Rifle Roti Awrat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A rifle is a long-barreled
A rifle is a long-barreled
 Historically, rifles only fired a single projectile with each squeeze of the trigger. Modern rifles are commonly classified as single-shot, bolt-action, semi-automatic, or automatic. Single-shot, bolt-action, and semi-automatic rifles are limited by their designs to fire a single shot for each trigger pull. Only automatic rifles are capable of firing more than one round per trigger squeeze; however, some automatic rifles are limited to fixed bursts of two, three, or more rounds per squeeze.
Modern automatic rifles overlap to some extent in design and function with machine guns. In fact, many light machine guns (such as the Russian
Historically, rifles only fired a single projectile with each squeeze of the trigger. Modern rifles are commonly classified as single-shot, bolt-action, semi-automatic, or automatic. Single-shot, bolt-action, and semi-automatic rifles are limited by their designs to fire a single shot for each trigger pull. Only automatic rifles are capable of firing more than one round per trigger squeeze; however, some automatic rifles are limited to fixed bursts of two, three, or more rounds per squeeze.
Modern automatic rifles overlap to some extent in design and function with machine guns. In fact, many light machine guns (such as the Russian
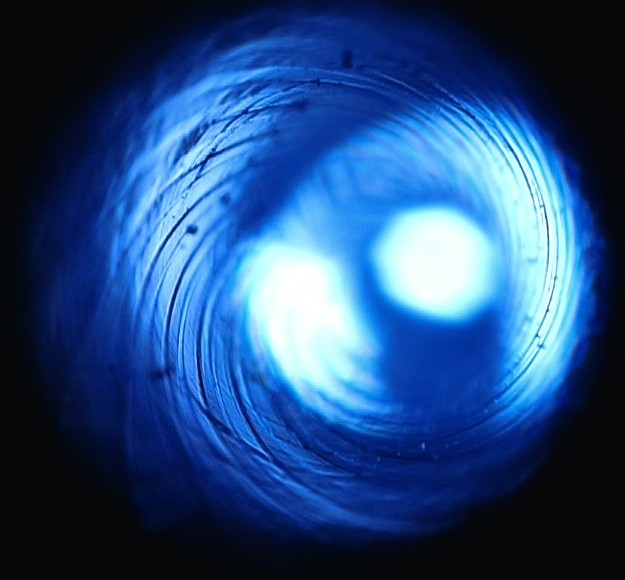

 The origins of rifling are as difficult to trace, but some of the earliest European experiments seem to have been carried out during the 15th century. Archers had long realized that a twist added to the tail feathers of their arrows gave them greater accuracy. Early
The origins of rifling are as difficult to trace, but some of the earliest European experiments seem to have been carried out during the 15th century. Archers had long realized that a twist added to the tail feathers of their arrows gave them greater accuracy. Early
 The original muzzle-loading rifle, with a closely fitting ball to take the rifling grooves, was loaded with difficulty, particularly when foul, and for this reason was not generally used for military purposes. With the advent of rifling the bullet itself did not initially change but was wrapped in a greased, cloth patch to grip the rifling grooves.
The first half of the 19th century saw a distinct change in the shape and function of the bullet. In 1826
The original muzzle-loading rifle, with a closely fitting ball to take the rifling grooves, was loaded with difficulty, particularly when foul, and for this reason was not generally used for military purposes. With the advent of rifling the bullet itself did not initially change but was wrapped in a greased, cloth patch to grip the rifling grooves.
The first half of the 19th century saw a distinct change in the shape and function of the bullet. In 1826
 One of the most famous was the Minié system, invented by French Army Captain Claude-Étienne Minié, which relied on a conical bullet (known as a Minié ball) with a hollow skirt at the base of the bullet. When fired, the skirt would expand from the pressure of the exploding charge and grip the rifling as the round was fired. The better seal gave more power, as less gas escaped past the bullet. Also, for the same
One of the most famous was the Minié system, invented by French Army Captain Claude-Étienne Minié, which relied on a conical bullet (known as a Minié ball) with a hollow skirt at the base of the bullet. When fired, the skirt would expand from the pressure of the exploding charge and grip the rifling as the round was fired. The better seal gave more power, as less gas escaped past the bullet. Also, for the same
 From 1836, breech-loading rifles were introduced with the German Dreyse Needle gun, followed by the French Tabatière in 1857, and the British Calisher and Terry carbine made in Birmingham and later in 1864 and the better known British Snider–Enfield. Primitive chamber-locking mechanisms were soon replaced by bolt-action mechanisms, exemplified by the Chassepot in 1866. Breech-loading was to have a major impact on warfare, as breech-loading rifles can be fired at a rate many times higher than muzzle-loaded rifles and significantly can be loaded from a prone rather than standing position. Firing prone (i.e., lying down) is more accurate than firing from a standing position, and a prone rifleman presents a much smaller target than a standing soldier. The higher accuracy and range, combined with reduced vulnerability generally benefited the defense while making the traditional battle between lines of standing and volleying infantrymen obsolete.
From 1836, breech-loading rifles were introduced with the German Dreyse Needle gun, followed by the French Tabatière in 1857, and the British Calisher and Terry carbine made in Birmingham and later in 1864 and the better known British Snider–Enfield. Primitive chamber-locking mechanisms were soon replaced by bolt-action mechanisms, exemplified by the Chassepot in 1866. Breech-loading was to have a major impact on warfare, as breech-loading rifles can be fired at a rate many times higher than muzzle-loaded rifles and significantly can be loaded from a prone rather than standing position. Firing prone (i.e., lying down) is more accurate than firing from a standing position, and a prone rifleman presents a much smaller target than a standing soldier. The higher accuracy and range, combined with reduced vulnerability generally benefited the defense while making the traditional battle between lines of standing and volleying infantrymen obsolete.
 Revolving rifles were an attempt to increase the rate of fire of rifles by combining them with the revolving firing mechanism that had been developed earlier for revolving pistols. Colt began experimenting with revolving rifles in the early 19th century, and other manufacturers like Remington later experimented with them as well. The Colt Revolving Rifle Model 1855 was an early repeating rifle and the first one to be used by the U.S. Government and saw some limited action during the American Civil War. Revolvers, both rifles and pistols, tend to spray fragments of metal from the front of the cylinder.
Revolving rifles were an attempt to increase the rate of fire of rifles by combining them with the revolving firing mechanism that had been developed earlier for revolving pistols. Colt began experimenting with revolving rifles in the early 19th century, and other manufacturers like Remington later experimented with them as well. The Colt Revolving Rifle Model 1855 was an early repeating rifle and the first one to be used by the U.S. Government and saw some limited action during the American Civil War. Revolvers, both rifles and pistols, tend to spray fragments of metal from the front of the cylinder.
