Riga Wall on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of
 Riga began to develop as a centre of Viking trade during the early Middle Ages.
Riga's inhabitants occupied themselves mainly with fishing,
Riga began to develop as a centre of Viking trade during the early Middle Ages.
Riga's inhabitants occupied themselves mainly with fishing,


 During these many centuries of war and changes of power in the Baltic, and despite demographic changes, the
During these many centuries of war and changes of power in the Baltic, and despite demographic changes, the
 During
During
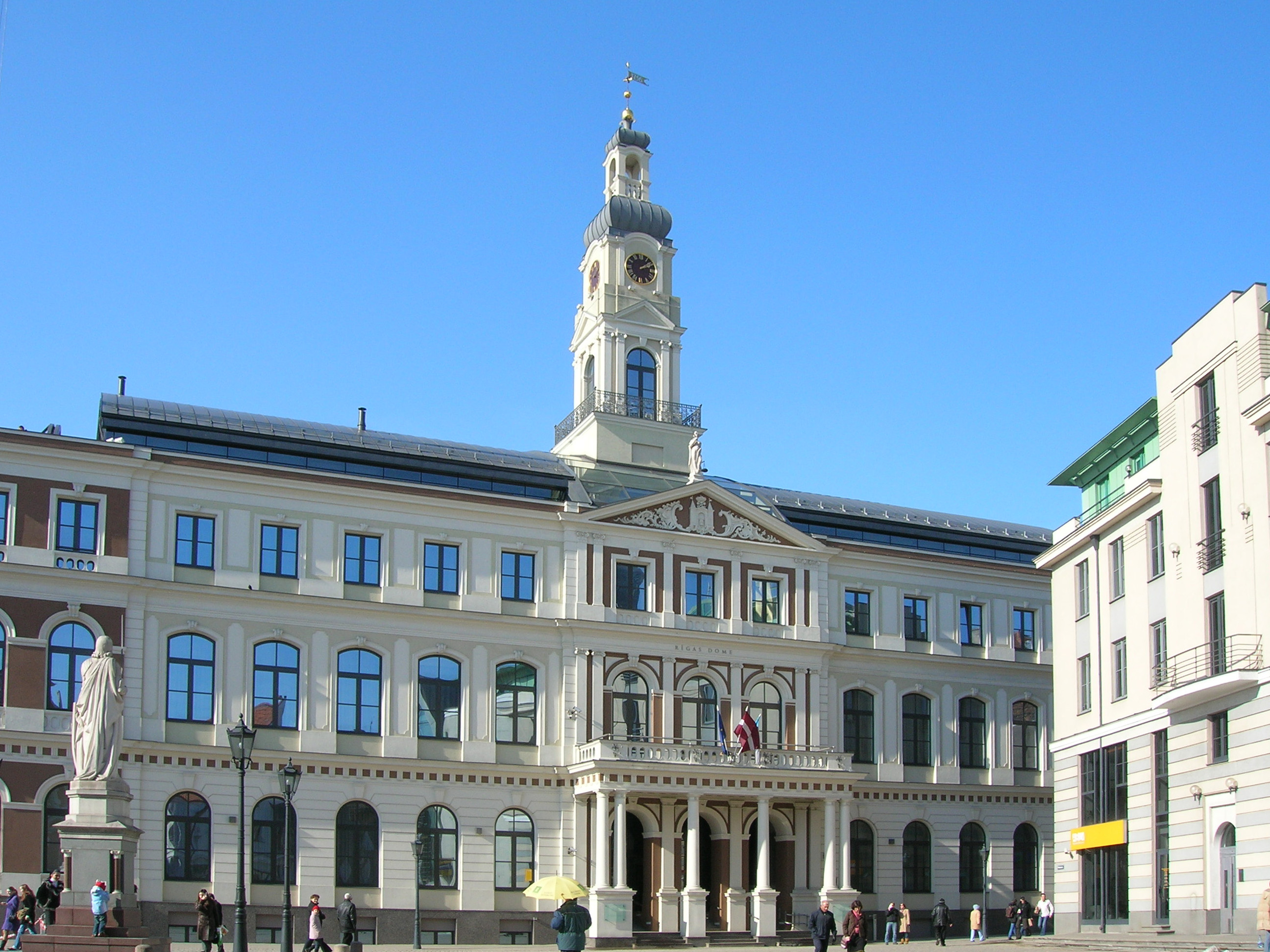 The head of the city government in Riga is the mayor, or officially the Chairman of the Riga City Council. He is assisted by one or more Vice Mayors (deputy mayors). The current mayor since October 2020 is Mārtiņš Staķis elected from Movement For!, which is a part of the Development/For!/The Progressives (Latvia), Progressives faction, but on 24 March 2022, he left the party. The three other parties in the governing coalition each received a Vice Mayor post.
The city council is a democratically elected institution and is the final decision-making authority in the city. The Council consists of 60 members or deputies who are elected every four years. The Presidium of the Riga City Council consists of the Chairman of the Riga City Council and the representatives delegated by the political parties or party blocks elected to the City Council. From February to October 2020, the offices of the Mayor and Vice Mayors were suspended and the council itself had been dissolved and replaced by an interim administration of representatives from three Government of Latvia, governmental ministries until snap 2020 Riga City Council election, elections were held in 2020.
The head of the city government in Riga is the mayor, or officially the Chairman of the Riga City Council. He is assisted by one or more Vice Mayors (deputy mayors). The current mayor since October 2020 is Mārtiņš Staķis elected from Movement For!, which is a part of the Development/For!/The Progressives (Latvia), Progressives faction, but on 24 March 2022, he left the party. The three other parties in the governing coalition each received a Vice Mayor post.
The city council is a democratically elected institution and is the final decision-making authority in the city. The Council consists of 60 members or deputies who are elected every four years. The Presidium of the Riga City Council consists of the Chairman of the Riga City Council and the representatives delegated by the political parties or party blocks elected to the City Council. From February to October 2020, the offices of the Mayor and Vice Mayors were suspended and the council itself had been dissolved and replaced by an interim administration of representatives from three Government of Latvia, governmental ministries until snap 2020 Riga City Council election, elections were held in 2020.
File:Latvias Banka.JPG, Bank of Latvia
File:Riga stock exchange.jpg, Riga Stock Exchange early 20th century. Now The Art Museum Riga Bourse
 The Riga Radio and TV Tower, radio and TV tower of Riga is the tallest structure in Latvia and the Baltic States, and one of the tallest in the European Union, reaching . Riga centre also has many great examples of Gothic revival architecture, such as the Kalpaka Boulevard Library, and a bevy of
The Riga Radio and TV Tower, radio and TV tower of Riga is the tallest structure in Latvia and the Baltic States, and one of the tallest in the European Union, reaching . Riga centre also has many great examples of Gothic revival architecture, such as the Kalpaka Boulevard Library, and a bevy of
File:Edificio modernista en Alberta iela 13, Riga, Letonia, 2012-08-07, DD 01.jpg, Albert Street, Riga, Alberta iela 13
File:Edificio modernista en Alberta iela 2a, Riga, Letonia, 2012-08-07, DD 02.JPG, Alberta iela 2a
File:Alberta ielā 12 20120728-05.JPG, Staircase of Alberta ielā 12
File:A. Čaka iela 26 Rīga 03.jpg, Aleksandra Čaka iela 26
File:La salle à manger (musée dart nouveau, Riga) (7562659988).jpg, Riga Art Nouveau Museum
File:Edificio modernista en Strelnieku Iela 4a, Riga, Letonia, 2012-08-07, DD 01.JPG, Strēlnieku iela 4a
FILE:0871 LVA Riga art noveau relief meistaru iela 10.jpg, meistaru iela 10 relief
FILE:0872 LVA Riga art noveau relief.jpg, Strelnieku iela relief
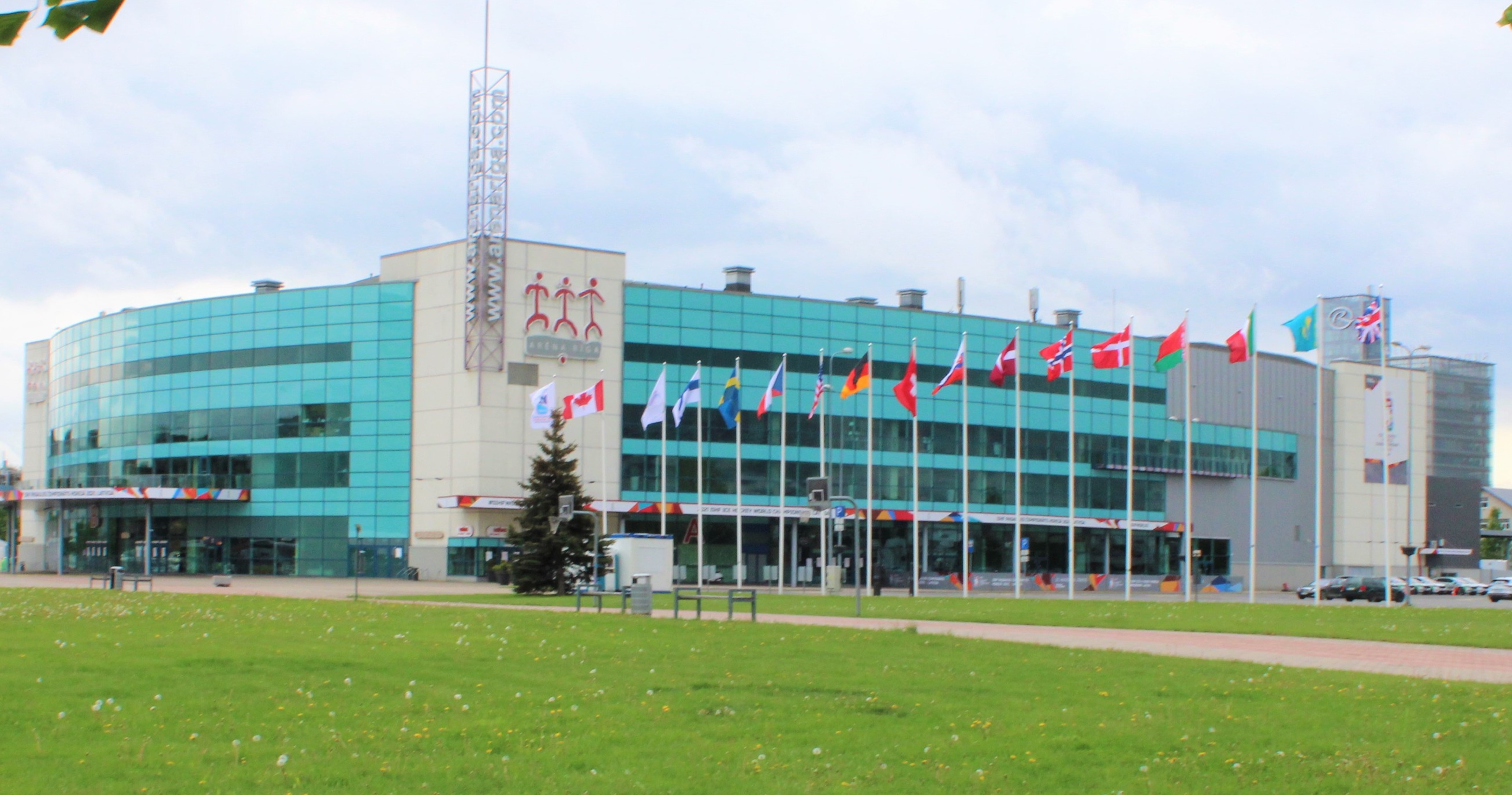 * Basketball
** BK VEF Rīga – a professional basketball team that is a three-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion. VEF also participates in high-level international competition such as Eurocup Basketball, Eurocup
** Barons LMT – a men's basketball team, two-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion, as well as the 2007–08 FIBA EuroCup, 2008 FIBA EuroCup winner
** TTT Riga – a women's basketball team, which between 1960 and 1982 won eighteen FIBA EuroLeague Women titles
* Ice hockey
** Dinamo Riga – a professional ice hockey club established in 2008. It played in the Kontinental Hockey League until 2022. Dinamo was established as a successor to the Dinamo Riga (original), former hockey team with the same name, which was founded in 1946 but ceased to exist in 1995.
