repeating firearm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A repeating firearm or repeater is any firearm (either a

 A revolver cannon is a large-caliber gun (
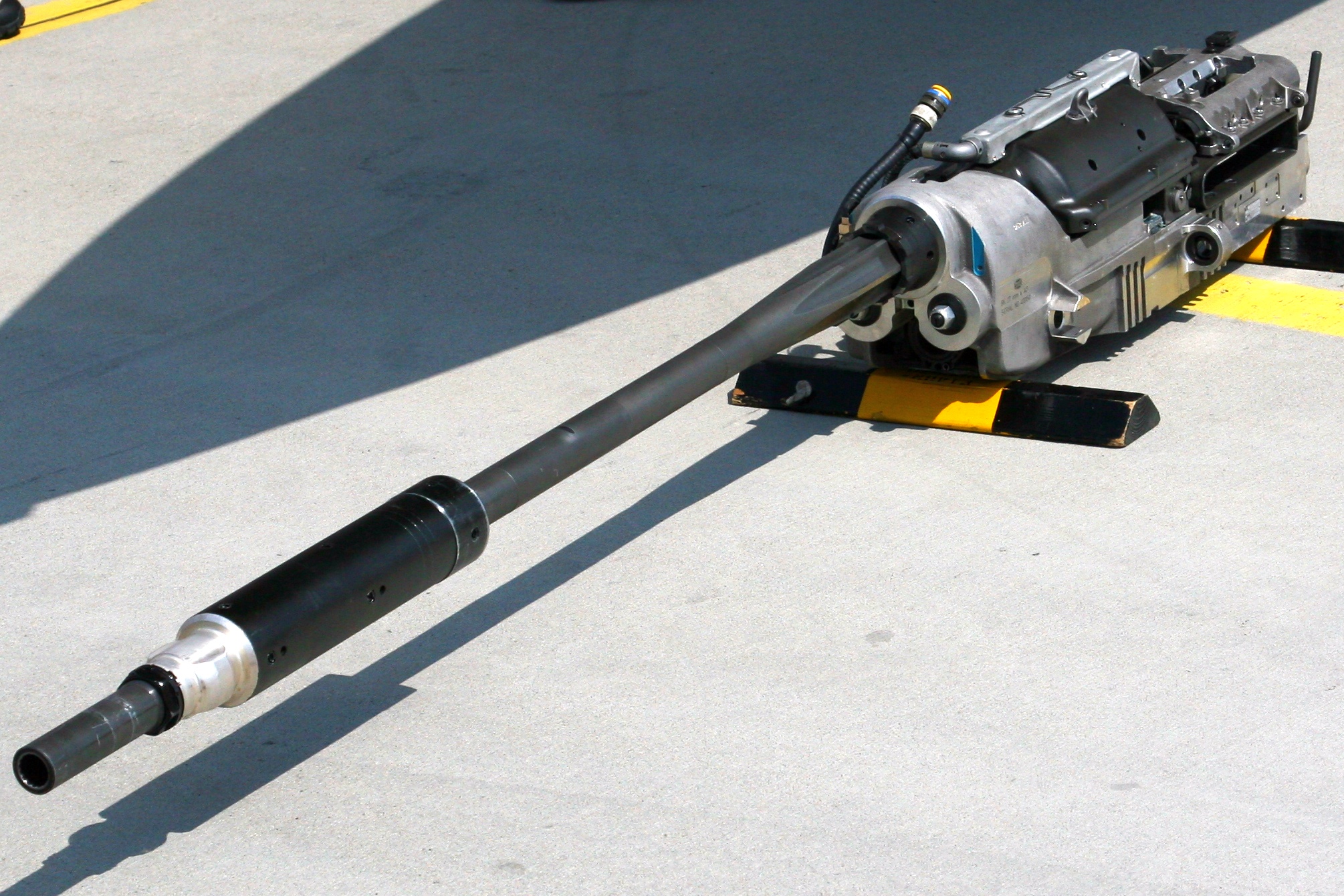
A revolver cannon is a large-caliber gun (
 In a classic Henry- Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandem">Winchester_Repeating_Arms.html" ;"title="Henry Repeating Arms">Henry-Winchester Repeating Arms">Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandemly into a tubular magazine below the barrel. A short
In a classic Henry- Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandem">Winchester_Repeating_Arms.html" ;"title="Henry Repeating Arms">Henry-Winchester Repeating Arms">Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandemly into a tubular magazine below the barrel. A short
 In bolt-action firearms, the
In bolt-action firearms, the
 In blowback operation, the bolt is not actually locked at the moment of firing. To prevent violent recoil, in most firearms using this mechanism the opening of the bolt is delayed in some way. In many small arms, the round is fired while the bolt is still travelling forward, and the bolt does not open until this forward momentum is overcome. Other methods involve delaying the opening until two rollers have been forced back into recesses in the receiver in which the bolt is carried. Simple blowback action is simple and inexpensive to manufacture, but is limited in the power it can handle, so it is seen on small caliber weapons such as
In blowback operation, the bolt is not actually locked at the moment of firing. To prevent violent recoil, in most firearms using this mechanism the opening of the bolt is delayed in some way. In many small arms, the round is fired while the bolt is still travelling forward, and the bolt does not open until this forward momentum is overcome. Other methods involve delaying the opening until two rollers have been forced back into recesses in the receiver in which the bolt is carried. Simple blowback action is simple and inexpensive to manufacture, but is limited in the power it can handle, so it is seen on small caliber weapons such as
 Rotary-barrel firearms (or ''rotary guns'' for short) uses multiple paraxial
Rotary-barrel firearms (or ''rotary guns'' for short) uses multiple paraxial 
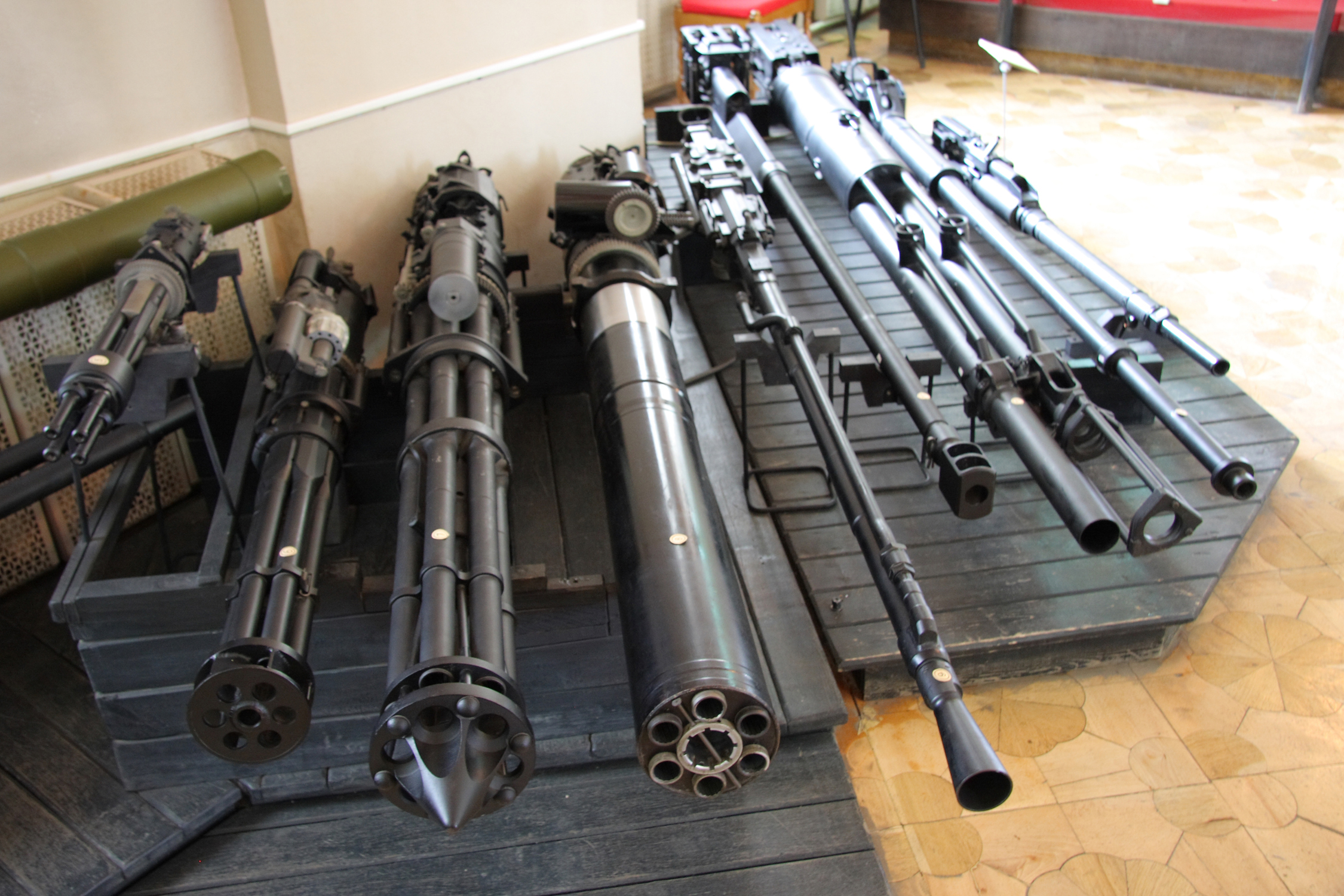



SPLIT BREECH GUNS: THE NUTCRACKER AND THE 40MM MK 18
Weyl
''Flight'', 8 March 1957, pages 313–314 Failures during the war were attributed to the poor quality of German wartime ammunition, although the type of breech employed had ruptured-case problems in a British 1950s experimental weapon. Fokker continued to experiment with this type of breech after his post-war move to the United States. A different Fokker prototype in a US museum attests to the failure of this line of development. After
handgun
A handgun is a short- barrelled gun, typically a firearm, that is designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long gun (i.e. rifle, shotgun or machine gun, etc.), which needs to be held by both hands and also brac ...
