RANSAC on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Random sample consensus (RANSAC) is an
Image:Line_with_outliers.svg, A data set with many outliers for which a line has to be fitted.
Image:Fitted_line.svg, Fitted line with RANSAC; outliers have no influence on the result.
Image:RANSAC Inliers and Outliers.png, RANSAC: Inliers and Outliers.
from copy import copy
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import default_rng
rng = default_rng()
class RANSAC:
def __init__(self, n=10, k=100, t=0.05, d=10, model=None, loss=None, metric=None):
self.n = n # `n`: Minimum number of data points to estimate parameters
self.k = k # `k`: Maximum iterations allowed
self.t = t # `t`: Threshold value to determine if points are fit well
self.d = d # `d`: Number of close data points required to assert model fits well
self.model = model # `model`: class implementing `fit` and `predict`
self.loss = loss # `loss`: function of `y_true` and `y_pred` that returns a vector
self.metric = metric # `metric`: function of `y_true` and `y_pred` and returns a float
self.best_fit = None
self.best_error = np.inf
def fit(self, X, y):
for _ in range(self.k):
ids = rng.permutation(X.shape
maybe_inliers = ids self.n maybe_model = copy(self.model).fit(X aybe_inliers y aybe_inliers
thresholded = (
self.loss(y dsself.n :], maybe_model.predict(X dsself.n :]))
< self.t
)
inlier_ids = ids elf.n :np.flatnonzero(thresholded).flatten()]
if inlier_ids.size > self.d:
inlier_points = np.hstack( aybe_inliers, inlier_ids
better_model = copy(self.model).fit(X nlier_points y nlier_points
this_error = self.metric(
y nlier_points better_model.predict(X nlier_points
)
if this_error < self.best_error:
self.best_error = this_error
self.best_fit = maybe_model
return self
def predict(self, X):
return self.best_fit.predict(X)
def square_error_loss(y_true, y_pred):
return (y_true - y_pred) ** 2
def mean_square_error(y_true, y_pred):
return np.sum(square_error_loss(y_true, y_pred)) / y_true.shape
class LinearRegressor:
def __init__(self):
self.params = None
def fit(self, X: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray):
r, _ = X.shape
X = np.hstack( p.ones((r, 1)), X
self.params = np.linalg.inv(X.T @ X) @ X.T @ y
return self
def predict(self, X: np.ndarray):
r, _ = X.shape
X = np.hstack( p.ones((r, 1)), X
return X @ self.params
if __name__ "__main__":
regressor = RANSAC(model=LinearRegressor(), loss=square_error_loss, metric=mean_square_error)
X = np.array([-0.848,-0.800,-0.704,-0.632,-0.488,-0.472,-0.368,-0.336,-0.280,-0.200,-0.00800,-0.0840,0.0240,0.100,0.124,0.148,0.232,0.236,0.324,0.356,0.368,0.440,0.512,0.548,0.660,0.640,0.712,0.752,0.776,0.880,0.920,0.944,-0.108,-0.168,-0.720,-0.784,-0.224,-0.604,-0.740,-0.0440,0.388,-0.0200,0.752,0.416,-0.0800,-0.348,0.988,0.776,0.680,0.880,-0.816,-0.424,-0.932,0.272,-0.556,-0.568,-0.600,-0.716,-0.796,-0.880,-0.972,-0.916,0.816,0.892,0.956,0.980,0.988,0.992,0.00400]).reshape(-1,1)
y = np.array([-0.917,-0.833,-0.801,-0.665,-0.605,-0.545,-0.509,-0.433,-0.397,-0.281,-0.205,-0.169,-0.0531,-0.0651,0.0349,0.0829,0.0589,0.175,0.179,0.191,0.259,0.287,0.359,0.395,0.483,0.539,0.543,0.603,0.667,0.679,0.751,0.803,-0.265,-0.341,0.111,-0.113,0.547,0.791,0.551,0.347,0.975,0.943,-0.249,-0.769,-0.625,-0.861,-0.749,-0.945,-0.493,0.163,-0.469,0.0669,0.891,0.623,-0.609,-0.677,-0.721,-0.745,-0.885,-0.897,-0.969,-0.949,0.707,0.783,0.859,0.979,0.811,0.891,-0.137]).reshape(-1,1)
regressor.fit(X, y)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use("seaborn-darkgrid")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax.set_box_aspect(1)
plt.scatter(X, y)
line = np.linspace(-1, 1, num=100).reshape(-1, 1)
plt.plot(line, regressor.predict(line), c="peru")
plt.show()
iterative method
In computational mathematics, an iterative method is a mathematical procedure that uses an initial value to generate a sequence of improving approximate solutions for a class of problems, in which the ''n''-th approximation is derived from the pre ...