** HK Riga – a junior hockey club, playing in the Minor Hockey League
* Association football, Football
**Riga FC – Riga Football Club, commonly referred to as Riga FC, were established in 2015 after a merger of two Riga based teams – FC Caramba Riga and Dinamo Rīga. In 2018 they became champions of the Virslīga Latvian Higher League for the first time.
** FK RFS, RFS – FK Rīgas Futbola Skola, known as RFS are based on the Riga Football School (RFS) academy, established in 1962.
** FS Metta-LU – founded in 2006. Metta play their home games at Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium.
** JDFS Alberts – Jura Docenko Futbola Skola Alberts, commonly referred to as JDFS Alberts was founded as a football school in 2008 and subsequently became a professional Latvian football league team.
**Riga United FC
**FC New Project
::Dissolved Football Clubs
:* Skonto FC – Skonto FC was a football club established in 1991. The club won fourteen successive Latvian Higher League titles. For a long time it provided the core of the Latvian national football team. Following financial problems, the club was demoted to the Latvian First League in 2016 and went bankrupt in December of that year and subsequently dissolved.
:* JFK Olimps – JFK Olimps played in the top division of Latvian football. The club was founded in 2005 and dissolved in 2012. According to a study from January 2011, the club was the youngest team in Europe, with an average age of 19.02 years.
* Basketball
** BK VEF Rīga – a professional basketball team that is a three-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion. VEF also participates in high-level international competition such as Eurocup Basketball, Eurocup
** Barons LMT – a men's basketball team, two-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion, as well as the 2007–08 FIBA EuroCup, 2008 FIBA EuroCup winner
** TTT Riga – a women's basketball team, which between 1960 and 1982 won eighteen FIBA EuroLeague Women titles
* Ice hockey
** Dinamo Riga – a professional ice hockey club established in 2008. It played in the Kontinental Hockey League until 2022. Dinamo was established as a successor to the Dinamo Riga (original), former hockey team with the same name, which was founded in 1946 but ceased to exist in 1995.
** HK Riga – a junior hockey club, playing in the Minor Hockey League
* Association football, Football
**Riga FC – Riga Football Club, commonly referred to as Riga FC, were established in 2015 after a merger of two Riga based teams – FC Caramba Riga and Dinamo Rīga. In 2018 they became champions of the Virslīga Latvian Higher League for the first time.
** FK RFS, RFS – FK Rīgas Futbola Skola, known as RFS are based on the Riga Football School (RFS) academy, established in 1962.
** FS Metta-LU – founded in 2006. Metta play their home games at Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium.
** JDFS Alberts – Jura Docenko Futbola Skola Alberts, commonly referred to as JDFS Alberts was founded as a football school in 2008 and subsequently became a professional Latvian football league team.
**Riga United FC
**FC New Project
::Dissolved Football Clubs
:* Skonto FC – Skonto FC was a football club established in 1991. The club won fourteen successive Latvian Higher League titles. For a long time it provided the core of the Latvian national football team. Following financial problems, the club was demoted to the Latvian First League in 2016 and went bankrupt in December of that year and subsequently dissolved.
:* JFK Olimps – JFK Olimps played in the top division of Latvian football. The club was founded in 2005 and dissolved in 2012. According to a study from January 2011, the club was the youngest team in Europe, with an average age of 19.02 years.
 * Arena Riga – a multi-purpose arena built in 2006 as the main venue for the 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships. It can hold up to 14,500 people and has hosted ice hockey, basketball and volleyball events, as well as Red Bull X-Fighters
* Skonto Stadium – a football stadium, built in 2000. It is the main stadium used for games of the Latvian national football team and the home stadium of Riga FC. The stadium was previously the home stadium of Skonto FC prior to the team's dissolution.
* Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium – a stadium built in 1958, used for both Association football, football and Sport of athletics, athletics
* Latvijas Universitates Stadions
* Biķernieku Kompleksā Sporta Bāze – Latvia's leading motorsport complex
* Arena Riga – a multi-purpose arena built in 2006 as the main venue for the 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships. It can hold up to 14,500 people and has hosted ice hockey, basketball and volleyball events, as well as Red Bull X-Fighters
* Skonto Stadium – a football stadium, built in 2000. It is the main stadium used for games of the Latvian national football team and the home stadium of Riga FC. The stadium was previously the home stadium of Skonto FC prior to the team's dissolution.
* Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium – a stadium built in 1958, used for both Association football, football and Sport of athletics, athletics
* Latvijas Universitates Stadions
* Biķernieku Kompleksā Sporta Bāze – Latvia's leading motorsport complex


 Riga, with its central geographic position and concentration of population, has always been the infrastructural hub of Latvia. Several List of national roads in Latvia, national roads begin in Riga, and European route E22 crosses Riga from the east and west, while the European route E67, Via Baltica crosses Riga from the south and north.
As a city situated by a river, Riga also has several bridges. The oldest-standing bridge is the Railway Bridge, Riga, Railway Bridge, which is also the only railroad-carrying bridge in Riga. The Stone Bridge, Riga, Stone Bridge (''Akmens tilts'') connects Old Riga and Pārdaugava; the Island Bridge, Riga, Island Bridge (''Salu tilts'') connects Maskavas Forštate and Pārdaugava via Zaķusala; and the Vanšu Bridge, Shroud Bridge (''Vanšu tilts'') connects Old Riga and Pārdaugava via Ķīpsala. In 2008, the first stage of the new Southern Bridge (''Dienvidu tilts'') route across the Daugava was completed, and was opened to traffic on 17 November.
The Southern Bridge was the biggest construction project in the Baltic states in 20 years, and its purpose was to reduce traffic congestion in the city centre. Another major construction project is the planned Riga Northern transport corridor; its first segment detailed project was completed in 2015.
The Freeport of Riga facilitates cargo and passenger traffic by sea. Sea ferries connect Riga Passenger Terminal to Stockholm operated by Tallink.
Riga has one active airport that serves commercial airlines—the
Riga, with its central geographic position and concentration of population, has always been the infrastructural hub of Latvia. Several List of national roads in Latvia, national roads begin in Riga, and European route E22 crosses Riga from the east and west, while the European route E67, Via Baltica crosses Riga from the south and north.
As a city situated by a river, Riga also has several bridges. The oldest-standing bridge is the Railway Bridge, Riga, Railway Bridge, which is also the only railroad-carrying bridge in Riga. The Stone Bridge, Riga, Stone Bridge (''Akmens tilts'') connects Old Riga and Pārdaugava; the Island Bridge, Riga, Island Bridge (''Salu tilts'') connects Maskavas Forštate and Pārdaugava via Zaķusala; and the Vanšu Bridge, Shroud Bridge (''Vanšu tilts'') connects Old Riga and Pārdaugava via Ķīpsala. In 2008, the first stage of the new Southern Bridge (''Dienvidu tilts'') route across the Daugava was completed, and was opened to traffic on 17 November.
The Southern Bridge was the biggest construction project in the Baltic states in 20 years, and its purpose was to reduce traffic congestion in the city centre. Another major construction project is the planned Riga Northern transport corridor; its first segment detailed project was completed in 2015.
The Freeport of Riga facilitates cargo and passenger traffic by sea. Sea ferries connect Riga Passenger Terminal to Stockholm operated by Tallink.
Riga has one active airport that serves commercial airlines—the
 *Isaiah Berlin, Sir Isaiah Berlin (1909–1997), a British social and political theorist, philosopher and historian of ideas
*Emil Friedrich von Boetticher (1836–1907) a politician, burgomaster of Riga
*Friedrich Heinrich von Boetticher (1826–1902) a German publisher, bookseller, scholar and art historian.
*Deniss Čalovskis (born 1985), Latvian computer hacker who created the Gozi virus.
*Valdis Dombrovskis (born 1971), a Latvian politician and EU Commissioner
*Laila Freivalds (born 1942), former Swedish Minister for Justice and Deputy Prime Minister of Sweden
*Juris Hartmanis (born 1928), a Latvian-American computer scientist, won the 1993 Turing Award
*Nicolai Hartmann (1882–1950), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German philosopher, an important Metaphysics, metaphysician
*Johann Gottfried Herder (1744–1803), a German philosopher, theologian, poet and literary critic
*Albert Woldemar Hollander (1796–1868), a German educator and pedagog.
*Yeshayahu Leibowitz (1903–1994), an Israeli public intellectual and polymath
*Yosef Mendelevich (born 1947), a Jewish refusenik from the Soviet Union, known as a ''"Prisoner of Zion"''
*Ernst Munzinger (1887–1945), German Abwehr (Army intelligence) officer, later anti-Nazi
*Valters Nollendorfs (born 1931), chairman of the board of the Museum of the Occupation of Latvia
*Alfred Rosenberg (1892–1946), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German theorist and ideologue of the Nazi Party
*Johann Steinhauer (1705–1779) a Latvian entrepreneur, social reformer and landowner
*Charlotte Wahl (1817–1899), a Latvian-born philanthropist
*Tatiana Warsher (1880–1960), a Russian archaeologist known for her studies of Pompeii
*Isaiah Berlin, Sir Isaiah Berlin (1909–1997), a British social and political theorist, philosopher and historian of ideas
*Emil Friedrich von Boetticher (1836–1907) a politician, burgomaster of Riga
*Friedrich Heinrich von Boetticher (1826–1902) a German publisher, bookseller, scholar and art historian.
*Deniss Čalovskis (born 1985), Latvian computer hacker who created the Gozi virus.
*Valdis Dombrovskis (born 1971), a Latvian politician and EU Commissioner
*Laila Freivalds (born 1942), former Swedish Minister for Justice and Deputy Prime Minister of Sweden
*Juris Hartmanis (born 1928), a Latvian-American computer scientist, won the 1993 Turing Award
*Nicolai Hartmann (1882–1950), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German philosopher, an important Metaphysics, metaphysician
*Johann Gottfried Herder (1744–1803), a German philosopher, theologian, poet and literary critic
*Albert Woldemar Hollander (1796–1868), a German educator and pedagog.