or long gun
A long gun is a category of firearms with long barrels. In small arms, a ''long gun'' or longarm is generally designed to be held by both hands and braced against the shoulder, in contrast to a handgun, which can be fired being held with a singl ...
) that is capable of being fired repeatedly before having to manually reload new ammunition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weapo ...
into the weapon.
Unlike single-shot
Single-shot firearms are firearms that hold only a single round of ammunition, and must be reloaded manually after every shot. The history of firearms began with single-shot designs, then multi-barreled designs appeared, and eventually many cen ...
firearms, which can only hold and fire one round, a repeating firearm can store multiple cartridges inside a magazine (either internal or detachable), a cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infi ...
(as in revolvers) or a belt (as in machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifl ...
s), and uses a moving action
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
to manipulate each cartridge into, and out of, battery position (within the chamber and in alignment with the bore
Bore or Bores often refer to:
*Boredom
* Drill
Relating to holes
* Boring (manufacturing), a machining process that enlarges a hole
** Bore (engine), the diameter of a cylinder in a piston engine or a steam locomotive
** Bore (wind instruments), ...
). This allows the weapon to be discharged repeatedly, in relatively quick succession, before a manual ammunition reload is needed.
Typically the term "repeaters" refers to the more ubiquitous single-barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, ...
ed variants. Multiple-barrel firearms such as derringer
A derringer is a small handgun that is neither a revolver nor a semi/ fully automatic pistol. It is not to be confused with mini-revolvers or pocket pistols, although some later derringers were manufactured with the pepperbox configuration ...
s, pepperbox guns, double-barreled rifles, double-barreled shotgun
A double-barreled shotgun is a break-action shotgun with two parallel barrels, allowing two single shots to be fired in quick succession or simultaneously.
Construction
Modern double-barreled shotguns, often known as ''doubles'', are almost ...
s, combination gun
A combination gun is a firearm that usually comprises at least one rifled barrel and one smoothbore barrel, that is typically used with shot or some types of shotgun slug. Most have been break-action guns, although there have been other desig ...
s, and volley gun
A volley gun is a gun with multiple single-shot barrels that shoot projectiles in volley fire, either simultaneously or in succession. Although capable of unleashing intense firepower, volley guns differ from modern machine guns in that ...
s can also hold and fire more than one cartridges (one in each barrel) before needing reloads, but do not use magazines for ammunition storage and also lack any moving actions to facilitate ammo-feeding, which makes them technically just bundled assemblies of multiple single-shot barrels fired in succession or simultaneously, therefore not ''true'' repeating firearms despite the functional resemblance. On the contrary, rotary-barrel firearms (e.g. Gatling guns), though also multi-barreled, ''do'' use belts/magazines with moving actions for feeding ammunition, which allow each barrel to fire repeatedly just like any single-barreled repeater, and therefore still qualify as repeating firearms from a technical point of view.
Although repeating flintlock breechloading firearms (e.g. the Lorenzóni/ Cookson repeater and Kalthoff repeater
The Kalthoff repeater was a type of repeating firearm that was designed by members of the Kalthoff family around 1630, and became the first repeating firearm to be brought into military service. At least nineteen gunsmiths are known to have ma ...
) had been invented as early as the 17th century
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movem ...
, the first repeating firearms that received widespread use were revolvers and lever-action
The toggle-link action used in the iconic Winchester Model 1873 rifle, one of the most famous lever-action firearms
Lever-action is a type of action for repeating firearms that uses a manually operated cocking handle located around the trigger ...
repeating rifle A repeating rifle is a single- barreled rifle capable of repeated discharges between each ammunition reloads. This is typically achieved by having multiple cartridges stored in a magazine (within or attached to the gun) and then fed individually ...
s in the 19th century
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium.
The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolis ...
. These were a significant advance over the preceding single-shot breechloading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition ( cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally br ...
guns, as they allowed a much greater rate of fire as well as a longer interval between reloads for more sustained firing, and the widespread use of metallic cartridge
A cartridge or a round is a type of pre-assembled firearm ammunition packaging a projectile (bullet, shot, or slug), a propellant substance (usually either smokeless powder or black powder) and an ignition device ( primer) within a metal ...
s also made reloading these weapons quicker and more convenient. Revolvers became very popular sidearms since its introduction by the Colt's Patent Firearms Manufacturing Company in the late 1830s, and repeating rifles saw use in the early 1860s during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
. Repeating pistols were invented during the 1880s, and became widely adopted after design contributions from inventors such as John Browning
John Moses Browning (January 23, 1855 – November 26, 1926) was an American firearm designer who developed many varieties of military and civilian firearms, cartridges, and gun mechanisms many of which are still in use around the world. He ...
and Georg Luger were introduced in the early 20th century.
The first repeating gun to see military service was actually not a firearm, but an airgun
An air gun or airgun is a gun that fires projectiles pneumatically with compressed air or other gases that are mechanically pressurized ''without'' involving any chemical reactions, in contrast to a firearm, which pressurizes gases ''chemical ...
. The Girardoni air rifle, designed by Italian inventor Bartolomeo Girardoni circa 1779 and more famously associated with the Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gr ...
into western North America during the early 1800s, was one of the first guns to make use of a tubular magazine.
Early repeaters
*Kalthoff repeater
The Kalthoff repeater was a type of repeating firearm that was designed by members of the Kalthoff family around 1630, and became the first repeating firearm to be brought into military service. At least nineteen gunsmiths are known to have ma ...
(about 1630)
* Lorenzoni repeater (about 1650)
* Lagatz Rifle: a modification of the Lorenzoni System, designed by Danzig gunsmith Daniel Lagatz around the year 1700.
* Harmonica gun
A harmonica gun or slide gun is a form of firearm which was breech loaded with a steel slide, containing a number of chambers bored in it and which were filled with projectiles. Most harmonica guns are percussion cap guns, although some designs ...
