Republic of Ragusa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta
it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo
"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world" , population_estimate = 90 000 in the
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Montenegro , footnotes = A Romance language similar to both Italian and Romanian.
While present in the region even before the establishment of the Republic, Croatian, also referred to as ''Slavic'' or ''Illyrian'' at the time, had not become widely spoken until late 15th century.
 The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian, German and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian, German and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost
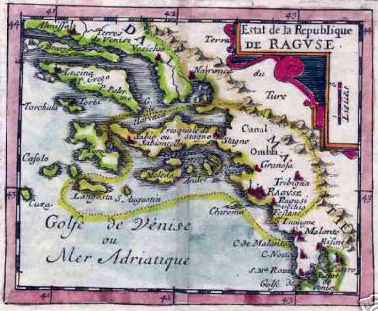
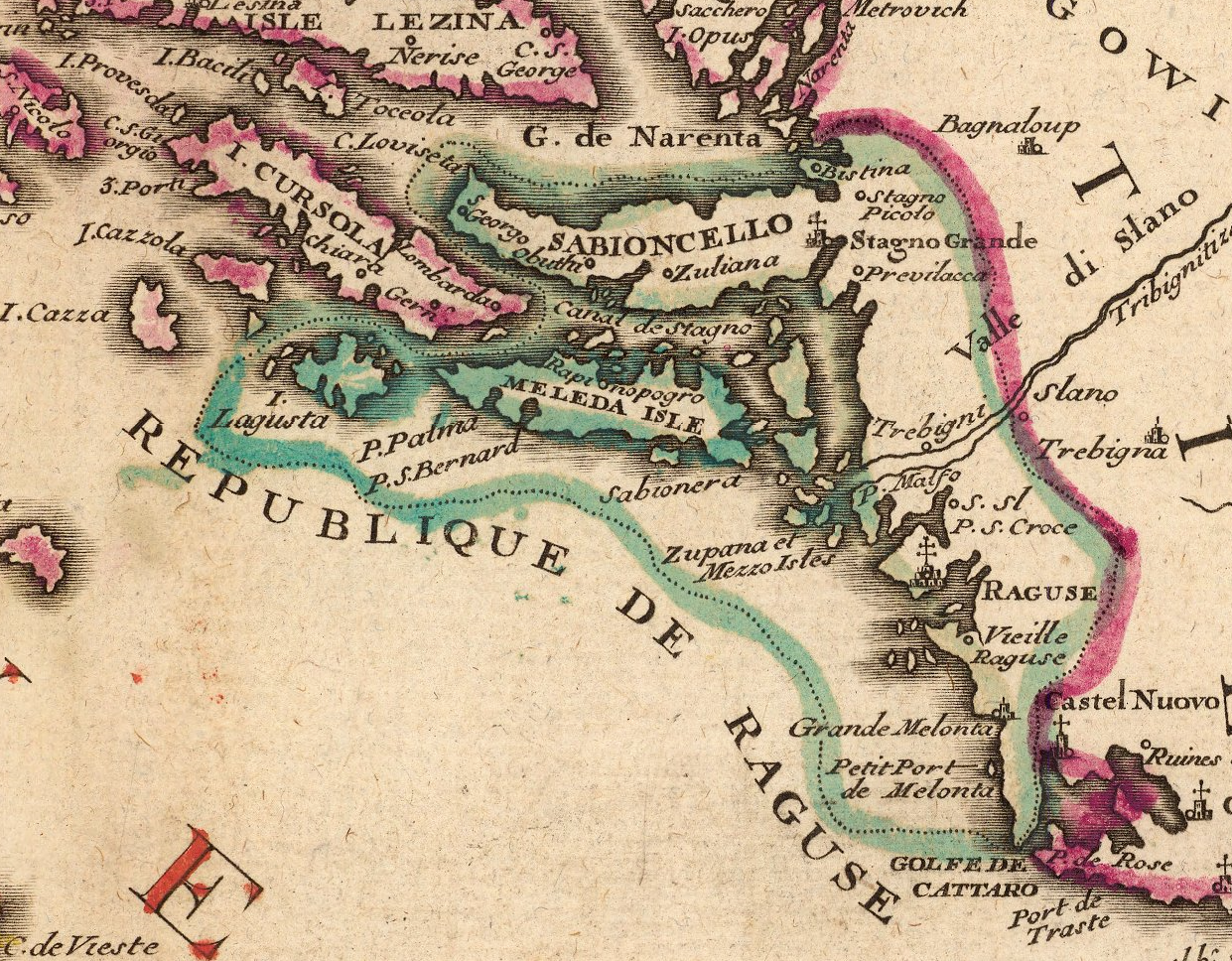 The Republic ruled a compact area of southern Dalmatia – its final borders were formed by 1426 – comprising the mainland coast from
The Republic ruled a compact area of southern Dalmatia – its final borders were formed by 1426 – comprising the mainland coast from
 The fate of Ragusa was linked to that of the Ottoman Empire. Ragusa and Venice lent technical assistance to the Ottoman– Mameluke– Zamorin alliance that was defeated by the Portuguese in the Battle of Diu in the Indian Ocean (1509).
There is some evidence of Ragusan trade with India in the 16th century.
On 6 April 1667, a devastating earthquake struck and killed around 2,000 citizens, and up to 1,000 in the rest of the republic, including many patricians and the
The fate of Ragusa was linked to that of the Ottoman Empire. Ragusa and Venice lent technical assistance to the Ottoman– Mameluke– Zamorin alliance that was defeated by the Portuguese in the Battle of Diu in the Indian Ocean (1509).
There is some evidence of Ragusan trade with India in the 16th century.
On 6 April 1667, a devastating earthquake struck and killed around 2,000 citizens, and up to 1,000 in the rest of the republic, including many patricians and the  In 1683 the Ottomans were defeated in the Battle of Kahlenberg outside Vienna. The Field marshal of the Austrian army was Ragusan Frano Đivo Gundulić. In 1684, the emissaries renewed an agreement contracted in
In 1683 the Ottomans were defeated in the Battle of Kahlenberg outside Vienna. The Field marshal of the Austrian army was Ragusan Frano Đivo Gundulić. In 1684, the emissaries renewed an agreement contracted in 
 In 1783, the Ragusan Council did not answer the proposition put forward by their diplomatic representative in Paris, Frano Favi, that they should establish diplomatic relations with America, although the Americans agreed to allow Ragusan ships free passage in their ports.
The first years of the French war were prosperous for Ragusa. The flag of Saint Blaise being neutral, the Republic became one of the chief carriers of the Mediterranean. The Continental blockade was the life of Ragusa; and before the rise of Lissa the manufactures of England, excluded from the ports of France, Italy, Holland, and Germany, found their way to the centre of Europe through Saloniki and Ragusa.
In 1783, the Ragusan Council did not answer the proposition put forward by their diplomatic representative in Paris, Frano Favi, that they should establish diplomatic relations with America, although the Americans agreed to allow Ragusan ships free passage in their ports.
The first years of the French war were prosperous for Ragusa. The flag of Saint Blaise being neutral, the Republic became one of the chief carriers of the Mediterranean. The Continental blockade was the life of Ragusa; and before the rise of Lissa the manufactures of England, excluded from the ports of France, Italy, Holland, and Germany, found their way to the centre of Europe through Saloniki and Ragusa.
 Around the year 1800, the Republic had a highly organized network of consulates and consular offices in more than eighty cities and ports around the world. In 1808, Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont, Marshal Marmont issued a proclamation abolishing the Republic of Ragusa and amalgamating its territory into the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy, himself claiming the newly created title of "Duke of Ragusa" (''Duc de Raguse''). In 1810, Ragusa, together with Dalmatia and Istria, went to the newly created French Illyrian Provinces. Later, in the 1814 Battle of Paris (1814), Battle of Paris, Marmont abandoned Napoleon and was branded a traitor. Since he was known as the "Duke of Ragusa", the word ''ragusade'' was coined in French to signify treason and ''raguser'' meant a cheat.
Article "44" of the ''1811 Decree'' abolished the centuries-old institution of ''fideicommissum'' in inheritance law, by which the French enabled younger noblemen to participate in that part of the family inheritance, which the former law had deprived them of. According to an 1813 inventory of the Ragusan district, 451 land proprietors were registered, including ecclesiastical institutions and the commune. Although there is no evidence of the size of their estates, the nobles, undoubtedly, were in possession of most of the land. Eleven members of the Sorgo family, eight of Gozze, six of Ghetaldi, six of Pozza, four of Zamagna and three of the Saraca family were among the greatest landowners. The citizens belonging to the confraternities of Anthony the Great, St. Anthony and Lazarus of Bethany, St. Lazarus owned considerable land outside the City.
After seven years of French occupation, encouraged by the desertion of French soldiers after the failed French Invasion of Russia, invasion of Russia and the reentry of Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition, war, all the social classes of the Ragusan people rose up in a general insurrection, led by the patricians, against the Napoleonic invaders. On 18 June 1813, together with British forces they forced the surrender of the French garrison of the island of Šipan, soon also the heavily fortified town of
Around the year 1800, the Republic had a highly organized network of consulates and consular offices in more than eighty cities and ports around the world. In 1808, Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont, Marshal Marmont issued a proclamation abolishing the Republic of Ragusa and amalgamating its territory into the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy, himself claiming the newly created title of "Duke of Ragusa" (''Duc de Raguse''). In 1810, Ragusa, together with Dalmatia and Istria, went to the newly created French Illyrian Provinces. Later, in the 1814 Battle of Paris (1814), Battle of Paris, Marmont abandoned Napoleon and was branded a traitor. Since he was known as the "Duke of Ragusa", the word ''ragusade'' was coined in French to signify treason and ''raguser'' meant a cheat.
