Rum, Romanism, And Rebellion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The
The
File:Bfbutler.jpg,
File:AllenGThurman.png,
File:James Weaver - Brady-Handy (cropped).jpg,
The Anti-Monopoly National Convention assembled in the Hershey Music Hall in Chicago, Illinois on May 14. The party had been formed to express opposition to the business practices of the emerging nationwide companies. There were around 200 delegates from 16 states, but 61 of them were from Michigan and Illinois.
Alson Streeter was the temporary chairman and John F. Henry was the permanent chairman.
File:Bfbutler.jpg,
File:Jesseharper.jpg,
The third Greenback National Convention assembled in English's Opera House in Indianapolis, Indiana. Delegates from 28 states and the
File:Samuel C. Pomeroy - Brady-Handy.jpg,
The American Prohibition Party held its national convention in the YMCA building in Chicago, Illinois. There were 150 delegates, including many non-voting delegates. The party sought to merge the reform movements of
File:John St John 1880.jpg,
The fourth Prohibition Party National Convention assembled in Lafayette Hall, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. There were 505 delegates from 31 states and territories at the convention. The national ticket was nominated unanimously: John St. John for president and William Daniel for vice president. The straightforward single-issue
File:Belva Ann Lockwood - Brady-Handy.jpg,
Dissatisfied with resistance by the men of the major parties to women's suffrage, a small group of women announced the formation in 1884 of the Equal Rights Party.
The Equal Rights Party held its national convention in San Francisco, California, on September 20. The convention nominated
 Commentator Jeff Jacoby notes that, "Not since George Washington had a candidate for president been so renowned for his rectitude." In July the Republicans found a refutation buried in Cleveland's past. Aided by sermons from a minister named George H. Ball, they charged that Cleveland had fathered an illegitimate child while he was a lawyer in Buffalo. When confronted with the scandal, Cleveland immediately instructed his supporters to "Above all, tell the truth." Cleveland admitted to paying child support in 1874 to Maria Crofts Halpin, the woman who claimed he fathered her child, named Oscar Folsom Cleveland after Cleveland's friend and law partner, but asserted that the child's paternity was uncertain. Shortly before election day, the Republican media published an affidavit from Halpin in which she stated that until she met Cleveland her "life was pure and spotless," and "there is not, and never was, a doubt as to the paternity of our child, and the attempt of Grover Cleveland, or his friends, to couple the name of Oscar Folsom, or any one else, with that boy, for that purpose is simply infamous and false." In a supplemental affidavit, Halpin also implied Cleveland had raped her, hence the conception of their child. Republican cartoonists across the land had a field day.
Cleveland's campaign decided that candor was the best approach to this scandal: it admitted that Cleveland had formed an "illicit connection" with the mother and that a child had been born and given the Cleveland surname. They also noted that there was no proof that Cleveland was the father, and claimed that, by assuming responsibility and finding a home for the child, he was merely doing his duty. Finally, they showed that the mother had not been forced into an asylum; her whereabouts were unknown. Blaine's supporters condemned Cleveland in the strongest of terms, singing "Ma, Ma, Where's my Pa?" (After Cleveland's victory, Cleveland supporters would respond to the taunt with: "Gone to the White House, Ha, Ha, Ha.") However, the Cleveland campaign's damage control worked well enough and the race remained a tossup through Election Day. The greatest threat to the Republicans came from reformers called "
Commentator Jeff Jacoby notes that, "Not since George Washington had a candidate for president been so renowned for his rectitude." In July the Republicans found a refutation buried in Cleveland's past. Aided by sermons from a minister named George H. Ball, they charged that Cleveland had fathered an illegitimate child while he was a lawyer in Buffalo. When confronted with the scandal, Cleveland immediately instructed his supporters to "Above all, tell the truth." Cleveland admitted to paying child support in 1874 to Maria Crofts Halpin, the woman who claimed he fathered her child, named Oscar Folsom Cleveland after Cleveland's friend and law partner, but asserted that the child's paternity was uncertain. Shortly before election day, the Republican media published an affidavit from Halpin in which she stated that until she met Cleveland her "life was pure and spotless," and "there is not, and never was, a doubt as to the paternity of our child, and the attempt of Grover Cleveland, or his friends, to couple the name of Oscar Folsom, or any one else, with that boy, for that purpose is simply infamous and false." In a supplemental affidavit, Halpin also implied Cleveland had raped her, hence the conception of their child. Republican cartoonists across the land had a field day.
