Rheumatic Fever on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammatory disease that can involve the
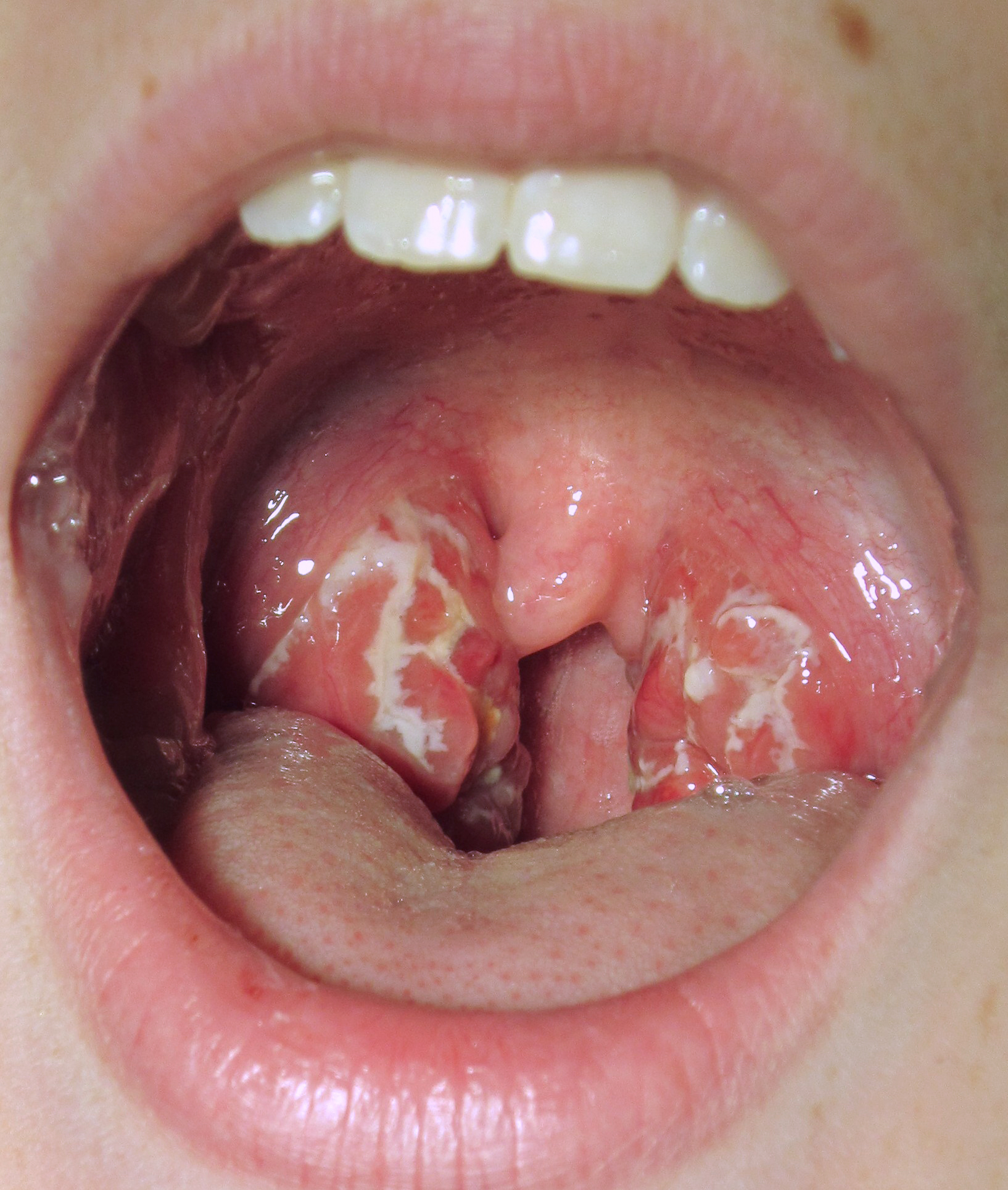 The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a
The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a

 Chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is characterized by repeated inflammation with fibrinous repair. The cardinal anatomic changes of the valve include leaflet thickening, commissural fusion, and shortening and thickening of the tendinous cords. It is caused by an autoimmune reaction to Group A β-hemolytic
Chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is characterized by repeated inflammation with fibrinous repair. The cardinal anatomic changes of the valve include leaflet thickening, commissural fusion, and shortening and thickening of the tendinous cords. It is caused by an autoimmune reaction to Group A β-hemolytic
 The original method of diagnosing rheumatic heart disease was through heart auscultation, specifically listening for the sound of blood regurgitation from possibly dysfunctional valves. However, studies have shown that echocardiography is much more efficient in detecting RHD due to its high sensitivity. An echocardiogram has the ability to detect signs of RHD before the development of more obvious symptoms such as tissue scarring and stenosis. Modified Jones criteria were first published in 1944 by
The original method of diagnosing rheumatic heart disease was through heart auscultation, specifically listening for the sound of blood regurgitation from possibly dysfunctional valves. However, studies have shown that echocardiography is much more efficient in detecting RHD due to its high sensitivity. An echocardiogram has the ability to detect signs of RHD before the development of more obvious symptoms such as tissue scarring and stenosis. Modified Jones criteria were first published in 1944 by

 About 33 million people are affected by rheumatic heart disease with an additional 47 million having asymptomatic damage to their heart valves. As of 2010 globally it resulted in 345,000 deaths, down from 463,000 in 1990.
