Rosetta Probe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Rosetta'' was a space probe built by the
 ''Rosetta'' was launched on 2 March 2004 from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana, on an
''Rosetta'' was launched on 2 March 2004 from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana, on an
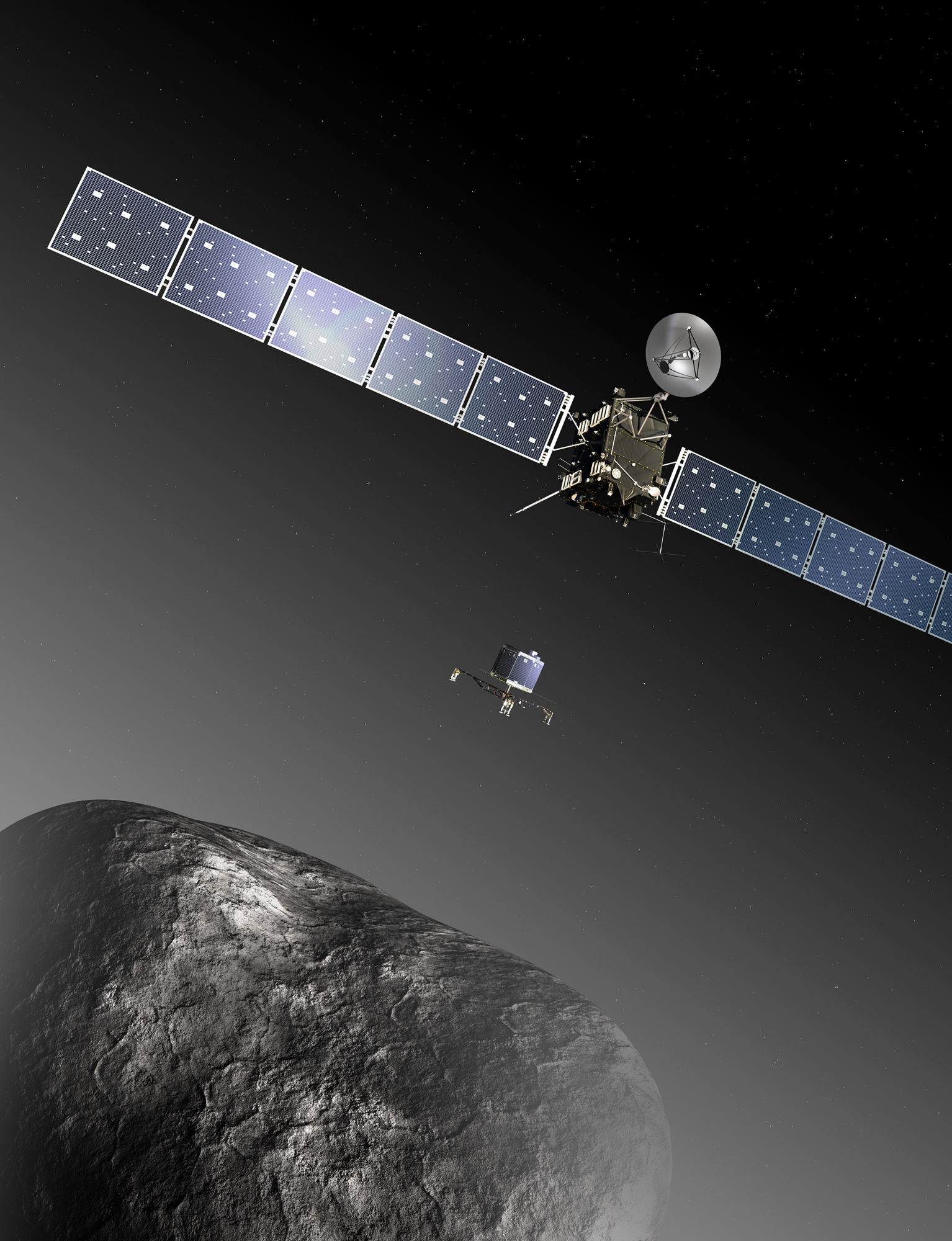 The ''Rosetta'' mission achieved many historic firsts.
On its way to comet 67P, ''Rosetta'' passed through the main asteroid belt, and made the first European close encounter with several of these primitive objects. ''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to fly close to Jupiter's orbit using solar cells as its main power source.
''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to orbit a comet nucleus, and was the first spacecraft to fly alongside a comet as it headed towards the inner Solar System. It became the first spacecraft to examine at close proximity the activity of a frozen comet as it is warmed by the Sun. Shortly after its arrival at 67P, the ''Rosetta'' orbiter dispatched the '' Philae'' lander for the first controlled touchdown on a comet nucleus. The robotic lander's instruments obtained the first images from a comet's surface and made the first '' in situ'' analysis of its composition.
The ''Rosetta'' mission achieved many historic firsts.
On its way to comet 67P, ''Rosetta'' passed through the main asteroid belt, and made the first European close encounter with several of these primitive objects. ''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to fly close to Jupiter's orbit using solar cells as its main power source.
''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to orbit a comet nucleus, and was the first spacecraft to fly alongside a comet as it headed towards the inner Solar System. It became the first spacecraft to examine at close proximity the activity of a frozen comet as it is warmed by the Sun. Shortly after its arrival at 67P, the ''Rosetta'' orbiter dispatched the '' Philae'' lander for the first controlled touchdown on a comet nucleus. The robotic lander's instruments obtained the first images from a comet's surface and made the first '' in situ'' analysis of its composition.
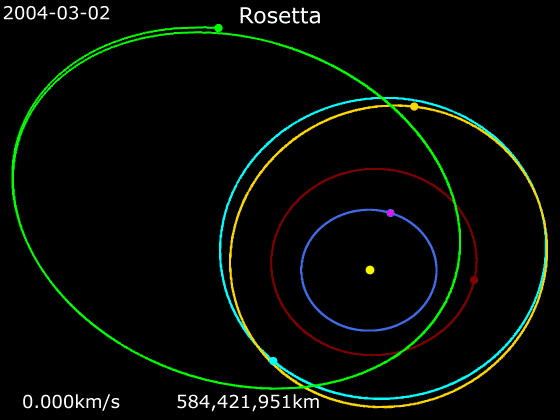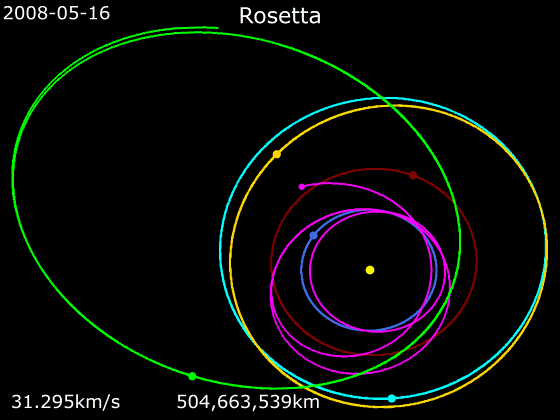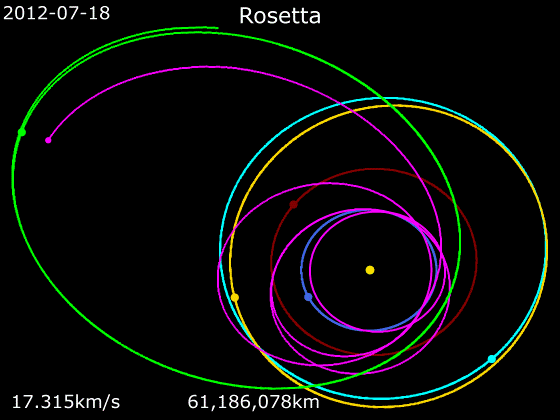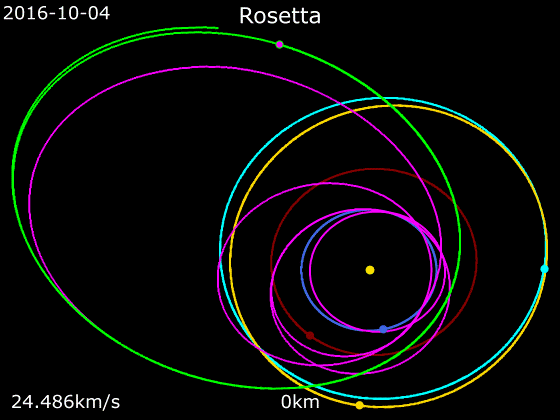
 ''Rosetta'' was set to be launched on 12 January 2003 to rendezvous with the comet
''Rosetta'' was set to be launched on 12 January 2003 to rendezvous with the comet

 After leaving its hibernation mode in January 2014 and getting closer to the comet, ''Rosetta'' began a series of eight burns in May 2014. These reduced the relative velocity between the spacecraft and 67P from to .
After leaving its hibernation mode in January 2014 and getting closer to the comet, ''Rosetta'' began a series of eight burns in May 2014. These reduced the relative velocity between the spacecraft and 67P from to .
