Registration, Evaluation, Authorization And Restriction Of Chemicals on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006, amended on 16 December 2008 by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008. REACH addresses the production and use of
report
“The numbers show a similar picture to previous years," it said. Industry group
the problem. Substance evaluation is performed by the relevant authorities when there is a reason to suspect that a substance presents a risk to human health or the environment (e.g. because of its structural similarity to another substance). Therefore, all registration dossiers submitted for a substance are examined together and any other available information is taken into account. Substance evaluation is carried out under a programme known as the Community Rolling Action Plan
CoRAP
. A
independent review
of progress by national officials published in late 2018 found that 352 substances have so far been prioritised for substance evaluation with 94 completed. For almost half the 94, officials concluded that existing commercial use of the substance is unsafe for human health and/or the environment. Risk management has been initiated for twelve substances since REACH came into force. For 74% of substances (34 out of 46), concerns were demonstrated, but no actual regulatory follow-up has yet been initiated. In addition, national officials concluded that 64% of the substances under evaluation (126 out of 196) lacked the information needed to demonstrate the safety of the chemicals marketed in Europe due to inadequate industry data.
185 times
with no eligible request ever having been rejected. NGO
have complained
that authorisations have been granted despite safer alternatives existing and that this was hindering substitution. In March 2019, the European Court of Justic
revoked
an authorisation in a ruling that criticised the European Chemicals Agency for failing to identify a safer alternative.
 Manufactures and importers should develop risk reduction measures for all known uses of the chemical including downstream uses. Downstream users such as plastic pipe producers should provide detail of their uses to their suppliers. In cases where downstream users decide not to disclose this information, they need to have their own CSR.
Manufactures and importers should develop risk reduction measures for all known uses of the chemical including downstream uses. Downstream users such as plastic pipe producers should provide detail of their uses to their suppliers. In cases where downstream users decide not to disclose this information, they need to have their own CSR.
report
for the European Commission. Apart from the potential costs to industry and the complexity of the new law, REACH has also attracted concern because of
European Chemicals Agency
- The organization responsible for implementing REACH
- for enterprise and industry
Database of REACH consortia
- Chemical Watch
Development of a mechanistic model for the Advanced REACH Tool
TNO Report
ECHA Guidance on REACH implementationAdvanced REACH Tool (ART)REACH resources and tools
- Institute of Occupational Medicine fact sheets
REACH and nanomaterials
* * * * * {{Authority control Occupational safety and health law Toxicology European Union regulations Evaluation 2006 in European Union law Chemical safety Regulation of chemicals in the European Union
chemical substance
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be com ...
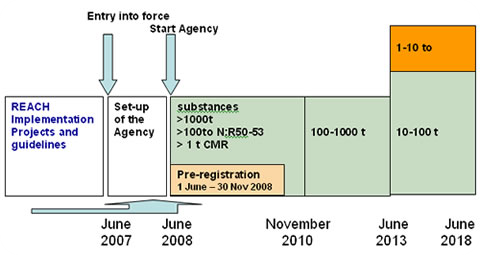
s, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Its 849 pages took seven years to pass, and it has been described as the most complex legislation in the Union's history and the most important in 20 years. It is the strictest law to date regulating chemical substances and will affect industries throughout the world. REACH entered into force on 1 June 2007, with a phased implementation over the next decade. The regulation also established the European Chemicals Agency, which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of REACH.
Overview
When REACH is fully in force, it will require all companies manufacturing or importing chemical substances into the European Union in quantities of onetonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
or more per year to register these substances with a new European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in , Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
. Since REACH applies to some substances that are contained in objects (''articles'' in REACH terminology), any company importing goods into Europe could be affected.
The European Chemicals Agency has set three major deadlines for registration of chemicals. In general these are determined by tonnage manufactured or imported, with 1000 tonnes/a. being required to be registered by 1 December 2010, 100 tonnes/a. by 1 June 2013 and 1 tonne/a. by 1 June 2018. In addition, chemicals of higher concern or toxicity also have to meet the 2010 deadline.
About 143,000 chemical substances marketed in the European Union were pre-registered by the 1 December 2008 deadline. Although pre-registering was not mandatory, it allows potential registrants much more time before they have to fully register. Supply of substances to the European market which have not been pre-registered or registered is illegal (known in REACH as "no data, no market").
