Replacement Rates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific
 The NRR is less widely used than the TFR, and the United Nations stopped reporting NRR data for member nations after 1998. But the NRR is particularly relevant where the number of male babies born is very high due to gender imbalance and
The NRR is less widely used than the TFR, and the United Nations stopped reporting NRR data for member nations after 1998. But the NRR is particularly relevant where the number of male babies born is very high due to gender imbalance and
 A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate would increase rapidly (doubling period ~ 32 years), whereas a population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration. However, it may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in
A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate would increase rapidly (doubling period ~ 32 years), whereas a population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration. However, it may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in
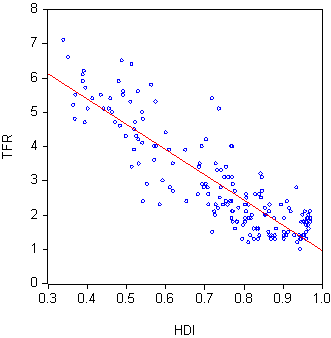 Factors generally associated with decreased fertility include rising
Factors generally associated with decreased fertility include rising  The effect of all these factors can be summarized with a plot of Total Fertility Rate against
The effect of all these factors can be summarized with a plot of Total Fertility Rate against  Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors, however, are not universal, and differ by region and social class. For instance, at a global level, religion is correlated with increased fertility, but in the West less so: Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors, however, are not universal, and differ by region and social class. For instance, at a global level, religion is correlated with increased fertility, but in the West less so: Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
 The table shows that after 1965 the Demographic Transition had spread around the world and global TFR began a long decline that continues to this day.
Global TFR today (2019) is 2.4. Because global fertility replacement rate for the contemporary period (2010–2015) has been estimated to be 2.3, humanity is therefore approaching a major milestone.
The chart shows that the decline in TFR since the 1960s has occurred in every region of the world and that the global TFR is projected to continue to decline for the remainder of this century.
The table shows that after 1965 the Demographic Transition had spread around the world and global TFR began a long decline that continues to this day.
Global TFR today (2019) is 2.4. Because global fertility replacement rate for the contemporary period (2010–2015) has been estimated to be 2.3, humanity is therefore approaching a major milestone.
The chart shows that the decline in TFR since the 1960s has occurred in every region of the world and that the global TFR is projected to continue to decline for the remainder of this century.
 Singapore, Macau, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and South Korea have lowest-low fertility, defined as TFR at or below 1.3, and are among the lowest in the world. Macau had a TFR below 1.0 in 2004. North Korea has the highest TFR in East Asia at 1.95.
Singapore, Macau, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and South Korea have lowest-low fertility, defined as TFR at or below 1.3, and are among the lowest in the world. Macau had a TFR below 1.0 in 2004. North Korea has the highest TFR in East Asia at 1.95.

 The total fertility rate in the United States after
The total fertility rate in the United States after
CIA World Factbook - Total Fertility Rate by country
eurostat - Your key to European statistics
Population Reference Bureau Glossary of Population Terms
How Fertility Changes Across Immigrant Generations
Global Total Fertility Rate
Fertility Trends, Marriage Patterns and Savant Typologies
Human Fertility Database: Collection of age specific fertility rates for some developed countries
{{DEFAULTSORT:Total Fertility Rate Human overpopulation Fertility Rates
fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were to live from birth until the end of her reproductive life.
It is obtained by summing the single-year age-specific rates at a given time. As of 2021, the total fertility rate varied from 0.81 in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eas ...
to 6.91 in Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesdeveloped countries
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
usually have a significantly lower fertility rate, generally correlated with greater wealth, education, urbanization, and other factors. Conversely, in undeveloped countries, fertility rates tend to be higher. Families desire children for their labor and as caregivers for their parents in old age. Fertility rates are also higher due to the lack of access to contraceptives, stricter adherence to traditional religious beliefs, generally lower levels of female education
Female education is a catch-all term of a complex set of issues and debates surrounding education (primary education, secondary education, tertiary education, and health education in particular) for girls and women. It is frequently called girl ...