Article "44" of the ''1811 Decree'' abolished the centuries-old institution of ''fideicommissum'' in inheritance law, by which the French enabled younger noblemen to participate in that part of the family inheritance, which the former law had deprived them of. According to an 1813 inventory of the Ragusan district, 451 land proprietors were registered, including ecclesiastical institutions and the commune. Although there is no evidence of the size of their estates, the nobles, undoubtedly, were in possession of most of the land. Eleven members of the Sorgo family, eight of Gozze, six of Ghetaldi, six of Pozza, four of Zamagna and three of the Saraca family were among the greatest landowners. The citizens belonging to the confraternities of Anthony the Great, St. Anthony and Lazarus of Bethany, St. Lazarus owned considerable land outside the City.
After seven years of French occupation, encouraged by the desertion of French soldiers after the failed French Invasion of Russia, invasion of Russia and the reentry of Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition, war, all the social classes of the Ragusan people rose up in a general insurrection, led by the patricians, against the Napoleonic invaders. On 18 June 1813, together with British forces they forced the surrender of the French garrison of the island of Šipan, soon also the heavily fortified town of 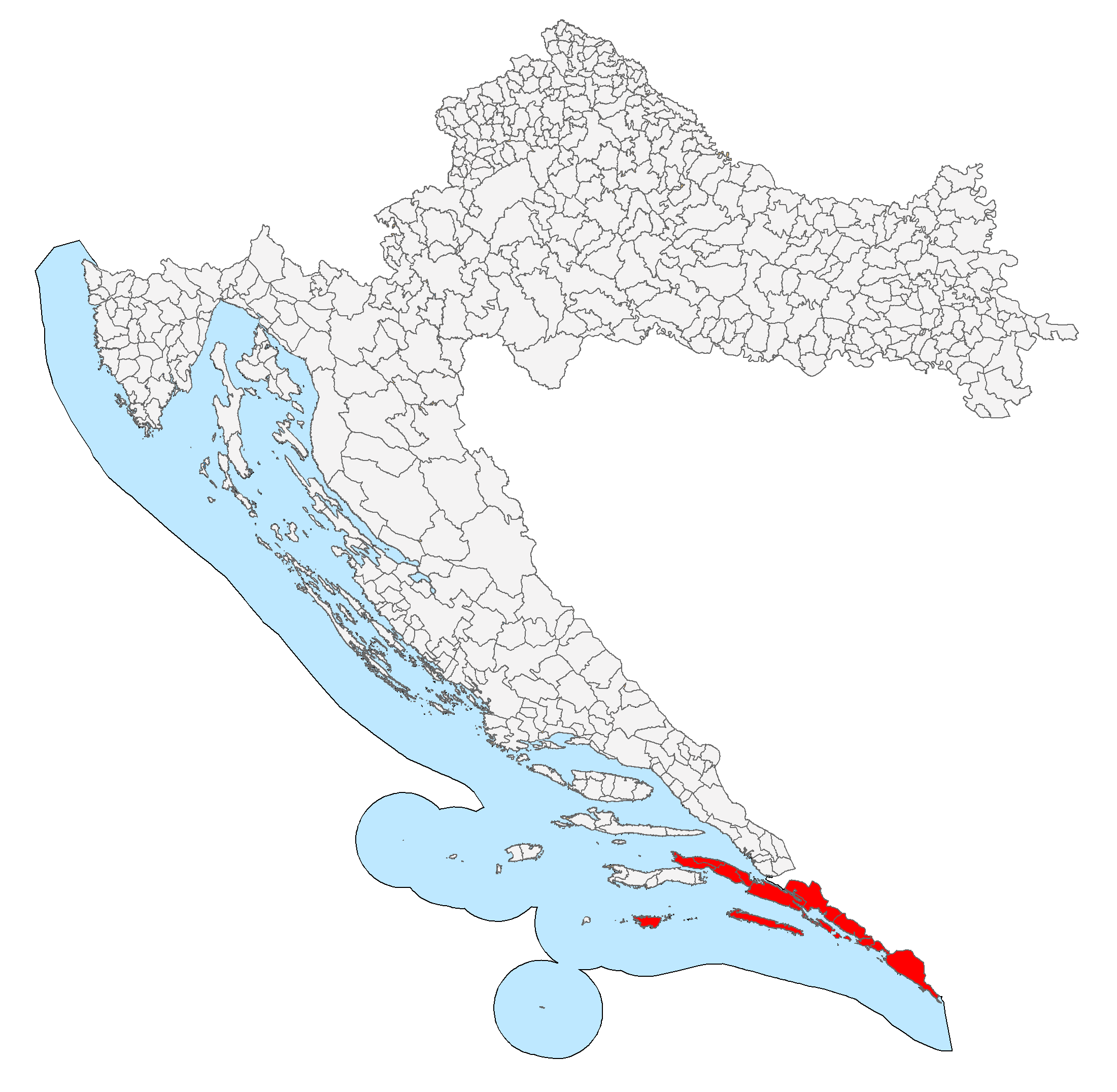
 The Republican Constitution of Ragusa was strictly Aristocracy (government), aristocratic. The population was divided into three classes: nobility, citizens, and plebeians, who were mainly artisans and Farmer, farmers (serfs, colonus (person), coloni and Freedman, freemen). All effective power was concentrated in the hands of the aristocracy. The citizens were permitted to hold only minor offices, while plebeians had no voice in government. Marriage between members of different classes of the society was forbidden.
The organization of the government was based on the Republic of Venice#Government, Venetian model: the administrative bodies were the Major Council (''Consilium maius'', ''Maggior Consiglio'', ''Velje vijeće''), the Minor Council (''Consilium minus'', ''Minor Consiglio'', ''Malo vijeće'') (from 1238) and the Senate (''Consilium rogatorum'', ''Consiglio dei Pregadi'', ''Vijeće umoljenih'') from 1253. The head of the state was the
The Republican Constitution of Ragusa was strictly Aristocracy (government), aristocratic. The population was divided into three classes: nobility, citizens, and plebeians, who were mainly artisans and Farmer, farmers (serfs, colonus (person), coloni and Freedman, freemen). All effective power was concentrated in the hands of the aristocracy. The citizens were permitted to hold only minor offices, while plebeians had no voice in government. Marriage between members of different classes of the society was forbidden.
The organization of the government was based on the Republic of Venice#Government, Venetian model: the administrative bodies were the Major Council (''Consilium maius'', ''Maggior Consiglio'', ''Velje vijeće''), the Minor Council (''Consilium minus'', ''Minor Consiglio'', ''Malo vijeće'') (from 1238) and the Senate (''Consilium rogatorum'', ''Consiglio dei Pregadi'', ''Vijeće umoljenih'') from 1253. The head of the state was the
 The nobility survived even when the classes were divided by internal disputes. When Marmont arrived in Dubrovnik in 1808, the nobility was divided into two blocks, the "Salamankezi" (''Salamanquinos'') and the "Sorbonezi" (''Sorboneses''). These names alluded to a certain controversy arisen from the wars between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and King Francis I of France, which happened some 250 years previously. After the 1667 earthquake killed many nobles, some plebeians were introduced into the noble class. The "salamanquinos", those in favor of Spanish Absolutism (European history), absolutism, did not treat these new nobles like equals; but the inclined "sorboneses", who sided with the French and to a certain liberalism, accepted them. Both sides retained their status and were seated together in the Council, but they did not maintain social relations and did not even greet each other in the streets; an inconvenient marriage between members of both groups was as striking as if it occurred between members of different classes. This social split was also reflected in the plebeians, who were divided into the rival brotherhoods of Saint Antony and Saint Lazarus, which were as unfriendly in their relations as the "salamanquinos" and "sorboneses".
The nobility survived even when the classes were divided by internal disputes. When Marmont arrived in Dubrovnik in 1808, the nobility was divided into two blocks, the "Salamankezi" (''Salamanquinos'') and the "Sorbonezi" (''Sorboneses''). These names alluded to a certain controversy arisen from the wars between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and King Francis I of France, which happened some 250 years previously. After the 1667 earthquake killed many nobles, some plebeians were introduced into the noble class. The "salamanquinos", those in favor of Spanish Absolutism (European history), absolutism, did not treat these new nobles like equals; but the inclined "sorboneses", who sided with the French and to a certain liberalism, accepted them. Both sides retained their status and were seated together in the Council, but they did not maintain social relations and did not even greet each other in the streets; an inconvenient marriage between members of both groups was as striking as if it occurred between members of different classes. This social split was also reflected in the plebeians, who were divided into the rival brotherhoods of Saint Antony and Saint Lazarus, which were as unfriendly in their relations as the "salamanquinos" and "sorboneses".
 Ragusan literature, in which Latin, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian coexisted, blossomed in the 15th and 16th centuries. According to Marcus Tanner:
Literary works of famous Ragusans were written in both Serbo-Croatian and Italian. Among them are the works of writers Džore Držić (Giorgio Darsa), Marin Držić (Marino Darsa), Ivan Bunić Vučić (Giovanni Serafino Bona), Ignjat Đurđević (Ignazio Giorgi), Ivan Gundulić (Giovanni Gondola), Šiško Menčetić, Šišmundo (Šiško) Menčetić (Sigismondo Menze), and Dinko Ranjina (Domenico Ragnina).
