The history of the Jews in Russia and areas historically connected with it goes back at least 1,500 years. Jews in Russia have historically constituted a large religious and ethnic diaspora; the
Russian Empire at one time hosted the largest population of Jews
in the world. Within these territories the primarily
Ashkenazi Jewish
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, ūÖų░ūöūĢų╝ūōųĄūÖ ūÉųĘū®ų░ūüūøų░ų╝ūĀųĘū¢, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, ūÉųĘū®ūøų╝ūĀū¢ūÖū®ūó ūÖūÖų┤ūōū¤, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
communities of many different areas flourished and developed many of modern Judaism's most distinctive theological and cultural traditions, while also facing periods of
anti-Semitic
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
discriminatory policies and persecutions. Some have described a "renaissance" in the Jewish community inside Russia since the beginning of the 21st century.
[Renaissance of Jewish life in Russia](_blank)
November 23, 2001, By John Daniszewski, Chicago Tribune Today Russia's Jewish population is still
among the largest in Europe.
Overview and background
The largest group among Russian Jews are Ashkenazi Jews, but the community also includes a significant proportion of other non-Ashkenazi from other
Jewish diaspora including
Mountain Jews,
Sephardi Jews,
Crimean Karaites,
Krymchaks,
Bukharan Jews
Bukharan Jews ( Bukharian: ūÖūöūĢūōūÖūÉūĀūÖ ūæūĢūøūÉū©ūÉ/čÅę│čāą┤ąĖčæąĮąĖ ąæčāčģąŠčĆąŠ, ''Yahudiyoni Bukhoro''; he, ūÖūöūĢūōūÖ ūæūĢūøū©ūö, ''Yehudey Bukhara''), in modern times also called Bukharian Jews ( Bukharian: ūÖūöūĢūōūÖūÉūĀūÖ ūæūĢūøūÉū© ...
and
Georgian Jews.
The presence of Jewish people in the European part of Russia can be traced to the 7thŌĆō14th centuries CE. In the 11th and 12th centuries, the Jewish population in
Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
, in present-day
Ukraine, was restricted to a separate quarter. Evidence of the presence of Jewish people in
Muscovite Russia is first documented in the chronicles of 1471. During the reign of
Catherine II in the 18th century, Jewish people were restricted to the
Pale of Settlement (1791ŌĆō1917) within Russia, the territory where they could live or immigrate to.
Alexander III escalated anti-Jewish policies. Beginning in the 1880s, waves of
anti-Jewish pogroms
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
swept across different regions of the empire for several decades. More than two million Jews fled Russia between 1880 and 1920, mostly to the United States and what is today the State of Israel. The Pale of Settlement took away many of the rights that the Jewish people of the late 17th century Russia had enjoyed. At this time, the Jewish people were restricted to an area of what is current day Belarus, Lithuania, eastern Poland and Ukraine.
Where Western Europe was experiencing emancipation at this time, in Russia the laws for the Jewish people were getting more strict. They were allowed to move further east, towards a less crowded region, though it was only a minority of Jews who took to this migration option.
The sporadic and often impoverished communities formed were known as
Shtetls.
Before 1917 there were 300,000
Zionists in Russia, while the main Jewish socialist organization,
the Bund, had 33,000 members. Only 958 Jews had joined the Bolshevik Party before 1917; thousands joined after the Revolution.
The chaotic years of
World War I, the
February
February is the second month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The month has 28 days in common years or 29 in leap years, with the 29th day being called the ''leap day''. It is the first of five months not to have 31 days (th ...
and
October Revolutions, and the
Russian Civil War had created social disruption that led to anti-Semitism. Some 150,000 Jews were killed in the pogroms of 1918ŌĆō1922, 125,000 of them in Ukraine, 25,000 in Belarus. The pogroms were mostly perpetrated by anti-communist forces; sometimes,
Red Army units engaged in pogroms as well.
's
White Army was a bastion of anti-Semitism, using "Strike at the Jews and save Russia!" as its motto. The
Bolshevik Red Army, although individual soldiers committed anti-Semitic abuses, had a policy of opposing anti-Semitism, and as a result, it won the support of much of the Jewish population. After a short period of confusion, the Soviets started executing guilty individuals and even disbanding the army units whose men had attacked Jews. Although pogroms were still perpetrated after this, mainly by Ukrainian units of the Red Army during its retreat from Poland (1920), in general, the Jews regarded the Red Army as the only force which was able and willing to defend them. The Russian Civil War pogroms shocked world Jewry and rallied many Jews to the Red Army and the Soviet regime, strengthening the desire for the creation of a homeland for the Jewish people.
[Modern Jewish History: Pogroms]
, ''Jewish Virtual Library'', 2008, retrieved September 9, 2015. In August 1919 the Soviet government arrested many rabbis, seized Jewish properties, including synagogues, and dissolved many Jewish communities. The
Jewish section of the Communist Party labeled the use of the
Hebrew language "reactionary" and "elitist" and the teaching of Hebrew was banned.
Zionists were persecuted harshly, with Jewish communists leading the attacks.
Following the civil war, however, the new Bolshevik government's policies produced a flourishing of secular Jewish culture in Belarus and western Ukraine in the 1920s. The Soviet government outlawed all expressions of anti-Semitism, with the public use of the ethnic slur ''ąČąĖą┤'' ("Yid") being punished by up to one year of imprisonment,
and tried to modernize the Jewish community by establishing 1,100 Yiddish-language schools, 40 Yiddish-language daily newspapers and by settling Jews on farms in Ukraine and Crimea; the number of Jews working in the industry had more than doubled between 1926 and 1931.
At the beginning of the 1930s, the Jews were 1.8 percent of the Soviet population but 12ŌĆō15 percent of all university students.
In 1934 the Soviet state established the
Jewish Autonomous Oblast in the Russian Far East. This region never came to have a majority Jewish population.
The JAO is Russia's only
autonomous oblast and, outside of Israel, the world's only Jewish territory with an official status.
The observance of the
Sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, commanded by God to be kept as a holy day of rest, as G ...
was banned in 1929,
foreshadowing the dissolution of the Communist Party's Yiddish-language
Yevsektsia
A Yevsektsiya ( rus, ąĄą▓čüąĄą║čåąĖčÅ, p=j╔¬f╦łs╩▓ekts╔©j╔Ö; yi, ūÖūóūĢūĢūĪūóū¦ū”ūÖūó) was a Jewish section of the Soviet Communist Party. These sections were established in fall of 1918 with consent of Vladimir Lenin to carry communist revolut ...
in 1930 and worse repression to come. Numerous Jews were victimized in Stalin's purges as "counterrevolutionaries" and "reactionary nationalists", although in the 1930s the Jews were underrepresented in the
Gulag population.
The share of Jews in the Soviet ruling elite declined during the 1930s, but was still more than double their proportion in the general Soviet population. According to Israeli historian
Benjamin Pinkus
Benjamin ( he, ''Bīnyāmīn''; "Son of (the) right") blue letter bible: https://www.blueletterbible.org/lexicon/h3225/kjv/wlc/0-1/ H3225 - yāmîn - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel (Jacob's thir ...
, "We can say that the Jews in the Soviet Union took over the privileged position, previously held by the
Germans in tsarist Russia".
In the 1930s, many Jews held high rank in the Red Army High Command: Generals
Iona Yakir,
Yan Gamarnik,
Yakov Smushkevich (Commander of the
Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, ąÆąŠąĄąĮąĮąŠ-ą▓ąŠąĘą┤čāčłąĮčŗąĄ čüąĖą╗čŗ, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
) and
Grigori Shtern (Commander-in-Chief in the
war against Japan and Commander at the front in the
Winter War).
During World War Two, an estimated 500,000 soldiers in the Red Army were Jewish; about 200,000 were killed in battle. About 160,000 were decorated, and more than a hundred achieved the rank of Red Army general.
Over 150 were designated
Heroes of the Soviet Union, the highest award in the country. More than two million Soviet Jews are believed to have died during
the Holocaust in warfare and in Nazi-occupied territories. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, many Soviet Jews took the opportunity of liberalized emigration policies, with more than half of the population leaving, most for
Israel and the West: Germany, the United States, Canada and Australia. For many years during this period, Russia had a higher rate of
immigration to Israel than any other country. Russia's Jewish population is still the third biggest in Europe, after France and United Kingdom. In November 2012, the
Jewish Museum and Tolerance Center, one of the world's biggest museums of Jewish history, opened in Moscow.
Early history

Jews have been present in contemporary
Armenia and
Georgia since the
Babylonian captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their defeat ...
. Records exist from the 4th century showing that there were Armenian cities possessing Jewish populations ranging from 10,000 to 30,000 along with substantial Jewish settlements in the
Crimea. The presence of Jewish people in the territories corresponding to modern Belarus, Ukraine, and the European part of Russia can be traced back to the 7thŌĆō14th centuries CE.
Under the influence of the Caucasian Jewish communities,
Bulan, the
Khagan Bek of the Turkic
Khazars, and the ruling classes of
Khazaria (located in what is now
Ukraine, southern Russia and
Kazakhstan), may have adopted and/or converted to Judaism at some point in the mid-to-late 8th or early 9th centuries. After the conquest of the Khazarian kingdom by
Sviatoslav I of Kiev
; (943 ŌĆō 26 March 972), also spelled Svyatoslav, was Grand Prince of Kiev famous for his persistent campaigns in the east and south, which precipitated the collapse of two great powers of Eastern Europe, Khazars, Khazaria and the First Bulgarian E ...
(969), the Khazar Jewish population may have assimilated or migrated in part.
Kievan Rus'
In the 11th and 12th centuries, the Jewish population may have been restricted to a separate quarter in Kiev, known as the Jewish Town (Old East Slav: ą¢ąĖą┤ąŠą▓ąĄ, ''Zhidovye'', i.e. "The Jews"), the gates probably leading to which were known as the Jewish Gates (Old East Slavic: ą¢ąĖą┤ąŠą▓čüą║ą░čÅ ą▓ąŠčĆąŠčéą░, ''Zhidovskaya vorota''). The Kievan community was oriented towards
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, ╬ÆŽģ╬Č╬¼╬ĮŽä╬╣╬┐╬Į) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
(the
Romaniotes),
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''m─üt Akkad─½'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
and
Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
in the 10th and 11th centuries, but appears to have been increasingly open to the
Ashkenazim from the 12th century on. Few products of Kievan Jewish intellectual activity exist, however.
[A. I. Pereswetoff-Morath, ''A Grin without a Cat'', vol. 2: ''Jews and Christians in Medieval Russia ŌĆō Assessing the Sources'' (Lund Slavonic Monographs, 5), Lund 2002] Other communities, or groups of individuals, are known from
Chernigov and, probably,
Volodymyr-Volynskyi. At that time, Jews were probably found also in northeastern Russia, in the domains of Prince
Andrei Bogolyubsky (1169ŌĆō1174), although it is uncertain to which degree they would have been living there permanently.
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
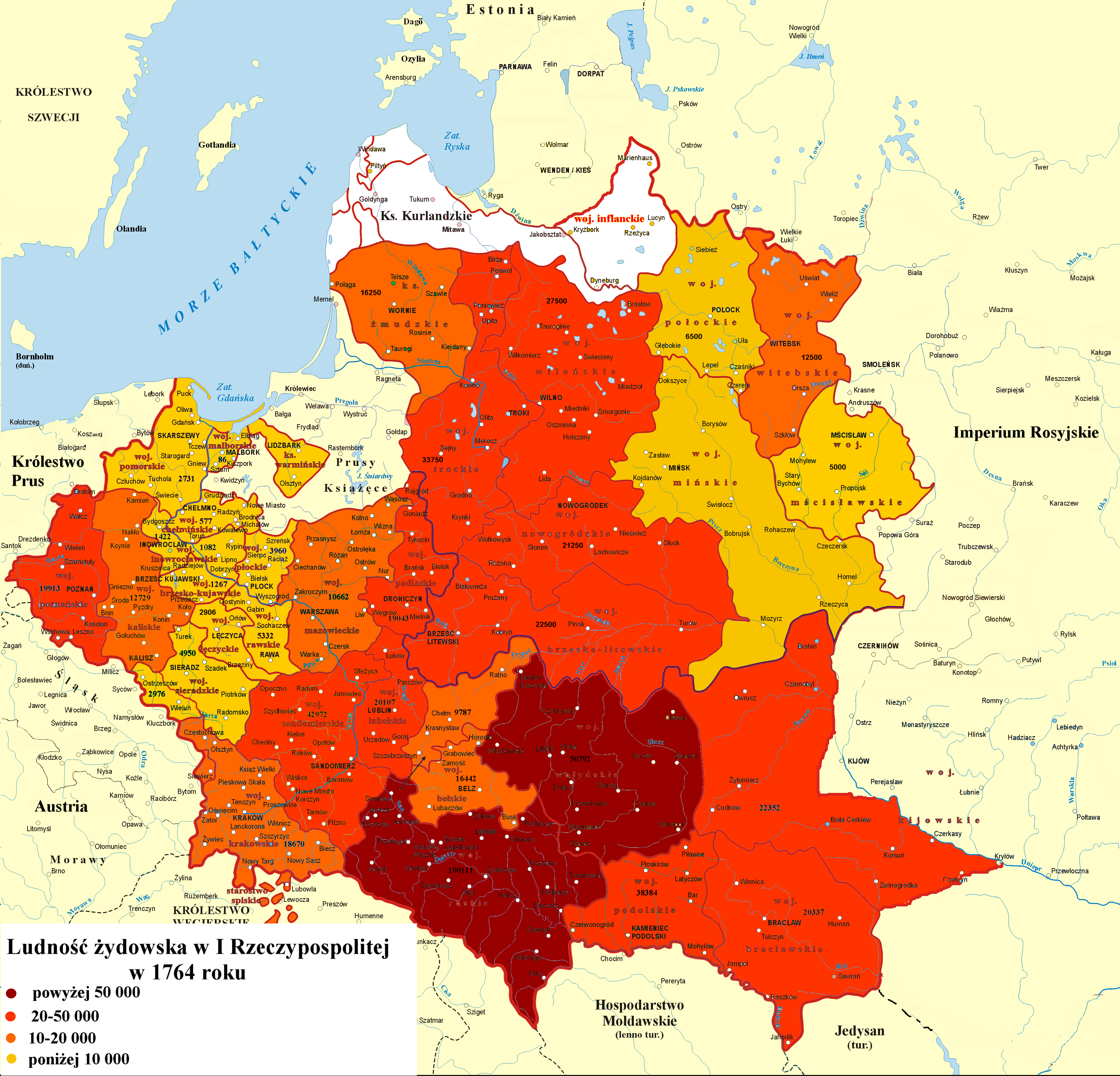
Although northeastern Russia had a low Jewish population, countries just to its west had rapidly growing Jewish populations, as waves of
anti-Jewish pogroms and expulsions from the countries of Western Europe marked the last centuries of the
Middle Ages, a sizable portion of the Jewish populations there moved to the more tolerant countries of
Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Eastern Europe, as well as the Middle East.
Expelled en masse from England, France, Spain and most other Western European countries at various times, and persecuted in Germany in the 14th century, many Western European Jews migrated to Poland upon the invitation of Polish ruler
Casimir III the Great to settle in Polish-controlled areas of Eastern Europe as a
third estate, although restricted to commercial, middleman services in an agricultural society for the Polish king and nobility between 1330 and 1370, during the reign of Casimir the Great.
After settling in Poland (later
PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth) and
Hungary (later
Austria-Hungary), the population expanded into the lightly populated areas of
Ukraine and
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, which were to become part of the expanding Russian Empire. In 1495,
Alexander the Jagiellonian expelled Jewish residents from
Grand Duchy of Lithuania, but reversed his decision in 1503.
In the ''
shtetls'' populated almost entirely by Jews, or in the middle-sized town where Jews constituted a significant part of population, Jewish communities traditionally ruled themselves according to
halakha, and were limited by the privileges granted them by local rulers. (See also
Shtadlan). These Jews were not assimilated into the larger eastern European societies, and identified as an
ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
with a unique set of religious beliefs and practices, as well as an ethnically unique economic role.
Tsardom of Russia