, and lower rates of female employment.
The total fertility rate for the world today (2019) is 2.4. Global TFR has been declining rapidly since the 1960s, and some forecasters like Sanjeev Sanyal
Sanjeev Sanyal is an Indian economist and popular historian. He is a member of the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister of India, and has helped prepare six editions of the Economic Survey of India starting in 2017.
Sanyal ha ...
argue that the effective global fertility rate will fall below replacement rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
, estimated to be 2.3, in the 2020s. This would stabilize world population sometime during the period 2050–2070. This differs from projections by the United Nations which estimates that some growth in world population will continue even up to 2100. Taken together, these projections imply that the population of this planet will reach zero growth sometime in the second half of this century.
Parameter characteristics
The TFR is not based on the fertility of any real group of women since this would involve waiting until they had completed childbearing. Nor is it based on counting up the total number of children actually born over their lifetime. Instead, the TFR is based on the age-specific fertility rates of women in their "child-bearing years", which in conventional international statistical usage is ages 15–44. The TFR is, therefore, a measure of the fertility of an ''imaginary'' woman who passes through her reproductive life subject to ''all'' the age-specific fertility rates for ages 15–49 that were recorded for a given population in a given year. The TFR represents the average number of children a woman ''would'' potentially have, were she to fast-forward through all her childbearing years in a single year, under all the age-specific fertility rates for that year. In other words, this rate is the number of children a woman would have if she was subject to prevailing fertility rates at all ages from a single given year and survives throughout all her childbearing years.Related parameters
Net reproduction rate
An alternative fertility measure is the net reproduction rate (NRR), which measures the number of ''daughters'' a woman would have in her lifetime if she were subject to prevailing age-specific fertility ''and mortality'' rates in the given year. When the NRR is exactly 1, then each generation of women is exactly reproducing itself. The NRR is less widely used than the TFR, and the United Nations stopped reporting NRR data for member nations after 1998. But the NRR is particularly relevant where the number of male babies born is very high due to gender imbalance and
The NRR is less widely used than the TFR, and the United Nations stopped reporting NRR data for member nations after 1998. But the NRR is particularly relevant where the number of male babies born is very high due to gender imbalance and sex selection
Sex selection is the attempt to control the sex of the offspring to achieve a desired sex. It can be accomplished in several ways, both pre- and post-implantation of an embryo, as well as at childbirth. It has been marketed under the title family ...
. This is a significant factor in world population, due to the high level of gender imbalance in the very populous nations of China and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. The gross reproduction rate (GRR), is the same as the NRR, except that—like the TFR—it ignores life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
.
Total period fertility rate
The TFR (or TPFR—total period fertility rate) is a better index of fertility than thecrude birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
(annual number of births per thousand population) because it is independent of the age structure of the population, but it is a poorer estimate of actual completed family size than the total cohort fertility rate, which is obtained by summing the age-specific fertility rates that actually applied to each cohort as they aged through time. In particular, the TFR does not necessarily predict how many children young women now will eventually have, as their fertility rates in years to come may change from those of older women now. However, the TFR is a reasonable summary of current fertility levels.
TFR and long term population growth rate, g, are closely related. For a population structure in a steady state, growth rate equals log(TFR/2)/Xm, where Xm is the mean age for childbearing women.
Tempo effect
The TPFR (total ''period'' fertility rate) is affected by atempo effect
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
—if age of childbearing increases (and life cycle fertility is unchanged) then while the age of childbearing is increasing, TPFR will be lower (because the births are occurring later), and then the age of childbearing stops increasing, the TPFR will increase (due to the deferred births occurring in the later period) even though the life cycle fertility has been unchanged. In other words, the TPFR is a misleading measure of life cycle fertility when childbearing age is changing, due to this statistical artifact. This is a significant factor in some countries, such as the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
in the 1990s. Some measures seek to adjust for this timing effect to gain a better measure of life-cycle fertility.