The literature of Dubrovnik had a defining role in the development of modern Croatian, Dubrovnik Shtokavian dialect having been the basis for standardized Croatian. Writers from the 16th to the 19th century (before the Age of Romantic National Awakenings) that were explicit in declaring themselves as Croats and their language as Croatian included Vladislav Menčetić, Dominko Zlatarić, Dominko (Dinko) Zlatarić, Bernardin Pavlović, Mavro Vetranović, Nikola Nalješković, Junije Palmotić, Jakov Mikalja, Joakim Stulli, Marc Bruère Desrivaux, Marko Bruerović, Peter Ignaz Sorgo, Antun Sorkočević (1749–1826), and Franatica Sorkočević (1706–71).
There also were Ragusan authors of Morlachism, a primarily Italian and Venetian literary movement.
Ragusan literature, in which Latin, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian coexisted, blossomed in the 15th and 16th centuries. According to Marcus Tanner:
Literary works of famous Ragusans were written in both Serbo-Croatian and Italian. Among them are the works of writers Džore Držić (Giorgio Darsa), Marin Držić (Marino Darsa), Ivan Bunić Vučić (Giovanni Serafino Bona), Ignjat Đurđević (Ignazio Giorgi), Ivan Gundulić (Giovanni Gondola), Šiško Menčetić, Šišmundo (Šiško) Menčetić (Sigismondo Menze), and Dinko Ranjina (Domenico Ragnina).
The literature of Dubrovnik had a defining role in the development of modern Croatian, Dubrovnik Shtokavian dialect having been the basis for standardized Croatian. Writers from the 16th to the 19th century (before the Age of Romantic National Awakenings) that were explicit in declaring themselves as Croats and their language as Croatian included Vladislav Menčetić, Dominko Zlatarić, Dominko (Dinko) Zlatarić, Bernardin Pavlović, Mavro Vetranović, Nikola Nalješković, Junije Palmotić, Jakov Mikalja, Joakim Stulli, Marc Bruère Desrivaux, Marko Bruerović, Peter Ignaz Sorgo, Antun Sorkočević (1749–1826), and Franatica Sorkočević (1706–71).
There also were Ragusan authors of Morlachism, a primarily Italian and Venetian literary movement.
The Population of the Dubrovnik Republic in the Fifteenth, Sixteenth, and Seventeenth Centuries
" ''Dubrovnik Annals'' 1998, Vol. 2, pp 7–28 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Historical facts about Dubrovnik
from Dubrovnik Online
''Dalmatia and Montenegro''
by John Gardner Wilkinson, on Google Books
''Aus Dalmatien''
by Ida Reinsberg-Düringsfeld (1857), on Google Books
''Universal Geography: Republic of Ragusa''
on Google Books
''Bibliografia della Dalmazia e del Montenegro''
by Giuseppe Valentinelli, on Google Books
''Bibliografia hrvatska''
Ivan Kukuljević Sakcinski, on Google Books
''Geschichte des Freystaates Ragusa''
by Johann Christian von Engel, on Google Books
''The Ethnology of Europe''
by Robert Gordon Latham, on Google Books
''Austria in 1848–49: Dalmatia''
by William Henry Stiles, on Google Books
Ragusa, the American Revolution, and Diplomatic Relations, 1763–1783
*[https://archive.org/details/notizieistorico00appegoog/page/n552 Notizie Istorico-Critiche Sulle Antichita Storia de Letteratura dei Ragusei] by Francesco Maria Appendini. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ragusa, Republic Republic of Ragusa, Dubrovnik Maritime republics Former Slavic countries Former republics, Ragusa 1358 establishments in Europe 1807 disestablishments in Europe Tributary states of the Ottoman Empire
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta
it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo
"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world" , population_estimate = 90 000 in the
XVI Century
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582).
The 16th cent ...
, currency = Ragusa perpera and others
, common_languages =
, title_leader = Rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
as Head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
, leader1 = Nikša Sorgo
, year_leader1 = 1358
, leader2 = Sabo Giorgi
, year_leader2 = 1807-1808
, today = Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Montenegro , footnotes = A Romance language similar to both Italian and Romanian.
While present in the region even before the establishment of the Republic, Croatian, also referred to as ''Slavic'' or ''Illyrian'' at the time, had not become widely spoken until late 15th century.

 The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian, German and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian, German and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's French Empire and formally annexed by the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was ''""'', a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
phrase which means "Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world".
Names
Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed by Venice rather than by Ragusa's own Major Council. In Italian it is called '; in Croatian it is called ' (). The Slavic name ''Dubrovnik'' is derived from the word ', an oak grove; by a folk etymology. The name ''Dubrovnik'' of the Adriatic city is first recorded in theCharter of Ban Kulin
The Charter of Ban Kulin ( Bosnian-Serbian-Croatian: Povelja Kulina bana / Повеља Кулина бана) was a trade agreement between the Banate of Bosnia and the Republic of Ragusa that effectively regulated Ragusan trade rights in Bosnia, ...
(1189). It came into use alongside ''Ragusa'' as early as the 14th century.
The Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, Italian and Dalmatian name ' maybe derives its name from ' (from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: ', "precipice"); it was later altered to ', ', ' or ' (even ', ', ' and ') and finally into '. Another theory is that the term "Ragusa" delivers from Proto-Albanian
The Proto-Albanian language is the unattested language from which Albanian later developed. Albanian evolved from an ancient Paleo-Balkan language, traditionally thought to be Illyrian, or otherwise a totally unattested Balkan Indo-European ...
''*rāguša'' meaning "berry" (compare Modern-Albanian ''rrush'' (meaning "grape")). The official change of name from Ragusa to Dubrovnik came into effect after World War I.
It is known in historiography as the ''Republic of Ragusa''.
Territory
 The Republic ruled a compact area of southern Dalmatia – its final borders were formed by 1426 – comprising the mainland coast from
The Republic ruled a compact area of southern Dalmatia – its final borders were formed by 1426 – comprising the mainland coast from Neum
Neum ( cyrl, Неум, ) is a town and municipality in Bosnia and Herzegovina, located in Herzegovina-Neretva Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the only town to be situated along the Bosnia and Herzegovina's coastline, m ...
to the Prevlaka
Prevlaka () is a small peninsula in southern Croatia, near the border with Montenegro, at the entrance to the Bay of Kotor on the eastern Adriatic coast.
Because of its strategic location in the southern Adriatic, in the aftermath of the SFR Yu ...
peninsula as well as the Pelješac peninsula and the islands of Lastovo and Mljet
Mljet (; la, Melita, it, Meleda) is the southernmost and easternmost of the larger Adriatic islands of the Dalmatia region of Croatia. The National Park includes the western part of the island, Veliko jezero, Malo jezero, Soline Bay and a sea be ...
, as well as a number of smaller islands such as Koločep, Lopud
Lopud () is a small island off the coast of Dalmatia, southern Croatia. Lopud is economically the most developed of the Elaphiti Islands, and can be reached by boat from Dubrovnik, Trsteno, Orašac and Zaton. The island is famous for its sandy ...
, and Šipan.
In the 15th century the Ragusan republic also acquired the islands of Korčula
Korčula (, it, Curzola) is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea. It has an area of , is long and on average wide, and lies just off the Dalmatian coast. Its 15,522 inhabitants (2011) make it the second most populous Adriatic island after ...
, Brač
Brač is an island in the Adriatic Sea within Croatia, with an area of ,
making it the largest island in Dalmatia, and the third largest in the Adriatic. It is separated from the mainland by the Brač Channel, which is wide. The island's tall ...
and Hvar
Hvar (; Chakavian: ''Hvor'' or ''For'', el, Φάρος, Pharos, la, Pharia, it, Lesina) is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea, located off the Dalmatian coast, lying between the islands of Brač, Vis and Korčula. Approximately long,
wi ...
for about eight years. However they had to be given up due to the resistance of local minor aristocrats sympathizing with Venice, which was granting them some privileges.
In the 16th century the administrative units of the Republic were: the City of Ragusa (Dubrovnik), counties (Konavle
Konavle () is a municipality and a small region located southeast of Dubrovnik, Croatia.
It is administratively part of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County and the center of the municipality is Cavtat.
Demographics
The total municipality population wa ...
, Župa dubrovačka
A župa (or zhupa, županija) is a historical type of administrative division in Southeast Europe and Central Europe, that originated in medieval South Slavic culture, commonly translated as "parish", later synonymous "kotar", commonly transla ...
– Breno, Slano – Ragusan Littoral, Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ant ...
, Island of Lastovo, Island of Mljet, Islands of Šipan, Lopud and Koločep) and captaincies ( Cavtat, Orebić, Janjina) with local magistrates appointed by the Major Council. Lastovo and Mljet were semi-autonomous communities each having its own Statute.
Historical background
Origin of the city
According to the '' De Administrando Imperio'' of the Byzantine emperorConstantine VII Porphyrogennetos
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe K ...
, the city was founded, probably in the 7th century, by the inhabitants of the Roman city of Epidaurum Epidaurus ( el, Ἐπίδαυρος, la, Epidaurum) or Epidauros was an ancient Greek colony founded sometime in the 6th century BC, renamed to Epidaurum during Roman rule in 228 BC, when it was part of the province of Illyricum, later Dalmatia.W ...
