replacement rate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific
 A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period, without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate, would increase rapidly, doubling period ≈32 years. A population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration.
It may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in
A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period, without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate, would increase rapidly, doubling period ≈32 years. A population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration.
It may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in
 Fertility factors are determinants of the number of children that an individual is likely to have. Fertility factors are mostly positive or negative correlations without certain causations.
Factors generally associated with increased fertility include the intention to have children, very high level of gender inequality, inter-generational transmission of values,
Fertility factors are determinants of the number of children that an individual is likely to have. Fertility factors are mostly positive or negative correlations without certain causations.
Factors generally associated with increased fertility include the intention to have children, very high level of gender inequality, inter-generational transmission of values,  Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors may differ by region and social class. For instance, Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors may differ by region and social class. For instance, Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
 The United Nations Population Division divides the world into six geographical regions. The table below shows the estimated TFR for each region.
In 2013, the TFR of
The United Nations Population Division divides the world into six geographical regions. The table below shows the estimated TFR for each region.
In 2013, the TFR of 

CIA World Factbook - Total Fertility Rate by country
eurostat - Your key to European statistics
Population Reference Bureau Glossary of Population Terms
How Fertility Changes Across Immigrant Generations
Fertility Trends, Marriage Patterns and Savant Typologies
Human Fertility Database: Collection of age specific fertility rates for some developed countries
{{DEFAULTSORT:Total Fertility Rate Human overpopulation Fertility Rates
fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were to live from birth until the end of their reproductive life.
As of 2023, the total fertility rate varied widely across the world, from 0.7 in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
, to 6.1 in Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
. Among sovereign countries that were not city states or had a very small number of inhabitants, in 2024 the following countries had a TFR of 1.0 or lower: South Korea, Taiwan, and Ukraine; the following countries had a TFR of 1.2 or lower: Chile, China, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, Malta, Poland, and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
.
Fertility tends to be inversely correlated with levels of economic development. Historically, developed countries
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
have significantly lower fertility rates, generally correlated with greater wealth, education, urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, and other factors. Conversely, in least developed countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed b ...
, fertility rates tend to be higher. Families desire children for their labor and as caregivers for their parents in old age. Fertility rates are also higher due to the lack of access to contraceptives
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
, generally lower levels of female education
Female education is a catch-all term for a complex set of issues and debates surrounding education (primary education, secondary education, tertiary education, and health education in particular) for girls and women. It is frequently called girls ...
, and lower rates of female employment.
From antiquity to the beginning of the industrial revolution, around the year 1800, total fertility rates of 4.5 to 7.5 were common around the world. 76-77, After this TFR declined only slightly and up until the 1960s the global average TFR was still 5. Since then, global average TFR has dropped steadily to less than half that number, 2.3 births per woman in 2023.
The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
predicts that global fertility will continue to decline for the remainder of this century and reach a below-replacement level of 1.8 by 2100, and that world population
In demographics of the world, world demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently alive. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded eight billion in mid-November 2022. It took around 300,000 years of h ...
will peak in 2084.
Parameter characteristics
The Total Fertility Rate (TFR) is not based on the actual fertility of a specific group of women, as that would require waiting until they have completed childbearing. It also does not involve counting the total number of children born over their lifetime. Instead, the TFR is based on the age-specific fertility rates of women in their "child-bearing years," typically considered to be ages 15–44 in international statistical usage. The TFR is a measure of the fertility of an imaginary woman who experiences the age-specific fertility rates for ages 15–49 that were recorded for a specific population in a given year. It represents the average number of children a woman would potentially have if she were to go through all her childbearing years in a single year, subject to the age-specific fertility rates for that year. In simpler terms, the TFR is the number of children a woman would have if she were to experience the prevailing fertility rates at all ages from a single given year and survived throughout her childbearing years.Related parameters
Net reproduction rate
An alternative measure of fertility is the net reproduction rate (NRR), which calculates the number of daughters a female would have in her lifetime if she were subject to prevailing age-specific fertility and mortality rates in a given year. When the NRR is exactly 1, each generation of females is precisely replacing itself. The NRR is not as commonly used as the TFR, but it is particularly relevant in cases where the number of male babies born is very high due to gender imbalance andsex selection
Sex selection is the attempt to control the sex of the offspring to achieve a desired sex. It can be accomplished in several ways, both pre- and post-implantation of an embryo, as well as at childbirth. It has been marketed under the title family ...