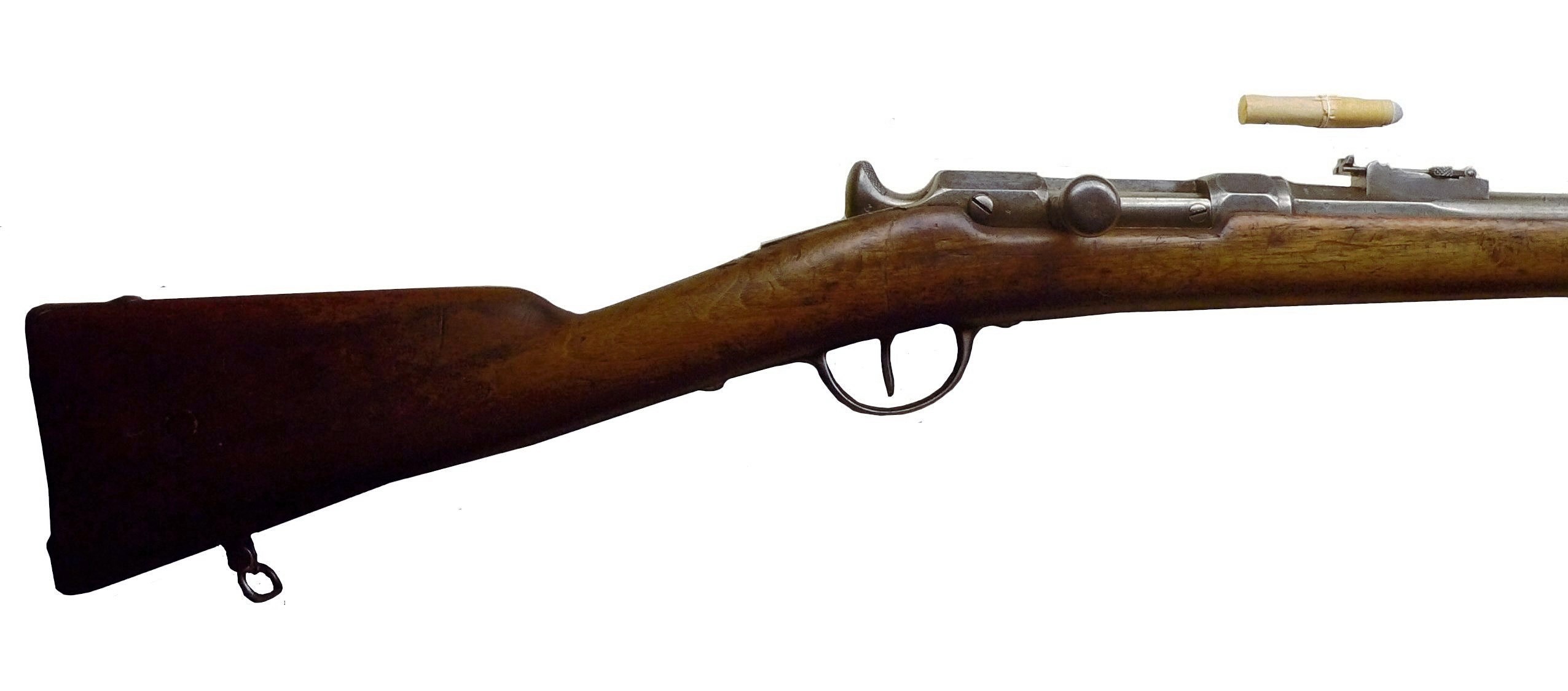
 In the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, military observers from Europe and the United States witnessed a major conflict fought with high velocity
In the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, military observers from Europe and the United States witnessed a major conflict fought with high velocity  During and after World War II it became accepted that most infantry engagements occurred at ranges of less than 300 m; the range and power of the large full-powered rifle cartridges were "overkill", requiring weapons heavier than otherwise necessary. This led to Germany's development of the 7.92×33mm ''Kurz'' (short) round, the MKb-42, and ultimately, the assault rifle. Today, an infantryman's rifle is optimized for ranges of 300 m or less, and soldiers are trained to deliver individual rounds or bursts of fire within these distances. Typically, the application of accurate, long-range fire is the domain of the marksman and the
During and after World War II it became accepted that most infantry engagements occurred at ranges of less than 300 m; the range and power of the large full-powered rifle cartridges were "overkill", requiring weapons heavier than otherwise necessary. This led to Germany's development of the 7.92×33mm ''Kurz'' (short) round, the MKb-42, and ultimately, the assault rifle. Today, an infantryman's rifle is optimized for ranges of 300 m or less, and soldiers are trained to deliver individual rounds or bursts of fire within these distances. Typically, the application of accurate, long-range fire is the domain of the marksman and the
NBC News, 26 July 2013. ()World's first 3D-printed rifle gets update, fires 14 shots
The Verge, 4 August 2013.() The original Grizzly fired a single shot before breaking. Grizzly 2.0 fired fourteen bullets before getting damaged due to the strain. In October 2020, another 3D-printed 9mm rifle known as the "FGC-9mm" was created. It is reported that it can be made in 2 weeks with $500 of tools. A second model was later made in April 2021.
 As the bullet enters the barrel, it inserts itself into the rifling, a process that gradually wears down the barrel, and also causes the barrel to heat up more rapidly. Therefore, some machine guns are equipped with quick-change barrels that can be swapped every few thousand rounds, or in earlier designs, were water-cooled. Unlike older carbon
As the bullet enters the barrel, it inserts itself into the rifling, a process that gradually wears down the barrel, and also causes the barrel to heat up more rapidly. Therefore, some machine guns are equipped with quick-change barrels that can be swapped every few thousand rounds, or in earlier designs, were water-cooled. Unlike older carbon
The Story of the Rifle
', a booklet from 1945 in
"On Rifled Cannon"
articles from the New York ''Tribune'', April, May and June, 1860, reprinted in ''Military Affairs'' 21, no. 4 (Winter 1957) ed. Morton Borden, 193–198. {{Authority control Hunting equipment Infantry Personal weapons
 A rifle is a long-barreled
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, ...
that has a helical pattern of grooves (rifling
In firearms, rifling is machining helical grooves into the internal (bore) surface of a gun's barrel for the purpose of exerting torque and thus imparting a spin to a projectile around its longitudinal axis during shooting to stabilize the pro ...
) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with both hands and braced firmly against the shooter's shoulder via a buttstock for stability during shooting. Rifles are used extensively in warfare, law enforcement, hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
, shooting sports
Shooting sports is a group of competitive sport, competitive and recreational sporting activities involving proficiency tests of accuracy, precision and speed in shooting — the art of using ranged weapons, mainly small arms (firearms and airgun ...
, and crime.
The term was originally ''rifled gun'', with the verb ''rifle'' referring to the early modern machining
Machining is a process in which a material (often metal) is cut to a desired final shape and size by a controlled material-removal process. The processes that have this common theme are collectively called subtractive manufacturing, which utilizes ...
process of creating groovings with cutting tools. By the 20th century, the weapon had become so common that the modern noun ''rifle'' is now often used for any long-shaped handheld ranged weapon
A ranged weapon is any weapon that can engage targets beyond hand-to-hand distance, i.e. at distances greater than the physical reach of the user holding the weapon itself. The act of using such a weapon is also known as shooting. It is someti ...
designed for well-aimed discharge activated by a trigger
Trigger may refer to:
Notable animals and people
;Mononym
* Trigger (horse), owned by cowboy star Roy Rogers
;Nickname
* Trigger Alpert (1916–2013), American jazz bassist
* "Trigger Mike" Coppola (1900–1966), American gangster
;Surname
* Bru ...
(e.g., personnel halting and stimulation response rifle, which is actually a laser dazzler
A dazzler is a non-lethal weapon which uses intense directed radiation to temporarily disorient its target with flash blindness. They can effectively deter further advances, regardless of language or cultural barriers, but can also be used for h ...
).
Like all typical firearms, a rifle's projectile
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found in ...
(bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and co ...
