Republican Party (United States) Presidential Primaries, 1976 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
From August 16 to August 19, 1976, voters of the
 More than any domestic issue in 1975, foreign policy drove a wedge between the President and his conservative critics. Following the American evacuation of Saigon and the collapse of South Vietnam, these criticisms grew vociferous. On his radio show, Reagan compared the withdrawal from Saigon to the
More than any domestic issue in 1975, foreign policy drove a wedge between the President and his conservative critics. Following the American evacuation of Saigon and the collapse of South Vietnam, these criticisms grew vociferous. On his radio show, Reagan compared the withdrawal from Saigon to the

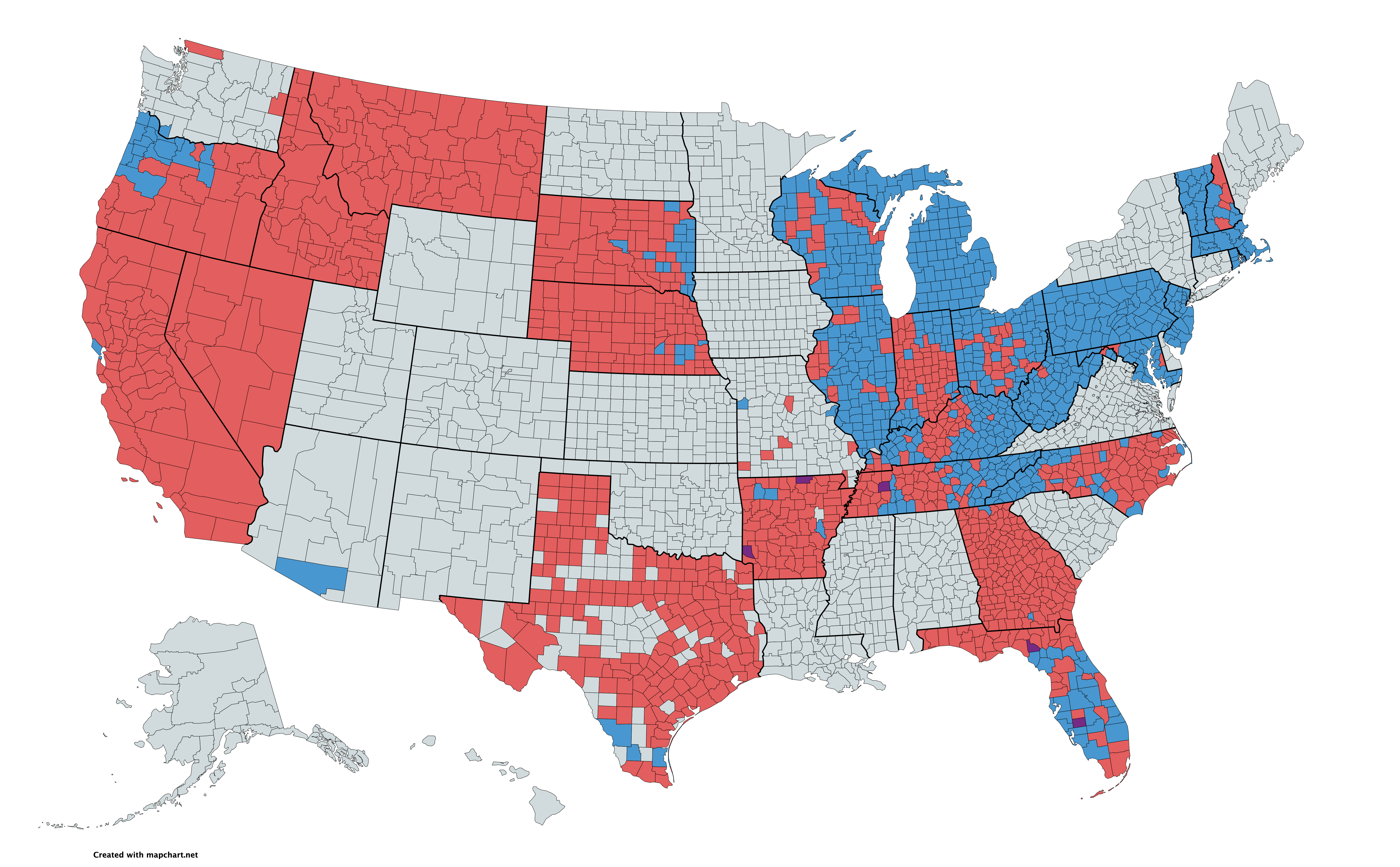 Convention tally:
Convention tally:Our Campaigns - US President - R Convention Race - Aug 16, 1976
/ref> *
Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
* Republican Party (Liberia)
*Republican Party ...