. This is a significant consideration in world population dynamics, especially given the high level of gender imbalance in the heavily populated nations of China and India. The gross reproduction rate (GRR) is the same as the NRR, except that, like the TFR, it disregards life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
.
Total period fertility rate
The TFR, sometimes called TPFR—total period fertility rate, is a better index of fertility than thecrude birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration syste ...
(annual number of births per thousand population) because it is independent of the age structure of the population, but it is a poorer estimate of actual completed family size than the total cohort fertility rate, which is obtained by summing the age-specific fertility rates that actually applied to each cohort as they aged through time.
In particular, the TFR does not necessarily predict how many children young women now will eventually have, as their fertility rates in years to come may change from those of older women now. However, the TFR is a reasonable summary of current fertility levels. TFR and long term population growth rate, ''g'', are closely related. For a population structure in a steady state, growth rate equals , where is the mean age for childbearing women.
Tempo effect
The TPFR (total ''period'' fertility rate) is affected by atempo effect
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
—if age of childbearing increases, and life cycle fertility is unchanged, then while the age of childbearing is increasing, TPFR will be lower, because the births are occurring later, and then the age of childbearing stops increasing, the TPFR will increase, due to the deferred births occurring in the later period, even though the life cycle fertility has been unchanged. In other words, the TPFR is a misleading measure of life cycle fertility when childbearing age is changing, due to this statistical artifact. This is a significant factor in some countries, such as the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
in the 1990s. Some measures seek to adjust for this timing effect to gain a better measure of life-cycle fertility.
Replacement rates
Replacement fertility is the total fertility rate at which women give birth to enough babies to sustain population levels, assuming that mortality rates remain constant and net migration is zero. If replacement level fertility is sustained over a sufficiently long period, each generation will exactly replace itself. In 2003, the replacement fertility rate was 2.1 births per female for most developed countries (2.1 in the UK, for example), but could be as high as 3.5 in undeveloped countries because of highermortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
s, especially child mortality
Child mortality is the death of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate (also under-five mortality rate) refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It encompa ...
. The global average for the replacement total fertility rate, eventually leading to a stable global population, for 2010–2015, was 2.3 children per female.
Lowest-low fertility
The term ''lowest-low fertility'' is defined as a TFR at or below 1.3. Lowest-low fertility is found almost exclusively withinEast Asian
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
countries and Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, C ...
an countries. The East Asian American community in the United States also exhibits lowest-low fertility. At one point in the late 20th century and early 21st century this was also observed in Eastern and Southern Europe. However, the fertility rate then began to rise in most countries of Europe. Since the 2020s, however, TFR are falling again: in 2023, Spain's TFR fell to 1.19, and Italy's TFR fell to 1.2 children per woman. In Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, the TFR in 2023 fell to its lowest ever recorded level, at 1.26 children per woman, with Statistics Canada reporting that Canada "has now joined the group of ‘lowest-low’ fertility countries".
The lowest TFR recorded anywhere in the world in recorded history, is for the Xiangyang district of Jiamusi
Jiamusi (Manchu: ; formerly Kiamusze) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China. Located along the middle and lower reaches of the Songhua River, it faces Russia's Khabarovsk Krai across the Ussuri ...
city (Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang is a province in northeast China. It is the northernmost and easternmost province of the country and contains China's northernmost point (in Mohe City along the Amur) and easternmost point (at the confluence of the Amur and Us ...
, China) which had a TFR of 0.41 in 2000. In 2023, South Korea's TFR was 0.72 the world's lowest for that year.
Outside Asia, the lowest TFR ever recorded was 0.80 for Eastern Germany in 1994. The low Eastern German value was influenced by a change to higher maternal age at birth, with the consequence that neither older cohorts (e.g. women born until the late 1960s), who often already had children, nor younger cohorts, who were postponing childbirth, had many children during that time. The total cohort fertility rate of each age cohort of women in East Germany did not drop as significantly.
Population-lag effect
 A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period, without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate, would increase rapidly, doubling period ≈32 years. A population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration.
It may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in
A population that maintained a TFR of 3.8 over an extended period, without a correspondingly high death or emigration rate, would increase rapidly, doubling period ≈32 years. A population that maintained a TFR of 2.0 over a long time would decrease, unless it had a large enough immigration.
It may take several generations for a change in the total fertility rate to be reflected in birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
, because the age distribution must reach equilibrium. For example, a population that has recently dropped below replacement-level fertility will continue to grow, because the recent high fertility produced large numbers of young couples, who would now be in their childbearing years.