*Yeshayahu Leibowitz (1903–1994), an Israeli public intellectual and polymath
*Yosef Mendelevich (born 1947), a Jewish refusenik from the Soviet Union, known as a ''"Prisoner of Zion"''
*Ernst Munzinger (1887–1945), German Abwehr (Army intelligence) officer, later anti-Nazi
*Valters Nollendorfs (born 1931), chairman of the board of the Museum of the Occupation of Latvia
*Alfred Rosenberg (1892–1946), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German theorist and ideologue of the Nazi Party
*Johann Steinhauer (1705–1779) a Latvian entrepreneur, social reformer and landowner
*Charlotte Wahl (1817–1899), a Latvian-born philanthropist
*Tatiana Warsher (1880–1960), a Russian archaeologist known for her studies of Pompeii
 *Rutanya Alda (born 1942), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American actress
*Mikhail Baryshnikov (born 1948), a Russian dancer, choreographer and actor
*Léopold Bernhard Bernstamm (1859–1939), a Russian sculptor
*Gunnar Birkerts (1925–2017), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American architect
*Leonīds Breikšs (1908–1942), a Latvian poet, author and newspaper editor
*Jacob W. Davis (born ''Jākobs Jufess'') (1831–1908) an American tailor, invented modern jeans.
*Mikhail Eisenstein (1867–1920) a Latvian civil engineer and architect
*Sergei Eisenstein (1898–1948), a Soviet Russian film director, filmed ''Battleship Potemkin''
*Heinz Erhardt (1909–1979), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German comedian, musician and entertainer
*Artur Fonvizin (1883–1973), a Soviet painter of watercolours
*Elīna Garanča (born 1976), a Latvian operatic mezzo-soprano
*Philippe Halsman (1906–1979), an American portrait photographer
*Aivars Kalējs (born 1951), a Latvian composer, organist and pianist
*Gidon Kremer (born 1947), a Latvian classical violinist and conductor
*Barbara von Krüdener (1764–1824), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German author, religious mystic and Pietism, Pietist Lutheran theologian.
*Ivan Krylov (1769–1844), a Russian fable writer
*DJ Lethal (born 1972), an American music producer, real name ''Leor Dimant''
*Captain Disillusion, Alan Melikdjanian (born 1980), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American independent filmmaker known as ''Captain Disillusion''
*Raimonds Pauls (born 1936), a Latvian composer and piano player
*Kristjan Jaak Peterson (1801–1822), an Estonian poet
*Valentin Pikul (1928–1990), a Soviet historical novelist
*Marie Seebach (1829–1897) a German actress.
*Ksenia Solo (born 1987), a Latvian Canadian, Latvian-Canadian actress and activist
*Rutanya Alda (born 1942), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American actress
*Mikhail Baryshnikov (born 1948), a Russian dancer, choreographer and actor
*Léopold Bernhard Bernstamm (1859–1939), a Russian sculptor
*Gunnar Birkerts (1925–2017), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American architect
*Leonīds Breikšs (1908–1942), a Latvian poet, author and newspaper editor
*Jacob W. Davis (born ''Jākobs Jufess'') (1831–1908) an American tailor, invented modern jeans.
*Mikhail Eisenstein (1867–1920) a Latvian civil engineer and architect
*Sergei Eisenstein (1898–1948), a Soviet Russian film director, filmed ''Battleship Potemkin''
*Heinz Erhardt (1909–1979), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German comedian, musician and entertainer
*Artur Fonvizin (1883–1973), a Soviet painter of watercolours
*Elīna Garanča (born 1976), a Latvian operatic mezzo-soprano
*Philippe Halsman (1906–1979), an American portrait photographer
*Aivars Kalējs (born 1951), a Latvian composer, organist and pianist
*Gidon Kremer (born 1947), a Latvian classical violinist and conductor
*Barbara von Krüdener (1764–1824), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German author, religious mystic and Pietism, Pietist Lutheran theologian.
*Ivan Krylov (1769–1844), a Russian fable writer
*DJ Lethal (born 1972), an American music producer, real name ''Leor Dimant''
*Captain Disillusion, Alan Melikdjanian (born 1980), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American independent filmmaker known as ''Captain Disillusion''
*Raimonds Pauls (born 1936), a Latvian composer and piano player
*Kristjan Jaak Peterson (1801–1822), an Estonian poet
*Valentin Pikul (1928–1990), a Soviet historical novelist
*Marie Seebach (1829–1897) a German actress.
*Ksenia Solo (born 1987), a Latvian Canadian, Latvian-Canadian actress and activist
 *Ernst von Bergmann (1836–1907), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German surgeon, pioneer of aseptic surgery
*Walter von Boetticher (1853–1945) a German historian, genealogist and physician.
*Jakob Benjamin Fischer (1731–1793), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German naturalist and apothecary
*Lola Hoffmann (1904–1988), a physiologist, psychiatrist and guide to self-development and transformation
*Charles Kalme (1939–2002), an American mathematician and International Master of chess
*Karlis Kaufmanis (1910–2003), astronomer, he lectured that the Star of Bethlehem was a conjunction in 7 BC of the planets Jupiter and Saturn
*Mstislav Keldysh (1911–1978), a Soviet mathematician, worked on the first Soviet space program, artificial satellite
*George Nagobads (born 1921), American physician, recipient of the Paul Loicq Award.
*Wilhelm Ostwald (1853–1932), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German chemist, Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909
*Georg August Schweinfurth (1836–1925) a Baltic Germans, Baltic German botanist and ethnologist who explored East Central Africa.
*Georg von Tiesenhausen (1914–2018), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German American Aerospace engineering, rocket scientist.
*Juris Upatnieks (born 1936), a Latvian-American physicist and inventor, pioneer in the field of holography.
*Friedrich Zander (1887–1933), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German engineer, designed the first Soviet liquid-fuelled rocket
*Walter Zapp (1905–2003), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German inventor, he created the Minox Subminiature photography, subminiature camera.
*Ernst von Bergmann (1836–1907), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German surgeon, pioneer of aseptic surgery
*Walter von Boetticher (1853–1945) a German historian, genealogist and physician.
*Jakob Benjamin Fischer (1731–1793), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German naturalist and apothecary
*Lola Hoffmann (1904–1988), a physiologist, psychiatrist and guide to self-development and transformation
*Charles Kalme (1939–2002), an American mathematician and International Master of chess
*Karlis Kaufmanis (1910–2003), astronomer, he lectured that the Star of Bethlehem was a conjunction in 7 BC of the planets Jupiter and Saturn
*Mstislav Keldysh (1911–1978), a Soviet mathematician, worked on the first Soviet space program, artificial satellite
*George Nagobads (born 1921), American physician, recipient of the Paul Loicq Award.
*Wilhelm Ostwald (1853–1932), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German chemist, Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909
*Georg August Schweinfurth (1836–1925) a Baltic Germans, Baltic German botanist and ethnologist who explored East Central Africa.
*Georg von Tiesenhausen (1914–2018), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German American Aerospace engineering, rocket scientist.
*Juris Upatnieks (born 1936), a Latvian-American physicist and inventor, pioneer in the field of holography.
*Friedrich Zander (1887–1933), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German engineer, designed the first Soviet liquid-fuelled rocket
*Walter Zapp (1905–2003), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German inventor, he created the Minox Subminiature photography, subminiature camera.


online
(in Latvian) *
i
{{Authority control Riga, Cities in Latvia Capitals in Europe Populated coastal places in Latvia Port cities in Latvia Port cities and towns of the Baltic Sea Republican cities of Latvia Gulf of Riga Kreis Riga Members of the Hanseatic League Vidzeme NUTS 3 statistical regions of the European Union World Heritage Sites in Latvia Holocaust locations in Latvia
Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, Bay of Riga, or Gulf of Livonia ( lv, Rīgas līcis, et, Liivi laht) is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia.
The island of Saaremaa (Estonia) partially separates it from the rest of the Baltic Sea. The main con ...
at the mouth of the Daugava
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic Se ...
river where it meets the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. Riga's territory covers and lies above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, on a flat and sandy plain.
Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
member. Riga's historical centre is a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, noted for its Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
/Jugendstil architecture and 19th century wooden architecture. Riga was the European Capital of Culture in 2014, along with Umeå
Umeå ( , , , locally ; South Westrobothnian: ;). fi, Uumaja; sju, Ubmeje; sma, Upmeje; se, Ubmi) is a city in northeast Sweden. It is the seat of Umeå Municipality and the capital of Västerbotten County.
Situated on the Ume River, Ume� ...
in Sweden. Riga hosted the 2006 NATO Summit, the Eurovision Song Contest 2003
The Eurovision Song Contest 2003 was the 48th edition of the Eurovision Song Contest. It took place in Riga, Latvia, following the country's victory at the with the song " I Wanna" by Marie N. Organised by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU) a ...
, the 2006 IIHF Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2013 World Women's Curling Championship
The 2013 World Women's Curling Championship (branded as the Titlis Glacier Mountain World Women's Curling Championship 2013 for sponsorship reasons) was held at the Volvo Sports Centre in Riga, Latvia from March 16 to 24. It marked the first time ...
and the 2021 IIHF World Championship
The 2021 IIHF World Championship () took place from 21 May to 6 June 2021. It was originally to be co-hosted by Minsk, Belarus and Riga, Latvia, as the IIHF announced on 19 May 2017 in Cologne, Germany. Their joint bid won by a very tight margin ...
. It is home to the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
's office of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC). In 2017, it was named the European Region of Gastronomy The European Region of Gastronomy is a title given every year to one or more cities or regions in Europe. The title is awarded by the International Institute of Gastronomy, Culture, Arts and Tourism (IGCAT). Kuopio, a city in eastern Finland, is the ...
.
In 2016, Riga received over 1.4 million visitors. The city is served by Riga International Airport
Riga International Airport ( lv, Starptautiskā lidosta "Rīga"; ) is the international airport of Riga, the capital of Latvia, and the largest airport in the Baltic states with direct flights to 76 destinations as of November 2019. It serves as ...
, the largest and busiest airport in the Baltic states. Riga is a member of Eurocities
Eurocities is a network of large cities in Europe, established in 1986 by the mayors of six large cities: Barcelona, Birmingham, Frankfurt, Lyon, Milan and Rotterdam. Today, Eurocities members includes over 200 of Europe's major cities from 38 c ...
, the Union of the Baltic Cities (UBC) and Union of Capitals of the European Union (UCEU).
Etymology
There are numerous and speculative theories for the origin of the name ''Riga'': * It is an adapted borrowing from the Livonian ''ringa'' meaning loop, referring to the ancient natural harbour formed by the tributary loop of the Daugava River. * It could be derived from Riege, the German name for the River Rīdzene, a former tributary of theDaugava
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic Se ...
.
* Bishop Albert claimed credit from his campaign to conquer and convert the local populace, as coming from the Latin ''rigata'' ("irrigated"), symbolising an "irrigation of dry pagan souls by Christianity".
