Runic transliteration and transcription on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a
on the site of the Swedish National Heritage Board, retrieved May 10, 2008.
 It is practically impossible to render the runes in all the various ways that they appear in the inscriptions, and so the way they look has to be presented in pictures and in drawings.
It is practically impossible to render the runes in all the various ways that they appear in the inscriptions, and so the way they look has to be presented in pictures and in drawings.

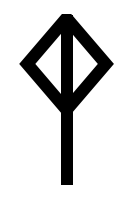 Transliteration means that the runes are represented by a corresponding Latin letter in bold. No consideration is given to the sound the rune represented in the actual inscription, and a good example of this is the
Transliteration means that the runes are represented by a corresponding Latin letter in bold. No consideration is given to the sound the rune represented in the actual inscription, and a good example of this is the
runic inscription
A runic inscription is an inscription made in one of the various runic alphabets. They generally contained practical information or memorials instead of magic or mythic stories. The body of runic inscriptions falls into the three categories of El ...
which involves transliteration
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one writing system, script to another that involves swapping Letter (alphabet), letters (thus ''wikt:trans-#Prefix, trans-'' + ''wikt:littera#Latin, liter-'') in predictable ways, such as ...
of the runes into Latin letters
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy ...
, transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
of the inscription into a modern language. There is a long-standing practice of formatting transliterations in boldface
In typography, emphasis is the strengthening of words in a text with a font in a different style from the rest of the text, to highlight them. It is the equivalent of prosody stress in speech.
Methods and use
The most common methods in W ...
and transcriptions in ''Italic type
In typography, italic type is a cursive font based on a stylised form of calligraphic handwriting. Owing to the influence from calligraphy, italics normally slant slightly to the right. Italics are a way to emphasise key points in a printed tex ...
'', as the two forms of rendering a runic text have to be kept distinct.
Overview
By not only showing the original inscription, but also transliterating, transcribing and translating, scholars present the analysis in a way that allows the reader to follow their interpretation of the runes. Every step has its challenges, but mostYounger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet and a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, with only 16 characters, in use from about the 9th century, after a "transitional period" during the 7th and 8th centuries.
The r ...
inscriptions are quite easy to interpret. Most Scandinavians can learn to read runic inscriptions with a little training. The Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Peri ...
inscriptions, however, are much more challenging and they demand a great deal of knowledge in historical linguistics. Standard works such as Sveriges runinskrifter contain extensive presentations of the ways inscriptions have been interpreted throughout the centuries.''Att läsa runor och runinskrifter''on the site of the Swedish National Heritage Board, retrieved May 10, 2008.
Runes
 It is practically impossible to render the runes in all the various ways that they appear in the inscriptions, and so the way they look has to be presented in pictures and in drawings.
It is practically impossible to render the runes in all the various ways that they appear in the inscriptions, and so the way they look has to be presented in pictures and in drawings.
Transliteration
 Transliteration means that the runes are represented by a corresponding Latin letter in bold. No consideration is given to the sound the rune represented in the actual inscription, and a good example of this is the
Transliteration means that the runes are represented by a corresponding Latin letter in bold. No consideration is given to the sound the rune represented in the actual inscription, and a good example of this is the ansuz rune
Ansuz is the conventional name given to the ''a''-rune of the Elder Futhark, .
The name is based on Proto-Germanic ''* ansuz'', denoting a deity belonging to the principal pantheon in Germanic paganism.
The shape of the rune is likely from N ...
, which could vary greatly in shape. In the oldest Younger Futhark inscriptions, it always represented a nasal a, as in French ''an'', but later it came to represent other phonemes such as /o/. However, some runemaster
A runemaster or runecarver is a specialist in making runestones.
Description
More than 100 names of runemasters are known from Viking Age Sweden with most of them from 11th-century eastern Svealand.The article ''Runristare'' in ''Nationalencyklo ...
s continued to use the ansuz rune for an ''a'' phoneme. The ansuz rune is always transliterated as o from the Younger Futhark, and consequently, the transliteration mon represents Old Norse ''man'' in a runestone from Bällsta, and hon represents Old Norse ''han'' in the Frösö Runestone
Frösöstenen ( J RS1928;66 $) is the northernmost raised runestone in ScandinaviaThe northernmost in the world is the Kingittorsuaq Runestone, in Greenland and Jämtland's only runestone. It originally stood at the tip of ferry terminal on the ...
, while forþom represents Old Norse ''forðom'' in an inscription from Replösa.
Sometimes the runes are "dotted" which means that a dot has been added, and in transliterations dotted runes are treated differently from ordinary runes. Dotted u, k and i are transliterated as y, g and e though they are rather variations of the non-dotted runes than runes in their own right.
Bind rune
A bind rune or bindrune ( is, bandrún) is a Migration Period Germanic typographic ligature, ligature of two or more Runic alphabet, runes. They are extremely rare in Viking Age inscriptions, but are common in earlier (Proto-Norse) and later (med ...
s are marked with an arch. Some bind runes look in a way that makes it impossible to know which rune preceded the other, and then the scholar has to test the various combinations that give a comprehensible word. Thus all transliterations of bind runes are scholarly interpretations.
Runes that are known from older depictions but that have since disappeared are rendered within square brackets.
Transcription or normalization
The runes are transcribed into normalized spellings of the languages the runes were written in, and normalizations are rendered with italics. Since a single rune may represent several different phonemes, normalizations can differ greatly from transliterations. The þ rune can represent both the Old Norse letter ''ð'' (as in English ''the'') or ''þ'' (as in English ''thing'').See also
*List of runestones
There are about 3,000 runestones in Scandinavia (out of a total of about 6,000 runic inscriptions). p. 38.
The runestones are unevenly distributed in Scandinavia:
The majority is found in Sweden, estimated at between 1,700 and 2,500 (depending o ...
*Old Norse orthography
The orthography of the Old Norse language was diverse, being written in both Runic and Latin alphabets, with many spelling conventions, variant letterforms, and unique letters and signs. In modern times, scholars established a standardized spellin ...
*Runology
Runology is the study of the Runic alphabets, Runic inscriptions and their history. Runology forms a specialized branch of Germanic linguistics.
History
Runology was initiated by Johannes Bureus (1568–1652), who was very interested in the lingu ...
Notes and references