to estimate parameters of a mathematical model from a set of observed data that contains outliers
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter ar ...
, when outliers are to be accorded no influence on the values of the estimates. Therefore, it also can be interpreted as an outlier detection method. It is a non-deterministic algorithm in the sense that it produces a reasonable result only with a certain probability, with this probability increasing as more iterations are allowed. The algorithm was first published by Fischler and Bolles at SRI International
SRI International (SRI) is an American nonprofit organization, nonprofit scientific research, scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California. The trustees of Stanford University established SRI in 1946 as ...
in 1981. They used RANSAC to solve the Location Determination Problem (LDP), where the goal is to determine the points in the space that project onto an image into a set of landmarks with known locations.
RANSAC uses repeated random sub-sampling.
A basic assumption is that the data consists of "inliers", i.e., data whose distribution can be explained by some set of model parameters, though may be subject to noise, and "outliers" which are data that do not fit the model. The outliers can come, for example, from extreme values of the noise or from erroneous measurements or incorrect hypotheses about the interpretation of data. RANSAC also assumes that, given a (usually small) set of inliers, there exists a procedure which can estimate the parameters of a model that optimally explains or fits this data.
Example
A simple example is fitting a line in two dimensions to a set of observations. Assuming that this set contains both inliers, i.e., points which approximately can be fitted to a line, and outliers, points which cannot be fitted to this line, a simple least squares method for line fitting will generally produce a line with a bad fit to the data including inliers and outliers. The reason is that it is optimally fitted to all points, including the outliers. RANSAC, on the other hand, attempts to exclude the outliers and find a linear model that only uses the inliers in its calculation. This is done by fitting linear models to several random samplings of the data and returning the model that has the best fit to a subset of the data. Since the inliers tend to be more linearly related than a random mixture of inliers and outliers, a random subset that consists entirely of inliers will have the best model fit. In practice, there is no guarantee that a subset of inliers will be randomly sampled, and the probability of the algorithm succeeding depends on the proportion of inliers in the data as well as the choice of several algorithm parameters.Overview
The RANSAC algorithm is a learning technique to estimate parameters of a model by random sampling of observed data. Given a dataset whose data elements contain both inliers and outliers, RANSAC uses the voting scheme to find the optimal fitting result. Data elements in the dataset are used to vote for one or multiple models. The implementation of this voting scheme is based on two assumptions: that the noisy features will not vote consistently for any single model (few outliers) and there are enough features to agree on a good model (few missing data). The RANSAC algorithm is essentially composed of two steps that are iteratively repeated: # In the first step, a sample subset containing minimal data items is randomly selected from the input dataset. A fitting model and the corresponding model parameters are computed using only the elements of this sample subset. The cardinality of the sample subset is the smallest sufficient to determine the model parameters. # In the second step, the algorithm checks which elements of the entire dataset are consistent with the model instantiated by the estimated model parameters obtained from the first step. A data element will be considered as an outlier if it does not fit the fitting model instantiated by the set of estimated model parameters within some error threshold that defines the maximum deviation attributable to the effect of noise. The set of inliers obtained for the fitting model is called the consensus set. The RANSAC algorithm will iteratively repeat the above two steps until the obtained consensus set in certain iteration has enough inliers. The input to the RANSAC algorithm is a set of observed data values, a way of fitting some kind of model to the observations, and someconfidence
Confidence is a state of being clear-headed either that a hypothesis or prediction is correct or that a chosen course of action is the best or most effective. Confidence comes from a Latin word 'fidere' which means "to trust"; therefore, having ...