Cleveland's campaign decided that candor was the best approach to this scandal: it admitted that Cleveland had formed an "illicit connection" with the mother and that a child had been born and given the Cleveland surname. They also noted that there was no proof that Cleveland was the father, and claimed that, by assuming responsibility and finding a home for the child, he was merely doing his duty. Finally, they showed that the mother had not been forced into an asylum; her whereabouts were unknown. Blaine's supporters condemned Cleveland in the strongest of terms, singing "Ma, Ma, Where's my Pa?" (After Cleveland's victory, Cleveland supporters would respond to the taunt with: "Gone to the White House, Ha, Ha, Ha.") However, the Cleveland campaign's damage control worked well enough and the race remained a tossup through Election Day. The greatest threat to the Republicans came from reformers called "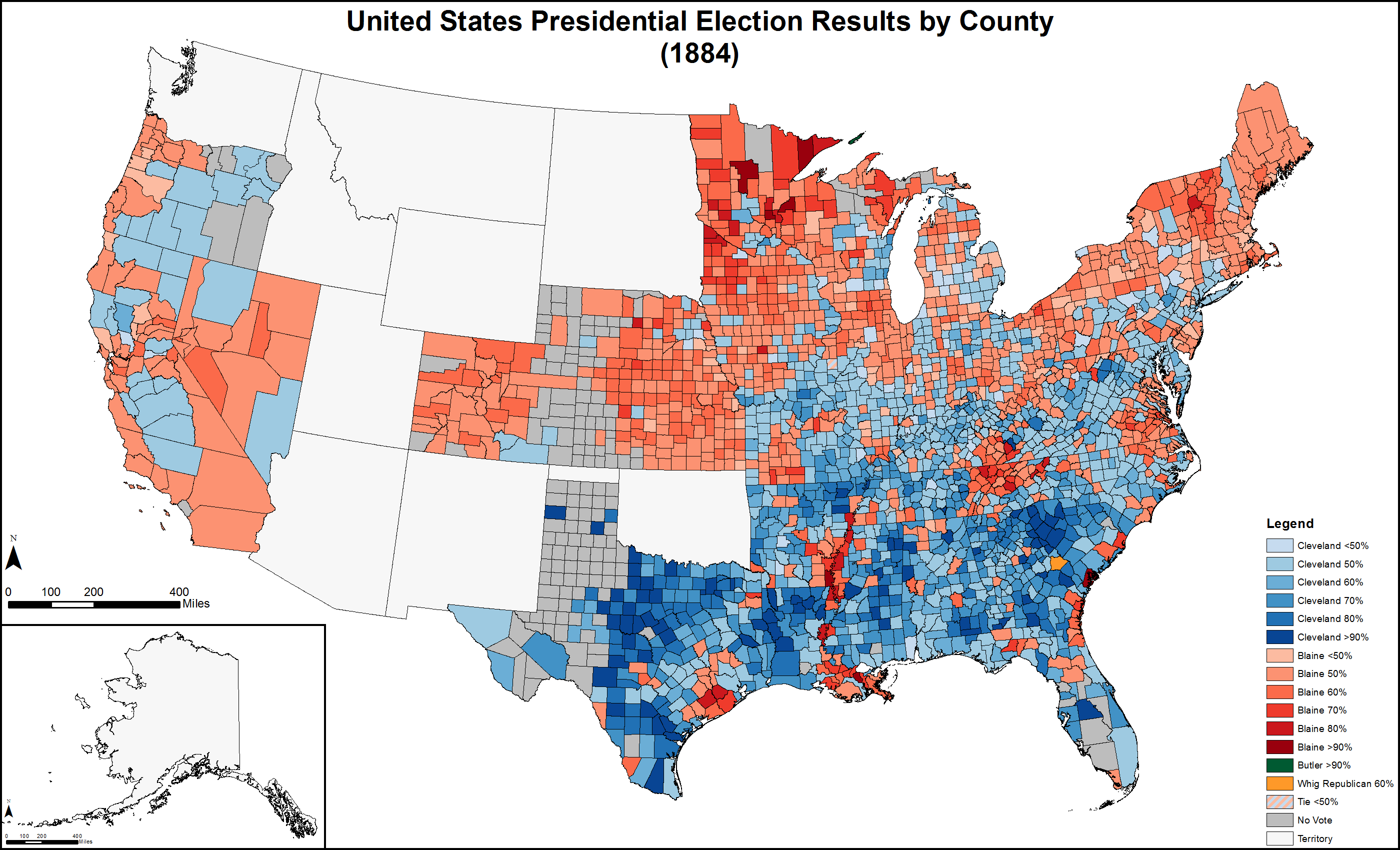 In the final week of the campaign, the Blaine campaign suffered a catastrophe. At a Republican meeting attended by Blaine, a group of New York preachers castigated the Mugwumps. Their spokesman, Reverend Dr. Samuel Burchard, said, "We are Republicans, and don't propose to leave our party and identify ourselves with the party whose antecedents have been
In the final week of the campaign, the Blaine campaign suffered a catastrophe. At a Republican meeting attended by Blaine, a group of New York preachers castigated the Mugwumps. Their spokesman, Reverend Dr. Samuel Burchard, said, "We are Republicans, and don't propose to leave our party and identify ourselves with the party whose antecedents have been
Image:1884 United States presidential election results map by county.svg, Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Image:PresidentialCounty1884Colorbrewer.gif, Map of presidential election results by county
Image:DemocraticPresidentialCounty1884Colorbrewer.gif, Map of Democratic presidential election results by county
Image:RepublicanPresidentialCounty1884Colorbrewer.gif, Map of Republican presidential election results by county
Image:OtherPresidentialCounty1884Colorbrewer.gif, Map of "other" presidential election results by county
online version
focus on 1884 * * * Summers, Mark Wahlgren. ''Rum, Romanism, and Rebellion: The Making of a President, 1884'
(2000) online version
''HarpWeek'', July 26, 2008. * * Thomas, Harrison Cook, ''The return of the Democratic Party to power in 1884'' (1919
online
online
* Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. ''National party platforms, 1840-1964'' (1965
online 1840-1956
from the Library of Congress
*
Election of 1884 in Counting the Votes
{{Authority control Presidencies of Grover Cleveland Grover Cleveland Thomas A. Hendricks James G. Blaine November 1884 1884 in American politics
Presidential elections
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The ...