(1742)
* Cookson repeater (1750)
* Fafting Rifle: In 1774 a rifle was invented by a Norwegian colonel by the name of Fafting capable of firing 18 to 20 shots a minute and being used as an ordinary rifle by taking off a spring-loaded container attached to the gun's lock. It was also stated that the inventor was working on a gun capable of firing up to 30 times in a minute on more or less the same principles.
* Girandoni air rifle
The Girardoni air rifle was an air gun
An air gun or airgun is a gun that fires projectiles pneumatically with compressed air or other gases that are mechanically pressurized ''without'' involving any chemical reactions, in contrast to ...
(1779)
* 1789 French Rifle: In 1791 it was mentioned in a book published in France that there existed since at least 1789 a rifle that held 5 or 6 shots and was capable of being reloaded three times in a minute for a total of 15 or 18 shots a minute. A rifle similar in type to this was also stated to be kept at the Hotel de la Guerre( fr).
* Church and Bartemy/Bartholomew gun: A repeating rifle designed by the Americans William Church and Chrostus Bartemy or Bartholomew in 1813 with three separate magazines for containing up to 42 charges of ammunition and capable of firing 25 shots a minute. It could be reloaded in one minute.
* Thomson Rifle: a flintlock repeating rifle patented in 1814, using multiple breeches to obtain repeating fire.
* Lepage Guns: In 1819 a French gunsmith called Lepage invented and presented at the French industrial exposition of that year percussion 2-shot and 4-shot turn-over rifles. In 1823 he exhibited a volley rifle that fired 7 rifled barrels simultaneously as well as a turn-over carbine. In 1827, the same inventor exhibited at another French industrial exposition 11 percussion and 1 flintlock firearms which included a 4-shot turn-over rifle, a 'double rifle' with a cylinder with 5 charges and a 'single rifle' and a pair of pistols also with a cylinder with 5 charges.
* Sutherland Magazine Pistol: In 1821 the British gunmakers R and R Sutherland advertised for auction, amongst a variety of firearms, a single-barrelled six-shot magazine pistol.
* Pirmet-Baucheron Revolving Rifle: In 1822 a French gunsmith called Pirmet-Baucheron presented a revolving rifle with 7 shots and a single lock.
* Hewson Magazine Gun: In 1824 an English gunsmith called W. P. Hewson advertised, amongst other firearms and one air gun, a magazine gun.
* Jobard Rifle: a turret rifle with 14 shots patented in Belgium in 1826 and presented to the government in 1835.
* Henry Rifle: a French 14 shot flintlock rifle in the style of the Kalthoff and Lorenzoni rifles patented in 1831 (granted in 1835) by Francois-Antoine Henry though possibly based on an earlier design published in 1809 by the same author.
* Kavanagh Pistol: In 1834 a variety of pistols were exhibited by the Irish gunsmith William Kavanagh, one of which had a 'revolving breech' capable of firing 7 or 8 times, as well as a 'self-loading pistol'.
* Silas Day Magazine Gun: A percussion revolving rifle to which was attached a loose-powder-and-ball magazine patented in the US in 1837.
* Colt Ring Lever rifles
The Colt First Model Ring Lever rifle and Colt Second Model Ring Lever rifle are two early caplock revolving rifles that were produced by the Patent Arms Manufacturing Company between 1837 and 1841. The First Model, produced between 1837 and 183 ...
(1837)
* Bailey, Ripley and Smith Magazine Rifle: In 1838 the Americans Lebbeus Bailey, John B. Ripley and William B. Smith patented a percussion repeating rifle with a gravity-operated tubular magazine in the stock which could hold up to 15 re-useable steel cartridge-chambers.
* Eaton Rifle: In 1838 a percussion rifle invented in America by James Eaton was described as being capable of holding 24 rounds in a rotating magazine and discharging them all in four minutes for a rate of fire of 6 rounds per minute.
* Kratsch Rifle: In 1839 it was reported that a mechanic called Kratsch from Bayreuth had invented a rifle capable of firing 30 times in a minute and being reloaded in one minute.
* Devisme Guns: In 1844 a French gunsmith known as Devisme presented a variety of repeating firearms for the French Industrial Exposition of 1844 including an 18 shot pistol with no visible hammer or lock, a 6 shot pistol, a rifle with 6 shots and a 'revolving thunder' and a four shot 'double acting' rifle.
* Jennings Magazine Rifle: in 1847 Walter Hunt patented in Britain a repeating rifle he called "the Volitional Repeater". He would patent it again in the United States in 1849. This rifle featured a tubular magazine beneath the barrel and a lever mechanism to raise cartridges into the chamber. Unable to finance the building of the rifle, Hunt sold the rights to George Arrowsmith
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd President ...
who in turn had an employee, Lewis Jennings Louis Jennings was an American gunsmith of 19th century who expanded upon the repeating rifle mechanism system of Walter Hunt,
, improve the lever mechanism. Courtland Palmer Courtland may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Courtland (RTA Rapid Transit station), Cleveland, Ohio
* Courtland, Alabama, a town
* Courtland, Arizona, a ghost town
* Courtland, California, a census-designated place
* Courtland, Kansas, ...
placed the first order for the "Jennings Magazine rifle" for his hardware store: Robbins & Lawrence. The rifle did not sell well as the ammunition was a hollow based bullet containing gunpowder. Most of the guns were later converted to single shot rifles. Two employees working at Robbins & Lawrence: Horace Smith and Daniel B. Wesson improved the design and sold it as the "Smith-Jennings Repeating Rifle". At first they used a slightly modified Flobert cartridge, patented in 1853, but later they would switch to a modified Rocket Ball type of ammunition altered so as to function as a self-contained centerfire cartridge.
* Cass Repeating Belt Gun: A percussion repeating rifle patented in 1848 in the US using a chain or belt in the stock which carried paper cartridges to the breech of the gun.
* Buchel Cartridge Magazine Gun: The first tubular cartridge magazine gun to be patented in the United States in February 1849.
* Perry 'Faucet-Breech' Gun: A hinged or tilting breech repeating rifle patented in the US in December 1849 by Alonzo Perry using paper cartridges contained in several gravity-operated tubular magazines in the stock and a separate magazine for fulminate pills which were used for ignition.
* Porter Self-Loading Gun: In February 1851 a loose-powder-and-ball percussion magazine gun invented by a Parry W. Porter, better known for the turret rifle he invented and to which the magazine for his loose-powder-and-ball gun was to be attached, was reported on in American newspapers and later in the same year a patent was procured by the inventor.
* Needham Self-Loading Carbine: A self-loading carbine demonstrated in June 1851 at the Great Exhibition by Joseph Needham.
* Dixon Self-Loading and Self-Priming Gun: A repeating gun demonstrated by a C. S. Dixon which won a silver award at the Annual Fair of the American Institute in October 1851.
* The first slide action patent: Issued in Britain in 1854, to Alexander Bain who modified the mechanism of a harmonica gun.
* 1854 Lindner Revolving Rifle: In 1854 the German Edward Lindner patented in the United States and Britain a repeating rifle which used a revolving cylinder to elevate the cartridges, which were paper and could be either self-contained needlefire cartridges or use external percussion caps for ignition, to the breech from a tubular magazine located under the barrel.
* Colette Gravity Pistol: a repeating saloon gun
A gallery gun, Flobert gun, parlor gun or saloon gun is a type of firearm designed for recreational indoor target shooting. These guns were developed in 1845, when French inventor Louis-Nicolas Flobert created the first rimfire metallic cart ...
premiered at the 1855 World's Fair. Despite popularly being known as the Colette Gravity Pistol its original inventor was actually a Belgian called Jean Nicolas Herman.
* Colt revolving rifle (1855)
* Leroux Magazine Gun: At the Exposition Universelle (1855)
The Exposition Universelle of 1855 was an International Exhibition held on the Champs-Élysées in Paris from 15 May to 15 November 1855. Its full official title was the Exposition Universelle des produits de l'Agriculture, de l'Industrie et des ...
in France a French gunsmith called Leroux demonstrated a repeating carbine with a magazine for 36 Flobert cartridges and which featured a novel cartridge extractor.