REACH also addresses the continued use of chemical '' substances of very high concern'' (SVHC) because of their potential negative impacts on human health or the environment. From 1 June 2011, the European Chemicals Agency must be notified of the presence of SVHCs in articles if the total quantity used is more than one tonne per year and the SVHC is present at more than 0.1% of the mass of the object. Some uses of SVHCs may be subject to prior authorisation from the European Chemicals Agency, and applicants for authorisation will have to include plans to replace the use of the SVHC with a safer alternative (or, if no safer alternative exists, the applicant must work to find one) – known as ''substitution''. , there were 247 SVHCs on the candidate list for authorization.
REACH applies to all chemicals
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
imported or produced in the EU. The European Chemicals Agency will manage the technical, scientific
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
and administrative aspects of the REACH system.
To somewhat simplify the registration of the 143,000 substances and to limit vertebrate animal testing as far as possible, substance information exchange forums (SIEFs) are formed amongst legal entities (such as manufacturers, importers, and data holders) who are dealing with the same substance. This allows them to join forces and finances to create 1 registration dossier. However, this creates a series of new problems as a SIEF is the cooperation between sometimes a thousand legal entities that did not know each other at all before but suddenly must:
*find each other and start communicating openly and honestly
*start sharing data
*start sharing costs in a fair and transparent way
*democratically and in full consensus take the most complex decisions
in order to complete a several thousand end points dossier in a limited time.
The European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
supports businesses affected by REACH by handing out – free of charge – a software application ( IUCLID) that simplifies capturing, managing, and submitting data on chemical properties and effects. Such submission is a mandatory part of the registration process. Under certain circumstances the performance of a chemical safety assessment (CSA) is mandatory and a chemical safety report (CSR) assuring the safe use of the substance has to be submitted with the dossier. Dossier submission is done using the web-based software REACH-IT.
The aim of REACH is to improve the protection of human health and the environment by identification of the intrinsic properties of chemical substances. At the same time, innovative capability and competitiveness of the EU chemicals industry should be enhanced.
Background
The European Commission's (EC) White Paper of 2001 on a 'future chemical strategy' proposed a system that requires chemicals manufactured in quantities of greater than 1 tonne to be 'registered', those manufactured in quantities greater than 100 tonnes to be 'evaluated', and certain substances of high concern (for example carcinogenic, mutagenic and toxic to reproduction – CMRs) to be 'authorised'. The EC adopted its proposal for a new scheme to manage the manufacture, importation and supply of chemicals in Europe on in October 2003. This proposal eventually became law once the European Parliament officially approved its final text of REACH. It came into force on 1 June 2007.Requirements
One of the major elements of the REACHregulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. Fo ...
is the requirement to communicate information on chemicals
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
up and down the supply chain
A supply chain is a complex logistics system that consists of facilities that convert raw materials into finished products and distribute them to end consumers or end customers, while supply chain management deals with the flow of goods in distri ...
. This ensures that manufacturers, importers, and also their customers are aware of information relating to health
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, p ...
and safety
Safety is the state of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
The word 'safety' entered the English language in the 1 ...
of the products supplied. For many retail
Retail is the sale of goods and services to consumers, in contrast to wholesaling, which is the sale to business or institutional customers. A retailer purchases goods in large quantities from manufacturers, directly or through a wholes ...
ers the obligation to provide information about substances in their products within 45 days of receipt of a request from a consumer
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or use purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. ...
is particularly challenging. Having detailed information on the substances present in their products will allow retailers to work with the manufacturing base to substitute or remove potentially harmful substances from products. The list of harmful substances is continuously growing and requires organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
s to constantly monitor any announcements and additions to the REACH scope. This can be done on the European Chemicals Agency's website.
Registration
A requirement is to collect, collate and submit data to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) on the hazardous properties of all substances (except Polymers and non-isolated intermediates) manufactured or imported into the EU in quantities above 1 tonne per year. Certain substances of high concern, such as carcinogenic, mutagenic and reproductive toxic substances (CMRs) will have to be authorised. Chemicals will be registered in three phases according to the tonnage of the substance evaluation: More than 1000 tonnes a year, or substances of highest concern, must be registered in the first 3 years; 100–1000 tonnes a year must be registered in the first 6 years; 1–100 tonnes a year must be registered in the first 11 years. In addition, industry should prepare risk assessments and provide controls measures for using the substance safely to downstream users.Evaluation
Evaluation provides a means for the authorities to require registrants, and in very limited cases downstream users, to provide further information. There are two types of evaluation: dossier evaluation and substance evaluation: Dossier evaluation is conducted by authorities to examine proposals for testing to ensure that unnecessary animal tests and costs are avoided, and to check the compliance of registration dossier with the registration requirements. Chemical companies failed to provide "important safety information" in nearly three quarters (74% or 211 of 286) of cases checked by authorities, according to the European Chemicals Agency's 2018 annual progresreport
“The numbers show a similar picture to previous years," it said. Industry group
Cefic
The European Chemical Industry Council or Cefic (from its former French name ''Conseil Européen des Fédérations de l'Industrie Chimique'') is the main European trade association for the chemical industry. It was founded in 1972. Its headquar ...