were held in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
on November 4, 1884. Democratic Governor Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Hist ...
of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
narrowly defeated Republican James G. Blaine
James Gillespie Blaine (January 31, 1830January 27, 1893) was an American statesman and Republican politician who represented Maine in the United States House of Representatives from 1863 to 1876, serving as speaker of the U.S. House of Rep ...
of Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
. Ending a streak of six consecutive Republican victories, Cleveland was the first Democrat to win a presidential election since James Buchanan
James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was the 15th president of the United States, serving from 1857 to 1861. He also served as the United States Secretary of State, secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and represented Pennsylvan ...
did so in 1856
Events
January–March
* January 8 – Borax deposits are discovered in large quantities by John Veatch in California.
* January 23 – The American sidewheel steamer SS ''Pacific'' leaves Liverpool (England) for a transatl ...
.
Cleveland won the presidential nomination on the second ballot of the 1884 Democratic National Convention
The 1884 Democratic National Convention was held July 8–11, 1884 and chose Governor Grover Cleveland of New York their presidential nominee with the former Governor Thomas A. Hendricks of Indiana as the vice presidential nominee. World Book
B ...
. President Chester A. Arthur
Chester Alan Arthur (October 5, 1829 – November 18, 1886) was the 21st president of the United States, serving from 1881 to 1885. He was a Republican from New York who previously served as the 20th vice president under President James A. ...
had acceded to the presidency in 1881 following the assassination of James A. Garfield, but he was unsuccessful in his bid for nomination to a full term. Blaine, who had served as Secretary of State under President Garfield, defeated Arthur and other candidates on the fourth ballot of the 1884 Republican National Convention
The 1884 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Exposition Hall in Chicago, on June 3–6, 1884. It resulted in the nomination of former House Speaker James G. Blaine from Maine for president and S ...
. A group of reformist Republicans known as "Mugwumps
The Mugwumps were History of the Republican Party (United States), Republican political activists in the United States who were intensely opposed to political corruption. They were never formally organized. They famously Party switching, swit ...
" abandoned Blaine's candidacy, viewing him as corrupt. The campaign was characterized by mudslinging
Negative campaigning is the process of deliberately spreading negative information about someone or something to damage their public image. A colloquial and more derogatory term for the practice is mudslinging.
Deliberate spreading of such in ...
and personal allegations that eclipsed substantive issues, such as civil administration change, and it was marred by exceptional political acrimony and personal invective. Blaine's reputation for public corruption and his inadvertent last minute alienation of Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
voters proved decisive, as well as voter exhaustion after a generation of Republican rule.
In the election, Cleveland won 48.8% of the nationwide popular vote and 219 electoral votes
An electoral college is a body whose task is to elect a candidate to a particular office. It is mostly used in the political context for a constitutional body that appoints the head of state or government, and sometimes the upper parliamenta ...
, carrying the Solid South
The Solid South was the electoral voting bloc for the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party in the Southern United States between the end of the Reconstruction era in 1877 and the Civil Rights Act of 1964. In the aftermath of the Co ...
and several key swing state
In United States politics, a swing state (also known as battleground state, toss-up state, or purple state) is any state that could reasonably be won by either the Democratic or Republican candidate in a statewide election, most often refe ...
s. Blaine won 48.3% of the popular vote and 182 electoral votes. Cleveland won his home state by just 1,149 votes. Two third-party candidates, John St. John of the Prohibition Party
The Prohibition Party (PRO) is a Political parties in the United States, political party in the United States known for its historic opposition to the sale or consumption of alcoholic beverages and as an integral part of the temperance movemen ...
and Benjamin Butler
Benjamin Franklin Butler (November 5, 1818 – January 11, 1893) was an American major general (United States), major general of the Union Army, politician, lawyer, and businessman from Massachusetts. Born in New Hampshire and raised in Lowell, ...
of the Greenback Party
The Greenback Party (known successively as the Independent Party, the National Independent Party and the Greenback Labor Party) was an Political parties in the United States, American political party with an Competition law, anti-monopoly ideolog ...
and the Anti-Monopoly Party
The Anti-Monopoly Party was a short-lived American political party. The party nominated Benjamin Butler for President of the United States in 1884, as did the Greenback Party, which ultimately supplanted the organization.