In Western countries, rheumatic fever has become fairly rare since the 1960s, probably due to the widespread use of antibiotics to treat streptococcus infections. While it has been far less common in the
About 33 million people are affected by rheumatic heart disease with an additional 47 million having asymptomatic damage to their heart valves. As of 2010 globally it resulted in 345,000 deaths, down from 463,000 in 1990.
In Western countries, rheumatic fever has become fairly rare since the 1960s, probably due to the widespread use of antibiotics to treat streptococcus infections. While it has been far less common in the
heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
, joints, skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, and brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and occasionally a characteristic non- itchy rash known as erythema marginatum
Erythema marginatum is a type of erythema (redness of the skin or mucous membranes) involving pink rings on the torso and inner surfaces of the limbs which come and go for as long as several months. It is found primarily on extensor surfaces.
An ...
. The heart is involved in about half of the cases. Damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease
Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painf ...
(RHD), usually occurs after repeated attacks but can sometimes occur after one. The damaged valves may result in heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
, atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.
Rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacterium '' Streptococcus pyogenes''. If the infection is left untreated, rheumatic fever occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
against a person's own tissues. Due to their genetics, some people are more likely to get the disease when exposed to the bacteria than others. Other risk factors include malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
and poverty. Diagnosis of RF is often based on the presence of signs and symptoms in combination with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection.
Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s, such as penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from '' Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum usin ...
, decreases the risk of developing rheumatic fever. In order to avoid antibiotic misuse
Antibiotic misuse, sometimes called antibiotic abuse or antibiotic overuse, refers to the misuse or overuse of antibiotics, with potentially serious effects on health. It is a contributing factor to the development of antibiotic resistance, includ ...
this often involves testing people with sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. Usually, causes of sore throat include
* viral infections
* group A streptococcal infection (GAS) bacterial infection
* pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat)
* to ...
s for the infection; however, testing might not be available in the developing world. Other preventive measures include improved sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
. In those with rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease, prolonged periods of antibiotics are sometimes recommended. Gradual return to normal activities may occur following an attack. Once RHD develops, treatment is more difficult. Occasionally valve replacement surgery or valve repair
Heart valve repair is a cardiac surgery procedure, carried out to repair one or more faulty heart valves. In some valvular heart diseases repair where possible is preferable to valve replacement. A mechanical heart valve is a replacement valve ...
is required. Otherwise complications are treated as usual.
Rheumatic fever occurs in about 325,000 children each year and about 33.4 million people currently have rheumatic heart disease. Those who develop RF are most often between the ages of 5 and 14, with 20% of first-time attacks occurring in adults. The disease is most common in the developing world and among indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
s in the developed world. In 2015 it resulted in 319,400 deaths down from 374,000 deaths in 1990. Most deaths occur in the developing world where as many as 12.5% of people affected may die each year. Descriptions of the condition are believed to date back to at least the 5th century BCE in the writings of Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
. The disease is so named because its symptoms are similar to those of some rheumatic disorders.
Signs and symptoms
throat infection
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse voice ...
. Symptoms include: fever, painful joints with those joints affected changing with time, involuntary muscle movements, and occasionally a characteristic non-itchy rash known as erythema marginatum
Erythema marginatum is a type of erythema (redness of the skin or mucous membranes) involving pink rings on the torso and inner surfaces of the limbs which come and go for as long as several months. It is found primarily on extensor surfaces.
