Roman trade with India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
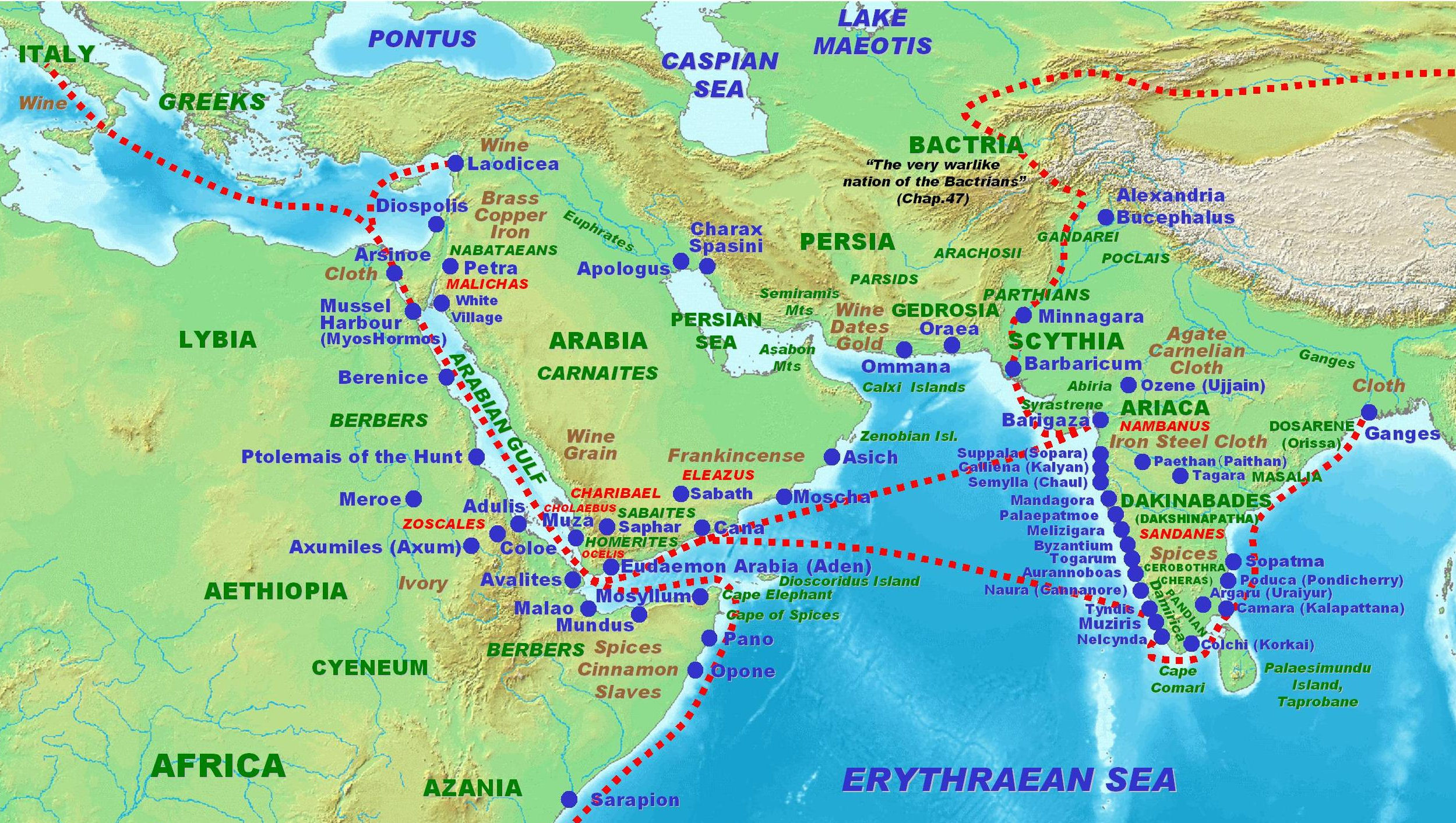

 Indo-Roman trade relations (see also the spice trade and
Indo-Roman trade relations (see also the spice trade and
 The
The
 Since the discoveries at Bet Dwarka are significant for the maritime history of the region, archeologists have researched the resources in India. Despite the unfavorable conditions the island is situated in, the following items have made Bet Dwarka as well as the rest of western India an important place for trade. From Latin literature, Rome imported Indian tigers, rhinoceros, elephants, and serpents to use for circus shows – a method employed as entertainment to prevent riots in Rome. It has been noted in the
Since the discoveries at Bet Dwarka are significant for the maritime history of the region, archeologists have researched the resources in India. Despite the unfavorable conditions the island is situated in, the following items have made Bet Dwarka as well as the rest of western India an important place for trade. From Latin literature, Rome imported Indian tigers, rhinoceros, elephants, and serpents to use for circus shows – a method employed as entertainment to prevent riots in Rome. It has been noted in the

 The replacement of Greek kingdoms by the Roman Empire as the administrator of the eastern
The replacement of Greek kingdoms by the Roman Empire as the administrator of the eastern
File:Gold coin of Claudius 50 51CE excavated in South India.jpg, Gold coin of Claudius (50–51 CE) excavated in South India.