Organizational hist ...
, each won less than 2% of the popular vote.
Marking an interruption in the era when Republicans largely controlled the presidency between Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
and the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, Cleveland (who would be elected to another non-consecutive term in 1892) was the first Democrat elected president since James Buchanan
James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was the 15th president of the United States, serving from 1857 to 1861. He also served as the United States Secretary of State, secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and represented Pennsylvan ...
in 1856
Events
January–March
* January 8 – Borax deposits are discovered in large quantities by John Veatch in California.
* January 23 – The American sidewheel steamer SS ''Pacific'' leaves Liverpool (England) for a transatl ...
, the first to hold office since Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. The 16th vice president, he assumed the presidency following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a South ...
left the White House in 1869, and the last to hold office until Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
, who began his first term in 1913. Blaine became the only Republican nominee in the 52-year period from 1860
Events
January
* January 2 – The astronomer Urbain Le Verrier announces the discovery of a hypothetical planet Vulcan (hypothetical planet), Vulcan at a meeting of the French Academy of Sciences in Paris, France.
* January 10 &ndas ...
to 1912
This year is notable for Sinking of the Titanic, the sinking of the ''Titanic'', which occurred on April 15.
In Albania, this leap year runs with only 353 days as the country achieved switching from the Julian to Gregorian Calendar by skippin ...
never to win a presidential election, and he was the last former secretary of state to be nominated by a major political party until 2016
2016 was designated as:
* International Year of Pulses by the sixty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly.
* International Year of Global Understanding (IYGU) by the International Council for Science (ICSU), the Internationa ...
.
Nominations
Democratic Party nomination
The Democrats convened in Chicago on July 8–11, 1884, with New York Governor Grover Cleveland as clear frontrunner, the candidate of northern reformers and sound-money men (as opposed to inflationists). AlthoughTammany Hall
Tammany Hall, also known as the Society of St. Tammany, the Sons of St. Tammany, or the Columbian Order, was an American political organization founded in 1786 and incorporated on May 12, 1789, as the Tammany Society. It became the main local ...
bitterly opposed his nomination, the machine represented a minority of the New York delegation. Its only chance to block Cleveland was to break the unit rule, which mandated that the votes of an entire delegation be cast for only one candidate, and this it failed to do. Daniel N. Lockwood from New York placed Cleveland's name in nomination. But this rather lackluster address was eclipsed by the seconding speech of Edward S. Bragg from Wisconsin, who roused the delegates with a memorable slap at Tammany. "They love him, gentlemen," Bragg said of Cleveland, "and they respect him, not only for himself, for his character, for his integrity and judgment and iron will, but they love him most of all for the enemies he has made." As the convention rocked with cheers, Tammany boss John Kelly lunged at the platform, screaming that he welcomed the compliment.
On the first ballot, Cleveland led the field with 392 votes, more than 150 votes short of the nomination. Trailing him were Thomas F. Bayard from Delaware, 170; Allen G. Thurman from Ohio, 88; Samuel J. Randall from Pennsylvania, 78; and Joseph E. McDonald from Indiana, 56; with the rest scattered. Randall then withdrew in Cleveland's favor. This move, together with the Southern bloc scrambling aboard the Cleveland bandwagon, was enough to put him over the top of the second ballot, with 683 votes to 81.5 for Bayard and 45.5 for Thomas A. Hendricks
Thomas Andrews Hendricks (September 7, 1819 – November 25, 1885) was an American politician and lawyer from Indiana who served as the 16th governor of Indiana from 1873 to 1877 and the 21st vice president of the United States from March until ...
from Indiana. Hendricks was nominated unanimously for vice president on the first ballot after John C. Black, William Rosecrans
William Starke Rosecrans (September 6, 1819March 11, 1898) was an American inventor, coal-oil company executive, diplomat, politician, and U.S. Army officer. He gained fame for his role as a Union general during the American Civil War. He was ...
, and George Washington Glick withdrew their names from consideration.
Republican Party nomination
 The
The 1884 Republican National Convention
The 1884 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Exposition Hall in Chicago, on June 3–6, 1884. It resulted in the nomination of former House Speaker James G. Blaine from Maine for president and S ...
was held in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, Illinois, on June 3–6, with former Secretary of State James G. Blaine from Maine, President Arthur, and Senator George F. Edmunds
George Franklin Edmunds (February 1, 1828February 27, 1919) was an American attorney and Republican politician who represented the state of Vermont in the United States Senate from 1866 to 1891. He was a candidate for the Republican president ...
from Vermont as the frontrunners. Though he was still popular, Arthur did not make a serious bid for a full-term nomination, knowing that his increasing health problems meant he would probably not survive a second term (he ultimately died in November 1886). Blaine led on the first ballot, with Arthur second, and Edmunds third. This order did not change on successive ballots as Blaine increased his lead, and he won a majority on the fourth ballot. After nominating Blaine, the convention chose Senator John A. Logan from Illinois as the vice-presidential nominee. Blaine remains the only presidential nominee ever to come from Maine.
