Retinal Mosaic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
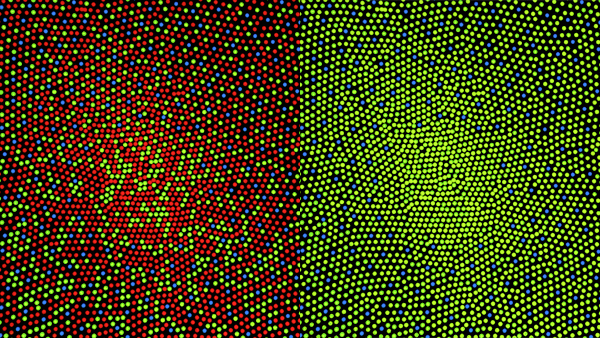 Retinal mosaic is the name given to the distribution of any particular type of
Retinal mosaic is the name given to the distribution of any particular type of
 Retinal mosaic is the name given to the distribution of any particular type of
Retinal mosaic is the name given to the distribution of any particular type of neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
across any particular layer in the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
. Typically such distributions are somewhat regular; it is thought that this is so that each part of the retina is served by each type of neuron in processing visual information.
The regularity of retinal mosaics can be quantitatively studied by modelling the mosaic as a spatial point pattern. This is done by treating each cell as a single point and using spatial statistics such as the Effective Radius, Packing Factor and Regularity Index.
Using adaptive optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical tele ...
, it is nowadays possible to image the photoreceptor mosaic (i.e. the distribution of rods and cones) in living humans, enabling the detailed study of photoreceptor density and arrangement across the retina.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 16;13(1):e0191141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191141. eCollection 2018.
In the fovea
Fovea () (Latin for "pit"; plural foveae ) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.
Human anatomy
*Fovea centralis of the retina
* Fovea buccalis or Dimple
* Fovea of the femoral head
* Trochlear fovea of the fr ...
(where photoreceptor density is highest) the spacing between adjacent receptors is about 6-8 micrometer. This corresponds to an angular resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolution. ...
of approximately 0.5 arc minute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
, effectively the upper limit of human visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
.
References
Visual system Color vision {{Neuroscience-stub