Documentary evidence as to the presence of Jews in
Muscovite Russia is first found in the chronicles of 1471. The relatively small population of them were subject to discriminatory laws, but these laws do not appear to have been enforced at all times. Jews residing in Russian and Ukrainian towns suffered numerous religious persecutions. Converted Jews occasionally rose to important positions in the Russian State, for example
Peter Shafirov, vice-chancellor under
Peter the Great
Peter I ( ŌĆō ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Aleks├®yevich ( rus, ą¤čæčéčĆ ąÉą╗ąĄą║čüąĄ╠üąĄą▓ąĖčć, p=╦łp╩▓╔Ątr ╔Él╩▓╔¬╦łks╩▓ej╔¬v╩▓╔¬t╔Ģ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
. Shafirov came,
as most Russian Jews after the fall of the
PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth in 1795, from a Jewish family of Polish origin. He had extraordinary knowledge of foreign languages and served as the chief translator in the Russian Foreign Office, subsequently he began to accompany Tsar Peter on his international travels. Following this, he was raised to the rank of vice-chancellor because of his many diplomatic talents and skills, but was later imprisoned, sentenced to death, and eventually banished.
Russian Empire


Their situation changed radically, during the reign of
Catherine II, when the
Russian Empire acquired rule over large Lithuanian and Polish territories which historically included a high proportion of Jewish residents, especially during the second (1793) and the third (1795)
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
. Under the Commonwealth's legal system, Jews endured economic restrictions euphemised as "
disabilities
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, se ...
", which also continued following the Russian occupation. Catherine established the
Pale of Settlement, which included
Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It w ...
, Lithuania, Ukraine, and the
Crimea (the latter was later excluded). Jewish people were restricted to residence within the Pale and were required to obtain special permission to immigrate into other parts of Russia. Within the Pale, the Jewish residents were given right of voting in municipal elections, but their vote was limited to one third of the total number of voters, even though their proportion in many areas was much higher, even a majority. This served to provide an aura of democracy, while institutionalizing conflict amongst ethnic groups on a local level.
Jewish communities in Russia were governed internally by local administrative bodies, called the Councils of Elders (''
Qahal'', ''
Kehilla''), constituted in every town or hamlet possessing a Jewish population. The Councils of Elders had jurisdiction over Jews in matters of internal litigation, as well as fiscal transactions relating to the collection and payment of taxes (
poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
,
land tax
A land value tax (LVT) is a levy on the value of land without regard to buildings, personal property and other improvements. It is also known as a location value tax, a point valuation tax, a site valuation tax, split rate tax, or a site-value r ...
, etc.). Later, this right of collecting taxes was much abused; in 1844 the civil authority of the Councils of Elders over its Jewish population was abolished.
Under Alexander I and Nicholas I, decrees were put forth requiring a Russian-speaking member of a Jewish community to be named to act as an intermediary between his community and the Imperial government to perform certain civil duties, such as registering births, marriages, and divorces. This position came to be known as the
crown rabbi although they were not always rabbis and often were not respected by members of their own communities because their main job qualification was fluency in Russian, and they often had no education in, or knowledge of Jewish law.
The beginning of the 19th century was marked by intensive movement of Jews to
Novorossiya, where towns, villages and
agricultural colonies rapidly sprang up.
Forcible conscription of Jewish cantonists

The 'decree of August 26, 1827' made Jews liable for military service, and allowed their conscription between the ages of twelve and twenty-five. Each year, the Jewish community had to supply four recruits per thousand of the population. However, in practice, Jewish children were often conscripted as young as eight or nine years old. At the age of twelve, they would be placed for their six-year military education in cantonist schools. They were then required to serve in the Imperial Russian army for 25 years after the completion of their studies, often never seeing their families again. Strict quotas were imposed on all communities and the ''qahals'' were given the unpleasant task of implementing conscription within the Jewish communities. Since the merchant-
guild members, agricultural colonists, factory mechanics, clergy, and all Jews with secondary education were exempt, and the wealthy
bribed their way out of having their children conscripted, fewer potential conscripts were available; the adopted policy deeply sharpened internal Jewish social tensions. Seeking to protect the socio-economic and religious integrity of Jewish society, the ''qahals'' did their best to include ŌĆ£non-useful JewsŌĆØ in the draft lists so that the heads of tax-paying middle-class families were predominantly exempt from conscription, whereas single Jews, as well as "heretics" (
Haskalah influenced individuals), paupers, outcasts, and orphaned children were drafted. They used their power to suppress protests and intimidate potential informers who sought to expose the arbitrariness of the ''qahal'' to the Russian government. In some cases, communal elders had the most threatening informers murdered (such as the
Ushitsa case, 1836).
The zoning rule was suspended during the
Crimean War, when conscription became annual. During this period the ''qahals'' leaders would employ informers and kidnappers (Russian: "", , yi,
khappers, script=Latn), as many potential conscripts preferred to run away rather than voluntarily submit. In the case of unfulfilled quotas, younger Jewish boys of eight and even younger were frequently taken. The official Russian policy was to encourage the
conversion of Jewish cantonists to the
state religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular state, secular, is not n ...
of
Orthodox Christianity and Jewish boys were coerced to
baptism. As
kosher
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, yi, ūøų╝ū®ū©), fro ...
food was unavailable, they were faced with the necessity of abandoning of
Jewish dietary laws. Polish
Catholic boys were subject to similar pressure to convert and assimilate as the Russian Empire was hostile to Catholicism and Polish nationalism.
Haskalah in the Russian Empire

The cultural and habitual isolation of the Jews gradually began eroding. An ever-increasing number of Jewish people adopted Russian customs and the Russian language. Russian education was spread among the Jewish population. A number of Jewish-Russian periodicals appeared.
Alexander II was known as the "Tsar liberator" for the 1861
abolition of serfdom in Russia. Under his rule Jewish people could not hire Christian servants, could not own land, and were restricted in travel.
Alexander III was a staunch reactionary and an antisemite (influenced by
Pobedonostsev) who strictly adhered to the old
doctrine of
Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality. His escalation of anti-Jewish policies sought to ignite "popular antisemitism", which portrayed the Jews as "
Christ-killers
Jewish deicide is the notion that the Jews as a people were Collective responsibility, collectively responsible for Crucifixion of Jesus, the killing of Jesus. A Biblical justification for the charge of Jewish deicide is derived from Matthew 27:2 ...
" and the oppressors of the Slavic, Christian victims.

A large-scale wave of
anti-Jewish pogroms
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
swept Ukraine in 1881, after Jews were
scapegoated
Scapegoating is the practice of singling out a person or group for unmerited blame and consequent negative treatment. Scapegoating may be conducted by individuals against individuals (e.g. "he did it, not me!"), individuals against groups (e.g., ...
for the assassination of Alexander II. In the 1881 outbreak, there were pogroms in 166 Ukrainian towns, thousands of Jewish homes were destroyed, many families reduced to extremes of poverty; large numbers of men, women, and children were injured and some killed. Disorders in the south once again recalled the government attention to the Jewish question. A conference was convened at the Ministry of Interior and on May 15, 1882, so-called ''Temporary Regulations'' were introduced that stayed in effect for more than thirty years and came to be known as the
May Laws.


The repressive legislation was repeatedly revised. Many historians noted the concurrence of these state-enforced antisemitic policies with waves of pogroms that continued until 1884, with at least tacit government knowledge and in some cases policemen were seen inciting or joining the mob.
The systematic policy of discrimination banned Jewish people from rural areas and towns of fewer than ten thousand people, even within the Pale, assuring the slow death of many
shtetls. In 1887, the
quotas placed on the number of Jews allowed into secondary and higher education were tightened down to 10% within the Pale, 5% outside the Pale, except Moscow and Saint Petersburg, held at 3%, even though the Jewish population was a majority or plurality in many communities. It was possible to evade these restrictions upon secondary education by combining private tuition with examination as an "outside student". Accordingly, within the Pale such outside pupils were almost entirely young Jews. The restrictions placed on education, traditionally highly valued in Jewish communities, resulted in ambition to excel over the peers and increased emigration rates. Special quotas restricted Jews from entering profession of law, limiting number of Jews admitted to the bar.
In 1886, an Edict of Expulsion was enforced on the historic Jewish population of
Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
. Most Jews were expelled from Moscow in 1891 (except few deemed
useful) and a newly built synagogue was closed by the city's authorities headed by the Tsar's brother. Tsar Alexander III refused to curtail repressive practices and reportedly noted: "But we must never forget that the Jews have crucified our Master and have shed his precious blood."
In 1892, new measures banned Jewish participation in local elections despite their large numbers in many towns of the Pale. The ''Town Regulations'' prohibited Jews from the right to elect or be elected to town
Dumas. Only a small number of Jews were allowed to be members of a town Duma, through appointment by special committees.


During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the Russian Empire had not only the largest Jewish population in the world, but actually a majority of the world's Jews living within its borders. In 1897, according to
Russian census of 1897
The first general census of the population of the Russian Empire in 1897 (Russian alphabet#Letters eliminated in 1917–18, pre-reform Russian: ) was the first and only nation-wide census performed in the Russian Empire (the Grand Duchy of Fi ...
, the total Jewish population of Russia was 5,189,401 persons of both sexes (4.13% of total population). Of this total, 93.9% lived in the 25 provinces of the
Pale of Settlement. The total population of the Pale of Settlement amounted to 42,338,367ŌĆöof these, 4,805,354 (11.5%) were Jews.
About 450,000 Jewish soldiers served in the Russian Army during
World War I, and fought side by side with their Slavic fellows. When hundreds of thousands of refugees from Poland and Lithuania, among them innumerable Jews, fled in terror before enemy invasion, the Pale of Settlement de facto ceased to exist. Most of the education restrictions on the Jews were removed with the appointment of count
Pavel Ignatiev
Count Pavel Nikolayevich Ignatiev (russian: ą¤ą░ą▓ąĄą╗ ąØąĖą║ąŠą╗ą░ąĄą▓ąĖčć ąśą│ąĮą░čéčīąĄą▓, sometimes rendered in English as Paul Ignatieff; June 30/July 12, 1870 – August 12, 1945) was an Imperial Russian politician who served as Educatio ...
as Minister of Education.
Mass emigration

Even though the persecutions provided the impetus for mass emigration, there were other relevant factors that can account for the Jews' migration. After the first years of large emigration from Russia, positive feedback from the emigrants in the U.S. encouraged further emigration. Indeed, more than two million Jews fled Russia between 1880 and 1920. While a large majority emigrated to the United States, some turned to Zionism. In 1882, members of
Bilu
Bilu may refer to:
People
* Bil├║ (footballer, 1900-1965), Virg├Łlio Pinto de Oliveira, Brazilian football manager and former centre-back
* Asher Bilu (born 1936), Australian artist
* Bil├║ (footballer, born 1974), Luciano Lopes de Souza, Brazi ...
and
Hovevei Zion made what came to be known the
First Aliyah to
Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, then a part of the
Ottoman Empire.
The Tsarist government sporadically encouraged Jewish emigration. In 1890, it approved the establishment of "The Society for the Support of Jewish Farmers and Artisans in
Syria
Syria ( ar, ž│┘Å┘łž▒┘É┘Ŗ┘Äž¦ or ž│┘Å┘łž▒┘É┘Ŗ┘Äž®, translit=S┼½riy─ü), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, ž¦┘äž¼┘ģ┘ć┘łž▒┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž©┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž│┘łž▒┘Ŗž®, al-Jumh┼½r─½yah al-╩╗Arab─½yah as-S┼½r─½yah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and
Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
" (known as the "
Odessa Committee" headed by Leon Pinsker) dedicated to practical aspects in establishing
agricultural Jewish settlements in Palestine.
Jewish members of the Duma