Replacement rates
Replacement fertility is the total fertility rate at which women give birth to enough babies to sustain population levels, assuming that mortality rates remain constant and net migration is zero. If replacement level fertility is sustained over a sufficiently long period, each generation will exactly replace itself. The replacement fertility rate is 2.1 births per woman for most developed countries (2.1 in the UK, for example), but can be as high as 3.5 in undeveloped countries because of highermortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
s, especially child mortality. The global average for the replacement total fertility rate (eventually leading to a stable global population) for the contemporary period (2010-2015) is 2.3 children per woman.
Lowest-low fertility
The term "lowest-low fertility" is defined as TFR at or below 1.3. This is characteristic of some Eastern European, Southern European, and East Asian countries. For example, in 2001, more than half of the population of Europe lived in countries with the lowest-low TFR, although TFRs there have increased slightly since then. The lowest TFR recorded anywhere in the world in recorded history is for Xiangyang district ofJiamusi
Jiamusi (Manchu: ; formerly Kiamusze) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China. Located along the middle and lower reaches of the Songhua River, it faces Russia's Khabarovsk Krai across the Ussuri R ...
city (Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
, China) which had a TFR of 0.41. Outside China, the lowest TFR ever recorded was 0.80 for Eastern Germany in 1994. The low Eastern German value was influenced by a change to higher age at birth, with the consequence that neither older cohorts (e.g. women born until the late 1960s), who often already had children, nor younger cohorts, who were postponing childbirth, had many children during that time. The total cohort fertility rate of each age cohort
Cohort or cohortes may refer to:
* Cohort (educational group), a group of students working together through the same academic curriculum
* Cohort (floating point), a set of different encodings of the same numerical value
* Cohort (military unit ...
of women in East German did not drop as significantly.
Population-lag effect
 A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate would increase rapidly (doubling period ~ 32 years), whereas a population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration. However, it may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in
A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate would increase rapidly (doubling period ~ 32 years), whereas a population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration. However, it may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
, because the age distribution must reach equilibrium. For example, a population that has recently dropped below replacement-level fertility will continue to grow, because the recent high fertility produced large numbers of young couples who would now be in their childbearing years.
This phenomenon carries forward for several generations and is called population momentum Population momentum is a consequence of the demographic transition. Population momentum explains why a population will continue to grow even if the fertility rate declines. Population momentum occurs because it is not only the number of children per ...
, ''population inertia,'' or ''population-lag effect''. This time-lag effect is of great importance to the growth rates of human populations.
TFR (net) and long-term population growth rate, g, are closely related. For a population structure in a steady state and with zero migration, g equals log(TFR/2)/Xm, where Xm is mean age for childbearing women and thus P(t) = P(0)exp(gt). At the left side is shown the empirical relation between the two variables in a cross-section of countries with the most recent y-y growth rate. The parameter 1/b should be an estimate of the Xm; here equal to 1/0.02 = 50 years, way off the mark because of population momentum. E.g. for log(TFR/2) = 0, g should be exactly zero, which is seen not to be the case.
Factors affecting total fertility rate
Fertility factors are determinants of the number of children that an individual is likely to have. Fertility factors are mostly positive or negative correlations without certain causations. Factors generally associated with increased fertility include the intention to have children, very high level of gender equality,religiosity
In sociology, the concept of religiosity has proven difficult to define. The Oxford English Dictionary suggests: "Religiousness; religious feeling or belief. ..Affected or excessive religiousness". Different scholars have seen this concept as ...
, inter-generational transmission of values, marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
and cohabitation
Cohabitation is an arrangement where people who are not married, usually couples, live together. They are often involved in a romantic or sexually intimate relationship on a long-term or permanent basis. Such arrangements have become increas ...
, maternal and social support, rural residence, pro family government programs, low IQ and increased food production.income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. Fo ...
, value and attitude changes, education, female labor participation
Since the industrial revolution, participation of women in the workforce outside the home has increased in industrialized nations, with particularly large growth seen in the 20th century. Largely seen as a boon for industrial society, women in ...
, population control
Population control is the practice of artificially maintaining the size of any population. It simply refers to the act of limiting the size of an animal population so that it remains manageable, as opposed to the act of protecting a species from ...