chose its nominee for president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
in the 1976 United States presidential election
The 1976 United States presidential election was the 48th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 2, 1976. Democrat Jimmy Carter of Georgia defeated incumbent Republican President Gerald Ford from Michigan by a nar ...
. The major candidates were incumbent President Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected ...
and former Governor of California Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
. After a series of primary election
Primary elections, or direct primary are a voting process by which voters can indicate their preference for their party's candidate, or a candidate in general, in an upcoming general election, local election, or by-election. Depending on the ...
s and caucus
A caucus is a meeting of supporters or members of a specific political party or movement. The exact definition varies between different countries and political cultures.
The term originated in the United States, where it can refer to a meeting ...
es, neither secured a majority of the delegates before the convention.
The 1976 election marks the first time that Republican primaries or caucuses were held in every state and D.C.; the Democrats had done so in 1972. It was also the last election in which the Republican nominee was undetermined at the start of the party's national convention.
Background
August 1974 – February 1975: The Ford presidency begins
Following theWatergate scandal
The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon from 1972 to 1974 that led to Nixon's resignation. The scandal stemmed from the Nixon administration's contin ...
and resignation of President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
, Vice President Gerald Ford was elevated to president on August 9, 1974. Because Ford had been appointed vice president by Nixon following the resignation of Spiro Agnew from the position, he became the only president inaugurated without having been previously voted into either the presidential or vice presidential office by the Electoral College.
On September 8, Ford's first major act in office was to grant a full and unconditional pardon for any crimes Richard Nixon might have committed against the United States while President. Following his pardon of Nixon, Ford's approval ratings among the American public dropped precipitously. Within a week, his approval rating fell from 69% to 49%, the steepest decline in history.
The economy was in dire condition upon Ford's elevation, marked by the worst peacetime inflation in American history and the highest interest rates in a century. The Dow Jones had declined 43 percent from October 1973 to September 1974. To combat inflation, Ford first proposed a tax increase and later, in response to Democratic calls for a permanent cut in taxes, a temporary moderate decrease. Reagan publicly criticized both proposals.
Race and education divided public opinion, especially over issues such as forced integration and changes to public school curriculum. Political violence over education policy broke out in Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and Charleston, West Virginia
Charleston is the capital and most populous city of West Virginia. Located at the confluence of the Elk and Kanawha rivers, the city had a population of 48,864 at the 2020 census and an estimated population of 48,018 in 2021. The Charlesto ...
. Abortion also became a nationally salient issue after the Supreme Court's ''Roe v. Wade
''Roe v. Wade'', 410 U.S. 113 (1973),. was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States conferred the right to have an abortion. The decision struck down many federal and st ...
'' decision, which was announced two days after Nixon's resignation and struck down state restrictions on abortion nationwide.
In the 1974 midterm elections, the Democratic Party dramatically expanded its majorities in both the House
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air cond ...
and Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
. The elections were seen as a referendum on the Republican Party post-Watergate and on the political establishment more generally. Newly elected members of Congress became known as "Watergate Babies
The Watergate Babies were Democrats first elected to the United States Congress in the 1974 elections, after President Richard Nixon's resignation over the Watergate scandal, on August 9, 1974.
Democrats picked up 49 seats in the House and 5 i ...
" and aggressively pursued procedural and oversight reforms.
During this period, Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
concluded his second term in office as Governor of California. His administration was marked by efforts to dismantle the welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equita ...
and a high-profile crackdown on urban crime and left-wing dissent, especially at the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant un ...