File:Gold coin of Justinian I 527CE 565CE excavated in India probably in the south.jpg, Gold coin of
 There is evidence of animal trade between Indian Ocean harbours and the
There is evidence of animal trade between Indian Ocean harbours and the
Ambulacro della Grande Caccia
the hunting and capture of animals is represented in such detail that it is possible to identify the species. There is a scene that shows a technique to distract a
 The Ptolemaic dynasty exploited the strategic position of
The Ptolemaic dynasty exploited the strategic position of
 The regional ports of
The regional ports of

->

 The Rome-subcontinental trade also saw several cultural exchanges which had a lasting effect on both the civilizations and others involved in the trade. The
The Rome-subcontinental trade also saw several cultural exchanges which had a lasting effect on both the civilizations and others involved in the trade. The
 Trade declined from the mid-3rd century during a crisis in the Roman Empire, but recovered in the 4th century until the early 7th century, when
Trade declined from the mid-3rd century during a crisis in the Roman Empire, but recovered in the 4th century until the early 7th century, when
pp. 48 sq
/ref> The
 The Arabs, led by
The Arabs, led by
Consumption, Trade and Innovation. Exploring the Botanical Remains from the Roman and Islamic Ports at Quseir al-Qadim, Egypt
'. Frankfurt: Africa Magna Verlag. * Raith, M. – Hoffbauer, R. – Euler, H. – Yule, P. – Damgaard, K. (2013). “The view from Ẓafār –An archaeometric study of the Aqaba late Roman period pottery complex and distribution in the 1st millennium CE”. ''Zeitschrift für Orient-Archäologie'' 6, 320–50. .
* ttp://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4970452.stm BBC News: Search for India's ancient city
Trade between the Romans and the Empires of Asia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Indo-Roman Trade And Relations Foreign relations of ancient India Ancient international relations Foreign relations of ancient Rome Bilateral trading relationships Maritime history of India Economic history of India Foreign trade of India Indian Ocean trade Historic trails and roads in India


 Indo-Roman trade relations (see also the spice trade and
Indo-Roman trade relations (see also the spice trade and incense road
The Incense Trade Route was an ancient network of major land and sea trading routes linking the Mediterranean world with eastern and southern sources of incense, spices and other luxury goods, stretching from Mediterranean ports across the Levant ...
) was trade between the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. Trade through the overland caravan routes via Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, though at a relative trickle compared to later times, preceded the southern trade route via the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
which started around the beginning of the Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the ...
(CE) following the reign of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
and his conquest of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
in 30 BCE.
The southern route so helped enhance trade between the ancient Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
and the Indian subcontinent, that Roman politicians and historians are on record decrying the loss of silver and gold to buy silk to pamper Roman wives, and the southern route grew to eclipse and then totally supplant the overland trade route. Roman and Greek traders frequented the ancient Tamil country
Tamiḻakam ( Tamil: தமிழகம்; Malayalam: തമിഴകം), refers to the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covering the southernmost region of the Indian subcontinent. Tamilakam covered today's Tami ...
, present day Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, securing trade with the seafaring Tamil states of the Pandyan, Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century B ...
and Chera dynasties and establishing trading settlements which secured trade with the Indian subcontinent by the Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were dir ...
since the time of the Ptolemaic dynasty a few decades before the start of the Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the ...
and remained long after the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
.Curtin 1984: 100
Sometime after the sundering of communications between the Christian Kingdom of Axum
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in wha ...
and the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
in the 7th century, the Kingdom of Axum fell into a slow decline, fading into obscurity in western sources. It survived, despite pressure from Islamic forces, until the 11th century, when it was reconfigured in a dynastic squabble. Communications were reinstated after the Muslim forces retreated.
Background
 The
The Seleucid dynasty
The Seleucid dynasty or the Seleucidae (from el, Σελευκίδαι, ') was a Macedonian Greek royal family, founded by Seleucus I Nicator, which ruled the Seleucid Empire centered in the Near East and regions of the Asian part of the earl ...
controlled a developed network of trade with the Indian Subcontinent which had previously existed under the influence of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
. The Greek-Ptolemaic dynasty, controlling the western and northern end of other trade routes to Southern Arabia
South Arabia () is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and ...
and the Indian Subcontinent,Potter 2004: 20 had begun to exploit trading opportunities in the region prior to the Roman involvement but, according to the historian Strabo, the volume of commerce between Indians and the Greeks was not comparable to that of later Indo-Roman trade.