In total, there were at least twelve Jewish deputies in the First
Duma (1906ŌĆō1907), falling to three or four in the Second Duma (February 1907 to June 1907), two in the Third Duma (1907ŌĆō1912) and again three in the fourth, elected in 1912. Converts to Christianity like
Mikhail Herzenstein and
Ossip Pergament Ossip (russian: ą×čüąĖą┐) may refer to:
*Ossip Bernstein (1882ŌĆō1962), Russian chess grandmaster and a financial lawyer
*Ossip Brik, also known as Osip Brik, (1888ŌĆō1945), Russian avant garde writer and literary critic
*Ossip Dimov, also known as ...
were still considered as Jews by the public (and antisemitic) opinion and are most of the time included in these figures.
At the 1906 elections, the
Jewish Labour Bund
The General Jewish Labour Bund in Lithuania, Poland and Russia ( yi, ŌĆÅūÉųĘū£ūÆūóū×ū▓ūĀūóū© ūÖūÖų┤ūōūÖū®ūóū© ūÉųĘū©ūæūóūśūóū©ųŠūæūĢūĀūō ūÉūÖū¤ ū£ūÖūśūó, ūżų╝ū▒ū£ū¤ ūÉūĢū¤ ū©ūĢūĪū£ūÉųĘūĀūō , translit=Algemeyner Yidisher Arbeter-bund in Lite, Poy ...
had made an electoral agreement with the Lithuanian Labourers' Party (''
Trudoviks''), which resulted in the election to the Duma of two (non-Bundist) candidates in the Lithuanian provinces: Dr.
Shmaryahu Levin for the
Vilnius province and
Leon Bramson for the
Kaunas
Kaunas (; ; also see other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai ...
province.
Among the other Jewish deputies were
Maxim Vinaver, chairman of the League for the Attainment of Equal Rights for the Jewish People in Russia (''
Folksgrupe'') and cofounder of the
Constitutional Democratic Party (''Kadets''), Dr.
Nissan Katzenelson (
Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kur─üm┼Ź; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: ąÜčāčĆą╗čÅąĮą┤ąĖčÅ; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kur┼Īas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. ...
province, Zionist, ''Kadet''), Dr.
Moisei Yakovlevich Ostrogorsky
Moisey Yakovlevich Ostrogorsky (also Moisei Ostrogorsky; russian: ą£ąŠąĖčüąĄ╠üą╣ ą»╠üą║ąŠą▓ą╗ąĄą▓ąĖčć ą×čüčéčĆąŠą│ąŠ╠üčĆčüą║ąĖą╣, Moisey Yakovlevich Ostrogorskiy; be, ą£ą░ą╣čüąĄą╣ ą»ą║ą░č׹╗ąĄą▓ičć AčüčéčĆaą│ąŠčĆčüą║i, Majsiej Jaka┼Łlievi─Ź Ast ...
(
Grodno
Grodno (russian: ąōčĆąŠą┤ąĮąŠ, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, ąōčĆąŠą┤ąĮą░ ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
province), attorney
Simon Yakovlevich Rosenbaum (
Minsk province, Zionist, ''Kadet''),
Mikhail Isaakovich Sheftel
Mikhail Isaakovich Sheftel (1862ŌĆō1919) was a Russian Jewish lawyer, member of the First Duma of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large par ...
(
Ekaterinoslav province, ''Kadet''), Dr.
Grigory Bruk Grigory, Grigori and Grigoriy are Russian masculine given names.
It may refer to watcher angels or more specifically to the egrßĖŚgoroi or Watcher angels.
Grigory
* Grigory Baklanov (1923ŌĆō2009), Russian novelist
* Grigory Barenblatt (1927201 ...
, Dr.
Benyamin Yakubson Benyamin may refer to
* Benyamin Bahadori, Iranian singer
* Benyamin (writer), pen name of Benny Daniel, Indian writer
* Benyamin Sueb, Indonesian Comedian, actor, singer. See also
*Benjamin (disambiguation) Benjamin is a figure in the Hebrew B ...
,
Zakhar Frenkel Zakhar (russian: ąŚą░čģą░čĆ) is a given name, the East Slavic form of the biblical name Zechariah or Zachary. Notable people with the name include:
*Zakhar Arzamastsev (born 1992), Russian ice hockey player
*Zakhar Bron (born 1947), Russian violi ...
,
Solomon Frenkel
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, ž│┘Å┘ä┘Ä┘Ŗ┘Æ┘ģ┘Äž¦┘å, ', , ; el, ╬Ż╬┐╬╗╬┐╬╝ŽÄ╬Į, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah ( Hebrew: , Modern: , Tiberian: ''Y─āßĖÅ─½ßĖÅ─āy─üh'', "beloved of Yah"), was a monarch of ancient Israel and the son and succes ...
,
Meilakh Chervonenkis.
There was also a Crimean Karaim deputy,
Salomon Krym
Solomon Samuilovich Krym (Russian: ąĪąŠą╗ąŠą╝ąŠąĮ ąĪą░ą╝ąŠą╣ą╗ąŠą▓ąĖčć ąÜčĆčŗą╝; 1864 – 1936) was a Crimean politician, statesman and agronomist of Crimean Karaite origin.
He was elected in 1906 to the First Duma (1906–07) as a ''Kade ...
.
Three of the Jewish deputies, Bramson, Chervonenkis and Yakubson, joined the Labour faction; nine others joined the Kadet fraction.
According to Rufus Learsi, five of them were Zionists, including Dr.
Shmaryahu Levin, Dr.
Victor Jacobson
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to:
* Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname
Arts and entertainment
Film
* ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film
* ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French shor ...
and
Simon Yakovlevich Rosenbaum.
Two of them,
Grigori Borisovich Iollos Grigory, Grigori and Grigoriy are Russian language, Russian masculine given names.
It may refer to watcher angels or more specifically to Watcher (angel)#Grigori, the egrßĖŚgoroi or Watcher angels.
Grigory
* Grigory Baklanov (1923ŌĆō2009), Russ ...
(
Poltava
Poltava (, ; uk, ą¤ąŠą╗čéą░ą▓ą░ ) is a city located on the Vorskla River in central Ukraine. It is the capital city of the Poltava Oblast (province) and of the surrounding Poltava Raion (district) of the oblast. Poltava is administratively ...
province) and
Mikhail Herzenstein (b. 1859, d. 1906 in
Terijoki), both from the Constitutional Democratic Party, were assassinated by the
Black Hundreds
The Black Hundred (russian: ą¦čæčĆąĮą░čÅ čüąŠčéąĮčÅ, translit=Chornaya sotnya), also known as the black-hundredists (russian: č湥čĆąĮąŠčüąŠč鹥ąĮčåčŗ; chernosotentsy), was a reactionary, monarchist and ultra-nationalist movement in Russia in t ...
antisemite terrorist group. "The ''Russkoye Znamya'' declares openly that 'Real Russians' assassinated Herzenstein and Iollos with knowledge of officials, and expresses regret that only two Jews perished in crusade against revolutionaries.
The Second Duma included seven Jewish deputies:
Shakho Abramson,
Iosif Gessen,
Vladimir Matveevich Gessen
Vladimir Matveevich Gessen (russian: ąÆą╗ą░ą┤ąĖ╠üą╝ąĖčĆ ą£ą░čéą▓ąĄ╠üąĄą▓ąĖčć ąōąĄ╠üčüčüąĄąĮ; ŌĆō 14 January 1920) was a Russian jurist and politician. He was the country's first theoretician of constitutional law and was instrumental for the spre ...
,
Lazar Rabinovich
Lazar may refer to:
* Lazar (name), any of various persons with this name
* Lazar BVT, Serbian mine resistant, ambush-protected, armoured vehicle
* Lazar 2, Serbian armored vehicle
* Lazar 3, Serbian armored van
* Laz─ār, a tributary of the river ...
,
Yakov Shapiro Yakov (alternative spellings: Jakov or Iakov, cyrl, ą»ą║ąŠą▓) is a Russian or Hebrew variant of the given names Jacob and James. People also give the nickname Yasha ( cyrl, ą»čłą░) or Yashka ( cyrl, ą»čłą║ą░) used for Yakov.
Notable people
People ...
(all of them Kadets) and
Avigdor Mandelberg
Avigdor ( he, ūÉų▓ūæų┤ūÖūÆų░ūōūĢų╣ū©) a small moshav in southern Israel. Located south of Kiryat Malakhi and 11 km north of Kiryat Gat and covering 3.75 km┬▓, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In its ...
(
Siberia Social Democrat),
plus a convert to Christianity, the attorney
Ossip Pergament Ossip (russian: ą×čüąĖą┐) may refer to:
*Ossip Bernstein (1882ŌĆō1962), Russian chess grandmaster and a financial lawyer
*Ossip Brik, also known as Osip Brik, (1888ŌĆō1945), Russian avant garde writer and literary critic
*Ossip Dimov, also known as ...
(
Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
).
The two Jewish members of the Third Duma were the Judge
Leopold Nikolayevich (or Lazar) Nisselovich (
Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kur─üm┼Ź; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: ąÜčāčĆą╗čÅąĮą┤ąĖčÅ; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kur┼Īas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. ...
province, Kadet) and
Naftali Markovich Friedman (
Kaunas
Kaunas (; ; also see other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai ...
province, Kadet). Ossip Pergament was reelected and died before the end of his mandate.
Friedman was the only one reelected to the Fourth Duma in 1912, joined by two new deputies,
Meer Bomash
Meer may refer to:
*Fatima Meer (1928ŌĆō2010), South African writer and anti-apartheid activist
*Johnny Vander Meer (1914ŌĆō1997), American baseball pitcher, famed for pitching two consecutive no-hitters
*Mark Meer, Canadian actor and writer
*, So ...
, and Dr.
Ezekiel Gurevich
Ezekiel (; he, ūÖų░ūŚųČū¢ų░ū¦ųĄūÉū£ ''Y╔ÖßĖźezq─ō╩Šl'' ; in the Septuagint written in grc-koi, ß╝Ė╬Ą╬Č╬Ą╬║╬╣╬«╬╗ ) is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible.
In Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, Ezekiel is ackn ...
.
Jews in the revolutionary movement

Many Jews were prominent in Russian revolutionary parties. The idea of overthrowing the Tsarist regime was attractive to many members of the Jewish
intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the in ...
because of the oppression of non-Russian nations and non-
Orthodox Christians
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Churc ...
within the
Russian Empire. For much the same reason, many non-Russians, notably
Latvians or
Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
, were disproportionately represented in the party leaderships.
In 1897
General Jewish Labour Bund
The General Jewish Labour Bund in Lithuania, Poland and Russia ( yi, ŌĆÅūÉųĘū£ūÆūóū×ū▓ūĀūóū© ūÖūÖų┤ūōūÖū®ūóū© ūÉųĘū©ūæūóūśūóū©ųŠūæūĢūĀūō ūÉūÖū¤ ū£ūÖūśūó, ūżų╝ū▒ū£ū¤ ūÉūĢū¤ ū©ūĢūĪū£ūÉųĘūĀūō , translit=Algemeyner Yidisher Arbeter-bund in Lite, Poy ...
(The Bund), was formed. Many Jews joined the ranks of two principal revolutionary parties:
Socialist-Revolutionary Party and
Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP; in , ''Rossiyskaya sotsial-demokraticheskaya rabochaya partiya (RSDRP)''), also known as the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party or the Russian Social Democratic Party, was a socialist pol ...
ŌĆöboth
Bolshevik and
Menshevik
The Mensheviks (russian: ą╝ąĄąĮčīčłąĄą▓ąĖą║ąĖ╠ü, from ą╝ąĄąĮčīčłąĖąĮčüčéą▓ąŠ 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries.
The factions eme ...
factions. A notable number of Bolshevik party members were ethnically Jewish, especially in the leadership of the party, and the percentage of Jewish party members among the rival Mensheviks was even higher. Both the founders and leaders of Menshevik faction,
Julius Martov
Julius Martov or L. Martov (ą£ą░╠üčĆč鹊ą▓; born Yuliy Osipovich Tsederbaum; 24 November 1873 ŌĆō 4 April 1923) was a politician and revolutionary who became the leader of the Mensheviks in early 20th-century Russia. He was arguably the closes ...
and
Pavel Axelrod, were Jewish.
Because some of the leading Bolsheviks were
Ethnic Jews, and
Bolshevism supports a policy of promoting international proletarian revolutionŌĆömost notably in the case of
Leon TrotskyŌĆömany enemies of Bolshevism, as well as contemporary antisemites, draw a picture of Communism as a political slur at Jews and accuse Jews of pursuing Bolshevism to benefit Jewish interests, reflected in the terms
Jewish Bolshevism or ''Judeo-Bolshevism''. The original
atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
ic and internationalistic ideology of the Bolsheviks (''See
proletarian internationalism,
bourgeois nationalism'') was incompatible with Jewish traditionalism. Bolsheviks such as Trotsky echoed sentiments dismissing Jewish heritage in place of "internationalism".
Soon after seizing power, the Bolsheviks established the
Yevsektsiya, the Jewish section of the
Communist party in order to destroy the rival Bund and
Zionist parties, suppress
Judaism and replace traditional Jewish culture with "proletarian culture".

In March 1919,
Vladimir Lenin delivered a speech "On Anti-Jewish Pogroms" on a
gramophone
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
disc. Lenin sought to explain the phenomenon of antisemitism in
Marxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
terms. According to Lenin, antisemitism was an "attempt to divert the hatred of the workers and peasants from the exploiters toward the Jews". Linking antisemitism to class struggle, he argued that it was merely a political technique used by the tsar to exploit religious fanaticism, popularize the despotic, unpopular regime, and divert popular anger toward a scapegoat. The Soviet Union also officially maintained this Marxist-Leninist interpretation under
Joseph Stalin, who expounded Lenin's critique of antisemitism. However, this did not prevent the widely publicized repressions of Jewish intellectuals during 1948ŌĆō1953 when Stalin increasingly associated Jews with "cosmopolitanism" and pro-Americanism.
Jews were prominent in the Russian
Constitutional Democrat Party
)
, newspaper = ''Rech''
, ideology = ConstitutionalismConstitutional monarchismLiberal democracyParliamentarism Political pluralismSocial liberalism
, position = Centre to centre-left
, international =
, colours ...
,
Russian Social Democratic Party (
Mensheviks) and
Socialist-Revolutionary Party. The Russian Anarchist movement also included many prominent Jewish revolutionaries. In Ukraine,
Makhnovist
The Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine ( uk, ąĀąĄą▓ąŠą╗čÄčåč¢ą╣ąĮą░ ą¤ąŠą▓čüčéą░ąĮčüčīą║ą░ ąÉčĆą╝č¢čÅ ąŻą║čĆą░茹ĮąĖ), also known as the Black Army or as Makhnovtsi ( uk, ą£ą░čģąĮąŠą▓čåč¢), named after their leader Nestor Makhno, was a ...
anarchist leaders also included several Jews.
The attempts of the socialist Bund to be the sole representative of the Jewish worker in Russia had always conflicted with Lenin's idea of a universal coalition of workers of all nationalities. Like some other socialist parties in Russia, the Bund was initially opposed to the Bolsheviks' seizing of power in 1917 and to the dissolution of the
Russian Constituent Assembly. Consequently, the Bund suffered repressions in the first months of the Soviet regime. However, the antisemitism of many Whites during the
Russian Civil War caused many if not most Bund members to readily join the Bolsheviks, and most of the factions eventually merged with the Communist Party. The movement did split in three; the Bundist identity survived in interwar
Poland, while many Bundists joined the Mensheviks.
Dissolution and seizure of Jewish properties and institutions
In August 1919 Jewish properties, including synagogues, were seized and many Jewish communities were dissolved. The anti-religious laws against all expressions of religion and religious education were imposed upon the Jewish population, just like on other religious groups. Many Rabbis and other religious officials were forced to resign from their posts under the threat of violent persecution. This type of persecution continued on into the 1920s.
In 1921, a large number of Jews opted for Poland, as they were entitled by the
peace treaty in Riga to choose the country they preferred. Several hundred thousand joined the already numerous
Jewish population of Poland.
The chaotic years of World War I, the February and October Revolutions, and the Civil War were fertile ground for the antisemitism that was endemic to tsarist Russia. During the World War, Jews were often accused of sympathizing with Germany and often persecuted.
Pogroms were unleashed throughout the Russian Civil War, perpetrated by virtually every competing faction, from Polish and Ukrainian nationalists to the Red and White Armies. 31,071 civilian Jews were killed during documented pogroms throughout the former
Russian Empire; the number of Jewish orphans exceeded 300,000. A majority of pogroms in Ukraine during 1918ŌĆō1920 were perpetrated by the Ukrainian nationalists, miscellaneous bands and anti-Communist forces.
[ Henry Abramson, Jewish Representation in the Independent Ukrainian Governments of 1917ŌĆō1920, ''Slavic review'', Vol. 50, No. 3 (Autumn, 1991), pp. 542ŌĆō550]
Soviet Union
Before World War II
Continuing the policy of the Bolsheviks before the Revolution, Lenin and the Bolshevik Party strongly condemned the pogroms, including official denunciations in 1918 by the Council of People's Commissars. Opposition to the pogroms and to manifestations of Russian antisemitism in this era were complicated by both the official Bolshevik policy of assimilationism towards all national and religious minorities, and concerns about overemphasizing Jewish concerns for fear of exacerbating popular antisemitism, as the White forces were openly identifying the Bolshevik regime with Jews.
Lenin recorded eight of his speeches on gramophone records in 1919. Only seven of these were later re-recorded and put on sale. The one suppressed in the
Nikita Khrushchev era recorded Lenin's feelings on antisemitism:
Despite the Soviet state's official opposition to antisemitism, the spring of 1918 saw widespread anti-Jewish violence perpetrated by members of the
Red Guard in the former
Pale of Settlement. In February 1918, as Russian forces advanced on the capital of
Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, ąĪą░ąĮą║čé-ą¤ąĄč鹥čĆą▒čāčĆą│, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=╦łsankt p╩▓╔¬t╩▓╔¬r╦łburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914ŌĆō1924) and later Leningrad (1924ŌĆō1991), i ...
, the Soviet government signed the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, which stipulated that Russia would withdraw from
World War I and cede large swaths of territory in eastern Russia to the German Empire. Even after the signing of the treaty, however, the Germans continued to advance and seize territory, as the Soviets had no choice but to retreat across the Ukraine. At this point in the war, the
Red Guard comprised mostly untrained workers and peasants with no overarching command structure, leaving the state with virtually no control over the volunteer forces. Between March and May of 1918, various Red Guard squadrons, embittered by their military defeat and animated by revolutionary sentiment, attacked Jews in cities and towns across the
Chernihiv region of the Ukraine. One of the most brutal instances of this violence occurred in the city of
Novhorod-Siverskyi, where it was reported that 88 Jews were killed and 11 injured in a pogrom incited by Red Guard soldiers. Similarly, after the successful capture of the city of
Hlukhiv, the Red Guard murdered at least 100 Jews, whom the soldiers accused of being 'exploiters of the proletariat.' In all, Jewish activist
Nahum Gergel
Nahum Gergel (April 4, 1887 ŌĆō November 18, 1931) was a Jewish rights activist, humanitarian, sociologist, and author in Yiddish. Nahum Gergel is best known for his thorough statistical studies of anti-Jewish atrocities ( pogroms) that took pla ...
estimated that the Red forces were responsible for about 8.6% of pogroms during the years 1918-1922, while Ukrainian and
White Army forces were responsible for 40% and 17.2%, respectively.