. He also led an effort to enforce the state's capital punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that ...
laws but was blocked by the California Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of California is the highest and final court of appeals in the courts of the U.S. state of California. It is headquartered in San Francisco at the Earl Warren Building, but it regularly holds sessions in Los Angeles and Sac ...
in the '' People v. Anderson'' decision. Following Reagan's retirement from office in January 1975, he began hosting a national radio show and writing a national newspaper column.
March–July 1975: Conservatives revolt and Reagan rises
Conservative opposition to Ford within the Republican Party began to surface in December 1974, following his appointment of New York GovernorNelson Rockefeller
Nelson Aldrich Rockefeller (July 8, 1908 – January 26, 1979), sometimes referred to by his nickname Rocky, was an American businessman and politician who served as the 41st vice president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. A member of t ...
as vice president. For more than a decade, Rockefeller had represented the party's liberal establishment, and the appointment faced immediate criticism from right-wing senators like Jesse Helms
Jesse Alexander Helms Jr. (October 18, 1921 – July 4, 2008) was an American politician. A leader in the conservative movement, he served as a senator from North Carolina from 1973 to 2003. As chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committe ...
, Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater (January 2, 1909 – May 29, 1998) was an American politician and United States Air Force officer who was a five-term U.S. Senator from Arizona (1953–1965, 1969–1987) and the Republican Party nominee for president ...
and John Tower
John Goodwin Tower (September 29, 1925 – April 5, 1991) was an American politician, serving as a Republican United States Senator from Texas from 1961 to 1985. He was the first Republican Senator elected from Texas since Reconstruction. Towe ...
, though Rockefeller's confirmation in the Senate was largely undeterred.
Discontent reached a fever pitch at the second annual Conservative Political Action Conference
The Conservative Political Action Conference (CPAC; ) is an annual political conference attended by conservative activists and elected officials from across the United States and beyond. CPAC is hosted by the American Conservative Union (ACU) ...
in February. Speaking there, Reagan dismissed calls to seek the presidency on a third-party ticket: "Is it a third party that we need, or is it a new and revitalized second party, raising a banner of no pale pastels, but bold colors which could make it unmistakably clear where we stand on all the issues troubling the people?" Speakers at CPAC also criticized Ford administration policy, Vice President Rockefeller, and First Lady Betty Ford
Elizabeth Anne Ford (; formerly Warren; April 8, 1918 – July 8, 2011) was the first lady of the United States from 1974 to 1977, as the wife of President Gerald Ford. As first lady, she was active in social policy and set a precedent as a p ...
's public campaign in support of abortion and the Equal Rights Amendment
The Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) is a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution designed to guarantee equal legal rights for all American citizens regardless of sex. Proponents assert it would end legal distinctions between men and ...
. In March, discussion began to build around Reagan's presidential prospects following an appearance on The Tonight Show
''The Tonight Show'' is an American late-night talk show that has aired on NBC since 1954. The show has been hosted by six comedians: Steve Allen (1954–1957), Jack Paar (1957–1962), Johnny Carson (1962–1992), Jay Leno (1992–2009 and 201 ...
and a profile in Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis (businessman), Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print m ...
that called him, "the most kinetic single presence in American political life." In defense, the administration drafted a letter of support for President Ford that received the signatures of 113 of 145 GOP Representatives and 31 of 38 Senators. Ford formally announced he would run for reelection on July 8.
 More than any domestic issue in 1975, foreign policy drove a wedge between the President and his conservative critics. Following the American evacuation of Saigon and the collapse of South Vietnam, these criticisms grew vociferous. On his radio show, Reagan compared the withdrawal from Saigon to the
More than any domestic issue in 1975, foreign policy drove a wedge between the President and his conservative critics. Following the American evacuation of Saigon and the collapse of South Vietnam, these criticisms grew vociferous. On his radio show, Reagan compared the withdrawal from Saigon to the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
and warned that it would "tempt the Soviet Union as it once tempted Hitler and the military rulers of Japan." While Ford regained some support from conservatives following the rescue of the SS Mayaguez in Cambodia, he soon drew the ire of the party's right wing with a series of foreign policy moves designed to improve relations with the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
.