) is propelled by the contained deflagration
Deflagration (Lat: ''de + flagrare'', "to burn down") is subsonic combustion in which a pre-mixed flame propagates through a mixture of fuel and oxidizer. Deflagrations can only occur in pre-mixed fuels. Most fires found in daily life are diffu ...
of a combustible propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the e ...
compound (originally black powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
, later cordite, and now nitrocellulose), although other propulsive means are used, such as compressed air
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air is an important medium for transfer of energy in industrial processes, and is used for power tools such as air hammers, drills, wrenches, and o ...
in air rifle
An air gun or airgun is a gun that fires projectiles pneumatically with compressed air or other gases that are mechanically pressurized ''without'' involving any chemical reactions, in contrast to a firearm, which pressurizes gases ''chem ...
s, which are popular for vermin control, small game hunting, competitive target shooting and casual sport shooting ('' plinking'').
The distinct feature that separates a rifle from the earlier smoothbore long guns (e.g., arquebuses, musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually d ...
s) is the rifling within its barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, ...
. The raised areas of a barrel's rifling are called ''lands''; they make contact with and exert torque on the projectile as it moves down the bore, imparting a spin. When the projectile leaves the barrel, this spin persists and lends gyroscopic stability to the projectile due to conservation of angular momentum, increasing accuracy and hence effective range. Early long rifle
The long rifle, also known as the longrifle, Kentucky rifle, Pennsylvania rifle, or American longrifle, a muzzle-loading firearm used for hunting and warfare, was one of the first commonly-used rifles. The American rifle was characterized by a ...
s were muzzle-loaders firing spherical balls; the introduction of breech-loading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally breech ...
allowed the use of elongated and aerodynamically efficient bullets, which did not yaw or tumble significantly in flight due to the spin.
Terminology
 Historically, rifles only fired a single projectile with each squeeze of the trigger. Modern rifles are commonly classified as single-shot, bolt-action, semi-automatic, or automatic. Single-shot, bolt-action, and semi-automatic rifles are limited by their designs to fire a single shot for each trigger pull. Only automatic rifles are capable of firing more than one round per trigger squeeze; however, some automatic rifles are limited to fixed bursts of two, three, or more rounds per squeeze.
Modern automatic rifles overlap to some extent in design and function with machine guns. In fact, many light machine guns (such as the Russian
Historically, rifles only fired a single projectile with each squeeze of the trigger. Modern rifles are commonly classified as single-shot, bolt-action, semi-automatic, or automatic. Single-shot, bolt-action, and semi-automatic rifles are limited by their designs to fire a single shot for each trigger pull. Only automatic rifles are capable of firing more than one round per trigger squeeze; however, some automatic rifles are limited to fixed bursts of two, three, or more rounds per squeeze.
Modern automatic rifles overlap to some extent in design and function with machine guns. In fact, many light machine guns (such as the Russian RPK
The RPK (russian: Ручной пулемёт Калашникова/РПК, Ruchnoy Pulemyot Kalashnikova, link=no, English: "Kalashnikov hand-held machine gun"), sometimes retroactively termed the RPK-47, is a Soviet 7.62×39mm light machine ...
) are adaptations of existing automatic rifle designs. A military's light machine guns are typically chambered for the same caliber ammunition as its service rifles. Generally, the difference between an automatic rifle and a machine gun comes down to weight, cooling system, and ammunition feed system. Rifles, with their relatively lighter components (which overheat quickly) and smaller capacity magazines, are incapable of sustained automatic fire in the way that machine guns are; they trade this capability in favor of increased mobility. Modern military rifles are fed by magazines, while machine guns are generally belt-fed. Many machine guns allow the operator to quickly exchange barrels in order to prevent overheating, whereas rifles generally do not. Most machine guns fire from an open bolt
The BOLT Browser was a web browser for mobile phones including feature phones and smartphones that can run Java ME applications. The BOLT Browser was offered free of charge to consumers and by license to mobile network operators and handset manuf ...
in order to reduce the danger of "cook-off", while almost all rifles fire from a closed bolt for accuracy. Machine guns are often crewed by more than one soldier; the rifle is an individual weapon.
The term "rifle" is sometimes used to describe larger rifled crew-served weapons firing explosive shells, for example, recoilless rifle
A recoilless rifle, recoilless launcher or recoilless gun, sometimes abbreviated "RR" or "RCL" (for ReCoilLess) is a type of lightweight artillery system or man-portable launcher that is designed to eject some form of countermass such as propel ...
s and naval rifle
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes ...
s.
In many works of fiction a rifle refers to any weapon that has a stock
In finance, stock (also capital stock) consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided.Longman Business English Dictionary: "stock - ''especially AmE'' one of the shares into which ownership of a company ...
and is shouldered before firing, even if the weapon is not rifled or does not fire solid projectiles (e.g., a "laser rifle").
Historical overview

 The origins of rifling are as difficult to trace, but some of the earliest European experiments seem to have been carried out during the 15th century. Archers had long realized that a twist added to the tail feathers of their arrows gave them greater accuracy. Early
The origins of rifling are as difficult to trace, but some of the earliest European experiments seem to have been carried out during the 15th century. Archers had long realized that a twist added to the tail feathers of their arrows gave them greater accuracy. Early musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually d ...
s produced large quantities of smoke and soot, which had to be cleaned from the action and bore of the musket frequently, either through the action of repeated bore scrubbing, or a deliberate attempt to create "soot grooves" that would allow for more shots to be fired from the firearm. Some of the earliest examples of European grooved gun barrels were reportedly manufactured as early as 1440 and further developed by Gaspard Kollner of Vienna circa 1498, although other scholars allege they were a joint effort between Kollner and Augustus Kotter of Nuremberg circa 1520. Military commanders preferred smoothbore weapons for infantry use because rifles were much more prone to problems due to powder fouling the barrel and because they took longer to reload and fire than muskets.
Rifles were created as an improvement in the accuracy of smoothbore muskets. In the early 18th century, Benjamin Robins
Benjamin Robins (170729 July 1751) was a pioneering British scientist, Newtonian mathematician, and military engineer.
He wrote an influential treatise on gunnery, for the first time introducing Newtonian science to military men, was an early en ...
, an English mathematician, realized that an elongated bullet would retain the momentum and kinetic energy of a musket ball, but would slice through the air with greater ease. The black powder used in early muzzle-loading rifles quickly fouled the barrel, making loading slower and more difficult. The greater range of the rifle was considered to be of little practical use since the smoke from black powder quickly obscured the battlefield and made it almost impossible to aim the weapon from a distance. Since musketeers could not afford to take the time to stop and clean their barrels in the middle of a battle, rifles were limited to use by sharpshooters and non-military uses like hunting.
Musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually d ...
s were smoothbore, large caliber weapons using spherical ammunition fired at relatively low velocity. Due to the high cost and great difficulty of precision manufacturing, and the need to load readily from the muzzle, the musket ball was a loose fit in the barrel. Consequently, on firing the ball bounced off the sides of the barrel when fired and the final direction on leaving the muzzle was unpredictable.
The performance of early muskets defined the style of warfare at the time. Due to the lack of accuracy, soldiers were deployed in long lines (thus line infantry
Line infantry was the type of infantry that composed the basis of European land armies from the late 17th century to the mid-19th century. Maurice of Nassau and Gustavus Adolphus are generally regarded as its pioneers, while Turenne and Monte ...