This phenomenon carries forward for several generations and is called population momentum
Population momentum or demographic inertia is the tendency of the Birth rate, raw birth rate to rise as a result of past high Total fertility rate, fertility rates, even after fertility rates have fallen, or vice-versa. This occurs because a curren ...
, ''population inertia,'' or ''population-lag effect''. This time-lag effect is of great importance to the growth rates of human populations.
TFR (net) and long-term population growth rate, g, are closely related. For a population structure in a steady state and with zero migration, , where is mean age for childbearing women and thus . At the left side is shown the empirical relation between the two variables in a cross-section of countries with the most recent y-y growth rate.
The parameter should be an estimate of the ; here equal to years, way off the mark because of population momentum. E.g. for , g should be exactly zero, which is seen not to be the case.
Influencing factors
 Fertility factors are determinants of the number of children that an individual is likely to have. Fertility factors are mostly positive or negative correlations without certain causations.
Factors generally associated with increased fertility include the intention to have children, very high level of gender inequality, inter-generational transmission of values,
Fertility factors are determinants of the number of children that an individual is likely to have. Fertility factors are mostly positive or negative correlations without certain causations.
Factors generally associated with increased fertility include the intention to have children, very high level of gender inequality, inter-generational transmission of values, marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognised union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children (if any), and b ...
and cohabitation
Cohabitation is an arrangement where people who are not legally married live together as a couple. They are often involved in a Romance (love), romantic or Sexual intercourse, sexually intimate relationship on a long-term or permanent basis. ...
, maternal and social support, rural residence, pro family government programs, low IQ and increased food production.
Factors generally associated with decreased fertility include rising income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. F ...
, value and attitude changes, education, female labor participation, population control, age, contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
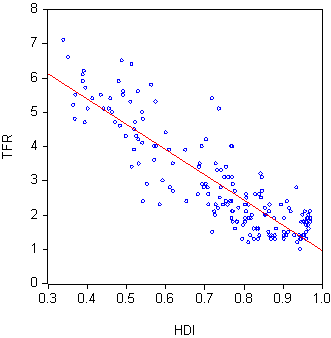
, partner reluctance to having children, a low level of gender inequality, and infertility. The effect of all these factors can be summarized with a plot of total fertility rate against Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
(HDI) for a sample of countries. The chart shows that the two factors are inversely correlated, that is, in general, the lower a country's HDI the higher its fertility.
Another common way of summarizing the relationship between economic development and fertility is a plot of TFR against per capita GDP, a proxy for standard of living. This chart shows that per capita GDP is also inversely correlated with fertility.
The impact of human development on TFR can best be summarized by a quote from Karan Singh, a former minister of population in India. At a 1974 United Nations population conference in Bucharest, he said "Development is the best contraceptive
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
."
 Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors may differ by region and social class. For instance, Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
Wealthy countries, those with high per capita GDP, usually have a lower fertility rate than poor countries, those with low per capita GDP. This may seem counter-intuitive. The inverse relationship between income and fertility has been termed a '' demographic-economic paradox'' because evolutionary biology suggests that greater means should enable the production of more offspring, not fewer.
Many of these factors may differ by region and social class. For instance, Scandinavian countries and France are among the least religious in the EU, but have the highest TFR, while the opposite is true about Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, Poland and Spain.
National efforts to increase or decrease fertility
Governments have often set population targets, to either increase or decrease the total fertility rate, or to have certain ethnic or socioeconomic groups have a lower or higher fertility rate. Often such policies have been interventionist, and abusive. The most notorious natalist policies of the 20th century include those incommunist Romania
The Socialist Republic of Romania (, RSR) was a Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist One-party state, one-party socialist state that existed officially in Romania from 1947 to 1989 (see Revolutions of 1989). From 1947 to 1965, the state was ...
and communist Albania
The People's Socialist Republic of Albania, () was the Marxist-Leninist state that existed in Albania from 10 January 1946 to the 29 April 1991. Originally founded as the People's Republic of Albania from 1946 to 1976, it was governed by the Pa ...
, under Nicolae Ceaușescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu ( ; ; – 25 December 1989) was a Romanian politician who was the second and last Communism, communist leader of Socialist Romania, Romania, serving as the general secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 u ...
and Enver Hoxha
Enver Halil Hoxha ( , ; ; 16 October 190811 April 1985) was an Albanian communist revolutionary and politician who was the leader of People's Socialist Republic of Albania, Albania from 1944 until his death in 1985. He was the Secretary (titl ...
respectively.
