the maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http ...
s throughout the property are tapped for syrup
In cooking, a syrup (less commonly sirup; from ar, شراب; , beverage, wine and la, sirupus) is a condiment that is a thick, viscous liquid consisting primarily of a solution of sugar in water, containing a large amount of dissolved sugars ...
making. In total, more than 10,000 trees grow on the grounds. Additionally, there is a long honorary segment of the Trans Canada Trail
The Trans Canada Trail, officially named The Great Trail between September 2016 and June 2021, is a cross-Canada system of greenways, waterways, and roadways that stretches from the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean, Pacific to the A ...
on the property.
inukshuk
An inuksuk (plural inuksuit) or inukshuk (from the iu, ᐃᓄᒃᓱᒃ, plural ; alternatively in Inuinnaqtun, in Iñupiaq, in Greenlandic) is a type of stone landmark or cairn built by, and for the use of, Inuit, Iñupiat, Kalaallit, Yu ...
erected by Kananginak Pootoogook
Kananginak Pootoogook (1 January 1935 – 23 November 2010) was an Inuk sculptor and printmaker who lived in Cape Dorset, Nunavut, in Canada. He died as a result of complications related to surgery for lung cancer.
Biography
Pootoogook was bo ...
File:GovernorGeneralSkatingRinkCanada.jpg, The grounds of Rideau Hall also includes a skating rink
trillium
''Trillium'' (trillium, wakerobin, toadshade, tri flower, birthroot, birthwort, and sometimes "wood lily") is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. ''Trillium'' species are native to temperate regions of No ...
s and orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowering ...
s; a totem pole
Totem poles ( hai, gyáaʼaang) are monumental carvings found in western Canada and the northwestern United States. They are a type of Northwest Coast art, consisting of poles, posts or pillars, carved with symbols or figures. They are usually ...
by Kwakiutl carver Mungo Martin
Chief Mungo Martin or ''Nakapenkem'' (lit. ''Potlatch chief "ten times over"''), ''Datsa'' (lit. ''"grandfather"''), was an important figure in Northwest Coast Art, Northwest Coast style art, specifically that of the Kwakwaka'wakw Aboriginal peopl ...
was gifted to the Earl Alexander of Tunis by the Lieutenant Governor of British Columbia
The lieutenant governor of British Columbia () is the viceregal representative of the , in the province of British Columbia, Canada. The office of lieutenant governor is an office of the Crown and serves as a representative of the monarchy in ...
- in-Council; the Fountain of Hope was initiated by Gerda Hnatyshyn
Karen Gerda Hnatyshyn ( ; ; born 1935 in Winnipeg, Manitoba) is a former viceregal consort of Canada, who held the role from 1990 to 1995 during her husband Ray Hnatyshyn's term as Governor General of Canada.
She attended the University of Saska ...
to mark the International Year of Disabled Persons
The year 1981 was proclaimed the International Year of Disabled Persons (IYDP) by the United Nations. It called for a plan of action with an emphasis on equalization of opportunities, rehabilitation and prevention of disabilities. The slogan of I ...
, built in front of Rideau Hall, and dedicated to Terry Fox
Terrance Stanley Fox (July 28, 1958 June 28, 1981) was a Canadian athlete, humanitarian, and cancer research activist. In 1980, with one leg having been amputated due to cancer, he embarked on an east-to-west cross-Canada run to raise money ...
; and an inukshuk
An inuksuk (plural inuksuit) or inukshuk (from the iu, ᐃᓄᒃᓱᒃ, plural ; alternatively in Inuinnaqtun, in Iñupiaq, in Greenlandic) is a type of stone landmark or cairn built by, and for the use of, Inuit, Iñupiat, Kalaallit, Yu ...
by artist Kananginak Pootoogook
Kananginak Pootoogook (1 January 1935 – 23 November 2010) was an Inuk sculptor and printmaker who lived in Cape Dorset, Nunavut, in Canada. He died as a result of complications related to surgery for lung cancer.
Biography
Pootoogook was bo ...
, from Cape Dorset
Kinngait (Inuktitut meaning "high mountain" or "where the hills are"; Syllabics: ᑭᙵᐃᑦ), formerly known as Cape Dorset until 27 February 2020, is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin ...
, Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' ...
, was built to commemorate the second National Aboriginal Day
National Aboriginal Day (informally National Indigenous Peoples Day) is a day recognizing and celebrating the cultures and contributions of the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis Indigenous peoples of Canada. The day was first celebrated in 199 ...
, in 1997. The Canadian Heritage Garden is a formal rose garden championed by Gerda Hnatyshyn and constructed to mark the 125th anniversary of Confederation. Also, each member of the royal family or visiting dignitary to Rideau Hall is asked to plant a tree; as such, the park, mostly along the main drive, is dotted with nearly 100 trees with small plaques at their bases listing the name and office of the person who planted each particular tree. These include Queen Elizabeth, the Queen Mother
Elizabeth Angela Marguerite Bowes-Lyon (4 August 1900 – 30 March 2002) was Queen of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 to 6 February 1952 as the wife of King George VI. She was the l ...
; Diana, Princess of Wales
Diana, Princess of Wales (born Diana Frances Spencer; 1 July 1961 – 31 August 1997) was a member of the British royal family. She was the first wife of King Charles III (then Prince of Wales) and mother of Princes William and Harry. Her ac ...
; Prince Charles, Prince of Wales
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to ...
; King George VI; and numerous by Queen Elizabeth II. Foreign dignitaries who have planted trees include John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
, Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis
Jacqueline Lee Kennedy Onassis ( ; July 28, 1929 – May 19, 1994) was an American socialite, writer, photographer, and book editor who served as first lady of the United States from 1961 to 1963, as the wife of President John F. Kennedy. A pop ...
, Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
, Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
, Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (; 8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founder ...
, Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
, Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
, Vicente Fox
Vicente Fox Quesada (; born 2 July 1942) is a Mexican businessman and politician who served as the 62nd president of Mexico from 1 December 2000 to 30 November 2006. After campaigning as a Right-wing populism, right-wing populist, Fox was elec ...
, and Emperor Akihito
is a member of the Imperial House of Japan who reigned as the 125th emperor of Japan from 7 January 1989 until his abdication on 30 April 2019. He presided over the Heisei era, ''Heisei'' being an expression of achieving peace worldwide.
Bo ...
.
Throughout their history as a royal park, the gardens have hosted numerous activities and events. The earliest governors general added amenities such as a curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
rink, a skating pond (which remains in operation, making it one of the oldest rinks in North America), toboggan
A toboggan is a simple sled traditionally used by children. It is also a traditional form of transport used by the Innu and Cree of northern Canada.
In modern times, it is used on snow to carry one or more people (often children) down a hill o ...
runs, tennis courts, and the like, and many of the guests at Rideau Hall would partake in these outdoor activities, including prime ministers William Lyon Mackenzie King
William Lyon Mackenzie King (December 17, 1874 – July 22, 1950) was a Canadian statesman and politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Canada for three non-consecutive terms from 1921 to 1926, 1926 to 1930, and 1935 to 1948. A L ...
and Robert Borden
Sir Robert Laird Borden (June 26, 1854 – June 10, 1937) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Canada from 1911 to 1920. He is best known for his leadership of Canada during World War I.
Borde ...
, who would often skate on the iced over pond with the viceregal family. Of the tobogganing, Lieutenant William Galwey, a member of the survey team that laid out the Canada–United States border
The border between Canada and the United States is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Can ...
and later visited Rideau Hall in November 1871, said: "It is a most favourite amusement at Government House. Ladies go in for it. I think they like rolling over and over with the gentlemen."
The grounds of Rideau Hall have been open to the public since 1921, when the Lord Byng of Vimy's aide-de-camp resolved to open Government House to "all who had a right to be there," a move that outraged the traditionalists. Today an expanded visitors' centre has been established to facilitate tours. Further, garden parties are held by the viceroy in the summer months, continuing the tradition started by the Lord Lisgar in 1869, and each year the governor general holds a New Year's Levée
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastlin ...
, an event that traces its roots back to the French royal government and which welcomes guests from the public to attend and participate in skating, sledding, and refreshments. The park also hosts the Rideau Hall Cricket Association and Ottawa Valley Cricket Council, which continues the tradition of cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
being played in the royal residence's gardens, beginning when the cricket pitch
In the game of cricket, the cricket pitch consists of the central strip of the cricket field between the wickets. It is long (1 chain) and wide. The surface is flat and is normally covered with extremely short grass, but can be completely d ...
was laid out by the Viscount Monck in 1866. Matches continue to be played at the hall during summer weekends.
Other structures
Other than Rideau Hall itself, there are 27 buildings around the property, including Rideau Cottage (currently serving as a temporary official home for the Prime Minister and his family), offices for the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, National Capital Commission, and Public Works and Government Services Canada, theGovernor General's Foot Guards
The Governor General's Foot Guards (GGFG) is the senior reserve infantry regiment in the Canadian Army. Located in Ottawa at the Cartier Square Drill Hall, the regiment is a Primary Reserve infantry unit, and the members are part-time soldiers.
...
' house, the Gasometer or Dome Building (Rideau Hall offices), the visitors' centre, the Farm Building, and stables. Additionally, there are six greenhouses.
Surrounding properties
Though not on the grounds of Rideau Hall, St. Bartholomew's Anglican Church is located across MacKay Street on property once belonging to the MacKay Villa estate. It is regularly used by governors general and their families and sometimes by the sovereign and other members of the royal family, as well as by viceregal household staff, their families, and members of the Governor General's Foot Guards, for whom the church also serves as a regimental chapel. Also nearby is 7 Rideau Gate, which is a guesthouse for distinguished visitors of the Crown situated just outside and facing onto the forecourt of the main gate of Rideau Hall.See also
*Government Houses in Canada
In Canada, Government House is a title given to the royal residences of the country's monarch, various viceroys (the governor general, the lieutenant governors), and territorial commissioners. Though not universal, in most cases the title is also ...
* Rideau Cottage
* 24 Sussex Drive
* Harrington Lake
Harrington Lake (french: La résidence du lac Mousseau) is the summer residence and all-season retreat of the prime minister of Canada, and also the name of the land which surrounds it. The farm that surrounded most of the lake was the property o ...
* Government Houses of the British Empire and Commonwealth
A Government House is any residence used by Governors-General, Governors and Lieutenant-Governors in the Commonwealth and the British Empire. Government Houses serve as the venue for Governors’ official business, as well as the many receptions ...
* List of palaces
The following is a list of palaces by country.
Afghanistan
* Darul Aman Palace, Kabul – the country's most famous palace.
* Tajbeg Palace – inaccurately known as the Queen's Palace in English
* Arg Presidential Palace – Home of the pr ...
* List of buildings in Ottawa
This is a list of notable buildings in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Museums
*Portrait Gallery of Canada
*National Gallery of Canada
*Canadian Museum of History (in Gatineau)
*Canadian War Museum
* Victoria Memorial Museum Building, housing the C ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
Governor General of Canada: Rideau Hall
Ottawa Tourism and Convention Authority: Rideau Hall
CPAC's interactive Rideau Hall: Inside Canada's House
YouTube: Government House, Ottawa
YouTube: Tour of Rideau Hall Monck Wing with Governor General David Johnston and Sharon Johnston
CBC Digital Archives: The Schreyers’ new life at Rideau Hall
YouTube: Gate Posting at the Governor Generals House in Ottawa
Toronto Public Library: Historic images of Rideau Hall
Order-in-Council 1868-0718 for purchase of Rideau Hall
Property record for Rideau Hall in the Directory of Federal Real Property
{{ Official Government residences in North America and the Caribbean Houses completed in 1838 Houses completed in 1914 Federal government buildings in Ottawa Monarchy in Canada Houses in Ottawa + Canadian heraldry Cricket grounds in Ontario Museums in Ottawa Historic house museums in Ontario Palaces in Canada Estate gardens in Canada National Historic Sites in Ontario Royal residences in Canada Sussex Drive