) to fire at the opposing forces. Precise aim was thus not necessary to hit an opponent. Muskets were used for comparatively rapid, imprecisely aimed volley fire, and the average soldier could be easily trained to use them.
In the territory of Kentucky, one of the most successful early rifles, the long rifle
The long rifle, also known as the longrifle, Kentucky rifle, Pennsylvania rifle, or American longrifle, a muzzle-loading firearm used for hunting and warfare, was one of the first commonly-used rifles. The American rifle was characterized by a ...
, was developed over the course of the 18th century. Compared to the more common Brown Bess, they had a tighter bore with no space between bullet and barrel, and still used balls instead of conical bullets. The balls the long rifle used were smaller, allowing the production of more rounds for a given amount of lead. These rifles also had longer barrels, allowing more accuracy, which were rifled with a helical groove. These first started appearing sometime before 1740, one early example being made by Jacob Dickert, a German immigrant. By 1750 there were a number of such manufacturers in the area. The longer barrel was a departure by local gunsmiths from their German roots, allowing bullets to achieve a higher speed (as the burning gunpowder was contained longer) before emerging from the barrel.
The rifle was used for precise shooting, aiming, and firing at individual targets, instead of the musket's use for imprecise fire.
By the time of the American Revolutionary War, these rifles were commonly used by frontiersmen, and Congress authorized the establishment of ten companies of riflemen. One of the most critical units was Morgan's Riflemen
Morgan's Riflemen or Morgan's Rifles, previously Morgan's Sharpshooters, and the one named Provisional Rifle Corps, were an elite light infantry unit commanded by General Daniel Morgan in the American Revolutionary War, which served a vital role e ...
, led by Daniel Morgan
Daniel Morgan (1735–1736July 6, 1802) was an American pioneer, soldier, and politician from Virginia. One of the most respected battlefield tacticians of the American Revolutionary War of 1775–1783, he later commanded troops during the sup ...
. This sharpshooting unit eventually proved itself integral to the Battle of Saratoga
The Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7, 1777) marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led an invasion ...
, and in the southern states where General Morgan commanded as well. Taking advantage of the rifle's improved accuracy, Morgan's sharpshooters picked off cannoneers and officers, reducing the impact of enemy artillery. This kind of advantage was considered pivotal in many battles, such as the battles of Cowpens, Saratoga, and King's Mountain.
Later during the Napoleonic Wars, the British 95th Regiment (Green Jackets) and 60th Regiment, (Royal American), as well as sharpshooters and riflemen during the War of 1812, used the rifle to great effect during skirmishing. Because of a slower loading time than a musket, they were not adopted by the whole army. Since rifles were used by sharpshooters who did not routinely fire over other men's shoulders, long length was not required to avoid the forward line. A shorter length made a handier weapon in which tight-fitting balls did not have to be rammed so far down the barrel.
The invention of the minie balls in the 1840s solved the slow loading problem, and in the 1850s and 1860s rifles quickly replaced muskets on the battlefield. Many rifles, often referred to as rifled musket
A rifled musket, rifle musket, or rifle-musket is a type of firearm made in the mid-19th century. Originally the term referred only to muskets that had been produced as a smoothbore weapon and later had their barrels replaced with rifled barrel ...
s, were very similar to the muskets they replaced, but the military also experimented with other designs. Breech-loading weapon
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally breec ...
s proved to have a much faster rate of fire than muzzleloaders, causing military forces to abandon muzzle loaders in favor of breech-loading designs in the late 1860s. In the later part of the 19th century, rifles were generally single-shot, breech-loading guns, designed for aimed, discretionary fire by individual soldiers. Then, as now, rifles had a stock, either fixed or folding, to be braced against the shoulder when firing.
The adoption of cartridges and breech-loading in the 19th century was concurrent with the general adoption of rifles. In the early part of the 20th century, soldiers were trained to shoot accurately over long ranges with high-powered cartridges. World War I Lee–Enfield rifles (among others) were equipped with long-range 'volley sights' for massed firing at ranges of up to . Individual shots were unlikely to hit, but a platoon firing repeatedly could produce a 'beaten ground' effect similar to light artillery or machine guns.
Currently, rifles are the most common firearm in general use for hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
(with the exception of bird hunting, where shotguns
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which usually discharges numerous small p ...
are favored). Rifles derived from military designs have long been popular with civilian shooters.
19th century
During the Napoleonic Wars the British army created several experimental units known as "Rifles", armed with the Baker rifle. These Rifle Regiments were deployed as skirmishers during the Peninsular war in Spain and Portugal, and were more effective than skirmishers armed with muskets due to their accuracy and long range.Muzzle-loading
Gradually, rifles appeared with cylindrical barrels cut with helical grooves, the surfaces between the grooves being "lands". The innovation was shortly followed by the mass adoption ofbreech-loading weapon
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally breec ...
s, as it was not practical to push an overbore bullet down through a rifled barrel. The dirt and grime from prior shots were pushed down ahead of a tight bullet or ball (which may have been a looser fit in the clean barrel before the first shot), and loading was far more difficult, as the lead had to be deformed to go down in the first place, reducing the accuracy due to deformation. Several systems were tried to deal with the problem, usually by resorting to an under-bore bullet that expanded upon firing.
 The original muzzle-loading rifle, with a closely fitting ball to take the rifling grooves, was loaded with difficulty, particularly when foul, and for this reason was not generally used for military purposes. With the advent of rifling the bullet itself did not initially change but was wrapped in a greased, cloth patch to grip the rifling grooves.
The first half of the 19th century saw a distinct change in the shape and function of the bullet. In 1826
The original muzzle-loading rifle, with a closely fitting ball to take the rifling grooves, was loaded with difficulty, particularly when foul, and for this reason was not generally used for military purposes. With the advent of rifling the bullet itself did not initially change but was wrapped in a greased, cloth patch to grip the rifling grooves.
The first half of the 19th century saw a distinct change in the shape and function of the bullet. In 1826 Delvigne
Henri-Gustave Delvigne (April 10, 1800 in Hamburg – October 18, 1876 in Toulon) was a French soldier and inventor. He became a captain in the French infantry service, from which he resigned on the outbreak of the 1830 July Revolution. Delvig ...
, a French infantry officer, invented a breech with abrupt shoulders on which a spherical bullet was rammed down until it caught the rifling grooves. Delvigne's method, however, deformed the bullet and was inaccurate.
Soon after, the Carabine à tige
The carabine à tige (sometimes called a "stem rifle") was a type of black-powder, muzzle-loading rifle invented by Louis-Etienne de Thouvenin. The method was an improvement of the invention of another Frenchman, Henri-Gustave Delvigne. Delvig ...
was invented by Louis-Etienne de Thouvenin, which had a stem at the bottom of the barrel that would deform and expand the base of the bullet when rammed, therefore enabling accurate contact with the rifling. However, the area around the stem clogged and got dirty easily.