An ...
. The heart is involved in about half of the cases. Damage to the heart valves usually occurs only after multiple attacks but may occasionally occur after a single case of RF. The damaged valves may result in heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
and also increase the risk of atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.
Pathophysiology
Rheumatic fever is a systemic disease affecting theconnective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
around arterioles, and can occur after an untreated strep throat infection, specifically due to group A streptococcus (GAS), '' Streptococcus pyogenes''. The similarity between antigens of '' Streptococcus pyogenes'' and multiple cardiac proteins can cause a life-threatening type II hypersensitivity reaction. Usually, self reactive B cells remain anergic in the periphery without T cell co-stimulation. During a streptococcal infection, mature antigen-presenting cells such as B cells present the bacterial antigen to CD4+T cells which differentiate into helper T2 cells. Helper T2 cells subsequently activate the B cells to become plasma cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B lymphocytes and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific subs ...
s and induce the production of antibodies against the cell wall of Streptococcus. However the antibodies may also react against the myocardium and joints, producing the symptoms of rheumatic fever. ''S. pyogenes'' is a species of aerobic, cocci, gram-positive bacteria that are non-motile, non- spore forming, and forms chains and large colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
.
''S. pyogenes'' has a cell wall composed of branched polymers
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
which sometimes contain M protein, a virulence factor that is highly antigenic
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
. The antibodies which the immune system generates against the M protein may cross-react with heart muscle cell protein myosin, heart muscle glycogen and smooth muscle cells of arteries, inducing cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
release and tissue destruction. However, the only proven cross-reaction is with perivascular connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
. This inflammation occurs through direct attachment of complement and Fc receptor-mediated recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages. Characteristic Aschoff bodies
In medicine, Aschoff bodies are nodules found in the hearts of individuals with rheumatic fever. They result from inflammation in the heart muscle and are characteristic of rheumatic heart disease. These nodules were discovered independently by Lu ...
, composed of swollen eosinophilic collagen surrounded by lymphocytes and macrophages can be seen on light microscopy. The larger macrophages may become Anitschkow cells or Aschoff giant cells. Rheumatic valvular lesions may also involve a cell-mediated immunity
Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines ...
reaction as these lesions predominantly contain T-helper
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
cells and macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
.
In rheumatic fever, these lesions can be found in any layer of the heart causing different types of carditis. The inflammation may cause a serofibrinous pericardial exudate described as "bread-and-butter" pericarditis, which usually resolves without sequelae. Involvement of the endocardium typically results in fibrinoid necrosis and wart formation along the lines of closure of the left-sided heart valves. Warty projections arise from the deposition, while subendocardial lesions may induce irregular thickenings called MacCallum plaques.
Rheumatic heart disease

 Chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is characterized by repeated inflammation with fibrinous repair. The cardinal anatomic changes of the valve include leaflet thickening, commissural fusion, and shortening and thickening of the tendinous cords. It is caused by an autoimmune reaction to Group A β-hemolytic
Chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is characterized by repeated inflammation with fibrinous repair. The cardinal anatomic changes of the valve include leaflet thickening, commissural fusion, and shortening and thickening of the tendinous cords. It is caused by an autoimmune reaction to Group A β-hemolytic streptococci
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occu ...
(GAS) that results in valvular damage. Fibrosis and scarring of valve leaflets, commissures and cusps leads to abnormalities that can result in valve stenosis or regurgitation. The inflammation caused by rheumatic fever, usually during childhood, is referred to as rheumatic valvulitis. About half of patients with rheumatic fever develop inflammation involving valvular endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
. The majority of morbidity and mortality associated with rheumatic fever is caused by its destructive effects on cardiac valve tissue. The complicated pathogenesis of RHD is not fully understood, though it has been observed to use molecular mimicry Molecular mimicry is defined as the theoretical possibility that sequence similarities between foreign and self-peptides are sufficient to result in the cross-activation of autoreactive T or B cells by pathogen-derived peptides. Despite the preval ...
via group A streptococci carbohydrates and genetic predisposition involving HLA Class II genes that trigger autoimmune reactions.
Molecular mimicry occurs when epitopes are shared between host antigens and ''Streptococcus'' antigens. This causes an autoimmune reaction against native tissues in the heart that are incorrectly recognized as "foreign" due to the cross-reactivity of antibodies generated as a result of epitope sharing. The valvular endothelium is a prominent site of lymphocyte-induced damage. CD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ce ...