parameters. RANSAC achieves its goal by repeating the following steps:
# Select a random subset of the original data. Call this subset the ''hypothetical inliers''.
# A model is fitted to the set of hypothetical inliers.
# All other data are then tested against the fitted model. Those points that fit the estimated model well, according to some model-specific loss function
In mathematical optimization and decision theory, a loss function or cost function (sometimes also called an error function) is a function that maps an event or values of one or more variables onto a real number intuitively representing some "cost ...
, are considered as part of the ''consensus set''.
# The estimated model is reasonably good if sufficiently many points have been classified as part of the consensus set.
# Afterwards, the model may be improved by reestimating it using all members of the consensus set.
This procedure is repeated a fixed number of times, each time producing either a model which is rejected because too few points are part of the consensus set, or a refined model together with a corresponding consensus set size. In the latter case, we keep the refined model if its consensus set is larger than the previously saved model.
Algorithm
The generic RANSAC algorithm works as follows: Given: data – A set of observations. model – A model to explain observed data points. n – Minimum number of data points required to estimate model parameters. k – Maximum number of iterations allowed in the algorithm. t – Threshold value to determine data points that are fit well by model. d – Number of close data points required to assert that a model fits well to data. Return: bestFit – model parameters which best fit the data (or null if no good model is found) iterations = 0 bestFit = null bestErr = something really large while ''iterations'' < ''k'' do maybeInliers := n randomly selected values from data maybeModel := model parameters fitted to maybeInliers alsoInliers := empty set for every point in data not in maybeInliers do if point fits maybeModel with an error smaller than t add point to alsoInliers end if end for if the number of elements in alsoInliers is > d then // This implies that we may have found a good model // now test how good it is. betterModel := model parameters fitted to all points in maybeInliers and alsoInliers thisErr := a measure of how well betterModel fits these points if thisErr < bestErr then bestFit := betterModel bestErr := thisErr end if end if increment iterations end while return bestFitExample Code
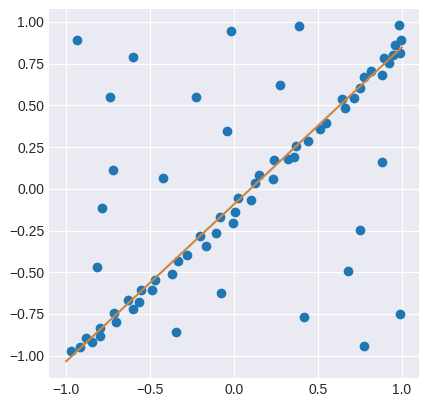
A Python implementation mirroring the pseudocode. This also defines aLinearRegressor based on least squares, applies RANSAC to a 2D regression problem, and visualizes the outcome:

Parameters
The threshold value to determine when a data point fits a model , and the number of close data points required to assert that a model fits well to data are determined based on specific requirements of the application and the dataset, and possibly based on experimental evaluation. The number of iterations , however, can be determined as a function of the desired probability of success using a theoretical result. Let be the desired probability that the RANSAC algorithm provides at least one useful result after running. RANSAC returns a successful result if in some iteration it selects only inliers from the input data set when it chooses the points from which the model parameters are estimated. Let be the probability of choosing an inlier each time a single point is selected, that is, : = number of inliers in data / number of points in data A common case is that is not well known beforehand, but some rough value can be given. Assuming that the points needed for estimating a model are selected independently, is the probability that all ''n'' points are inliers and is the probability that at least one of the points is an outlier, a case which implies that a bad model will be estimated from this point set. That probability to the power of is the probability that the algorithm never selects a set of points which all are inliers and this must be the same as . Consequently, : which, after taking the logarithm of both sides, leads to : This result assumes that the data points are selected independently, that is, a point which has been selected once is replaced and can be selected again in the same iteration. This is often not a reasonable approach and the derived value for should be taken as an upper limit in the case that the points are selected without replacement. For example, in the case of finding a line which fits the data set illustrated in the above figure, the RANSAC algorithm typically chooses two points in each iteration and computesmaybe_model as the line between the points and it is then critical that the two points are distinct.