* Spencer repeating rifle (1860)
* Roper repeating shotgun (1866)
Mechanisms
Manual
In a manually-operated repeating firearm (or "manual repeater" for short), the user needs to manually apply force to theaction
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
to operate it, either directly via a handle
A handle is a part of, or attachment to, an object that allows it to be grasped and manipulated by hand. The design of each type of handle involves substantial ergonomic issues, even where these are dealt with intuitively or by following tr ...
on the bolt
The BOLT Browser was a web browser for mobile phones including feature phones and smartphones that can run Java ME applications. The BOLT Browser was offered free of charge to consumers and by license to mobile network operators and handset manuf ...
or an external hammer, or indirectly via linkaged lever or slide.
Revolver action
Colt Holster Model Paterson Revolver No. 5 Circuit Judge revolver mechanism carbine Revolvers use a rotatingcylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infi ...
containing multiple chambers, which functions similarly to a rotary magazine
A magazine is an ammunition storage and feeding device for a repeating firearm, either integral within the gun (internal/fixed magazine) or externally attached (detachable magazine). The magazine functions by holding several cartridges withi ...
(with each chamber holding a round of cartridge). When the hammer
A hammer is a tool, most often a hand tool, consisting of a weighted "head" fixed to a long handle that is swung to deliver an impact to a small area of an object. This can be, for example, to drive nails into wood, to shape metal (as ...
is cocked (either directly by hand, or indirect via trigger-pull), internal linkage will rotate the cylinder and index
Index (or its plural form indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, an item on a Halo megastru ...
each chamber into alignment with the barrel bore. When firing, the bullet will make a slight "jump" across the gap between the cylinder and the barrel, creating out a small "breech blast" from any hot, high-pressure propellant gas that leaks out of the gap. The breech portion of the bore is also often widened slightly into a funnel
A funnel is a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom, used for guiding liquid or powder into a small opening.
Funnels are usually made of stainless steel, aluminium, glass, or plastic. The material used in its construc ...
-like "cone" to better facilitate the bullet jump across the cylinder gap.
Although multiple-barrel
A multiple-barrel firearm is any type of firearm with more than one gun barrel, usually to increase the rate of fire or hit probability and to reduce barrel erosion/overheating.
History Volley gun
Multiple-barrel firearms date back to the ...
"pepper-box
The pepper-box revolver or simply pepperbox (also "pepper-pot", from its resemblance to the household pepper shakers) is a multiple-barrel firearm, mostly in the form of a handgun, that has three or more gun barrels in a coaxially revolving ...
" guns had appeared for centuries and were popular handguns in the early 19th century, the revolver was the first ''true'' repeating handgun. In 1836, Samuel Colt
Samuel Colt (; July 19, 1814 – January 10, 1862) was an American inventor, industrialist, and businessman who established Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Manufacturing Company (now Colt's Manufacturing Company) and made the mass production of ...
applied patent for a "revolving gun" later named the Colt Paterson
The Colt Paterson revolver was the first commercial repeating firearm employing a revolving cylinder with multiple chambers aligned with a single, stationary barrel. Its design was patented by Samuel Colt on February 25, 1836, in the Unite ...
; he was granted the patent on 25 February 1836 (later numbered 9430X). This instrument and patent No. 1304, dated 29 August 1836, protected the basic principles of his revolving-breech-loading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition ( cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally b ...
, folding- trigger firearm and gave him a monopoly of revolver manufacture until 1857. It was the first practical revolver and the first practical repeating firearm, and became an industrial and cultural legacy as well as a contribution to the development of war technology, represented ironically by the name of one of his company's later innovations, the " Peacemaker".
While some early long guns were also made using the revolver mechanism, these did not have longevity as it posed a problem with long guns: without special sealing details, the cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infi ...
produces a gas discharge close to the face when the weapon is fired from the shoulder, as was a common approach with rifles.
Revolver cannon


 A revolver cannon is a large-caliber gun (
A revolver cannon is a large-caliber gun (cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder duri ...
) that uses a revolver-like cylinder to speed up the loading-firing-ejection cycle. Unlike a rotary cannon
A rotary cannon, rotary autocannon, rotary gun or Gatling cannon, is any large- caliber multiple-barreled automatic firearm that uses a Gatling-type rotating barrel assembly to deliver a sustained saturational direct fire at much greater r ...
, a revolver cannon has only a single gun barrel
A gun barrel is a crucial part of gun-type weapons such as small arms, small firearms, artillery pieces, and air guns. It is the straight shooting tube, usually made of rigid high-strength metal, through which a contained rapid expansion of high ...
. An early precursor was the Puckle gun of 1718, a large manually-operated flintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also known ...
gun, whose design idea was impractical due to it being far ahead of what 18th century technology could achieve. During the 19th century, The Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighti ...
used a single 2-inch revolver cannon with 5 manually rotated chambers during the Siege of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War. Although it is more popularly known as the Siege of Petersburg, it was not a cla ...
. The gun was captured in Danville, Virginia
Danville is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States, located in the Southside Virginia region and on the fall line of the Dan River. It was a center of tobacco production and was an area of Confederate activi ...
by the Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to th ...
on 27 April 1865.
Modern revolver cannons are actually automatically operated weapons. In 1905, C. M. Clarke patented the first fully automatic, gas-operated
Gas-operation is a system of operation used to provide energy to operate locked breech, autoloading firearms. In gas-operation, a portion of high-pressure gas from the cartridge being fired is used to power a mechanism to dispose of the spen ...
rotary chamber gun, but his design was ignored at the time as it came as reciprocating-bolt automatic weapons like the Maxim gun
The Maxim gun is a recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first fully automatic machine gun in the world.
The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most associated with imperial conquest" by historia ...
and the Browning gun were peaking in popularity. In 1932, the Soviet ShKAS machine gun, a 7.62 mm calibre aircraft ordnance, used a twelve-round capacity, revolver-style feeding mechanism with a single barrel and single chamber, to achieve firing rates of well over 1800 rounds per minute, and as high as 3,000 rounds per minute in special test versions in 1939, all operating from internal gas-operated reloading
Gas-operation is a system of operation used to provide energy to operate locked breech, autoloading firearms. In gas-operation, a portion of high-pressure gas from the cartridge being fired is used to power a mechanism to dispose of the spen ...
. Some 150,000 ShKAS weapons were produced for arming Soviet military aircraft through 1945. Around 1935, Silin
Silin is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Morąg, within Ostróda County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately south of Morąg, north of Ostróda, and west of the regional capital Olsztyn
...
, Berezin Berezin (feminine: Berezina) is a Russian surname which may refer to:
People
* Aleksei Berezin (born 1993), Russian footballer
* André Berezin (born 1960), Brazilian rower
* Evelyn Berezin (1925–2018), American computer designer best known fo ...
and Morozenko worked on a 6000 rpm 7.62 mm aircraft machine gun using revolver design, called SIBEMAS (СИБЕМАС), but the project was abandoned.
It was not until the mid-1940s that the first practical modern revolver cannon emerged. The archetypal revolver cannon is the Mauser MK 213
The Mauser MG 213 was a 20 mm aircraft-mounted revolver cannon developed for the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. It was never put into service, but the principles formed the basis for several post-war developments by the Allies. A 30 mm vers ...
, from which almost all current revolver cannons are derived. In the immediate post-war era, Mauser engineers spread out from Germany and developed similar weapons around the world. Both the British and French made outright copies of the 30 mm versions of the MK 213, as the ADEN and DEFA
DEFA (''Deutsche Film-Aktiengesellschaft'') was the state-owned film studio of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) throughout the country's existence.
Since 2019, DEFA's film heritage has been made accessible and licensable on the PRO ...