Famed Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
general William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a General officer, general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), earning recognit ...
was considered a possible Republican candidate, but ruled himself out with what has become known as the Sherman pledge: "If drafted, I will not run; if nominated, I will not accept; if elected, I will not serve." Robert Todd Lincoln
Robert Todd Lincoln (August 1, 1843 – July 26, 1926) was an American lawyer and businessman. The eldest son of President Abraham Lincoln and Mary Todd Lincoln, he was the only one of their four children to survive past the teenage years ...
, Secretary of War of the United States, and son of the past President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
, was also strongly courted by politicians and the media of the day to seek the presidential or vice-presidential nomination, but Lincoln was as averse to the nomination as Sherman.
Other parties and candidates
Anti-Monopoly Party nomination
Anti-Monopoly candidates:Benjamin Butler
Benjamin Franklin Butler (November 5, 1818 – January 11, 1893) was an American major general (United States), major general of the Union Army, politician, lawyer, and businessman from Massachusetts. Born in New Hampshire and raised in Lowell, ...
was nominated for president on the first ballot. Delegates from New York, Washington, D.C., and Maryland bolted the convention when it appeared that no discussion of other candidates would be allowed. Allen G. Thurman and James B. Weaver were put forward as alternatives to Butler, but Weaver declined, not wishing to run another national campaign for political office, and Thurman generated little enthusiasm. Butler, while far from opposed to the nomination, hoped to be nominated by the Democratic or Republican party, or at least in the case of the former, to make its platform more favorable to greenbacks. Ultimately only the Greenback Party
The Greenback Party (known successively as the Independent Party, the National Independent Party and the Greenback Labor Party) was an Political parties in the United States, American political party with an Competition law, anti-monopoly ideolog ...
endorsed his candidacy.
The convention chose not to nominate a candidate for vice president, hoping that other conventions would endorse a similar platform and name a suitable vice-presidential nominee. The committee ultimately nominated Absolom Madden West
Absolom Madden West (c. 1818 – September 30, 1894) was an American planter, Confederate militia general, state politician, railroad president and labor organizer. Born in Alabama, he became a plantation owner in Holmes County, Mississippi, ...
as their vice-presidential candidate.
Greenback Party nomination
Greenback candidates:District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
were in attendance. The convention nominated former Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
Benjamin Butler for president over chairman Jesse Harper on the first ballot. Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
State Senator
A state senator is a member of a State legislature (United States), state's senate in the bicameral legislature of 49 U.S. states, or a member of the unicameral Nebraska Legislature.
History
There are typically fewer state senators than there ...
Absolom M. West was nominated unanimously for vice president. The ticket was subsequently adopted by the Anti-Monopoly Party.
Butler initially hoped to organize fusion tickets with the minority party in each state, a strategy designed to capitalize on the cross-partisan popularity of many elements of the candidate's program. The Greenbacks succeeded in negotiating fusion arrangements with the Democrats in Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Ill ...
, Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, and Nebraska
Nebraska ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Ka ...
and with the Republicans in Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
and West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
. The fusion electors agreed to divide their votes between Butler and Cleveland, or Butler and Blaine, in proportion to the statewide popular vote for each candidate; however, the fusion ticket was not elected in any state, and Butler received no votes in the Electoral College.
American Prohibition Party nomination
anti-masonry
Anti-Masonry (alternatively called anti-Freemasonry) is "avowed opposition to Freemasonry",''Oxford English Dictionary'' (1979 ed.), p. 369. which has led to multiple forms of religious discrimination, Religious violence, violent Religious persec ...
, prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
, anti-polygamy, and direct election of the president into a new party. Jonathan Blanchard was a major figure within the party. He traveled throughout northern states in the spring and gave an address entitled "The American Party – Its Principles and Its Claims."
During the convention, the party name was changed from the American Party to the American Prohibition Party. The party had been known as the Anti-Masonic Party in 1880. Many of the delegates at the convention were initially interested in nominating John St. John, the former governor of Kansas, but it was feared that such a nomination might cost him that of the Prohibition Party, which he was actively seeking. Party leaders met with Samuel C. Pomeroy, a former senator from the same state who was the convention's runner-up for the nomination, and at Pomeroy's suggestion they agreed to withdraw the ticket from the race should St. John win the Prohibition Party nomination. Nominated alongside Pomeroy was John A. Conant from Connecticut.
St. John later unanimously won the Prohibition Party nomination, with Pomeroy and Conant withdrawing from the presidential contest and endorsing him. The ''New York Times'' speculated that the endorsement would "give him 40,000 votes".
Prohibition Party nomination
Prohibition Party
The Prohibition Party (PRO) is a Political parties in the United States, political party in the United States known for its historic opposition to the sale or consumption of alcoholic beverages and as an integral part of the temperance movemen ...
platform advocated the criminalization of alcoholic beverage
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ...
s.