 In August 2014, ''Rosetta'' rendezvoused with the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P) and commenced a series of manoeuvres that took it on two successive triangular paths, averaging from the nucleus, whose segments are hyperbolic escape trajectories alternating with thruster burns. After closing to within about from the comet on 10 September, the spacecraft entered actual orbit about it.
The surface layout of 67P was unknown before ''Rosetta'' arrival. The orbiter mapped the comet in anticipation of detaching its lander. By 25 August 2014, five potential landing sites had been determined. On 15 September 2014, ESA announced Site J, named ''Agilkia'' in honour of Agilkia Island by an ESA public contest and located on the "head" of the comet, as the lander's destination.
In August 2014, ''Rosetta'' rendezvoused with the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P) and commenced a series of manoeuvres that took it on two successive triangular paths, averaging from the nucleus, whose segments are hyperbolic escape trajectories alternating with thruster burns. After closing to within about from the comet on 10 September, the spacecraft entered actual orbit about it.
The surface layout of 67P was unknown before ''Rosetta'' arrival. The orbiter mapped the comet in anticipation of detaching its lander. By 25 August 2014, five potential landing sites had been determined. On 15 September 2014, ESA announced Site J, named ''Agilkia'' in honour of Agilkia Island by an ESA public contest and located on the "head" of the comet, as the lander's destination.
 '' Philae'' detached from ''Rosetta'' on 12 November 2014 at 08:35 UTC, and approached 67P at a relative speed of about . It initially landed on 67P at 15:33 UTC, but bounced twice, coming to rest at 17:33 UTC. Confirmation of contact with 67P reached Earth at 16:03 UTC.
On contact with the surface, two harpoons were to be fired into the comet to prevent the lander from bouncing off, as the comet's escape velocity is only around . Analysis of telemetry indicated that the surface at the initial touchdown site is relatively soft, covered with a layer of granular material about 0.82 feet (0.25 meters) deep, and that the harpoons had not fired upon landing. After landing on the comet, ''Philae'' had been scheduled to commence its science mission, which included:
* Characterisation of the nucleus
* Determination of the chemical compounds present, including amino acid
'' Philae'' detached from ''Rosetta'' on 12 November 2014 at 08:35 UTC, and approached 67P at a relative speed of about . It initially landed on 67P at 15:33 UTC, but bounced twice, coming to rest at 17:33 UTC. Confirmation of contact with 67P reached Earth at 16:03 UTC.
On contact with the surface, two harpoons were to be fired into the comet to prevent the lander from bouncing off, as the comet's escape velocity is only around . Analysis of telemetry indicated that the surface at the initial touchdown site is relatively soft, covered with a layer of granular material about 0.82 feet (0.25 meters) deep, and that the harpoons had not fired upon landing. After landing on the comet, ''Philae'' had been scheduled to commence its science mission, which included:
* Characterisation of the nucleus
* Determination of the chemical compounds present, including amino acid
 Researchers expect the study of data gathered will continue for decades to come. One of the first discoveries was that the magnetic field of 67P oscillated at 40–50 millihertz. A German composer and sound designer created an artistic rendition from the measured data to make it audible. Although it is a natural phenomenon, it has been described as a "song" and has been compared to ''Continuum'' for harpsichord by György Ligeti. However, results from ''Philae'' landing show that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field, and that the field originally detected by ''Rosetta'' is likely caused by the solar wind.
The isotopic signature of water vapour from comet 67P, as determined by the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, is substantially different from that found on Earth. That is, the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen in the water from the comet was determined to be three times that found for terrestrial water. This makes it very unlikely that water found on Earth came from comets such as comet 67P, according to the scientists. On 22 January 2015, NASA reported that, between June and August 2014, the rate at which water vapour was released by the comet increased up to tenfold.
On 2 June 2015, NASA reported that the Alice spectrograph on ''Rosetta'' determined that electrons within above the comet nucleus — produced from photoionization of water molecules, and not direct photons from the Sun as thought earlier — are responsible for the degradation of water and carbon dioxide molecules released from the comet nucleus into its
Researchers expect the study of data gathered will continue for decades to come. One of the first discoveries was that the magnetic field of 67P oscillated at 40–50 millihertz. A German composer and sound designer created an artistic rendition from the measured data to make it audible. Although it is a natural phenomenon, it has been described as a "song" and has been compared to ''Continuum'' for harpsichord by György Ligeti. However, results from ''Philae'' landing show that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field, and that the field originally detected by ''Rosetta'' is likely caused by the solar wind.
The isotopic signature of water vapour from comet 67P, as determined by the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, is substantially different from that found on Earth. That is, the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen in the water from the comet was determined to be three times that found for terrestrial water. This makes it very unlikely that water found on Earth came from comets such as comet 67P, according to the scientists. On 22 January 2015, NASA reported that, between June and August 2014, the rate at which water vapour was released by the comet increased up to tenfold.
On 2 June 2015, NASA reported that the Alice spectrograph on ''Rosetta'' determined that electrons within above the comet nucleus — produced from photoionization of water molecules, and not direct photons from the Sun as thought earlier — are responsible for the degradation of water and carbon dioxide molecules released from the comet nucleus into its

 ;Amino acids
Upon landing on the comet, ''Philae'' should have also tested some hypotheses as to why essential amino acids are almost all "left-handed", which refers to how the atoms arrange in orientation in relation to the carbon core of the molecule. Most asymmetrical molecules are oriented in approximately equal numbers of left- and right-handed configurations (
;Amino acids
Upon landing on the comet, ''Philae'' should have also tested some hypotheses as to why essential amino acids are almost all "left-handed", which refers to how the atoms arrange in orientation in relation to the carbon core of the molecule. Most asymmetrical molecules are oriented in approximately equal numbers of left- and right-handed configurations (
 ;2004
* 2 March – ''Rosetta'' was successfully launched at 07:17 UTC (04:17 local time) from Kourou, French Guiana.
;2005
* 4 March – ''Rosetta'' executed its first planned close swing-by (gravity assist passage) of Earth. The Moon and the Earth's magnetic field were used to test and calibrate the instruments on board of the spacecraft. The minimum altitude above the Earth's surface was .
* 4 July – Imaging instruments on board observed the collision between the comet Tempel 1 and the impactor of the Deep Impact mission.
;2007
* 25 February – Mars flyby.
* 8 November – Catalina Sky Survey briefly misidentified the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, approaching for its second Earth flyby, as a newly discovered asteroid.
* 13 November – Second Earth swing-by at a minimum altitude of , travelling at .
;2004
* 2 March – ''Rosetta'' was successfully launched at 07:17 UTC (04:17 local time) from Kourou, French Guiana.
;2005
* 4 March – ''Rosetta'' executed its first planned close swing-by (gravity assist passage) of Earth. The Moon and the Earth's magnetic field were used to test and calibrate the instruments on board of the spacecraft. The minimum altitude above the Earth's surface was .
* 4 July – Imaging instruments on board observed the collision between the comet Tempel 1 and the impactor of the Deep Impact mission.
;2007
* 25 February – Mars flyby.
* 8 November – Catalina Sky Survey briefly misidentified the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, approaching for its second Earth flyby, as a newly discovered asteroid.
* 13 November – Second Earth swing-by at a minimum altitude of , travelling at .
 ;2008
* 5 September – Flyby of asteroid 2867 Šteins. The spacecraft passed the main-belt asteroid at a distance of and the relatively slow speed of .
;2009
* 13 November – Third and final swing-by of Earth at .
;2010
* 16 March – Observation of the dust tail of asteroid P/2010 A2. Together with observations by Hubble Space Telescope it could be confirmed that P/2010 A2 is not a comet, but an asteroid, and that the tail most likely consists of particles from an impact by a smaller asteroid.
* 10 July – Flew by and photographed the asteroid
;2008
* 5 September – Flyby of asteroid 2867 Šteins. The spacecraft passed the main-belt asteroid at a distance of and the relatively slow speed of .
;2009
* 13 November – Third and final swing-by of Earth at .
;2010
* 16 March – Observation of the dust tail of asteroid P/2010 A2. Together with observations by Hubble Space Telescope it could be confirmed that P/2010 A2 is not a comet, but an asteroid, and that the tail most likely consists of particles from an impact by a smaller asteroid.
* 10 July – Flew by and photographed the asteroid  ;2014
* May to July – Starting on 7 May, ''Rosetta'' began orbital correction manoeuvres to bring itself into orbit around 67P. At the time of the first deceleration burn ''Rosetta'' was approximately away from 67P and had a relative velocity of +; by the end of the last burn, which occurred on 23 July, the distance had been reduced to just over with a relative velocity of +. In total eight burns were used to align the trajectories of ''Rosetta'' 67P with the majority of the deceleration occurring during three burns: Delta-''v'' of on 21 May, on 4 June, and on 18 June.
* 14 July – The OSIRIS on-board imaging system returned images of comet 67P which confirmed the irregular shape of the comet.