, age, contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
, partner reluctance to having children, a low level of gender equality, and infertility. The effect of all these factors can be summarized with a plot of Total Fertility Rate against
The effect of all these factors can be summarized with a plot of Total Fertility Rate against Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
(HDI) for a sample of countries. The chart shows that the two factors are inversely correlated, that is, in general, the lower a country’s HDI the higher its fertility.
Another common way of summarizing the relationship between economic development and fertility is a plot of TFR against Per Capita GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
, a proxy for standard of living. This chart shows that Per Capita GDP is also inversely correlated with fertility.
The impact of human development on TFR can best be summarized by a quote from Karan Singh
Karan Singh (born 9 March 1931) is an Indian politician and philosopher. He is the son of the last ruling Maharaja of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, Sir Hari Singh. He was the prince regent of Jammu and Kashmir until 1952. From 1 ...
, a former minister of population in India. At a 1974 United Nations population conference in Bucharest, he said "Development is the best contraceptive."
 Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors, however, are not universal, and differ by region and social class. For instance, at a global level, religion is correlated with increased fertility, but in the West less so: Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors, however, are not universal, and differ by region and social class. For instance, at a global level, religion is correlated with increased fertility, but in the West less so: Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
National efforts to increase or decrease fertility
Governments have often set population targets, to either increase or decrease the total fertility rate; or to have certain ethnic or socioeconomic groups have a lower or higher fertility rate. Often such policies have been interventionist, and abusive. The most notoriousnatalist
Natalism (also called pronatalism or the pro-birth position) is an ideology that promotes the reproduction of human life as the preeminent objective of being human.
Compare:
The term, as it relates to the belief itself, comes from the French wor ...
policies of the 20th century include those in communist Romania and communist Albania
The People's Socialist Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika Popullore Socialiste e Shqipërisë, links=no) was the Marxist–Leninist one party state that existed in Albania from 1946 to 1992 (the official name of the country was the People's R ...
, under Nicolae Ceaușescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu ( , ; – 25 December 1989) was a Romanian communist politician and dictator. He was the general secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 to 1989, and the second and last Communist leader of Romania. He ...
and Enver Hoxha respectively. The policy of Romania (1967–1990) was very aggressive, including outlawing abortion and contraception, routine pregnancy tests for women, taxes on childlessness, and legal discrimination against childless people; and resulted in large numbers of children put into Romanian orphanages
Orphanhood in Romania became prevalent as a consequence of the Socialist Republic of Romania's pro-natality policy under Nicolae Ceaușescu. Its effectiveness led to an increase in birth rates at the expense of adequate family planning and reproduc ...
by parents who couldn't cope with raising them, street children in the 1990s (when many orphanages were closed and the children ended up on the streets), overcrowding in homes and schools, and over 9,000 women who died due to illegal abortion
Abortion laws vary widely among countries and territories, and have changed over time. Such laws range from abortion being freely available on request, to regulation or restrictions of various kinds, to outright prohibition in all circumstances ...
s.Kligman, Gail. "Political Demography: The Banning of Abortion in Ceausescu's Romania". In Ginsburg, Faye D.; Rapp, Rayna, eds. ''Conceiving the New World Order: The Global Politics of Reproduction.'' Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1995 :234–255. Unique Identifier : AIDSLINE KIE/49442. Conversely, in China the government sought to lower the fertility rate, and, as such, enacted the one-child policy
The term one-child policy () refers to a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1980 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child. That initiative was part of a much br ...
(1978–2015), which included abuses such as forced abortions.
Some governments have sought to regulate which groups of society could reproduce through eugenic
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or ...
policies of forced sterilizations of 'undesirable' population groups. Such policies were carried out against ethnic minorities in Europe and North America in the first half of the 20th century, and more recently in Latin America against the Indigenous population in the 1990s; in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, President Alberto Fujimori
Alberto Kenya Fujimori Inomoto ( or ; born 28 July 1938) is a Peruvian politician, professor and former engineer who was President of Peru from 28 July 1990 until 22 November 2000. Frequently described as a dictator,
*
*
*
*
*
*
he remains a ...