Equal Rights Party nomination
Belva Ann Lockwood
Belva Ann Bennett Lockwood (October 24, 1830 – May 19, 1917) was an American lawyer, politician, educator, and author who was active in the women's rights and women's suffrage movements. She was one of the first women lawyers in the United St ...
, an attorney in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, for president. Chairman Marietta Stow, the first woman to preside over a national nominating convention, was nominated for vice president.
Lockwood agreed to be the party's presidential candidate even though most women in the United States did not yet have the right to vote. She said, "I cannot vote but I can be voted for." She was the first woman to run a full campaign for the office (Victoria Woodhull
Victoria Claflin Woodhull (born Victoria California Claflin; September 23, 1838 – June 9, 1927), later Victoria Woodhull Martin, was an American leader of the women's suffrage movement who ran for president of the United States in the 187 ...
conducted a more limited campaign in 1872
Events January
* January 12 – Yohannes IV is crowned Emperor of Ethiopia in Axum, the first ruler crowned in that city in over 500 years.
*January 20 – The Cavite mutiny was an uprising of Filipino military personnel of Fort S ...
). The Equal Rights Party had no treasury, but Lockwood gave lectures to pay for campaign travel. She received approximately 4,194 votes nationally.
General election
Campaign
The issue of personal character was paramount in the 1884 campaign. Blaine had been prevented from getting the Republican presidential nomination during the previous two elections because of the stigma of the "Mulligan letters": in 1876, a Boston bookkeeper named James Mulligan had located some letters showing that Blaine had sold his influence in Congress to various businesses. One such letter ended with the phrase "burn this letter", from which a popular chant of the Democrats arose – "Burn, burn, burn this letter!" In just one deal, he had received $110,150 (over $1.5 million in 2010 dollars) from the Little Rock and Fort Smith Railroad for securing a federal land grant, among other things. Democrats and anti-Blaine Republicans made unrestrained attacks on his integrity as a result. Cleveland, on the other hand, was known as "Grover the Good" for his personal integrity; in the space of the three previous years he had become successively the mayor ofBuffalo, New York
Buffalo is a Administrative divisions of New York (state), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York and county seat of Erie County, New York, Erie County. It lies in Western New York at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of ...
, and then the governor of the state of New York, cleaning up large amounts of Tammany Hall's graft
Graft or grafting may refer to:
*Graft (politics), a form of political corruption
*Graft, Netherlands, a village in the municipality of Graft-De Rijp
Science and technology
*Graft (surgery), a surgical procedure
*Grafting, the joining of plant ti ...
.
 Commentator Jeff Jacoby notes that, "Not since George Washington had a candidate for president been so renowned for his rectitude." In July the Republicans found a refutation buried in Cleveland's past. Aided by sermons from a minister named George H. Ball, they charged that Cleveland had fathered an illegitimate child while he was a lawyer in Buffalo. When confronted with the scandal, Cleveland immediately instructed his supporters to "Above all, tell the truth." Cleveland admitted to paying child support in 1874 to Maria Crofts Halpin, the woman who claimed he fathered her child, named Oscar Folsom Cleveland after Cleveland's friend and law partner, but asserted that the child's paternity was uncertain. Shortly before election day, the Republican media published an affidavit from Halpin in which she stated that until she met Cleveland her "life was pure and spotless," and "there is not, and never was, a doubt as to the paternity of our child, and the attempt of Grover Cleveland, or his friends, to couple the name of Oscar Folsom, or any one else, with that boy, for that purpose is simply infamous and false." In a supplemental affidavit, Halpin also implied Cleveland had raped her, hence the conception of their child. Republican cartoonists across the land had a field day.
Cleveland's campaign decided that candor was the best approach to this scandal: it admitted that Cleveland had formed an "illicit connection" with the mother and that a child had been born and given the Cleveland surname. They also noted that there was no proof that Cleveland was the father, and claimed that, by assuming responsibility and finding a home for the child, he was merely doing his duty. Finally, they showed that the mother had not been forced into an asylum; her whereabouts were unknown. Blaine's supporters condemned Cleveland in the strongest of terms, singing "Ma, Ma, Where's my Pa?" (After Cleveland's victory, Cleveland supporters would respond to the taunt with: "Gone to the White House, Ha, Ha, Ha.") However, the Cleveland campaign's damage control worked well enough and the race remained a tossup through Election Day. The greatest threat to the Republicans came from reformers called "
Commentator Jeff Jacoby notes that, "Not since George Washington had a candidate for president been so renowned for his rectitude." In July the Republicans found a refutation buried in Cleveland's past. Aided by sermons from a minister named George H. Ball, they charged that Cleveland had fathered an illegitimate child while he was a lawyer in Buffalo. When confronted with the scandal, Cleveland immediately instructed his supporters to "Above all, tell the truth." Cleveland admitted to paying child support in 1874 to Maria Crofts Halpin, the woman who claimed he fathered her child, named Oscar Folsom Cleveland after Cleveland's friend and law partner, but asserted that the child's paternity was uncertain. Shortly before election day, the Republican media published an affidavit from Halpin in which she stated that until she met Cleveland her "life was pure and spotless," and "there is not, and never was, a doubt as to the paternity of our child, and the attempt of Grover Cleveland, or his friends, to couple the name of Oscar Folsom, or any one else, with that boy, for that purpose is simply infamous and false." In a supplemental affidavit, Halpin also implied Cleveland had raped her, hence the conception of their child. Republican cartoonists across the land had a field day.