* 6 August – ''Rosetta'' arrives at 67P, approaching to and carrying out a thruster burn that reduces its relative velocity to . Commences comet mapping and characterisation to determine a stable orbit and viable landing location for ''Philae''.
* 4 September – The first science data from ''Rosetta'' Alice instrument was reported, showing that the comet is unusually dark in ultraviolet wavelengths, hydrogen and oxygen are present in the
;2014
* May to July – Starting on 7 May, ''Rosetta'' began orbital correction manoeuvres to bring itself into orbit around 67P. At the time of the first deceleration burn ''Rosetta'' was approximately away from 67P and had a relative velocity of +; by the end of the last burn, which occurred on 23 July, the distance had been reduced to just over with a relative velocity of +. In total eight burns were used to align the trajectories of ''Rosetta'' 67P with the majority of the deceleration occurring during three burns: Delta-''v'' of on 21 May, on 4 June, and on 18 June.
* 14 July – The OSIRIS on-board imaging system returned images of comet 67P which confirmed the irregular shape of the comet.
* 6 August – ''Rosetta'' arrives at 67P, approaching to and carrying out a thruster burn that reduces its relative velocity to . Commences comet mapping and characterisation to determine a stable orbit and viable landing location for ''Philae''.
* 4 September – The first science data from ''Rosetta'' Alice instrument was reported, showing that the comet is unusually dark in ultraviolet wavelengths, hydrogen and oxygen are present in the  ;2015
* 14 April 2015 – Scientists report that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field of its own.
* 2 July 2015 – Scientists report that active pits, related to sinkhole collapses and possibly associated with outbursts, have been found on the comet.
;2015
* 14 April 2015 – Scientists report that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field of its own.
* 2 July 2015 – Scientists report that active pits, related to sinkhole collapses and possibly associated with outbursts, have been found on the comet.
 * 11 August 2015 – Scientists release images of a comet outburst that occurred on 29 July 2015.
* 28 October 2015 – Scientists publish an article in '' Nature'' reporting high levels of molecular oxygen around 67P.
* November 2014 to December 2015 – ''Rosetta'' escorted the comet around the Sun and performed riskier investigations.
;2016
* 27 July 2016 – ESA switched off the Electrical Support System Processor Unit (ESS) aboard ''Rosetta'', disabling any possibility of further communications with the ''Philae'' lander.
* 2 September 2016 - ''Rosetta'' photographs the ''Philae'' lander for the first time after its landing, finding it wedged against a large overhang.
* 30 September 2016 - Mission ended in an attempt to slow land on the comet's surface near a wide pit called Deir el-Medina. The walls of the pit contain wide so-called "goose bumps", believed to represent the building blocks of the comet. Although ''Philae'' sent back some data during its descent, ''Rosetta'' has more powerful and more varied sensors and instruments, offering the opportunity to get some very close-in science to complement the more distant remote sensing it has been doing. The orbiter descended more slowly than ''Philae'' did.
* 11 August 2015 – Scientists release images of a comet outburst that occurred on 29 July 2015.
* 28 October 2015 – Scientists publish an article in '' Nature'' reporting high levels of molecular oxygen around 67P.
* November 2014 to December 2015 – ''Rosetta'' escorted the comet around the Sun and performed riskier investigations.
;2016
* 27 July 2016 – ESA switched off the Electrical Support System Processor Unit (ESS) aboard ''Rosetta'', disabling any possibility of further communications with the ''Philae'' lander.
* 2 September 2016 - ''Rosetta'' photographs the ''Philae'' lander for the first time after its landing, finding it wedged against a large overhang.
* 30 September 2016 - Mission ended in an attempt to slow land on the comet's surface near a wide pit called Deir el-Medina. The walls of the pit contain wide so-called "goose bumps", believed to represent the building blocks of the comet. Although ''Philae'' sent back some data during its descent, ''Rosetta'' has more powerful and more varied sensors and instruments, offering the opportunity to get some very close-in science to complement the more distant remote sensing it has been doing. The orbiter descended more slowly than ''Philae'' did.
German Aerospace Center">
File:CHASING A COMET - The Rosetta Mission.webm, About ''Rosetta'' mission
(9 min., 1080p HD, English) File:Landing on a Comet - The Rosetta Mission.webm, About ''Philae'' landing
(10 min., 1080p HD, English)
''Rosetta'' website
by ESA
''Rosetta'' news site
by ESA
''Rosetta'' website
by NASA
''Rosetta'' mission profile
by NASA
''Rosetta'' mission archive
at the NASA Planetary Data System ;Media
''Rosetta'' processed image gallery
on Flickr, by ESA
''Rosetta'' raw image gallery
at ESA's ''Archive Image Browser''
''Rosetta'' image gallery
at ESA's ''Space in Images''
"''Rosetta'' twelve-year journey in space"
on YouTube, by ESA
"''Rosetta'': landing on a comet"
by ESA
"''Rosetta'' journey around the comet"
on YouTube, by ESA
"''Rosetta'' final images"
on YouTube, by ESA
"How to land on a comet"
by Fred Jansen, at TED2015
Landing News and Comments
('' The New York Times''; 12 November 2014) {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Solar System, Space, Spaceflight 1 Missions to comets Astrobiology space missions European Space Agency space probes Orbiters (space probe) Space probes launched in 2004 Articles containing video clips 2004 in French Guiana Destroyed space probes
European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
launched on 2 March 2004. Along with '' Philae'', its lander module, ''Rosetta'' performed a detailed study of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P). During its journey to the comet, the spacecraft performed flybys
Flyby may refer to:
* Flypast or flyover, a celebratory display or ceremonial flight
* Flyby (spaceflight), a spacecraft concept
* Planetary flyby, a type of interplanetary spacecraft mission
* Gravity assist, a spaceflight maneuver
* Fly-by, cir ...
of Earth, Mars, and the asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
s 21 Lutetia
)
, mp_category=Main belt
, mpc_name=(21) Lutetia
, orbit_ref =
, epoch=May 31, 2020 ( JD 2459000.5)
, semimajor=2.435 AU
, perihelion=2.037 AU
, aphelion=2.833 AU
, eccentricity=0.16339
, period=3.80 yr (1388.1 d)
, inclination=3.064� ...
and 2867 Šteins. It was launched as the third cornerstone mission of the ESA's Horizon 2000 programme, after '' SOHO'Cluster
may refer to:
Science and technology Astronomy
* Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft
* Asteroid cluster, a small asteroid family
* Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study th ...
'' and '' XMM-Newton''.
On 6 August 2014, the spacecraft reached the comet and performed a series of manoeuvers to eventually orbit the comet at distances of . On 12 November, its lander module ''Philae'' performed the first successful landing on a comet, though its battery power ran out two days later. Communications with ''Philae'' were briefly restored in June and July 2015, but due to diminishing solar power, ''Rosetta'' communications module with the lander was turned off on 27 July 2016. On 30 September 2016, the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft ended its mission by hard-landing on the comet in its Ma'at region.
The probe was named after the Rosetta Stone, a stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
of Egyptian origin featuring a decree in three scripts. The lander was named after the Philae obelisk, which bears a bilingual Greek and Egyptian hieroglyphic inscription.
Mission overview
 ''Rosetta'' was launched on 2 March 2004 from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana, on an
''Rosetta'' was launched on 2 March 2004 from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana, on an Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It is launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) in French Guiana. It has been used to deliver payloads int ...
rocket and reached Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko on 7 May 2014. It performed a series of manoeuvres to enter orbit between then and 6 August 2014, when it became the first spacecraft to orbit a comet. ( Previous missions had conducted successful flybys of seven other comets.) It was one of ESA's Horizon 2000 cornerstone missions. The spacecraft consisted of the ''Rosetta'' orbiter, which featured 12 instruments, and the ''Philae'' lander, with nine additional instruments. The ''Rosetta'' mission orbited Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko for 17 months and was designed to complete the most detailed study of a comet ever attempted. The spacecraft was controlled from the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC), in Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it th ...
, Germany. The planning for the operation of the scientific payload, together with the data retrieval, calibration, archiving and distribution, was performed from the European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC), in Villanueva de la Cañada
Villanueva de la Cañada is a municipality in the Community of Madrid, Spain. Located 30 km north-west from Madrid, the municipality covers an area of 34.92 km2. Geographically, it sits on a large plain, in which there are several pr ...
, near Madrid, Spain. It has been estimated that in the decade preceding 2014, some 2,000 people assisted in the mission in some capacity.
In 2007, ''Rosetta'' made a Mars gravity assist (flyby) on its way to Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko. The spacecraft also performed two asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
flybys. The craft completed its flyby of asteroid 2867 Šteins in September 2008 and of 21 Lutetia
)
, mp_category=Main belt
, mpc_name=(21) Lutetia
, orbit_ref =
, epoch=May 31, 2020 ( JD 2459000.5)
, semimajor=2.435 AU
, perihelion=2.037 AU
, aphelion=2.833 AU
, eccentricity=0.16339
, period=3.80 yr (1388.1 d)
, inclination=3.064� ...
in July 2010. Later, on 20 January 2014, ''Rosetta'' was taken out of a 31-month hibernation mode as it approached Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko.