The natalist policy in Romania between 1967 and 1989 was very aggressive, including outlawing abortion and contraception, routine pregnancy tests for women, taxes on childlessness, and legal discrimination against childless people. It resulted in large numbers of children put into Romanian orphanages by parents who could not cope with raising them, street children in the 1990s, when many orphanages were closed and the children ended up on the streets, overcrowding
Overcrowding or crowding is the condition where more people are located within a given space than is considered tolerable from a safety and health perspective. Safety and health perspectives depend on current environments and on local cultural ...
in homes and schools, and over 9,000 women who died due to illegal abortions.Kligman, Gail. "Political Demography: The Banning of Abortion in Ceausescu's Romania". In Ginsburg, Faye D.; Rapp, Rayna, eds. ''Conceiving the New World Order: The Global Politics of Reproduction.'' Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1995 :234–255. Unique Identifier : AIDSLINE KIE/49442.
Conversely, in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
the government sought to lower the fertility rate, and, as such, enacted the one-child policy
The one-child policy ( zh, c=一孩政策, p=yī hái zhèngcè) was a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1979 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child. The progr ...
(1978–2015), which included abuses such as forced abortion
Forced abortion is a form of reproductive coercion that refers to the act of compelling a woman to undergo termination of a pregnancy against her will or without explicit consent. Forced abortion may also be defined as coerced abortion, and may o ...
s. In India, during the national emergency of 1975, a massive compulsory sterilization
Compulsory sterilization, also known as forced or coerced sterilization, refers to any government-mandated program to involuntarily sterilize a specific group of people. Sterilization removes a person's capacity to reproduce, and is usually do ...
drive was carried out in India, but it is considered to be a failure and is criticized for being an abuse of power.
Some governments have sought to regulate which groups of society could reproduce through eugenic policies, including forced sterilizations of population groups they considered undesirable. Such policies were carried out against ethnic minorities in Europe and North America in the first half of the 20th century, and more recently in Latin America against the Indigenous population in the 1990s; in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, former President Alberto Fujimori has been accused of genocide
Genocide is violence that targets individuals because of their membership of a group and aims at the destruction of a people. Raphael Lemkin, who first coined the term, defined genocide as "the destruction of a nation or of an ethnic group" by ...
and crimes against humanity
Crimes against humanity are certain serious crimes committed as part of a large-scale attack against civilians. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity can be committed during both peace and war and against a state's own nationals as well as ...
as a result of a sterilization program put in place by his administration targeting indigenous people (mainly the Quechua and Aymara people).
Within these historical contexts, the notion of reproductive rights
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to human reproduction, reproduction and reproductive health that vary amongst countries around the world. The World Health Organization defines reproductive rights:
Reproductive rights ...
has developed. Such rights are based on the concept that each person freely decides if, when, and how many children to have - not the state or religion. According to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) is a department of the United Nations Secretariat that works to promote and protect human rights that are guaranteed under international law and stipulated in the Univers ...
, reproductive rights "rest on the recognition of the basic rights of all couples and individuals to decide freely and responsibly the number, spacing and timing of their children and to have the information and means to do so, and the right to attain the highest standard of sexual and reproductive health. It also includes the right to make decisions concerning reproduction free of discrimination, coercion and violence, as expressed in human rights documents".
History and future projections
From around 10,000 BC to the beginning of theIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, fertility rates around the world were high by 21st-century standards, ranging from 4.5 to 7.5 children per woman.76-77,. The onset of the Industrial Revolution around the year 1800 brought about what has come to be called the demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory in the Social science, social sciences referring to the historical shift from high birth rates and high Mortality rate, death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as societi ...
. This eventually led to a long-term decline in TFR in every region of the world that has continued in the 21st century.
Before 1800
During this period fertility rates of 4.5 to 7.5 were common around the world. 76-77Child mortality
Child mortality is the death of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate (also under-five mortality rate) refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It encompa ...
could reach 50% and that plus the need to produce workers, male heirs, and old-age caregivers required a high fertility rate by 21st-century standards. To produce two adult children in this high mortality environment required at least four or more births. For example, fertility rates in Western Europe before 1800 ranged from 4.5 in Scandinavia to 6.2 in Belgium. In 1800, the TFR in the United States was 7.0. Fertility rates in East Asia during this period were similar to those in Europe. Fertility rates in Roman Egypt were 7.4., p77
Despite these high fertility rates, the number of surviving children per woman was always around two because of high mortality rates. As a result, global population growth was still very slow, about 0.04% per year.
