Robinson House (Manassas, Virginia) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Robinson House sits at the bottom of Henry Hill, near Bull Run in
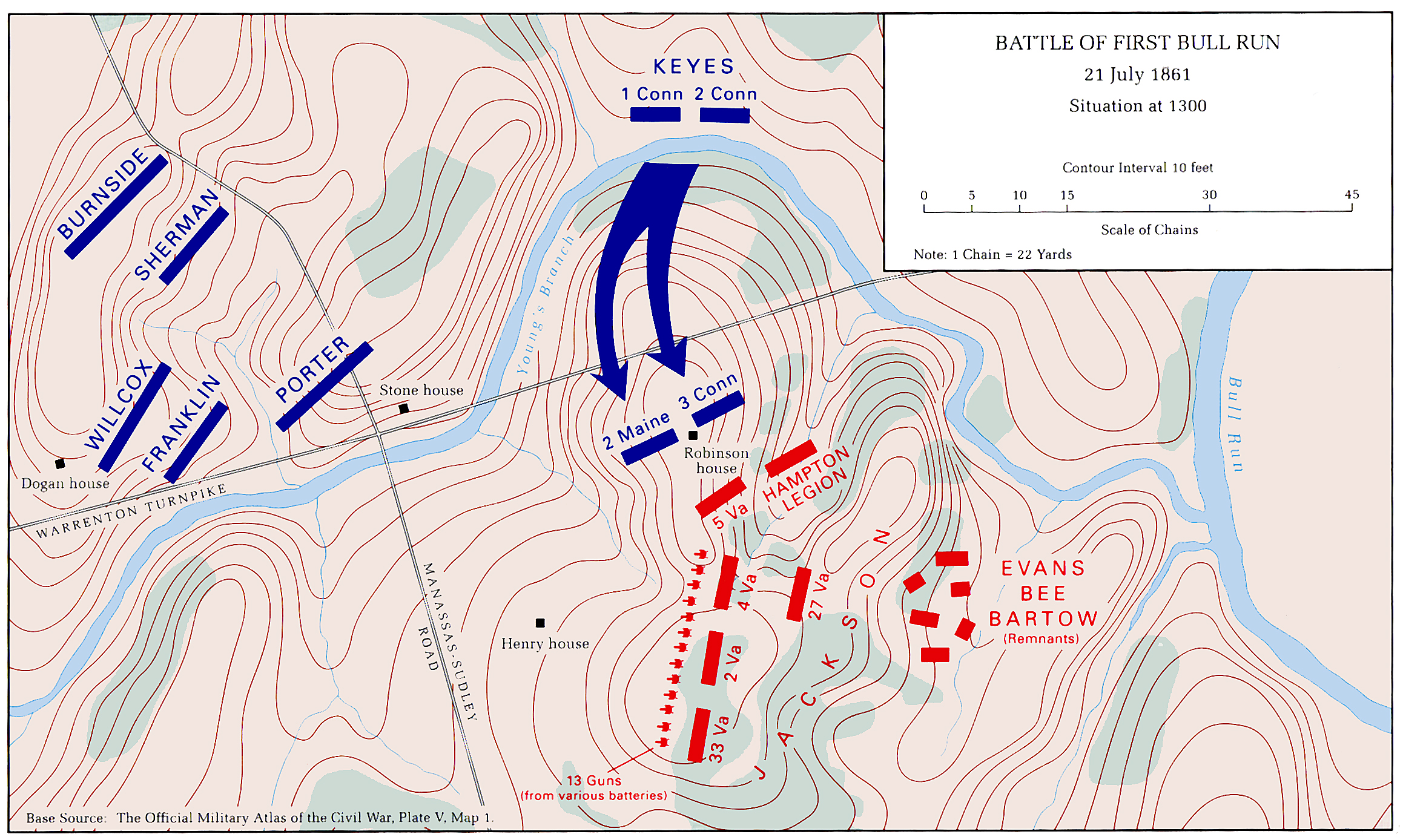 Two major battles of the Civil War were waged around the Robinson House. During the
Two major battles of the Civil War were waged around the Robinson House. During the
/ref> The
Manassas National Battlefield Park
{{DEFAULTSORT:Robinson-house Historic district contributing properties in Virginia Houses in Prince William County, Virginia Houses completed in 1848 Protected areas of Prince William County, Virginia African-American historic places Manassas National Battlefield Park National Register of Historic Places in Prince William County, Virginia
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
. The house was named for the family of James "Gentleman Jim" Robinson, a free African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, who built the house. The Robinson family, descendants of Gentleman Jim, owned and occupied the house and a large portion of the land around it from the 1840s until 1936. The National Park Service acquired this parcel as part of their effort to commemorate two major battles of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
battles of Bull Run (also known as First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second Manassas
The Second Battle of Bull Run or Battle of Second Manassas was fought August 28–30, 1862, in Prince William County, Virginia, as part of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of the Northern Virginia Campaign waged by Confederat ...