To gain additional confidence, the standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, whil ...
or multiples thereof can be added to . The standard deviation of is defined as
:
Advantages and disadvantages
An advantage of RANSAC is its ability to do robust estimation of the model parameters, i.e., it can estimate the parameters with a high degree of accuracy even when a significant number ofoutlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter ar ...
s are present in the data set. A disadvantage of RANSAC is that there is no upper bound on the time it takes to compute these parameters (except exhaustion). When the number of iterations computed is limited the solution obtained may not be optimal, and it may not even be one that fits the data in a good way. In this way RANSAC offers a trade-off; by computing a greater number of iterations the probability of a reasonable model being produced is increased. Moreover, RANSAC is not always able to find the optimal set even for moderately contaminated sets and it usually performs badly when the number of inliers is less than 50%. Optimal RANSAC was proposed to handle both these problems and is capable of finding the optimal set for heavily contaminated sets, even for an inlier ratio under 5%. Another disadvantage of RANSAC is that it requires the setting of problem-specific thresholds.
RANSAC can only estimate one model for a particular data set. As for any one-model approach when two (or more) model instances exist, RANSAC may fail to find either one. The Hough transform is one alternative robust estimation technique that may be useful when more than one model instance is present. Another approach for multi model fitting is known as PEARL, which combines model sampling from data points as in RANSAC with iterative re-estimation of inliers and the multi-model fitting being formulated as an optimization problem with a global energy function describing the quality of the overall solution.
Applications
The RANSAC algorithm is often used incomputer vision
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human ...
, e.g., to simultaneously solve the correspondence problem
The correspondence problem refers to the problem of ascertaining which parts of one image correspond to which parts of another image, where differences are due to movement of the camera, the elapse of time, and/or movement of objects in the photo ...
and estimate the fundamental matrix related to a pair of stereo cameras; see also: Structure from motion
Structure from motion (SfM) is a photogrammetric range imaging technique for estimating three-dimensional structures from two-dimensional image sequences that may be coupled with local motion signals. It is studied in the fields of computer visi ...
, scale-invariant feature transform
The scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) is a computer vision algorithm to detect, describe, and match local '' features'' in images, invented by David Lowe in 1999.
Applications include object recognition, robotic mapping and navigation, i ...
, image stitching
Image stitching or photo stitching is the process of combining multiple photographic images with overlapping fields of view to produce a segmented panorama or high-resolution image. Commonly performed through the use of computer software, most a ...
, rigid motion segmentation.
Development and improvements
Since 1981 RANSAC has become a fundamental tool in thecomputer vision
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human ...
and image processing community. In 2006, for the 25th anniversary of the algorithm, a workshop was organized at the International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
The Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) is an annual conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, which is regarded as one of the most important conferences in its field. According to Google Scholar Metrics (2022 ...
(CVPR) to summarize the most recent contributions and variations to the original algorithm, mostly meant to improve the speed of the algorithm, the robustness and accuracy of the estimated solution and to decrease the dependency from user defined constants.
RANSAC can be sensitive to the choice of the correct noise threshold that defines which data points fit a model instantiated with a certain set of parameters. If such threshold is too large, then all the hypotheses tend to be ranked equally (good). On the other hand, when the noise threshold is too small, the estimated parameters tend to be unstable ( i.e. by simply adding or removing a datum to the set of inliers, the estimate of the parameters may fluctuate). To partially compensate for this undesirable effect, Torr et al. proposed two modification of RANSAC called MSAC (M-estimator SAmple and Consensus) and MLESAC (Maximum Likelihood Estimation SAmple and Consensus). The main idea is to evaluate the quality of the consensus set ( i.e. the data that fit a model and a certain set of parameters) calculating its likelihood (whereas in the original formulation by Fischler and Bolles the rank was the cardinality of such set). An extension to MLESAC which takes into account the prior probabilities associated to the input dataset is proposed by Tordoff. The resulting algorithm is dubbed Guided-MLESAC. Along similar lines, Chum proposed to guide the sampling procedure if some a priori information regarding the input data is known, i.e. whether a datum is likely to be an inlier or an outlier. The proposed approach is called PROSAC, PROgressive SAmple Consensus.