+ T cells are the major effectors of heart tissue autoimmune reactions in RHD. Normally, T cell activation is triggered by the presentation of bacterial antigens. In RHD, molecular mimicry results in incorrect T cell activation, and these T lymphocytes can go on to activate B cells, which will begin to produce self-antigen-specific antibodies. This leads to an immune response attack mounted against tissues in the heart that have been misidentified as pathogens. Rheumatic valves display increased expression of VCAM-1, a protein that mediates the adhesion of lymphocytes. Self-antigen-specific antibodies generated via molecular mimicry between human proteins and streptococcal antigens up-regulate VCAM-1 after binding to the valvular endothelium. This leads to the inflammation and valve scarring observed in rheumatic valvulitis, mainly due to CD4+ T cell infiltration.
While the mechanisms of genetic predisposition remain unclear, a few genetic factors have been found to increase susceptibility to autoimmune reactions in RHD. The dominant contributors are a component of MHC class II molecules, found on lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells, specifically the DR and DQ alleles on human chromosome 6. Certain allele combinations appear to increase RHD autoimmune susceptibility. Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
(HLA) class II allele DR7 (HLA-DR7
HLA-DR7 (DR7) is a HLA- DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*0701 to *0705 gene products.
Serology
The serological reaction of DR7 is excellent for *0701. The serology of *0703 to *0705 to *0709, and *0711 to *0714 serotypes is unknown. DRB1*0 ...
) is most often associated with RHD, and its combination with certain DQ alleles is seemingly associated with the development of valvular lesions. The mechanism by which MHC class II molecules increase a host's susceptibility to autoimmune reactions in RHD is unknown, but it is likely related to the role HLA molecules play in presenting antigens to T cell receptors, thus triggering an immune response. Also found on human chromosome 6 is the cytokine TNF-α which is also associated with RHD. High expression levels of TNF-α may exacerbate valvular tissue inflammation, because as this cytokine circulates in the bloodstream, it triggers the activation of multiple pathways that stimulate further pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion. Mannose-binding lectin
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), also called mannan-binding lectin or mannan-binding protein (MBP), is a lectin that is instrumental in innate immunity as an opsonin and via the lectin pathway.
Structure
MBL has an oligomeric structure (400-700 kDa) ...
(MBL) is an inflammatory protein involved in pathogen recognition. Different variants of MBL2 gene regions are associated in RHD. RHD-induced mitral valve stenosis has been associated with MBL2 alleles encoding for high production of MBL. Aortic valve regurgitation in RHD patients has been associated with different MBL2 alleles that encode for low production of MBL. In addition, the allele IGHV4-61, located on chromosome 14, which helps code for the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) is linked to greater susceptibility to RHD because it may affect protein structure of the IgH. Other genes are also being investigated to better understand the complexity of autoimmune reactions that occur in RHD.
Diagnosis
 The original method of diagnosing rheumatic heart disease was through heart auscultation, specifically listening for the sound of blood regurgitation from possibly dysfunctional valves. However, studies have shown that echocardiography is much more efficient in detecting RHD due to its high sensitivity. An echocardiogram has the ability to detect signs of RHD before the development of more obvious symptoms such as tissue scarring and stenosis. Modified Jones criteria were first published in 1944 by
The original method of diagnosing rheumatic heart disease was through heart auscultation, specifically listening for the sound of blood regurgitation from possibly dysfunctional valves. However, studies have shown that echocardiography is much more efficient in detecting RHD due to its high sensitivity. An echocardiogram has the ability to detect signs of RHD before the development of more obvious symptoms such as tissue scarring and stenosis. Modified Jones criteria were first published in 1944 by T. Duckett Jones
Thomas Duckett Jones (February 2, 1899, Petersburg, Virginia – November 22, 1954, New York City) was an American physician, cardiologist, and leading expert on rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. He is known for the "Jones criteria" in ...
, MD. They have been periodically revised by the American Heart Association in collaboration with other groups. According to revised Jones criteria, the diagnosis of rheumatic fever can be made when two of the major criteria, or one major criterion plus two minor criteria, are present along with evidence of streptococcal infection: elevated or rising antistreptolysin O titre Anti-streptolysin O (ASO or ASLO) is the antibody made against streptolysin O, an immunogenic, oxygen-labile streptococcal hemolytic exotoxin produced by most strains of group A and many strains of groups C and G '' Streptococcus'' bacteria. The ...
or anti-DNase B
Anti-Deoxyribonuclease B (anti-DNase B) titres are a quantitative measure of the presence of serologic antibodies obtained from patients suspected of having a recent group A (Beta-hemolytic) streptococcus bacteria infection, from ''Streptococcus p ...