However, the most reliably documented explanation is the affirmation by German historian Dionysius Fabricius (1610) that Riga's name comes from its already established role in trade: "''Riga nomen sortita est suum ab aedificiis vel horreis quorum a litus Dunae magna fuit copia, quas livones sua lingua Rias vocare soliti.''" ("Riga obtained its name from the buildings or warehouses found in great number along the banks of the Duna, which the Livs in their own language are accustomed to call Riae."). The "j" in Latvian ''rīja'' (REE-eh) hardened to a "g" in German. English geographer Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Pri ...
(1589) corroborates this account, calling Riga ''Rie'', as pronounced in Latvian.
History
Founding
The riverDaugava
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic Se ...
has been a trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
since antiquity, part of the Vikings' Dvina–Dnieper navigation route to Byzantium.Bilmanis, A. Latvia as an Independent State. Latvian Legation. 1947. A sheltered natural harbour
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
upriver from the mouth of the Daugava—the site of today's Riga—has been recorded, as ''Duna Urbs'', as early as the 2nd century. It was settled by the Livs
The Livonians, or Livs ( Livonian: ''līvlizt''; Estonian: ''liivlased''; Latvian: ''līvi'', ''lībieši''), are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to northern and northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian, a Uralic language ...
, a Finnic tribe.
animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starti ...
, and trading, later developing crafts (in bone, wood, amber, and iron).
The ''Livonian Chronicle of Henry
The ''Livonian Chronicle of Henry'' ( la, Heinrici Cronicon Lyvoniae) offers a Latin narrative of events in Livonia (roughly corresponding to today's inland Estonia and the northern part of Latvia) and surrounding areas from 1180 to 1227. It was ...
'' testifies to Riga having long been a trading centre by the 12th century, referring to it as ''portus antiquus'' (ancient port), and describes dwellings and warehouses used to store mostly flax, and hides. German traders began visiting Riga, establishing a nearby outpost in 1158.
Along with German traders the monk Meinhard of SegebergVauchez et al. Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages. Routledge, 2001 arrived to convert the Livonian pagans to Christianity. Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and Orthodox Christianity
Orthodoxy (from Ancient Greek, Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Late antiquity, A ...
had already arrived in Latvia more than a century earlier, and many Latvians had been baptised. Meinhard settled among the Livs, building a castle and church at Uexküll (now known as Ikšķile
Ikšķile (; german: Uexküll; liv, Ikškilā; et, Üksküla; also known as ''Üxküll'') is a town in Latvia, in Ogre Municipality. It was the first capital of the Roman Catholic Bishopric of Livonia, known by the German name of Üxküll ...
), upstream from Riga, and established his bishopric there. The Livs, however, continued to practice paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christianity, early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions ot ...
and Meinhard died in Uexküll in 1196, having failed in his mission.Germanis, U. The Latvian Saga. 10th ed. 1998. Memento, Stockholm. In 1198, the Bishop Berthold arrived with a contingent of crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
and commenced a campaign of forced Christianisation
Christianization (American and British English spelling differences#-ise.2C -ize .28-isation.2C -ization.29, or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of ...
. Berthold died soon afterwards and his forces were defeated.
The Church mobilised to avenge this defeat. Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 J ...
issued a bull declaring a crusade against the Livonians
The Livonians, or Livs ( Livonian: ''līvlizt''; Estonian: ''liivlased''; Latvian: ''līvi'', ''lībieši''), are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to northern and northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian, a Uralic language c ...
. Bishop Albert was proclaimed Bishop of Livonia
The Diocese of Livonia, later Roman Catholic Diocese of Inflanty was a territorial division of the Roman Catholic Church established in 1186 as the Diocese of Üxküll and promoted as Metropolitan Archdiocese of Riga in 1255.
Re-established afte ...
by his uncle Hartwig of Uthlede
Hartwig of Uthlede (died 3 November 1207) was a German nobleman who – as Hartwig II – Prince-Archbishop of Bremen (1185–1190 and de facto again 1192–1207) and one of the originators of the Livonian Crusade.
Biography
Coming from a family ...
, Prince-Archbishop of Bremen and Hamburg in 1199. Albert landed in Riga in 1200 with 23 shipsLaffort, R. (censor), ''Catholic Encyclopedia'', Robert Appleton Co., 1907 and 500 Westphalian crusaders.Tolstoy-Miloslavsky, D. ''The Tolstoys: Genealogy and Origin''. A2Z, 1991 In 1201, he transferred the seat of the Livonian bishopric from Uexküll to Riga, extorting agreement to do this from the elders of Riga by force.
Under Bishop Albert
The year 1201 also marked the first arrival of German merchants in Novgorod, via the Dvina.Dollinger, P. ''The Emergence of International Business 1200–1800'', 1964; translated Macmillan and Co edition, 1970 To defend territoryReiner et al. ''Riga''. Axel Menges, Stuttgart. 1999. and trade, Albert established the Order of Livonian Brothers of the Sword in 1202, which was open to nobles and merchants. The Christianisation of the Livs continued. In 1207, Albert started to fortify the town.Zarina, D. ''Old Riga: Tourist Guide'', Spriditis, 1992 Emperor Philip invested Albert with Livonia as a fiefMoeller et al. History of the Christian Church. MacMillan & Co. 1893. and principality of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
. To promote a permanent military presence, territorial ownership was divided between the Church and the ''Order'', with the Church taking Riga and two-thirds of all lands conquered and granting the ''Order'' a third.Palmieri, A. ''Catholic Origin of Latvia'', ed. Cororan, J.A. et al. ''The American Catholic Quarterly Review'', Volume XLVI, January–October 1921. Philadelphia. Until then, it had been customary for crusaders to serve for a year and then return home.
Albert had ensured Riga's commercial future by obtaining papal bulls which decreed that all German merchants had to carry on their Baltic trade through Riga. In 1211, Riga minted its first coinage, and Albert laid the cornerstone for the Riga Dom. Riga was not yet secure as an alliance of tribes failed to take Riga. In 1212, Albert led a campaign to compel Polotsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Distr ...
to grant German merchants free river passage. Polotsk conceded Kukenois (Koknese
Koknese () is a town in Aizkraukle Municipality in the Vidzeme region of Latvia, on the right bank of the Daugava River. It has a population of nearly 3,000.
According to the provisions of the 2021 Latvian administrative reform, Koknese gained ...
) and Jersika
The principality of Jersika ( la, Gerzika, terra Lettia, german: Gerzika, Zargrad, russian: Ерсика, Герцике; also known as ''Лотыголa'') was an early medieval Latgalians, Latgalian principality in eastern modern-day Latvia an ...
to Albert, also ending the Livs' tribute to Polotsk.Kooper, E. ''The Medieval Chronicle'' V. Radopi, 2008.
Riga's merchant citizenry chafed and sought greater autonomy from the Church. In 1221, they acquired the right to independently self-administer Riga and adopted a city constitution.Wright, C.T.H. ''The Edinburgh Review'', ''The Letts'', 1917
That same year Albert was compelled to recognise Danish rule over lands they had conquered in Estonia and Livonia.Murray, A., ''Crusade and Conversion on the Baltic Frontier, 1150–1500''. Ashgate, London. 2001. Albert had sought the aid of King Valdemar of Denmark to protect Riga and Livonian lands against Liv insurrection when reinforcements could not reach Riga. The Danes landed in Livonia, built a fortress at Reval (Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
) and set about conquering Estonian and Livonian lands. The Germans attempted, but failed, to assassinate Valdemar."The Ecclesiastical Review", Vol. LVI. ''American Ecclesiastical Review''. Dolphin Press. 1917. Albert was able to reach an accommodation with them a year later, however, and in 1222 Valdemar returned all Livonian lands and possessions to Albert's control.Fonnesberg-Schmidt, I. ''The Popes and the Baltic Crusades, 1147–1254''. Brill. 2006.
Albert's difficulties with Riga's citizenry continued; with papal intervention, a settlement was reached in 1225 whereby they no longer had to pay tax to the Bishop of Riga,Švābe, A., ed. Latvju Enciklopēdija. Trīs Zvaigznes, Stockholm. 1953–1955 (in Latvian) and Riga's citizens acquired the right to elect their magistrates and town councillors. In 1226, Albert consecrated the Dom Cathedral, built St. James's Church, (now a cathedral) and founded a parochial school at the Church of St. George.
In 1227, Albert conquered OeselFletcher, R.A., ''The Conversion of Europe: From Paganism to Christianity, 371–1386AD''. Harper Collins. 1991. and the city of Riga concluded a treaty with the Principality of Smolensk
The Principality of Smolensk (eventually Grand Principality of Smolensk) was a Kievan Rus' lordship from the 11th to the 16th century. Until 1127, when it passed to Rostislav Mstislavich, the principality was part of the land of Kiev. The princip ...
giving Polotsk to Riga.Michell, Thomas. ''Handbook for Travelers in Russia, Poland, and Finland''. London, John Murray, 1888.
Albert died in January 1229.Fonnesberg-Schmidt, I., ''The Popes and the Baltic Crusades, 1147–1254''. Brill, 2007 He failed in his aspiration to be anointed archbishop but the German hegemony he established over the Livonia would last for seven centuries.

Hanseatic League
In 1282, Riga became a member of theHanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
. The Hansa was instrumental in giving Riga economic and political stability, thus providing the city with a strong foundation which endured the political conflagrations that were to come, down to modern times.

Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Swedish and Russian Empires
As the influence of the Hanseatic League waned, Riga became the object of foreign military, political, religious and economic aspirations. Riga accepted theReformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in 1522, ending the power of the archbishops. In 1524, iconoclast
Iconoclasm (from Greek: grc, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, εἰκών + κλάω, lit=image-breaking. ''Iconoclasm'' may also be conside ...
s targeted a statue of the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother o ...
in the cathedral to make a statement against religious icons. It was accused of being a witch, and given a trial by water in the Daugava
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic Se ...
river. The statue floated, so it was denounced as a witch and burnt at Kubsberg. With the demise of the Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order,
formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation.
History
The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after the ...
during the Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) was the Russian invasion of Old Livonia, and the prolonged series of military conflicts that followed, in which Tsar Ivan the Terrible of Russia (Muscovy) unsuccessfully fought for control of the region (pre ...
, Riga for twenty years had the status of a free imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
before it came under the influence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
by the Treaty of Drohiczyn
The Treaty of Drohiczyn was concluded on 14 January 1581, during the Livonian War, between the city of Riga and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The former Free imperial city Riga was added to Polish-Lithuanian Livonia. Its freedoms and pri ...
, which ended the war for Riga in 1581. In 1621, during the Polish–Swedish War (1621–1625)
The Polish–Swedish War of 1621 to 1625 was a war in a long-running series of conflicts between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Swedish Empire. It began with a Swedish invasion of the Polish–Lithuanian fiefdom Livonia. Swedish f ...
, Riga and the outlying fortress of Daugavgrīva
Daugavgrīva (german: Dünamünde; pl, Dynemunt; russian: Усть-Двинск or ''Ust`-Dvinsk'') is a neighbourhood in North West Riga, Latvia on the left bank of the Daugava river. In this neighbourhood there is a Swedish-built fortress ...
came under the rule of Gustavus Adolphus
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">N.S_19_December.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/now ...