Lenin was supported by the
Labor Zionist (
Poale Zion) movement, then under the leadership of Marxist theorist
Ber Borochov
Dov Ber Borochov (russian: ąöąŠą▓-ąæąĄčĆ ąæąŠčĆąŠčģąŠą▓; 3 July 1881 ŌĆō 17 December 1917) was a Marxist Zionist and one of the founders of the Labor Zionist movement. He was also a pioneer in the study of the Yiddish language.
Biogr ...
, which was fighting for the creation of a Jewish workers' state in
Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
and also participated in the October Revolution (and in the Soviet political scene afterwards until being banned by Stalin in 1928). While Lenin remained opposed to outward forms of
antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
(and all forms of racism), allowing Jewish people to rise to the highest offices in both party and state, certain historians such as
Dmitri Volkogonov argue that the record of his government in this regard was highly uneven. A former official Soviet historian (turned staunch anti-communist), Volkogonov claims that Lenin was aware of pogroms carried out by units of the Red Army during the war with Poland, particularly those carried out by Semyon
Budyonny's troops, though the whole issue was effectively ignored. Volkogonov writes that "While condemning anti-Semitism in general, Lenin was unable to analyze, let alone eradicate, its prevalence in Soviet society".
[Dmitrij Volkogonov: ''Lenin. Po─Ź├Ītek teroru.'' Dialog, Liberec 1996, p. 173] Likewise, the hostility of the Soviet regime towards all religion made no exception for
Judaism, and the 1921 campaign against religion saw the seizure of many synagogues (whether this should be regarded as antisemitism is a matter of definitionŌĆösince Orthodox churches received the same treatment). In any event, there was still a fair degree of tolerance for Jewish religious practice in the 1920s: in the Belarusian capital Minsk, for example, of the 657 synagogues existing in 1917, 547 were still functioning in 1930.

According to
Zvi Gitelman Zvi Gitelman is a Professor of Political Science, and Professor of Judaic Studies at the University of Michigan.
Career
Gitelman received a Ph.D., an M.A., and a B.A. degree from Columbia University. He has usually written about the connection of ...
: "Never before in Russian historyŌĆöand never subsequently has a government made such an effort to uproot and stamp out antisemitism."
By contrast with the situation after the beginning of forced collectivization and breakneck industrialization at the end of the 1920s, the New Economic Policy of 1921ŌĆō1928 also offered economic opportunities to Soviet Jewish traders and artisans. Because most non-Jewish capitalists had fled during the civil war, Jews played a disproportionate role among the 'Nepmen' who constituted the private sector in the 1920s. From the 1930s, however, Soviet laws offered hardly any economic independence to artisans, and none whatever to traders. For many Jewish artisans and tradesmen, Soviet policies led to loss of their property and trade.

According to the
census of 1926, the total number of Jews in the USSR was 2,672,398ŌĆöof whom 59% lived in
Ukrainian SSR, 15.2% in
Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, ąæąĄą╗ą░čĆčāčüą║ą░čÅ ąĪą░ą▓ąĄčåą║ą░čÅ ąĪą░čåčŗčÅą╗č¢čüčéčŗčćąĮą░čÅ ąĀčŹčüą┐čāą▒ą╗č¢ą║ą░, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalisty─Źnaja Respublika; russian: ąæąĄą╗ąŠčĆč ...
, 22% in
Russian SFSR and 3.8% in other Soviet republics.

Russian Jews were long considered to be a non-native
Semitic
Semitic most commonly refers to the Semitic languages, a name used since the 1770s to refer to the language family currently present in West Asia, North and East Africa, and Malta.
Semitic may also refer to:
Religions
* Abrahamic religions
** ...
ethnic group among the
Slavic Russians, and such categorization was solidified when ethnic minorities in the
Soviet Union were categorized according to ethnicity (). In his 1913 theoretical work ''
Marxism and the National Question'', Stalin described Jews as "not a living and active nation, but something mystical, intangible and supernatural. For, I repeat, what sort of nation, for instance, is a Jewish nation which consists of Georgian, Daghestanian, Russian, American and other Jews, the members of which do not understand each other (since they speak different languages), inhabit different parts of the globe, will never see each other, and will never act together, whether in time of peace or in time of war?!" According to Stalin, who became the
People's Commissar for Nationalities Affairs after the revolution, to qualify as a nation, a minority was required to have a culture, a language, and a homeland.
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
, rather than Hebrew, would be the
national language, and
proletarian socialist literature and arts would replace Judaism as the quintessence of culture. The use of Yiddish was strongly encouraged in the 1920s in areas of the USSR with substantial Jewish populations, especially in the Ukrainian and Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republics. Yiddish was one of the Belarusian SSR's four official languages, alongside Belarusian, Russian, and Polish. The equality of the official languages was taken seriously. A visitor arriving at main train station of the Belarusian capital Minsk saw the city's name written in all four languages above the main station entrance. Yiddish was a language of newspapers, magazines, book publishing, theater, radio, film, the post office, official correspondence, election materials, and even a Central Jewish Court. Yiddish writers like Sholem Aleichem and Mendele Mocher Seforim were celebrated in the 1920s as Soviet Jewish heroes.
Minsk had a public, state-supported Yiddish-language school system, extending from kindergarten to the Yiddish-language section of the Belarusian State University. Although Jewish students tended to switch to studying in Russian as they moved on to secondary and higher education, 55.3 percent of the city's Jewish primary school students attended Yiddish-language schools in 1927. At its peak, the Soviet Yiddish-language school system had 160,000 students in it.
Such was the prestige of Minsk's Yiddish scholarship that researchers trained in Warsaw and Berlin applied for faculty positions at the university. All this leads historian Elissa Bemporad to conclude that this ŌĆ£very ordinary Jewish cityŌĆØ was in the 1920s ŌĆ£one of the world capitals of Yiddish language and culture."
Jews also played a disproportionate role in Belarusian politics and Soviet politics more generally in the 1920s, especially through the Bolshevik Party's Yiddish-language branch, the Yevsekstsia. Because there were few Jewish Bolsheviks before 1917 (with a few prominent exceptions like
Zinoviev and
Kamenev), the Yevsekstia's leaders in the 1920s were largely former Bundists, who pursued as Bolsheviks their campaign for secular Jewish education and culture. Although for example only a bit over 40 percent of Minsk's population was Jewish at the time, 19 of its 25 Communist Party cell secretaries were Jewish in 1924. Jewish predominance in the party cells was such that several cell meetings were held in Yiddish. In fact, Yiddish was spoken at citywide party meetings in Minsk into the late 1930s.
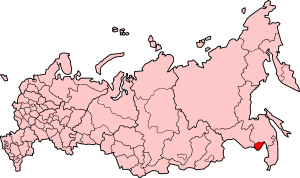
To offset the growing Jewish national and religious aspirations of
Zionism and to successfully categorize Soviet Jews under Stalin's definition of nationality, an alternative to the
Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
was established with the help of
Komzet and
OZET in 1928. The
Jewish Autonomous Oblast with its center in
Birobidzhan in the
Russian Far East was to become a "Soviet Zion". Despite a massive domestic and international state propaganda campaign, however, the Jewish population in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast never reached 30% (in 2003 it was only about 1.2%). The experiment ground to a halt in the mid-1930s, during Stalin's first campaign of purges.
In fact the Bolshevik Party's Yiddish-language Yevsekstia was dissolved in 1930, as part of the regime's overall turn away from encouraging minority languages and cultures and towards Russification. Many Jewish leaders, especially those with Bundist backgrounds, were arrested and executed in the purges later in the 1930s, and Yiddish schools were shut down. The Belasusian SSR shut down its entire network of Yiddish-language schools in 1938.
In his January 12, 1931, letter "Antisemitism: Reply to an Inquiry of the Jewish News Agency in the United States" (published domestically by ''
Pravda'' in 1936), Stalin officially condemned antisemitism:
In answer to your inquiry: National and racial chauvinism is a vestige of the misanthropic customs characteristic of the period of cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
. Antisemitism, as an extreme form of racial chauvinism, is the most dangerous vestige of cannibalism.
Antisemitism is of advantage to the exploiters as a lightning conductor that deflects the blows aimed by the working people at capitalism. Antisemitism is dangerous for the working people as being a false path that leads them off the right road and lands them in the jungle. Hence Communists, as consistent internationalists, cannot but be irreconcilable, sworn enemies of antisemitism.
In the U.S.S.R. antisemitism is punishable with the utmost severity of the law as a phenomenon deeply hostile to the Soviet system. Under U.S.S.R. law active antisemites are liable to the death penalty.
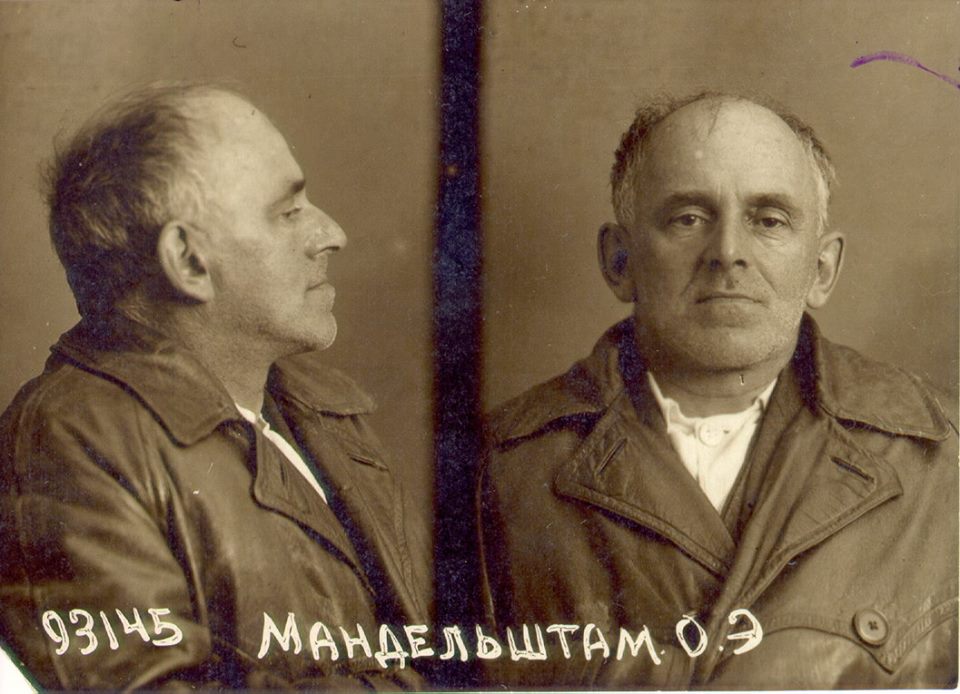

The
MolotovŌĆōRibbentrop pactŌĆöthe 1939 non-aggression pact with
Nazi GermanyŌĆöcreated further suspicion regarding the Soviet Union's position toward Jews. According to the pact, Poland, the nation with the world's largest Jewish population, was divided between Germany and the Soviet Union in September 1939. While the pact had no basis in ideological sympathy (as evidenced by Nazi propaganda about "
Jewish Bolshevism"), Germany's occupation of Western Poland was a disaster for Eastern European Jews. Evidence suggests that some, at least, of the Jews in the eastern Soviet zone of occupation welcomed the Russians as having a more liberated policy towards their civil rights than the preceding antisemitic Polish regime. Jews in areas annexed by the Soviet Union were deported eastward in great waves; as these areas would soon be invaded by Nazi Germany, this forced migration, deplored by many of its victims, paradoxically also saved the lives of several hundred thousand Jewish deportees.

Jews who escaped the purges include
Lazar Kaganovich
Lazar Moiseyevich Kaganovich, also Kahanovich (russian: ąøą░╠üąĘą░čĆčī ą£ąŠąĖčüąĄ╠üąĄą▓ąĖčć ąÜą░ą│ą░ąĮąŠ╠üą▓ąĖčć, L├Īzar' Mois├®yevich Kagan├│vich; ŌĆō 25 July 1991), was a Soviet politician and administrator, and one of the main associates of ...
, who came to Stalin's attention in the 1920s as a successful bureaucrat in
Tashkent and participated in the purges of the 1930s. Kaganovich's loyalty endured even after Stalin's death, when he and Molotov were expelled from the party ranks in 1957 due to their opposition to
destalinization.
Beyond longstanding controversies, ranging from the
MolotovŌĆōRibbentrop Pact to
anti-Zionism
Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestin ...
, the Soviet Union did grant official "equality of all citizens regardless of status, sex, race, religion, and nationality". The years before
the Holocaust were an era of rapid change for Soviet Jews, leaving behind the dreadful poverty of the Pale of Settlement. Forty percent of the population in the former Pale left for large cities within the USSR.
Emphasis on education and movement from countryside ''
shtetls'' to newly
industrialized cities allowed many Soviet Jews to enjoy overall advances under Stalin and to become one of the most educated population groups in the world.

Because of Stalinist emphasis on its urban population, interwar migration inadvertently rescued countless Soviet Jews;
Nazi Germany penetrated the entire former Jewish PaleŌĆöbut were kilometers short of
Leningrad and Moscow. The migration of many Jews farther East from the Jewish Pale, which would become occupied by Nazi Germany, saved at least 40 percent of the Pale's original Jewish population.
By 1941, it was estimated that the Soviet Union was home to 4.855 million Jews, around 30% of all Jews worldwide. However, the majority of these were residents of rural western
Belarus and
UkraineŌĆöpopulations that suffered greatly due to the German occupation and the
Holocaust. Only around 800,000 Jews lived outside the occupied territory, and 1,200,000 to 1,400,000 Jews were eventually evacuated eastwards. Of the three million left in occupied areas, the vast majority is thought to have perished in German
extermination camps.
World War II and the Holocaust
Over two million Soviet Jews are believed to have died during the Holocaust, second only to the number of Polish Jews to have fallen victim to
Hitler. Among some of the larger massacres in 1941 were: 33,771 Jews of
Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
shot in ditches at
Babi Yar; 100,000 Jews and Poles of
Vilnius killed in the forests of
Ponary
Ponary is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Miłakowo, within Ostróda County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately south of Miłakowo, north of Ostróda, and north-west of the regional capit ...
, 20,000 Jews killed in Kharkiv at Drobnitzky Yar, 36,000 Jews machine-gunned in Odessa, 25,000 Jews of
Riga
Riga (; lv, R─½ga , liv, R─½g├Ą) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
killed in the woods at
Rumbula, and 10,000 Jews slaughtered in
Simferopol in the Crimea. Although mass shootings continued through 1942, most notably 16,000 Jews shot at Pinsk, Jews were increasingly shipped to concentration camps in German Nazi-occupied Poland.
Local residents of German-occupied areas, especially Ukrainians, Lithuanians, and Latvians, sometimes played key roles in the genocide of other Latvians, Lithuanians, Ukrainians, Slavs,
Romani, homosexuals and Jews alike. Under the Nazi occupation, some members of the Ukrainian and Latvian Nazi police carried out deportations in the
Warsaw Ghetto, and Lithuanians marched Jews to their death at Ponary. Even as some assisted the Germans, a significant number of individuals in the territories under German control also helped Jews escape death (''see
Righteous Among the Nations''). In
Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Le┼Żm┼Ź), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Le┼Żm┼Ź Vab─üm┼Ź, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, particularly, the number of Nazi-collaborators was only slightly more than that of Jewish saviours. It is estimated that up to 1.4 million Jews fought in
Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
armies; 40% of them in the
Red Army. In total, at least 142,500 Soviet soldiers of Jewish nationality lost their lives fighting against the German invaders and their allies

The typical Soviet policy regarding the Holocaust was to present it as
atrocities against Soviet citizens, not emphasizing the genocide of the Jews. For example, after the liberation of
Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
from the Nazi occupation, the ''Extraordinary State Commission'' (ą¦čĆąĄąĘą▓čŗčćą░ą╣ąĮą░čÅ ąōąŠčüčāą┤ą░čĆčüčéą▓ąĄąĮąĮą░čÅ ąÜąŠą╝ąĖčüčüąĖčÅ; ''Chrezv'chaynaya Gosudarstvennaya Komissiya'') was set out to investigate Nazi crimes. The description of the
Babi Yar massacre was officially
censored as follows:
Stalinist antisemitic campaigns
The revival of Jewish identity after the war, stimulated by the creation of the state of Israel in 1948, was cautiously welcomed by Stalin as a means to put pressure on Western imperialism in the Middle East, but when it became evident that many Soviet Jews expected the revival of Zionism to enhance their own aspirations for separate cultural and religious development in the Soviet Union, a wave of repression was unleashed.
In January 1948
Solomon Mikhoels, a popular actor-director of the
Moscow State Jewish Theater and the chairman of the
Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee, was killed in a suspicious car accident. Mass arrests of prominent Jewish intellectuals and suppression of Jewish culture followed under the banners of campaign against "
rootless cosmopolitans" and
anti-Zionism
Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestin ...
. On August 12, 1952, in the event known as the
Night of the Murdered Poets, thirteen of the most prominent
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
writers, poets, actors and other intellectuals were executed on the orders of Joseph Stalin, among them
Peretz Markish,
Leib Kvitko,
David Hofstein,
Itzik Feffer and
David Bergelson
David (or Dovid) Bergelson (, russian: ąöą░ą▓ąĖą┤ ąæąĄčĆą│ąĄą╗čīčüąŠąĮ, 12 August 1884 ŌĆō 12 August 1952) was a Yiddish language writer born in the Russian Empire. He lived for a time in Berlin, Germany before moving to the Soviet Union following ...
. In the 1955
United Nations General Assembly's session a high Soviet official still denied the "rumors" about their disappearance.
The
Doctors' Plot allegation in 1953 was a deliberately antisemitic policy: Stalin targeted "corrupt Jewish bourgeois nationalists", eschewing the usual code words like "rootless cosmopolitans" or "cosmopolitans". Stalin died, however, before this next wave of arrests and executions could be launched in earnest. A number of historians claim that the Doctors' Plot was intended as the opening of a campaign that would have resulted in the mass
deportation of Soviet Jews had Stalin not died on March 5, 1953. Days after Stalin's death the plot was declared a
hoax
A hoax is a widely publicized falsehood so fashioned as to invite reflexive, unthinking acceptance by the greatest number of people of the most varied social identities and of the highest possible social pretensions to gull its victims into pu ...
by the Soviet government.

