Rhodium Acetate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rhodium(II) acetate is the

through the
Rhodium acetate catalyzes both two-component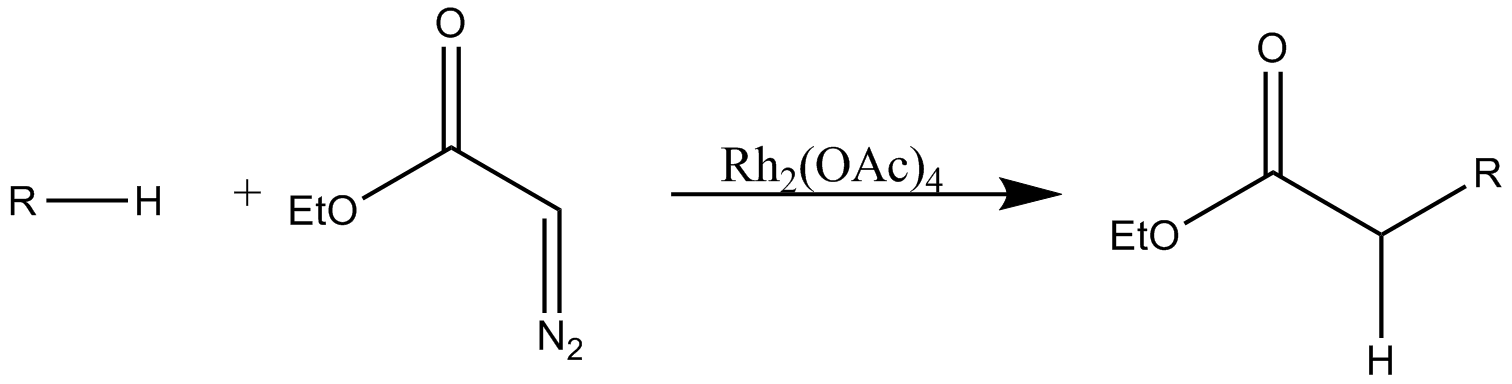
Rh(II)-catalyzed

Rh(II)
coordination compound
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many ...
with the formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwee ...
Rh2(AcO)4, where AcO− is the acetate
An acetate is a salt (chemistry), salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. Alkali metal, alkaline, Alkaline earth metal, earthy, Transition metal, metallic, nonmetallic or radical Radical (chemistry), base). "Acetate" als ...
ion (). This dark green powder is slightly soluble in polar solvents, including water. It is used as a catalyst for cyclopropanation
In organic chemistry, cyclopropanation refers to any chemical process which generates cyclopropane () rings. It is an important process in modern chemistry as many useful compounds bear this motif; for example pyrethroids and a number of quinolo ...
of alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
s. It is a widely studied example of a transition metal carboxylate complex
Transition metal carboxylate complexes are coordination complexes with carboxylate (RCO2−) ligands. Reflecting the diversity of carboxylic acids, the inventory of metal carboxylates is large. Many are useful commercially, and many have attracted ...
.
Preparation
Rhodium(II) acetate is usually prepared by the heating ofhydrated
Drinking is the act of ingesting water or other liquids into the body through the mouth, proboscis, or elsewhere. Humans drink by swallowing, completed by peristalsis in the esophagus. The physiological processes of drinking vary widely among ot ...
rhodium(III) chloride
Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)''n'', where ''n'' varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of ''n'', the material is either a den ...
in acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
(CH3COOH): Rhodium(II) acetate dimer undergoes ligand exchange
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
, the replacement of the acetate group by other carboxylate
In organic chemistry, a carboxylate is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, (or ). It is an ion with negative charge.
Carboxylate salts are salts that have the general formula , where M is a metal and ''n'' is 1, 2,...; ''carboxylat ...
s and related groups.
:Rh2(OAc)4 + 4 HO2CR → Rh2(O2CR)4 + 4 HOAc
Structure and properties
The structure of rhodium(II) acetate features a pair ofrhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element with the symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isoto ...
atoms, each with octahedral molecular geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The oc ...
, defined by four acetate oxygen atoms, water, and a Rh–Rh bond of length 2.39 Å. The water adduct
An adduct (from the Latin ''adductus'', "drawn toward" alternatively, a contraction of "addition product") is a product of a direct addition of two or more distinct molecules, resulting in a single reaction product containing all atoms of all co ...
is exchangeable, and a variety of other Lewis base
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
s bind to the axial positions. Copper(II) acetate
Copper(II) acetate, also referred to as cupric acetate, is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(OAc)2 where AcO− is acetate (). The hydrated derivative, Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2, which contains one molecule of water for each copper atom, is avail ...
and chromium(II) acetate
Chromium(II) acetate hydrate, also known as chromous acetate, is the coordination compound with the formula Cr2(CH3CO2)4(H2O)2. This formula is commonly abbreviated Cr2(OAc)4(H2O)2. This red-coloured compound features a quadruple bond. The prepara ...
adopt similar structures.