, King of Sweden
The monarchy of Sweden is the monarchical head of state of Sweden,See the Instrument of Government, Chapter 1, Article 5. which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system.Parliamentary system: see the Instrument o ...
, who intervened in the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
not only for political and economic gain but also in favour of German Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
. During the Russo-Swedish War (1656–1658)
The Russo-Swedish War of 1656–1658 was fought by Russia and Sweden as a theater of the Second Northern War. It took place during a pause in the contemporary Russo-Polish War (1654–1667) as a consequence of the Truce of Vilna. Despite i ...
, Riga withstood a siege by Russian forces.
Riga remained one of the largest cities under the Swedish crown until 1710, a period during which the city retained a great deal of autonomous self-government. In July 1701, during the opening phase of the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedi ...
, the ''Crossing of the Düna
The Crossing of the Düna (also known as Battle of Daugava or Battle of Spilves) took place during the Great Northern War on July 19, 1701 near the city of Riga, present-day Latvia. The Swedish king Charles XII was in hot pursuit of king Augustu ...
'' took place nearby, resulting in a victory for king Charles XII of Sweden
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII ( sv, Karl XII) or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 O.S.), was King of Sweden (including current Finland) from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of t ...
. Between November 1709 and June 1710, however, the Russians under Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
besieged and captured Riga, which was at the time struck by a plague. Along with the other Livonian towns and gentry, Riga capitulated to Russia, but largely retained their privileges. Riga was made the capital of the Governorate of Riga (later, Livonia). Sweden's northern dominance had ended, and Russia's emergence as the strongest Northern power was formalised through the Treaty of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad (russian: Ништадтский мир; fi, Uudenkaupungin rauha; sv, Freden i Nystad; et, Uusikaupunki rahu) was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War of 1700–1721. It was concluded between the Tsardom of ...
in 1721. At the beginning of the 20th century Riga was the largest timber export port in the Russian Empire and ranked the 3rd according to the external trade volume. At the same time, Riga was also the third largest city in Russian Empire.

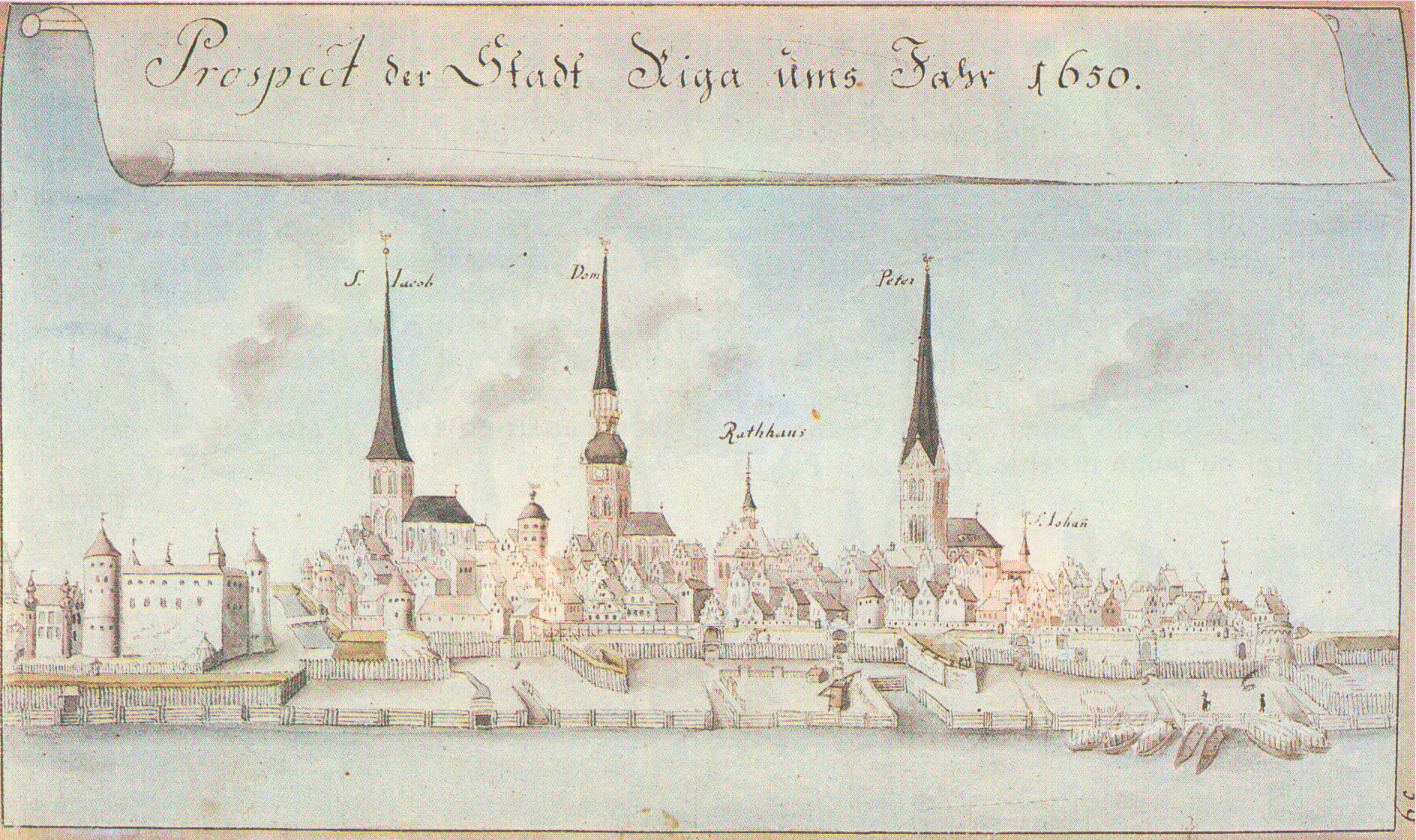
 During these many centuries of war and changes of power in the Baltic, and despite demographic changes, the
During these many centuries of war and changes of power in the Baltic, and despite demographic changes, the Baltic Germans
Baltic Germans (german: Deutsch-Balten or , later ) were ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their coerced resettlement in 1939, Baltic Germans have markedly declin ...
in Riga had maintained a dominant position. By 1867, Riga's population was 42.9% German. Riga employed German as its official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
of administration until the installation of Russian in 1891 as the official language in the Baltic provinces
The Baltic governorates (russian: Прибалтийские губернии), originally the Ostsee governorates (german: Ostseegouvernements, russian: Остзейские губернии), was a collective name for the administrative units ...
, as part of the policy of Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
of the non-Russian-speaking territories of the Russian Empire, including Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It w ...
, Finland and the Baltics, undertaken by Tsar Alexander III
Alexander III ( rus, Алекса́ндр III Алекса́ндрович, r=Aleksandr III Aleksandrovich; 10 March 18451 November 1894) was Emperor of Russia, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 13 March 1881 until his death in 18 ...
. More and more Latvians started moving to the city during the mid-19th century. The rise of a Latvian bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
made Riga a centre of the Latvian National Awakening
The Latvian National Awakening ( lv, latviešu
with the founding of the Riga Latvian Association in 1868 and the organisation of the first national song festival in 1873. The nationalist movement of the Neo-Latvians was followed by the socialist r latvju
R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ar'' (pronounced ), plural ''ars'', or in Irelan ...
tautas atmoda) refers to three distinct but ideologically related Romantic nationalism, National revival movements:
* the ''The First Latvian National Awakening, First Awakening'' refers ...New Current
The New Current ( lv, Jaunā strāva) in the history of Latvia was a broad leftist social and political movement that followed the First Latvian National Awakening (led by the Young Latvians from the 1850s to the 1880s) and culminated in the 1905 ...
during the city's rapid industrialisation, culminating in the 1905 Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed again ...
led by the Latvian Social Democratic Workers' Party
)
, colours = Maroon Green
, headquarters = Riga, Lāčplēša iela 60, LV-1011
, seats1_title = Saeima
, seats1 =
, seats2_title = European Parliament
, seats2 =
, website lsdsp.lv, membership_year = 2017
, membership = 633
The Latv ...
.
World War I
The 20th century broughtWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the impact of the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
of 1917 to Riga. As a result of the battle of Jugla
The Battle of Jugla was a defensive battle of the Russian Republic's 12th Army of the First World War from 1 to 5 September 1917. It was part of the German offensive called the ''Battle of Riga'' or ''Schlacht um Riga''. The main objective for ...
, the German army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
marched into Riga on 3 September 1917. On 3 March 1918, the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace, separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russian SFSR, Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Kingdom of ...
was signed, giving the Baltic countries
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
to Germany. Because of the armistice with Germany
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
of 11 November 1918, Germany had to renounce that treaty, as did Russia, leaving Latvia and the other Baltic States in a position to claim independence. Latvia, with Riga as its capital city, thus declared its independence on 18 November 1918.
Between World War I and World War II (1918–1940), Riga and Latvia shifted their focus from Russia to the countries of Western Europe. The United Kingdom and Germany replaced Russia as Latvia's major trade partners. The majority of the Baltic Germans were resettled in late 1939, prior to the occupation of Estonia and Latvia by the Soviet Union in June 1940.
World War II
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Latvia was occupied by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
in June 1940 and then was occupied by German occupation of Latvia during World War II, Nazi Germany in 1941–1944. On 17 June 1940, the Soviet forces invaded Latvia occupying bridges, post/telephone, telegraph, and broadcasting offices. Three days later, Latvian president Karlis Ulmanis was forced to approve a pro-Soviet government which had taken office. On 14–15 July, rigged elections were held in Latvia and the other Baltic states, The ballots held the following instructions: "Only the list of the Latvian Working People's Bloc must be deposited in the ballot box. The ballot must be deposited without any changes." The alleged voter activity index was 97.6%. Most notably, the complete election results were published in Moscow 12 hours before the election closed. Soviet electoral documents found later substantiated that the results were completely fabricated. The Soviet authorities, having regained control over Riga and Latvia imposed a regime of terror, opening the headquarters of the KGB, massive deportations started. Hundreds of men were arrested, including leaders of the former Latvian government. The most notorious deportation, the June deportation took place on 13 and 14 June 1941, estimated at 15,600 men, women, and children, and including 20% of Latvia's last legal government. Similar deportations were repeated after the end of WWII. The building of the KGB located at 61 Brīvības iela, known as 'the corner house', is now a museum. Stalin's deportations also included thousands of Latvian Jews. (The mass deportation totalled 131,500 across the Baltics.)
During the Nazi occupation, the History of the Jews in Latvia, Jewish community was forced into the Riga Ghetto and a Nazi concentration camp was constructed in Kaiserwald concentration camp, Kaiserwald. On 25 October 1941, the Nazis relocated all Jews from Riga and the vicinity to the ghetto. Most of Latvia's Jews (about 24,000) were killed on 30 November and 8 December 1941 in the Rumbula massacre. By the end of the war, the remaining Baltic Germans
Baltic Germans (german: Deutsch-Balten or , later ) were ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their coerced resettlement in 1939, Baltic Germans have markedly declin ...
were Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950)#Soviet Union and annexed territories, expelled to Germany.