Minié system – the "rifled musket"
 One of the most famous was the Minié system, invented by French Army Captain Claude-Étienne Minié, which relied on a conical bullet (known as a Minié ball) with a hollow skirt at the base of the bullet. When fired, the skirt would expand from the pressure of the exploding charge and grip the rifling as the round was fired. The better seal gave more power, as less gas escaped past the bullet. Also, for the same
One of the most famous was the Minié system, invented by French Army Captain Claude-Étienne Minié, which relied on a conical bullet (known as a Minié ball) with a hollow skirt at the base of the bullet. When fired, the skirt would expand from the pressure of the exploding charge and grip the rifling as the round was fired. The better seal gave more power, as less gas escaped past the bullet. Also, for the same bore
Bore or Bores often refer to:
*Boredom
* Drill
Relating to holes
* Boring (manufacturing), a machining process that enlarges a hole
** Bore (engine), the diameter of a cylinder in a piston engine or a steam locomotive
** Bore (wind instruments), ...
(caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge (firearms) , bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the f ...
) diameter a long bullet was heavier than a round ball. The extra grip also spun the bullet more consistently, which increased the range from about 50 yards for a smoothbore musket to about 300 yards for a rifle using the Minié system. The expanding skirt of the Minié ball also solved the problem that earlier tight-fitting bullets were difficult to load as black powder residue fouled the inside of the barrel. The Minié system allowed conical bullets to be loaded into rifles just as quickly as round balls in smooth bores, which allowed rifle muskets to replace muskets on the battlefield. Minié system rifles, notably the U.S. Springfield and the British Enfield of the early 1860s featured prominently in the U.S. Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, due to their enhanced power and accuracy.
Over the 19th century, bullet design also evolved, the bullets becoming gradually smaller and lighter. By 1910 the standard blunt-nosed bullet had been replaced by the pointed, 'spitzer' bullet, an innovation that increased range and penetration. Cartridge design evolved from simple paper tubes containing black powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
and shot, to sealed brass cases with integral primers for ignition, and black powder was replaced by cordite, and then other nitro-cellulose-based smokeless powder mixtures, propelling bullets to higher velocities than before.
The increased velocity meant that new problems arrived, and so bullets went from being soft lead to harder lead, then to copper-jacketed, in order to better engage the spiral grooves without "stripping" them in the same way that a screw or bolt thread would be stripped if subjected to extreme forces.
Breech loading
 From 1836, breech-loading rifles were introduced with the German Dreyse Needle gun, followed by the French Tabatière in 1857, and the British Calisher and Terry carbine made in Birmingham and later in 1864 and the better known British Snider–Enfield. Primitive chamber-locking mechanisms were soon replaced by bolt-action mechanisms, exemplified by the Chassepot in 1866. Breech-loading was to have a major impact on warfare, as breech-loading rifles can be fired at a rate many times higher than muzzle-loaded rifles and significantly can be loaded from a prone rather than standing position. Firing prone (i.e., lying down) is more accurate than firing from a standing position, and a prone rifleman presents a much smaller target than a standing soldier. The higher accuracy and range, combined with reduced vulnerability generally benefited the defense while making the traditional battle between lines of standing and volleying infantrymen obsolete.
From 1836, breech-loading rifles were introduced with the German Dreyse Needle gun, followed by the French Tabatière in 1857, and the British Calisher and Terry carbine made in Birmingham and later in 1864 and the better known British Snider–Enfield. Primitive chamber-locking mechanisms were soon replaced by bolt-action mechanisms, exemplified by the Chassepot in 1866. Breech-loading was to have a major impact on warfare, as breech-loading rifles can be fired at a rate many times higher than muzzle-loaded rifles and significantly can be loaded from a prone rather than standing position. Firing prone (i.e., lying down) is more accurate than firing from a standing position, and a prone rifleman presents a much smaller target than a standing soldier. The higher accuracy and range, combined with reduced vulnerability generally benefited the defense while making the traditional battle between lines of standing and volleying infantrymen obsolete.
Revolving rifle
Repeating rifle
TheWinchester repeating rifle
Winchester rifle is a comprehensive term describing a series of lever action repeating rifles manufactured by the Winchester Repeating Arms Company. Developed from the 1860 Henry rifle, Winchester rifles were among the earliest repeaters. The M ...
was invented in 1866. The firer pulled on a lever to reload the rifle with a stored cartridge.
Cartridge storage
An important area of development was the way that cartridges were stored and used in the weapon. The Spencer repeating rifle was a breech-loading manually operated lever-action rifle that was adopted by the United States. Over 20,000 were used during the American Civil War. It was the first adoption of a removablemagazine
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...
-fed infantry rifle. The design was completed by Christopher Spencer in 1860. It used copper rimfire cartridges
Rimfire ammunition is a type of firearm metallic cartridge whose primer is located within a hollow circumferential rim protruding from the base of its casing. When fired, the gun's firing pin will strike and crush the rim against the edge ...
stored in a removable seven-round tube magazine, enabling the rounds to be fired one after another. When the magazine was empty, it could be exchanged for another.
20th century
 In the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, military observers from Europe and the United States witnessed a major conflict fought with high velocity
In the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, military observers from Europe and the United States witnessed a major conflict fought with high velocity bolt-action rifles
Bolt-action is a type of manual firearm action that is operated by ''directly'' manipulating the bolt via a bolt handle, which is most commonly placed on the right-hand side of the weapon (as most users are right-handed).
Most bolt-action ...
firing smokeless powder. The Battle of Mukden
The , one of the largest land battles to be fought before World War I and the last and the most decisive major land battle of the Russo-Japanese War, was fought from 20 February to 10 March 1905 between Japan and Russia near Mukden ...
fought in 1905 consisted of nearly 343,000 Russian troops against over 281,000 Japanese troops. The Russian Mosin–Nagant
The Mosin–Nagant is a five-shot, bolt-action, internal magazine–fed military rifle. Known officially as the 3-line rifle M1891 and informally in Russia and former Soviet Union as Mosin's rifle ( ru , винтовка Мосина, ISO 9: ) ...
Model 1891 in 7.62mm was pitted against the Japanese Arisaka Type 30 bolt-action rifle in 6.5mm; both had velocities well over the 19th-century black powder velocities of under 2,000 feet per second (610 m/s).
Until the late 19th century rifles tended to be very long, some long rifle
The long rifle, also known as the longrifle, Kentucky rifle, Pennsylvania rifle, or American longrifle, a muzzle-loading firearm used for hunting and warfare, was one of the first commonly-used rifles. The American rifle was characterized by a ...
s reaching approximately 2 m (6 ft) in length to maximize accuracy, making early rifles impractical for use by cavalry. However, following the advent of more powerful smokeless powder, a shorter barrel did not impair accuracy as much. As a result, cavalry saw limited, but noteworthy, usage in 20th-century conflicts.
The advent of the massed, rapid firepower of the machine gun, submachine gun
A submachine gun (SMG) is a magazine-fed, automatic carbine designed to fire handgun cartridges. The term "submachine gun" was coined by John T. Thompson, the inventor of the Thompson submachine gun, to describe its design concept as an autom ...
and rifled artillery was so quick as to outstrip the development of any way to attack a trench defended by riflemen and machine gunners. The carnage of World War I was perhaps the greatest vindication and vilification of the rifle as a military weapon.
The M1 Garand was a semi-automatic rapid-fire rifle developed for modern warfare use in World War II.
