Ruptured eardrum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
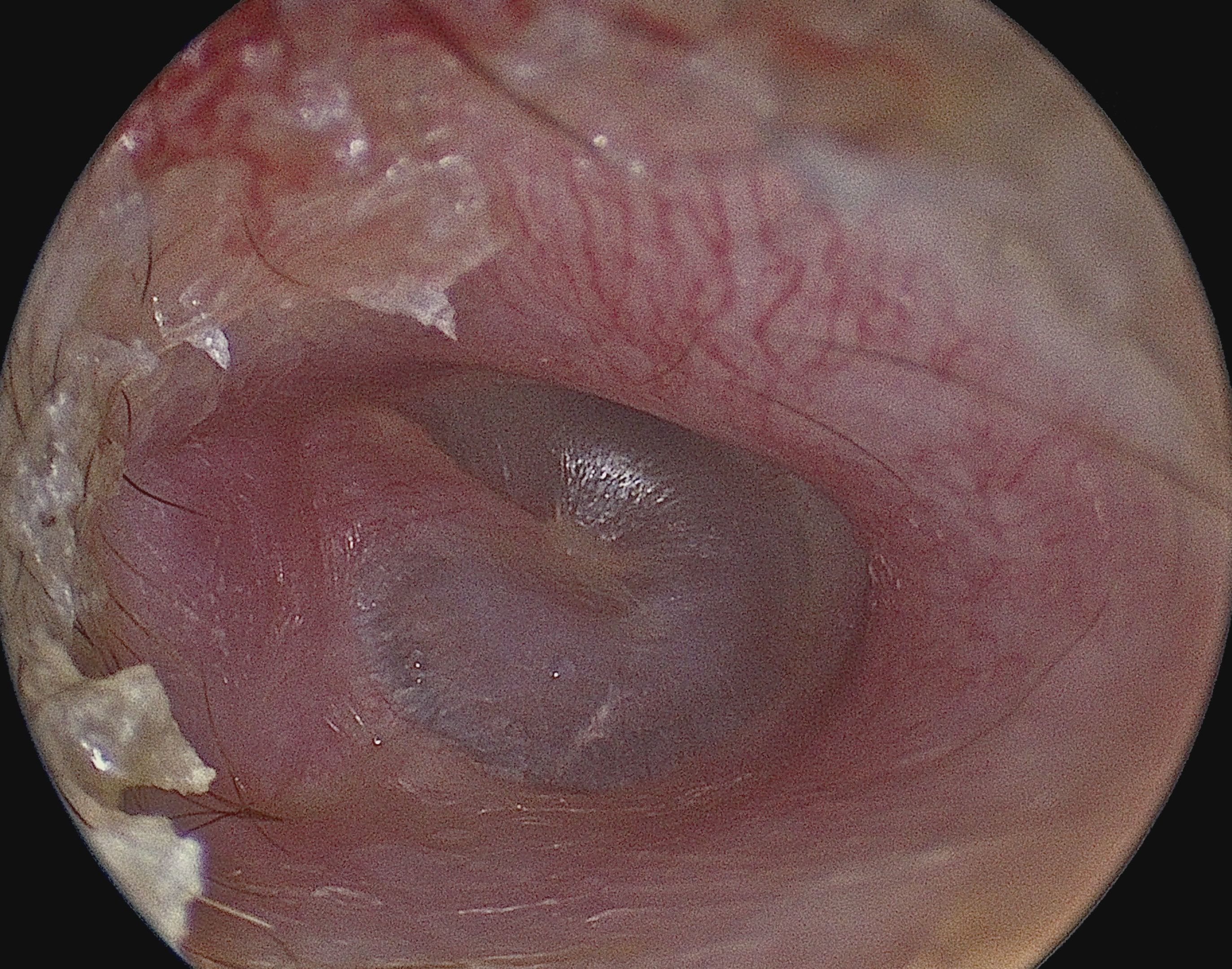 A perforated eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) is a hole in the
A perforated eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) is a hole in the
 A perforated eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) is a hole in the
A perforated eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) is a hole in the eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the extern ...
. It can be caused by infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
(otitis media
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, ...
), trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
* Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
* Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic i ...
, overpressure (loud noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arise ...