The Soviet Red Army re-entered Riga on 13 October 1944. In the following years the massive influx of labourers, administrators, military personnel, and their dependents from Russia and other Soviet republics started. Microdistricts of the large multi-storied housing blocks were built to house immigrant workers.
By the end of the war, Vecrīga, Riga's historical centre was heavily damaged from constant bombing. After the war, huge efforts were made to reconstruct and renovate most of the famous buildings that had been part of the skyline of the city before the war. Such buildings were, amongst others, St. Peter's Church, Riga, St. Peter's Church which lost its wooden tower after a fire caused by the Wehrmacht (renovated in 1954). Another example is the House of the Blackheads (Riga), House of the Blackheads, completely destroyed, its ruins subsequently demolished; a facsimile was constructed in 1995.
In 1989, the percentage of Latvians in Riga had fallen to 36.5%.
21st century
In 2004, the arrival of low-cost airlines resulted in cheaper flights from other European cities such as London and Berlin, and consequently a substantial increase in numbers of tourists. In the spring of 2006, the hitherto biggest party of hospitality exchange service Hospitality Club, HC took place in Riga, counting 430 participants from 36 countries. On 21 November 2013, the Zolitūde shopping centre roof collapse, roof of a supermarket collapsed in Zolitūde, one of the neighbourhoods of the city, possibly as a result of the weight of materials used in the construction of a garden on the roof. Fifty-four people were killed. Latvian President Andris Bērziņš (Latvian President), Andris Bērziņš described the disaster as "a large-scale murder of many defenceless people". Riga was the European Capital of Culture in 2014. During Latvia's Presidency of the Council of the European Union in 2015, the 4th Eastern Partnership Summit took place in Riga.Geography
Riga is the second Baltic states#Cities, largest city (after Vilnius) in the three Baltic states: Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. Riga is home to approximately one tenth of the three Baltic countries' combined population.Administrative divisions
*Central District, Riga, Central District () *Kurzeme District, Riga, Kurzeme District () *Zemgale Suburb, Riga, Zemgale Suburb () *Northern District, Riga, Northern District () *Vidzeme Suburb, Riga, Vidzeme Suburb () *Latgale Suburb, Riga, Latgale Suburb () Riga's administrative divisions consist of six administrative entities: Central District, Riga, Central, Kurzeme District, Riga, Kurzeme and Northern District, Riga, Northern districts and the Latgale Suburb, Riga, Latgale, Vidzeme Suburb, Riga, Vidzeme and Zemgale Suburb, Riga, Zemgale suburbs. Three entities were established on 1 September 1941, and the other three were established in October 1969. There are no official lower-level administrative units, but the Riga City Council Development Agency is working on a plan, which officially makes Riga consist of 58 neighbourhoods. The current names were confirmed on 28 December 1990.Climate
The climate of Riga is humid continental climate, humid continental (Köppen ''Dfb''). The coldest months are January and February, when the average temperature is but temperatures as low as can be observed almost every year on the coldest days. The proximity of the sea causes frequent autumn rains and fogs. Continuous snow cover may last eighty days. The summers in Riga are mild and rainy with an average temperature of , while the temperature on the hottest days can exceed .Government
 The head of the city government in Riga is the mayor, or officially the Chairman of the Riga City Council. He is assisted by one or more Vice Mayors (deputy mayors). The current mayor since October 2020 is Mārtiņš Staķis elected from Movement For!, which is a part of the Development/For!/The Progressives (Latvia), Progressives faction, but on 24 March 2022, he left the party. The three other parties in the governing coalition each received a Vice Mayor post.
The city council is a democratically elected institution and is the final decision-making authority in the city. The Council consists of 60 members or deputies who are elected every four years. The Presidium of the Riga City Council consists of the Chairman of the Riga City Council and the representatives delegated by the political parties or party blocks elected to the City Council. From February to October 2020, the offices of the Mayor and Vice Mayors were suspended and the council itself had been dissolved and replaced by an interim administration of representatives from three Government of Latvia, governmental ministries until snap 2020 Riga City Council election, elections were held in 2020.
The head of the city government in Riga is the mayor, or officially the Chairman of the Riga City Council. He is assisted by one or more Vice Mayors (deputy mayors). The current mayor since October 2020 is Mārtiņš Staķis elected from Movement For!, which is a part of the Development/For!/The Progressives (Latvia), Progressives faction, but on 24 March 2022, he left the party. The three other parties in the governing coalition each received a Vice Mayor post.
The city council is a democratically elected institution and is the final decision-making authority in the city. The Council consists of 60 members or deputies who are elected every four years. The Presidium of the Riga City Council consists of the Chairman of the Riga City Council and the representatives delegated by the political parties or party blocks elected to the City Council. From February to October 2020, the offices of the Mayor and Vice Mayors were suspended and the council itself had been dissolved and replaced by an interim administration of representatives from three Government of Latvia, governmental ministries until snap 2020 Riga City Council election, elections were held in 2020.
Demographics
With 605,800 inhabitants in 2022 as according to the Central Statistical Bureau of Latvia, Riga was the largest city in the Baltic states, though its population has decreased from just over 900,000 in 1991 and it is expected to be decrowned by Vilnius. Notable causes include emigration and Ageing of Europe, low birth rates. According to the 2017 data, ethnic Latvians made up 44.03% of the population of Riga. Slavs (mainly East Slavs, Eastern ones) made up the same percentage - Russians in Latvia, Russians formed 37.88%, Belarusians 3.72%, Ukrainians 3.66%, Poles 1.83%, other ethnicities consisted 8.10%. By comparison, 60.1% of Latvia's total population was ethnically Latvian, 26.2% Russian, 3.3% Belarusian, 2.4% Ukrainian, 2.1% Polish, 1.2% are Lithuanian and the rest of other origins. Upon the History of Latvia#Restoration of independence, restoration of Latvia's independence in 1991, Soviet-era immigrants (and any of their offspring born before 1991) were not automatically granted Latvian citizenship because they had migrated to the territory of Latvia during the years when Latvia was part of the Soviet Union. The proportion of ethnic Latvians in Riga increased from 36.5% in 1989 to 42.4% in 2010. In contrast, the percentage of Russians fell from 47.3% to 40.7% in the same time period. Latvians overtook Russians as the largest ethnic group in 2006. In 2013 citizens of Latvia made up 73.1%, non-citizens (Latvia), non-citizens 21.9% and citizens of other countries 4.9% of the population of Riga.Historic population figures
Economy
Riga is one of the key economic and financial centres of the Baltic states. Roughly half of all the jobs in Latvia are in Riga and the city generates more than 50% of Latvia's GDP as well as around half of Latvia's exports. The biggest exporters are in wood products, IT, food and beverage manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, transport and metallurgy. Riga Port is one of the largest in the Baltics. It handled a record 34 million tons of cargo in 2011 and has potential for future growth with new port developments on Krievu Sala. Tourism is also a large industry in Riga and after a slowdown during the Great Recession, global economic recessions of the late 2000s, grew 22% in 2011 alone. Riga was intended to become the global financial centre in the former Soviet Union. Parex, One bank, which provided high levels of secrecy for its customers, promoted itself as "We are closer than Switzerland!" (russian: «Мы ближе, чем Швейцария!») On 28 July 1995, twenty Latvian banks with assistance of persons from the Paris Stock Exchange organised the Riga Stock Exchange which was the first Latvian stock exchange in Riga.Culture
Theatres
* The Latvian National Opera was founded in 1918. The repertoire of the theatre embraces all opera masterpieces. The Latvian National Opera is famous not only for its operas, but for its ballet troupe as well. * The Latvian National Theatre was founded in 1919. The Latvian National Theatre preserves the traditions of Culture of Latvia, Latvian drama school. It is one of the biggest theatres in Latvia. * The Mikhail Chekhov Riga Russian Theatre is the oldest professional drama theatre in Latvia, established in 1883. The repertoire of the theatre includes classical plays and experimental performances of Russian and other foreign playwrights. * The Daile Theatre was opened for the first time in 1920. It is one of the most successful theatres in Latvia and is distinguished by its frequent productions of modern foreign plays. * Latvian State Puppet Theatre was founded in 1944 and presents shows for children and adults. * The New Riga Theatre was opened in 1992.World Choir Games
Riga hosted the biannual 2014 World Choir Games from 9 to 19 July 2014 which coincided with the city being named European Capital of Culture for 2014. The event, organised by the choral foundation, Interkultur, takes place at various host cities every two years and was originally known as the "Choir Olympics". The event regularly sees over 15,000 choristers in over 300 choirs from over 60 nations compete for gold, silver and bronze medals in over 20 categories. The competition is further divided into a Champions Competition and an Open Competition to allow choirs from all backgrounds to enter. Choral workshops and festivals are also witnessed in the host cities and are usually open to the public.Architecture
 The Riga Radio and TV Tower, radio and TV tower of Riga is the tallest structure in Latvia and the Baltic States, and one of the tallest in the European Union, reaching . Riga centre also has many great examples of Gothic revival architecture, such as the Kalpaka Boulevard Library, and a bevy of
The Riga Radio and TV Tower, radio and TV tower of Riga is the tallest structure in Latvia and the Baltic States, and one of the tallest in the European Union, reaching . Riga centre also has many great examples of Gothic revival architecture, such as the Kalpaka Boulevard Library, and a bevy of Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
architecture, as well as a medieval old town.
Art Nouveau
Riga has one of the largest collections ofArt Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
buildings in the world, with at least 800 buildings. This is due to the fact that at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries, when Art Nouveau was at the height of its popularity, Riga experienced an unprecedented financial and demographic boom. In the period from 1857 its population grew from 282,000 (256,200 in Riga itself and another 26,200 inhabitants beyond the city limits in the Pierīga, patrimonial district and military town of Ust-Dvinsk) to 472,100 in 1913. The middle class of Riga used their acquired wealth to build imposing apartment blocks outside the former city walls. Local architects, mostly graduates of Riga Technical University, adopted current European movements and in particular Art Nouveau. Between 1910 and 1913, between 300 and 500 new buildings were built each year in Riga, most of them in Art Nouveau style and most of them outside the old town.
Sports
Riga has a rich basketball history. In the 1950s, Rīgas ASK became the best club in the Soviet Union and also in Europe, winning the first three editions of the EuroLeague, European Cup for Men's Champions Clubs from 1958 to 1960. In 1960, ASK was not the only team from Riga to take the European crown. TTT Riga clinched their first title in the EuroLeague Women, European Cup for Women's Champion Clubs, turning Riga into the capital city of European basketball because for the first and, to date, only time in the history of European basketball, clubs from the same city were concurrent European men's and women's club champions. In 2015, Riga was one of the hosts for EuroBasket 2015.Sports clubs
 * Basketball
** BK VEF Rīga – a professional basketball team that is a three-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion. VEF also participates in high-level international competition such as Eurocup Basketball, Eurocup
** Barons LMT – a men's basketball team, two-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion, as well as the 2007–08 FIBA EuroCup, 2008 FIBA EuroCup winner
** TTT Riga – a women's basketball team, which between 1960 and 1982 won eighteen FIBA EuroLeague Women titles
* Ice hockey
** Dinamo Riga – a professional ice hockey club established in 2008. It played in the Kontinental Hockey League until 2022. Dinamo was established as a successor to the Dinamo Riga (original), former hockey team with the same name, which was founded in 1946 but ceased to exist in 1995.