(modern Cavtat) after its destruction by the Avars and Slavs c. 615. Some of the survivors moved north to a small island near the coast where they founded a new settlement, Lausa. It has been claimed that a second raid by the Slavs in 656 resulted in the total destruction of Epidaurum.Andrew Archibald Paton (1861). ''Researches on the Danube and the Adriatic; Or Contributions to the Modern History of Hungary and Transylvania, Dalmatia and Croatia, Servia and Bulgaria'', Brockhaus Slavs settled along the coast in the 7th century. The Slavs named their settlement ''Dubrovnik''. The Romans ("Latin") and Slavs had an antagonistic relationship, though by the 12th century the two settlements had merged. The channel that divided the city was filled, creating the present-day main street (the '' Stradun'') which became the city centre. Thus, ''Dubrovnik'' became the Slavic name for the united town. Peter F. Sugar (1983). ''Southeastern Europe Under Ottoman Rule, 1354–1804'', University of Washington Press, . There are recent theories based on excavations that the city was established much earlier, at least in the 5th century and possibly during the Ancient Greek period (as per Antun Ničetić, in his book ''Povijest dubrovačke luke''). The key element in this theory is the fact that ships in ancient time traveled about 45 to 50 nautical miles per day, and mariners required a sandy shore to pull their ships out of the water for the rest period during the night. An ideal combination would have a fresh water source in the vicinity. Dubrovnik had both, being halfway between the Greek settlements of Budva and Korčula
Korčula (, it, Curzola) is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea. It has an area of , is long and on average wide, and lies just off the Dalmatian coast. Its 15,522 inhabitants (2011) make it the second most populous Adriatic island after ...
, which are apart.
Early centuries
During its first centuries the city was under the rule of the Byzantine Empire. The Saracens laid siege to the city in 866–867; it lasted for fifteen months and was raised due to the intervention of Byzantine Emperor who sent a fleet under Niketas Ooryphas in relief. Ooryphas' "showing of the flag" had swift results, as the Slavic tribes sent envoys to the Emperor, once more acknowledging his suzerainty. Basil dispatched officials, agents and missionaries to the region, restoring Byzantine rule over the coastal cities and regions in the form of the new theme of Dalmatia, while leaving the Slavic tribal principalities of the hinterland largely autonomous under their own rulers. The christianization of the Croats and the other Slavic tribes also began at this time. With the weakening of Byzantium,Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
began to see Ragusa as a rival that needed to be brought under its control, but an attempt to conquer the city in 948 failed. The citizens of the city attributed this to Saint Blaise, whom they adopted as their patron saint.
The city remained under Byzantine domination until 1204, with the exception of periods of Venetian (1000–1030) and later Norman (1081–1085, 1172, 1189–1190) rule. In 1050, Croatian king Stjepan I (Stephen) made a land grant along the coast that extended the boundaries of Ragusa to Zaton, north of the original city, giving the republic control of the abundant supply of fresh water that emerges from a spring at the head of the Ombla inlet. Stephen's grant also included the harbour of Gruž
Gruž ( it, Gravosa - ''Santa Croce'') is a neighborhood in Dubrovnik, Croatia, about 2 km northwest of the Old City. It has a population of approximately 15,000 people. The main port for Dubrovnik is in Gruž as well as its largest market and ...
, which is now the commercial port for Dubrovnik.
Thus the original territory of the Ragusan municipality or community comprised the city of Ragusa, Župa dubrovačka, Gruž
Gruž ( it, Gravosa - ''Santa Croce'') is a neighborhood in Dubrovnik, Croatia, about 2 km northwest of the Old City. It has a population of approximately 15,000 people. The main port for Dubrovnik is in Gruž as well as its largest market and ...
, Ombla, Zaton, the Elafiti islands (Šipan, Lopud and Koločep) and some smaller islands near the city.
The famous 12th century Arab geographer Muhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abdullah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani as-Sabti, or simply al-Idrisi ( ar, أبو عبد الله محمد الإدريسي القرطبي الحسني السبتي; la, Dreses; 1100 – 1165), was a Muslim geographer, cartogra ...
mentioned Ragusa and the surrounding area. In his work, he referred to Ragusa as the southernmost city of Croatia.
In 1191, Emperor Isaac II Angelos
Isaac II Angelos or Angelus ( grc-gre, Ἰσαάκιος Κομνηνός Ἄγγελος, ; September 1156 – January 1204) was Byzantine Emperor from 1185 to 1195, and again from 1203 to 1204.
His father Andronikos Doukas Angelos was a ...
granted the city's merchants the right to trade freely in Byzantium. Similar privileges were obtained several years earlier from Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
(1186) and from Bosnia (1189). The Charter of Ban Kulin
The Charter of Ban Kulin ( Bosnian-Serbian-Croatian: Povelja Kulina bana / Повеља Кулина бана) was a trade agreement between the Banate of Bosnia and the Republic of Ragusa that effectively regulated Ragusan trade rights in Bosnia, ...
of Bosnia is also the first official document where the city is referred to as ''Dubrovnik''.
Venetian suzerainty (1205–1358)
In 1202, the Venetian Republic invaded Dalmatia with the forces of the Fourth Crusade, and Ragusa was forced to pay tribute. Ragusa began supplying Venice with products such as hides, wax, silver, and other metals. Venice used the city as its naval base in the southernAdriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
. Unlike with Zadar, there was not much friction between Ragusa and Venice as the city had not yet begun to compete as an alternative carrier in the trade between East and West; in addition, the city retained most of its independence. The people, however, resented the ever-growing tribute. Frederic Chapin Lane (1973). ''Venice, a Maritime Republic'', Johns Hopkins University Press,
In the middle of the 13th century the island of Lastovo was added to the original territory. On 22 January 1325, Serbian king Stefan Uroš III issued a document for the sale of his maritime possessions of the city of Ston and peninsula of Pelješac to Ragusa. In 1333, during the rule of Serbian king Stefan Dušan
Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан, ), known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr, / ; circa 1308 – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Tsar (or Emperor) and autocrat of the Serbs, Gre ...
(Stefan Uroš IV, r. 1331–1355), the two possessions were handed over to Ragusa. In January 1348, the Black Death struck the city and decimated the urban population.
History
Independence from Venice (1358)
In 1358, the Treaty of Zadar forced Venice to yield all claims to Dalmatia. The city accepted the mild hegemony of King Louis I of Hungary. On 27 May 1358, the final agreement was reached atVisegrád
Visegrád (; german: Plintenburg; la, Pone Navata or ; sk, Vyšehrad) is a castle town in Pest County, Hungary. It is north of Budapest on the right bank of the Danube in the Danube Bend. It had a population of 1,864 in 2010. The town is the ...
between Louis and the Archbishop Ivan Saraka. The city recognized Hungarian sovereignty, but the local nobility continued to rule with little interference from the Hungarian court at Buda. The Republic profited from the suzerainty of Louis of Hungary, whose kingdom was not a naval power, and with whom they would have little conflict of interest. The last Venetian conte left, apparently in a hurry. Although under the Visegrád agreement Dubrovnik was formally under the jurisdiction of the ban of Croatia
Ban of Croatia ( hr, Hrvatski ban) was the title of local rulers or office holders and after 1102, viceroys of Croatia. From the earliest periods of the Croatian state, some provinces were ruled by bans as a ruler's representative (viceroy) an ...
, the city successfully resisted both the royal and ban authority.
In 1399, the city acquired the area between Ragusa and Pelješac, called the ''Primorje'' (Dubrovačko primorje) with Slano (lat. ''Terrae novae''). It was purchased from Bosnian King Stephen Ostoja. A brief war with Bosnia in 1403 and 1404 ended with Bosnian withdrawal. Between 1419 and 1426, the Konavle
Konavle () is a municipality and a small region located southeast of Dubrovnik, Croatia.
It is administratively part of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County and the center of the municipality is Cavtat.
Demographics
The total municipality population wa ...
region, south of Astarea (Župa dubrovačka), including the city of Cavtat, was added to the Republic's possessions.
In the first half of the 15th century Cardinal Ivan Stojković (''Johannes de Carvatia'') was active in Dubrovnik as a Church reformer and writer. Trading with the Bosnian kingdom was at a peak, and the largest caravan trade between Podvisoki
Podvisoki ( cyrl, Подвисоки) was a medieval settlement, a castle town (in ), as part of wider area just beneath of the fortress Visoki, located on the Visočica hill above modern-day Visoko, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
History
Podvisoki w ...
and Ragusa would happen in 1428. That year, on 9 August, Vlachs committed to Ragusan lord Tomo Bunić, that they would deliver 600 horses with 1500 modius of salt. Delivery was meant for Dobrašin Veseoković, and Vlachs price was half of delivered salt.
Ottoman suzerainty
In 1430 and 1442, the Republic signed short-term arrangements with theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
defining its status. In 1458, the Republic signed a treaty with the Ottomans which made it a tributary of the sultan. Under the treaty, the Republic owed the sultan "fidelity", "truthfulness", and "submission", and an annual tribute, which was in 1481 defined at 12,500 gold coins. The sultan guaranteed to protect Ragusa and granted them extensive trading privileges. Under the agreement, the republic retained its autonomous status and was virtually independent, and usually allied with the Maritime Republic of Ancona.
