Robert De Vaugondy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Gilles Robert de Vaugondy (1688–1766), also known as Le
Gilles Robert de Vaugondy (1688–1766), also known as Le
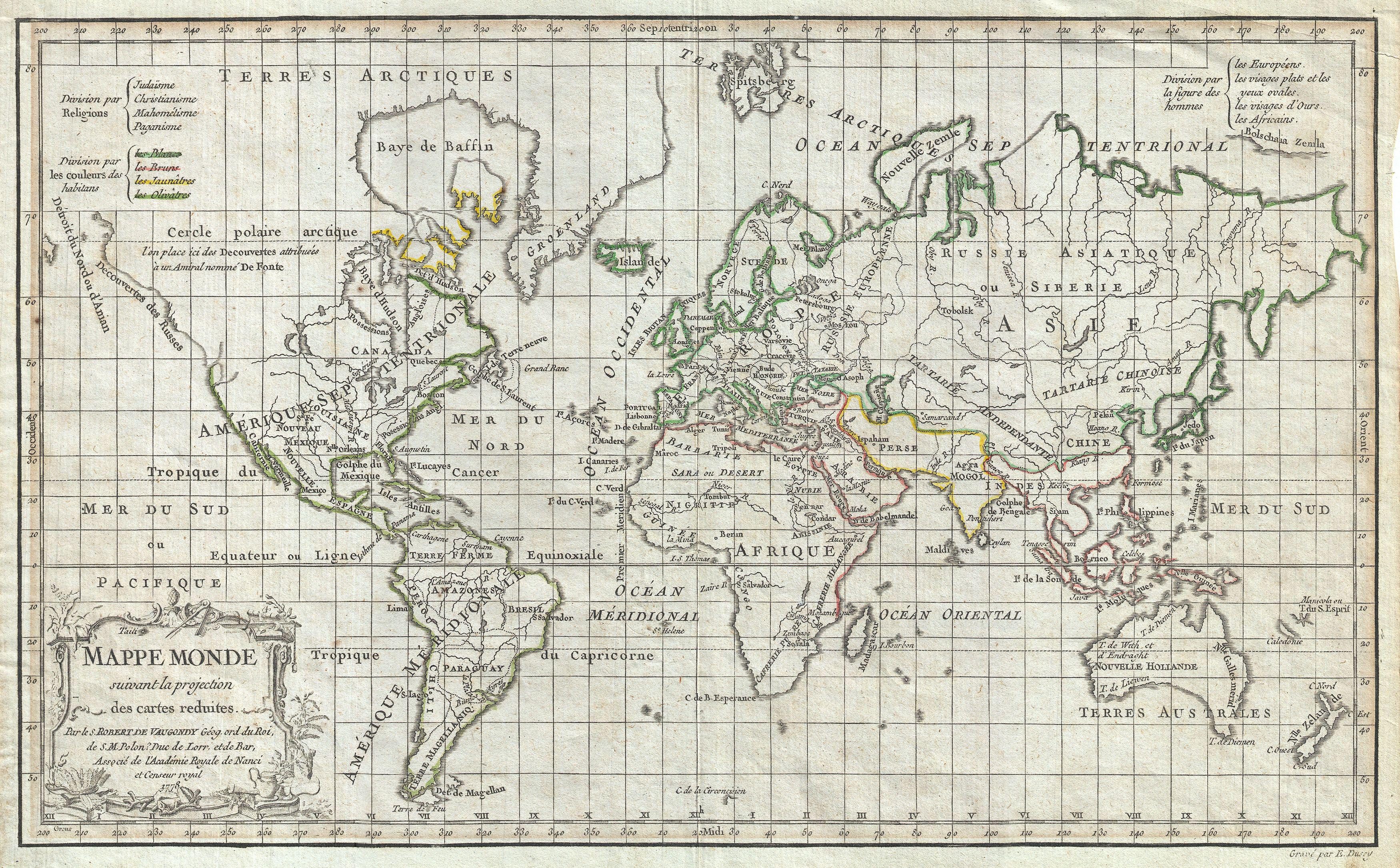 In 1757, Gilles and Didier Robert De Vaugondy published ''The Atlas Universel'', one of the most important
In 1757, Gilles and Didier Robert De Vaugondy published ''The Atlas Universel'', one of the most important
 Gilles Robert de Vaugondy (1688–1766), also known as Le
Gilles Robert de Vaugondy (1688–1766), also known as Le Sieur
Lord of the Manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England, referred to the landholder of a rural estate. The lord enjoyed manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seig ...
or Monsieur Robert, and his son, Didier Robert de Vaugondy (c.1723–1786), were leading cartographers
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
during the 18th century.
Life
 In 1757, Gilles and Didier Robert De Vaugondy published ''The Atlas Universel'', one of the most important
In 1757, Gilles and Didier Robert De Vaugondy published ''The Atlas Universel'', one of the most important atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
es of the 18th century. To produce the atlas, the Vaugondys integrated older sources with more modern surveyed maps. They verified and corrected the latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
of many regional maps in the atlas with astronomical observation
Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical m ...
s. The older material was revised with the addition of many new place names. In 1760, Didier Robert de Vaugondy was appointed geographer to Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached ...
.
Gilles and Didier Robert De Vaugondy produced their maps and terrestrial globes working together as father and son. Globes of a variety of sizes were made by gluing copperplate-printed gores on a plaster-finished papier-mache core, a complicated and expensive manufacturing process, employing several specialists. In some cases it is uncertain whether Gilles or Didier made a given map. Gilles often signed maps as "M.Robert", while Didier commonly signed his maps as "Robert de Vaugondy", or added "fils" or "filio" after his name.
The Robert de Vaugondys were descended from the Nicolas Sanson
Nicolas Sanson (20 December 1600 – 7 July 1667) was a French cartographer who served under two kings in matters of geography. He has been called the "father of French cartography."
Life and work
He was born of an old Picard family of Sco ...
family through Sanson's grandson, Pierre Moulard-Sanson. From him, they inherited much of Sanson's cartographic material, which they combined with maps and plates acquired after Hubert Jaillot's death in 1712 to form the basis the ''Atlas Universel''. Sources from the Dépôt de la Marine, the official French repository for maritime-related information, were used for their maps of Canada and South America.
Like Ortelius
Abraham Ortelius (; also Ortels, Orthellius, Wortels; 4 or 14 April 152728 June 1598) was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer, conventionally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the ''Theatrum Orbis Terrarum ...
and Mercator __NOTOC__
Mercator (Latin for "merchant") may refer to:
People
* Marius Mercator (c. 390–451), a Catholic ecclesiastical writer
* Arnold Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer
* Gerardus Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer
** Mercator 1569 ...
, the Vaugondy's credited their sources, which has greatly benefited the study of the history of cartography during that period.
References
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Vaugondy, Robert De 18th-century French cartographers 1688 births 1766 deaths French encyclopedists French male non-fiction writers 18th-century French male writers