1800 to 1950
After 1800, the Industrial Revolution began in some places, particularly Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, and they underwent the beginnings of what is now called the demographic transition. Stage two of this process fueled a steady reduction in mortality rates due to improvements in public sanitation, personal hygiene and thefood supply
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Similarly, househo ...
, which reduced the number of famines.
These reductions in mortality rates, particularly reductions in child mortality, that increased the fraction of children surviving, plus other major societal changes such as urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, and the increased social status of women, led to stage three of the demographic transition. There was a reduction in fertility rates, because there was simply no longer a need to birth so many children.
The example from the US of the correlation between child mortality and the fertility rate is illustrative. In 1800, child mortality in the US was 33%, meaning that one third of all children born would die before their fifth birthday. The TFR in 1800 was 7.0, meaning that the average female would bear seven children during their lifetime. In 1900, child mortality in the US had declined to 23%, a reduction of almost one third, and the TFR had declined to 3.9, a reduction of 44%. By 1950, child mortality had declined dramatically to 4%, a reduction of 84%, and the TFR declined to 3.2. By 2018, child mortality had declined further to 0.6% and the TFR declined to 1.9, below replacement level.
The chart shows that the decline in the TFR since the 1960s has occurred in every region of the world. The global TFR is projected to continue declining for the remainder of the century, and reach a below-replacement level of 1.8 by 2100.
In 2022, the global TFR was 2.3. Because the global fertility replacement rate for 2010–2015 was estimated to be 2.3, humanity has achieved or is approaching a significant milestone where the global fertility rate is equal to the global replacement rate.
The global fertility rate may have fallen below the global replacement level of 2.2 children per woman as early as 2023. Numerous developing countries have experienced an accelerated fertility decline in the 2010s and early 2020s. The average fertility rate in countries such as Thailand or Chile approached the mark of one child per woman, which triggered concerns about the rapid aging of populations worldwide.
Total fertility rates in 2050 and 2100
The table shows that after 1965, the demographic transition spread around the world, and the global TFR began a long decline that continues in the 21st century.By region
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, Latin America and the Caribbean
The term Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) is an English language, English-language acronym referring to the Latin American and the Caribbean region. The term LAC covers an extensive region, extending from The Bahamas and Mexico to Argentina ...
, and Northern America
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America, as well as the northernmost region in the Americas. The boundaries may be drawn significantly differently depending on the source of the definition. In one definition, it lies dir ...
were below the global replacement-level fertility rate of 2.1 children per female.

Africa
Africa has a TFR of 4.1, the highest in the world.Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
, Benin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ...
, DR Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, and the Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
have the highest TFR. In 2023, the most populous country in Africa, Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, had an estimated TFR of 4.57. In 2023, the second most populous African country, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, had an estimated TFR of 3.92.
The poverty of Africa, and the high maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to p ...
and infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
had led to calls from WHO for family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marit ...
, and the encouragement of smaller families.
Asia
Eastern Asia

Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
, Macau
Macau or Macao is a special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of the People's Republic of China (PRC). With a population of about people and a land area of , it is the most List of countries and dependencies by p ...
, Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
, and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
have the lowest-low fertility, defined as TFR at or below 1.3, and are among the lowest in the world. In 2004, Macau had a TFR below 1.0. In 2018, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
had the highest TFR in East Asia, at 1.95.
=China
= In 2022, China's TFR was 1.09. China implemented theone-child policy
The one-child policy ( zh, c=一孩政策, p=yī hái zhèngcè) was a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1979 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child. The progr ...
in January 1979 as a drastic population planning measure to control the ever-growing population at the time. In January 2016, the policy was replaced with the two-child policy. In July 2021, a three-child policy
The three-child policy ( zh, , p=Sānhái Zhèngcè, s=三孩政策), whereby a couple can have three children, is a Family planning policies of China, family planning policy in the China, People's Republic of China. The policy was announced on ...
was introduced, as China's population is aging faster than almost any other country in modern history.