These cases may have reflected Stalin's paranoia, rather than state ideologyŌĆöa distinction that made no practical difference as long as Stalin was alive, but which became salient on his death.
In April 1956, the
Warsaw Yiddish language
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
Jewish newspaper ''
Folkshtimme
''Folks-Sztyme'' ( yi, ūżų┐ūÉųĖū£ū¦ūĪ ū®ūśūÖū×ūó), or ''People's Voice'' in English, was a bilingual magazine published in Polish and Yiddish in Communist Poland between 1946 and 1991.
An homonymous newspaper existed before World War II. According ...
'' published sensational long lists of Soviet Jews who had perished before and after the Holocaust. The world press began demanding answers from Soviet leaders, as well as inquiring about the current condition of the Jewish education system and culture. The same autumn, a group of leading Jewish world figures publicly requested the heads of Soviet state to clarify the situation. Since no cohesive answer was received, their concern was only heightened. The fate of Soviet Jews emerged as a major human rights issue in the West.
The Soviet Union and Zionism
Marxist
anti-nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
and
anti-clericalism
Anti-clericalism is opposition to religious authority, typically in social or political matters. Historical anti-clericalism has mainly been opposed to the influence of Roman Catholicism. Anti-clericalism is related to secularism, which seeks to ...
had a mixed effect on Soviet Jews. Jews were the immediate benefactors, but they were also long-term victims, of the Marxist notion that any manifestation of
nationalism is "socially retrogressive". On one hand, Jews were liberated from the religious persecution of the Tsarist years of "
Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality". On the other, this notion was threatening to Jewish cultural institutions, the Bund,
Jewish autonomy,
Judaism and
Zionism.
Political Zionism was officially stamped out as a form of
bourgeois nationalism during the
entire history of the
Soviet Union. Although
Leninism
Leninism is a political ideology developed by Russian Marxist revolutionary Vladimir Lenin that proposes the establishment of the Dictatorship of the proletariat#Vladimir Lenin, dictatorship of the proletariat led by a revolutionary Vanguardis ...
emphasizes the belief in "self-determination", this fact did not make the Soviet state more accepting of Zionism. Leninism defines self-determination by territory or
culture, rather than by
religion, which allowed Soviet minorities to have separate oblasts, autonomous regions, or republics, which were nonetheless symbolic until its later years. Jews, however, did not fit such a theoretical model; Jews in the
Diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
did not even have an agricultural base, as Stalin often asserted when he attempted to deny the existence of a Jewish nation, and they certainly did not have a territorial unit.
Marxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
notions even denied the existence of a Jewish identity beyond the existence of a religion and caste; Marx defined Jews as a "chimerical nation".

Lenin, who claimed to be deeply committed to egalitarian ideals and the universality of all humanity, rejected Zionism as a reactionary movement, "bourgeois nationalism", "socially retrogressive", and a backward force that deprecates class divisions among Jews. Moreover,
Zionism entailed contact between Soviet citizens and westerners, which was dangerous in a closed society. Soviet authorities were likewise fearful of any mass-movement which was independent of the
monopolistic
A monopoly (from Greek el, ╬╝Žī╬Į╬┐Žé, m├│nos, single, alone, label=none and el, ŽĆŽē╬╗╬Ąß┐¢╬Į, p┼Źle├«n, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a spec ...
Communist Party, and not tied to the state or the
ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied pri ...
of
Marxism-Leninism.
Without changing his official
anti-Zionist
Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestine ...
stance, from late 1944 until 1948
Joseph Stalin adopted a ''de facto'' pro-Zionist foreign policy, apparently believing that the new country would be socialist and hasten the decline of British influence in the Middle East.
In a May 14, 1947 speech during the
UN Partition Plan debate, published in ''
Izvestiya'' two days later, the
Soviet ambassador
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
Andrei Gromyko announced:
Soviet approval in the
United Nations Security Council was critical to the UN partitioning of the
British Mandate of Palestine, which led to the founding of the
State of Israel
Israel (; he, ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£, ; ar, žź┘Éž│┘Æž▒┘Äž¦ž”┘É┘Ŗ┘ä, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, ū×ų░ūōų┤ūÖūĀųĘū¬ ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£, label=none, translit=Med─½nat Y─½sr─ü╩Š─ōl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
.
Three days after
Israel declared its independence, the Soviet Union legally recognized it
de jure. In addition, the USSR allowed
Czechoslovakia to continue supplying arms to the Jewish forces during the
1948 ArabŌĆōIsraeli War
The 1948 (or First) ArabŌĆōIsraeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
, even though this conflict took place after the Soviet-supported
Czechoslovak coup d'├®tat of 1948. At the time, the U.S. maintained an arms embargo on both sides in the conflict. See
Arms shipments from Czechoslovakia to Israel 1947ŌĆō1949
Between June 1947 and October 31, 1949 Jewish agency, the Jewish agency (later to become the Israeli government) seeking weapons for Operation Balak, made several purchases of weapons in Czechoslovakia, some of them of former German army weapons, ...
.
By the end of 1957 the USSR switched sides in the
ArabŌĆōIsraeli conflict and throughout the course of the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
unequivocally supported various Arab regimes against Israel. The official position of the Soviet Union and its satellite states and agencies was that Zionism was a tool used by the Jews and Americans for "racist imperialism".

As
Israel was emerging as a close Western ally, the specter of
Zionism raised fears of internal dissent and opposition. During the later parts of the Cold War, Soviet Jews were suspected of being possible traitors, Western sympathisers, or a security liability. The Communist leadership closed down various Jewish organizations and declared Zionism an ideological enemy. Synagogues were often placed under police surveillance, both openly and through the use of informers.
As a result of the persecution, both state-sponsored and unofficial, antisemitism was ingrained in the society and remained for years: ordinary Soviet Jews often suffered hardships, epitomized by often not being allowed to enlist in universities, work in certain professions, or participate in government. However, it should be mentioned that this was not always the case and this kind of persecution varied depending on the region. Still many Jews felt compelled to hide their identities by changing their names.
The word "Jew" was also avoided in the media when criticising undertakings by
Israel, which the Soviets often accused of racism, chauvinism etc. Instead of ''Jew'', the word ''Israeli'' was used almost exclusively, so as to paint its harsh criticism not as antisemitism but anti-Zionism. More controversially, the Soviet media, when depicting political events, sometimes used the term 'fascism' to characterise Israeli nationalism (e.g. calling Jabotinsky a 'fascist', and claiming 'new fascist organisations were emerging in Israel in the 1970s' etc.).
1967ŌĆō1985

According to the census of 1959 the Jewish population of the city
Leningrad numbered 169,000 and the Great Choral synagogue was open in the 1960s with some 1,200 seats. The rabbi was
Avraham Lubanov
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
. This synagogue has never been closed. The great majority of the Leningrad Jews were not religious, but several thousand used to visit the synagogue on great holidays, mostly on Simchat Torah.
A mass emigration was politically undesirable for the Soviet regime. As increasing numbers of Soviet Jews applied to emigrate to Israel in the period following the 1967
Six-Day War, many were
formally refused permission to leave. A typical excuse given by the ''OVIR'' (ą×ąÆąĖąĀ), the
MVD department responsible for the provisioning of
exit visas, was that persons who had been given access at some point in their careers to information vital to Soviet
national security
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military atta ...
could not be allowed to leave the country.
After the
DymshitsŌĆōKuznetsov hijacking affair in 1970 and the crackdown that followed, strong international condemnations caused the Soviet authorities to increase the emigration
quota. From 1960 to 1970, only 4,000 people left the USSR; in the following decade, the number rose to 250,000.
In 1972, the USSR imposed the so-called "diploma tax" on would-be emigrants who received higher education in the USSR.
In some cases, the fee was as high as twenty annual salaries. This measure was possibly designed to combat the
brain drain caused by the growing emigration of Soviet Jews and other members of the
intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the in ...
to the West. Although Jews now made up less than 1% of the population, some surveys have suggested that around one-third of the emigrating Jews had achieved some form of higher education. Furthermore, Jews holding positions requiring specialized training tended to be highly concentrated in a small set of specialties, including medicine, mathematics, biology and music.
Following international protests, the
Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, ą£ąŠčüą║ąŠą▓čüą║ąĖą╣ ąÜčĆąĄą╝ą╗čī, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=╦łm╔É╦łskofsk╩▓╔¬j kr╩▓eml╩▓, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty, Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of th ...
soon revoked the tax, but continued to sporadically impose various limitations. Besides, an unofficial
Jewish quota was introduced in the leading institutions of higher education by subjecting Jewish applicants to harsher entrance examinations.
At first almost all of those who managed to get exit visas to Israel actually made
aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, ūóų▓ū£ų┤ūÖųĖų╝ūö ''╩┐─āl─½yy─ü'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel ...
, but after the mid-1970s, most of those allowed to leave for Israel actually chose other destinations, most notably the United States.
Glasnost and end of the USSR
In 1989 a record 71,000 Soviet Jews were granted exodus from the USSR, of whom only 12,117 immigrated to Israel. At first, American policy treated Soviet Jews as refugees and allowed unlimited numbers to emigrate, but this policy eventually came to an end. As a result, more Jews began moving to Israel, as it was the only country willing to take them unconditionally.
In the 1980s, the liberal government of
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 ŌĆō 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
allowed unlimited Jewish emigration, and the Soviet Union itself collapsed in 1991. As a result, a mass emigration of Jews from the former Soviet Union took place. Since the 1970s, over 1.1 million Russians of Jewish origin immigrated to Israel, of whom 100,000 emigrated to third countries such as the United States and Canada soon afterward and 240,000 were not considered Jewish under ''
Halakha'', but were eligible under the
Law of Return due to Jewish ancestry or marriage. Since the adoption of the
JacksonŌĆōVanik amendment, over 600,000 Soviet Jews have emigrated.
Modern-day Russia


 Judaism
Judaism today is officially designated as one of Russia's four "traditional religions", alongside
Orthodox Christianity,
Islam
Islam (; ar, █śž¦┘ä┘Éžźž│┘ä┘Äž¦┘ģ, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and
Buddhism.
Jews make up about 0.16% of the total population of Russia, which would be 232,267 people, according to the 2002 census. Most Russian Jews are secular and identify themselves as Jews via ethnicity rather than religion, although interest about
Jewish identity as well as practice of Jewish tradition amongst Russian Jews is growing. The
Lubavitch
Chabad, also known as Lubavitch, Habad and Chabad-Lubavitch (), is an Orthodox Jewish Hasidic dynasty. Chabad is one of the world's best-known Hasidic movements, particularly for its outreach activities. It is one of the largest Hasidic groups ...
er Jewish Movement has been active in this sector, setting up synagogues and Jewish kindergartens in Russian cities with Jewish populations. In addition, most Russian Jews have relatives who live in Israel.
There are several major Jewish organizations in the territories of the former USSR. The central Jewish organization is the
Federation of Jewish Communities of the CIS under the leadership of Chief Rabbi
Berel Lazar.
A linguistic distinction remains to this day in the Russian language where there are two distinct terms that correspond to the word ''Jew'' in English. The word ''ąĄą▓čĆąĄą╣'' ("yevrey" ŌĆō Hebrew) typically denotes a Jewish ethnicity, as "Hebrew" did in English up until the early 20th century. The word ''ąĖčāą┤ąĄą╣'' ("iudey" ŌĆō Judean, etymologically related to the English ''Jew'') is reserved for denoting a follower of the Jewish religion, whether he or she is ethnically Jewish or ethnically Gentile; this term has largely fallen out of use in favor of the equivalent term ''ąĖčāą┤ą░ąĖčüčé'' ("iudaist"-Judaist). For example, according to a 2012 Russian survey, ''ąĄą▓čĆąĄąĖ'' account for only 32.2% of ''ąĖčāą┤ą░ąĖčüčéčŗ'' in Russia, with nearly half (49.8%) being Ethnic Russians (''čĆčāčüčüą║ąĖąĄ''),. An ethnic slur, ąČąĖą┤ (borrowed from the
Polish ''┼╗yd'', Jew), also remains in widespread use in Russia.
Antisemitism is one of the most common expressions of
xenophobia in post-Soviet Russia, even among some groups of politicians. Despite stipulations against fomenting hatred based on ethnic or religious grounds (Article 282 of
Russian Federation
Penal Code
A criminal code (or penal code) is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might ...
), In 2002, the number of anti-Semitic neo-Nazi groups in the republics of the former Soviet Union, led ''
Pravda'' to declare in 2002 that "Anti-Semitism is booming in Russia". In January 2005, a group of 15
Duma members demanded that Judaism and Jewish organizations be banned from Russia. In 2005, 500 prominent Russians, including some 20 members of the nationalist
Rodina party, demanded that the state prosecutor investigate ancient Jewish texts as "anti-Russian" and ban Judaism. An investigation was in fact launched, but halted after an international outcry.
Overall, in recent years, particularly since the early 2000s, levels of anti-semitism in Russia have been reportedly low, and steadily decreasing. In 2019, Ilya Yablogov wrote that many Russians were keen on antisemitic conspiracy theories in 1990s but it declined after 2000 and many high-ranking officials were forced to apologize for the antisemitic behavior.
In Russia, both historical and contemporary antisemitic materials are frequently published. For example, a set (called ''Library of a Russian Patriot'') consisting of twenty five antisemitic titles was recently published, including ''
Mein Kampf
(; ''My Struggle'' or ''My Battle'') is a 1925 autobiographical manifesto by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler. The work describes the process by which Hitler became antisemitic and outlines his political ideology and future plans for Germ ...
'' translated to Russian (2002), which although was banned in 2010, ''The Myth of Holocaust'' by
J├╝rgen Graf, a title by
Douglas Reed, ''
Protocols of the Elders of Zion'', and others.

Antisemitic incidents are mostly conducted by extremist, nationalist, and Islamist groups. Most of the antisemitic incidents are against Jewish cemeteries and building (community centers and synagogues) such as the assault against the Jewish community's center in Perm in March 2013 and the attack on Jewish nursery school in Volgograd in August 2013. Nevertheless, there were several violent attacks against Jews in Moscow in 2006 when a neo-Nazi stabbed 9 people at the Bolshaya Bronnaya Synagogue, the failed bomb attack on the same synagogue in 1999.


Attacks against Jews made by extremist Islamic groups are rare in Russia although there has been increase in the scope of the attacks mainly in Muslim populated areas. On July 25, 2013, the rabbi of Derbent was attacked and badly injured by an unknown person near his home, most likely by a terrorist. The incident sparked concerns among the local Jews of further acts against the Jewish community.
After the passage of some anti-gay laws in Russia in 2013 and the incident with the "Pussy-riot" band in 2012 causing a growing criticism on the subject inside and outside Russia a number of verbal anti-Semitic attacks were made against Russian gay activists by extremist activists and anti-Semitic writers such as Israel Shamir who viewed the "Pussy-riot" incident as the war of Judaism on the Christian Orthodox church.