''Rosetta'' ''Philae'' lander successfully made the first soft landing on a comet nucleus when it touched down on Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko on 12 November 2014. On 5 September 2016, ESA announced that the lander was discovered by the narrow-angle camera aboard ''Rosetta'' as the orbiter made a low, pass over the comet. The lander sits on its side wedged into a dark crevice of the comet, explaining the lack of electrical power to establish proper communication with the orbiter.
History
Background
During the 1986 approach of Halley's Comet, international space probes were sent to explore the comet, most prominent among them being ESA's ''Giotto''. After the probes returned valuable scientific information, it became obvious that follow-ons were needed that would shed more light on cometary composition and answer new questions. Both ESA and NASA started cooperatively developing new probes. The NASA project was the Comet Rendezvous Asteroid Flyby (CRAF) mission. The ESA project was the follow-on Comet Nucleus Sample Return (CNSR) mission. Both missions were to share the Mariner Mark II spacecraft design, thus minimising costs. In 1992, after NASA cancelled CRAF due to budgetary limitations, ESA decided to develop a CRAF-style project on its own. By 1993 it was evident that the ambitious sample return mission was infeasible with the existing ESA budget, so the mission was redesigned and subsequently approved by the ESA, with the final flight plan resembling the cancelled CRAF mission: an asteroid flyby followed by a comet rendezvous with in-situ examination, including a lander. After the spacecraft launch,Gerhard Schwehm Gerhard Schwehm (born 13 March 1949, Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Germany) is Head of Solar System Science Operations Division for the European Space Agency (ESA). He was Mission Manager for the Rosetta mission until his retirement.
Education
Schwehm ...
was named mission manager; he retired in March 2014.
The ''Rosetta'' mission included generational team management; this allowed mission continuity over the long period of the mission and for special knowledge to be maintained and passed on to future team members. In particular, several younger scientists were brought on as principal science investigators, and regular training sessions were conducted.
Naming
The probe was named after the Rosetta Stone, astele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
of Egyptian origin featuring a decree in three scripts. The lander was named after the Philae obelisk, which bears a bilingual Greek and Egyptian hieroglyphic inscription. A comparison of its hieroglyphs with those on the Rosetta Stone catalysed the deciphering of the Egyptian writing system. Similarly, it was hoped that these spacecraft would result in better understanding of comets and the early Solar System. In a more direct analogy to its namesake, the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft also carried a micro-etched pure nickel prototype of the Rosetta disc donated by the Long Now Foundation. The disc was inscribed with 6,500 pages of language translations.
Mission firsts
 The ''Rosetta'' mission achieved many historic firsts.
On its way to comet 67P, ''Rosetta'' passed through the main asteroid belt, and made the first European close encounter with several of these primitive objects. ''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to fly close to Jupiter's orbit using solar cells as its main power source.
''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to orbit a comet nucleus, and was the first spacecraft to fly alongside a comet as it headed towards the inner Solar System. It became the first spacecraft to examine at close proximity the activity of a frozen comet as it is warmed by the Sun. Shortly after its arrival at 67P, the ''Rosetta'' orbiter dispatched the '' Philae'' lander for the first controlled touchdown on a comet nucleus. The robotic lander's instruments obtained the first images from a comet's surface and made the first '' in situ'' analysis of its composition.
The ''Rosetta'' mission achieved many historic firsts.
On its way to comet 67P, ''Rosetta'' passed through the main asteroid belt, and made the first European close encounter with several of these primitive objects. ''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to fly close to Jupiter's orbit using solar cells as its main power source.
''Rosetta'' was the first spacecraft to orbit a comet nucleus, and was the first spacecraft to fly alongside a comet as it headed towards the inner Solar System. It became the first spacecraft to examine at close proximity the activity of a frozen comet as it is warmed by the Sun. Shortly after its arrival at 67P, the ''Rosetta'' orbiter dispatched the '' Philae'' lander for the first controlled touchdown on a comet nucleus. The robotic lander's instruments obtained the first images from a comet's surface and made the first '' in situ'' analysis of its composition.
Design and construction
The ''Rosetta''bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
was a central frame and aluminium honeycomb platform. Its total mass was approximately , which included the ''Philae'' lander and of science instruments. The Payload Support Module was mounted on top of the spacecraft and housed the scientific instruments, while the Bus Support Module was on the bottom and contained spacecraft support subsystems. Heaters placed around the spacecraft kept its systems warm while it was distant from the Sun. ''Rosetta'' communications suite included a steerable high-gain parabolic dish antenna, a fixed-position medium-gain antenna, and two omnidirectional low-gain antennas.
Electrical power for the spacecraft came from two solar arrays totalling . Each solar array was subdivided into five solar panels, with each panel being . The individual solar cells were made of silicon, 200 μm thick, and . The solar arrays generated a maximum of approximately 1,500 watts at perihelion, a minimum of 400 watts in hibernation mode at 5.2 AU, and 850 watts when comet operations begin at 3.4 AU. Spacecraft power was controlled by a redundant Terma power module also used in the '' Mars Express'' spacecraft, and was stored in four 10-A·h
An ampere hour or amp hour (symbol: A⋅h or A h; often simplified as Ah) is a Unit of measurement, unit of electric charge, having Dimensional analysis, dimensions of electric current multiplied by time, equal to the charge transferred by a ...
i-ionbatteries supplying 28 volts to the bus.
Main propulsion comprised 24 paired bipropellant 10 N thrusters, with four pairs of thrusters being used for delta-''v'' burns. The spacecraft carried of propellant at launch: of monomethylhydrazine fuel and of dinitrogen tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium ...
oxidiser, contained in two grade 5 titanium alloy tanks and providing delta-''v'' of at least over the course of the mission. Propellant pressurisation was provided by two high-pressure helium tanks.
''Rosetta'' was built in a clean room according to COSPAR rules, but " sterilisation generally not crucial since comets are usually regarded as objects where you can find prebiotic molecules, that is, molecules that are precursors of life, but not living microorganisms", according to Gerhard Schwehm, ''Rosetta'' project scientist. The total cost of the mission was about €1.3 billion (US$1.8 billion).
Launch

 ''Rosetta'' was set to be launched on 12 January 2003 to rendezvous with the comet
''Rosetta'' was set to be launched on 12 January 2003 to rendezvous with the comet 46P/Wirtanen
46P/Wirtanen is a small short-period comet with a current orbital period of 5.4 years. It was the original target for close investigation by the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, planned by the European Space Agency, but an inability to meet the launch wi ...
in 2011. This plan was abandoned after the failure of an Ariane 5 ECA
Ariane 5 is a European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It is launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) in French Guiana. It has been used to deliver payloads into ...
carrier rocket during Hot Bird 7's launch on 11 December 2002, grounding it until the cause of the failure could be determined. In May 2003, a new plan was formed to target the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, with a revised launch date of 26 February 2004 and comet rendezvous in 2014. The larger mass and the resulting increased impact velocity made modification of the landing gear necessary.
After two scrubbed launch attempts, ''Rosetta'' was launched on 2 March 2004 at 07:17 UTC from the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana, using Ariane 5 G+ carrier rocket. Aside from the changes made to launch time and target, the mission profile remained almost identical. Both co-discoverers of the comet, Klim Churyumov and Svetlana Gerasimenko
Svetlana Ivanovna Gerasimenko (russian: Светлана Ивановна Герасименко; uk, Світлана Іванівна Герасименко; born 1945) is a Soviet and Tajikistani astronomer origin and discoverer of comet 67P/ ...
, were present at the spaceport during the launch.
Deep space manoeuvres
To achieve the required velocity to rendezvous with 67P, ''Rosetta'' used gravity assist manoeuvres to accelerate throughout the inner Solar System. The comet's orbit was known before ''Rosetta'' launch, from ground-based measurements, to an accuracy of approximately . Information gathered by the onboard cameras beginning at a distance of were processed at ESA's Operation Centre to refine the position of the comet in its orbit to a few kilometres. The first Earth flyby was on 4 March 2005. On 25 February 2007, the craft was scheduled for a low-altitude flyby of Mars, to correct the trajectory. This was not without risk, as the estimated altitude of the flyby was a mere . During that encounter, the solar panels could not be used since the craft was in the planet's shadow, where it would not receive any solar light for 15 minutes, causing a dangerous shortage of power. The craft was therefore put into standby mode, with no possibility to communicate, flying on batteries that were originally not designed for this task. This Mars manoeuvre was therefore nicknamed "The Billion Euro Gamble". The flyby was successful, with ''Rosetta'' even returning detailed images of the surface and atmosphere of the planet, and the mission continued as planned. The second Earth flyby was on 13 November 2007 at a distance of . In observations made on 7 and 8 November, ''Rosetta'' was briefly mistaken for anear-Earth asteroid
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). ...
about in diameter by an astronomer of the Catalina Sky Survey and was given the provisional designation . Calculations showed that it would pass very close to Earth, which led to speculation that it could impact Earth. However, astronomer Denis Denisenko
Denis Denisenko (born January 16, 1971) is a Russian astronomer of the late 20th – early 21st century, discoverer of 10 supernovae, more than 150 variable stars, an asteroid, and a comet.