The Periplus Maris Erythraei
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
mentions a time when sea trade between Egypt and the subcontinent did not involve direct sailings.Young 2001: 19 The cargo under these situations was shipped to Aden:
The Ptolemaic dynasty had developed trade with Indian kingdoms using the Red Sea ports.Shaw 2003: 426 With the establishment of Roman Egypt, the Romans took over and further developed the already existing trade using these ports.
Classical geographers such as Strabo and Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
were generally slow to incorporate new information into their works and, from their positions as esteemed scholars, were seemingly prejudiced against lowly merchants and their topographical
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary scie ...
accounts.Parker 2008: 118. Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
's ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, a ...
'' represents somewhat of a break from this since he demonstrated an openness to their accounts and would not have been able to chart the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
so accurately had it not been for the input of traders. It is perhaps no surprise then that Marinus and Ptolemy relied on the testimony of a Greek sailor named Alexander for how to reach " Cattigara" (most likely Oc Eo, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
, or Kathiawar
Kathiawar () is a peninsula, near the far north of India's west coast, of about bordering the Arabian Sea. It is bounded by the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest and by the Gulf of Khambhat (Gulf of Cambay) in the east. In the northeast, it ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, where Antonine-period Roman artefacts have been discovered) in the '' Magnus Sinus'' (i.e. Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand, also known as the Gulf of Siam, is a shallow inlet in the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around in l ...
and South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
) located east of the Golden Chersonese
The Golden Chersonese or Golden Khersonese ( grc, Χρυσῆ Χερσόνησος, ''Chrysḗ Chersónēsos''; la, Chersonesus Aurea), meaning the Golden Peninsula, was the name used for the Malay Peninsula by Greek and Roman geographers in cla ...
(i.e. Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The are ...
).Young 2001: 29. In the 1st-century CE ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
'', its anonymous Greek-speaking author, a merchant of Roman Egypt, provides such vivid accounts of trade cities in Arabia and India, including travel times from rivers and towns, where to drop anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ...
, the locations of royal courts, lifestyles of the locals and goods found in their markets, and favorable times of year to sail from Egypt to these places in order to catch the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
winds, that it is clear he visited many of these locations.
Early Common Era
Prior to Roman expansion, the various peoples of the subcontinent had established strong maritime trade with other countries. The dramatic increase in the importance of Indian ports, however, did not occur until the opening of the Red Sea by the Greeks and the Romans' attainment concerning the region’s seasonal monsoons. The first two centuries of the Common Era indicate a marked increase in trade between western India and the Roman east by sea. The expansion of trade was made possible by the stability brought to the region by the Roman Empire from the time of Augustus (r. 27 BCE–14 CE) which allowed for new explorations and the creation of a sound silver and gold coinage. . The west coast of present-day India is mentioned frequently in literature, such as thePeriplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
. The area was noted for its strong tidal currents, turbulent waves and rocky sea-beds were dangerous for shipping experience. The anchors of ships would be caught by the waves and quickly detach to capsize the vessel or cause a shipwreck. Stone anchors have been observed near Bet Dwarka, an island situated in the Gulf of Kachchh, from ship lost at sea. Onshore and offshore explorations have been carried out around Bet Dwarka Island since 1983. The finds discovered include lead and stone objects buried in sediment and considered to be anchors due to their axial holes. Though it is unlikely that the remains of the shipwreck’s hull survived, offshore explorations in 2000 and 2001 have yielded seven differently-sized amphoras, two lead anchors, forty-two stone anchors of different types, a supply of potsherds, and a circular lead ingot. The remains of the seven amphoras were of a thick, coarse fabric with a rough surface, which was used for exporting wine and olive oil from the Roman Empire. Archeologists have concluded that most of these were wine amphoras, since olive oil was in less demand in the subcontinent.  Since the discoveries at Bet Dwarka are significant for the maritime history of the region, archeologists have researched the resources in India. Despite the unfavorable conditions the island is situated in, the following items have made Bet Dwarka as well as the rest of western India an important place for trade. From Latin literature, Rome imported Indian tigers, rhinoceros, elephants, and serpents to use for circus shows – a method employed as entertainment to prevent riots in Rome. It has been noted in the
Since the discoveries at Bet Dwarka are significant for the maritime history of the region, archeologists have researched the resources in India. Despite the unfavorable conditions the island is situated in, the following items have made Bet Dwarka as well as the rest of western India an important place for trade. From Latin literature, Rome imported Indian tigers, rhinoceros, elephants, and serpents to use for circus shows – a method employed as entertainment to prevent riots in Rome. It has been noted in the Periplus
A periplus (), or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus wa ...
that Roman women also wore Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
pearls and used a supply of herbs, spices, pepper, lycium
''Lycium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. The genus has a disjunct distribution around the globe, with species occurring on most continents in temperate and subtropical regions. South America has the most sp ...