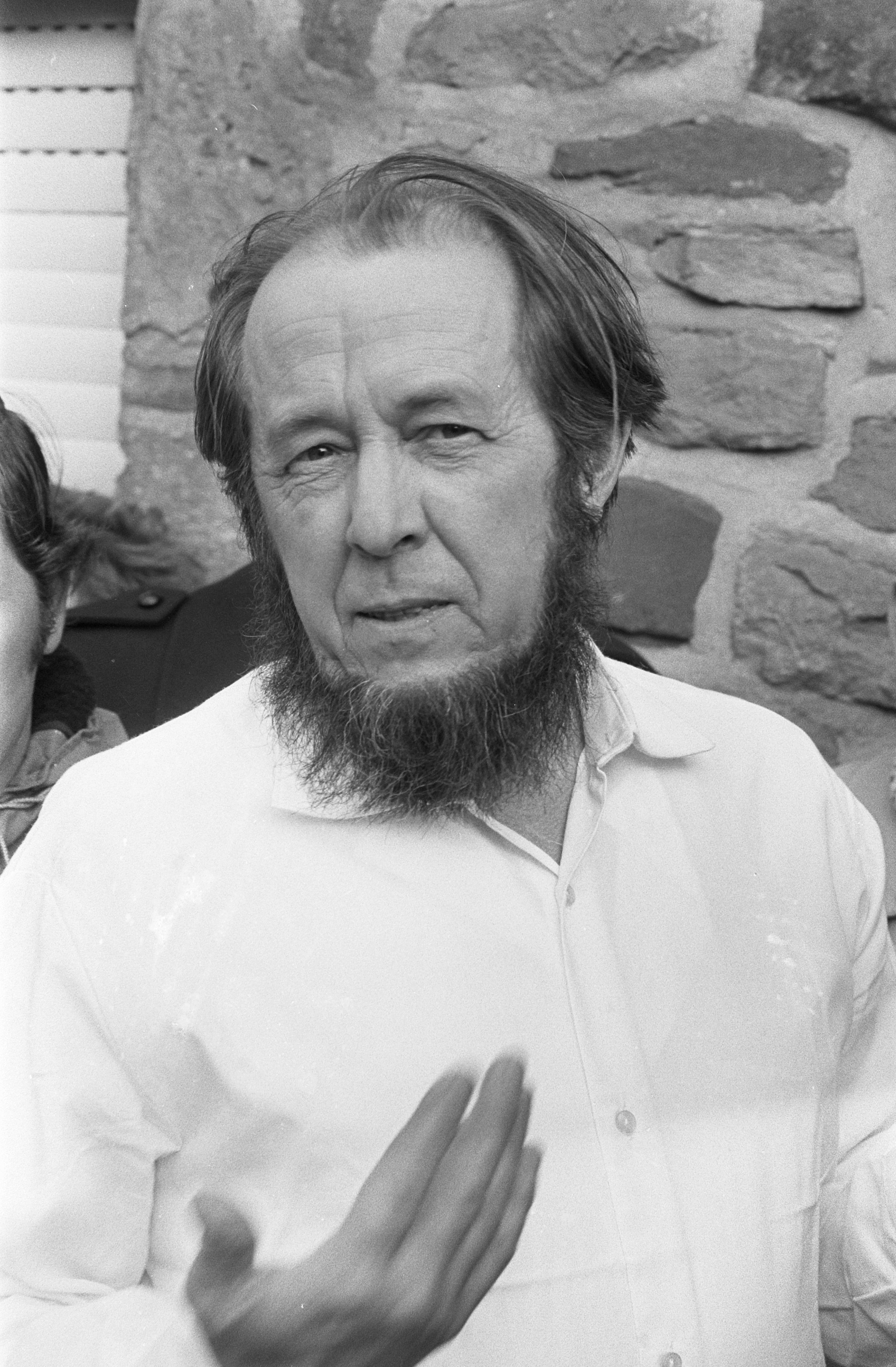
First, President Ford refused to meet with Soviet dissident Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn
Aleksandr Isayevich Solzhenitsyn. (11 December 1918 – 3 August 2008) was a Russian novelist. One of the most famous Soviet dissidents, Solzhenitsyn was an outspoken critic of communism and helped to raise global awareness of political repr ...
on his visit to the United States on June 21. In response, Reagan publicly criticized Ford by name for the first time in his national newspaper column, contrasting the popular Solzhenitsyn to other "guests the President had entertained in the White House, "the Strawberry Queen of West Virginia and the Maid of Cotton." The day after this column ran, Senator Paul Laxalt announced the formation of a committee named "Friends of Ronald Reagan," organized for the purpose of drafting Reagan to run for president.