=Japan
= In 2022, Japan had a TFR of 1.26. Japan's population is rapidly aging due to both a long life expectancy and a low birth rate. The total population is shrinking, losing 430,000 in 2018, to a total of 126.4 million. Hong Kong and Singapore mitigate this through immigrant workers. In Japan, a serious demographic imbalance has developed, partly due to limited immigration to Japan.=South Korea
= In South Korea, a low birthrate is one of its most urgent socio-economic challenges. Rising housing expenses, shrinking job opportunities for younger generations, insufficient support to families with newborns either from the government or employers are among the major explanations for its crawling TFR, which fell to 0.92 in 2019. Koreans are yet to find viable solutions to make the birthrate rebound, even after trying out dozens of programs over a decade, including subsidizing rearing expenses, giving priorities for public rental housing to couples with multiple children, funding day care centers, reserving seats in public transportation for pregnant women, and so on. In the past 20 years, South Korea has recorded some of the lowest fertility and marriage levels in the world. As of 2022, South Korea is the country with the world's lowest total fertility rate, at 0.78. In 2022, the TFR of the capital Seoul was 0.57.Southern Asia
=Bangladesh
= The fertility rate fell from 6.8 in 1970–1975, to 2.0 in 2020, an interval of about 47 years, or a little less than two generations.=India
= The Indian fertility rate has declined significantly over the early 21st century. The Indian TFR declined from 5.2 in 1971 to 2.2 in 2018. The TFR in India declined to 2.0 in 2019–2020, marking the first time it has gone below replacement level.=Iran
= In the Iranian calendar year (March 2019 – March 2020), Iran's total fertility rate fell to 1.8.Western Asia
In 2023, the TFR of Turkey reached 1.51.Europe
The average total fertility rate in theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU-27) was calculated at 1.53 children per female in 2021. In 2021, France had the highest TFR among EU countries at 1.84, followed by Czechia (1.83), Romania (1.81), Ireland (1.78) and Denmark (1.72). In 2021, Malta had the lowest TFR among the EU countries, at 1.13. Other southern European countries also had very low TFR (Portugal 1.35, Cyprus 1.39, Greece 1.43, Spain 1.19, and Italy 1.25).
In 2021, the United Kingdom had a TFR of 1.53. In 2021 estimates for the non-EU European post-Soviet states group, Russia had a TFR of 1.60, Moldova 1.59, Ukraine 1.57, and Belarus 1.52.
Emigration of young adults from Eastern Europe to the West aggravates the demographic problems of those countries. People from countries such as Bulgaria, Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine are particularly moving abroad.
Latin America and the Caribbean
In 2023, the TFR of Brazil, the most populous country in the region, was estimated at 1.75. In 2021, the second most populous country, Mexico, had an estimated TFR of 1.73. The next most populous four countries in the region had estimated TFRs of between 1.9 and 2.2 in 2023, including Colombia (1.94), Argentina (2.17), Peru (2.18), and Venezuela (2.20). Belize had the highest estimated TFR in the region at 2.59 in 2023. In 2021, Puerto Rico had the lowest, at 1.25.Northern America
Canada
In 2023, the TFR of Canada was 1.26.United States
The total fertility rate in the United States afterWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
peaked at about 3.8 children per female in the late 1950s, dropped to below replacement in the early 70s, and by 1999 was at 2 children. Currently, the fertility is below replacement among those native born, and above replacement among immigrant
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short- ...
families, most of whom come to the US from countries with higher fertility. However, the fertility rate of immigrants to the US has been found to decrease sharply in the second generation, correlating with improved education and income. In 2021, the US TFR was 1.664, ranging between over 2 in some states and under 1.6 in others.
Oceania
Australia
After World War II, Australia's TFR was approximately 3.0. In 2017, Australia's TFR was 1.74, i.e. below replacement.See also
*List of countries by total fertility rate
This is a list of all sovereign states and dependencies by total fertility rate (TFR): the expected number of children born per woman in her child-bearing years.
Methodology
The first lists show the most recent year where there is published to ...
* Birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
* Fertility and intelligence
* Income and fertility
Income and fertility is the association between monetary gain on one hand, and the tendency to produce offspring on the other. There is generally an inverse correlation between income and the total fertility rate within and between nations. The h ...
* List of countries by past fertility rate
This is a list of countries showing past fertility rate, ranging from 1950 to 2015 in five-year periods, as estimated by the 2017 revision of the World Population Prospects database by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth ...
* Sub-replacement fertility
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
* Zero population growth
Zero population growth, sometimes abbreviated ZPG, is a condition of demography, demographic balance where the number of people in a specified population neither population growth, grows nor population decline, declines; that is, the number of bi ...
References
Further reading
*External links
CIA World Factbook - Total Fertility Rate by country
eurostat - Your key to European statistics
Population Reference Bureau Glossary of Population Terms
How Fertility Changes Across Immigrant Generations
Fertility Trends, Marriage Patterns and Savant Typologies
Human Fertility Database: Collection of age specific fertility rates for some developed countries
{{DEFAULTSORT:Total Fertility Rate Human overpopulation Fertility Rates