, costus nowiki/>Saussurea costus">Saussurea_costus.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Saussurea costus">nowiki/>Saussurea costus sesame oil and sugar for food. Indigo was used as a color while cotton cloth was used as articles of clothing. Furthermore, the subcontinent exported ebony for fashioned furniture in Rome. The Roman Empire also imported Indian lime, peach, and various other fruits for medicine. Western India, as a result, was the recipient of large amounts of Roman gold during this time.
Since one must sail against the narrow gulfs of western India, special large boats were used and ship development was demanded. At the entrance of the gulf, large ships called trappaga and cotymba helped guide foreign vessels safely to the harbor. These ships were capable of relatively long coastal cruises, and several seals have depicted this type of ship. In each seal, parallel bands were suggested to represent the beams of the ship. In the center of the vessel is a single mast with a tripod base.
Apart from the recent explorations, close trade relations, as well as the development of ship building, were supported by the discovery of several Roman coins. On these coins were depictions of two strongly constructed masted ships. Thus, these depictions of Indian ships, originating from both coins and literature (Pliny and Pluriplus), indicate Indian development in seafaring due to the increase in Indo-Roman commerce. In addition, the silver Roman coins discovered in western India primarily come from the 1st, 2nd, and 5th centuries. These Roman coins also suggest that the Indian peninsula possessed a stable seaborne trade with Rome during 1st and 2nd century AD. Land routes, during the time of Augustus, were also used for Indian embassies to reach Rome.
The discoveries found on Bet Dwarka and on other areas on the western coast of India strongly indicate that there were strong Indo-Roman trade relations during the first two centuries of the Common Era. The 3rd century, however, was the demise of the Indo-Roman trade. The sea-route between Rome and India was shut down, and as a result, the trading reverted to the time prior to Roman expansion and exploration.
Establishment

 The replacement of Greek kingdoms by the Roman Empire as the administrator of the eastern
The replacement of Greek kingdoms by the Roman Empire as the administrator of the eastern Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
basin led to the strengthening of direct maritime trade with the east and the elimination of the taxes extracted previously by the middlemen of various land based trading routes.Lach 1994: 13 Strabo's mention of the vast increase in trade following the Roman annexation of Egypt indicates that monsoon was known from his time.
The trade started by Eudoxus of Cyzicus in 130 BCE kept increasing according to Strabo (II.5.12.):
By the time of Augustus up to 120 ships were setting sail every year from Myos Hormos to India. So much gold was used for this trade, and apparently recycled by the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi ...
(Kushans) for their own coinage, that Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
(NH VI.101) complained about the drain of specie to India:
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
(527–565 CE) excavated in India probably in the south.
Trade of exotic animals
 There is evidence of animal trade between Indian Ocean harbours and the
There is evidence of animal trade between Indian Ocean harbours and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
. This can be seen in the mosaics
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
and frescoes
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plast ...
of the remains of Roman villas
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house built in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.
Typology and distribution
Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD) distinguished two kinds of villas n ...
in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. For example, the Villa del Casale has mosaics depicting the capture of animals in India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. The intercontinental trade of animals was one of the sources of wealth for the owners of the villa. In thAmbulacro della Grande Caccia
the hunting and capture of animals is represented in such detail that it is possible to identify the species. There is a scene that shows a technique to distract a
tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus '' Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ...
with a shimmering ball of glass
Glass is a non-Crystallinity, crystalline, often transparency and translucency, transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most ...
or mirror
A mirror or looking glass is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the ...
in order to take her cubs. Tiger hunting with red ribbons serving as a distraction is also shown. In the mosaic there are also numerous other animals such as rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family (biology), family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member ...
, an Indian elephant
The Indian elephant (''Elephas maximus indicus'') is one of four extant recognised subspecies of the Asian elephant and native to mainland Asia.
Since 1986, the Asian elephant has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List as the wild po ...
(recognized from the ears) with his Indian conductor, and the Indian peafowl
The Indian peafowl (''Pavo cristatus''), also known as the common peafowl, and blue peafowl, is a peafowl species native to the Indian subcontinent. It has been introduced to many other countries. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and ...
, and other exotic birds. There are also numerous animals from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. Tigers, leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia ...
s and Asian and African lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
s were used in the arena
An arena is a large enclosed platform, often circular or oval-shaped, designed to showcase theatre, musical performances, or sporting events. It is composed of a large open space surrounded on most or all sides by tiered seating for spectato ...
s and circus
A circus is a company of performers who put on diverse entertainment shows that may include clowns, acrobats, trained animals, trapeze acts, musicians, dancers, hoopers, tightrope walkers, jugglers, magicians, ventriloquists, and uni ...
es. The European lion
The history of lions in Europe is based on fossils of Pleistocene and Holocene lions excavated in Europe since the early 19th century.