br>acknowledgedthe problem. Substance evaluation is performed by the relevant authorities when there is a reason to suspect that a substance presents a risk to human health or the environment (e.g. because of its structural similarity to another substance). Therefore, all registration dossiers submitted for a substance are examined together and any other available information is taken into account. Substance evaluation is carried out under a programme known as the Community Rolling Action Plan
CoRAP
. A
independent review
of progress by national officials published in late 2018 found that 352 substances have so far been prioritised for substance evaluation with 94 completed. For almost half the 94, officials concluded that existing commercial use of the substance is unsafe for human health and/or the environment. Risk management has been initiated for twelve substances since REACH came into force. For 74% of substances (34 out of 46), concerns were demonstrated, but no actual regulatory follow-up has yet been initiated. In addition, national officials concluded that 64% of the substances under evaluation (126 out of 196) lacked the information needed to demonstrate the safety of the chemicals marketed in Europe due to inadequate industry data.
Authorisation
REACH allows restricted substances of very high concern to continue being used, subject to authorisation. This authorisation requirement attempts to ensure that risks from the use of such substances are either adequately controlled or justified by socio-economic grounds, having taken into account the available information on alternative substances or processes. The Regulation enables restrictions of use to be introduced across the European Community where this is shown to be necessary. Member States or the Commission may prepare such proposals. By March 2019, authorisation had been grante185 times
with no eligible request ever having been rejected. NGO
have complained
that authorisations have been granted despite safer alternatives existing and that this was hindering substitution. In March 2019, the European Court of Justic
revoked
an authorisation in a ruling that criticised the European Chemicals Agency for failing to identify a safer alternative.
Information exchange
 Manufactures and importers should develop risk reduction measures for all known uses of the chemical including downstream uses. Downstream users such as plastic pipe producers should provide detail of their uses to their suppliers. In cases where downstream users decide not to disclose this information, they need to have their own CSR.
Manufactures and importers should develop risk reduction measures for all known uses of the chemical including downstream uses. Downstream users such as plastic pipe producers should provide detail of their uses to their suppliers. In cases where downstream users decide not to disclose this information, they need to have their own CSR.
History
REACH is the product of a wide-ranging overhaul of EU chemical policy. It passed the first reading in theEuropean Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
on 17 November 2005, and the Council of Ministers
Council of Ministers is a traditional name given to the supreme Executive (government), executive organ in some governments. It is usually equivalent to the term Cabinet (government), cabinet. The term Council of State is a similar name that also m ...
reached a political agreement for a common position on 13 December 2005. The European Parliament approved REACH on 13 December 2006 and the Council of Ministers formally adopted it on 18 December 2006. Weighing up expenditure versus profit has always been a significant issue, with the estimated cost of compliance being around €5 billion over 11 years, and the assumed health benefits of saved billions of euro in healthcare costs. However, there have been different studies on the estimated cost which vary considerably in the outcome. It came into force on 20 January 2009, and will be fully implemented by 2015.
A separate regulation – the CLP Regulation
The CLP Regulation (for "Classification, Labelling and Packaging") is a European Union regulation from 2008, which aligns the European Union system of classification, labelling and packaging of chemical substances and mixtures to the Globally ...
(for "Classification, Labelling, Packaging") – implements the United Nations Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labellin ...
(GHS) and will steadily replace the previous Dangerous Substances Directive and Dangerous Preparations Directive
The Dangerous Preparations Directive was a European Union directive in the field of occupational safety and health and consumer protection that came into force in 30 July 1999. It complemented the Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) an ...
.
The REACH regulation was amended in April 2018 to include specific information requirements for nanomaterials
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science ...
.