The
Jewish Autonomous Oblast continues to be an
autonomous oblast of the Russian state. The
Chief Rabbi
Chief Rabbi ( he, ū©ūæ ū©ūÉū®ūÖ ''Rav Rashi'') is a title given in several countries to the recognized religious leader of that country's Jewish community, or to a rabbinic leader appointed by the local secular authorities. Since 1911, through a ...
of
Birobidzhan,
Mordechai Scheiner
Mordechai Sheiner ( he, ū×ū©ūōūøūÖ ū®ūÖūÖūĀū©; russian: ą£ąŠčĆą┤ąĄčģą░╠üą╣ ą©ąĄą╣ąĮąĄčĆ) is an Israeli Orthodox rabbi associated with the Chabad Hasidic movement. Sheiner served as Chief Rabbi of Jewish Autonomous Oblast from 2002 to 2011. , says there are 4,000 Jews in the capital city. Governor
Nikolay Mikhaylovich Volkov has stated that he intends to "support every valuable initiative maintained by our local Jewish organizations". The
Birobidzhan Synagogue opened in 2004 on the 70th anniversary of the regions founding in 1934.

Today, the Jewish population of Russia is shrinking due to small family sizes, and high rates of assimilation and intermarriage. This shrinkage has been slowed by some Russian-Jewish emigrants having returned from abroad, especially from Germany. The great majority of up to 90% of children born to a Jewish parent are the offspring of mixed marriages, and most Jews have only one or two children. The majority of Russian Jews live in the Moscow metropolitan area, with another 20% in the
Saint Petersburg area, and the rest in large cities with a population of at least 1 million.
The Jewish population in the
Jewish Autonomous Oblast of the
Russian Far East in 2002 was 2,327 (1.22%).
The
Bukharan Jews
Bukharan Jews ( Bukharian: ūÖūöūĢūōūÖūÉūĀūÖ ūæūĢūøūÉū©ūÉ/čÅę│čāą┤ąĖčæąĮąĖ ąæčāčģąŠčĆąŠ, ''Yahudiyoni Bukhoro''; he, ūÖūöūĢūōūÖ ūæūĢūøū©ūö, ''Yehudey Bukhara''), in modern times also called Bukharian Jews ( Bukharian: ūÖūöūĢūōūÖūÉūĀūÖ ūæūĢūøūÉū© ...
, self-designating as ''Yahudi'', ''Isroel'' or ''Banei Isroel'', live mainly in Uzbek cities. The number of Central Asian Jews was around 20,800 in 1959. Before mass emigration, they spoke a dialect of the
Tajik language.
The
Georgian Jews numbered about 35,700 in 1964, most of them living in
Georgia.
The Caucasian
Mountain Jews, also known as
Tats or Dagchufuts, live mostly in
Israel and the United States, with a scattered population in
Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, ąöą░ą│ąĄčüčéą░╠üąĮ, , d╔Ö╔Ī╩▓╔¬╦łstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: ąĀąĄčüą┐čā╠üą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░ ąöą░ą│ąĄčüčéą░╠üąĮ, Resp├║blika Dagest├Īn, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North C ...
and
Azerbaijan. In 1959, they numbered around 15,000 in Dagestan and 10,000 in Azerbaijan. Their
Tat language is a dialect of
Middle Persian.
The Crimean Jews, self-designating as
Krymchaks, traditionally lived in the
Crimea, numbering around 5,700 in 1897. Due to a famine, a number emigrated to Turkey and the U.S. in the 1920s. The remaining population was virtually annihilated in the
Holocaust during the Nazi occupation of the Crimea, but Krymchaks re-settled the Crimea after the war, and in 1959, between 1,000 and 1,800 had returned.
The EuroStars young adults program provides Jewish learning and social activities in 32 cities across Russia. Some have described a 'renaissance' in the Jewish community inside Russia since the beginning of the 21st century.
Historical demographics
SSR">
File:USSR Jewish % 1939.png, 1939
File:Soviet Jewish % 1959.png, 1959
File:Soviet Jewish % 1989.png, 1989
a The Jewish population data for all of the years includes Mountain Jews, Georgian Jews, Bukharan Jews
Bukharan Jews ( Bukharian: ūÖūöūĢūōūÖūÉūĀūÖ ūæūĢūøūÉū©ūÉ/čÅę│čāą┤ąĖčæąĮąĖ ąæčāčģąŠčĆąŠ, ''Yahudiyoni Bukhoro''; he, ūÖūöūĢūōūÖ ūæūĢūøū©ūö, ''Yehudey Bukhara''), in modern times also called Bukharian Jews ( Bukharian: ūÖūöūĢūōūÖūÉūĀūÖ ūæūĢūøūÉū© ...
(or Central Asian Jews), Krymchaks (all per the 1959 Soviet census), and Tats.
b The data is from 1925.
c The data is from 1941.
d The data is from 2009.
e The data is from 2011.
Russian Jewish aliyah and immigration to countries outside Israel
Israel

In present times, the largest number of Russian Jews are ''
olim'' (ūóūĢų╣ū£ūÖūØ) and ''
sabras''. In 2011 Russians were around 15% of Israel's 7.7 million population (including Halakhally non-Jews who constituted about 30% of immigrants from the former Soviet Union). The Aliyah in the 1990s accounts for 85ŌĆō90% of this population.
The population growth rate for
Former Soviet Union (FSU)-born
''olim'' were among the lowest for any Israeli groups, with a Fertility rate of 1.70 and natural increase of just +0.5% per year.
The increase in Jewish birth rate in Israel during the 2000ŌĆō2007 period was partly due to the increasing birth rate among the FSU ''olim'', who now form 20% of the Jewish population of Israel.
96.5% of the enlarged Russian Jewish population in Israel either belong to
Judaism or are non-religious, while 3.5% (35,000) belong to other religions (mostly Christianity) and about 10,000 identifying as
Messianic Jews separate from
Jewish Christians.
The Total Fertility Rate for FSU-born ''olim'' in Israel is given in the table below. The TFR increased with time, peaking in 1997, then slightly decreased after that and then again increased after 2000.
In 1999, about 1,037,000 FSU-born ''olim'' lived in Israel, of whom about 738,900 made aliyah after 1989. The second largest ''oleh'' (ūóūĢų╣ū£ųČūö) group (
Moroccan Jews
Moroccan Jews ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘Ŗ┘ć┘łž» ž¦┘ä┘ģž║ž¦ž▒ž©ž®, al-Yah┼½d al-Magh─üriba he, ūÖūöūĢūōūÖūØ ū×ū©ūĢū¦ūÉūÖūØ, Yehudim Maroka'im) are Jews who live in or are from Morocco. Moroccan Jews constitute an ancient community dating to Roman times. Jews b ...
) numbered just 1,000,000. From 2000 to 2006, 142,638 FSU-born ''olim'' moved to Israel, while 70,000 of them emigrated from Israel to countries like the U.S. and CanadaŌĆöbringing the total population to 1,150,000 by
January 2007.
The natural increase was around 0.3% in the late 1990s. For example, 2,456 in 1996 (7,463 births to 5,007 deaths), 2,819 in 1997 (8,214 to 5,395), 2,959 in 1998 (8,926 to 5,967) and 2,970 in 1999 (9,282 to 6,312). In 1999, the natural growth was +0.385%. (Figures only for FSU-born ''olim'' moved in after 1989).
An estimated 45,000 illegal immigrants from the Former Soviet Union lived in Israel at the end of 2010, but it is not clear how many of them are actually Jews.
In 2013, 7,520 people, nearly 40% of all ''olim'', made ''aliyah'' from the Former Soviet Union. In 2014 4,685 Russian citizens relocated to Israel, more than double than usual in any of the previous 16 years.
[Jews Are Fleeing Russia Because Of Putin]
, Radio Free Europe (July 3, 2015) In 2015, nearly 7,000 or just over twenty percent of all olim came from the former Soviet Union.
Recent ''olim'' and ''olot'' (ūóūĢų╣ū£ūĢū¬) from the Former Soviet Union include notables such as
Anna Zak,
Natan Sharansky,
Yuri Foreman,
Yuli-Yoel Edelstein,
Ze'ev Elkin,
Nachman Dushanski
Nachman Dushanski ( lt, Nachmanas Du┼Īanskis, russian: ąØą░čģą╝ą░ąĮ ąØąŠą░čģąŠą▓ąĖčć ąöčāčłą░ąĮčüą║ąĖą╣, he, ūĀūŚū×ū¤ ūōūĢū®ūĀūĪū¦ūÖ; December 29, 1919 in ┼Āiauliai ŌĆō February 20, 2008 in Haifa) was a Lithuanian officer of Soviet security age ...
,
Boris Gelfand,
Natasha Mozgovaya
Natasha Mozgovaya ( he, ūĀūśū®ūö ū×ūĢū¢ūÆūĢūæūÖūö, russian: ąØą░čéą░čłą░ ą£ąŠąĘą│ąŠą▓ą░čÅ; born 1979) is an American-Israeli journalist. She is a TV host for Voice of America.
Biography
Natasha Mozgovaya was born in the Soviet Union in 1979 in ...
,
Avigdor Lieberman,
Roman Dzindzichashvili
Roman Yakovlevich Dzindzichashvili ( ka, ßāĀßāØßāøßāÉßā£ ßāśßāÉßāÖßāØßāæßāśßāĪ-ßā½ßāö ßā»ßāśßā£ßā»ßāśßā«ßāÉßā©ßāĢßāśßāÜßāś; pronounced ''jin-jee-khash-VEE-lee''; born May 5, 1944) is a Soviet-born Israeli-American chess player. He was awarded th ...
,
Anastassia Michaeli,
Haim Megrelashvili
The name ''Haim'' can be a first name or surname originating in the Hebrew language, or deriving from the Old German name ''Haimo''.
Hebrew etymology
Chayyim ( he, ūŚųĘūÖų┤ų╝ūÖūØ ', Classical Hebrew: , Israeli Hebrew: ), also transcribed ''Haim ...
,
Victor Mikhalevski
Victor (Viktor) Mikhalevski ( he, ūĢūÖū¦ūśūĢū© ū×ūÖūøū£ūæūĪū¦ūÖ; born 8 July 1972) is an Israeli chess grandmaster who lives in Beersheba.
his Elo rating was 2611, making him the #7 player in Israel and the 171st-highest rated player in the ...
,
Evgeny Postny
Evgeny Postny (born 3 July 1981) is an Israeli chess player. He was awarded the title Grandmaster by FIDE in 2002. Postny was a member of the Israeli team which took the silver medal in the Chess Olympiad of 2008. He competed in the FIDE World ...
,
Maxim Rodshtein,
Tatiana Zatulovskaya,
Maria Gorokhovskaya,
Katia Pisetsky
Katerina "Katya" Pisetsky ( he, ū¦ūśū©ūÖūĀūö "ū¦ūśūÖūö" ūÉūÖūæūÆūĀūÖūö ūżūÖūĪū”ū¦ūÖ) is a Ukrainian-born Israeli rhythmic gymnast who competed at the 2004 and 2008 Olympic Games.
Early life
Katerina Pisetsky was born Yekaterina Yevgenyevna Pisets ...
,
Aleksandr Averbukh
Aleksandr "Alex" Valeryevich Averbukh ( he, ūÉū£ūøūĪ ūÉūæū©ūæūĢūÜ, russian: ąÉą╗ąĄą║čüą░ąĮą┤čĆ ąÆą░ą╗ąĄčĆčīąĄą▓ąĖčć ąÉą▓ąĄčĆą▒čāčģ; born October 1, 1974) is a retired Russian decathlete and Israeli Olympic athlete, who competed in the pole vault. ...
,
Anna Smashnova
Anna Smashnova ( he, ūÉūĀūö ūĪū×ū®ūĀūĢūæūö, russian: ąÉąĮąĮą░ ąĪą╝ą░čłąĮąŠą▓ą░; born July 16, 1976) is a Soviet-born Israeli former tennis player. She retired from professional tour after Wimbledon 2007.
Smashnova reached her career-high single ...
,
Jan Talesnikov
Jan Talesnikov ( he, ū¢'ūÉū¤ ūśū£ūĪūĀūÖū¦ūĢūæ, russian: ą»ąĮ ąóą░ą╗ąĄčüąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓, born December 11, 1972) is an Israelis, Israeli retired Football (soccer), footballer and current manager.
Early life
Talesnikov was born on 11 December 1972 in th ...
,
Vadim Alexeev,
Michael Kolganov,
Alexander Danilov,
Evgenia Linetskaya,
Marina Kravchenko,
David Kazhdan
David Kazhdan ( he, ūōūĢūō ū¦ū®ūōū¤), born Dmitry Aleksandrovich Kazhdan (russian: ąöą╝ąĖ╠üčéčĆąĖą╣ ąÉą╗ąĄą║čüą░ąĮą┤čĆąŠ╠üą▓ąĖčć ąÜą░ąČą┤ą░╠üąĮ), is a Soviet and Israeli mathematician known for work in representation theory. Kazhdan is a 1990 Ma ...
,
Leonid Nevzlin,
Vadim Akolzin,
Roman Bronfman
Roman Bronfman ( he, ū©ūĢū×ū¤ ūæū©ūĢūĀūżū×ū¤, born 22 April 1954) is a Ukrainian-born Israeli politician. He speaks Hebrew ,English, Russian, and Ukrainian.
Biography
Bronfman was born in Chernivtsi, Ukrainian SSR (now Ukraine), ,
Michael Cherney,
Arcadi Gaydamak,
Sergei Sakhnovski
Sergei Sakhnovski ( he, ūĪū©ūÆūÖūÖ ūĪūŚūĀūĢūæūĪū¦ūÖ, russian: ąĪąĄčĆą│ąĄ╠üą╣ ąĪą░čģąĮąŠ╠üą▓čüą║ąĖą╣; born May 15, 1975) is an Israeli ice dancer. With partner Galit Chait, he is the 2002 World bronze medalist for Israel. With previous partner Ek ...
,
Roman Zaretski
Roman Zaretsky ( he, ū©ūĢū×ū¤ ū¢ū©ū”ū¦ūÖ, russian: ąĀąŠą╝ą░ąĮ ąŚą░čĆąĄčåą║ąĖą╣, be, ąĀą░ą╝ą░ąĮ ąŚą░čĆčŹčåą║č¢; born December 4, 1983) is an Israeli retired Ice dancing, ice dancer. With his sister, Alexandra Zaretsky, he is the 2009 Skate America ...
,
Alexandra Zaretski
Alexandra "Sasha" Zaretsky ( he, ūÉū£ūøūĪūĀūōū©ūö ū¢ū©ū”ū¦ūÖ, russian: ąÉą╗ąĄą║čüą░ąĮą┤čĆą░ ąŚą░čĆąĄčåą║ą░čÅ, , be, ąÉą╗čÅą║čüą░ąĮą┤čĆą░ ąŚą░čĆčŹčåą║ą░čÅ) (born December 23, 1987) is an Israeli retired ice dancer. With her brother Roman Zaretsky, ...
,
Larisa Trembovler,
Boris Tsirelson,
Ania Bukstein, and
Margarita Levieva.
United States