It could enter into relations with foreign powers and make treaties with them (as long as not conflicting with Ottoman interests), and its ships sailed under its own flag. Ottoman vassalage also conferred special trade rights that extended within the Empire. Ragusa handled the Adriatic trade on behalf of the Ottomans, and its merchants received special tax exemptions and trading benefits from the Porte. It also operated colonies that enjoyed extraterritorial rights in major Ottoman cities.
Merchants from Ragusa could enter the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, which was otherwise closed to non-Ottoman shipping. They paid less in customs duties than other foreign merchants, and the city-state enjoyed diplomatic support from the Ottoman administration in trade disputes with the Venetians. Suraiya Faroqhi, Bruce McGowan, Donald Quataert Donald George Quataert (September 10, 1941 – February 10, 2011) was a historian at Binghamton University. He taught courses on Middle East/Ottoman history, with an interest in labor, social and economics, during the early and modern periods. H ...
, Sevket Pamuk (1997). ''An Economic and Social History of the Ottoman Empire'', Vol. 2, Cambridge University Press,
For their part, Ottomans regarded Ragusa as a port of major importance, since most of the traffic between Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany Regions of Italy, region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilan ...
and Bursa (an Ottoman port in northwestern Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
) was carried out via Ragusa. Florentine cargoes would leave the Italian ports of Pesaro, Fano or Ancona to reach Ragusa. From that point on they would take the land route Bosnasaray (Sarajevo)– Novibazar– Skopje– Plovdiv–Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis ( Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders ...
.
When, in the late 16th century, Ragusa placed its merchant marine at the disposal of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
on condition that its participation in the Spanish military ventures would not affect the interest of the Ottoman Empire; the latter tolerated the situation as the trade of Ragusa permitted the importation of goods from states with which the Ottoman Empire was at war.
Along with England, Spain and Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
, Ragusa was one of Venice's most damaging competitors in the 15th century on all seas, even in the Adriatic. Thanks to its proximity to the plentiful oak forests of Gargano, it was able to bid cargoes away from the Venetians.
Decline of the Republic
With the Portuguese explorations which opened up new ocean routes, the spice trade no longer went through theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
. Moreover, the discovery of the Americas
The prehistory of the Americas (North America, North, South America, South, and Central America, and the Caribbean) begins with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an ice age. These groups are generally believed to have ...
started a crisis of Mediterranean shipping. This was the beginning of the decline of both the Venetian and Ragusan republics.
Charles VIII of France granted trading rights to the Ragusans in 1497, and Louis XII
Louis XII (27 June 14621 January 1515), was King of France from 1498 to 1515 and King of Naples from 1501 to 1504. The son of Charles, Duke of Orléans, and Maria of Cleves, he succeeded his 2nd cousin once removed and brother in law at the tim ...
in 1502. In the first decade of the 16th century, Ragusan consuls were sent to France while their French counterparts were sent to Ragusa. Prominent Ragusans in France included Simon de Benessa, Lovro Gigants, D. de Bonda, Ivan Cvletković, captain Ivan Florio, Petar Lukarić (Petrus de Luccari), Serafin Gozze, and Luca de Sorgo. The Ragusan aristocracy was also well represented at the Sorbonne University
Sorbonne University (french: Sorbonne Université; la Sorbonne: 'the Sorbonne') is a public research university located in Paris, France. The institution's legacy reaches back to 1257 when Sorbonne College was established by Robert de Sor ...
in Paris at this time.
 The fate of Ragusa was linked to that of the Ottoman Empire. Ragusa and Venice lent technical assistance to the Ottoman– Mameluke– Zamorin alliance that was defeated by the Portuguese in the Battle of Diu in the Indian Ocean (1509).
There is some evidence of Ragusan trade with India in the 16th century.
On 6 April 1667, a devastating earthquake struck and killed around 2,000 citizens, and up to 1,000 in the rest of the republic, including many patricians and the
The fate of Ragusa was linked to that of the Ottoman Empire. Ragusa and Venice lent technical assistance to the Ottoman– Mameluke– Zamorin alliance that was defeated by the Portuguese in the Battle of Diu in the Indian Ocean (1509).
There is some evidence of Ragusan trade with India in the 16th century.
On 6 April 1667, a devastating earthquake struck and killed around 2,000 citizens, and up to 1,000 in the rest of the republic, including many patricians and the Rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
( hr, knez) Šišmundo Getaldić. The earthquake also levelled most of the city's public buildings, leaving only the outer walls intact. Buildings in the Gothic and Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
styles – palaces, churches and monasteries – were destroyed. Of the city's major public buildings, only the Sponza Palace and the front part of the Rector's Palace at Luža Square survived. Gradually the city was rebuilt in the more modest Baroque style. With great effort Ragusa recovered a bit, but still remained a shadow of the former Republic.
In 1677 Marin Caboga (1630–1692) and Nikola Bunić (ca. 1635–1678) arrived in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
in an attempt to avert an imminent threat to Ragusa: Kara-Mustafa's pretensions for the annexation of Ragusa to the Ottoman Empire. The Grand-Vizier, struck with the capacity Marin showed in the arts of persuasion, and acquainted with his resources in active life, resolved to deprive his country of so able a diplomat, and on 13 December he was imprisoned, where he was to remain for several years. In 1683, Kara-Mustafa was killed in the attacks on Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, and Marin was soon free to return to Ragusa.
 In 1683 the Ottomans were defeated in the Battle of Kahlenberg outside Vienna. The Field marshal of the Austrian army was Ragusan Frano Đivo Gundulić. In 1684, the emissaries renewed an agreement contracted in
In 1683 the Ottomans were defeated in the Battle of Kahlenberg outside Vienna. The Field marshal of the Austrian army was Ragusan Frano Đivo Gundulić. In 1684, the emissaries renewed an agreement contracted in Visegrád
Visegrád (; german: Plintenburg; la, Pone Navata or ; sk, Vyšehrad) is a castle town in Pest County, Hungary. It is north of Budapest on the right bank of the Danube in the Danube Bend. It had a population of 1,864 in 2010. The town is the ...
in the year 1358 and accepted the sovereignty of Habsburg as Hungarian Kings over Ragusa, with an annual tax of 500 ducats. At the same time Ragusa continued to recognize the sovereignty of the Ottomans, a common arrangement at the time. This opened up greater opportunities for Ragusa ships in ports all along the Dalmatian coast, in which they anchored frequently. In the Treaty of Karlowitz (1699), the Ottomans ceded all of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
, Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baran ...
, Dalmatia and Podolia to the victorious Habsburgs, Venetians, and Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
. After this, Venice captured a part of Ragusa's inland area and approached its borders. They presented the threat of completely surrounding and cutting off Ragusa's trade inland. In view of this danger and anticipating the defeat of the Ottomans in 1684 Ragusa sent emissaries to Emperor Leopold in Vienna, hoping that the Austrian Army would capture Bosnia. Fortunately for the Republic, the Ottomans retained control over their hinterland. With the 26 January 1699 peace agreement, the Republic of Ragusa ceded two patches of its coast to the Ottoman Empire so that the Republic of Venice would be unable to attack from land, only from the sea. One of them, the northwestern land border with the small town of Neum, is today the only outlet of present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina to the Adriatic Sea. The southeastern border village of Sutorina later became part of Montenegro, which has coastline to the south. After the treaty, Neum and Sutorina were attached to Sanjak of Herzegovina of Bosnia Eyalet
The Eyalet of Bosnia ( ota, ایالت بوسنه ,Eyālet-i Bōsnâ; By Gábor Ágoston, Bruce Alan Masters ; sh, Bosanski pašaluk), was an eyalet (administrative division, also known as a ''beylerbeylik'') of the Ottoman Empire, mostly based o ...
. Ragusa continued its policy of strict neutrality in the War of Austrian succession
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
(1741–48) and in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
(1756–63).

 In 1783, the Ragusan Council did not answer the proposition put forward by their diplomatic representative in Paris, Frano Favi, that they should establish diplomatic relations with America, although the Americans agreed to allow Ragusan ships free passage in their ports.
The first years of the French war were prosperous for Ragusa. The flag of Saint Blaise being neutral, the Republic became one of the chief carriers of the Mediterranean. The Continental blockade was the life of Ragusa; and before the rise of Lissa the manufactures of England, excluded from the ports of France, Italy, Holland, and Germany, found their way to the centre of Europe through Saloniki and Ragusa.
In 1783, the Ragusan Council did not answer the proposition put forward by their diplomatic representative in Paris, Frano Favi, that they should establish diplomatic relations with America, although the Americans agreed to allow Ragusan ships free passage in their ports.
The first years of the French war were prosperous for Ragusa. The flag of Saint Blaise being neutral, the Republic became one of the chief carriers of the Mediterranean. The Continental blockade was the life of Ragusa; and before the rise of Lissa the manufactures of England, excluded from the ports of France, Italy, Holland, and Germany, found their way to the centre of Europe through Saloniki and Ragusa.
French occupation
The Battle of Austerlitz and the consequent peace treaty, having compelled Austria to hand over Dalmatia to France, put Ragusa in a dilemma. The nearbyBay of Kotor
The Bay of Kotor ( Montenegrin and Serbian: , Italian: ), also known as the Boka, is a winding bay of the Adriatic Sea in southwestern Montenegro and the region of Montenegro concentrated around the bay. It is also the southernmost part of the hi ...
was a Venetian frontier against the Ottomans. But while France held the land, the United Kingdom and Russia held the sea; and while French troops marched from Austerlitz to Dalmatia, eleven Russian ships of the line entered the Bay of Kotor, and landed 6,000 men, later supported by 16,000 Montenegrins under Petar I Petrović-Njegoš
Petar I Petrović-Njegoš (Serbian Cyrillic: Петар I Петровић Његош; 1748 – 31 October 1830) was the ruler of the Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro as the Metropolitan (''vladika'') of Cetinje, and Exarch (legate) of the Serbi ...