) which occurred about one year apart. Both battles were Confederate victories. However, Robinson House managed to survive virtually unscathed.
Pre-Civil War
The homestead was constructed in the 1840s by James "Gentleman Jim" Robinson, anAfrican American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, on land he purchased from local planter John Lee. James would become the third richest African American in the area.Biography of James Robinson http://www.nps.gov/mana/forteachers/upload/Res1_JamesRobinsonBio.pdf
As the son of Landon Carter, Jr. and a free African American woman, James received an education in his youth. In honor of the private tutor who taught him and the Carters' daughters Bladen and Tasco
Tasco (also known as Tasco Worldwide) sells consumer telescopes. Tasco mainly imports telescopes for amateur astronomers but has expanded into other optical products, such as spotting scopes, microscopes, binoculars, telescopic sights, and other ...
, he took the last name of his tutor as his own. Although he was born free, he was bound out for a period of time under the pretense of learning a trade. In fact, he worked as a field laborer during this time. After serving his time, he went to work for Thomas Hampton in Brentsville, Virginia
Brentsville is an unincorporated community village in Prince William County, Virginia, United States.
History
Originally known as Brent Town after its colonial era founder George Brent, it was settled as part of Stafford County. Some dispute exi ...
, as a waiter in his tavern. He established a good relationship with Hampton, as indicated by the numerous formal contracts they entered into over a ten-year span. During this period, he used his earnings to add to his land holdings. In 1847, John Lee died. As was common throughout the United States at that time, Lee owned land and slaves, including Jim's wife and children. Upon his death, those family members who were still on his plantation were willed to Jim, who took them to live with him in his new home.
Around the same time Jim established his own roadhouse on the Warrenton Turnpike, the main road from Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
to Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
, the capital of what would become the Confederacy. This was a prime location that would make him one of the wealthiest African Americans in the Manassas area, but would also bring the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
right into his front yard.
Civil War
First Battle of Bull Run
 Two major battles of the Civil War were waged around the Robinson House. During the
Two major battles of the Civil War were waged around the Robinson House. During the First Battle of Bull Run
The First Battle of Bull Run (the name used by Union forces), also known as the Battle of First Manassas
the map to the right shows the troops of two brigadier generals engaging in a pitched battle, that resulted in a total rout of the Union Forces, under the command of Erasmus Keyes. The Confederate forces held their ground, under the command of Thomas J. Jackson, so well that from then on he would be known as Stonewall Jackson. His forces held the line on one side of the Robinson House as the Union troops attempted to overcome their stiff opposition.
Before the fighting began Gentleman Jim took his family to a neighbor's home where he hoped they would be safe. After securing the house Jim attempted to reunite with his family, but was caught in the crossfire of the battle and had to take shelter under a bridge over Young's Branch of the Bull Run River until hostilities ceased. That first battle left thousands of bodies littering the fields throughout Manassas. For days after the fighting was over, the Robinsons buried many in unmarked graves. Well into the 20th century family members reported that they were still digging up the bones of some of these soldiers.
