Roman Pot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Roman pot is the name of a technique (and of the relevant device) used in accelerator physics. Named after its implementation by the
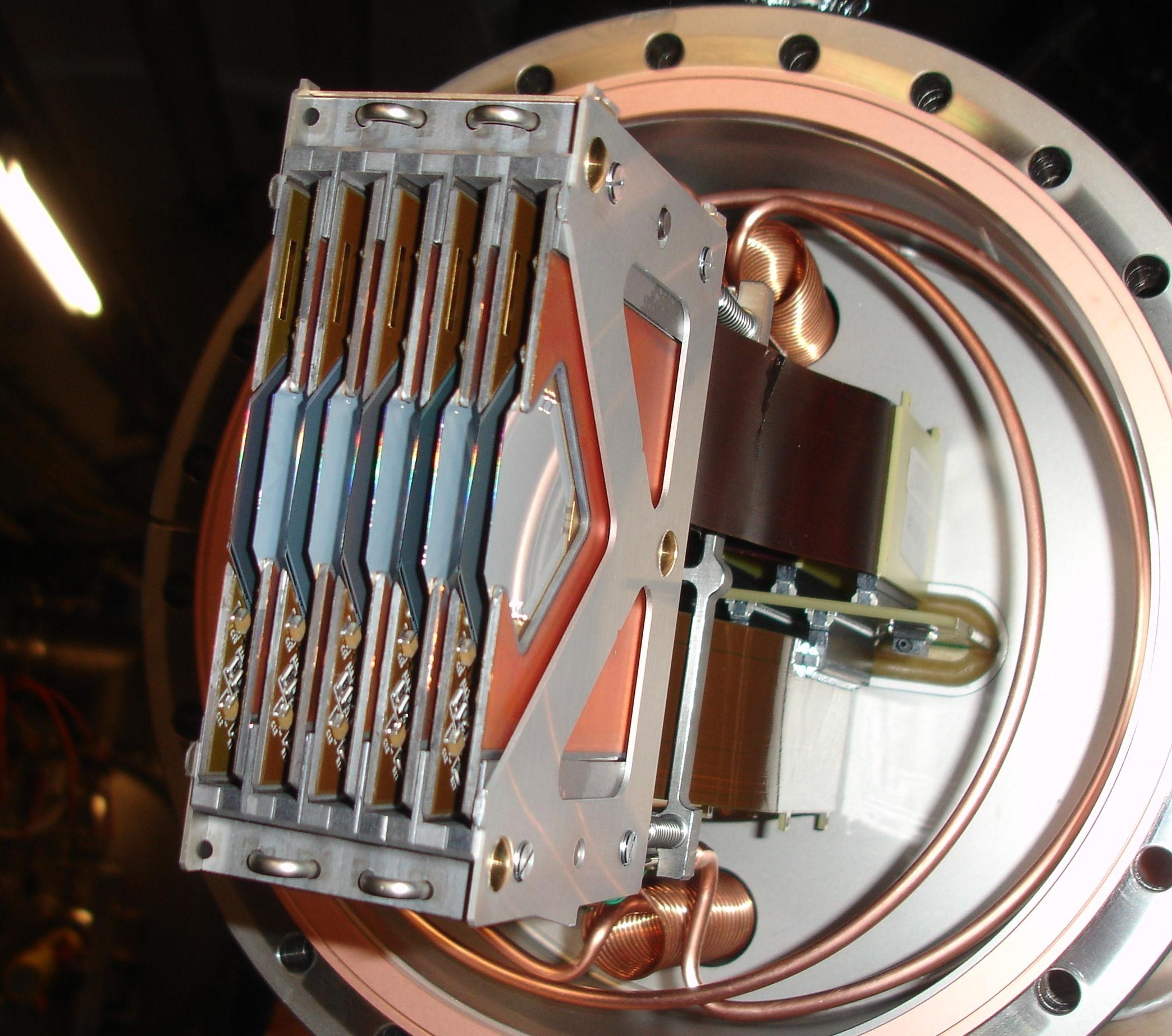 The figure below shows a single Roman pot unit, located about 220 meters forward of the IP5 interaction point. The detectors are the bulkiest bits wrapped in insulation.
The figure below shows a single Roman pot unit, located about 220 meters forward of the IP5 interaction point. The detectors are the bulkiest bits wrapped in insulation.

CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Gene ...