. As 5,000 Frenchmen under General Molitor marched southwards and peacefully took control of the fortresses of Dalmatia, the Russians pressed the senators of Ragusa to allow them to occupy the city, as it was an important fortress – thus anticipating that France might block further progress to Kotor. As there was no way from Dalmatia to Kotor but through Ragusa, General Molitor was equally ardent in trying to win Ragusa's support.
The Republic was determined to maintain its strict neutrality, knowing that anything else would mean its destruction. The Senate dispatched two emissaries to Molitor to dissuade him from entering Ragusan territory. Despite his statement that he intended to respect and defend the independence of the Ragusan Republic, his words demonstrated that he had no qualms about violating the territory of a neutral nation on his way to take possession of Kotor, and he even said that he would cross the Ottoman territories of Klek and Sutorina (bordering the Republic to the north and south, respectively) without asking permission from the Ottoman Empire. To the emissaries' protestation he responded by promising to respect Ragusan neutrality and not enter its territory in exchange for a loan of 300,000 francs. It was clearly blackmail (a similar episode occurred in 1798, when a Revolutionary French fleet threatened invasion if the Republic did not pay a huge contribution). The Ragusan government instructed the emissaries to inform Molitor that the Russians told the Republic quite clearly that should any French troops enter Ragusan territory, the Russians and their Montenegrin allies would proceed to pillage and destroy every part of the Republic, and also to inform him that the Republic could neither afford to pay such an amount of money, nor could it raise such an amount from its population without the Russians being alerted, provoking an invasion. Even though the emissaries managed to persuade General Molitor not to violate Ragusan territory, Napoleon was not content with the stalemate between France and Russia concerning Ragusa and the Bay of Kotor and soon decided to order the occupation of the Republic.
Upon entering Ragusan territory and approaching the capital, the French General Jacques Lauriston
Jacques Alexandre Bernard Law, marquis de Lauriston (1 February 1768 – 12 June 1828) was a French soldier and diplomat of Scottish descent, and a general officer in the French Army during the Napoleonic Wars. He was born in Pondicherry in Fren ...
demanded that his troops be allowed to rest and be provided with food and drink in the city before continuing on to Kotor. However, this was a deception because as soon as they entered the city, they proceeded to occupy it in the name of Napoleon. The next day, Lauriston demanded an impossible contribution of a million francs.
This is what ''The Times'' in London reported about those events in its edition of 24 June 1806:
Almost immediately after the beginning of the French occupation, Russian and Montenegrin troops entered Ragusan territory and began fighting the French army, raiding and pillaging everything along the way and culminating in a siege of the occupied city (during which 3,000 cannonballs fell on the city). The environs, thick with villas, the results of a long prosperity, were plundered, including half a million pound sterling, sterling.
The city was in the utmost straits; General Molitor, who had advanced within a few days' march of Ragusa, made an appeal to the Dalmatians to rise and expel the Russian–Montenegrin force, which met with a feeble response. Only three hundred men joined him, but a stratagem made up for his deficiency of numbers. A letter, seemingly confidential, was dispatched to General Lauriston in Ragusa, announcing his proximate arrival to raise the siege with such a force of Dalmatians as must overwhelm the Russians and the vast Montenegrin army; which letter was, as intended by Molitor, intercepted and believed by the besieging Russians. With his force thinly scattered, to make up a show, Molitor now advanced towards Ragusa, and turning the Montenegrin position in the valley behind, threatened to surround the Russians who occupied the summit of the hill between him and the city; but seeing the risk of this, the Russians retreated back towards the Bay of Kotor, and the city was relieved. The Montenegrin army had followed the order of Admiral Dmitry Senyavin who was in charge of the Russian troops, and retreated to Cetinje.
End of the Republic
 Around the year 1800, the Republic had a highly organized network of consulates and consular offices in more than eighty cities and ports around the world. In 1808, Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont, Marshal Marmont issued a proclamation abolishing the Republic of Ragusa and amalgamating its territory into the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy, himself claiming the newly created title of "Duke of Ragusa" (''Duc de Raguse''). In 1810, Ragusa, together with Dalmatia and Istria, went to the newly created French Illyrian Provinces. Later, in the 1814 Battle of Paris (1814), Battle of Paris, Marmont abandoned Napoleon and was branded a traitor. Since he was known as the "Duke of Ragusa", the word ''ragusade'' was coined in French to signify treason and ''raguser'' meant a cheat.
Article "44" of the ''1811 Decree'' abolished the centuries-old institution of ''fideicommissum'' in inheritance law, by which the French enabled younger noblemen to participate in that part of the family inheritance, which the former law had deprived them of. According to an 1813 inventory of the Ragusan district, 451 land proprietors were registered, including ecclesiastical institutions and the commune. Although there is no evidence of the size of their estates, the nobles, undoubtedly, were in possession of most of the land. Eleven members of the Sorgo family, eight of Gozze, six of Ghetaldi, six of Pozza, four of Zamagna and three of the Saraca family were among the greatest landowners. The citizens belonging to the confraternities of Anthony the Great, St. Anthony and Lazarus of Bethany, St. Lazarus owned considerable land outside the City.
After seven years of French occupation, encouraged by the desertion of French soldiers after the failed French Invasion of Russia, invasion of Russia and the reentry of Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition, war, all the social classes of the Ragusan people rose up in a general insurrection, led by the patricians, against the Napoleonic invaders. On 18 June 1813, together with British forces they forced the surrender of the French garrison of the island of Šipan, soon also the heavily fortified town of
Around the year 1800, the Republic had a highly organized network of consulates and consular offices in more than eighty cities and ports around the world. In 1808, Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont, Marshal Marmont issued a proclamation abolishing the Republic of Ragusa and amalgamating its territory into the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy, himself claiming the newly created title of "Duke of Ragusa" (''Duc de Raguse''). In 1810, Ragusa, together with Dalmatia and Istria, went to the newly created French Illyrian Provinces. Later, in the 1814 Battle of Paris (1814), Battle of Paris, Marmont abandoned Napoleon and was branded a traitor. Since he was known as the "Duke of Ragusa", the word ''ragusade'' was coined in French to signify treason and ''raguser'' meant a cheat.
Article "44" of the ''1811 Decree'' abolished the centuries-old institution of ''fideicommissum'' in inheritance law, by which the French enabled younger noblemen to participate in that part of the family inheritance, which the former law had deprived them of. According to an 1813 inventory of the Ragusan district, 451 land proprietors were registered, including ecclesiastical institutions and the commune. Although there is no evidence of the size of their estates, the nobles, undoubtedly, were in possession of most of the land. Eleven members of the Sorgo family, eight of Gozze, six of Ghetaldi, six of Pozza, four of Zamagna and three of the Saraca family were among the greatest landowners. The citizens belonging to the confraternities of Anthony the Great, St. Anthony and Lazarus of Bethany, St. Lazarus owned considerable land outside the City.
After seven years of French occupation, encouraged by the desertion of French soldiers after the failed French Invasion of Russia, invasion of Russia and the reentry of Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition, war, all the social classes of the Ragusan people rose up in a general insurrection, led by the patricians, against the Napoleonic invaders. On 18 June 1813, together with British forces they forced the surrender of the French garrison of the island of Šipan, soon also the heavily fortified town of Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ant ...
and the island of Lopud
Lopud () is a small island off the coast of Dalmatia, southern Croatia. Lopud is economically the most developed of the Elaphiti Islands, and can be reached by boat from Dubrovnik, Trsteno, Orašac and Zaton. The island is famous for its sandy ...
, after which the insurrection spread throughout the mainland, starting with Konavle
Konavle () is a municipality and a small region located southeast of Dubrovnik, Croatia.
It is administratively part of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County and the center of the municipality is Cavtat.
Demographics
The total municipality population wa ...
. They laid Siege of Ragusa, siege to the occupied city, helped by the British Royal Navy, who had enjoyed Adriatic campaign of 1807–1814, unopposed domination over the Adriatic sea, under the command of Captain William Hoste, with his ships HMS ''Bacchante'' and . Soon the population inside the city joined the insurrection. The Austrian Empire sent a force under General Todor Milutinović offering to help their Ragusan allies. However, as was soon shown, their intention was to in fact replace the French occupation of Ragusa with their own. Seducing one of the temporary governors of the Republic, Biagio Bernardo Caboga, with promises of power and influence (which were later cut short and who died in ignominy, branded as a traitor by his people), they managed to convince him that the gate to the east was to be kept closed to the Ragusan forces and to let the Austrian forces enter the City from the west, without any Ragusan soldiers, once the French garrison of 500 troops under General Joseph Hélie Désiré Perruquet de Montrichard, Joseph de Montrichard had surrendered.
The Major Council of the Ragusan nobility (as the assembly of 44 patricians who had been members of the Major Council before the Republic was occupied by France) met for the last time on 18 January 1814 in the Villa Giorgi in Mokošica, Ombla, in an effort to restore the Republic of Ragusa.
On 27 January, the French capitulation was signed in Gruž and ratified the same day. It was then that Biagio Bernardo Caboga openly sided with the Austrians, dismissing the part of the rebel army which was from Konavle
Konavle () is a municipality and a small region located southeast of Dubrovnik, Croatia.