 During and after World War II it became accepted that most infantry engagements occurred at ranges of less than 300 m; the range and power of the large full-powered rifle cartridges were "overkill", requiring weapons heavier than otherwise necessary. This led to Germany's development of the 7.92×33mm ''Kurz'' (short) round, the MKb-42, and ultimately, the assault rifle. Today, an infantryman's rifle is optimized for ranges of 300 m or less, and soldiers are trained to deliver individual rounds or bursts of fire within these distances. Typically, the application of accurate, long-range fire is the domain of the marksman and the
During and after World War II it became accepted that most infantry engagements occurred at ranges of less than 300 m; the range and power of the large full-powered rifle cartridges were "overkill", requiring weapons heavier than otherwise necessary. This led to Germany's development of the 7.92×33mm ''Kurz'' (short) round, the MKb-42, and ultimately, the assault rifle. Today, an infantryman's rifle is optimized for ranges of 300 m or less, and soldiers are trained to deliver individual rounds or bursts of fire within these distances. Typically, the application of accurate, long-range fire is the domain of the marksman and the sniper
A sniper is a military/paramilitary marksman who engages targets from positions of concealment or at distances exceeding the target's detection capabilities. Snipers generally have specialized training and are equipped with high-precision r ...
in warfare, and of enthusiastic target shooters in peacetime. The modern marksman rifle
A designated marksman rifle (DMR) is a modern scoped high- precision rifle used by infantrymen in the designated marksman (DM) role. It generally fills the engagement range gap between a service rifle and a dedicated sniper rifle, at around . ...
and sniper rifle
A sniper rifle is a high-precision, long-range rifle. Requirements include accuracy, reliability, mobility, concealment and optics for anti-personnel, anti-materiel and surveillance uses of the military sniper. The modern sniper rifle is a por ...
are usually capable of accuracy better than 0.3 mrad
The Barrett MRAD (Multi-role Adaptive Design) is a bolt-action sniper rifle designed by Barrett to meet the requirements of the SOCOM PSR. The MRAD is based on the Barrett 98B and includes a number of modifications and improvements. The Barrett ...
at 100 yards (1 arcminute).
3D printed rifle
The Grizzly is a 3D printed .22-caliber rifle created around August 2013. It was created using a Stratasys Dimension 1200es printer. It was created by a Canadian only known by the pseudonym "Matthew" who told The Verge that he was in his late 20s, and his main job was making tools for the construction industry.First 3-D printed rifle fires bullet, then breaksNBC News, 26 July 2013. ()World's first 3D-printed rifle gets update, fires 14 shots
The Verge, 4 August 2013.() The original Grizzly fired a single shot before breaking. Grizzly 2.0 fired fourteen bullets before getting damaged due to the strain. In October 2020, another 3D-printed 9mm rifle known as the "FGC-9mm" was created. It is reported that it can be made in 2 weeks with $500 of tools. A second model was later made in April 2021.
Youth rifle
A youth rifle is a rifle designed or modified for fitting children or other small-framed shooters. A youth rifle is often a single-shot.22 caliber .22 caliber, or 5.6 mm caliber, refers to a common firearms bore diameter of 0.22 inch (5.6 mm).
Cartridges in this caliber include the very widely used .22 Long Rifle and .223 Remington / 5.56×45mm NATO.
.22 inch is also a popular ...
rifle, or a bolt-action rifle, although some youth rifles are semi-automatic. They are usually very light, with a greatly shortened length of pull, which is necessary to accommodate children. Youth stocks are available for many popular rifles, such as the Ruger 10/22, a semi-automatic .22 LR rifle, allowing a youth rifle to be made from a standard rifle by simply changing the stock. The typical ages of shooters for such rifles vary from about age 5+.
Technical aspects
Rifling
The usual form of rifling was helical grooves in a round bore. Some early rifled firearms had barrels with a twisted polygonal bore. The Whitworth rifle was the first such type designed to spin the round for accuracy. Bullets for these guns were made to match the shape of the bore so the bullet would grip the rifle bore and take a spin that way. These were generally large caliber weapons, and the ammunition still did not fit tightly in the barrel. Many different shapes and degrees of spiraling were used in experimental designs. One widely produced example was the Metford rifling in the Pattern 1888Lee–Metford
The Lee–Metford rifle (a.k.a. ''Magazine Lee–Metford'', abbreviated ''MLM'') was a bolt-action British army service rifle, combining James Paris Lee's rear-locking bolt system and detachable magazine with an innovative seven groove rifled ba ...
service rifle. Although uncommon, polygonal rifling
Polygonal rifling ( ) is a type of gun barrel rifling where the traditional sharp-edged "lands and grooves" are replaced by less pronounced "hills and valleys", so the barrel bore has a polygonal (usually hexagonal or octagonal) cross-sectional p ...
is still used in some weapons today, one example being the Glock line of pistols (which fire standard bullets). Many of the early designs were prone to dangerous backfiring, which could lead to the destruction of the weapon and serious injury to the person firing it.
Barrel wear
 As the bullet enters the barrel, it inserts itself into the rifling, a process that gradually wears down the barrel, and also causes the barrel to heat up more rapidly. Therefore, some machine guns are equipped with quick-change barrels that can be swapped every few thousand rounds, or in earlier designs, were water-cooled. Unlike older carbon
As the bullet enters the barrel, it inserts itself into the rifling, a process that gradually wears down the barrel, and also causes the barrel to heat up more rapidly. Therefore, some machine guns are equipped with quick-change barrels that can be swapped every few thousand rounds, or in earlier designs, were water-cooled. Unlike older carbon steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
barrels, which were limited to around 1,000 shots before the extreme heat caused accuracy to fade, modern stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
barrels for target rifles are much more resistant to wear, allowing many thousands of rounds to be fired before accuracy drops. (Many shotguns and small arms have chrome
Chrome may refer to:
Materials
* Chrome plating, a process of surfacing with chromium
* Chrome alum, a chemical used in mordanting and photographic film
Computing
* Google Chrome, a web browser developed by Google
** ChromeOS, a Google Chrome- ...
-lined barrels to reduce wear and enhance corrosion resistance. This is rare on rifles designed for extreme accuracy, as the plating process is difficult and liable to reduce the effect of the rifling.) Modern ammunition has a hardened lead core with a softer outer cladding or jacket, typically of an alloy of copper and nickel – cupro-nickel. Some ammunition is coated with molybdenum disulfide
Molybdenum disulfide (or moly) is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur. Its chemical formula is .
The compound is classified as a transition metal dichalcogenide. It is a silvery black solid that occurs as the mineral molybdenit ...
to further reduce internal friction – the so-called 'moly-coated' bullet.
Rate of fire
Rifles were initially single-shot, muzzle-loading weapons. During the 18th century, breech-loading weapons were designed, which allowed the rifleman to reload while under cover, but defects in manufacturing and the difficulty in forming a reliable gas-tight seal prevented widespread adoption. During the 19th century, multi-shotrepeating rifle A repeating rifle is a single- barreled rifle capable of repeated discharges between each ammunition reloads. This is typically achieved by having multiple cartridges stored in a magazine (within or attached to the gun) and then fed individually i ...
s using lever, pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they u ...
or linear bolt actions became standard, further increasing the rate of fire and minimizing the fuss involved in loading a firearm. The problem of proper seal creation had been solved with the use of brass cartridge cases, which expanded in an elastic
Elastic is a word often used to describe or identify certain types of elastomer, elastic used in garments or stretchable fabrics.
Elastic may also refer to:
Alternative name
* Rubber band, ring-shaped band of rubber used to hold objects togeth ...
fashion at the point of firing and effectively sealed the breech while the pressure remained high, then relaxed back enough to allow for easy removal. By the end of the 19th century, the leading bolt-action design was that of Paul Mauser
Peter Paul von Mauser (born Peter Paul Mauser) (27 June 1838 – 29 May 1914) was a German weapon designer, manufacturer, industrialist and politician.