** HK Riga – a junior hockey club, playing in the Minor Hockey League
* Association football, Football
**Riga FC – Riga Football Club, commonly referred to as Riga FC, were established in 2015 after a merger of two Riga based teams – FC Caramba Riga and Dinamo Rīga. In 2018 they became champions of the Virslīga Latvian Higher League for the first time.
** FK RFS, RFS – FK Rīgas Futbola Skola, known as RFS are based on the Riga Football School (RFS) academy, established in 1962.
** FS Metta-LU – founded in 2006. Metta play their home games at Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium.
** JDFS Alberts – Jura Docenko Futbola Skola Alberts, commonly referred to as JDFS Alberts was founded as a football school in 2008 and subsequently became a professional Latvian football league team.
**Riga United FC
**FC New Project
::Dissolved Football Clubs
:* Skonto FC – Skonto FC was a football club established in 1991. The club won fourteen successive Latvian Higher League titles. For a long time it provided the core of the Latvian national football team. Following financial problems, the club was demoted to the Latvian First League in 2016 and went bankrupt in December of that year and subsequently dissolved.
:* JFK Olimps – JFK Olimps played in the top division of Latvian football. The club was founded in 2005 and dissolved in 2012. According to a study from January 2011, the club was the youngest team in Europe, with an average age of 19.02 years.
* Basketball
** BK VEF Rīga – a professional basketball team that is a three-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion. VEF also participates in high-level international competition such as Eurocup Basketball, Eurocup
** Barons LMT – a men's basketball team, two-time Latvijas Basketbola līga, Latvian champion, as well as the 2007–08 FIBA EuroCup, 2008 FIBA EuroCup winner
** TTT Riga – a women's basketball team, which between 1960 and 1982 won eighteen FIBA EuroLeague Women titles
* Ice hockey
** Dinamo Riga – a professional ice hockey club established in 2008. It played in the Kontinental Hockey League until 2022. Dinamo was established as a successor to the Dinamo Riga (original), former hockey team with the same name, which was founded in 1946 but ceased to exist in 1995.
** HK Riga – a junior hockey club, playing in the Minor Hockey League
* Association football, Football
**Riga FC – Riga Football Club, commonly referred to as Riga FC, were established in 2015 after a merger of two Riga based teams – FC Caramba Riga and Dinamo Rīga. In 2018 they became champions of the Virslīga Latvian Higher League for the first time.
** FK RFS, RFS – FK Rīgas Futbola Skola, known as RFS are based on the Riga Football School (RFS) academy, established in 1962.
** FS Metta-LU – founded in 2006. Metta play their home games at Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium.
** JDFS Alberts – Jura Docenko Futbola Skola Alberts, commonly referred to as JDFS Alberts was founded as a football school in 2008 and subsequently became a professional Latvian football league team.
**Riga United FC
**FC New Project
::Dissolved Football Clubs
:* Skonto FC – Skonto FC was a football club established in 1991. The club won fourteen successive Latvian Higher League titles. For a long time it provided the core of the Latvian national football team. Following financial problems, the club was demoted to the Latvian First League in 2016 and went bankrupt in December of that year and subsequently dissolved.
:* JFK Olimps – JFK Olimps played in the top division of Latvian football. The club was founded in 2005 and dissolved in 2012. According to a study from January 2011, the club was the youngest team in Europe, with an average age of 19.02 years.
Sports facilities
 * Arena Riga – a multi-purpose arena built in 2006 as the main venue for the 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships. It can hold up to 14,500 people and has hosted ice hockey, basketball and volleyball events, as well as Red Bull X-Fighters
* Skonto Stadium – a football stadium, built in 2000. It is the main stadium used for games of the Latvian national football team and the home stadium of Riga FC. The stadium was previously the home stadium of Skonto FC prior to the team's dissolution.
* Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium – a stadium built in 1958, used for both Association football, football and Sport of athletics, athletics
* Latvijas Universitates Stadions
* Biķernieku Kompleksā Sporta Bāze – Latvia's leading motorsport complex
* Arena Riga – a multi-purpose arena built in 2006 as the main venue for the 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships. It can hold up to 14,500 people and has hosted ice hockey, basketball and volleyball events, as well as Red Bull X-Fighters
* Skonto Stadium – a football stadium, built in 2000. It is the main stadium used for games of the Latvian national football team and the home stadium of Riga FC. The stadium was previously the home stadium of Skonto FC prior to the team's dissolution.
* Daugava Stadium (Riga), Daugava Stadium – a stadium built in 1958, used for both Association football, football and Sport of athletics, athletics
* Latvijas Universitates Stadions
* Biķernieku Kompleksā Sporta Bāze – Latvia's leading motorsport complex
Sports events
* EuroBasket 1937 * 1999 European Athletics Junior Championships * EuroBasket Women 2009 * 2006 IIHF World Championship, 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships * Riga Marathon *2013 World Women's Curling Championship
The 2013 World Women's Curling Championship (branded as the Titlis Glacier Mountain World Women's Curling Championship 2013 for sponsorship reasons) was held at the Volvo Sports Centre in Riga, Latvia from March 16 to 24. It marked the first time ...
* 2014 Cricket Latvia play Masstor Cricket Club
* EuroBasket 2015
* 2016 Men's World Floorball Championships
* 2021 IIHF World Championship
The 2021 IIHF World Championship () took place from 21 May to 6 June 2021. It was originally to be co-hosted by Minsk, Belarus and Riga, Latvia, as the IIHF announced on 19 May 2017 in Cologne, Germany. Their joint bid won by a very tight margin ...
* FIDE Grand Swiss Tournament 2021
Transport


Riga International Airport
Riga International Airport ( lv, Starptautiskā lidosta "Rīga"; ) is the international airport of Riga, the capital of Latvia, and the largest airport in the Baltic states with direct flights to 76 destinations as of November 2019. It serves as ...
(RIX), built in 1973. Renovation and modernisation of the airport was completed in 2001, coinciding with the 800th anniversary of the city. In 2006, a new terminal extension was opened. Extension of the runway was completed in October 2008, and the airport is now able to accommodate large aircraft such as the Airbus A340, Boeing 747, 757, 767 and 777. Another terminal extension is under construction . The annual number of passengers has grown from 310,000 in 1993 to 4.7 million in 2014, making Riga International Airport the largest in the Baltic States.
The former international airport of Riga, Spilve Airport, located from Riga city centre, is used for small aircraft, pilot training and recreational aviation. Riga was also home to a military air base during the Cold War—Rumbula Air Base.
Public transport in the city is provided by Rīgas Satiksme which operates a large number of trams, buses and trolleybuses on an extensive network of routes across the city. In addition, up until 2012 many private owners operated minibus services, after which the City Council established the unified transport company ''Rīgas mikroautobusu satiksme'', establishing a monopoly over the service.
Riga International Coach Terminal provides domestic and international connections by Coach (bus), coach.
As the population of Riga city started to approach 1 million people in the 1980s, the city became eligible (under the Soviet standards of the time) for the construction of a subway system Riga Metro, which would have been paid for by the Soviet government. However, the population decline and shortage of funding following Latvian independence put an end to this plan.
Riga is connected to the rest of Latvia by Latvian Railways#Domestic routes, domestic trains operated by the national carrier Pasažieru vilciens, Passenger Train, whose headquarters are in Riga. The main railway station is the Riga Central Station. It has stops for public transport along the streets Satekles iela, 13. janvāra iela Marijas iela, and Merķeļa iela. There are also Latvian Railways#International routes, international rail services to Russia and Belarus, and plans to revive passenger rail traffic with Estonia. International overnight service is with Latvia Express trains ( lv, Latvijas Ekspresis). A TEN-T project called Rail Baltica envisages building a high-speed railway line via Riga connecting Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
to Warsaw using standard gauge, expected to be put into operation in 2024. Latvian Railways ( lv, Latvijas dzelzceļš or ''LDz'') operates the Latvian Rail History Museum in Riga.
Universities
*University of Latvia (LU) *Art Academy of Latvia (LMA) *Riga Technical University (RTU) *Riga Stradiņš University (RSU) *Riga Graduate School of Law (RGSL) *Stockholm School of Economics in Riga (SSE Riga) *BA School of Business and Finance (BA) *Transport and Telecommunication Institute (TTI) *Riga International School of Economics and Business Administration (RISEBA) *Turība University *Riga Aeronautical Institute (RAI)Notable people
Public service
 *Isaiah Berlin, Sir Isaiah Berlin (1909–1997), a British social and political theorist, philosopher and historian of ideas
*Emil Friedrich von Boetticher (1836–1907) a politician, burgomaster of Riga
*Friedrich Heinrich von Boetticher (1826–1902) a German publisher, bookseller, scholar and art historian.
*Deniss Čalovskis (born 1985), Latvian computer hacker who created the Gozi virus.
*Valdis Dombrovskis (born 1971), a Latvian politician and EU Commissioner
*Laila Freivalds (born 1942), former Swedish Minister for Justice and Deputy Prime Minister of Sweden
*Juris Hartmanis (born 1928), a Latvian-American computer scientist, won the 1993 Turing Award
*Nicolai Hartmann (1882–1950), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German philosopher, an important Metaphysics, metaphysician
*Johann Gottfried Herder (1744–1803), a German philosopher, theologian, poet and literary critic
*Albert Woldemar Hollander (1796–1868), a German educator and pedagog.
*Yeshayahu Leibowitz (1903–1994), an Israeli public intellectual and polymath
*Yosef Mendelevich (born 1947), a Jewish refusenik from the Soviet Union, known as a ''"Prisoner of Zion"''
*Ernst Munzinger (1887–1945), German Abwehr (Army intelligence) officer, later anti-Nazi
*Valters Nollendorfs (born 1931), chairman of the board of the Museum of the Occupation of Latvia
*Alfred Rosenberg (1892–1946), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German theorist and ideologue of the Nazi Party
*Johann Steinhauer (1705–1779) a Latvian entrepreneur, social reformer and landowner
*Charlotte Wahl (1817–1899), a Latvian-born philanthropist
*Tatiana Warsher (1880–1960), a Russian archaeologist known for her studies of Pompeii
*Isaiah Berlin, Sir Isaiah Berlin (1909–1997), a British social and political theorist, philosopher and historian of ideas
*Emil Friedrich von Boetticher (1836–1907) a politician, burgomaster of Riga
*Friedrich Heinrich von Boetticher (1826–1902) a German publisher, bookseller, scholar and art historian.
*Deniss Čalovskis (born 1985), Latvian computer hacker who created the Gozi virus.