Biography
Born in 1971 in Moscow, Denisenko graduated ...
recognised that the trajectory matched that of ''Rosetta'', which the Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
Function
...
confirmed in an editorial release on 9 November.
The spacecraft performed a close flyby of asteroid 2867 Šteins on 5 September 2008. Its onboard cameras were used to fine-tune the trajectory, achieving a minimum separation of less than . Onboard instruments measured the asteroid from 4 August to 10 September. Maximum relative speed between the two objects during the flyby was .
''Rosetta'' third and final flyby of Earth happened on 12 November 2009 at a distance of .
On 10 July 2010, ''Rosetta'' flew by 21 Lutetia
)
, mp_category=Main belt
, mpc_name=(21) Lutetia
, orbit_ref =
, epoch=May 31, 2020 ( JD 2459000.5)
, semimajor=2.435 AU
, perihelion=2.037 AU
, aphelion=2.833 AU
, eccentricity=0.16339
, period=3.80 yr (1388.1 d)
, inclination=3.064� ...
, a large main-belt asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
, at a minimum distance of km ( mi) at a velocity of . The flyby provided images of up to per pixel resolution and covered about 50% of the surface, mostly in the northern hemisphere. The 462 images were obtained in 21 narrow- and broad-band filters extending from 0.24 to 1 μm. Lutetia was also observed by the visible–near-infrared imaging spectrometer VIRTIS, and measurements of the magnetic field and plasma environment were taken as well.

 After leaving its hibernation mode in January 2014 and getting closer to the comet, ''Rosetta'' began a series of eight burns in May 2014. These reduced the relative velocity between the spacecraft and 67P from to .
After leaving its hibernation mode in January 2014 and getting closer to the comet, ''Rosetta'' began a series of eight burns in May 2014. These reduced the relative velocity between the spacecraft and 67P from to .
Reaction control system problems
In 2006, ''Rosetta'' suffered a leak in its reaction control system (RCS). The system, which consists of 24 bipropellant 10-newton
Newton most commonly refers to:
* Isaac Newton (1642–1726/1727), English scientist
* Newton (unit), SI unit of force named after Isaac Newton
Newton may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Newton'' (film), a 2017 Indian film
* Newton ( ...
thrusters, was responsible for fine tuning the trajectory of ''Rosetta'' throughout its journey. The RCS operated at a lower pressure than designed due to the leak. While this may have caused the propellants to mix incompletely and burn 'dirtier' and less efficiently, ESA engineers were confident that the spacecraft would have sufficient fuel reserves to allow for the successful completion of the mission.
Prior to ''Rosetta'' deep space hibernation period, two of the spacecraft's four reaction wheel
A reaction wheel (RW) is used primarily by spacecraft for three-axis attitude control, and does not require rockets or external applicators of torque. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be ...
s began exhibiting increased levels of "bearing friction noise". Increased friction levels in Reaction Wheel Assembly (RWA) B were noted after its September 2008 encounter with asteroid Šteins. Two attempts were made to relubricate the RWA using an on-board oil reservoir, but in each case noise levels were only temporarily lowered, and the RWA was turned off in mid-2010 after the flyby of asteroid Lutetia to avoid possible failure. Shortly after this, RWA C also began showing evidence of elevated friction. Relubrication was also performed on this RWA, and methods were found to temporarily increase its operating temperature to better improve the transfer of oil from its reservoir. In addition, the reaction wheel's speed range was decreased to limit lifetime accumulated rotations. These changes resulted in RWA C performance stabilising.
During the spacecraft's Deep Space Hibernation flight phase, engineers performed ground testing on a flight spare RWA at the European Space Operations Centre. After ''Rosetta'' exited hibernation in January 2014, lessons learned from the ground testing were applied to all four RWAs, such as increasing their operating temperatures and limiting their wheel speeds to below 1000 rpm. After these fixes, the RWAs showed nearly identical performance data. Three RWAs were kept operational, while one of the malfunctioning RWAs was held in reserve. Additionally, new on-board software was developed to allow ''Rosetta'' to operate with only two active RWAs if necessary. These changes allowed the four RWAs to operate throughout ''Rosetta'' mission at 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko despite occasional anomalies in their friction plots and a heavy workload imposed by numerous orbital changes.
Orbit around 67P
 In August 2014, ''Rosetta'' rendezvoused with the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P) and commenced a series of manoeuvres that took it on two successive triangular paths, averaging from the nucleus, whose segments are hyperbolic escape trajectories alternating with thruster burns. After closing to within about from the comet on 10 September, the spacecraft entered actual orbit about it.
The surface layout of 67P was unknown before ''Rosetta'' arrival. The orbiter mapped the comet in anticipation of detaching its lander. By 25 August 2014, five potential landing sites had been determined. On 15 September 2014, ESA announced Site J, named ''Agilkia'' in honour of Agilkia Island by an ESA public contest and located on the "head" of the comet, as the lander's destination.
In August 2014, ''Rosetta'' rendezvoused with the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P) and commenced a series of manoeuvres that took it on two successive triangular paths, averaging from the nucleus, whose segments are hyperbolic escape trajectories alternating with thruster burns. After closing to within about from the comet on 10 September, the spacecraft entered actual orbit about it.
The surface layout of 67P was unknown before ''Rosetta'' arrival. The orbiter mapped the comet in anticipation of detaching its lander. By 25 August 2014, five potential landing sites had been determined. On 15 September 2014, ESA announced Site J, named ''Agilkia'' in honour of Agilkia Island by an ESA public contest and located on the "head" of the comet, as the lander's destination.
''Philae'' lander
 '' Philae'' detached from ''Rosetta'' on 12 November 2014 at 08:35 UTC, and approached 67P at a relative speed of about . It initially landed on 67P at 15:33 UTC, but bounced twice, coming to rest at 17:33 UTC. Confirmation of contact with 67P reached Earth at 16:03 UTC.
On contact with the surface, two harpoons were to be fired into the comet to prevent the lander from bouncing off, as the comet's escape velocity is only around . Analysis of telemetry indicated that the surface at the initial touchdown site is relatively soft, covered with a layer of granular material about 0.82 feet (0.25 meters) deep, and that the harpoons had not fired upon landing. After landing on the comet, ''Philae'' had been scheduled to commence its science mission, which included:
* Characterisation of the nucleus
* Determination of the chemical compounds present, including amino acid
'' Philae'' detached from ''Rosetta'' on 12 November 2014 at 08:35 UTC, and approached 67P at a relative speed of about . It initially landed on 67P at 15:33 UTC, but bounced twice, coming to rest at 17:33 UTC. Confirmation of contact with 67P reached Earth at 16:03 UTC.
On contact with the surface, two harpoons were to be fired into the comet to prevent the lander from bouncing off, as the comet's escape velocity is only around . Analysis of telemetry indicated that the surface at the initial touchdown site is relatively soft, covered with a layer of granular material about 0.82 feet (0.25 meters) deep, and that the harpoons had not fired upon landing. After landing on the comet, ''Philae'' had been scheduled to commence its science mission, which included:
* Characterisation of the nucleus
* Determination of the chemical compounds present, including amino acid enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical ant ...
s
* Study of comet activities and developments over time
After bouncing, ''Philae'' settled in the shadow of a cliff, canted at an angle of around 30 degrees. This made it unable to adequately collect solar power, and it lost contact with ''Rosetta'' when its batteries ran out after three days, well before much of the planned science objectives could be attempted. Contact was briefly and intermittently reestablished several months later at various times between 13 June and 9 July, before contact was lost once again. There was no communication afterwards, and the transmitter to communicate with ''Philae'' was switched off in July 2016 to reduce power consumption of the probe. The precise location of the lander was discovered in September 2016 when ''Rosetta'' came closer to the comet and took high-resolution pictures of its surface. Knowing its exact location provides information needed to put Philae's two days of science into proper context.
Notable results
 Researchers expect the study of data gathered will continue for decades to come. One of the first discoveries was that the magnetic field of 67P oscillated at 40–50 millihertz. A German composer and sound designer created an artistic rendition from the measured data to make it audible. Although it is a natural phenomenon, it has been described as a "song" and has been compared to ''Continuum'' for harpsichord by György Ligeti. However, results from ''Philae'' landing show that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field, and that the field originally detected by ''Rosetta'' is likely caused by the solar wind.
The isotopic signature of water vapour from comet 67P, as determined by the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, is substantially different from that found on Earth. That is, the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen in the water from the comet was determined to be three times that found for terrestrial water. This makes it very unlikely that water found on Earth came from comets such as comet 67P, according to the scientists. On 22 January 2015, NASA reported that, between June and August 2014, the rate at which water vapour was released by the comet increased up to tenfold.