Early life
Mauser was born in Oberndorf am Neckar, in what was then the Kingdom of Württembe ...
, whose action—wedded to a reliable design possessing a five-shot magazine—became a world standard through two world wars and beyond. The Mauser rifle was paralleled by Britain's ten-shot Lee–Enfield and America's 1903 Springfield Rifle
The term Springfield rifle may refer to any one of several types of small arms produced by the Springfield Armory in Springfield, Massachusetts, for the United States armed forces.
In modern usage, the term "Springfield rifle" most commonly ref ...
models. The American M1903 closely copied Mauser's original design.
Range
Barrelrifling
In firearms, rifling is machining helical grooves into the internal (bore) surface of a gun's barrel for the purpose of exerting torque and thus imparting a spin to a projectile around its longitudinal axis during shooting to stabilize the pro ...
dramatically increased the range and accuracy of the musket. Indeed, throughout its development, the rifle's history has been marked by increases in range and accuracy. From the Minié rifle and beyond, the rifle has become ever more potent at long-range strikes.
In recent decades, large-caliber anti-materiel rifles, typically firing between 12.7 mm and 20 mm caliber cartridges, have been developed. The US Barrett M82A1
The Barrett M82 (standardized by the U.S. military as the M107) is a Recoil operation, recoil-operated, semi-automatic rifle, semi-automatic anti-materiel rifle developed by the American company Barrett Firearms Manufacturing.
Also called the ...
is probably the best-known such rifle. A second example is the AX50 by Accuracy International. These weapons are typically used to strike critical, vulnerable targets such as computerized command and control vehicles, radio trucks, radar antennae, vehicle engine blocks and the jet engines of enemy aircraft. Anti-materiel rifles can be used against human targets, but the much higher weight of rifle and ammunition, and the massive recoil and muzzle blast, usually make them less than practical for such use. The Barrett M82 is designed with a maximum effective range of , although it has a confirmed kill distance of in Afghanistan during Operation Anaconda in 2002. The record for the longest confirmed kill shot stands at , set by an unnamed soldier with Canada's elite special operations unit Joint Task Force 2 using a McMillan TAC-50 sniper rifle.
Bullet rotational speed (RPM)
Bullets leaving a rifled barrel can spin at a rotational speed of over 100,000 revolutions per minute (rpm) (or over about 1.67 kilohertz, since 1 RPM = 1/60 Hz). The rotational speed depends both on themuzzle velocity
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile (bullet, pellet, slug, ball/shots or shell) with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel (i.e. the muzzle). Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately to i ...
of the bullet and the pitch of the rifling. Excessive rotational speed can exceed the bullet's designed limits and the inadequate centripetal force will fail to keep the bullet from disintegrating in a radial fashion. The rotational speed of the bullet can be calculated by using the formula below.
*MV / twist rate = rotational speed
Using metric units, the formula divides the number of millimeters in a meter (1000) by the barrel twist in millimeters (the length of travel along the barrel per full rotation). This number is then multiplied by the muzzle velocity in meters per second (m/s) and the number of seconds in a minute (60).
*MV (in m/s) × (1000 mm /twist) × 60 s/min = Bullet RPM
For example, using a barrel that has a twist rate of 190 mm with a muzzle velocity of 900 m/s:
*900 m/s × (1000 mm /(190 mm)) × 60 s/min = 284 210 RPM
Using imperial units, the formula divides the number of inches in a foot (12) by the rate of twist that the barrel has. This number is multiplied by the muzzle velocity (MV) and the number of seconds in a minute (60). For example, a bullet with a muzzle velocity of leaving a barrel that twists once per foot (1/12") would rotate at 180,000rpm.
*MV (in fps) × (12 in. /twist rate) × 60 s/min. = Bullet RPM
For example, using a barrel that has a twist rate of 1 turn in 8" with a muzzle velocity of 3000 ft/s:
*3000 fps × (12"/(8"/rotation)) × 60 s/min. = 270,000 RPM
Caliber
Rifles may be chambered in a variety ofcaliber
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge (firearms) , bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the f ...
s (bullet or barrel diameters), from as low as 4.4 mm ( .17 inch) varmint calibers to as high as 20 mm
20 mm caliber is a specific size of popular autocannon ammunition. It is typically used to distinguish smaller-caliber weapons, commonly called "guns", from larger-caliber "cannons" (e.g. machine gun vs. autocannon). All 20 mm cartridges ha ...
(.80 caliber) in the case of the largest anti-tank rifles. The term caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge (firearms) , bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the f ...
essentially refers to the width of the bullet fired through a rifle's barrel. Armies have consistently attempted to find and procure the most lethal and accurate caliber for their firearms.
The standard calibers used by the world's militaries tend to follow worldwide trends. These trends have significantly changed during the centuries of firearm design and re-design. Muskets were normally chambered for large calibers, such as .50 or .59 (12.7 mm or 15 mm), with the theory that these large bullets caused the most damage.
During World War I and II, most rifles were chambered in .30 caliber (7.62 mm), a combination of power and speed. Examples would be the .303 British
The .303 British (designated as the 303 British by the C.I.P. and SAAMI) or 7.7×56mmR, is a calibre rimmed rifle cartridge. The .303 inch bore diameter is measured between rifling lands as is the common practice in Europe which follows th ...
Lee–Enfield, the American M1903 .30-06, and the German 8mm Mauser K98.
An exception was the Italian Modello 91 rifle, which used the 6.5×52mm Mannlicher–Carcano cartridge.
Detailed study of infantry combat during and after World War II revealed that most small-arms engagements occurred within 100 meters, meaning that the power and range of the traditional .30-caliber weapons (designed for engagements at 500 meters and beyond) were essentially wasted. The single greatest predictor of an individual soldier's combat effectiveness was the number of rounds he fired. Weapons designers and strategists realized that service rifles firing smaller-caliber projectiles would allow troops to carry far more ammunition for the same weight. The lower recoil and more generous magazine capacities of small-caliber weapons also allow troops a much greater volume of fire, compared to historical battle rifles. Smaller, faster traveling, less stable projectiles have also demonstrated greater terminal ballistics and therein, a greater lethality than traditional .30-caliber rounds. Most modern service rifles fire a projectile of approximately 5.56 mm. Examples of firearms in this range are the American 5.56 mm M16
The M16 rifle (officially designated Rifle, Caliber 5.56 mm, M16) is a family of military rifles adapted from the ArmaLite AR-15 rifle for the United States military. The original M16 rifle was a 5.56×45mm automatic rifle with a 20-roun ...
and the Russian 5.45×39mm
The 5.45×39mm Cartridge (firearms), cartridge is a Rim (firearms), rimless bottlenecked intermediate cartridge. It was introduced into service in 1974 by the Soviet Union for use with the new AK-74. The 5.45×39mm gradually supplemented and then ...
AK-74.
Types of rifle
By mechanism
*Air gun
An air gun or airgun is a gun that fires projectiles pneumatically with compressed air or other gases that are mechanically pressurized ''without'' involving any chemical reactions, in contrast to a firearm, which pressurizes gases ''chemica ...