-Rome collaboration in the early 1970s, it is an important tool to measure the total cross section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture & engineering 3D
*Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
**Abs ...
of two particle beams
A particle beam is a stream of charged or neutral particles. In particle accelerators, these particles can move with a velocity close to the speed of light. There is a difference between the creation and control of charged particle beams and neu ...
in a collider. They are called ''pots'' because the detectors are housed in cylindrical vessels. The first generation of Roman pots was purpose-built by the CERN Central Workshops and used in the measurement of the total cross-section of proton-proton inter-actions in the ISR
ISR may refer to:
Organizations
* Institute for Strategy and Reconciliation, a think tank, relief and development organization
* Institutional and Scientific Relations, a Directorate of the European Commission
* International Star Registry, a com ...
.
Roman pots are located as close to the beamline as possible, to capture the accelerated particles which scatter by very small angles.
Roman pots used at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
Roman pots were first used in theTOTEM experiment
The TOTEM experiment (TOTal Elastic and diffractive cross section Measurement) is one of the nine detector experiments at CERN's Large Hadron Collider. The other eight are: ATLAS, ALICE, CMS, LHCb, LHCf, MoEDAL, FASER and SND@LHC. It shares a ...
and later by the ATLAS
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic ...
and the CMS
CMS may refer to:
Computing
* Call management system
* CMS-2 (programming language), used by the United States Navy
* Code Morphing Software, a technology used by Transmeta
* Collection management system for a museum collection
* Color managem ...
collaborations at the LHC
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle collider. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and hundre ...
. The figure below shows a detector used on the beamline near IP5 (interaction point 5), the location of the CMS
CMS may refer to:
Computing
* Call management system
* CMS-2 (programming language), used by the United States Navy
* Code Morphing Software, a technology used by Transmeta
* Collection management system for a museum collection
* Color managem ...
detector. Three of these are used per Roman pot unit. Each is shoved into place to within 10 microns of the beamline. Two detectors are placed above and below the beamline, and a third to the side. These detectors will record any protons that are not travelling precisely along the beamline, and thus record the elastic scattering of the protons. This is used to measure the total elastic cross-section, including Coulomb scattering
In particle physics, Rutherford scattering is the elastic scattering of charged particles by the Coulomb interaction. It is a physical phenomenon explained by Ernest Rutherford in 1911 that led to the development of the planetary Rutherford model ...
as well as diffractive scattering (i.e. diffraction because the protons are not point particles, and have an internal structure (i.e. quark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly o ...
s)). Effectively, these are detectors for studying Regge theory
Regge may refer to
* Tullio Regge (1931-2014), Italian physicist, developer of Regge calculus and Regge theory
* Regge calculus, formalism for producing simplicial approximations of spacetimes
* Regge theory, study of the analytic properties of ...
. The goal is to search for elastic scattering effects beyond the Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetism, electromagnetic, weak interaction, weak and strong interactions - excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying a ...
, such as hypothetical "colorless gluons", as well confirming ideas of pomeron
In physics, the pomeron is a Regge trajectory — a family of particles with increasing spin — postulated in 1961 to explain the slowly rising cross section of hadronic collisions at high energies. It is named after Isaak Pomeranchuk.
Overview ...
exchange, and the possible existence of an odderon In particle physics, the odderon corresponds to an elusive family of odd-gluon states, dominated by a three-gluon state. When protons collide elastically with protons or with anti-protons at high energies, even or odd numbers of gluons are exchanged ...
.
Odderons were potentially observed only in 2017 by the TOTEM experiment
The TOTEM experiment (TOTal Elastic and diffractive cross section Measurement) is one of the nine detector experiments at CERN's Large Hadron Collider. The other eight are: ATLAS, ALICE, CMS, LHCb, LHCf, MoEDAL, FASER and SND@LHC. It shares a ...
at the LHC
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle collider. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and hundre ...
. This observation was later confirmed in a joint analysis with the DØ experiment
The DØ experiment (sometimes written D0 experiment, or DZero experiment) was a worldwide collaboration of scientists conducting research on the fundamental nature of matter. DØ was one of two major experiments (the other was the CDF experim ...
at the Tevatron.
 The figure below shows a single Roman pot unit, located about 220 meters forward of the IP5 interaction point. The detectors are the bulkiest bits wrapped in insulation.
The figure below shows a single Roman pot unit, located about 220 meters forward of the IP5 interaction point. The detectors are the bulkiest bits wrapped in insulation.

References