), inappropriate ear clearing
Ear clearing or clearing the ears or equalization is any of various maneuvers to equalize the pressure in the middle ear with the outside pressure, by letting air enter along the Eustachian tubes, as this does not always happen automatically w ...
, and changes in middle ear pressure. An otoscope
An otoscope or auriscope is a medical device which is used to look into the ears. Health care providers use otoscopes to screen for illness during regular check-ups and also to investigate ear symptoms. An otoscope potentially gives a view of ...
can be used to view the eardrum to diagnose a perforation. Perforations may heal naturally, or require surgery.
Presentation
A perforated eardrum leads toconductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss (CHL) occurs when there is a problem transferring sound waves anywhere along the pathway through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear ( ossicles). If a conductive hearing loss occurs in conjunction wi ...
, which is usually temporary. Other symptoms may include tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
, ear pain
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain i ...
, vertigo
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties w ...
, or a discharge of mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
. Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
and/or vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, foo ...
secondary to vertigo may occur.
Causes
A perforated eardrum can have one of many causes, such as: *infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
(otitis media
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, ...
). This infection may then spread through the middle ear, and may reoccur.
* trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
* Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
* Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic i ...
. This may be caused by trying to clean ear wax with sharp instruments. It may also occur due to surgical complications.
* overpressure (loud noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arise ...
or shockwave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
from an explosion
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume associated with an extreme outward release of energy, usually with the generation of high temperatures and release of high-pressure gases. Supersonic explosions created by high explosives are known ...
).
* inappropriate ear clearing
Ear clearing or clearing the ears or equalization is any of various maneuvers to equalize the pressure in the middle ear with the outside pressure, by letting air enter along the Eustachian tubes, as this does not always happen automatically w ...
.
* flying with a severe cold
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic ...
, due to changes in air pressure and blocked Eustachian tube
In anatomy, the Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in d ...
s resulting from the cold. This is especially true on landing.
Diagnosis
Anotoscope
An otoscope or auriscope is a medical device which is used to look into the ears. Health care providers use otoscopes to screen for illness during regular check-ups and also to investigate ear symptoms. An otoscope potentially gives a view of ...
can be used to look at the ear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
Struc ...
. This gives a view of the ear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
Struc ...
and eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the extern ...
, so that a perforated eardrum can be seen. Tympanometry
Tympanometry is an acoustic evaluation of the condition of the middle ear eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the conduction bones by creating variations of air pressure in the ear canal.
Tympanometry is an objective test of middle-ear function. It is ...
may also be used.
Treatment
Conservative management
A perforated eardrum often heals naturally. It may heal in a few weeks, or may take up to a few months.Surgery
Some perforations require surgical intervention. This may take the form of a paper patch to promote healing (a simple procedure by an ear, nose and throat specialist), or surgery (tympanoplasty
Tympanoplasty is the surgical operation performed to reconstruct hearing mechanism of middle ear
Classification
Tympanoplasty is classified into five different types, originally described by Horst Ludwig Wullstein (1906–1987) in 1956.
# Type 1 ...
). However, in some cases, the perforation can last several years and will be unable to heal naturally. For patients with persistent perforation, surgery is usually undertaken to close the perforation. The objective of the surgery is to provide a platform of sort to support the regrowth and healing of the tympanic membrane in the two weeks post surgery period. There are two ways of doing the surgery:
# Traditional tympanoplasty, usually using the microscope and performed through a 10 cm incision behind the ear lobe. This technique was introduced by Wullstien and Zollner and popularized by the Jim Sheehy at the House Ear Institute.
# Endoscopic tympanoplasty, usually using the endoscope through the ear canal without the need for incision. This technique was introduced and popularized by Professor Tarabichi of TSESI: Tarabichi Stammberger Ear and Sinus Institute.
The success of surgery is variable based on the cause of perforation and the technique being used. Predictors of success include traumatic perforation, dry ear, and central perforations. Predictors of failure includes young age and poor eustachian tube function. The use of minimally invasive endoscopic technique does not reduce the chance of successful outcome. Hearing is usually recovered fully, but chronic infection over a long period may lead to permanent hearing loss. Those with more severe ruptures may need to wear an ear plug to prevent water contact with the ear drum.
References
External links
{{Nonmusculoskeletal injuries of head, neck, and thorax Diseases of middle ear and mastoid Injuries of head