** Spring-piston
*** Break barrel
*** Fixed barrel
**** Underlever
**** Sidelever
**** Overlever
** Pneumatic (internal pressure reservoir)
*** Pump pneumatic, either single-stroke or multi-stroke
*** Pre-charged pneumatic (PCP)
** Compressed gas (external pressure reservoir)
*** CO2
*** High pressure air (HPA)
* Firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
** Single-shot
*** Muzzle-loading rifle, some flintlock and mostly caplock
*** Breech-loading rifle
**** Breechblock
A breechblock (or breech block) is the part of the firearm action that closes the breech of a breech loading weapon (whether small arms or artillery) before or at the moment of firing. It seals the breech and contains the pressure generated by th ...
rifle, either trapdoor, rolling, dropping, tilting or screwed
**** Break-action
Break action is a type of firearm action in which the barrel or barrels are hinged much like a door and rotate perpendicularly to the bore axis to expose the breech and allow loading and unloading of cartridges. A separate operation may be require ...
rifle
**** Double rifle
The double rifle, also known as a double-barreled rifle, is a rifle with two barrels mounted parallel to each other. Synonymous with big game hunting found primarily in Africa and India, the double rifle is a purely sporting weapon with no militar ...
( list)
** Repeating
*** Manual
**** Revolving rifle
**** Lever-action rifle, e.g. Winchester rifle, Spencer rifle
The Spencer repeating rifles and carbines were 19th-century American lever-action firearms invented by Christopher Spencer. The Spencer was the world's first military metallic-cartridge repeating rifle, and over 200,000 examples were manufacture ...
**** Pump-action rifle, e.g. Colt Lightning Carbine
**** Bolt-action rifle
***** Turn-pull, e.g. Mauser G98, Lee-Enfield, Mosin-Nagant
***** Straight-pull, e.g. Ross rifle, K31, Mannlicher M1895, Blaser R93
The Blaser R93 is a straight-pull action precision rifle offered in a multitude of calibers and barrel lengths manufactured by the German firearms manufacturer Blaser. Designed by Blasers' designer Mr. Meinhard Zeh in 1993, it had a number ...
/ R8
**** Bolt-release rifle, also known as lever-release rifle, e.g. Verney-Carron
Verney-Carron S.A. is a French firearm manufacturing company based in Saint-Etienne, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. The company makes a wide range of hunting shotguns and rifles. In 2004, Verney-Carron purchased the traditional artisan gun making compa ...
SpeedLine
*** Self-loading
**** Semi-automatic rifle
**** Automatic rifle
***** Selective-fire rifle
By usage
* Military and law enforcement **Anti-materiel rifle
An anti-materiel rifle (AMR) is a rifle designed for use against military equipment, structures, and other hardware (materiel). Anti-materiel rifles are chambered in significantly larger calibers than conventional rifles and are employed to elimin ...
** Anti-tank rifle
**Long rifle
The long rifle, also known as the longrifle, Kentucky rifle, Pennsylvania rifle, or American longrifle, a muzzle-loading firearm used for hunting and warfare, was one of the first commonly-used rifles. The American rifle was characterized by a ...
** Personal defense weapon
**Precision rifle
*** Designated marksman rifle
***Sniper rifle
A sniper rifle is a high-precision, long-range rifle. Requirements include accuracy, reliability, mobility, concealment and optics for anti-personnel, anti-materiel and surveillance uses of the military sniper. The modern sniper rifle is a por ...
( list)
** Scout rifle
** Service rifle
*** Assault rifle ( list)
***Battle rifle
A battle rifle is a service rifle chambered to fire a fully powered cartridge.
The term "battle rifle" is a retronym created largely out of a need to better differentiate the intermediate cartridge, intermediate-powered assault rifles (e.g. the S ...
( list)
*** Carbine ( list)
* Civilian
** Hunting rifle
***Buffalo rifle
Buffalo rifle generally refers to large-calibre, generally single-shot black powder cartridge firearms which were used to hunt the American Bison to near-extinction in the late-19th Century. Three types of rifles in particular were used by profe ...
***Elephant rifle
An elephant gun is a large caliber gun, Rifling, rifled or smoothbore, originally developed for use by big-game hunters for elephant and other big game hunting, large game. Elephant guns were Gunpowder, black powder muzzle-loaders at first, th ...
*** Express rifle
** Match/target rifle
***Benchrest rifle
A benchrest rifle, also colloquially called a "rail gun", is a rifle with its barrel and action
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film ...
**Modern sporting rifle
An AR-15-style rifle is any lightweight semi-automatic rifle based on the Colt AR-15 design. The original ArmaLite AR-15 is a scaled-down derivative of Eugene Stoner's ArmaLite AR-10 design. The then Fairchild Engine and Airplane Corporation d ...
** Short-barreled rifle
**Varmint rifle
Varmint rifle is an American English term for a small-caliber precision firearm or high-powered airgun primarily used for both varmint hunting (the elimination of outdoor animals which harass properties) and pest control (the eradication of indoor ...
See also
* Advanced Combat Rifle/ Project Abakan * Antique firearms * British military rifles *Gun safety
Gun safety is the study and practice of using, transporting, storing and disposing of firearms and ammunition, including the training of gun users, the design of weapons, and formal and informal regulation of gun production, distribution, and ...
*Handgun
A handgun is a short- barrelled gun, typically a firearm, that is designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long gun (i.e. rifle, shotgun or machine gun, etc.), which needs to be held by both hands and also braced ...
*List of assault rifles
An assault rifle is a rifle that uses an intermediate cartridge, a detachable magazine, and can switch between semi-automatic/fully automatic fire. Assault rifles are currently the standard service rifles in most modern armies. Some rifles listed ...
* List of battle rifles
* List of multiple barrel rifles
* List of rifle cartridges
* List of sniper rifles
* Objective Individual Combat Weapon
* Rifle grenade
*Rifling
In firearms, rifling is machining helical grooves into the internal (bore) surface of a gun's barrel for the purpose of exerting torque and thus imparting a spin to a projectile around its longitudinal axis during shooting to stabilize the pro ...
*Rifled musket
A rifled musket, rifle musket, or rifle-musket is a type of firearm made in the mid-19th century. Originally the term referred only to muskets that had been produced as a smoothbore weapon and later had their barrels replaced with rifled barrel ...
* Service rifle
* Shooting
* Shooting at the Summer Olympics
*Shooting range
A shooting range, firing range, gun range or shooting ground is a specialized facility, sports venue, venue or playing field, field designed specifically for firearm usage qualifications, training, practice or shooting sport, competitions. So ...
*Shooting sport
Shooting sports is a group of competitive and recreational sporting activities involving proficiency tests of accuracy, precision and speed in shooting — the art of using ranged weapons, mainly small arms (firearms and airguns, in forms such ...
*Shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which usually discharges numerous small p ...
* Silencer (firearms)
* Telescopic sight
*Precision-guided firearm
Precision guided firearms (PGFs) are long-range rifle systems designed to improve the accuracy of shooting at targets at extended ranges through target tracking, heads-up display, and advanced fire control. Inspired by missile lock-on and fighter j ...
References
External links
* Mick Bennett,The Story of the Rifle
', a booklet from 1945 in
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
format
* Friedrich Engels"On Rifled Cannon"
articles from the New York ''Tribune'', April, May and June, 1860, reprinted in ''Military Affairs'' 21, no. 4 (Winter 1957) ed. Morton Borden, 193–198. {{Authority control Hunting equipment Infantry Personal weapons