In the European Green Deal of 2020, a commitment was made to update the REACH regulation to ban between 7,000 and 12,000 toxic substances in all consumer products, except where truly essential. The goal was among the priorities of the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
, but is in danger of being radically revised due to lobbying
Lobbying is a form of advocacy, which lawfully attempts to directly influence legislators or government officials, such as regulatory agency, regulatory agencies or judiciary. Lobbying involves direct, face-to-face contact and is carried out by va ...
by the EU chemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies and other organizations that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, the chemical industry converts raw materials ( oil, natural gas, air, ...
and the positions taken by the European People's Party
The European People's Party (EPP) is a European political party with Christian democracy, Christian democratic, liberal conservatism, liberal-conservative, and conservative member parties. A transnational organisation, it is composed of other p ...
.
Rationale
The legislation was proposed under dual reasoning: protection ofhuman health
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, pain ...
and protection of the environment.
Using potentially toxic substances (such as phthalate
Phthalates ( ), or phthalate esters, are esters of phthalic acid. They are mainly used as plasticizers, i.e., substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity. They are used primarily to soften ...
s or brominated flame retardant
Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) are organobromine compounds that have an inhibitory effect on combustion chemistry and tend to reduce the flammability of products containing them. The brominated variety of commercialized chemical flame retarda ...
s) is deemed undesirable and REACH will force the use of certain substances to be phased out. Using potentially toxic substances in products other than those ingested by humans (such as electronic device
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and ...
s) may seem to be safe, but there are several ways in which chemicals can enter the human body and the environment. Substances can leave particles during consumer
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or use purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. ...
use, for example into the air where they can be inhaled or ingested. Even where they might not do direct harm to humans, they can contaminate the air or water, and can enter the food chain through plants, fish or other animals. According to the European Commission, little safety information exists for 99 percent of the tens of thousands of chemicals placed on the market before 1981. There were 100,106 chemicals in use in the EU in 1981, when the last survey was performed. Of these only 3,000 have been tested and over 800 are known to be carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic to reproduction. These are listed in the Annex 1 of the Dangerous Substances Directive (now Annex VI of the CLP Regulation
The CLP Regulation (for "Classification, Labelling and Packaging") is a European Union regulation from 2008, which aligns the European Union system of classification, labelling and packaging of chemical substances and mixtures to the Globally ...
).
Continued use of many toxic chemicals is sometimes justified because "at very low levels they are not a concern to health". However, many of these substances may bioaccumulate in the human body, thus reaching dangerous concentrations. They may also chemically react with one another, producing new substances with new risks.
In non-EU countries
A number of countries outside of the European Union have started to implement REACH regulations or are in the process of adopting such a regulatory framework to approach a more globalized system of chemicals registration under theGlobally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labellin ...
(GHS).
Balkan countries such as Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
and Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
are in the process of adopting the EU REACH system under the auspices of the EU IPA programme. Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
has moved towards implementation of REACH through partial revision of the Swiss Chemical Ordinance on February 1, 2009. The new Chemicals Management Regulation in Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
is paving the way for the planned adoption of REACH in 2013. China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
has moved towards a more efficient and coherent system for the control of chemicals in compliance with GHS.
In the UK, the government announced a "UK REACH" that the UK's Chemical Industry Association described as a "hugely expensive duplication" of the EU's safety data. The new regulations were to be enforced from October 2021 but deferred to October 2023, and then to October 2025. Following industry representations, the responsible Minister announced "that officials would now explore 'a new model' for UK REACH registrations that would look to 'reduce the need for replicating EU Reach data packages'". In March 2021, a group of more than 20 leading UK organisations, including the CHEM Trust and Breast Cancer UK, "rejected industry proposals to streamline UK Reach as a 'major weakening' of the envisaged post-Brexit regime".
Controversy
Over a decade after REACH came into force, progress has been slow. Of the 100,000 chemicals used in Europe today, “only a small fraction has been thoroughly evaluated by authorities regarding their health and environmental properties and impacts, and even fewer are actually regulated,” according toreport
for the European Commission. Apart from the potential costs to industry and the complexity of the new law, REACH has also attracted concern because of
animal testing
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, animal research, and ''in vivo'' testing, is the use of animals, as model organisms, in experiments that seek answers to scientific and medical questions. This approach can be contrasted ...
. Animal tests on vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s are now required but allowed only once per each new substance and if suitable alternatives cannot be used. If a company pays for such tests, it must sell the rights of the results for a "reasonable" price, which is not defined. There are additional concerns that access to the necessary information may prove very costly for potential registrants needing to purchase it.