Ford followed the Solzhenitsyn affair with an overseas trip to Eastern Europe, where he signed the Helsinki Accords
The Helsinki Final Act, also known as Helsinki Accords or Helsinki Declaration was the document signed at the closing meeting of the third phase of the Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE) held in Helsinki, Finland, betwee ...
, a treaty establishing that the current boundaries of Eastern European nations were "inviolable by force." Conservatives and anti-communists harshly criticized Ford for capitulating to Soviet demands and formally recognizing the Eastern bloc. The Wall Street Journal called the Helsinki agreement the "new Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
." By late August, Ford's approval rating was polled at 34%.
On September 5 in Sacramento, Ford survived the first of two attempts on his life by lone assassins. A second attempt followed on September 21. Neither assassin struck Ford.
September–December 1975: Reagan enters the race
In September, Reagan began to actively campaign in key early states. He stumped inNew Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
for Louis Wyman in the special election for Senate and began to assemble a campaign staff led by campaign manager John Sears. He secured the endorsement of New Hampshire's conservative governor Meldrim Thomson Jr. and state party chairman, as well as support from moderate former governor Hugh Gregg.
On November 4, Vice President Nelson Rockefeller
Nelson Aldrich Rockefeller (July 8, 1908 – January 26, 1979), sometimes referred to by his nickname Rocky, was an American businessman and politician who served as the 41st vice president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. A member of t ...
announced he would not seek nomination as Ford's running mate in 1976. That same day, Ford fired Secretary of Defense James R. Schlesinger, whose critical comments on the Helsinki summit had been leaked to the press earlier in the fall. That week, Ford traveled to Massachusetts and pledged to campaign in every primary in the nation.
On November 20, Ronald Reagan officially announced his campaign for president.
Campaign
Ford narrowly defeated Reagan in theNew Hampshire primary
The New Hampshire presidential primary is the first in a series of nationwide party primary elections and the second party contest (the first being the Iowa caucuses) held in the United States every four years as part of the process of choos ...
, and then won the Florida and Illinois primaries by comfortable margins. During the first six contests, Reagan followed the "eleventh commandment" he used during his initial campaign for governor of California: "Thou shalt not speak ill of any fellow Republican." By the North Carolina primary, Reagan's campaign was nearly out of money, and it was widely believed that another defeat would force him to quit the race. But with the help of U.S. Senator Jesse Helms
Jesse Alexander Helms Jr. (October 18, 1921 – July 4, 2008) was an American politician. A leader in the conservative movement, he served as a senator from North Carolina from 1973 to 2003. As chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committe ...
's powerful political organization, Reagan upset Ford. Reagan had abandoned the approach of invoking the commandment and beat Ford 52% to 46%, regaining momentum.
Reagan then had a string of impressive victories, including Texas, where he won all delegates at stake in its first binding primary. Four other delegates chosen at the Texas state convention went to Reagan and the state shut out its U.S. senator, John G. Tower
John Goodwin Tower (September 29, 1925 – April 5, 1991) was an American politician, serving as a Republican United States Senator from Texas from 1961 to 1985. He was the first Republican Senator elected from Texas since Reconstruction. Towe ...
, who had been named to manage the Ford campaign on the convention floor. Ford bounced back to win his home state of Michigan, and from there, the two candidates engaged in an increasingly bitter nip-and-tuck contest for delegates. By the time the party's convention opened in August 1976, the race was still too close to call.
Reagan was the first candidate to win a presidential primary against an incumbent actively running for reelection since Estes Kefauver
Carey Estes Kefauver (;
July 26, 1903 – August 10, 1963) was an American politician from Tennessee. A member of the Democratic Party, he served in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1939 to 1949 and in the Senate from 1949 until his ...
defeated Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
in the 1952 New Hampshire primary. Former Texas governor John Connally
John Bowden Connally Jr. (February 27, 1917June 15, 1993) was an American politician. He served as the 39th governor of Texas and as the 61st United States secretary of the Treasury. He began his career as a Democrat and later became a Republic ...
speculated that Reagan's attacks weakened Ford in the general election against his opponent and eventual successor, Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 76th governor of Georgia from 1 ...