Cleveland's campaign decided that candor was the best approach to this scandal: it admitted that Cleveland had formed an "illicit connection" with the mother and that a child had been born and given the Cleveland surname. They also noted that there was no proof that Cleveland was the father, and claimed that, by assuming responsibility and finding a home for the child, he was merely doing his duty. Finally, they showed that the mother had not been forced into an asylum; her whereabouts were unknown. Blaine's supporters condemned Cleveland in the strongest of terms, singing "Ma, Ma, Where's my Pa?" (After Cleveland's victory, Cleveland supporters would respond to the taunt with: "Gone to the White House, Ha, Ha, Ha.") However, the Cleveland campaign's damage control worked well enough and the race remained a tossup through Election Day. The greatest threat to the Republicans came from reformers called "Mugwump
The Mugwumps were History of the Republican Party (United States), Republican political activists in the United States who were intensely opposed to political corruption. They were never formally organized. They famously Party switching, swit ...
s" who were angrier at Blaine's public corruption than at Cleveland's private affairs.
 In the final week of the campaign, the Blaine campaign suffered a catastrophe. At a Republican meeting attended by Blaine, a group of New York preachers castigated the Mugwumps. Their spokesman, Reverend Dr. Samuel Burchard, said, "We are Republicans, and don't propose to leave our party and identify ourselves with the party whose antecedents have been
In the final week of the campaign, the Blaine campaign suffered a catastrophe. At a Republican meeting attended by Blaine, a group of New York preachers castigated the Mugwumps. Their spokesman, Reverend Dr. Samuel Burchard, said, "We are Republicans, and don't propose to leave our party and identify ourselves with the party whose antecedents have been rum
Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is often aged in barrels of oak. Rum originated in the Caribbean in the 17th century, but today it is produced i ...
, Romanism
''Romanism'' is a derogatory term for Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholicism used when anti-Catholicism was more common in the United States.
The term was frequently used in late-nineteenth and early-twentieth century Republican Party (United ...
, and rebellion
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
." Blaine did not notice Burchard's anti-Catholic slur, nor did the assembled newspaper reporters, but a Democratic operative did, and Cleveland's campaign managers made sure it was widely publicized. The statement energized the Irish and Catholic vote in New York City heavily against Blaine, costing him New York state and the election by a narrow margin.
In addition to Burchard's statement, it is also believed that John St. John's campaign was responsible for winning Cleveland the election in New York. Since Prohibitionists tended to ally more with Republicans, the Republican Party attempted to convince St. John to drop out. When they failed, they resorted to slandering him. Because of this, he redoubled his efforts in upstate New York, where Blaine was vulnerable on his prohibition stance, and took votes away from the Republicans.
Results
35.6% of the voting age population and 78.3% of eligible voters participated in the election. While the results remained broadly the same as those from 1880, Cleveland narrowly won three states (New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
, Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
, and Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
) that James A. Garfield
James Abram Garfield (November 19, 1831 – September 19, 1881) was the 20th president of the United States, serving from March 1881 until his death in September that year after being shot two months earlier. A preacher, lawyer, and Civi ...
had won, while Blaine won two states (California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
) that Winfield Hancock had won. But most of those states had relatively small numbers of electoral votes, and Cleveland's victory in New York was decisive. Cleveland won by a slightly larger margin than Garfield (0.57% compared to 0.11%) in the popular vote, but a slightly smaller margin in the Electoral College (29 votes to 59). Cleveland became the first Democrat to ever win without Pennsylvania, California, Nevada, and Illinois. Pennsylvania voted for the losing candidate for the first time since 1824, and the loser of the popular vote since 1800.
The result marked an electoral breakthrough for the Prohibition Party, who had been little more than a fringe party in the previous three elections. While they never seriously challenged for the presidency and had only limited success in congressional and state-level elections, they regularly earned at least a percentage point of the popular vote (and occasionally finished third in that vote) in presidential elections for the next three decades before declining back to fringe status after the passage of the Eighteenth Amendment in 1919. By contrast, Butler earned less than half the popular vote share that James B. Weaver had won in 1880, accelerating the decline of the Greenback Party. This was the last presidential election the party contested; it collapsed after failing to nominate a ticket in 1888.