The first lion fossil was excavated in southern Germany, and described by Georg August Goldfuss using the sci ...
was already extinct at that time. Probably the last lived in the Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whol ...
and were hunted to stock arenas. The birds and monkeys entertained the guests of many villas. Also in the Villa Romana del Tellaro there is a mosaic with a tiger in the jungle attacking a man with Roman clothes, probably a careless hunter. The animals were transported in cages by ship.
Ports
Roman ports
The three main Roman ports involved with eastern trade wereArsinoe Arsinoe grc, Ἀρσινόη, Arsinoë, pronounced Arsinoi in modern Greek, may refer to:
People
* Arsinoe of Macedon, mother of Ptolemy I Soter
* Apama II or Arsinoe (c. 292 BC–after 249 BC), wife of Magas of Cyrene and mother of Berenice II
...
, Berenice and Myos Hormos. Arsinoe was one of the early trading centers but was soon overshadowed by the more easily accessible Myos Hormos and Berenice.
Arsinoe
 The Ptolemaic dynasty exploited the strategic position of
The Ptolemaic dynasty exploited the strategic position of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandr ...
to secure trade with the subcontinent.Lindsay 2006: 101 The course of trade with the east then seems to have been first through the harbor of Arsinoe, the present day Suez
Suez ( ar, السويس '; ) is a seaport city (population of about 750,000 ) in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez (a branch of the Red Sea), near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same b ...
. The goods from the East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the histori ...
n trade were landed at one of the three main Roman ports, Arsinoe, Berenice or Myos Hormos. The Romans repaired and cleared out the silted up canal from the Nile to harbor center of Arsinoe on the Red Sea.Fayle 2006: 52 This was one of the many efforts the Roman administration had to undertake to divert as much of the trade to the maritime routes as possible.
Arsinoe was eventually overshadowed by the rising prominence of Myos Hormos. The navigation to the northern ports, such as Arsinoe-Clysma, became difficult in comparison to Myos Hormos due to the northern winds in the Gulf of Suez
The Gulf of Suez ( ar, خليج السويس, khalīǧ as-suwais; formerly , ', "Sea of Calm") is a gulf at the northern end of the Red Sea, to the west of the Sinai Peninsula. Situated to the east of the Sinai Peninsula is the smaller Gulf o ...
.Freeman 2003: 72 Venturing to these northern ports presented additional difficulties such as shoals
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It ...
, reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic component, abiotic processes—deposition (geology), deposition of ...
s and treacherous currents.
Myos Hormos and Berenice
Myos Hormos and Berenice appear to have been important ancient trading ports, possibly used by the Pharaonic traders of ancient Egypt and the Ptolemaic dynasty before falling into Roman control. The site of Berenice, since its discovery by Belzoni (1818), has been equated with the ruins near Ras Banas in Southern Egypt. However, the precise location of Myos Hormos is disputed with the latitude and longitude given inPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
's ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, a ...
'' favoring Abu Sha'ar and the accounts given in classical literature
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics ...
and satellite images
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell im ...
indicating a probable identification with Quseir el-Quadim at the end of a fortified road from Koptos on the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
. The Quseir el-Quadim site has further been associated with Myos Hormos following the excavations at el-Zerqa, halfway along the route, which have revealed ostraca
An ostracon (Greek: ''ostrakon'', plural ''ostraka'') is a piece of pottery, usually broken off from a vase or other earthenware vessel. In an archaeological or epigraphical context, ''ostraca'' refer to sherds or even small pieces of sto ...
leading to the conclusion that the port at the end of this road may have been Myos Hormos.
Major regional ports
 The regional ports of
The regional ports of Barbaricum
Barbaricum (from the gr, Βαρβαρικόν, "foreign", "barbarian") is a geographical name used by historical and archaeological experts to refer to the vast area of barbarian-occupied territory that lay, in Roman Empire, Roman times, beyond ...
(modern Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former ...
), Sounagoura (central Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe ...
), Barygaza (Bharuch in Gujarat), Muziris
Muziris ( grc, Μουζιρίς, Old Malayalam: ''Muciri'' or ''Muciripattanam'' possibly identical with the medieval ''Muyirikode'') was an ancient harbour and an urban centre on the Malabar Coast. Muziris found mention in the ''Periplus o ...
(present day Kodungallur
Kodungallur (; also Cranganore, Portuguese: Cranganor; formerly known as Mahodayapuram, Shingly, Vanchi, Muchiri, Muyirikkode, and Muziris) is a historically significant town situated on the banks of river Periyar on the Malabar Coast in ...
), Korkai, Kaveripattinam and Arikamedu
Arikamedu is an archaeological site in Southern India, in Kakkayanthope, Ariyankuppam Commune, Puducherry.
Sir Mortimer Wheeler 1945, and Jean-Marie Casal conducted archaeological excavations there in 1947–1950. The site was identified as th ...
(Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil languag ...