(in office from 1990 to 2000) has been accused of genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Lat ...
and crimes against humanity as a result of a sterilization program put in place by his administration targeting indigenous people (mainly the Quechuas and the Aymaras). Within these historical contexts, the notion of reproductive rights
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to reproduction and reproductive health that vary amongst countries around the world. The World Health Organization defines reproductive rights as follows:
Reproductive rights rest o ...
has developed. Such rights are based on the concept that each person freely decides if, when, and how many children to have - not the state or church. According to the OHCHR
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, commonly known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) or the United Nations Human Rights Office, is a department of the Secretariat of the United Nat ...
reproductive rights "rest on the recognition of the basic rights of all couples and individuals to decide freely and responsibly the number, spacing and timing of their children and to have the information and means to do so, and the right to attain the highest standard of sexual and reproductive health. It also includes the right to make decisions concerning reproduction free of discrimination, coercion and violence, as expressed in human rights documents".
History of total fertility rate and projections for the future
From around 10,000 BC to the beginning of the Industrial Revolution fertility rates around the world were high by today's standards, but the onset of the Industrial Revolution, around 1800, brought about what has come to be called the Demographic Transition, and TFR began a long-term decline in almost every region of the world, a decline that continues to this day.Before 1800
Because all nations before theIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
were caught in what is now labeled the "Malthusian Trap
Malthusianism is the idea that population growth is potentially exponential while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of triggering a population die off. This event, ...
", improvements in standards of living could only be achieved by reductions in population growth through either increases in mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
s (via wars, plagues, famines, etc) or reductions in birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
s. However, at the same time, other realities such as child mortality, that could reach 50%, and the need to produce workers, male heirs, and old-age care givers required fertility rates to be high by today’s standards.
For example, fertility rates in Europe in the years before 1800 ranged from 4.5 (Scandinavia) to 6.2 (Belgium). The Total Fertility Rate in America in 1800 was 7.0. Fertility rates in Asia during this period were similar to those in Europe. In spite of these high fertility rates, global population growth was still very slow, about 0.04% per year, mostly due to high mortality rates and the equally slow growth in the production of food.
1800 to 1950
After 1800 the Industrial Revolution got underway in some countries, particularly Great Britain, other countries in Europe, and the United States, and they underwent the beginnings of what is now called theDemographic Transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to l ...
. Stage two of this process fueled a steady reduction in mortality rates due to, for example, improvements in public sanitation, personal hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
and the food supply
Food security speaks to the availability of food in a country (or geography) and the ability of individuals within that country (geography) to access, afford, and source adequate foodstuffs. According to the United Nations' Committee on World Fo ...
(that, for example, reduced the number of famines).
These reductions in mortality rates, particularly reductions in child mortality that increased the fraction of children surviving, plus other major societal changes such as urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
, then led to stage three of the Demographic Transition and a reduction in fertility rates because there was simply no longer a need to birth so many children.
The example from the US of the correlation between child mortality and the fertility rate is illustrative. In 1800 child mortality in the US was 33%. That is, one third of all children born would die before their fifth birthday. The Total Fertility Rate in 1800 was 7.0, meaning that the average woman would bear seven children during her lifetime. One hundred years later, in 1900, child mortality in the US had declined to 23%, a reduction of almost one third, and TFR had declined to 3.9, a reduction of 44%. By 1950, just fifty years later, child mortality had declined dramatically to 4%, a reduction of 84%, and TFR had declined to 3.2. By 2018 child mortality had declined further to 0.6% and TFR had declined further to 1.9, below replacement level.
1950 to the present and projections
 The table shows that after 1965 the Demographic Transition had spread around the world and global TFR began a long decline that continues to this day.
Global TFR today (2019) is 2.4. Because global fertility replacement rate for the contemporary period (2010–2015) has been estimated to be 2.3, humanity is therefore approaching a major milestone.
The chart shows that the decline in TFR since the 1960s has occurred in every region of the world and that the global TFR is projected to continue to decline for the remainder of this century.