The second largest Russian Jewish population is in the United States. According to RINA, there is a core Russian Jewish population of 350,000 in the U.S. The enlarged Russian Jewish population in the U.S. is estimated to be 700,000.
Notable Russia, Imperial Russia, Soviet Union, and former Soviet Union, born Jewish Americans (living and deceased) include
Alexei Abrikosov,
Isaac Asimov
yi, ūÖū”ūŚū¦ ūÉū¢ūÖū×ūÉū░
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920ŌĆō1922)Soviet (192 ...
,
Leonard Blavatnik,
Sergey Brin,
Joseph Brodsky
Iosif Aleksandrovich Brodsky (; russian: link=no, ąśąŠčüąĖčä ąÉą╗ąĄą║čüą░ąĮą┤čĆąŠą▓ąĖčć ąæčĆąŠą┤čüą║ąĖą╣ ; 24 May 1940 ŌĆō 28 January 1996) was a Russian and American poet and essayist.
Born in Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg), USSR in 1940, ...
,
Sergei Dovlatov,
Anthony Fedorov,
Israel Gelfand,
Emma Goldman
Emma Goldman (June 27, 1869 ŌĆō May 14, 1940) was a Russian-born anarchist political activist and writer. She played a pivotal role in the development of anarchist political philosophy in North America and Europe in the first half of the ...
,
Vladimir Horowitz,
Gregory Kaidanov,
Avi Kaplan,
Anna Khachiyan,
Jan Koum,
Savely Kramarov
Savely Viktorovich Kramarov (russian: ąĪą░ą▓ąĄ╠üą╗ąĖą╣ ąÆąĖ╠üą║č鹊čĆąŠą▓ąĖčć ąÜčĆą░╠üą╝ą░čĆąŠą▓; 13 October 1934 ŌĆō 6 June 1995) was a Soviet, Russian and American actor. He acted in at least 42 Soviet films, and later appeared in several mo ...
,
Mila Kunis,
Leonid Levin,
Lev Loseff,
Alexander Migdal,
Eugene Mirman,
Alla Nazimova,
Ayn Rand
Alice O'Connor (born Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum;, . Most sources transliterate her given name as either ''Alisa'' or ''Alissa''. , 1905 ŌĆō March 6, 1982), better known by her pen name Ayn Rand (), was a Russian-born American writer and p ...
,
Markus Rothkovich (Mark Rothko),
Dmitry Salita
Dmitry Salita (russian: ąöą╝ąĖčéčĆąĖą╣ ąĪą░ą╗ąĖčéą░; uk, ąöą╝ąĖčéčĆąŠ ąĪą░ą╗č¢čéą░), Dmitry Aleksandrovich Lekhtman, is an American boxing promoter and former professional boxer. Born in Ukraine, he grew up in New York City from the age of nin ...
,
Menachem Mendel Schneerson,
Yakov Sinai,
Mikhail Shifman, Mikhail Shufutinsky, Regina Spektor, Willi Tokarev, and Arkady Vainshtein.
Large Russian Jewish communities include Brighton Beach and Sheepshead Bay in the Brooklyn Borough (New York City), Borough of New York City; Fair Lawn, New Jersey, Fair Lawn and nearby areas in Bergen County, New Jersey; Bucks County, Pennsylvania, Bucks and Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery Counties near Philadelphia; Pikesville, Maryland, a predominantly-Jewish suburb of Baltimore; Washington Heights in the Sunny Isles Beach neighborhood of South Florida; Skokie, Illinois, Skokie and Buffalo Grove, Illinois, Buffalo Grove, suburbs of Chicago; and West Hollywood, California.
Germany
The fourth largest Russian-Jewish community exists in Germany with a core Russian-Jewish population of 119,000 and an enlarged population of 250,000.
In the 1991ŌĆō2006 period, approximately 230,000 ethnic Jews from the FSU immigrated to Germany. In the beginning of 2006, Germany tightened the immigration program. A survey conducted among approximately 215,000 enlarged Russian Jewish population (taking natural decrease into consideration) indicated that about 81% of the enlarged population was religiously Jewish or Atheist, while about 18.5% identified as Christian. That gives a core Russian Jewish population of 111,800 (religiously Jewish, 52%) or 174,150 (religiously Jewish or Atheist).
Notable Russian Jews in Germany include Valery Belenky, Maxim Biller, Friedrich Gorenstein, Wladimir Kaminer, Lev Kopelev, Elena Kuschnerova, Alfred Schnittke, Vladimir Voinovich, and Lilya Zilberstein.
Canada
The fifth largest Russian Jewish community is in Canada. The core Russian Jewish population in Canada numbers 30,000 and the enlarged Russian Jewish population numbered 50,000+, mostly in Montreal and Toronto. Notable Russian Jewish residents include judoka Mark Berger (judoka), Mark Berger, ice hockey player Eliezer Sherbatov, voice actress Tara Strong, and the musical group Tasseomancy (band), Tasseomancy.
Australia
Jews from the former Soviet Union settled in Australia in two migration waves in the 1970s and 1990s. About 5,000 immigrated in the 1970s and 7,000 to 8,000 in the 1990s.
[Gruzman, Emmanuel (May 12, 2018). ] The estimated population of Jews from the former Soviet Union in Australia is 10,000 to 11,000, constituting about 10% of the Australian Jewish population. About half of the Jews from the former Soviet Union are from Ukraine and a third from the Russian Federation.
Finland
Hundreds of Russian Jews have moved to Finland since 1990 and have helped to stem the negative population growth of the Jewish community there.
The total number of Jews in Finland have grown from 800 in 1980 to 1,200 in 2006. Of all the schoolgoing Jewish children, 75% have at least one Russian born parent.
Other countries

Austria, Belgium, United Kingdom, Britain, Italy, Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, New Zealand and Switzerland also have small populations of Russian Jews. The addition of Russian Jews have neutralized the negative Jewish population trends in some European countries like the Netherlands and Austria. Notable Russian Jews in France include L├®on Bakst, Marc Chagall, Leon Poliakov, Evgeny Kissin, Alexandre Koyr├®, Ida Rubinstein, Lev Shestov, and Anatoly Vaisser. Some other notable Russian Jews are Roman Abramovich, Vladimir Ashkenazy, Boris Berezovsky (businessman), Boris Berezovsky, and Maxim Vengerov (United Kingdom), Gennadi Sosonko (Netherlands), Viktor Korchnoi (Switzerland), and Maya Plisetskaya (Spain).
Russian Prime Ministers of Jewish origin
* Sergey Kiriyenko, Prime Minister of Russia (1998)
* Yevgeny Primakov, Prime Minister of Russia (1998ŌĆō1999)
* Mikhail Fradkov, Prime Minister of Russia (2004ŌĆō2007)
* Mikhail Mishustin, Prime Minister of Russia (2020ŌĆōpresent)
See also
* History of the Jews in Central Asia
* History of the Jews in Armenia
* History of the Jews in Azerbaijan
* History of the Jews in Georgia
* History of the Jews in Ukraine
* History of the Jews in Belarus
* History of the Jews in Estonia
* History of the Jews in Latvia
* History of the Jews in Lithuania
*
Jewish Autonomous Oblast
* Jews and Judaism in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast
* Jewish Cossacks
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
* Gitelman, Zvi. ''A Century of Ambivalence: The Jews of Russia and the Soviet Union, 1881 to the Present'' (2001)
* Goldenweiser, E.A. "Economic Conditions of the Jews in Russia," ''Publications of the American Statistical Association'' 9#70 (1905), pp. 238ŌĆō24
online
*
*
*
* Antony Polonsky, Polonsky, Antony. ''The Jews in Poland and Russia: A Short History'' (2013)
*
*
External links
Federation of Jewish Communities of the CIS
by Karina Ioffee, ''The Huffington Post'', July 13, 2009
RJCF ŌĆō Russian Jewish Community Foundation
*Genesis Philanthropy Group's movie ŌĆ
Russian Jews: Trilogy by Leonid Parfenov / English Subtitles
on YouTube
Collected news and commentary
at ''The Times of Israel''
{{Immigration to Russia
Jewish Russian and Soviet history,
 Jews have been present in contemporary Armenia and Georgia since the
Jews have been present in contemporary Armenia and Georgia since the  Documentary evidence as to the presence of Jews in Muscovite Russia is first found in the chronicles of 1471. The relatively small population of them were subject to discriminatory laws, but these laws do not appear to have been enforced at all times. Jews residing in Russian and Ukrainian towns suffered numerous religious persecutions. Converted Jews occasionally rose to important positions in the Russian State, for example Peter Shafirov, vice-chancellor under
Documentary evidence as to the presence of Jews in Muscovite Russia is first found in the chronicles of 1471. The relatively small population of them were subject to discriminatory laws, but these laws do not appear to have been enforced at all times. Jews residing in Russian and Ukrainian towns suffered numerous religious persecutions. Converted Jews occasionally rose to important positions in the Russian State, for example Peter Shafirov, vice-chancellor under 
 Their situation changed radically, during the reign of Catherine II, when the Russian Empire acquired rule over large Lithuanian and Polish territories which historically included a high proportion of Jewish residents, especially during the second (1793) and the third (1795)
Their situation changed radically, during the reign of Catherine II, when the Russian Empire acquired rule over large Lithuanian and Polish territories which historically included a high proportion of Jewish residents, especially during the second (1793) and the third (1795)  The 'decree of August 26, 1827' made Jews liable for military service, and allowed their conscription between the ages of twelve and twenty-five. Each year, the Jewish community had to supply four recruits per thousand of the population. However, in practice, Jewish children were often conscripted as young as eight or nine years old. At the age of twelve, they would be placed for their six-year military education in cantonist schools. They were then required to serve in the Imperial Russian army for 25 years after the completion of their studies, often never seeing their families again. Strict quotas were imposed on all communities and the ''qahals'' were given the unpleasant task of implementing conscription within the Jewish communities. Since the merchant- guild members, agricultural colonists, factory mechanics, clergy, and all Jews with secondary education were exempt, and the wealthy bribed their way out of having their children conscripted, fewer potential conscripts were available; the adopted policy deeply sharpened internal Jewish social tensions. Seeking to protect the socio-economic and religious integrity of Jewish society, the ''qahals'' did their best to include ŌĆ£non-useful JewsŌĆØ in the draft lists so that the heads of tax-paying middle-class families were predominantly exempt from conscription, whereas single Jews, as well as "heretics" ( Haskalah influenced individuals), paupers, outcasts, and orphaned children were drafted. They used their power to suppress protests and intimidate potential informers who sought to expose the arbitrariness of the ''qahal'' to the Russian government. In some cases, communal elders had the most threatening informers murdered (such as the Ushitsa case, 1836).
The zoning rule was suspended during the Crimean War, when conscription became annual. During this period the ''qahals'' leaders would employ informers and kidnappers (Russian: "", , yi, khappers, script=Latn), as many potential conscripts preferred to run away rather than voluntarily submit. In the case of unfulfilled quotas, younger Jewish boys of eight and even younger were frequently taken. The official Russian policy was to encourage the conversion of Jewish cantonists to the
The 'decree of August 26, 1827' made Jews liable for military service, and allowed their conscription between the ages of twelve and twenty-five. Each year, the Jewish community had to supply four recruits per thousand of the population. However, in practice, Jewish children were often conscripted as young as eight or nine years old. At the age of twelve, they would be placed for their six-year military education in cantonist schools. They were then required to serve in the Imperial Russian army for 25 years after the completion of their studies, often never seeing their families again. Strict quotas were imposed on all communities and the ''qahals'' were given the unpleasant task of implementing conscription within the Jewish communities. Since the merchant- guild members, agricultural colonists, factory mechanics, clergy, and all Jews with secondary education were exempt, and the wealthy bribed their way out of having their children conscripted, fewer potential conscripts were available; the adopted policy deeply sharpened internal Jewish social tensions. Seeking to protect the socio-economic and religious integrity of Jewish society, the ''qahals'' did their best to include ŌĆ£non-useful JewsŌĆØ in the draft lists so that the heads of tax-paying middle-class families were predominantly exempt from conscription, whereas single Jews, as well as "heretics" ( Haskalah influenced individuals), paupers, outcasts, and orphaned children were drafted. They used their power to suppress protests and intimidate potential informers who sought to expose the arbitrariness of the ''qahal'' to the Russian government. In some cases, communal elders had the most threatening informers murdered (such as the Ushitsa case, 1836).
The zoning rule was suspended during the Crimean War, when conscription became annual. During this period the ''qahals'' leaders would employ informers and kidnappers (Russian: "", , yi, khappers, script=Latn), as many potential conscripts preferred to run away rather than voluntarily submit. In the case of unfulfilled quotas, younger Jewish boys of eight and even younger were frequently taken. The official Russian policy was to encourage the conversion of Jewish cantonists to the  The cultural and habitual isolation of the Jews gradually began eroding. An ever-increasing number of Jewish people adopted Russian customs and the Russian language. Russian education was spread among the Jewish population. A number of Jewish-Russian periodicals appeared.
Alexander II was known as the "Tsar liberator" for the 1861 abolition of serfdom in Russia. Under his rule Jewish people could not hire Christian servants, could not own land, and were restricted in travel.
Alexander III was a staunch reactionary and an antisemite (influenced by Pobedonostsev) who strictly adhered to the old doctrine of Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality. His escalation of anti-Jewish policies sought to ignite "popular antisemitism", which portrayed the Jews as "
The cultural and habitual isolation of the Jews gradually began eroding. An ever-increasing number of Jewish people adopted Russian customs and the Russian language. Russian education was spread among the Jewish population. A number of Jewish-Russian periodicals appeared.
Alexander II was known as the "Tsar liberator" for the 1861 abolition of serfdom in Russia. Under his rule Jewish people could not hire Christian servants, could not own land, and were restricted in travel.
Alexander III was a staunch reactionary and an antisemite (influenced by Pobedonostsev) who strictly adhered to the old doctrine of Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality. His escalation of anti-Jewish policies sought to ignite "popular antisemitism", which portrayed the Jews as " A large-scale wave of
A large-scale wave of  The repressive legislation was repeatedly revised. Many historians noted the concurrence of these state-enforced antisemitic policies with waves of pogroms that continued until 1884, with at least tacit government knowledge and in some cases policemen were seen inciting or joining the mob.
The systematic policy of discrimination banned Jewish people from rural areas and towns of fewer than ten thousand people, even within the Pale, assuring the slow death of many shtetls. In 1887, the quotas placed on the number of Jews allowed into secondary and higher education were tightened down to 10% within the Pale, 5% outside the Pale, except Moscow and Saint Petersburg, held at 3%, even though the Jewish population was a majority or plurality in many communities. It was possible to evade these restrictions upon secondary education by combining private tuition with examination as an "outside student". Accordingly, within the Pale such outside pupils were almost entirely young Jews. The restrictions placed on education, traditionally highly valued in Jewish communities, resulted in ambition to excel over the peers and increased emigration rates. Special quotas restricted Jews from entering profession of law, limiting number of Jews admitted to the bar.
In 1886, an Edict of Expulsion was enforced on the historic Jewish population of
The repressive legislation was repeatedly revised. Many historians noted the concurrence of these state-enforced antisemitic policies with waves of pogroms that continued until 1884, with at least tacit government knowledge and in some cases policemen were seen inciting or joining the mob.
The systematic policy of discrimination banned Jewish people from rural areas and towns of fewer than ten thousand people, even within the Pale, assuring the slow death of many shtetls. In 1887, the quotas placed on the number of Jews allowed into secondary and higher education were tightened down to 10% within the Pale, 5% outside the Pale, except Moscow and Saint Petersburg, held at 3%, even though the Jewish population was a majority or plurality in many communities. It was possible to evade these restrictions upon secondary education by combining private tuition with examination as an "outside student". Accordingly, within the Pale such outside pupils were almost entirely young Jews. The restrictions placed on education, traditionally highly valued in Jewish communities, resulted in ambition to excel over the peers and increased emigration rates. Special quotas restricted Jews from entering profession of law, limiting number of Jews admitted to the bar.
In 1886, an Edict of Expulsion was enforced on the historic Jewish population of 
 During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the Russian Empire had not only the largest Jewish population in the world, but actually a majority of the world's Jews living within its borders. In 1897, according to
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the Russian Empire had not only the largest Jewish population in the world, but actually a majority of the world's Jews living within its borders. In 1897, according to  Even though the persecutions provided the impetus for mass emigration, there were other relevant factors that can account for the Jews' migration. After the first years of large emigration from Russia, positive feedback from the emigrants in the U.S. encouraged further emigration. Indeed, more than two million Jews fled Russia between 1880 and 1920. While a large majority emigrated to the United States, some turned to Zionism. In 1882, members of
Even though the persecutions provided the impetus for mass emigration, there were other relevant factors that can account for the Jews' migration. After the first years of large emigration from Russia, positive feedback from the emigrants in the U.S. encouraged further emigration. Indeed, more than two million Jews fled Russia between 1880 and 1920. While a large majority emigrated to the United States, some turned to Zionism. In 1882, members of  In total, there were at least twelve Jewish deputies in the First Duma (1906ŌĆō1907), falling to three or four in the Second Duma (February 1907 to June 1907), two in the Third Duma (1907ŌĆō1912) and again three in the fourth, elected in 1912. Converts to Christianity like Mikhail Herzenstein and
In total, there were at least twelve Jewish deputies in the First Duma (1906ŌĆō1907), falling to three or four in the Second Duma (February 1907 to June 1907), two in the Third Duma (1907ŌĆō1912) and again three in the fourth, elected in 1912. Converts to Christianity like Mikhail Herzenstein and  Many Jews were prominent in Russian revolutionary parties. The idea of overthrowing the Tsarist regime was attractive to many members of the Jewish
Many Jews were prominent in Russian revolutionary parties. The idea of overthrowing the Tsarist regime was attractive to many members of the Jewish  In March 1919, Vladimir Lenin delivered a speech "On Anti-Jewish Pogroms" on a
In March 1919, Vladimir Lenin delivered a speech "On Anti-Jewish Pogroms" on a  Lenin was supported by the Labor Zionist ( Poale Zion) movement, then under the leadership of Marxist theorist
Lenin was supported by the Labor Zionist ( Poale Zion) movement, then under the leadership of Marxist theorist  According to
According to  According to the census of 1926, the total number of Jews in the USSR was 2,672,398ŌĆöof whom 59% lived in Ukrainian SSR, 15.2% in
According to the census of 1926, the total number of Jews in the USSR was 2,672,398ŌĆöof whom 59% lived in Ukrainian SSR, 15.2% in  Russian Jews were long considered to be a non-native
Russian Jews were long considered to be a non-native  To offset the growing Jewish national and religious aspirations of Zionism and to successfully categorize Soviet Jews under Stalin's definition of nationality, an alternative to the
To offset the growing Jewish national and religious aspirations of Zionism and to successfully categorize Soviet Jews under Stalin's definition of nationality, an alternative to the  The MolotovŌĆōRibbentrop pactŌĆöthe 1939 non-aggression pact with Nazi GermanyŌĆöcreated further suspicion regarding the Soviet Union's position toward Jews. According to the pact, Poland, the nation with the world's largest Jewish population, was divided between Germany and the Soviet Union in September 1939. While the pact had no basis in ideological sympathy (as evidenced by Nazi propaganda about " Jewish Bolshevism"), Germany's occupation of Western Poland was a disaster for Eastern European Jews. Evidence suggests that some, at least, of the Jews in the eastern Soviet zone of occupation welcomed the Russians as having a more liberated policy towards their civil rights than the preceding antisemitic Polish regime. Jews in areas annexed by the Soviet Union were deported eastward in great waves; as these areas would soon be invaded by Nazi Germany, this forced migration, deplored by many of its victims, paradoxically also saved the lives of several hundred thousand Jewish deportees.
The MolotovŌĆōRibbentrop pactŌĆöthe 1939 non-aggression pact with Nazi GermanyŌĆöcreated further suspicion regarding the Soviet Union's position toward Jews. According to the pact, Poland, the nation with the world's largest Jewish population, was divided between Germany and the Soviet Union in September 1939. While the pact had no basis in ideological sympathy (as evidenced by Nazi propaganda about " Jewish Bolshevism"), Germany's occupation of Western Poland was a disaster for Eastern European Jews. Evidence suggests that some, at least, of the Jews in the eastern Soviet zone of occupation welcomed the Russians as having a more liberated policy towards their civil rights than the preceding antisemitic Polish regime. Jews in areas annexed by the Soviet Union were deported eastward in great waves; as these areas would soon be invaded by Nazi Germany, this forced migration, deplored by many of its victims, paradoxically also saved the lives of several hundred thousand Jewish deportees.
 Jews who escaped the purges include
Jews who escaped the purges include  Because of Stalinist emphasis on its urban population, interwar migration inadvertently rescued countless Soviet Jews; Nazi Germany penetrated the entire former Jewish PaleŌĆöbut were kilometers short of Leningrad and Moscow. The migration of many Jews farther East from the Jewish Pale, which would become occupied by Nazi Germany, saved at least 40 percent of the Pale's original Jewish population.
By 1941, it was estimated that the Soviet Union was home to 4.855 million Jews, around 30% of all Jews worldwide. However, the majority of these were residents of rural western Belarus and UkraineŌĆöpopulations that suffered greatly due to the German occupation and the Holocaust. Only around 800,000 Jews lived outside the occupied territory, and 1,200,000 to 1,400,000 Jews were eventually evacuated eastwards. Of the three million left in occupied areas, the vast majority is thought to have perished in German extermination camps.
Because of Stalinist emphasis on its urban population, interwar migration inadvertently rescued countless Soviet Jews; Nazi Germany penetrated the entire former Jewish PaleŌĆöbut were kilometers short of Leningrad and Moscow. The migration of many Jews farther East from the Jewish Pale, which would become occupied by Nazi Germany, saved at least 40 percent of the Pale's original Jewish population.
By 1941, it was estimated that the Soviet Union was home to 4.855 million Jews, around 30% of all Jews worldwide. However, the majority of these were residents of rural western Belarus and UkraineŌĆöpopulations that suffered greatly due to the German occupation and the Holocaust. Only around 800,000 Jews lived outside the occupied territory, and 1,200,000 to 1,400,000 Jews were eventually evacuated eastwards. Of the three million left in occupied areas, the vast majority is thought to have perished in German extermination camps.
 The typical Soviet policy regarding the Holocaust was to present it as atrocities against Soviet citizens, not emphasizing the genocide of the Jews. For example, after the liberation of
The typical Soviet policy regarding the Holocaust was to present it as atrocities against Soviet citizens, not emphasizing the genocide of the Jews. For example, after the liberation of  These cases may have reflected Stalin's paranoia, rather than state ideologyŌĆöa distinction that made no practical difference as long as Stalin was alive, but which became salient on his death.
In April 1956, the Warsaw
These cases may have reflected Stalin's paranoia, rather than state ideologyŌĆöa distinction that made no practical difference as long as Stalin was alive, but which became salient on his death.
In April 1956, the Warsaw  Lenin, who claimed to be deeply committed to egalitarian ideals and the universality of all humanity, rejected Zionism as a reactionary movement, "bourgeois nationalism", "socially retrogressive", and a backward force that deprecates class divisions among Jews. Moreover, Zionism entailed contact between Soviet citizens and westerners, which was dangerous in a closed society. Soviet authorities were likewise fearful of any mass-movement which was independent of the
Lenin, who claimed to be deeply committed to egalitarian ideals and the universality of all humanity, rejected Zionism as a reactionary movement, "bourgeois nationalism", "socially retrogressive", and a backward force that deprecates class divisions among Jews. Moreover, Zionism entailed contact between Soviet citizens and westerners, which was dangerous in a closed society. Soviet authorities were likewise fearful of any mass-movement which was independent of the  According to the census of 1959 the Jewish population of the city Leningrad numbered 169,000 and the Great Choral synagogue was open in the 1960s with some 1,200 seats. The rabbi was
According to the census of 1959 the Jewish population of the city Leningrad numbered 169,000 and the Great Choral synagogue was open in the 1960s with some 1,200 seats. The rabbi was 