On 8 June 2006, the REACH proposal was criticized by non-EU countries, including the United States, India and Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, which stated that the bill would hamper global trade.
The cosmetics company Lush were critical of the legislation when it was first proposed in 2006, as they believed it would increase animal testing
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, animal research, and ''in vivo'' testing, is the use of animals, as model organisms, in experiments that seek answers to scientific and medical questions. This approach can be contrasted ...
. The cosmetics company wrote to its European customers and also ran an in-store marketing campaign, asking for postcards objecting to the legislation be sent to MEPs
A member of the European Parliament (MEP) is a person who has been elected to serve as a popular representative in the European Parliament.
When the European Parliament (then known as the Common Assembly of the European Coal and Steel Comm ...
, a move which resulted in 80,000 Lush customers sending postcards. In December 2006, Lush protested outside the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
in Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
, by dumping horse manure outside the building.
An opinion in ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'' in 2009 by Thomas Hartung and Constanza Rovida estimated that 54 million vertebrate animals would be used under REACH and that the costs would amount to €9.5 billion, set against the annual European industry annual turnover of €507 billion. Hartung is the former head of European Centre for the Validation of Alternative Methods (ECVAM). In a news release, ECHA criticised assumptions made by Hartung and Rovida; ECHA's alternative assumptions reduced sixfold the number of animals.
Only representative services
Only representatives are EU-based entities that must comply with REACH (Article 8) and should operate standard, transparent working practices. The Only Representative assumes responsibility and liability for fulfilling obligations of importers in accordance with REACH for substances being brought into the EU by a non-EU manufacturer. Non-EU consultancies offer "only representative" services, though according to REACH it is not possible to register a substance if your "only representative" consultancy company is not based in the EU, unless it is subcontracted to an EU-based registrant. The SIEFs will bring new challenges. An article in the business news service Chemical Watch described how some "pre-registrants" may simply be consultants hoping for work ("gold diggers") while others may be aiming to charge exorbitant rates for the data they have to offer ("jackals").Example of chemical inventories in various countries/regions
Source: * Regulation (EC) Nr. 1907/2006 (REACH) * AICS – Australian Inventory of Chemical Substances * DSL – Canadian Domestic Substances List * NDSL – Canadian Non-Domestic Substances List * KECL (Korean ECL) – Korean Existing Chemicals List * ENCS (MITI) – Japanese Existing and New Chemical Substances * PICCS – Philippine Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances * TSCA – US Toxic Substances Control Act * Giftliste 1 (Swiss list of toxic substances, repealed in 2005)Authorisation List
The European Chemical Agency (ECHA) has published the REACH Authorisation List, in an effort to tighten the use of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs). The list is an official recommendation from the ECHA to theEuropean Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
. The list is also regularly updated and expanded. Currently the Candidate List for Authorisation comprises a total of 247 SVHCs (see ECHA list at https://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table), some of which are already active on the Authorization List.
To sell or use these substances, manufacturers, importers, and retailers in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU) must apply for authorization from the ECHA
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA; ) is an agency of the European Union working for the safe use of chemicals. It manages the technical and administrative aspects of the implementation of the European Union regulation called Registration, ...
. The applicant is to submit a chemical safety report on the risks entailed by the substance, as well as an analysis of possible alternative substances or technologies including present and future research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage ...
processed.
See also
* Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability Towards a Toxic-Free Environment *Consumer protection
Consumer protection is the practice of safeguarding buyers of goods and services, and the public, against unfair practices in the marketplace. Consumer protection measures are often established by law. Such laws are intended to prevent business ...
* Environmental health
Environmental health is the branch of public health concerned with all aspects of the natural environment, natural and built environment affecting human health. To effectively control factors that may affect health, the requirements for a hea ...
* International Material Data System
* Kashinhou – Japanese law
* Pesticides in the European Union
* Porter hypothesis
* Quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
* Toxic Substances Control Act of 1976 – US law
References
External links
* *European Chemicals Agency
- The organization responsible for implementing REACH
- for enterprise and industry
Database of REACH consortia
- Chemical Watch
Development of a mechanistic model for the Advanced REACH Tool
TNO Report
ECHA Guidance on REACH implementation
- Institute of Occupational Medicine fact sheets
REACH and nanomaterials
* * * * * {{Authority control Occupational safety and health law Toxicology European Union regulations Evaluation 2006 in European Union law Chemical safety Regulation of chemicals in the European Union