resilience (materials science) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
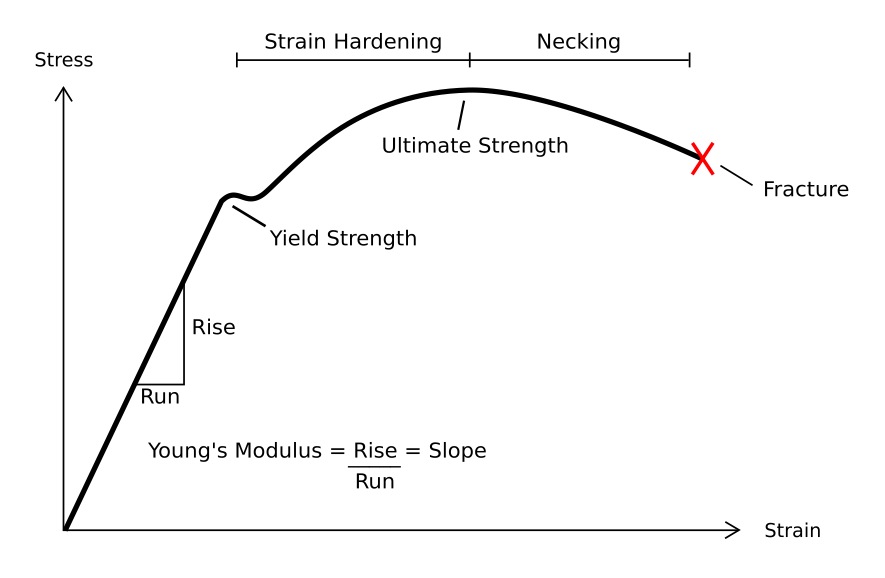 In material science, resilience is the ability of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically, and release that energy upon unloading. Proof resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit, without creating a permanent distortion. The modulus of resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed per unit volume without creating a permanent distortion. It can be calculated by integrating the
In material science, resilience is the ability of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically, and release that energy upon unloading. Proof resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit, without creating a permanent distortion. The modulus of resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed per unit volume without creating a permanent distortion. It can be calculated by integrating the
 In material science, resilience is the ability of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically, and release that energy upon unloading. Proof resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit, without creating a permanent distortion. The modulus of resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed per unit volume without creating a permanent distortion. It can be calculated by integrating the
In material science, resilience is the ability of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically, and release that energy upon unloading. Proof resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit, without creating a permanent distortion. The modulus of resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed per unit volume without creating a permanent distortion. It can be calculated by integrating the stress–strain curve
In engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain. It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress ...
from zero to the elastic limit. In uniaxial tension, under the assumptions of linear elasticity,
:
where ''Ur'' is the modulus of resilience, ''σy'' is the yield strength
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and wi ...
, ''εy'' is the yield strain, and ''E'' is the Young's modulus
Young's modulus E, the Young modulus, or the modulus of elasticity in tension or compression (i.e., negative tension), is a mechanical property that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness of a solid material when the force is applied ...
. This analysis is not valid for non-linear elastic materials like rubber, for which the approach of area under the curve until elastic limit must be used.
Unit of resilience
Modulus of resilience (''U''r) is measured in a unit ofjoule
The joule ( , ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of 1 newton displaces a mass through a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force appli ...
per cubic meter (J·m−3) in the SI system, ''i.e.'' elastical deformation energy per surface of test specimen (merely for gauge-length part).
Like the unit of tensile toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.Pa × % = (N·m−2)·(unitless)
:''U''r N·m·m−3
:''U''r J·m−3
See also
*Toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.Elasticity (physics)
hu:Reziliencia
simple:Resilience
sr:Резилијенција