, respectively. Switzerland produced the Oerlikon KCA
The Oerlikon KCA is a Swiss gas-operated single-barrel revolver cannon developed for aircraft use. Its most noticeable use was on the JA 37 Viggen fighter mounted in a conformal pod as the ''akan m/75''. The KCA fires a shell that is 50% heavi ...
. The American M39 cannon used the 20 mm version, re-chambered for a slightly longer 102 mm cartridge, intermediate between the 213's 82 mm and Hispano-Suiza HS.404's 110 mm. Several generations of the basic ADEN/DEFA weapons followed, remaining largely unchanged into the 1970s. Around that time, a new generation of weapons developed, based on the proposed NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
25 mm caliber
25 mm caliber is a specific size of popular autocannon ammunition. It has also been recently used for the Barrett XM109 anti-materiel rifle. Such ammunition includes the NATO-standard 25×137mm and 25×184mm, the Soviet 25x218mmSR, and the Chi ...
standard and the Mauser 27 mm round. A leading example is the Mauser BK-27. In the 1980s, the French developed the GIAT 30, a newer generation power-driven revolver cannon. The Rheinmetall RMK30 modifies the GIAT system further, by venting the gas to the rear to eliminate recoil. Larger experimental weapons have also been developed for anti-aircraft use, like the Anglo-Swiss twin barrel but single chamber 42 mm Oerlikon RK 421 Oerlikon may refer to:
Companies
* OC Oerlikon (former ''Unaxis''), a Swiss technology conglomerate, or one of its business units:
** Oerlikon Solar
** Oerlikon Balzers
** Oerlikon Leybold Vacuum
* Oerlikon-Bührle, a company in Zürich, Switzer ...
given the code name "Red King" and the related single-barrel "Red Queen" – all of which were cancelled during development. The largest to see service is the Rheinmetall Millennium 35 mm Naval Gun System.
Soviet revolver cannon are less common than Western ones, especially on aircraft. A mechanism for a Soviet revolver-based machine gun was patented in 1944. The virtually unknown Rikhter R-23
The Rikhter R-23 is an aircraft autocannon developed for the Soviet Air Force starting in the late 1950s. It was designed to be as short as possible to avoid problems found on high-speed aircraft when the guns were pointed into the airstream. The ...
was fitted only to some Tu-22
The Tupolev Tu-22 (NATO reporting name: Blinder) was the first supersonic bomber to enter production in the Soviet Union. Manufactured by Tupolev, the Tu-22 entered service with the Soviet military in the 1960s.
The aircraft was a disappointme ...
models, but later abandoned in favor of the two-barrel, Gast gun Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23
The Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23 ( rus, ГШ-23) is a twin-barreled 23 mm autocannon developed in the Soviet Union, primarily for military aircraft use. It entered service in 1965, replacing the earlier Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23 and Rikhter R-23. ...
in the Tu-22M. The Rikhter R-23 does have the distinction of being fired from the space station Salyut 3
Salyut 3 (russian: Салют-3; en, Salute 3; also known as OPS-2 or Almaz 2Portree (1995).) was a Soviet Union, Soviet space station launched on 25 June 1974. It was the second Almaz military space station, and the first such station to be lau ...
. The Soviet navy has also adopted a revolver design, the NN-30, typically in a dual mount in the AK-230
The AK-230 is a Soviet fully automatic naval twin 30 mm gun. Its primary function is anti-aircraft. It is mounted in an enclosed automatic turret and directed by radar. AK-230 is widely used, mounted on big warships as well as small craft. ...
turret.
Lever-action
Marlin Model 1894C lever-action carbine in .357 Magnum caliber">.357_Magnum.html" ;"title="Marlin Model 1894C lever-action carbine in .357 Magnum">Marlin Model 1894C lever-action carbine in .357 Magnum caliber In a classic Henry- Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandem">Winchester_Repeating_Arms.html" ;"title="Henry Repeating Arms">Henry-Winchester Repeating Arms">Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandemly into a tubular magazine below the barrel. A short
In a classic Henry- Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandem">Winchester_Repeating_Arms.html" ;"title="Henry Repeating Arms">Henry-Winchester Repeating Arms">Winchester type lever-action firearm, cartridges are loaded tandemly into a tubular magazine below the barrel. A short bolt
The BOLT Browser was a web browser for mobile phones including feature phones and smartphones that can run Java ME applications. The BOLT Browser was offered free of charge to consumers and by license to mobile network operators and handset manuf ...
is manipulated via linkage to a pivoted cocking handle">cocking lever. Once closed, an over-center toggle action helps locking the bolt in place and prevents the breech from opening accidentally when the weapon is fired. The cocking lever is often integral with the trigger guard, and gets manually flexed down and forward when operated. An interlock (engineering), interlock prevents firing unless the toggle is fully closed. The famous Winchester rifle#Winchester Model 1873, Model 1873 Winchester is exemplary of this type. Later lever-action designs, such as Marlin Firearms, Marlin lever guns and those designed for Winchester by John Browning
John Moses Browning (January 23, 1855 – November 26, 1926) was an American firearm designer who developed many varieties of military and civilian firearms, cartridges, and gun mechanisms many of which are still in use around the world. He ...
, use one or two vertical locking blocks instead of a toggle-link. There also exist lever-action rifle/shotguns that feed from a box magazine
A magazine is an ammunition storage and feeding device for a repeating firearm, either integral within the gun (internal/fixed magazine) or externally attached (detachable magazine). The magazine functions by holding several cartridges with ...
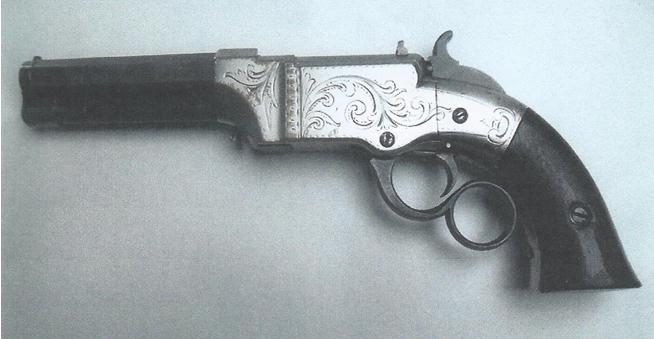
, which allows them to use pointed bullets. Some of the early manual repeating pistols (e.g. Volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates ...
pistol) also use a scaled-down version of lever-action.
A one-off example of lever-action loading on an automatic firearm is the M1895 Colt–Browning machine gun
The Colt–Browning M1895, nicknamed "potato digger" because of its unusual operating mechanism, is an air-cooled, belt-fed, gas-operated machine gun that fires from a closed bolt with a cyclic rate of 450 rounds per minute. Based on an 1889 des ...
. This weapon had a swinging lever beneath its barrel that was actuated by a gas bleed in the barrel, unlocking the breech to reload. This unique operation gave the nickname "potato digger" as the lever swung each time the weapon fired.
Pump-action
The Colt Lightning .22 pump action rifle With a pump-action firearm, the action is operated by sliding a movablehandguard
A barrel shroud is an external covering that envelops (either partially or full-length) the barrel of a firearm, to prevent unwanted direct contact with the barrel (e.g. accidental collision with surrounding objects, or the user accidentally t ...
on the fore-end backwards and forwards, with manipulated the bolt
The BOLT Browser was a web browser for mobile phones including feature phones and smartphones that can run Java ME applications. The BOLT Browser was offered free of charge to consumers and by license to mobile network operators and handset manuf ...
via linkage to eject a spent round, and extract and chamber a fresh round of ammunition. Pump-actions are usually associated with shotguns, but one example of a pump-action rifle is the Remington Model 7600 series. Rifles with pump action are also called slide-action. This style of rifle is still popular with some local law enforcement branches as a rifle that is easy to train officers who are already familiar with the pump shotgun.
Bolt-action
Opened bolt on a engine turned finish">brushed_metal.html" ;"title="Winchester Model 70, with an brushed metal">engine turned finish In bolt-action firearms, the
In bolt-action firearms, the bolt
The BOLT Browser was a web browser for mobile phones including feature phones and smartphones that can run Java ME applications. The BOLT Browser was offered free of charge to consumers and by license to mobile network operators and handset manuf ...
is operated by directly gripping a bolt handle (usually on the right side) to extract spent cartridges case, push new rounds into the chamber and reset the
to ready the weapon for firing again.