*Valdis Dombrovskis (born 1971), a Latvian politician and EU Commissioner
*Laila Freivalds (born 1942), former Swedish Minister for Justice and Deputy Prime Minister of Sweden
*Juris Hartmanis (born 1928), a Latvian-American computer scientist, won the 1993 Turing Award
*Nicolai Hartmann (1882–1950), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German philosopher, an important Metaphysics, metaphysician
*Johann Gottfried Herder (1744–1803), a German philosopher, theologian, poet and literary critic
*Albert Woldemar Hollander (1796–1868), a German educator and pedagog.
*Yeshayahu Leibowitz (1903–1994), an Israeli public intellectual and polymath
*Yosef Mendelevich (born 1947), a Jewish refusenik from the Soviet Union, known as a ''"Prisoner of Zion"''
*Ernst Munzinger (1887–1945), German Abwehr (Army intelligence) officer, later anti-Nazi
*Valters Nollendorfs (born 1931), chairman of the board of the Museum of the Occupation of Latvia
*Alfred Rosenberg (1892–1946), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German theorist and ideologue of the Nazi Party
*Johann Steinhauer (1705–1779) a Latvian entrepreneur, social reformer and landowner
*Charlotte Wahl (1817–1899), a Latvian-born philanthropist
*Tatiana Warsher (1880–1960), a Russian archaeologist known for her studies of Pompeii
The Arts

 *Rutanya Alda (born 1942), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American actress
*Mikhail Baryshnikov (born 1948), a Russian dancer, choreographer and actor
*Léopold Bernhard Bernstamm (1859–1939), a Russian sculptor
*Gunnar Birkerts (1925–2017), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American architect
*Leonīds Breikšs (1908–1942), a Latvian poet, author and newspaper editor
*Jacob W. Davis (born ''Jākobs Jufess'') (1831–1908) an American tailor, invented modern jeans.
*Mikhail Eisenstein (1867–1920) a Latvian civil engineer and architect
*Sergei Eisenstein (1898–1948), a Soviet Russian film director, filmed ''Battleship Potemkin''
*Heinz Erhardt (1909–1979), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German comedian, musician and entertainer
*Artur Fonvizin (1883–1973), a Soviet painter of watercolours
*Elīna Garanča (born 1976), a Latvian operatic mezzo-soprano
*Philippe Halsman (1906–1979), an American portrait photographer
*Aivars Kalējs (born 1951), a Latvian composer, organist and pianist
*Gidon Kremer (born 1947), a Latvian classical violinist and conductor
*Barbara von Krüdener (1764–1824), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German author, religious mystic and Pietism, Pietist Lutheran theologian.
*Ivan Krylov (1769–1844), a Russian fable writer
*DJ Lethal (born 1972), an American music producer, real name ''Leor Dimant''
*Captain Disillusion, Alan Melikdjanian (born 1980), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American independent filmmaker known as ''Captain Disillusion''
*Raimonds Pauls (born 1936), a Latvian composer and piano player
*Kristjan Jaak Peterson (1801–1822), an Estonian poet
*Valentin Pikul (1928–1990), a Soviet historical novelist
*Marie Seebach (1829–1897) a German actress.
*Ksenia Solo (born 1987), a Latvian Canadian, Latvian-Canadian actress and activist
*Rutanya Alda (born 1942), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American actress
*Mikhail Baryshnikov (born 1948), a Russian dancer, choreographer and actor
*Léopold Bernhard Bernstamm (1859–1939), a Russian sculptor
*Gunnar Birkerts (1925–2017), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American architect
*Leonīds Breikšs (1908–1942), a Latvian poet, author and newspaper editor
*Jacob W. Davis (born ''Jākobs Jufess'') (1831–1908) an American tailor, invented modern jeans.
*Mikhail Eisenstein (1867–1920) a Latvian civil engineer and architect
*Sergei Eisenstein (1898–1948), a Soviet Russian film director, filmed ''Battleship Potemkin''
*Heinz Erhardt (1909–1979), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German comedian, musician and entertainer
*Artur Fonvizin (1883–1973), a Soviet painter of watercolours
*Elīna Garanča (born 1976), a Latvian operatic mezzo-soprano
*Philippe Halsman (1906–1979), an American portrait photographer
*Aivars Kalējs (born 1951), a Latvian composer, organist and pianist
*Gidon Kremer (born 1947), a Latvian classical violinist and conductor
*Barbara von Krüdener (1764–1824), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German author, religious mystic and Pietism, Pietist Lutheran theologian.
*Ivan Krylov (1769–1844), a Russian fable writer
*DJ Lethal (born 1972), an American music producer, real name ''Leor Dimant''
*Captain Disillusion, Alan Melikdjanian (born 1980), a Latvian-Americans, Latvian-American independent filmmaker known as ''Captain Disillusion''
*Raimonds Pauls (born 1936), a Latvian composer and piano player
*Kristjan Jaak Peterson (1801–1822), an Estonian poet
*Valentin Pikul (1928–1990), a Soviet historical novelist
*Marie Seebach (1829–1897) a German actress.
*Ksenia Solo (born 1987), a Latvian Canadian, Latvian-Canadian actress and activist
Science
 *Ernst von Bergmann (1836–1907), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German surgeon, pioneer of aseptic surgery
*Walter von Boetticher (1853–1945) a German historian, genealogist and physician.
*Jakob Benjamin Fischer (1731–1793), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German naturalist and apothecary
*Lola Hoffmann (1904–1988), a physiologist, psychiatrist and guide to self-development and transformation
*Charles Kalme (1939–2002), an American mathematician and International Master of chess
*Karlis Kaufmanis (1910–2003), astronomer, he lectured that the Star of Bethlehem was a conjunction in 7 BC of the planets Jupiter and Saturn
*Mstislav Keldysh (1911–1978), a Soviet mathematician, worked on the first Soviet space program, artificial satellite
*George Nagobads (born 1921), American physician, recipient of the Paul Loicq Award.
*Wilhelm Ostwald (1853–1932), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German chemist, Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909
*Georg August Schweinfurth (1836–1925) a Baltic Germans, Baltic German botanist and ethnologist who explored East Central Africa.
*Georg von Tiesenhausen (1914–2018), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German American Aerospace engineering, rocket scientist.
*Juris Upatnieks (born 1936), a Latvian-American physicist and inventor, pioneer in the field of holography.
*Friedrich Zander (1887–1933), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German engineer, designed the first Soviet liquid-fuelled rocket
*Walter Zapp (1905–2003), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German inventor, he created the Minox Subminiature photography, subminiature camera.
*Ernst von Bergmann (1836–1907), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German surgeon, pioneer of aseptic surgery
*Walter von Boetticher (1853–1945) a German historian, genealogist and physician.
*Jakob Benjamin Fischer (1731–1793), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German naturalist and apothecary
*Lola Hoffmann (1904–1988), a physiologist, psychiatrist and guide to self-development and transformation
*Charles Kalme (1939–2002), an American mathematician and International Master of chess
*Karlis Kaufmanis (1910–2003), astronomer, he lectured that the Star of Bethlehem was a conjunction in 7 BC of the planets Jupiter and Saturn
*Mstislav Keldysh (1911–1978), a Soviet mathematician, worked on the first Soviet space program, artificial satellite
*George Nagobads (born 1921), American physician, recipient of the Paul Loicq Award.
*Wilhelm Ostwald (1853–1932), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German chemist, Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909
*Georg August Schweinfurth (1836–1925) a Baltic Germans, Baltic German botanist and ethnologist who explored East Central Africa.
*Georg von Tiesenhausen (1914–2018), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German American Aerospace engineering, rocket scientist.
*Juris Upatnieks (born 1936), a Latvian-American physicist and inventor, pioneer in the field of holography.
*Friedrich Zander (1887–1933), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German engineer, designed the first Soviet liquid-fuelled rocket
*Walter Zapp (1905–2003), a Baltic Germans, Baltic German inventor, he created the Minox Subminiature photography, subminiature camera.


Sport
*Helmuts Balderis (born 1952) a Latvian former ice hockey player *Dāvis Bertāns (born 1992), a Latvian professional basketball player *Jānis Beinarovičs (1907-1967), a Latvian wrestler *Andris Biedriņš (born 1986), a Latvian former basketball player *Sergejs Boldaveško (born 1970), retired ice hockey player, born in Riga *Teddy Blueger (born 1994), ice hockey player for the Pittsburgh Penguins *Tanhum Cohen-Mintz (1939–2014), an Israeli basketball player *Kaspars Dubra (born 1990), a footballer with 50 caps for Latvia national football team, Latvia *Zemgus Girgensons (born 1994), ice hockey player, highest-ever drafted Latvian in the NHL Entry Draft *Jørgen Hviid (1916–2001), a Danish and Latvian athlete; ice hockey, speed skating and sailing. *Miervaldis Jurševskis (1921–2014), a Latvian Canadian, Latvian-Canadian chess master and a professional artist. *Matīss Kivlenieks (1996–2021), an ice hockey goaltender for the Columbus Blue Jackets *Jeļena Ostapenko (born 1997) women's tennis player, 2017 French Open – Women's singles winner *Sandis Ozoliņš (born 1972), Latvian ice hockey player, a seven-time NHL All-Star, Stanley Cup champion *Marians Pahars (born 1976), footballer with 75 caps for Latvia national football team, Latvia *Alexei Shirov (born 1972), Latvian / Spanish chess grandmaster, ranked world No. 2 in 1994 *Mikhail Tal (1936–1992), Soviet-Latvian chess grandmaster, 8th. World Chess Champion. *Valdis Valters (born 1957) a retired Latvian basketball player.Twin towns – sister cities
Riga is twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: * Aalborg, Denmark * Almaty, Kazakhstan * Astana, Kazakhstan * Beijing, China * Bordeaux, France * Bremen, Germany * Cairns, Australia * Dallas, United States * Florence, Italy * Kaunas, Lithuania * Kyiv, Ukraine * Kobe, Japan * Norrköping, Sweden * Pori, Finland * Rostock, Germany * Santiago, Chile * Stockholm, Sweden * Suzhou, China * Taipei, Taiwan *Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
, Estonia
* Tartu, Estonia
* Tashkent, Uzbekistan
* Tbilisi, Georgia
* Vilnius, Lithuania
* Warsaw, Poland
* Yerevan, Armenia
See also
*Riga Charter, on cultural heritage conservation, adopted here in 2000 *Riga Region *Riga Salsa FestivalOther capitals of the Baltic states
*Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
*Vilnius
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Grava, Sigurd. "The Urban Heritage of the Soviet Regime The Case of Riga, Latvia." ''Journal of the American Planning Association'' 59.1 (1993): 9-30. * * Šolks, Guntis, Gita Dejus, and Krists Legzdiņš. "Transformation of Historic Industrial Areas in Riga." ''Book of Proceedings''. (2012online
External links
(in Latvian) *
i
{{Authority control Riga, Cities in Latvia Capitals in Europe Populated coastal places in Latvia Port cities in Latvia Port cities and towns of the Baltic Sea Republican cities of Latvia Gulf of Riga Kreis Riga Members of the Hanseatic League Vidzeme NUTS 3 statistical regions of the European Union World Heritage Sites in Latvia Holocaust locations in Latvia