) on the southern tip of present-day India were the main centers of this trade, along with Kodumanal
Kodumanal is a village located in the Erode district in the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It was once a flourishing ancient trade city known as Kodumanam, as inscribed in ''Patittrupathu'' of Sangam Literature. The place is an important ...
, an inland city. The Periplus Maris Erythraei
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
describes Greco-Roman merchants selling in Barbaricum "thin clothing, figured linens, topaz
Topaz is a silicate mineral of aluminium and fluorine with the chemical formula Al Si O( F, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can ma ...
, coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secre ...
, storax
Storax ( la, storax; el, στύραξ, ''stúrax''), often commercially sold as styrax, is a natural resin isolated from the wounded bark of '' Liquidambar orientalis'' Mill. (Asia Minor) and ''Liquidambar styraciflua'' L. (Central America) ( H ...
, frankincense, vessels of glass, silver and gold plate, and a little wine" in exchange for "costus
''Costus'' is a group of herbaceous perennial plants in the family Costaceae, described by Linnaeus as a genus in 1753. It was formerly known as ''Hellenia'' after the Finnish botanist Carl Niclas von Hellens. It is widespread through tropica ...
, bdellium
Bdellium (also bdellion or false myrrh) is a semi-transparent oleo-gum resin extracted from '' Commiphora wightii'' plants of India, and from ''Commiphora africana'' trees growing in sub-saharan Africa. According to Pliny the best quality came ...
, lycium
''Lycium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. The genus has a disjunct distribution around the globe, with species occurring on most continents in temperate and subtropical regions. South America has the most sp ...
, nard, turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrated phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula . It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone and ornamental stone for thousands of y ...
, lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
, Seric skins, cotton cloth, silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
yarn, and indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', ...
". In Barygaza, they would buy wheat, rice, sesame oil, cotton and cloth.
Barigaza
Trade with Barigaza, under the control of theIndo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
Western Satrap
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Prade ...
Nahapana
Nahapana (Ancient Greek: ; Kharosthi: , ; Brahmi: , ;), was an important ruler of the Western Kshatrapas, descendant of the Indo-Scythians, in northwestern India, who ruled during the 1st or 2nd century CE. According to one of his coins, he ...
("Nambanus"), was especially flourishing:
Muziris

Muziris
Muziris ( grc, Μουζιρίς, Old Malayalam: ''Muciri'' or ''Muciripattanam'' possibly identical with the medieval ''Muyirikode'') was an ancient harbour and an urban centre on the Malabar Coast. Muziris found mention in the ''Periplus o ...
is a lost port city on the south-western coast of India which was a major center of trade in the ancient Tamil land between the Chera kingdom and the Roman Empire. Its location is generally identified with modern-day Cranganore
Kodungallur (; also Cranganore, Portuguese: Cranganor; formerly known as Mahodayapuram, Shingly, Vanchi, Muchiri, Muyirikkode, and Muziris) is a historically significant town situated on the banks of river Periyar on the Malabar Coast in ...
(central Kerala). Large hoards of coins and innumerable shards of amphora
An amphora (; grc, ἀμφορεύς, ''amphoreús''; English plural: amphorae or amphoras) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storag ...
e found at the town of Pattanam
Pattanam is a village located in the Ernakulam District in the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is located 2 km north of North Paravur, 6 km and East of Chendamangalam 25 km north of Kochi (Cochin).
History
A branch of the Ka ...
(near Cranganore) have elicited recent archeological interest in finding a probable location of this port city.
According to the Periplus
A periplus (), or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus wa ...
, numerous Greek seamen managed an intense trade with Muziris:
->
Arikamedu
ThePeriplus Maris Erythraei
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
mentions a marketplace named Poduke (ch. 60), which G.W.B. Huntingford identified as possibly being Arikamedu
Arikamedu is an archaeological site in Southern India, in Kakkayanthope, Ariyankuppam Commune, Puducherry.
Sir Mortimer Wheeler 1945, and Jean-Marie Casal conducted archaeological excavations there in 1947–1950. The site was identified as th ...
in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil languag ...
, a centre of early Chola trade (now part of Ariyankuppam), about from the modern Pondicherry
Pondicherry (), now known as Puducherry ( French: Pondichéry ʊdʊˈtʃɛɹi(listen), on-dicherry, is the capital and the most populous city of the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the sout ...
.Huntingford 1980: 119. Huntingford further notes that Roman pottery was found at Arikamedu in 1937, and archeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes ...
excavations between 1944 and 1949 showed that it was "a trading station to which goods of Roman manufacture were imported during the first half of the 1st century AD".