It is administratively part of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County and the center of the municipality is Cavtat.
Demographics
The total municipality population wa ...
. Meanwhile, Đivo Natali and his men were still waiting outside the Ploče Gates. After almost eight years of occupation, the French troops marched out of Dubrovnik on 27 and 28 January 1814. On the afternoon of 28 January 1814, the Austrian and British troops made their way into the city through the Pile Gates. With Caboga's support, General Milutinović ignored the agreement he had made with the nobility in Gruž. The events which followed can be best epitomized in the so-called flag episode.
The Flag of Saint Blaise was flown alongside the Austrian and British colors, but only for two days because, on 30 January, General Milutinović ordered Mayor Sabo Giorgi to lower it. Overwhelmed by a feeling of deep patriotic pride, Giorgi, the last Rector of the Republic and a loyal francophile, refused to do so "for the masses had hoisted it". Subsequent events proved that Austria took every possible opportunity to invade the entire coast of the eastern Adriatic, from Venice to Kotor. The Austrians did everything in their power to eliminate the Ragusa issue at the Congress of Vienna. Ragusan representative Miho Bona, elected at the last meeting of the Major Council, was denied participation in the Congress, while Milutinović, prior to the final agreement of the allies, assumed complete control of the city.
Regardless of the fact that the government of the Ragusan Republic never signed any capitulation nor relinquished its sovereignty, which according to the rules of Klemens von Metternich that Austria adopted for the Vienna Congress should have meant that the Republic would be restored, the Austrian Empire managed to convince the other allies to allow it to keep the territory of the Republic. While many smaller and less significant cities and former countries were permitted an audience, that right was refused to the representative of the Ragusan Republic. All of this was in blatant contradiction to the solemn treaties that the Austrian Emperors signed with the Republic: the first on 20 August 1684, in which Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold I promised and guaranteed inviolate liberty ("inviolatam libertatem") to the Republic, and the second in 1772, in which the Empress Maria Theresa promised protection and respect of the inviolability of the freedom and territory of the Republic.
At the Congress of Vienna, Ragusa and the territories of the former Republic were made part of the crown land of the Kingdom of Dalmatia, ruled by the Habsburg monarchy, which became known as Austria-Hungary in 1867, which it remained a part of until 1918.
After the fall of the Republic, most of the aristocracy died out or emigrated overseas; around one fifth of the noble families were recognized by the Habsburg Monarchy. Some of the families that were recognized and survived were the Ghetaldi-Gundula, Gozze, Kaboga, Sorgo, Zlatarić, Zamagna, Pozza, Gradi and Bona.

Government
 The Republican Constitution of Ragusa was strictly Aristocracy (government), aristocratic. The population was divided into three classes: nobility, citizens, and plebeians, who were mainly artisans and Farmer, farmers (serfs, colonus (person), coloni and Freedman, freemen). All effective power was concentrated in the hands of the aristocracy. The citizens were permitted to hold only minor offices, while plebeians had no voice in government. Marriage between members of different classes of the society was forbidden.
The organization of the government was based on the Republic of Venice#Government, Venetian model: the administrative bodies were the Major Council (''Consilium maius'', ''Maggior Consiglio'', ''Velje vijeće''), the Minor Council (''Consilium minus'', ''Minor Consiglio'', ''Malo vijeće'') (from 1238) and the Senate (''Consilium rogatorum'', ''Consiglio dei Pregadi'', ''Vijeće umoljenih'') from 1253. The head of the state was the
The Republican Constitution of Ragusa was strictly Aristocracy (government), aristocratic. The population was divided into three classes: nobility, citizens, and plebeians, who were mainly artisans and Farmer, farmers (serfs, colonus (person), coloni and Freedman, freemen). All effective power was concentrated in the hands of the aristocracy. The citizens were permitted to hold only minor offices, while plebeians had no voice in government. Marriage between members of different classes of the society was forbidden.
The organization of the government was based on the Republic of Venice#Government, Venetian model: the administrative bodies were the Major Council (''Consilium maius'', ''Maggior Consiglio'', ''Velje vijeće''), the Minor Council (''Consilium minus'', ''Minor Consiglio'', ''Malo vijeće'') (from 1238) and the Senate (''Consilium rogatorum'', ''Consiglio dei Pregadi'', ''Vijeće umoljenih'') from 1253. The head of the state was the Rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
.
The Major Council consisted only of members of the aristocracy; every noble took his seat at the age of 18 (from 1332 when the council was "closed" and only male members of Ragusian noble families had seat in it – ''Serrata del Maggior Consiglio Raguseo''). It was the supreme governing and legislative body which (after 1358) elected other councils, officials and the Rector.
Every year, members of the Minor Council were elected by the Major Council. Together with the Rector, the Minor Council had both executive and ceremonial functions. It consisted first of eleven members and after 1667 of seven members.
The main power was in the hands of the Senate, which had 45 members over 40 years of age, elected for one year also by the Major Council. First it had only consultative functions, later (during the 16th century) the Senate became the real government of the Republic. In the 18th century the Senate was ''de facto'' the highest institution of the Republic and senators became "nobles of the nobility".
While the Republic was under the rule of Venice (1204–1358), the duke – head of the state (Latin language, Latin: ''comes'', Italian: ''conte'', Croatian language, Croatian: ''knez'') was Venetian; but after 1358 the elected Rector (from 1358 nominal head of the state was known as Latin language, Latin: ''rector'', Italian: ''rettore'', Croatian language, Croatian: ''knez'') was always a person from the Republic of Ragusa chosen by the Major Council. The length of the Rector's service was only one month, and a person was eligible for reelection after two years. The rector lived and worked in the Rector's Palace.
This organization was designed to prevent any single family from gaining absolute control, such as the Medici had done in Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany Regions of Italy, region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilan ...
. Nevertheless, historians agree that the House of Giorgi, Giorgi and House of Sorgo, Sorgo families generally had the greatest influence (especially during the 18th century).
Until the 15th century, judicial functions were in the hand of the Minor Council, then a separate civil court and criminal court were established, leaving the Minor Council and the Senate only supreme appellate jurisdiction. Judges of the criminal and civil court were Ragusan patricians elected annually by the Major Council.
The officials known as ''provveditori'' supervised the work and acts of the councils, courts, and other officials. Known as the "guardians of justice", they could suspend decisions of the Minor Council, presenting them to the Senate for final deliberation. ''Provveditori'' were annually elected by the Major Council among patricians above 50 years of age.
The government of the Republic was liberal in character and early showed its concern for justice and humanitarian principles, but also conservative considering government structure and social order. An inscription on the Council's offices read: ''Obliti privatorum publica curate'' (Manage the public affairs as if you had no private interests). The Republic's flag had the word ''Libertas'' (freedom) on it, and the entrance to the Saint Lawrence fortress (Lovrijenac) just outside the Ragusa city walls bears the inscription ''Non bene pro toto libertas venditur auro'' (Liberty can not be sold for all the gold of the world). The slave trade was forbidden in 1416. The Republic was a staunch opponent of the Eastern Orthodox Church and only Roman Catholics could acquire Ragusan citizenship.
Aristocracy
The city was ruled by the aristocracy, and marriage between members of three different social classes was strictly forbidden. The Ragusan aristocracy evolved in the 12th century through the 14th century. It was finally established by statute in 1332. New families were accepted only after the earthquake in 1667. The Ragusan archives document, ''Speculum Maioris Consilii Rectores'', lists all the persons that were involved in the Republic's government between September 1440 and January 1808. Of 4397 rectors elected, 2764 (63%) were from "old patrician" families: Gozze, Bona, Caboga, Cerva, Ghetaldi, Giorgi, Gradi, Pozza, Saraca, Sorgo, and Zamanya. An 1802 list of the republic's governing bodies showed that six of the eight Minor Council and 15 of the 20 Major Council members were from the same 11 families. Because of the decrease of their numbers and lack of noble families in the neighborhood (the surroundings of Dubrovnik was under Ottoman control) the aristocracy became increasingly closely related, and marriages between relatives of the third and fourth degree were frequent.Relations among the nobility
 The nobility survived even when the classes were divided by internal disputes. When Marmont arrived in Dubrovnik in 1808, the nobility was divided into two blocks, the "Salamankezi" (''Salamanquinos'') and the "Sorbonezi" (''Sorboneses''). These names alluded to a certain controversy arisen from the wars between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and King Francis I of France, which happened some 250 years previously. After the 1667 earthquake killed many nobles, some plebeians were introduced into the noble class. The "salamanquinos", those in favor of Spanish Absolutism (European history), absolutism, did not treat these new nobles like equals; but the inclined "sorboneses", who sided with the French and to a certain liberalism, accepted them. Both sides retained their status and were seated together in the Council, but they did not maintain social relations and did not even greet each other in the streets; an inconvenient marriage between members of both groups was as striking as if it occurred between members of different classes. This social split was also reflected in the plebeians, who were divided into the rival brotherhoods of Saint Antony and Saint Lazarus, which were as unfriendly in their relations as the "salamanquinos" and "sorboneses".