Most bolt-action firearms use a rotating-bolt ("turn-and-pull") design. When the bolt is closed against the breech end of the hammer
A hammer is a tool, most often a hand tool, consisting of a weighted "head" fixed to a long handle that is swung to deliver an impact to a small area of an object. This can be, for example, to drive nails into wood, to shape metal (as ...
/ striker
Striker or The Strikers may refer to:
People
*A participant in a strike action
*A participant in a hunger strike
*Blacksmith's striker, a type of blacksmith's assistant
*Striker's Independent Society, the oldest mystic krewe in America
People wi ...gun barrel
A gun barrel is a crucial part of gun-type weapons such as small arms, small firearms, artillery pieces, and air guns. It is the straight shooting tube, usually made of rigid high-strength metal, through which a contained rapid expansion of high ...
, it is locked onto the receiver via protruded Bolt (firearms)">lugs (usually on the bolt head) and occasionally also aided by the bolt handle that fits into a notch. To unlock the bolt, the handle must be rotated upwards first, which will shift the locking lugs out of their corresponding sockets. This allows the bolt to then be physically pulled rearwards, opening the barrel breech. An extractor on the bolt will hook onto the rim (firearms)">rim and pull out any cartridge (either fired or unused) remaining in the chamber, allowing it to be ejected from the gun. When the bolt is fully pulled to the rearmost position, the hammer/striker will get loaded against a spring and trapped by the sear (firearm)">sear, a process known as ''cocking''. At the same time, the magazine will lift another round of its stored cartridges up into the path of the bolt head, so moving the bolt forwards will push this new round into the chamber. The bolt handle is then rotated downward for relocking, the gun is safe and ready for another firing. The Mauser Gewehr 98 rifle is the most famous and influential bolt-action design, with many similar weapons derived from its pioneering design concept, such as the Karabiner 98 Kurz (abbreviated often as Kar98k or simply K98), the M1903 Springfield
The M1903 Springfield, officially the United States Rifle, Caliber .30-06, Model 1903, is an American five-round magazine-fed, bolt-action service repeating rifle, used primarily during the first half of the 20th century.
The M1903 was first ...
and the Arisaka Type 38 rifles. The Russian Mosin–Nagant
The Mosin–Nagant is a five-shot, bolt-action, internal magazine–fed military rifle. Known officially as the 3-line rifle M1891 and informally in Russia and former Soviet Union as Mosin's rifle ( ru , винтовка Мосина, ISO 9: ...
rifle, the British Lee–Enfield
The Lee–Enfield or Enfield is a bolt-action, magazine-fed repeating rifle that served as the main firearm of the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth during the first half of the 20th century, and was the British Army's s ...
, and the Norwegian Krag–Jørgensen
The Krag–Jørgensen is a repeating bolt-action rifle designed by the Norwegians Ole Herman Johannes Krag and Erik Jørgensen in the late 19th century. It was adopted as a standard arm by Norway, Denmark, and the United States. About 300 wer ...
are examples of alternate bolt-action designs.
Another much rarer type of bolt-action is the straight-pull system, which uses complex bolt head mechanisms to facilitate locking. Straight-pull designs do not require the bolt handle to be rotated, allowing the user to cycle the action linearly, reducing the movements needed from four to only two and thus significantly increasing the rate of fire. Examples of such firearms include the Schmidt–Rubin
The Schmidt–Rubin rifles were a series of Swiss Army service rifles in use between 1889 and 1958. They are distinguished by the straight-pull bolt action invented by Rudolf Schmidt and use Eduard Rubin's 7.5×55mm Schmidt–Rubin rifle cartridg ...
, Mannlicher M1886
The Repeating Rifle Model 1886 commonly known as Mannlicher Model 1886 was a late 19th-century Austrian straight-pull bolt-action rifle, adopted in 1886. It used a wedge-lock straight pull action bolt. It was the first straight-pull bolt-action se ...
/ M1888/ M1890/ M1895, M1895 Lee Navy, Ross rifle, Anschütz 1827 Fortner, Blaser R93/ R8 and VKS.
Autoloading
Self-loading (or autoloading) repeating firearms can use some of the excess energy released frompropellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the ...
combustion to cycle its action
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
and facilitate loading of subsequent rounds of ammunition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weapo ...
into the chamber, without needing the user to do any extra loading work with his hands. Depending on whether the action can automatically perform both the loading and ignition procedures, or only automatically load the ammo but require manual actuation of the hammer
A hammer is a tool, most often a hand tool, consisting of a weighted "head" fixed to a long handle that is swung to deliver an impact to a small area of an object. This can be, for example, to drive nails into wood, to shape metal (as ...
/striker
Striker or The Strikers may refer to:
People
*A participant in a strike action
*A participant in a hunger strike
*Blacksmith's striker, a type of blacksmith's assistant
*Striker's Independent Society, the oldest mystic krewe in America
People wi ...
, self-loading repeaters can be categorized into ''fully automatic
An automatic firearm is an auto-loading firearm that continuously chambers and fires rounds when the trigger mechanism is actuated. The action of an automatic firearm is capable of harvesting the excess energy released from a previous disch ...
'' and '' semi-automatic'' firearms.
Blowback
 In blowback operation, the bolt is not actually locked at the moment of firing. To prevent violent recoil, in most firearms using this mechanism the opening of the bolt is delayed in some way. In many small arms, the round is fired while the bolt is still travelling forward, and the bolt does not open until this forward momentum is overcome. Other methods involve delaying the opening until two rollers have been forced back into recesses in the receiver in which the bolt is carried. Simple blowback action is simple and inexpensive to manufacture, but is limited in the power it can handle, so it is seen on small caliber weapons such as
In blowback operation, the bolt is not actually locked at the moment of firing. To prevent violent recoil, in most firearms using this mechanism the opening of the bolt is delayed in some way. In many small arms, the round is fired while the bolt is still travelling forward, and the bolt does not open until this forward momentum is overcome. Other methods involve delaying the opening until two rollers have been forced back into recesses in the receiver in which the bolt is carried. Simple blowback action is simple and inexpensive to manufacture, but is limited in the power it can handle, so it is seen on small caliber weapons such as machine pistol
A machine pistol is an autoloading pistol capable of fully automatic fire. The term can also be used to describe a stockless handgun-style submachine gun. The term is a calque of ''Maschinenpistole'', the German word for submachine guns. Machi ...
s and submachine guns. Lever-delayed blowback, as seen in for example the French FAMAS
The FAMAS (''Fusil d'Assaut de la Manufacture d'Armes de Saint-Étienne'', "Assault Rifle from the Saint-Étienne Weapon Factory") is a bullpup assault rifle designed and manufactured in France by MAS in 1978, a year after the Austrian Steyr A ...
assault rifle, can also handle more powerful cartridges but is more complicated and expensive to manufacture.
Blow-forward
Blow-forward firearms incorporates a frame with a fixed breech face and the barrel moves away from the breech (frame) during the cycle of operation, in contrast to blowback firearms, which have the frame fixed to the barrel and the breech face moves in relation to the frame. The breech face is a part of the moving slide or bolt, depending on the layout of the blowback firearm. During firing, the friction of the bullet traveling down the barrel and the bore pressure pulls the barrel forward. This mechanism contains a minimum of moving parts (the barrel and spring are generally the only moving parts) and is more compact than other operating mechanism of equal barrel length. However, due to the reduced mass of rear-moving parts coupled with the increased mass of the forward-moving parts (the barrel plus the bullet and propellant gasses),recoil
Recoil (often called knockback, kickback or simply kick) is the rearward thrust generated when a gun is being discharged. In technical terms, the recoil is a result of conservation of momentum, as according to Newton's third law the force r ...
energy is significantly greater than other operating mechanisms. Most blow-forward guns rely partially on the inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law o ...
of the barrel as the rest of the firearm recoil away from it.