Cultural exchanges

 The Rome-subcontinental trade also saw several cultural exchanges which had a lasting effect on both the civilizations and others involved in the trade. The
The Rome-subcontinental trade also saw several cultural exchanges which had a lasting effect on both the civilizations and others involved in the trade. The Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Er ...
n kingdom of Aksum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
was involved in the Indian Ocean trade network and was influenced by Roman culture and Indian architecture. Traces of Indian influences are visible in Roman works of silver and ivory, or in Egyptian cotton and silk fabrics used for sale in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
.Lach 1994: 18 The Indian presence in Alexandria may have influenced the culture but little is known about the manner of this influence. Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria ( grc , Κλήμης ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς; – ), was a Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen an ...
mentions the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in ...
in his writings and other Indian religion
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification of ...
s find mentions in other texts of the period.
Han China
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
was perhaps also involved in the Roman trade, with Roman embassies recorded for the years 166, 226, and 284 that allegedly landed in Rinan
Rinan (; vi, Nhật Nam), also rendered as Jih-nan, was the southernmost commandery of the Chinese Han dynasty. It was located in the central area of modern-day Vietnam between Quảng Bình and Bình Định provinces. It was administered by ...
(Jianzhi
The art of paper cutting ( zh, t=剪纸, p=jiǎnzhǐ) in China may date back to the 2nd century CE, when paper was invented by Cai Lun, a court official of the Eastern Han Dynasty.
As paper became more affordable, paper-cutting became one ...
) in northern Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
, according to Chinese histories.Ball 2016: 152–53 Roman coins and goods such as glasswares and silverwares have been found in China, as well as Roman coins, bracelets, glass beads, a bronze lamp, and Antonine-period medallions in Vietnam, especially at Oc Eo (belonging to the Funan Kingdom). The 1st-century ''Periplus
A periplus (), or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus wa ...
'' notes how a country called ''This'', with a great city called ''Thinae'' (comparable to ''Sinae
The names of China include the many contemporary and historical appellations given in various languages for the East Asian country known as ''Zhōngguó'' (/, "middle country") in its national language, Standard Mandarin. China, the name in Eng ...
'' in Ptolemy's ''Geography''), produced silk and exported it to Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, so ...
before it traveled overland to Barygaza in India and down the Ganges River
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
. While Marinus of Tyre
Marinus of Tyre ( grc-gre, Μαρῖνος ὁ Τύριος, ''Marînos ho Týrios''; 70–130) was a Greek geographer, cartographer and mathematician, who founded mathematical geography and provided the underpinnings of Claudius Ptolemy's i ...
and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
provided vague accounts of the Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand, also known as the Gulf of Siam, is a shallow inlet in the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around in l ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
, the Alexandrian Greek monk and former merchant Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
, in his ''Christian Topography
The ''Christian Topography'' ( grc, Χριστιανικὴ Τοπογραφία, la, Topographia Christiana) is a 6th-century work, one of the earliest essays in scientific geography written by a Christian author. It originally consisted of fiv ...
'' (c. 550), spoke clearly about China, how to sail there, and how it was involved in the clove
Cloves are the aromatic flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae, ''Syzygium aromaticum'' (). They are native to the Maluku Islands (or Moluccas) in Indonesia, and are commonly used as a spice, flavoring or fragrance in consumer products ...
trade stretching to Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
. Comparing the small amount of Roman coins found in China as opposed to India, Warwick Ball
Warwick Ball is an Australia-born Near-Eastern archaeologist.
Ball has been involved in excavations, architectural studies and monumental restorations in Jordan, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Ethiopia and Afghanistan. As a lecturer, he has been involved ...
asserts that most of the Chinese silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
purchased by the Romans was done so in India, with the land route through ancient Persia
The history of Iran is intertwined with the history of a larger region known as Greater Iran, comprising the area from Anatolia in the west to the borders of Ancient India and the Syr Darya in the east, and from the Caucasus and the Eurasian Step ...
playing a secondary role.
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
and Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
ish settlers from Rome continued to live in India long after the decline in bilateral trade. Large hoards of Roman coins have been found throughout India, and especially in the busy maritime trading centers of the south. The Tamilakkam kings reissued Roman coinage in their own name after defacing the coins in order to signify their sovereignty.Kulke 2004: 108 Mentions of the traders are recorded in the Tamil Sangam literature
The Sangam literature ( Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' ( Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connote ...
of India. One such mention reads: "The beautifully built ships of the Yavanas came with gold and returned with pepper, and Muziris resounded with the noise." (from poem no. 149 of 'Akananuru' of Sangam Literature)"
Decline and aftermath
Roman decline
 Trade declined from the mid-3rd century during a crisis in the Roman Empire, but recovered in the 4th century until the early 7th century, when
Trade declined from the mid-3rd century during a crisis in the Roman Empire, but recovered in the 4th century until the early 7th century, when Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩, Husrō), also known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian king (shah) of Iran, ruling f ...