 Judaism today is officially designated as one of Russia's four "traditional religions", alongside Orthodox Christianity,
Judaism today is officially designated as one of Russia's four "traditional religions", alongside Orthodox Christianity,  Antisemitic incidents are mostly conducted by extremist, nationalist, and Islamist groups. Most of the antisemitic incidents are against Jewish cemeteries and building (community centers and synagogues) such as the assault against the Jewish community's center in Perm in March 2013 and the attack on Jewish nursery school in Volgograd in August 2013. Nevertheless, there were several violent attacks against Jews in Moscow in 2006 when a neo-Nazi stabbed 9 people at the Bolshaya Bronnaya Synagogue, the failed bomb attack on the same synagogue in 1999.
Antisemitic incidents are mostly conducted by extremist, nationalist, and Islamist groups. Most of the antisemitic incidents are against Jewish cemeteries and building (community centers and synagogues) such as the assault against the Jewish community's center in Perm in March 2013 and the attack on Jewish nursery school in Volgograd in August 2013. Nevertheless, there were several violent attacks against Jews in Moscow in 2006 when a neo-Nazi stabbed 9 people at the Bolshaya Bronnaya Synagogue, the failed bomb attack on the same synagogue in 1999.

 Attacks against Jews made by extremist Islamic groups are rare in Russia although there has been increase in the scope of the attacks mainly in Muslim populated areas. On July 25, 2013, the rabbi of Derbent was attacked and badly injured by an unknown person near his home, most likely by a terrorist. The incident sparked concerns among the local Jews of further acts against the Jewish community.
After the passage of some anti-gay laws in Russia in 2013 and the incident with the "Pussy-riot" band in 2012 causing a growing criticism on the subject inside and outside Russia a number of verbal anti-Semitic attacks were made against Russian gay activists by extremist activists and anti-Semitic writers such as Israel Shamir who viewed the "Pussy-riot" incident as the war of Judaism on the Christian Orthodox church.
Attacks against Jews made by extremist Islamic groups are rare in Russia although there has been increase in the scope of the attacks mainly in Muslim populated areas. On July 25, 2013, the rabbi of Derbent was attacked and badly injured by an unknown person near his home, most likely by a terrorist. The incident sparked concerns among the local Jews of further acts against the Jewish community.
After the passage of some anti-gay laws in Russia in 2013 and the incident with the "Pussy-riot" band in 2012 causing a growing criticism on the subject inside and outside Russia a number of verbal anti-Semitic attacks were made against Russian gay activists by extremist activists and anti-Semitic writers such as Israel Shamir who viewed the "Pussy-riot" incident as the war of Judaism on the Christian Orthodox church.
 The Jewish Autonomous Oblast continues to be an autonomous oblast of the Russian state. The
The Jewish Autonomous Oblast continues to be an autonomous oblast of the Russian state. The  Today, the Jewish population of Russia is shrinking due to small family sizes, and high rates of assimilation and intermarriage. This shrinkage has been slowed by some Russian-Jewish emigrants having returned from abroad, especially from Germany. The great majority of up to 90% of children born to a Jewish parent are the offspring of mixed marriages, and most Jews have only one or two children. The majority of Russian Jews live in the Moscow metropolitan area, with another 20% in the Saint Petersburg area, and the rest in large cities with a population of at least 1 million.
The Jewish population in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast of the Russian Far East in 2002 was 2,327 (1.22%).
The
Today, the Jewish population of Russia is shrinking due to small family sizes, and high rates of assimilation and intermarriage. This shrinkage has been slowed by some Russian-Jewish emigrants having returned from abroad, especially from Germany. The great majority of up to 90% of children born to a Jewish parent are the offspring of mixed marriages, and most Jews have only one or two children. The majority of Russian Jews live in the Moscow metropolitan area, with another 20% in the Saint Petersburg area, and the rest in large cities with a population of at least 1 million.
The Jewish population in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast of the Russian Far East in 2002 was 2,327 (1.22%).
The  In present times, the largest number of Russian Jews are '' olim'' (ūóūĢų╣ū£ūÖūØ) and '' sabras''. In 2011 Russians were around 15% of Israel's 7.7 million population (including Halakhally non-Jews who constituted about 30% of immigrants from the former Soviet Union). The Aliyah in the 1990s accounts for 85ŌĆō90% of this population.
The population growth rate for Former Soviet Union (FSU)-born ''olim'' were among the lowest for any Israeli groups, with a Fertility rate of 1.70 and natural increase of just +0.5% per year. The increase in Jewish birth rate in Israel during the 2000ŌĆō2007 period was partly due to the increasing birth rate among the FSU ''olim'', who now form 20% of the Jewish population of Israel.
96.5% of the enlarged Russian Jewish population in Israel either belong to Judaism or are non-religious, while 3.5% (35,000) belong to other religions (mostly Christianity) and about 10,000 identifying as Messianic Jews separate from Jewish Christians.
The Total Fertility Rate for FSU-born ''olim'' in Israel is given in the table below. The TFR increased with time, peaking in 1997, then slightly decreased after that and then again increased after 2000.
In 1999, about 1,037,000 FSU-born ''olim'' lived in Israel, of whom about 738,900 made aliyah after 1989. The second largest ''oleh'' (ūóūĢų╣ū£ųČūö) group (
In present times, the largest number of Russian Jews are '' olim'' (ūóūĢų╣ū£ūÖūØ) and '' sabras''. In 2011 Russians were around 15% of Israel's 7.7 million population (including Halakhally non-Jews who constituted about 30% of immigrants from the former Soviet Union). The Aliyah in the 1990s accounts for 85ŌĆō90% of this population.
The population growth rate for Former Soviet Union (FSU)-born ''olim'' were among the lowest for any Israeli groups, with a Fertility rate of 1.70 and natural increase of just +0.5% per year. The increase in Jewish birth rate in Israel during the 2000ŌĆō2007 period was partly due to the increasing birth rate among the FSU ''olim'', who now form 20% of the Jewish population of Israel.
96.5% of the enlarged Russian Jewish population in Israel either belong to Judaism or are non-religious, while 3.5% (35,000) belong to other religions (mostly Christianity) and about 10,000 identifying as Messianic Jews separate from Jewish Christians.
The Total Fertility Rate for FSU-born ''olim'' in Israel is given in the table below. The TFR increased with time, peaking in 1997, then slightly decreased after that and then again increased after 2000.
In 1999, about 1,037,000 FSU-born ''olim'' lived in Israel, of whom about 738,900 made aliyah after 1989. The second largest ''oleh'' (ūóūĢų╣ū£ųČūö) group ( The second largest Russian Jewish population is in the United States. According to RINA, there is a core Russian Jewish population of 350,000 in the U.S. The enlarged Russian Jewish population in the U.S. is estimated to be 700,000.
Notable Russia, Imperial Russia, Soviet Union, and former Soviet Union, born Jewish Americans (living and deceased) include Alexei Abrikosov,
The second largest Russian Jewish population is in the United States. According to RINA, there is a core Russian Jewish population of 350,000 in the U.S. The enlarged Russian Jewish population in the U.S. is estimated to be 700,000.
Notable Russia, Imperial Russia, Soviet Union, and former Soviet Union, born Jewish Americans (living and deceased) include Alexei Abrikosov,  Austria, Belgium, United Kingdom, Britain, Italy, Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, New Zealand and Switzerland also have small populations of Russian Jews. The addition of Russian Jews have neutralized the negative Jewish population trends in some European countries like the Netherlands and Austria. Notable Russian Jews in France include L├®on Bakst, Marc Chagall, Leon Poliakov, Evgeny Kissin, Alexandre Koyr├®, Ida Rubinstein, Lev Shestov, and Anatoly Vaisser. Some other notable Russian Jews are Roman Abramovich, Vladimir Ashkenazy, Boris Berezovsky (businessman), Boris Berezovsky, and Maxim Vengerov (United Kingdom), Gennadi Sosonko (Netherlands), Viktor Korchnoi (Switzerland), and Maya Plisetskaya (Spain).
Austria, Belgium, United Kingdom, Britain, Italy, Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, New Zealand and Switzerland also have small populations of Russian Jews. The addition of Russian Jews have neutralized the negative Jewish population trends in some European countries like the Netherlands and Austria. Notable Russian Jews in France include L├®on Bakst, Marc Chagall, Leon Poliakov, Evgeny Kissin, Alexandre Koyr├®, Ida Rubinstein, Lev Shestov, and Anatoly Vaisser. Some other notable Russian Jews are Roman Abramovich, Vladimir Ashkenazy, Boris Berezovsky (businessman), Boris Berezovsky, and Maxim Vengerov (United Kingdom), Gennadi Sosonko (Netherlands), Viktor Korchnoi (Switzerland), and Maya Plisetskaya (Spain).