The first battle was over in a matter of a few days. Many thought that the Civil War would be decided in one, winner take all battle. But this was not to be the case. Confederate troops won the First Battle of Manassas, with federal troops retreating back to Washington, D.C., but the Civil War continued.
Second Battle of Bull Run
The Second Battle of Bull Run lasted for about a week and also resulted in a Confederate victory. Again, Federal troops retreated back to Washington and the Confederates did not pursue. The casualties on both sides were even higher following this second battle.Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
and McClellan were strategically out maneuvered by Lee and Jackson
Jackson may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Jackson (name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the surname or given name
Places
Australia
* Jackson, Queensland, a town in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson North, Qu ...
, despite the fact that they had more troops.
Again the battle raged around Robinson House. Following the destruction of Henry House during the First Battle of Bull Run, Robinson House was one of the most strategically located buildings on the battlefield. Because of this it was used as a Union hospital and planning station. In sworn testimony before the Southern Claims Commission
The Southern Claims Commission (SCC) was an organization of the executive branch of the United States government from 1871 to 1880, created under President Ulysses S. Grant. Its purpose was to allow Union sympathizers who had lived in the Southern ...
, Gentleman Jim described how following the battle, troops raided his farm in search of food and supplies, causing more than $2,000 in damages.
Post-Civil War
Southern Claims Commission
On February 2, 1872, James Robinson presented his case to the Southern Claims Commission. This commission was set up to handle damage claims of property owners who were loyal to the Union. Jim's testimony, as well as that of the witnesses called in regarding his case, offered up valuable insights into the military maneuvers of the Union and Confederate troops. In the claim Jim and his neighbors detail how Union troops took food, livestock, fence posts, and goods from his house. The house was also used as a field hospital for the wounded and dying, during the 2nd Battle of Bull Run. As one reporter put it,The Robinson House is used as a Yankee hospital. In a visit there this morning, I found 100 of them ankeespacked in the rooms as thick as sardines. ... The wounds of the majority were undressed, the blood had dried upon their persons and garments, and altogether there (sic.) the most horrible set of beings it has been my lot to encounter.
After the death of Gentleman Jim
Following the death of Gentleman Jim in 1875, his son Alfred took over as head of the household. According to available census records, he moved in with his mother and other family members as the head of the Robinson clan, until his death in 1904. The house remained in the family up until 1936 when it was sold to the National Park Service (NPS). This site of the house and the surrounding property makes up an important part of the battlefield park today.Manassas Battlefield Park
Robinson House was one of the few houses on the battlefield that was occupied during the 19th and 20th centuries. Even before the First Battle of Bull Run some of the other homes in the area, such as the Carter mansion at Pittsylvania, had been abandoned and fallen into disrepair. Henry House was completely demolished during the First Battle of Bull Run, killing its resident, Judith Carter Henry, in the process. Robinson House managed to remain intact in spite of its location in the center of heavy gunfire and artillery barrages. Although the house was able to survive the Civil War, it was destroyed by arsonists in 1993. The perpetrators were never caught, but there was evidence that it was a hate crime. Apparently, just a few weeks prior to the destruction of the house someone had vandalized the structure with graffiti.'Gentleman Jim' has a Unique Spot in Histor/ref> The
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
, in accordance with their current guidelines, has no plans to rebuild the structure, but they did conduct an archeological dig on the property, which resulted in the publication of the most significant document on the house and the family that owned and occupied it from pre-Civil War days into the early 20th century.
The site of Robinson House is preserved as part of the Manassas National Battlefield Park
Manassas National Battlefield Park is a unit of the National Park Service located in Prince William County, Virginia, north of Manassas that preserves the site of two major American Civil War battles: the First Battle of Bull Run, also called th ...
.
References
External links
Manassas National Battlefield Park
{{DEFAULTSORT:Robinson-house Historic district contributing properties in Virginia Houses in Prince William County, Virginia Houses completed in 1848 Protected areas of Prince William County, Virginia African-American historic places Manassas National Battlefield Park National Register of Historic Places in Prince William County, Virginia