On 2 June 2015, NASA reported that the Alice spectrograph on ''Rosetta'' determined that electrons within above the comet nucleus — produced from photoionization of water molecules, and not direct photons from the Sun as thought earlier — are responsible for the degradation of water and carbon dioxide molecules released from the comet nucleus into its
Researchers expect the study of data gathered will continue for decades to come. One of the first discoveries was that the magnetic field of 67P oscillated at 40–50 millihertz. A German composer and sound designer created an artistic rendition from the measured data to make it audible. Although it is a natural phenomenon, it has been described as a "song" and has been compared to ''Continuum'' for harpsichord by György Ligeti. However, results from ''Philae'' landing show that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field, and that the field originally detected by ''Rosetta'' is likely caused by the solar wind.
The isotopic signature of water vapour from comet 67P, as determined by the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, is substantially different from that found on Earth. That is, the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen in the water from the comet was determined to be three times that found for terrestrial water. This makes it very unlikely that water found on Earth came from comets such as comet 67P, according to the scientists. On 22 January 2015, NASA reported that, between June and August 2014, the rate at which water vapour was released by the comet increased up to tenfold.
On 2 June 2015, NASA reported that the Alice spectrograph on ''Rosetta'' determined that electrons within above the comet nucleus — produced from photoionization of water molecules, and not direct photons from the Sun as thought earlier — are responsible for the degradation of water and carbon dioxide molecules released from the comet nucleus into its coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
.
End of mission
As the orbit of comet 67P took it farther from the Sun, the amount of sunlight reaching ''Rosetta'' solar panels decreased. While it would have been possible to put ''Rosetta'' into a second hibernation phase during the comet's aphelion, there was no assurance that enough power would be available to run the spacecraft's heaters to keep it from freezing. To guarantee a maximum science return, mission managers made the decision to instead guide ''Rosetta'' down to the comet's surface and end the mission on impact, gathering photographs and instrument readings along the way. On 23 June 2015, at the same time as a mission extension was confirmed, ESA announced that end of mission would occur at the end of September 2016 after two years of operations at the comet. ''Rosetta'' began a descent with a 208-second thruster burn executed on 29 September 2016 at approximately 20:50 UTC. Its trajectory targeted a site in the Ma'at region near an area of dust- and gas-producing active pits. Impact on the comet's surface occurred 14.5 hours after its descent manoeuvre; the final data packet from ''Rosetta'' was transmitted at 10:39:28.895 UTC ( SCET) by the OSIRIS instrument and was received at the European Space Operations Centre in Darmstadt, Germany, at 11:19:36.541 UTC. Note: Times in the left column areSpacecraft Event Time
Spacecraft Event Time (SCET) is the spacecraft-local time for events that happen at the spacecraft. SCET is used for command programs that control the timing of spacecraft operations and to identify when specific events occur on the spacecraft rel ...
, while the right column is Earth Received Time. All times are in UTC. The spacecraft's estimated speed at the time of impact was , and its touchdown location, named ''Sais'' by the operations team after the Rosetta Stone's original temple home, is believed to be only off-target. The final complete image transmitted by the spacecraft of the comet was taken by its OSIRIS instrument at an altitude of about 10 seconds before impact, showing an area across. ''Rosetta'' computer included commands to send it into safe mode upon detecting that it had hit the comet's surface, turning off its radio transmitter and rendering it inert in accordance with International Telecommunication Union rules.
On 28 September 2017, a previously unrecovered image taken by the spacecraft was reported. This image was recovered from three data packets discovered on a server after completion of the mission. While blurry due to data loss, it shows an area of the comet's surface approximately one square meter in size taken from an altitude of , and represents ''Rosetta'' closest image of the surface.
Instruments

Nucleus
The investigation of the nucleus was done by three optical spectrometers, one microwave radio antenna and one radar: *Alice
Alice may refer to:
* Alice (name), most often a feminine given name, but also used as a surname
Literature
* Alice (''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''), a character in books by Lewis Carroll
* ''Alice'' series, children's and teen books by ...
(an ultraviolet imaging spectrograph). The ultraviolet spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
searched for and quantified the noble gas content in the comet nucleus, from which the temperature during the comet creation could be estimated. The detection was done by an array of potassium bromide
Potassium bromide ( K Br) is a salt, widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with over-the-counter use extending to 1975 in the US. Its action is due to the bromide ion (sodium bromide is equall ...
and caesium iodide photocathodes. The instrument used 2.9 watts, with an improved version onboard New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
. It operated in the extreme and far ultraviolet spectrum, from . ALICE was built and operated by the Southwest Research Institute
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, is an independent and nonprofit applied research and development (R&D) organization. Founded in 1947 by oil businessman Tom Slick, it provides contract research and develop ...
for NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
* OSIRIS (Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System). The camera system had a narrow-angle lens (700 mm) and a wide-angle lens (140 mm), with a 2048×2048 pixel CCD chip. The instrument was constructed in Germany. Development and construction of the instrument was led by the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS).
* VIRTIS (Visible and Infrared Thermal Imaging Spectrometer). The Visible and IR spectrometer was able to make pictures of the nucleus in the IR and also search for IR spectra of molecules in the coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
. The detection was done by a mercury cadmium telluride array for IR and with a CCD chip for the visible wavelength range. The instrument was produced in Italy, and improved versions were used for Dawn and Venus Express.
* MIRO (Microwave Instrument for the Rosetta Orbiter). The abundance and temperature of volatile substances like water, ammonia and carbon dioxide could be detected by MIRO via their microwave emissions. The radio antenna along with the rest of the instrument was built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory with international contributions by the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS), among others.
* CONSERT (Comet Nucleus Sounding Experiment by Radiowave Transmission). The CONSERT experiment provided information about the deep interior of the comet using radar. The radar performed tomography of the nucleus by measuring electromagnetic wave propagation between the '' Philae'' lander and the ''Rosetta'' orbiter through the comet nucleus. This allowed it to determine the comet's internal structure and deduce information on its composition. The electronics were developed by France and both antennas were constructed in Germany. Development was led by the Laboratoire de Planétologie de Grenoble with contributions by the Ruhr-Universität Boch and the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS).
*RSI (Radio Science Investigation). RSI made use of the probe's communication system for physical investigation of the nucleus and the inner coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
of the comet.
Gas and particles
* ROSINA (Rosetta Orbiter Spectrometer for Ion and Neutral Analysis). The instrument consisted of a double-focus magnetic mass spectrometer (DFMS) and a reflectron typetime of flight mass spectrometer
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS) is a method of mass spectrometry in which an ion's mass-to-charge ratio is determined by a time of flight measurement. Ions are accelerated by an electric field of known strength. This acceleration result ...
(RTOF). The DFMS had a high resolution (could resolve N2 from CO) for molecules up to 300 amu. The RTOF was highly sensitive for neutral molecules and for ions. The Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS) has contributed to the development and construction of the instrument. ROSINA was developed at the University of Bern in Switzerland.
* MIDAS (Micro-Imaging Dust Analysis System). The high-resolution atomic force microscope investigated several physical aspects of the dust particles which are deposited on a silicon plate.
* COSIMA (Cometary Secondary Ion Mass Analyser). COSIMA analysed the composition of dust particles by secondary ion mass spectrometry, using indium ions. It could detect ions up to a mass of 6500 amu. COSIMA was built by the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE, Germany) with international contributions. The COSIMA team is led by the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS, Germany).
* GIADA (Grain Impact Analyser and Dust Accumulator). GIADA analysed the dust environment of the comet coma by measuring the optical cross section, momentum, speed and mass of each grain entering inside the instrument.
Solar wind interaction
* RPC (Rosetta Plasma Consortium).Search for organic compounds
Previous observations have shown that comets contain complex organic compounds. These are the elements that make upnucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s and amino acids, essential ingredients for life as we know it. Comets are thought to have delivered a vast quantity of water to Earth, and they may have also seeded Earth with organic molecules. ''Rosetta'' and ''Philae'' also searched for organic molecules, nucleic acids (the building blocks of DNA and RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
) and amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) by sampling and analysing the comet's nucleus and coma cloud of gas and dust, helping assess the contribution comets made to the beginnings of life on Earth. Before succumbing to falling power levels, ''Philae'' COSAC instrument was able to detect organic molecules in the comet's atmosphere.
chirality
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from ...
), and the primarily left-handed structure of essential amino acids used by living organisms is unique. One hypothesis that will be tested was proposed in 1983 by William A. Bonner and Edward Rubenstein, Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
professors emeritus of chemistry and medicine respectively. They conjectured that when spiralling radiation is generated from a supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
, the circular polarisation of that radiation could then destroy one type of "handed" molecules. The supernova could wipe out one type of molecules while also flinging the other surviving molecules into space, where they could eventually end up on a planet.