.
Schedule and results
Candidates
This was the last time during the 20th century (and the last time to date) that a primary season had ended without a presumptive nominee.Candidates who declined to run
*Senator Howard Baker ofTennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
*Senator Edward Brooke
Edward William Brooke III (October 26, 1919 – January 3, 2015) was an American politician of the Republican Party, who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1967 until 1979. Prior to serving in the Senate, he served as th ...
of Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
*Senator James L. Buckley of New York
*Representative John Conlan of Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
*Former Secretary of the Treasury
The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal a ...
John Connally
John Bowden Connally Jr. (February 27, 1917June 15, 1993) was an American politician. He served as the 39th governor of Texas and as the 61st United States secretary of the Treasury. He began his career as a Democrat and later became a Republic ...
of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
*Senator Charles Mathias
Charles McCurdy Mathias Jr. (July 24, 1922 – January 25, 2010) was an American politician and attorney. A Republican, he served as a member of the United States Senate, representing Maryland from 1969 to 1987. He was also a member of ...
of Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
*Senator Charles Percy of Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
*Ambassador Elliot Richardson
Elliot Lee Richardson (July 20, 1920December 31, 1999) was an American lawyer and public servant who was a member of the cabinet of Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford. As U.S. Attorney General, he was a prominent figure in the Watergat ...
of Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
*Vice President Nelson Rockefeller
Nelson Aldrich Rockefeller (July 8, 1908 – January 26, 1979), sometimes referred to by his nickname Rocky, was an American businessman and politician who served as the 41st vice president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. A member of t ...
of New York
* Former Vice President Spiro Agnew
Spiro Theodore Agnew (November 9, 1918 – September 17, 1996) was the 39th vice president of the United States, serving from 1969 until his resignation in 1973. He is the second vice president to resign the position, the other being John ...
of Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
Polling
National polling
Before August 1974
August 1974–December 1975
Head-to-head polling
Convention
The1976 Republican National Convention
The 1976 Republican National Convention was a United States political convention of the Republican Party that met from August 16 to August 19, 1976, to select the party's nominee for President. Held in Kemper Arena in Kansas City, Missouri, the ...
was held in Kansas City. As the convention began, Ford was seen as having a slight lead in delegate votes, but fewer than the 1,130 he needed to win. Reagan and Ford competed for the votes of individual delegates and state delegations. In a bid to woo moderate Northern Republicans, Reagan shocked the convention by announcing that if he won the nomination, Senator Richard Schweiker
Richard Schultz Schweiker (June 1, 1926 – July 31, 2015) was an American businessman and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he served as the 14th U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services under President Ronald Reagan from 198 ...
of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, from the northern liberal wing of the party, would be his running mate. The move backfired, however, as few moderates switched to Reagan while many conservative delegates were outraged. The key state of Mississippi, which Reagan needed, narrowly voted for Ford; it was believed that Reagan's choice of Schweiker led Clarke Reed, Mississippi's chairman, to switch to Ford. Ford then narrowly won the nomination on the first ballot. He chose Senator Robert Dole of Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
as his running mate. After giving his acceptance speech, Ford asked Reagan to say a few words to the convention.
Results
 Convention tally:
Convention tally:/ref> *
President Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected ...
1187
*Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
1070
* Elliot L. Richardson 1
Vice-presidential nomination
Ford chose Senator Robert J. Dole ofKansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
as his running mate, while Reagan chose Pennsylvania Senator Richard Schweiker
Richard Schultz Schweiker (June 1, 1926 – July 31, 2015) was an American businessman and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he served as the 14th U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services under President Ronald Reagan from 198 ...
.
See also
*1976 Democratic Party presidential primaries
From January 27 to June 8, 1976, voters of the Democratic Party chose its nominee for president in the 1976 United States presidential election. Former Georgia governor Jimmy Carter was selected as the nominee through a series of primary electio ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Republican Party (United States) presidential primaries, 1976