Chemical properties
The application of dirhodium tetraacetate to organic synthesis was pioneered by Teyssie and co-workers. An extensive range of reactions including insertion into bonds and thecyclopropanation
In organic chemistry, cyclopropanation refers to any chemical process which generates cyclopropane () rings. It is an important process in modern chemistry as many useful compounds bear this motif; for example pyrethroids and a number of quinolo ...
of alkenes
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
and aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to satur ...
systems. It selectively binds ribonucleosides A ribonucleoside is a type of nucleoside including ribose as a component.
One example of a ribonucleoside is cytidine
Cytidine (symbol C or Cyd) is a nucleoside molecule that is formed when cytosine is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ...
(vs. deoxynucleosides
A deoxyribonucleotide is a nucleotide that contains deoxyribose. They are the monomeric units of the informational biopolymer, deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA). Each deoxyribonucleotide comprises three parts: a deoxyribose sugar (monosaccharide), a nit ...
) by binding selectively to ribonucleosides at their 2′ and 3′ –OH groups. Rhodium(II) acetate dimer, compared to copper(II) acetate
Copper(II) acetate, also referred to as cupric acetate, is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(OAc)2 where AcO− is acetate (). The hydrated derivative, Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2, which contains one molecule of water for each copper atom, is avail ...
, is more reactive and useful in differentiating ribonucleosides and deoxynucleosides because it is soluble in aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be rep ...
solution like water whereas copper(II) acetate only dissolves in non-aqueous solution.
Selected catalytic reactions
Dirhodium tetraacetate is also used ascatalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
for insertion into C–H and X–H bonds (X = N, S, O).
#Cyclopropanation
#:
through the
decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is e ...
of diazocarbonyl compounds, the intra- and intermolecular cyclopropanation
In organic chemistry, cyclopropanation refers to any chemical process which generates cyclopropane () rings. It is an important process in modern chemistry as many useful compounds bear this motif; for example pyrethroids and a number of quinolo ...
reactions occurs.
#Aromatic cycloaddition
#:
Rhodium acetate catalyzes both two-component
cycloaddition
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more Unsaturated hydrocarbon, unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of th ...
as well as three-component 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions.
#C–H insertion
#: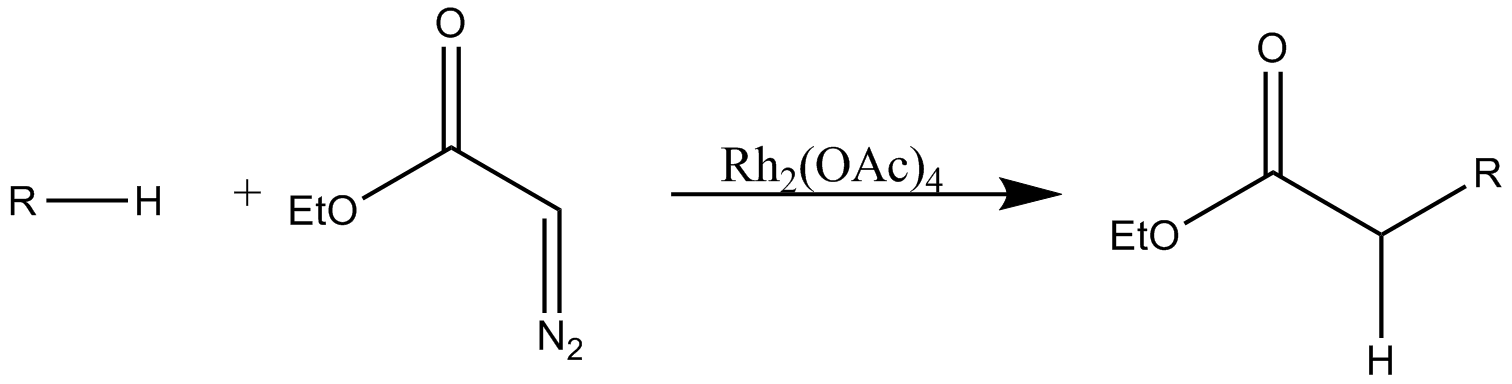
Rh(II)-catalyzed
regioselective
In chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of chemical bonding or breaking in one direction over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a strong base ...
intramolecular and regiospecific intermolecular C–H insertion into aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane, or ...
and aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to satur ...
C–H bonds is a useful method for the synthesis of a diverse range of organic compounds.
#Oxidation of alcohols
#:
Allylic
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . ...
and benzylic
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group () group.
Nomenclature
In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substi ...
alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is ...
were oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds using ''tert''-butyl hydroperoxide in stoichiometric
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equal ...
amounts and Rh2(OAc)4 as catalyst in dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with ...
at ambient temperature.
#X–H insertion (X = N, S, O)
#:
Rh(II)
carbenoid In chemistry a carbenoid is a reactive intermediate that shares reaction characteristics with a carbene. In the Simmons–Smith reaction the carbenoid intermediate is a zinc / iodine complex that takes the form of
:I-CH2-Zn-I
This complex reacts w ...
reacts with amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
s, alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is ...
or thiols
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl grou ...
to yield the product of a formal intra- or intermolecular X–H bond (X = N, S, O) insertion via the formation of an ylide An ylide or ylid () is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms h ...
intermediate.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rhodium(II) Acetate Rhodium compounds Acetates Dimers (chemistry) Chemical compounds containing metal–metal bonds