Chum et al. also proposed a randomized version of RANSAC called R-RANSAC to reduce the computational burden to identify a good consensus set. The basic idea is to initially evaluate the goodness of the currently instantiated model using only a reduced set of points instead of the entire dataset. A sound strategy will tell with high confidence when it is the case to evaluate the fitting of the entire dataset or when the model can be readily discarded. It is reasonable to think that the impact of this approach is more relevant in cases where the percentage of inliers is large. The type of strategy proposed by Chum et al. is called preemption scheme. Nistér proposed a paradigm called Preemptive RANSAC that allows real time robust estimation of the structure of a scene and of the motion of the camera. The core idea of the approach consists in generating a fixed number of hypothesis so that the
comparison happens with respect to the quality of the generated hypothesis rather than against some absolute quality metric.
Other researchers tried to cope with difficult situations where the noise scale is not known and/or multiple model instances are present. The first problem has been tackled in the work by Wang and Suter. Toldo et al. represent each datum with the characteristic function of the set of random models that fit the point. Then multiple models are revealed as clusters which group the points supporting the same model. The clustering algorithm, called J-linkage, does not require prior specification of the number of models, nor does it necessitate manual parameters tuning.
RANSAC has also been tailored for recursive state estimation applications, where the input measurements are corrupted by outliers and Kalman filter
For statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering, also known as linear quadratic estimation (LQE), is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, and produces esti ...
approaches, which rely on a Gaussian distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu ...
of the measurement error, are doomed to fail. Such an approach is dubbed KALMANSAC.
Related methods
* MLESAC (Maximum Likelihood Estimate Sample Consensus) – maximizes the likelihood that the data was generated from the sample-fitted model, e.g. amixture model
In statistics, a mixture model is a probabilistic model for representing the presence of subpopulations within an overall population, without requiring that an observed data set should identify the sub-population to which an individual observation ...
of inliers and outliers
* MAPSAC (Maximum A Posterior Sample Consensus) – extends MLESAC to incorporate a prior probability
In Bayesian statistical inference, a prior probability distribution, often simply called the prior, of an uncertain quantity is the probability distribution that would express one's beliefs about this quantity before some evidence is taken into ...
of the parameters to be fitted and maximizes the posterior probability
The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that results from updating the prior probability with information summarized by the likelihood via an application of Bayes' rule. From an epistemological perspective, the posterior ...
* KALMANSAC – causal inference
Causal inference is the process of determining the independent, actual effect of a particular phenomenon that is a component of a larger system. The main difference between causal inference and inference of association is that causal inference ana ...
of the state of a dynamical system
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in ...
* Resampling (statistics)
In statistics, resampling is the creation of new samples based on one observed sample.
Resampling methods are:
# Permutation tests (also re-randomization tests)
# Bootstrapping
# Cross validation
Permutation tests
Permutation tests rely on r ...
* Hop-Diffusion Monte Carlo uses randomized sampling involve global jumps and local diffusion to choose the sample at each step of RANSAC for epipolar geometry estimation between very wide-baseline images.
See also
* Hough transformNotes
References
* * * * * * * * *{{Cite journal , author1=Hossam Isack , author2=Yuri Boykov , title=Energy-based Geometric Multi-Model Fitting , journal=International Journal of Computer Vision , volume=97 , issue = 2: 1 , pages=23–147 , year=2012 , url=http://www.csd.uwo.ca/~yuri/Papers/tr735.pdf , doi=10.1007/s11263-011-0474-7 , citeseerx=10.1.1.381.2434 , s2cid=5461268 Geometry in computer vision Statistical algorithms Statistical outliers Robust statistics Articles with example pseudocode SRI International Articles with example MATLAB/Octave code