Preliminary results
The mission has yielded a significant science return, collecting a wealth of data from the nucleus and its environment at various levels of cometary activity. The VIRTISspectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
on board the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft has provided evidence of nonvolatile organic macromolecular compounds everywhere on the surface of comet 67P with little to no water ice visible. Preliminary analyses strongly suggest the carbon is present as polyaromatic organic solids mixed with sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds lar ...
s and iron-nickel alloys.
Solid organic compounds were also found in the dust particles emitted by the comet; the carbon in this organic material is bound in "very large macromolecular compounds", analogous to those found in carbonaceous chondrite
Carbonaceous chondrites or C chondrites are a class of chondritic meteorites comprising at least 8 known groups and many ungrouped meteorites. They include some of the most primitive known meteorites. The C chondrites represent only a small prop ...
meteorites. However, no hydrated minerals were detected, suggesting no link with carbonaceous chondrites.
In turn, the ''Philae'' lander's COSAC instrument detected organic molecules in the comet's atmosphere as it descended to its surface. Measurements by the COSAC and Ptolemy instruments on the ''Philae'' lander revealed sixteen organic compounds, four of which were seen for the first time on a comet, including acetamide, acetone, methyl isocyanate and propionaldehyde. The only amino acid detected thus far on the comet is glycine, along with the precursor molecules methylamine
Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of . This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.
Methylamine is sold as a solution in methanol, ...
and ethylamine
Ethylamine, also known as ethanamine, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. It condenses just below room temperature to a liquid miscible with virtually all solvents. It is a nucleo ...
.
One of the most outstanding discoveries of the mission was the detection of large amounts of free molecular oxygen () gas surrounding the comet. A local abundance of oxygen was reported to be in range from 1% to 10% relative to H2O.
Timeline of major events and discoveries
 ;2004
* 2 March – ''Rosetta'' was successfully launched at 07:17 UTC (04:17 local time) from Kourou, French Guiana.
;2005
* 4 March – ''Rosetta'' executed its first planned close swing-by (gravity assist passage) of Earth. The Moon and the Earth's magnetic field were used to test and calibrate the instruments on board of the spacecraft. The minimum altitude above the Earth's surface was .
* 4 July – Imaging instruments on board observed the collision between the comet Tempel 1 and the impactor of the Deep Impact mission.
;2007
* 25 February – Mars flyby.
* 8 November – Catalina Sky Survey briefly misidentified the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, approaching for its second Earth flyby, as a newly discovered asteroid.
* 13 November – Second Earth swing-by at a minimum altitude of , travelling at .
;2004
* 2 March – ''Rosetta'' was successfully launched at 07:17 UTC (04:17 local time) from Kourou, French Guiana.
;2005
* 4 March – ''Rosetta'' executed its first planned close swing-by (gravity assist passage) of Earth. The Moon and the Earth's magnetic field were used to test and calibrate the instruments on board of the spacecraft. The minimum altitude above the Earth's surface was .
* 4 July – Imaging instruments on board observed the collision between the comet Tempel 1 and the impactor of the Deep Impact mission.
;2007
* 25 February – Mars flyby.
* 8 November – Catalina Sky Survey briefly misidentified the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft, approaching for its second Earth flyby, as a newly discovered asteroid.
* 13 November – Second Earth swing-by at a minimum altitude of , travelling at .
 ;2008
* 5 September – Flyby of asteroid 2867 Šteins. The spacecraft passed the main-belt asteroid at a distance of and the relatively slow speed of .
;2009
* 13 November – Third and final swing-by of Earth at .
;2010
* 16 March – Observation of the dust tail of asteroid P/2010 A2. Together with observations by Hubble Space Telescope it could be confirmed that P/2010 A2 is not a comet, but an asteroid, and that the tail most likely consists of particles from an impact by a smaller asteroid.
* 10 July – Flew by and photographed the asteroid
;2008
* 5 September – Flyby of asteroid 2867 Šteins. The spacecraft passed the main-belt asteroid at a distance of and the relatively slow speed of .
;2009
* 13 November – Third and final swing-by of Earth at .
;2010
* 16 March – Observation of the dust tail of asteroid P/2010 A2. Together with observations by Hubble Space Telescope it could be confirmed that P/2010 A2 is not a comet, but an asteroid, and that the tail most likely consists of particles from an impact by a smaller asteroid.
* 10 July – Flew by and photographed the asteroid 21 Lutetia
)
, mp_category=Main belt
, mpc_name=(21) Lutetia
, orbit_ref =
, epoch=May 31, 2020 ( JD 2459000.5)
, semimajor=2.435 AU
, perihelion=2.037 AU
, aphelion=2.833 AU
, eccentricity=0.16339
, period=3.80 yr (1388.1 d)
, inclination=3.064� ...
.
 ;2014
* May to July – Starting on 7 May, ''Rosetta'' began orbital correction manoeuvres to bring itself into orbit around 67P. At the time of the first deceleration burn ''Rosetta'' was approximately away from 67P and had a relative velocity of +; by the end of the last burn, which occurred on 23 July, the distance had been reduced to just over with a relative velocity of +. In total eight burns were used to align the trajectories of ''Rosetta'' 67P with the majority of the deceleration occurring during three burns: Delta-''v'' of on 21 May, on 4 June, and on 18 June.
* 14 July – The OSIRIS on-board imaging system returned images of comet 67P which confirmed the irregular shape of the comet.
* 6 August – ''Rosetta'' arrives at 67P, approaching to and carrying out a thruster burn that reduces its relative velocity to . Commences comet mapping and characterisation to determine a stable orbit and viable landing location for ''Philae''.
* 4 September – The first science data from ''Rosetta'' Alice instrument was reported, showing that the comet is unusually dark in ultraviolet wavelengths, hydrogen and oxygen are present in the
;2014
* May to July – Starting on 7 May, ''Rosetta'' began orbital correction manoeuvres to bring itself into orbit around 67P. At the time of the first deceleration burn ''Rosetta'' was approximately away from 67P and had a relative velocity of +; by the end of the last burn, which occurred on 23 July, the distance had been reduced to just over with a relative velocity of +. In total eight burns were used to align the trajectories of ''Rosetta'' 67P with the majority of the deceleration occurring during three burns: Delta-''v'' of on 21 May, on 4 June, and on 18 June.
* 14 July – The OSIRIS on-board imaging system returned images of comet 67P which confirmed the irregular shape of the comet.
* 6 August – ''Rosetta'' arrives at 67P, approaching to and carrying out a thruster burn that reduces its relative velocity to . Commences comet mapping and characterisation to determine a stable orbit and viable landing location for ''Philae''.
* 4 September – The first science data from ''Rosetta'' Alice instrument was reported, showing that the comet is unusually dark in ultraviolet wavelengths, hydrogen and oxygen are present in the coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
, and no significant areas of water-ice have been found on the comet's surface. Water-ice was expected to be found as the comet is too far from the Sun to turn water into vapour.
* 10 September 2014 – ''Rosetta'' enters the Global Mapping Phase, orbiting 67P at an altitude of .
* 12 November 2014 – ''Philae'' lands on the surface of 67P.
* 10 December 2014 – Data from the ROSINA mass spectrometers show that the ratio of heavy water to normal water on comet 67P is more than three times that on Earth. The ratio is regarded as a distinctive signature, and the discovery means that Earth's water is unlikely to have originated from comets like 67P.
 ;2015
* 14 April 2015 – Scientists report that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field of its own.
* 2 July 2015 – Scientists report that active pits, related to sinkhole collapses and possibly associated with outbursts, have been found on the comet.
;2015
* 14 April 2015 – Scientists report that the comet's nucleus has no magnetic field of its own.
* 2 July 2015 – Scientists report that active pits, related to sinkhole collapses and possibly associated with outbursts, have been found on the comet.
 * 11 August 2015 – Scientists release images of a comet outburst that occurred on 29 July 2015.
* 28 October 2015 – Scientists publish an article in '' Nature'' reporting high levels of molecular oxygen around 67P.
* November 2014 to December 2015 – ''Rosetta'' escorted the comet around the Sun and performed riskier investigations.
;2016
* 27 July 2016 – ESA switched off the Electrical Support System Processor Unit (ESS) aboard ''Rosetta'', disabling any possibility of further communications with the ''Philae'' lander.
* 2 September 2016 - ''Rosetta'' photographs the ''Philae'' lander for the first time after its landing, finding it wedged against a large overhang.
* 30 September 2016 - Mission ended in an attempt to slow land on the comet's surface near a wide pit called Deir el-Medina. The walls of the pit contain wide so-called "goose bumps", believed to represent the building blocks of the comet. Although ''Philae'' sent back some data during its descent, ''Rosetta'' has more powerful and more varied sensors and instruments, offering the opportunity to get some very close-in science to complement the more distant remote sensing it has been doing. The orbiter descended more slowly than ''Philae'' did.
* 11 August 2015 – Scientists release images of a comet outburst that occurred on 29 July 2015.