This is one of only four U.S. presidential elections in which the winner did not carry any of the three Rust Belt
The Rust Belt, formerly the Steel Belt or Factory Belt, is an area of the United States that underwent substantial Deindustrialization, industrial decline in the late 20th century. The region is centered in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic (Uni ...
states of Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin; the others were 1916
Events
Below, the events of the First World War have the "WWI" prefix.
January
* January 1 – The British Empire, British Royal Army Medical Corps carries out the first successful blood transfusion, using blood that has been stored ...
, 2000
2000 was designated as the International Year for the Culture of Peace and the World Mathematics, Mathematical Year.
Popular culture holds the year 2000 as the first year of the 21st century and the 3rd millennium, because of a tende ...
, and 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and Its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 60 ...
.
16.08% of Blaine's votes came from the eleven states of the former Confederacy, with him taking 40.15% of the vote in that region.
In Burke County, Georgia
Burke County is a county located along the eastern border of the U.S. state of Georgia in the Piedmont. As of the 2020 census, the population was 24,596. The county seat is Waynesboro. Burke County is part of the Augusta-Richmond County, G ...
, 897 votes were cast for bolting "Whig Republican" electors for president (they were not counted for Blaine).An American Almanac and Treasury of Facts, Statistical, Financial, and Political, for the year 1886., Ainsworth R. Spofford, https://books.google.com/books?id=1ZcYAAAAIAAJ (pg. 207) The Republicans won in 20 of the 33 cities with populations over 50,000 outside the southern U.S.
Source (Popular Vote):
Source (Electoral Vote):
Geography of results
Cartographic gallery
Results by state
Source: Data fromWalter Dean Burnham
Walter Dean Burnham (June 15, 1930 – October 4, 2022) was an American political scientist who was an expert on elections and voting patterns. He was known for his quantitative analysis of national trends and patterns in voting behavior, t ...
, ''Presidential ballots, 1836–1892'' (Johns Hopkins University Press, 1955) pp 247–57.
States that flipped from Democratic to Republican
*California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
* Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
States that flipped from Republican to Democratic
*Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
* Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
* New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
Close states
Margin of victory less than 1% (55 electoral votes): # ''New York, 0.10% (1,149 votes) (tipping point state)'' #Michigan, 0.82% (3,308 votes) #Connecticut, 0.94% (1,284 votes) Margin of victory between 1% and 5% (117 electoral votes): #Indiana, 1.32% (6,516 votes) #New Jersey, 1.67% (4,358 votes) #Virginia, 2.15% (6,135 votes) #West Virginia, 3.19% (4,215 votes) #Tennessee, 3.72% (9,669 votes) #Illinois, 3.73% (25,118 votes) #Ohio, 4.05% (31,802 votes) #Oregon, 4.28% (2,256 votes) #Wisconsin, 4.59% (14,682 votes) #New Hampshire, 4.80% (4,056 votes) Margin of victory between 5% and 10% (104 electoral votes): #Iowa, 5.24% (19,773 votes) #Maryland, 5.98% (11,118 votes) #Florida, 6.23% (3,738 votes) #California, 6.64% (13,081 votes) #North Carolina, 6.66% (17,884 votes) #Missouri, 7.47% (32,942 votes) #Massachusetts, 8.03% (24,372 votes) #Pennsylvania, 9.52% (86,019 votes)See also
* American election campaigns in the 19th century *History of the United States (1865–1918)
The history of the present-day United States began in roughly 15,000 BC with the arrival of Peopling of the Americas, the first people in the Americas. In the late 15th century, European colonization of the Americas, European colonization beg ...
* First inauguration of Grover Cleveland
The inauguration of Grover Cleveland as the 22nd president of the United States took place on Wednesday, March 4, 1885, at the East Portico of the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. This was the 25th inauguration and marked the commencement ...
* 1884 United States House of Representatives elections
* 1884–1885 United States Senate elections
* President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
* Third Party System
The Third Party System was a period in the history of political parties in the United States from the 1850s until the 1890s, which featured profound developments in issues of American nationalism, modernization, and race. This period was marke ...
Notes
References
Works cited
* *Sources
* * Hirsch, Mark. "Election of 1884", in ''History of Presidential Elections: Volume III 1848–1896'', ed. Arthur Schlesinger and Fred Israel (1971), 3:1578. * * * * * Norgren, Jill. ''Belva Lockwood: The Woman Who Would be President'' (2007)online version
focus on 1884 * * * Summers, Mark Wahlgren. ''Rum, Romanism, and Rebellion: The Making of a President, 1884'
(2000) online version
''HarpWeek'', July 26, 2008. * * Thomas, Harrison Cook, ''The return of the Democratic Party to power in 1884'' (1919
online
Primary sources
* * Chester, Edward W ''A guide to political platforms'' (1977online
* Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. ''National party platforms, 1840-1964'' (1965
online 1840-1956
External links
from the Library of Congress
*
Election of 1884 in Counting the Votes
{{Authority control Presidencies of Grover Cleveland Grover Cleveland Thomas A. Hendricks James G. Blaine November 1884 1884 in American politics