The first blow-forward firearm was the Mannlicher M1894 pistol and protected under . The principle has been used in a few other weapons, including Schwarzlose Model 1908, Hino Komuro M1908, HIW VSK, Mk 20 Mod 0 grenade launcher, Pancor Jackhammer and Howa Type 96.
Recoil-operated
M1941 Johnson rifle In a recoil-operated firearm, the breech is locked, and the barrel recoils as part of the firing cycle. In long-recoil actions, such as the Browning Auto-5 shotgun, the barrel and breechblock remain locked for the full recoil travel, and separate on the return; in short-recoil actions, typical of most semiautomatic handguns (e.g. theColt M1911
The M1911 (Colt 1911 or Colt Government) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered for the .45 ACP cartridge. The pistol's formal U.S. military designation as of 1940 was ''Automatic Pistol, Caliber .45, M1911'' for the ...
), the barrel recoils only a short distance before decoupling from the breechblock.
Gas-operated
FN FAL battle rifle In a gas-operated mechanism, a portion of the gases propelling the bullet from the barrel are extracted and used to operate a piston. The motion of this piston in turn unlocks and operates the bolt, which performs extraction of the spent cartridge and via spring action readies the next round. Almost all modern military rifles use mechanisms of this type.Rotary-barrel
 Rotary-barrel firearms (or ''rotary guns'' for short) uses multiple paraxial
Rotary-barrel firearms (or ''rotary guns'' for short) uses multiple paraxial barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, ...
s in a rotating assembly, with each barrel firing automatically when rotated to a designated position, to achieve a rate of fire proportional to the speed of the barrel rotation. Rotary guns are typically belt-fed, though the earlier versions used top-mounted box magazine
A magazine is an ammunition storage and feeding device for a repeating firearm, either integral within the gun (internal/fixed magazine) or externally attached (detachable magazine). The magazine functions by holding several cartridges with ...
s. Each barrel is paired with a cam-driven reciprocating action
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
, so every barrel-action group is technically an independent ''repeater'' unit whose operating status corresponds to its rotational position within the assembly, and at any moment all the groups are at different stages of operating cycle to each other. Due to their capability to tolerate extremely rapid-firing (much higher than single-barreled automatic weapon
An automatic firearm is an Repeating firearm#Autoloading, auto-loading firearm that continuously Chamber (firearms), chambers and fires Cartridge (firearms), rounds when the trigger (firearms), trigger mechanism is actuated. The action (firearms) ...
s of the same caliber), rotary guns are frequently used to deliver direct
Direct may refer to:
Mathematics
* Directed set, in order theory
* Direct limit of (pre), sheaves
* Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces
Computing
* Direct access (disambiguation), ...
saturation fire for suppression and area denial. Early rotary guns are manually powered, and though quite successful at the time, was largely replaced from the battlefield before the turn of the 20th century by newer and more reliable machine guns such as the Maxim gun
The Maxim gun is a recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first fully automatic machine gun in the world.
The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most associated with imperial conquest" by historia ...
, but made a comeback during the Cold War in the form of automatic rotary cannon
A rotary cannon, rotary autocannon, rotary gun or Gatling cannon, is any large- caliber multiple-barreled automatic firearm that uses a Gatling-type rotating barrel assembly to deliver a sustained saturational direct fire at much greater r ...
s.
One of the main reasons for the resurgence of these electrically/hydraulic
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counter ...
ally powered multiple-barrel guns is the system's inherent tolerance for continuous high rates of fire. For example, 1000 rounds per minute of continuous fire from a conventional single-barrel weapon ordinarily results in rapid barrel overheating followed by action stoppages caused also by overheating; in contrast, a five-barreled rotary gun firing 1000 rounds per minute endures only 200 rounds per minute for each barrel. The other factor is that while single-barrel designs can achieve high cycling rates, each loading-extraction cycle can only commence ''after'' the previous cycle is physically complete, or else the system will jam mechanically, and the risk of such malfunction increases exponentially with increasingly higher cycling rates; a multiple-barrel design however allows multiple barrel-action groups to work simultaneously in overlapped, differentially timed cycles, thus diffusing the operational stress of each action into the duration of an entire barrel rotation (which is multitudes more than the cycle time of a single-barrel automatic firearm with the same firing rate). The design also solves the problem of defective ammunition, which can cause a typical single-barrel machine gun to cease operation when a cartridge fails to load, fire or eject; as a rotary gun is normally powered by an external power source, the barrel rotation will continue independently, ejecting any defective rounds indifferently as part of the operational cycle, and the firing will merely experience a brief pause for that non-firing barrel before resuming to usual firing with other barrels.




Manual
The earliest rotary-barrel firearm is the Gatling gun, invented by Richard Jordan Gatling in 1861, and patented on 4 November 1862. The Gatling gun operated by a hand-crank mechanism, with six barrels revolving around a central shaft (although some models had as many as ten). Each barrel fires once per revolution at about the same 4 o'clock position. The barrels, a carrier and a lock cylinder were separate and all mounted on a solid plate, mounted on an oblong fixed frame. Manually turning the crank rotated the shaft. The carrier was grooved and the lock cylinder was drilled with holes corresponding to the barrels. Cartridges, held in a hopper-like magazine on top, dropped individually into the grooves of the carrier. The lock was simultaneously forced by the cam to move forward and load the cartridge, and when the cam was at its highest point, the cocking ring freed the lock and fired the cartridge. After the cartridge was fired the continuing action of the cam drew back the lock bringing with it the spent casing which then dropped to the ground. The Gatling gun was first used in combat during theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
. Twelve of the guns were purchased personally by Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to th ...
commanders and used in the trenches during the Siege of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War. Although it is more popularly known as the Siege of Petersburg, it was not a cla ...
(June 1864 – April 1865). Eight other Gatling guns were fitted on gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.
History Pre-ste ...
s. The gun was not accepted by the Army until 1866, when a sales representative of the manufacturing company demonstrated it in combat.Emmott, N.W. "The Devil's Watering Pot" ''United States Naval Institute
The United States Naval Institute (USNI) is a private non-profit military association that offers independent, nonpartisan forums for debate of national security issues. In addition to publishing magazines and books, the Naval Institute holds s ...
Proceedings'' September 1972 p. 70. On 17 July 1863, Gatling guns were purportedly used to overawe New York anti-draft rioters. Post-Civil War, two Gatling guns were brought by a Pennsylvania National Guard
The Pennsylvania National Guard is one of the oldest and largest National Guards in the United States Department of Defense. It traces its roots to 1747 when Benjamin Franklin established the Associators in Philadelphia.
With more than 18,000 per ...
unit from Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
to use against strikers in the Pittsburgh Railway riots. During the American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
, Gatling guns saw frequent service, though famously ''not'' used at the Battle of the Little Bighorn
The Battle of the Little Bighorn, known to the Lakota and other Plains Indians as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, and also commonly referred to as Custer's Last Stand, was an armed engagement between combined forces of the Lakota Sioux, No ...
when Gen. George Armstrong Custer chose not to bring any with his main force. In 1885, Lieutenant Arthur L. Howard of the Connecticut National Guard took a personally owned Gatling gun to Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North ...
, Canada for use with the Canadian military against Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which deri ...
rebels during Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its first ...
's North-West Rebellion
The North-West Rebellion (french: Rébellion du Nord-Ouest), also known as the North-West Resistance, was a resistance by the Métis people under Louis Riel and an associated uprising by First Nations Cree and Assiniboine of the District of ...
.