* 28 October 2015 – Scientists publish an article in '' Nature'' reporting high levels of molecular oxygen around 67P.
* November 2014 to December 2015 – ''Rosetta'' escorted the comet around the Sun and performed riskier investigations.
;2016
* 27 July 2016 – ESA switched off the Electrical Support System Processor Unit (ESS) aboard ''Rosetta'', disabling any possibility of further communications with the ''Philae'' lander.
* 2 September 2016 - ''Rosetta'' photographs the ''Philae'' lander for the first time after its landing, finding it wedged against a large overhang.
* 30 September 2016 - Mission ended in an attempt to slow land on the comet's surface near a wide pit called Deir el-Medina. The walls of the pit contain wide so-called "goose bumps", believed to represent the building blocks of the comet. Although ''Philae'' sent back some data during its descent, ''Rosetta'' has more powerful and more varied sensors and instruments, offering the opportunity to get some very close-in science to complement the more distant remote sensing it has been doing. The orbiter descended more slowly than ''Philae'' did.
Public image
''Once upon a time...'' cartoon
As part of the European Space Agency's media campaign in support of the ''Rosetta'' mission, both the ''Rosetta'' and '' Philae'' spacecraft were givenanthropomorphic
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology.
Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics t ...
personalities in an animated web series titled ''Once upon a time...''. The series depicts various stages in the ''Rosetta'' mission, involving the personified ''Rosetta'' and ''Philae'' on "a classic road trip story into the depths of our universe", complemented with various visual gags presented in an educational context. Produced by animation studio Design & Data GmbH, the series was initially conceived by the ESA as a four-part fantasy-like series with a '' Sleeping Beauty'' theme that promoted community involvement in ''Rosetta''s wake up from hibernation in January 2014. After the success of the series, however, the ESA commissioned the studio to continue producing new episodes in the series throughout the course of the mission. A total of twelve videos in the series were produced from 2013 to 2016, with a 25-minute compilation of the series released in December 2016, after the end of the mission. In 2019, Design & Data adapted the series into a 26-minute planetarium
A planetarium ( planetariums or ''planetaria'') is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation.
A dominant feature of most planetarium ...
show that was commissioned by the Swiss Museum of Transport, and solicited to eighteen planetariums across Europe, with an aim "to inspire the young generation to explore the universe."
The ''Rosetta'' and ''Philae'' characters featured in ''Once upon a time...'', designed by ESA employee and cartoonist Carlo Palazzari, became a central part of public image of the ''Rosetta'' mission, appearing in promotional material for the mission such as posters and merchandise, and often credited as a major factor in the popularity of the mission among the public. ESA employees also role-played as the characters on Twitter throughout the course of the mission. The characters were inspired by the JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orb ...
's "kawaii" characters, whom portrayed a number of their spacecraft, such as ''Hayabusa2
is an asteroid sample-return mission operated by the Japanese state space agency JAXA. It is a successor to the ''Hayabusa'' mission, which returned asteroid samples for the first time in June 2010. ''Hayabusa2'' was launched on 3 December 2 ...
'' and ''Akatsuki
may refer to:
* Akatsuki (spacecraft), an uncrewed Venus orbiter
* , any of three classes of destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy
* , any of three destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy
* ''Akatsuki'' (train), operated between Kyoto and Na ...
'', with distinct anime-like personalities. The script for each episode of the series is written by science communicators at the European Space Research and Technology Centre, who kept close with mission operators and the producers at Design & Data. Canonically, ''Rosetta'' and ''Philae'' are depicted as siblings, with ''Rosetta'' being the older sister, inspired by the spacecraft's feminine name, of ''Philae'', her younger brother. The '' Giotto'' spacecraft is also depicted as the duo's grandfather, whereas others in the Halley Armada as well as NASA's '' Deep Impact'' and ''Stardust
Stardust may refer to:
* A type of cosmic dust, composed of particles in space
Entertainment Songs
* “Stardust” (1927 song), by Hoagy Carmichael
* “Stardust” (David Essex song), 1974
* “Stardust” (Lena Meyer-Landrut song), 2012
* ...
'' spacecraft are depicted as their cousins.
''Ambition''
To promote the spacecraft's arrival at comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko and the landing of ''Philae'' in 2014, a short film was produced by the European Space Agency with Polish visual effects production company Platige Image. Titled ''Ambition'', the film, shot in Iceland, stars Irish actor Aidan Gillen, known for his roles in ''Game of Thrones
''Game of Thrones'' is an American fantasy drama television series created by David Benioff and D. B. Weiss for HBO. It is an adaptation of ''A Song of Ice and Fire'', a series of fantasy novels by George R. R. Martin, the first ...
'' and '' The Wire'', and Irish actress Aisling Franciosi
Aisling Franciosi ( , ; born 6 June 1993) is an Irish actress. She won an AACTA Award for her leading performance in the film '' The Nightingale'' (2018). On television, she is known for her roles in the RTÉ-BBC Two crime drama '' The Fall'' (20 ...
, also of ''Game of Thrones'' fame, and was directed by Oscar-nominated Polish director Tomasz Bagiński. Set in the far future, ''Ambition'' centers around a discussion between a master, played by Gillen, discussing the importance of ambition with his apprentice, played by Franciosi, using the ''Rosetta'' mission as an example of such. ''Ambition'' was premiered at the British Film Institute's ''Sci-Fi: Days of Fear and Wonder'' film festival in London on 24 October 2014, three weeks before the landing of ''Philae'' on 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. British science fiction author and former ESA employee Alastair Reynolds spoke about the film's message at the premiere, stating to the audience that "our distant descendants may look back to Rosetta with the same sense of admiration that we reserve for, say, Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
or Magellan." The film's conception was the result of the BFI's inquiry to the ESA for a contribution to their celebration of science fiction, with the ESA taking the opportunity to promote the ''Rosetta'' mission through the festival.
Critical reception of the film upon its premiere was mostly positive. Tim Reyes of ''Universe Today
Universe Today (U.T.) is a popular North American-based non-commercial space and astronomy news website. The domain was registered on December 30, 1998, and the website went live in March 1999, founded by Canadian Fraser Cain. The ''Universe Today ...
'' complimented the titular theme of ambition in the film, stating that it "shows us the forces at work in and around ESA", and that it "might accomplish more in 7 minutes than '' Gravity'' did in 90." Ryan Wallace of '' The Science Times'' also gave praise to the film, writing, "whether you're a sci-fi fanatic, or simply an interested humble astronomer, the short clip will undoubtedly give you a new view of our solar system, and the research out there in space today."
Media coverage
The entire mission was featured heavily in social media, with a Facebook account for the mission and both the satellite and the lander having an official Twitter account portraying apersonification
Personification occurs when a thing or abstraction is represented as a person, in literature or art, as a type of anthropomorphic metaphor. The type of personification discussed here excludes passing literary effects such as "Shadows hold their b ...
of both spacecraft. The hashtag
A hashtag is a metadata tag that is prefaced by the hash (also known as pound or octothorpe) sign, ''#''. On social media, hashtags are used on microblogging and photo-sharing services such as Twitter or Instagram as a form of user-generated ...
"#CometLanding" gained widespread traction. A Livestream of the control centres was set up, as were multiple official and unofficial events around the world to follow ''Philae'' landing on 67P. On 23 September 2016, Vangelis released the studio album '' Rosetta'' in honour of the mission, which was used on 30 September in the "Rosetta's final hour" streaming video of the ESA Livestream event "Rosetta Grand Finale".
Gallery
(9 min., 1080p HD, English) File:Landing on a Comet - The Rosetta Mission.webm, About ''Philae'' landing
(10 min., 1080p HD, English)
See also
* ''Deep Impact'' (spacecraft) * ''Giotto'' (spacecraft) * Halley Armada * '' Hayabusa'' — successful sample-return mission to an asteroid * List of missions to Mars * ''Stardust'' (spacecraft) * Timeline of Solar System explorationReferences
External links
''Rosetta'' website
by ESA
''Rosetta'' news site
by ESA
''Rosetta'' website
by NASA
''Rosetta'' mission profile
by NASA
''Rosetta'' mission archive
at the NASA Planetary Data System ;Media
''Rosetta'' processed image gallery
on Flickr, by ESA
''Rosetta'' raw image gallery
at ESA's ''Archive Image Browser''
''Rosetta'' image gallery
at ESA's ''Space in Images''
"''Rosetta'' twelve-year journey in space"
on YouTube, by ESA
"''Rosetta'': landing on a comet"
by ESA
"''Rosetta'' journey around the comet"
on YouTube, by ESA
"''Rosetta'' final images"
on YouTube, by ESA
"How to land on a comet"
by Fred Jansen, at TED2015
Landing News and Comments
('' The New York Times''; 12 November 2014) {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Solar System, Space, Spaceflight 1 Missions to comets Astrobiology space missions European Space Agency space probes Orbiters (space probe) Space probes launched in 2004 Articles containing video clips 2004 in French Guiana Destroyed space probes