The table shows that after 1965 the Demographic Transition had spread around the world and global TFR began a long decline that continues to this day.
Global TFR today (2019) is 2.4. Because global fertility replacement rate for the contemporary period (2010–2015) has been estimated to be 2.3, humanity is therefore approaching a major milestone.
The chart shows that the decline in TFR since the 1960s has occurred in every region of the world and that the global TFR is projected to continue to decline for the remainder of this century.
Total fertility rate by region
The United Nations Population Division divides the world into six geographic regions. The table below shows the estimated TFR for each.Africa
This region has a TFR of 4.4, the highest in the world.Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesAngola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
, Congo, Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mal ...
, and Chad are the highest. The most populous country in Africa, Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, had an estimated TFR of 4.7 in 2021. The second most populous country, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, had an estimated TFR of 4.1 in 2021.
The poverty of the region, and the high maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
and infant mortality had led to calls from WHO of family planning and encouragement of smaller families.
South Asia
India
The Indian fertility rate has declined significantly over the early 21st century. The Indian TFR declined from 5.2 in 1971 to 2.2 in 2018. According to recent surveys, TFR in India has further declined to 2.0 in 2019-2020, marking the first time it has gone below replacement level.Bangladesh
The fertility rate fell from 6.9 during the years 1970–1975 to 2.0 in 2020, an interval of about 47 years, or a little more than one generation.East Asia
 Singapore, Macau, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and South Korea have lowest-low fertility, defined as TFR at or below 1.3, and are among the lowest in the world. Macau had a TFR below 1.0 in 2004. North Korea has the highest TFR in East Asia at 1.95.
Singapore, Macau, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and South Korea have lowest-low fertility, defined as TFR at or below 1.3, and are among the lowest in the world. Macau had a TFR below 1.0 in 2004. North Korea has the highest TFR in East Asia at 1.95.
China
The TFR of China was 1.15 in 2021. China implemented theone-child policy
The term one-child policy () refers to a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1980 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child. That initiative was part of a much br ...
in 1979 as a drastic population planning measure to control the ever-growing population at the time. In 2015, the policy was replaced with two-child policy as China's population is aging faster than almost any other country in modern history.
Japan
Japan had a TFR of 1.4 in 2021. Japan's population is rapidly aging due to both a long life expectancy and a low birth rate. The total population is shrinking, losing 430,000 in 2018 to a total of 126.4 million. Hong Kong and Singapore mitigate this through immigrant workers, but in Japan, a serious demographic imbalance has developed, partly due to limitedimmigration to Japan
According to the Japanese Ministry of Justice, the number of foreign residents in Japan has steadily increased in the post Second World War period, and the number of foreign residents (excluding illegal immigrants and short-term foreign visitor ...
.
South Korea
In South Korea, a low birthrate is one of its most urgent socio-economic challenges. Rising housing expenses, shrinking job opportunities for younger generations, insufficient support to families with newborns either from the government or employers are among the major explanations for its crawling TFR, which fell to 0.92 in 2019. Koreans are yet to find viable solutions to make the birthrate rebound, even after trying out dozens of programs over a decade, including subsidizing rearing expenses, giving priorities for public rental housing to couples with multiple children, funding day care centers, reserving seats in public transportation for pregnant women, and so on. In the past 20 years, South Korea has recorded some of the lowest fertility and marriage levels in the world. As of 2021, South Korea is the country with the world’s lowest total fertility rate at 0.81. The TFR of the capital Seoul was 0.63 in 2021.West Asia
In 2019, the TFR of Turkey reached 1.88. In theIranian calendar
The Iranian calendars or Iranian chronology ( fa, گاهشماری ایرانی, ) are a succession of calendars invented or used for over two millennia in Iran, also known as Persia. One of the longest chronological records in human history, ...
year (March 2019 – March 2020), Iran's total fertility rate fell to 1.8.