, Shah of the Sasanian Empire, occupied the Roman parts of the Fertile Crescent and Egypt until being defeated by the Eastern Roman Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
at the end of 627, after which the lost territories were returned to the Eastern Romans. Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
('Cosmas who sailed to India') was a Greek-Egyptian trader, and later monk, who wrote about his trade trips to India and Sri Lanka in the 6th century.
Ravaging of the Gupta Empire by the Huns
In India, theAlchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
' invasions (496–534 CE) are said to have seriously damaged India's trade with Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
.The First Spring: The Golden Age of India by Abraham Eralpp. 48 sq
/ref> The
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Go ...
had been benefiting greatly from Indo-Roman trade. They had been exporting numerous luxury products such as silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
, leather goods, fur, iron products, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
, pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium ca ...
or pepper from centers such as Nashik
Nashik (, Marathi: aːʃik, also called as Nasik ) is a city in the northern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Situated on the banks of river Godavari, Nashik is the third largest city in Maharashtra, after Mumbai and Pune. Nash ...
, Prathisthana, Pataliputra
Pataliputra ( IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at ...
and Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
. The Huna invasions probably disrupted these trade relations and the tax revenues that came with it. Soon after the invasions, the Gupta Empire, already weakened by these invasions and the rise of local rulers, ended as well. Following the invasions, northern India was left in disarray, with numerous smaller Indian powers emerging after the crumbling of the Guptas.
Arab expansion
'Amr ibn al-'As
( ar, عمرو بن العاص السهمي; 664) was the Arab commander who led the Muslim conquest of Egypt and served as its governor in 640–646 and 658–664. The son of a wealthy Qurayshite, Amr embraced Islam in and was assigned import ...
, crossed into Egypt in late 639 or early 640 CE.Meri 2006: 224 This advance marked the beginning of the Islamic conquest of Egypt. The capture of Alexandria and the rest of the country, Holl 2003: 9 brought an end to 670 years of Roman trade with the subcontinent.
Tamil speaking south India turned to Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
for international trade where Indian culture influenced the native culture to a greater degree than the sketchy impressions made on Rome seen in the adoption of Hinduism and then Buddhism. However, knowledge of the Indian subcontinent and its trade was preserved in Byzantine books and it is likely that the court of the Emperor still maintained some form of diplomatic relation to the region up until at least the time of Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zo ...
, seeking an ally against the rising influence of the Islamic states in the Middle East and Persia, appearing in a work on ceremonies called De Ceremoniis
The ''De Ceremoniis'' (fully ''De cerimoniis aulae Byzantinae'') is the conventional Latin name for a Greek book of ceremonial protocol at the court of the Byzantine emperors in Constantinople. Its Greek title is often cited as ("Explanation of th ...
.
The Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
conquered Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
in the 15th century (1453), marking the beginning of Turkish control over the most direct trade routes between Europe and Asia.The Encyclopedia Americana 1989: 176 The Ottomans initially cut off eastern trade with Europe, leading in turn to the attempt by Europeans to find a sea route around Africa, spurring the European Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafari ...
, and the eventual rise of European Mercantilism and Colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their rel ...
.
See also
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Lionel Casson, ''The Periplus Maris Erythraei: Text With Introduction, Translation, and Commentary''.Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent Academic publishing, publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large.
The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, ...
, 1989. .
* Chakrabarti D.K. (1990). The External Trade of the Indus Civilization. Delhi: Manoharlal Publishers Private Limited
* Chami, F. A. 1999. “The Early Iron Age on Mafia island and its relationship with the mainland.” ''Azania'' Vol. XXXIV.
* McLaughlin, Raoul. (2010). ''Rome and the Distant East: Trade Routes to the Ancient Lands of Arabia, India and China''. Continuum, London and New York. .
* Miller, J. Innes. 1969. ''The Spice Trade of The Roman Empire: 29 B.C. to A.D. 641''. Oxford University Press. Special edition for Sandpiper Books. 1998. .
* Sidebotham, Steven E. (2011). ''Berenike and the Ancient Maritime Spice Route''. University of California Press. .
* Van der Veen, Marijke (2011). Consumption, Trade and Innovation. Exploring the Botanical Remains from the Roman and Islamic Ports at Quseir al-Qadim, Egypt
'. Frankfurt: Africa Magna Verlag. * Raith, M. – Hoffbauer, R. – Euler, H. – Yule, P. – Damgaard, K. (2013). “The view from Ẓafār –An archaeometric study of the Aqaba late Roman period pottery complex and distribution in the 1st millennium CE”. ''Zeitschrift für Orient-Archäologie'' 6, 320–50. .
External links
* ttp://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4970452.stm BBC News: Search for India's ancient city
Trade between the Romans and the Empires of Asia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Indo-Roman Trade And Relations Foreign relations of ancient India Ancient international relations Foreign relations of ancient Rome Bilateral trading relationships Maritime history of India Economic history of India Foreign trade of India Indian Ocean trade Historic trails and roads in India