The nobility survived even when the classes were divided by internal disputes. When Marmont arrived in Dubrovnik in 1808, the nobility was divided into two blocks, the "Salamankezi" (''Salamanquinos'') and the "Sorbonezi" (''Sorboneses''). These names alluded to a certain controversy arisen from the wars between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and King Francis I of France, which happened some 250 years previously. After the 1667 earthquake killed many nobles, some plebeians were introduced into the noble class. The "salamanquinos", those in favor of Spanish Absolutism (European history), absolutism, did not treat these new nobles like equals; but the inclined "sorboneses", who sided with the French and to a certain liberalism, accepted them. Both sides retained their status and were seated together in the Council, but they did not maintain social relations and did not even greet each other in the streets; an inconvenient marriage between members of both groups was as striking as if it occurred between members of different classes. This social split was also reflected in the plebeians, who were divided into the rival brotherhoods of Saint Antony and Saint Lazarus, which were as unfriendly in their relations as the "salamanquinos" and "sorboneses".
Coat of arms
Today the coat of arms of Ragusa, in its red and blue version, can be seen in the coat of arms on the Croatian flag as it constitutes a historic part of Croatia.Population
The historian Nenad Vekarić used tax evidence from the Dubrovnik littoral ( hr, Dubrovačko Primorje) and a census to find that the Republic of Dubrovnik (Ragusa) had a population of nearly 90,000 by 1500. From then to 1700 the population declined: in the first half of the 16th century it had more than 50,000 inhabitants; in the second half of the 16th century, between 50,000 and 60,000; in the 1630s, about 40,000; and in 1673–74, only 26,000 inhabitants. In the second half of the 15th century, due to Turkish expansion, Dubrovnik received a large number of Christian refugees from Bosnia and Herzegovina, offering them the less fertile land. Numerous epidemics, the Candian War of 1645–69, the 1667 earthquake, and emigration greatly reduced the population levels. The population of the republic never again reached its previous levels.Languages and literature
Originally,Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
was used in official documents of the Republic. Italian language, Italian came to use in the 1420s. Both languages were used in official correspondence by the Republic. The Republic was influenced by the Venetian language and the Tuscan dialect.
Population spoke the local variant of the Shtokavian dialect, the same dialect upon which modern Serbo-Croatian and its forms, Croatian language, Croatian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, Montenegrin language, Montenegrin and Serbian language, Serbian, are all based. Old Ragusan, a variant of Dalmatian (language), Dalmatian that was spoken on the Dalmatian coast following the end of the Roman Empire, with elements of old Slavic vernacular, commonly referred to as ''ilirski'' (Illyrian), and Italian, was among the common languages. Since it was mainly used in speech, it is poorly documented. Its use started declining in the 15th century.
The use of Serbo-Croatian in everyday speech increased in late 13th century, and in literary works in mid-15th century. At the end of the 14th century, inhabitants of the republic were mostly native speakers of Serbo-Croatian, referred to by them as ''Croatian'', ''Slavic'', or ''Illyrian'' at the time.
There is still some debate over whether Shtokavian or Chakavian was the oldest Slavic vernacular in Ragusa. The oldest Slavic documents and the earlier prose was Shtokavian, while 16th-century poetry was Chakavian. The Cyrillic script in handwriting was sometimes used.
When Ragusa was part of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy, between 1808 and 1810, Italian was still in official use. Serbo-Croatian was normally spoken among lower classes, Italian among the upper. Ragusans were in general bilingual, speaking Serbo-Croatian in common day-to-day duties and Italian in official occasions or mixing both.
Ragusan literature
 Ragusan literature, in which Latin, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian coexisted, blossomed in the 15th and 16th centuries. According to Marcus Tanner:
Literary works of famous Ragusans were written in both Serbo-Croatian and Italian. Among them are the works of writers Džore Držić (Giorgio Darsa), Marin Držić (Marino Darsa), Ivan Bunić Vučić (Giovanni Serafino Bona), Ignjat Đurđević (Ignazio Giorgi), Ivan Gundulić (Giovanni Gondola), Šiško Menčetić, Šišmundo (Šiško) Menčetić (Sigismondo Menze), and Dinko Ranjina (Domenico Ragnina).
The literature of Dubrovnik had a defining role in the development of modern Croatian, Dubrovnik Shtokavian dialect having been the basis for standardized Croatian. Writers from the 16th to the 19th century (before the Age of Romantic National Awakenings) that were explicit in declaring themselves as Croats and their language as Croatian included Vladislav Menčetić, Dominko Zlatarić, Dominko (Dinko) Zlatarić, Bernardin Pavlović, Mavro Vetranović, Nikola Nalješković, Junije Palmotić, Jakov Mikalja, Joakim Stulli, Marc Bruère Desrivaux, Marko Bruerović, Peter Ignaz Sorgo, Antun Sorkočević (1749–1826), and Franatica Sorkočević (1706–71).
There also were Ragusan authors of Morlachism, a primarily Italian and Venetian literary movement.
Ragusan literature, in which Latin, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian coexisted, blossomed in the 15th and 16th centuries. According to Marcus Tanner:
Literary works of famous Ragusans were written in both Serbo-Croatian and Italian. Among them are the works of writers Džore Držić (Giorgio Darsa), Marin Držić (Marino Darsa), Ivan Bunić Vučić (Giovanni Serafino Bona), Ignjat Đurđević (Ignazio Giorgi), Ivan Gundulić (Giovanni Gondola), Šiško Menčetić, Šišmundo (Šiško) Menčetić (Sigismondo Menze), and Dinko Ranjina (Domenico Ragnina).
The literature of Dubrovnik had a defining role in the development of modern Croatian, Dubrovnik Shtokavian dialect having been the basis for standardized Croatian. Writers from the 16th to the 19th century (before the Age of Romantic National Awakenings) that were explicit in declaring themselves as Croats and their language as Croatian included Vladislav Menčetić, Dominko Zlatarić, Dominko (Dinko) Zlatarić, Bernardin Pavlović, Mavro Vetranović, Nikola Nalješković, Junije Palmotić, Jakov Mikalja, Joakim Stulli, Marc Bruère Desrivaux, Marko Bruerović, Peter Ignaz Sorgo, Antun Sorkočević (1749–1826), and Franatica Sorkočević (1706–71).
There also were Ragusan authors of Morlachism, a primarily Italian and Venetian literary movement.
Ethnic groups
The inhabitants of the Republic of Ragusa were Catholics and spoke the local variant of the Shtokavian dialect, the same dialect upon which modern Croatian language, Croatian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, Montenegrin language, Montenegrin and Serbian language, Serbian are all based. Among the modern South Slavic nations, Ragusans are mostly attributed to Croats.Matjaž Klemenčič, Mitja Žagar; ''The former Yugoslavia's diverse peoples: a reference sourcebook''; ABC-CLIO, 2004 However, discussions on the subject of Ragusan ethnicity are mainly based on revised concepts which developed after the fall of the Republic; in particular, the time of Romantic Nationalism resulting from the French Revolution. Before this, states in general were not based on the contemporary unifying concepts such as nation, language, or ethnicity; loyalty was chiefly to family, city, and (among Catholics such as the Ragusans) the Church. Vlachs, also named Morlachs, were active within Ragusa's city walls but the majority of them were shepherds, guards, or carters living in Dalmatia.Currency
The Republic of Ragusa used various currencies over time and in a variety of systems, including the artiluc, Ragusan perpera, perpera, Dukat (currency), dukat and Ragusian libertine, libertine.See also
*List of notable Ragusans *Walls of Dubrovnik *Septinsular Republic *Republic of Poljica *Collegium RagusinumReferences
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * Tomaz, Luigi, ''Il confine d'Italia in Istria e Dalmazia. Duemila anni di storia'', Think ADV, Conselve 2007. *Further reading
*D'Atri, Stefano. "Ragusa (Dubrovnik) In Eta Moderna: Alcune Considerazioni Storiografiche," [Ragusa (Dubrovnik) in the modern era: some historiographic considerations] ''Societa e Storia''(giu 2005), Vol. 28 Issue 109, pp. 599–609, covers 1500 to 1600 * Delis, Apostolos. "Shipping Finance and Risks in Sea Trade during the French Wars: Maritime Loan Operations in the Republic of Ragusa" ''International Journal of Maritime History'' (June 2012) 24#1 pp. 229–242 * * Vekaric, Nenad.The Population of the Dubrovnik Republic in the Fifteenth, Sixteenth, and Seventeenth Centuries
" ''Dubrovnik Annals'' 1998, Vol. 2, pp 7–28 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
External links
Historical facts about Dubrovnik
from Dubrovnik Online
''Dalmatia and Montenegro''
by John Gardner Wilkinson, on Google Books
''Aus Dalmatien''
by Ida Reinsberg-Düringsfeld (1857), on Google Books
''Universal Geography: Republic of Ragusa''
on Google Books
''Bibliografia della Dalmazia e del Montenegro''
by Giuseppe Valentinelli, on Google Books
''Bibliografia hrvatska''
Ivan Kukuljević Sakcinski, on Google Books
''Geschichte des Freystaates Ragusa''
by Johann Christian von Engel, on Google Books
''The Ethnology of Europe''
by Robert Gordon Latham, on Google Books
''Austria in 1848–49: Dalmatia''
by William Henry Stiles, on Google Books
Ragusa, the American Revolution, and Diplomatic Relations, 1763–1783
*[https://archive.org/details/notizieistorico00appegoog/page/n552 Notizie Istorico-Critiche Sulle Antichita Storia de Letteratura dei Ragusei] by Francesco Maria Appendini. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ragusa, Republic Republic of Ragusa, Dubrovnik Maritime republics Former Slavic countries Former republics, Ragusa 1358 establishments in Europe 1807 disestablishments in Europe Tributary states of the Ottoman Empire