Europe
The average total fertility rate in theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
(EU-27) is calculated at 1.55 children per woman in 2018. France had the highest TFR in 2018 among EU countries at 1.88, followed by Romania and Sweden (1.76), Ireland (1.75) and Denmark (1.73). Malta had the lowest TFR in 2018 among EU countries at 1.23. Other southern European countries also had very low TFR (Portugal 1.38, Cyprus, 1.32, Greece 1.35, Spain 1.26, and Italy 1.29). The United Kingdom had a TFR of 1.53 in 2021. According to 2021 estimates for the non-EU European post-Soviet states group, Russia had a TFR of 1.61, Moldova 1.57, Ukraine 1.55, and Belarus 1.49. Bosnia and Herzegovina had the lowest estimated TFR in Europe in 2018, at 1.31.
Emigration of young adults from Eastern Europe to the West aggravates the demographic problems of those countries. People from countries such as Ukraine, Moldova, Romania, and Bulgaria are particularly moving abroad.
Latin America and Caribbean
The TFR of Brazil, the most populous country in the region, was estimated at 1.73 in 2021. The second most populous country, Mexico, had an estimated TFR of 2.17. The next most populous four countries in the region had estimated TFRs of between 1.9 and 2.3 in 2018, including Colombia (2.14), Argentina (2.2), Peru (2.0), and Venezuela (2.2). Guatemala had the highest estimated TFR in the region at 2.7 in 2018; and Puerto Rico the lowest at 1.21.North America
United States
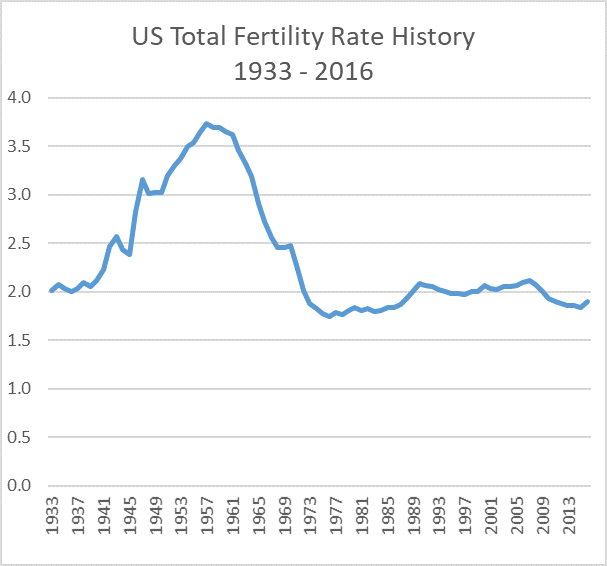
 The total fertility rate in the United States after
The total fertility rate in the United States after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
peaked at about 3.8 children per woman in the late 1950s, dropped to below replacement in the early 70s, and by 1999 was at 2 children. Currently, the fertility is below replacement among those native born, and above replacement among immigrant families, most of whom come to the United States from countries with higher fertility. However, the fertility rate of immigrants to the United States has been found to decrease sharply in the second generation, correlating with improved education and income. In 2021, U.S. TFR was 1.84, ranging between over 2 in some states and under 1.6 in others.
Canada
The TFR of Canada was 1.4 in 2020.See also
*Birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
* Fertility and intelligence
* Income and fertility
Income and fertility is the association between monetary gain on one hand, and the tendency to produce offspring on the other. There is generally an inverse correlation between income and the total fertility rate within and between nations. The h ...
* List of countries by past fertility rate
* List of sovereign states and dependencies by total fertility rate
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
* Sub-replacement fertility
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
* Zero population growth
Zero population growth, sometimes abbreviated ZPG, is a condition of demographic balance where the number of people in a specified population neither grows nor declines; that is, the number of births plus in-migrants equals the number of death ...
References
Further reading
*External links
CIA World Factbook - Total Fertility Rate by country
eurostat - Your key to European statistics
Population Reference Bureau Glossary of Population Terms
How Fertility Changes Across Immigrant Generations
Global Total Fertility Rate
Fertility Trends, Marriage Patterns and Savant Typologies
Human Fertility Database: Collection of age specific fertility rates for some developed countries
{{DEFAULTSORT:Total Fertility Rate Human overpopulation Fertility Rates