. A recurrent episode is also diagnosed when three minor criteria are present. Exceptions are chorea and indolent carditis, each of which by itself can indicate rheumatic fever. An April 2013 review article in the ''Indian Journal of Medical Research'' stated that echocardiographic and Doppler (E & D) studies, despite some reservations about their utility, have identified a massive burden of rheumatic heart disease, which suggests the inadequacy of the 1992 Jones' criteria. E & D studies have identified subclinical carditis in patients with rheumatic fever, as well as in follow-ups of rheumatic heart disease patients who initially presented as having isolated cases of Sydenham's chorea. Signs of a preceding streptococcal infection include: recent scarlet fever
Scarlet fever, also known as Scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by '' Streptococcus pyogenes'' a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection (Group A strep). It most commonly affects chi ...
, raised antistreptolysin O or other streptococcal antibody titre, or positive throat culture. The last revision of 2015 suggested variable diagnostic criteria in low-risk and high-risk populations to avoid overdiagnosis in the first category and underdiagnosis in the last one. Low-risk populations were defined as those with acute rheumatic fever annual incidence ≤2 per 100 000 school-aged children or all-age rheumatic heart disease prevalence of ≤1 per 1000. All other populations were categorised as having a moderate or high risk.
Major criteria
# Joint manifestations are the unique clinical signs that have different implications for different population-risk categories : Only ''polyarthritis'' (a temporary migrating inflammation of the large joints, usually starting in the legs and migrating upwards) is considered as a major criterion in low-risk populations, whereas ''monoarthritis, polyarthritis and polyarthralgia (joint pain without swelling)'' are all included as major criteria in high-risk populations. # '' Carditis'': Carditis can involve the pericardium (pericarditis which resolves without sequelae), some regions of the myocardium (which might not provoke systolic dysfunction), and more consistently the endocardium in the form of valvulitis. Carditis is diagnosed clinically (palpitations, shortness of breath, heart failure, or a new heart murmur) or by echocardiography/Doppler studies revealing mitral or aortic valvulitis. Both of clinical and subclinical carditis are now considered a major criterion. # ''Subcutaneous nodules'': Painless, firm collections of collagen fibers over bones or tendons. They commonly appear on the back of the wrist, the outside elbow, and the front of the knees. # ''Erythema marginatum'': A long-lasting reddishrash
A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, c ...
that begins on the trunk or arms as macules, which spread outward and clear in the middle to form rings, which continue to spread and coalesce with other rings, ultimately taking on a snake-like appearance. This rash typically spares the face and is made worse with heat.
# '' Sydenham's chorea (St. Vitus' dance)'': A characteristic series of involuntary rapid movements of the face and arms. This can occur very late in the disease for at least three months from onset of infection.
Minor criteria
# '' Arthralgia'': ''Polyarthralgia'' in low-risk populations and ''monoarthralgia'' in others. However, joint manifestations cannot be considered in both major and minor categories in the same patient.
# ''Fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
'': ≥ 38.5 °C (101.3 °F) in low-incidence populations and ≥ 38 °C (100.4 °F) in high-risk populations.
# ''Raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of ...
'' (≥60 mm in the first hour in lox-risk populations and ≥30 mm/h in others) or ''C reactive protein'' (>3.0 mg/dL).
# ECG showing a ''prolonged PR interval
In electrocardiography, the PR interval is the period, measured in milliseconds, that extends from the beginning of the P wave (the onset of atrial depolarization) until the beginning of the QRS complex (the onset of ventricular depolarization); ...
''Ed Boon, Davidson's General Practice of Medicine, 20th edition. P. 617. after accounting for age variability (Cannot be included if carditis is present as a major symptom)
Prevention
Rheumatic fever can be prevented by effectively and promptly treating strep throat with antibiotics. In those who have previously had rheumatic fever, antibiotics in a preventative manner are occasionally recommended. As of 2017 the evidence to support long term antibiotics in those with underlying disease is poor. The American Heart Association suggests that dental health be maintained, and that people with a history of bacterial endocarditis, a heart transplant, artificial heart valves, or "some types of congenital heart defects" may wish to consider long-term antibiotic prophylaxis.Treatment
The management of rheumatic fever is directed toward the reduction of inflammation with anti-inflammatory medications such asaspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
or corticosteroids. Individuals with positive cultures for strep throat should also be treated with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s.