Gatling guns were used by the U.S. Army during both the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cl ...
and the Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
. A four-gun battery of Colt-made Model 1895 ten-barrel Gatling guns in .30 Army
The .30-40 Krag (also known as .30 U.S. and .30 Army) was a cartridge developed in the early 1890s to provide the U.S. armed forces with a smokeless powder cartridge suited for use with modern small-bore repeating rifles to be selected in the 1 ...
was formed into a separate detachment led by Lt. John "Gatling Gun" Parker. The detachment proved very effective, supporting the advance of American forces at the Battle of San Juan Hill
The Battle of San Juan Hill, also known as the Battle for the San Juan Heights, was a major battle of the Spanish–American War fought between an American force under the command of William Rufus Shafter and Joseph Wheeler against a Spanish ...
. Three of the Gatlings with swivel mountings were used with great success against the Spanish defenders.Parker, John H. (Lt.), ''The Gatlings at Santiago'', Middlesex, UK: Echo Library (reprinted 2006) Despite this, the Gatling's weight and cumbersome artillery carriage hindered its ability to keep up with infantry forces over difficult ground, particularly in Cuba and the Philippines, where outside the major cities there were heavily foliaged forests and steep mountain paths, and the roads were often little more than jungle footpaths.
Elsewhere, a Gatling gun was purchased in April 1867 for the Argentine Army
The Argentine Army ( es, Ejército Argentino, EA) is the land force branch of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic and the senior military service of Argentina. Under the Argentine Constitution, the president of Argentina is the command ...
by minister Domingo F. Sarmiento
Domingo Faustino Sarmiento (; born Domingo Faustino Fidel Valentín Sarmiento y Albarracín; 15 February 1811 – 11 September 1888) was an Argentine activist, intellectual, writer, statesman and the second President of Argentina. His writing sp ...
under instructions from president Bartolomé Mitre
Bartolomé Mitre Martínez (26 June 1821 – 19 January 1906) was an Argentine statesman, soldier and author. He was President of Argentina from 1862 to 1868 and the first president of unified Argentina.
Mitre is known as the most versatile ...
. Captain Luis Germán Astete of the Peruvian Navy
The Peruvian Navy ( es, link=no, Marina de Guerra del Perú, abbreviated MGP) is the branch of the Peruvian Armed Forces tasked with surveillance, patrol and defense on lakes, rivers and the Pacific Ocean up to from the Peruvian littoral. Addit ...
took dozens of Gatling guns with him in December 1879 from the United States for use during the Peru-Chile War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific ( es, link=no, Guerra del Pacífico), also known as the Saltpeter War ( es, link=no, Guerra del salitre) and by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought ...
, especially in the Battle of Tacna (May 1880) and the Battle of San Juan (January 1881). The Gatling gun was used most successfully to expand European colonial empires
A colonial empire is a collective of territories (often called colonies), either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.
Before the expansion of early mod ...
in Africa to defeat mounting massed attacks by indigenous warriors (e.g. the Zulu, Bedouin, and Mahdists
The Mahdist War ( ar, الثورة المهدية, ath-Thawra al-Mahdiyya; 1881–1899) was a war between the Mahdist Sudanese of the religious leader Muhammad Ahmad bin Abd Allah, who had proclaimed himself the "Mahdi" of Islam (the "Guided On ...
). Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. T ...
purchased 400 Gatling guns against Turkmen
Turkmen, Türkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish desc ...
cavalry and other nomads of Central Asia.Emmott, N.W. "The Devil's Watering Pot" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' September 1972 p. 71. The British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gur ...
first deployed the Gatling gun in 1873–74 during the Anglo-Ashanti wars
The Anglo-Ashanti wars were a series of five conflicts that took place between 1824 and 1900 between the Ashanti Empire—in the Akan interior of the Gold Coast—and the British Empire and its African allies. Though the Ashanti emerged victor ...
, and extensively during the latter actions of the 1879 Anglo-Zulu war
The Anglo-Zulu War was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Following the passing of the British North America Act of 1867 forming a federation in Canada, Lord Carnarvon thought that a similar political effort, coup ...
. The Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
used Gatling guns during the 1882 Anglo-Egyptian War
The British conquest of Egypt (1882), also known as Anglo-Egyptian War (), occurred in 1882 between Egyptian and Sudanese forces under Ahmed ‘Urabi and the United Kingdom. It ended a nationalist uprising against the Khedive Tewfik Pasha. ...
.Emmott, N.W. "The Devil's Watering Pot" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' September 1972 p. 72.
Automatic
After the original Gatling gun was replaced in service by newer recoil-/gas-operated
Gas-operation is a system of operation used to provide energy to operate locked breech, autoloading firearms. In gas-operation, a portion of high-pressure gas from the cartridge being fired is used to power a mechanism to dispose of the spen ...
machine guns, the approach of using multiple rotating barrels fell into disuse for many decades. However, some prototypes were developed during the interwar years, but rarely used. During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, Imperial Germany
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
worked on the Fokker-Leimberger
The Fokker-Leimberger was an externally powered, 12-barrel rifle-caliber rotary gun developed in Germany during the First World War. The action of the Fokker-Leimberger differed from that of a Gatling in that it employed a rotary split-breech ...
, an externally powered 12-barrel Gatling gun nicknamed "nutcracker
A nutcracker is a tool designed to open nuts by cracking their shells. There are many designs, including levers, screws, and ratchets. The lever version is also used for cracking lobster and crab shells.
A decorative version portrays a person w ...
", that could fire more than 7,200 rounds per minute, though many accused it of exaggeration.Anthony G Williams (8 November 2005)SPLIT BREECH GUNS: THE NUTCRACKER AND THE 40MM MK 18
Weyl
''Flight'', 8 March 1957, pages 313–314 Failures during the war were attributed to the poor quality of German wartime ammunition, although the type of breech employed had ruptured-case problems in a British 1950s experimental weapon. Fokker continued to experiment with this type of breech after his post-war move to the United States. A different Fokker prototype in a US museum attests to the failure of this line of development. After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the U.S. Army Air Force determined that an improved automatic cannon with an extremely high rate of fire was required against fast-moving enemy jet aircraft
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by jet engines.
Whereas the engines in propeller-powered aircraft generally achieve their maximum efficiency at much lower speeds and altitudes, jet ...
. Using experience gained from the ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
'' MG 151 and MK 108 cannon
The MK 108 (German: ''Maschinenkanone''—"machine cannon") was a 30 mm caliber autocannon manufactured in Germany during World War II by Rheinmetall‑ Borsig for use in aircraft.
The cannon saw widespread use as an anti-bomber weapon during t ...
s, a larger-caliber cannon shell for the new gun was deemed desirable. In June 1946, the General Electric Company
The General Electric Company (GEC) was a major British industrial conglomerate involved in consumer and defence electronics, communications, and engineering. The company was founded in 1886, was Britain's largest private employer with over 250 ...
was awarded a U.S. military defense contract to develop a high-ROF aircraft gun, which GE termed "Project Vulcan". While researching prior work, ordnance engineers recalled the experimental electrically-driven Gatling weapons from the turn of the 20th century. In 1946, a Model 1903 Gatling gun borrowed from a museum was set up with an electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
and test-fired, briefly managing a rate of 5,000 rounds per minute. In 1949, GE began testing the first model of its modified Gatling design, now called the ''Vulcan Gun''. The first prototype was designated the T45 (Model A), firing ammunition at about 2,500 rounds per minute from six barrels, and in 1950 GE delivered ten initial Model A .60 cal. T45 guns for evaluation. Thirty-three model C T45 guns in three calibers (.60 cal., 20 mm and 27 mm) were delivered in 1952 for additional testing. After extensive testing, the T171 20mm gun was selected for further development, and was standardized by the U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force in 1956 as the M61 Vulcan
The M61 Vulcan is a hydraulically, electrically, or pneumatically driven, six-barrel, air-cooled, electrically fired Gatling-style rotary cannon which fires rounds at an extremely high rate (typically 6,000 rounds per minute). The M61 and its ...
gun.
See also
*Repeating rifle A repeating rifle is a single- barreled rifle capable of repeated discharges between each ammunition reloads. This is typically achieved by having multiple cartridges stored in a magazine (within or attached to the gun) and then fed individually ...
* Semi-automatic
References
{{Firearms Firearm actions