Aspirin is the drug of choice and should be given at high doses.
One should watch for side effects like gastritis and salicylate poisoning
Salicylate poisoning, also known as aspirin poisoning, is the acute or chronic poisoning with a salicylate such as aspirin. The classic symptoms are ringing in the ears, nausea, abdominal pain, and a fast breathing rate. Early on, these may be su ...
. In children and teenagers, the use of aspirin and aspirin-containing products can be associated with Reye's syndrome
Reye syndrome is a rapidly worsening brain disease. Symptoms of Reye syndrome may include vomiting, personality changes, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness. While liver toxicity typically occurs in the syndrome, jaundice usually doe ...
, a serious and potentially deadly condition. The risks, benefits, and alternative treatments must always be considered when administering aspirin and aspirin-containing products in children and teenagers. Ibuprofen for pain and discomfort and corticosteroids for moderate to severe inflammatory reactions manifested by rheumatic fever should be considered in children and teenagers.
Vaccine
No vaccines are currently available to protect against ''S. pyogenes'' infection, although research is underway to develop one. Difficulties in developing a vaccine include the wide variety of strains of ''S. pyogenes'' present in the environment and the large amount of time and people that will be needed for appropriate trials for safety and efficacy of the vaccine.Infection
People with positive cultures for ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' should be treated with penicillin as long asallergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
is not present. The use of antibiotics will not alter cardiac involvement in the development of rheumatic fever. Some suggest the use of benzathine benzylpenicillin.
Monthly injections of long-acting penicillin must be given for a period of five years in patients having one attack of rheumatic fever. If there is evidence of carditis, the length of therapy may be up to 40 years. Another important cornerstone in treating rheumatic fever includes the continual use of low-dose antibiotics (such as penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from '' Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum usin ...
, sulfadiazine, or erythromycin) to prevent recurrence.
Inflammation
While corticosteroids are often used, evidence to support this is poor.Salicylates
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substanc ...
are useful for pain.
Steroids are reserved for cases where there is evidence of an involvement of the heart. The use of steroids may prevent further scarring of tissue and may prevent the development of sequelae such as mitral stenosis.
Heart failure
Some patients develop significant carditis which manifests ascongestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
. This requires the usual treatment for heart failure: ACE inhibitors, diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
s, beta blockers, and digoxin. Unlike typical heart failure, rheumatic heart failure responds well to corticosteroids.
Epidemiology
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
since the beginning of the 20th century, there have been a few outbreaks since the 1980s. The disease is most common among Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
(particularly in central and northern Australia), Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
, and Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/ racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
s, and is also common in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
, the Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
.
Rheumatic fever primarily affects children between ages 5 and 17 years and occurs approximately 20 days after strep throat. In up to a third of cases, the underlying strep infection may not have caused any symptoms.
The rate of development of rheumatic fever in individuals with untreated strep infection is estimated to be 3%. The incidence of recurrence with a subsequent untreated infection is substantially greater (about 50%). The rate of development is far lower in individuals who have received antibiotic treatment. Persons who have had a case of rheumatic fever have a tendency to develop flare-ups with repeated strep infections.
The recurrence of rheumatic fever is relatively common in the absence of maintenance of low dose antibiotics, especially during the first three to five years after the first episode. Recurrent bouts of rheumatic fever can lead to valvular heart disease. Heart complications may be long-term and severe, particularly if valves are involved. In countries in Southeast-Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, and Oceania, the percentage of people with rheumatic heart disease detected by listening to the heart was 2.9 per 1000 children and by echocardiography it was 12.9 per 1000 children. Echocardiographic screening among children and timely initiation of secondary antibiotic prophylaxis in children with evidence of early stages of rheumatic heart disease may be effective to reduce the burden of rheumatic heart disease in endemic regions.
See also
*Rapid strep test
The rapid strep test (RST) is a rapid antigen detection test (RADT) that is widely used in clinics to assist in the diagnosis of bacterial pharyngitis caused by group A streptococci (GAS), sometimes termed strep throat. There are currently sever ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Rheumatic Fever Chronic rheumatic heart diseases Inflammations Pediatrics Rheumatology Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate