Regio XII Piscina Publica on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
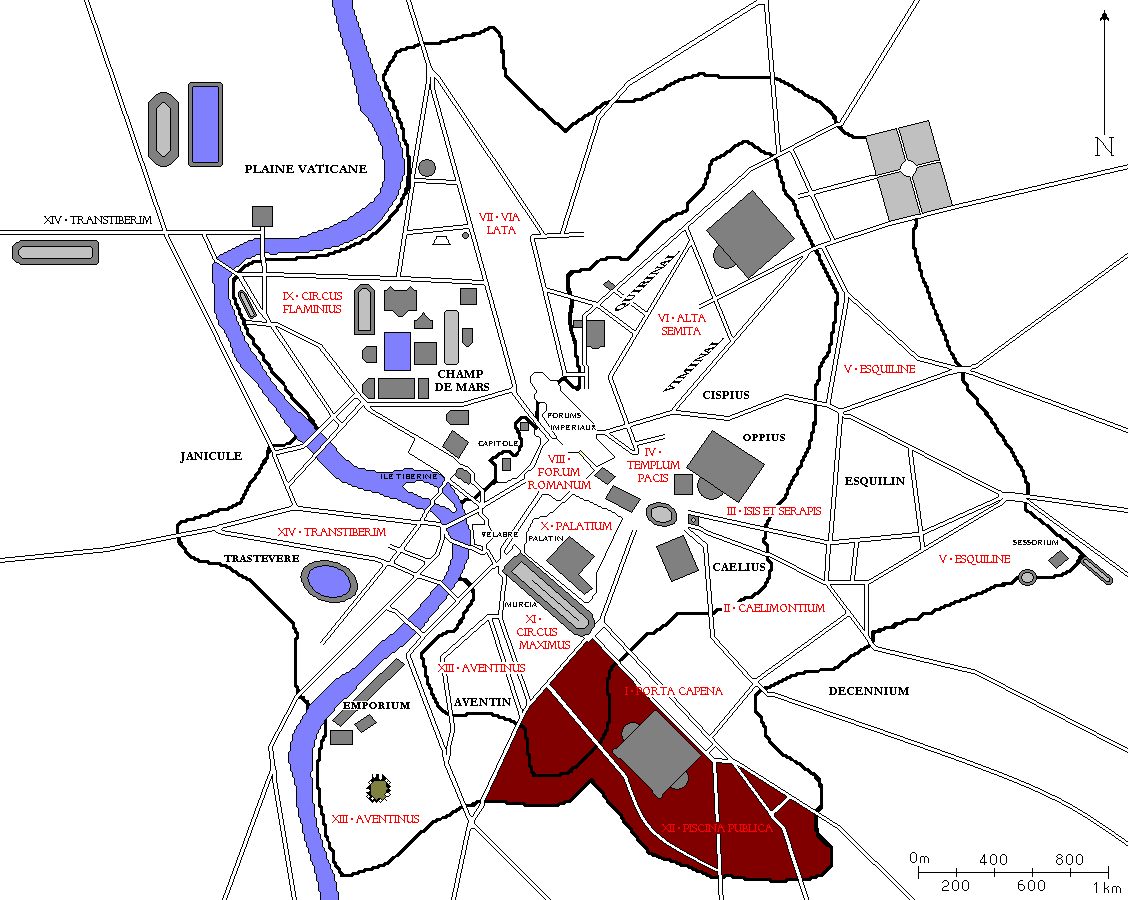 The Regio XII Piscina Publica is the twelfth regio of imperial
The Regio XII Piscina Publica is the twelfth regio of imperial
 Regio XII was named after the principal feature of this area during the reign of Augustus, the ''Piscina Publica'', a public reservoir and swimming pool, built around the 3rd century BCE. In extent, this region was bordered by the ''Vicus Piscinae Publicae'' to the north, the
Regio XII was named after the principal feature of this area during the reign of Augustus, the ''Piscina Publica'', a public reservoir and swimming pool, built around the 3rd century BCE. In extent, this region was bordered by the ''Vicus Piscinae Publicae'' to the north, the  The ''Piscina'' itself sat in the low-lying area between the Via Appia, the
The ''Piscina'' itself sat in the low-lying area between the Via Appia, the
(online version)
* Gregorovius, Ferdinand, ''History of the City of Rome in the Middle Ages'', Vol. 1, (1894)
''Curiosum - Notitia''. 4th-century descriptions of the regions of Rome and their main buildings
from the original on 8 June 2019. Regions of Augustan Rome Subdivisions of Rome Topography of the ancient city of Rome
 The Regio XII Piscina Publica is the twelfth regio of imperial
The Regio XII Piscina Publica is the twelfth regio of imperial Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, under Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
's administrative reform. Regio XII took its name from the ''Piscina Publica
In ancient Rome, the Piscina Publica ("Public Pool") was a public reservoir and swimming pool located in Regio XII. The region itself came to be called informally ''Piscina Publica'' from the landmark. The ''piscina'' was situated in the low-lying ...
'', a swimming pool that disappeared during the middle imperial period.
Geographic extent and important features
 Regio XII was named after the principal feature of this area during the reign of Augustus, the ''Piscina Publica'', a public reservoir and swimming pool, built around the 3rd century BCE. In extent, this region was bordered by the ''Vicus Piscinae Publicae'' to the north, the
Regio XII was named after the principal feature of this area during the reign of Augustus, the ''Piscina Publica'', a public reservoir and swimming pool, built around the 3rd century BCE. In extent, this region was bordered by the ''Vicus Piscinae Publicae'' to the north, the Via Ostiensis
The Via Ostiensis ( it, via Ostiense) was an important road in ancient Rome. It ran west from the city of Rome to its important sea port of Ostia Antica, from which it took its name. The road began near the Forum Boarium, ran between the Aventin ...
to the west, the Via Appia
The Appian Way (Latin and Italian: ''Via Appia'') is one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, in southeast Italy. Its importance is indicated by its common name, rec ...
and the Via Latina
The Via Latina (Latin for "Latin Road") was a Roman road of Italy, running southeast from Rome for about 200 kilometers.
Route
It led from the Porta Latina in the Aurelian walls of Rome to the pass of Mount Algidus; it was important in the ear ...
to the east, and the Aurelian Walls to the south. Its principal gates through the walls were the Porta Appia
The Porta San Sebastiano is the largest and one of the best-preserved gates passing through the Aurelian Walls in Rome (Italy).
History
Originally known as the Porta Appia, the gate sat astride the Appian Way, the ''regina viarum'' (queen of th ...
and the Porta Ardeatina
Porta Ardeatina was one of the gates of the Aurelian Walls in Rome (Italy).
The gate was built in the time of Nero. It stands at an angle in the Aurelian Walls.
It was placed in a halfway point between Porta Appia and Porta San Paolo, close t ...
. A measurement taken at the end of the 4th century recorded that the perimeter of the region was 12,000 Roman feet
The ancient Roman units of measurement were primarily founded on the Hellenic system, which in turn was influenced by the Egyptian system and the Mesopotamian system. The Roman units were comparatively consistent and well documented.
Length
T ...
(approximately 3.5 km), making it one of the smaller of the Augustan regions.
 The ''Piscina'' itself sat in the low-lying area between the Via Appia, the
The ''Piscina'' itself sat in the low-lying area between the Via Appia, the Servian Wall
The Servian Wall ( la, Murus Servii Tullii; it, Mura Serviane) was an ancient Roman defensive barrier constructed around the city of Rome in the early 4th century BC. The wall was built of volcanic tuff and was up to in height in places, wide ...
, and the northeast slope of the Aventine Hill
The Aventine Hill (; la, Collis Aventinus; it, Aventino ) is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth ''rione'', or ward, of Rome.
Location and boundaries
The Aventine Hill is the sou ...
. If it was still present, it was eventually destroyed to make way for the monumental Baths of Caracalla
The Baths of Caracalla ( it, Terme di Caracalla) in Rome, Italy, were the city's second largest Ancient Rome, Roman public baths, or ''thermae'', after the Baths of Diocletian. The baths were likely built between AD 212 (or 211) and 216/217, durin ...
in the 3rd century CE, whose massive ruins are still visible. In addition, the region hosted the Temple of Bona Dea
The Temple of Bona Dea was an ancient sanctuary in Ancient Rome, erected the 3rd century BC and dedicated to the Bona Dea, goddess Bona Dea.Samuel Ball Platner, "Bona Dea Subsaxana", A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome, Oxford University Pre ...
and contained the house of the Roman consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politic ...
Lucius Fabius Cilo
Lucius Fabius Cilo, full name Lucius Fabius Cilo Septiminus Catinius Acilianus Lepidus Fulcinianus, was a Roman senator, who was a confidant of Septimius Severus. He held a number of appointments that have been dated to the reigns of Commodus and S ...
, which was eventually turned into the church of Santa Balbina
Santa Balbina is a Roman Catholic basilica church in located in the Aventine rione, adjacent to the Baths of Caracalla in Rome.
History
A church at the site initially was built in the 4th century over the house of consul Lucius Fabius Cilo. P ...
. Its principal street was the ''Via Nova'', which ran parallel to the Via Appia, and took people from the Circus Maximus to the Baths of Caracalla.
In the 180s, a bank and exchange for Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
operated in this region. The region also contained the station of the fourth cohort of the ''Vigiles
The ''Vigiles'' or more properly the ''Vigiles Urbani'' ("watchmen of the City") or ''Cohortes Vigilum'' ("cohorts of the watchmen") were the firefighters and police of ancient Rome.
History
The ''Triumviri Nocturni'' (meaning ''three men of th ...
''. At the turn of the 5th century, the Regio contained 17''aedicula
In ancient Roman religion, an ''aedicula'' (plural ''aediculae'') is a small shrine, and in classical architecture refers to a niche covered by a pediment or entablature supported by a pair of columns and typically framing a statue,"aedicula, n." ...
e'' (shrines), 113 '' domūs'' (patrician houses), 27 ''horrea
A ''horreum'' (plural: ''horrea'') was a type of public warehouse used during the ancient Roman period. Although the Latin term is often used to refer to granaries, Roman ''horrea'' were used to store many other types of consumables; the giant Hor ...
'' (warehouses), 63 '' balneae'' (bath houses) and 81 ''loci'' (fountains).
Subdivisions
At the turn of the 5th century, the Regio was divided into 17 '' vici'' (districts) and 2,487 ''insulae
The Latin word ''insula'' (literally meaning "island", plural ''insulae'') was used in Roman cities to mean either a city block in a city plan, i.e. a building area surrounded by four streets, or, later, a type of apartment building that occup ...
'' (blocks). It had two curators
A curator (from la, cura, meaning "to take care") is a manager or overseer. When working with cultural organizations, a curator is typically a "collections curator" or an "exhibitions curator", and has multifaceted tasks dependent on the parti ...
and was served by 48 Roman magistrate
The Roman magistrates were elected officials in Ancient Rome.
During the period of the Roman Kingdom, the King of Rome was the principal executive magistrate.Abbott, 8 His power, in practice, was absolute. He was the chief priest, lawgiver, judg ...
s.''Notitia'', REGIO XII PISCINA PVBLICA
Notes
{{reflistReferences
* Platner, Samuel Ball, ''A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome'', Oxford University Press (1929(online version)
* Gregorovius, Ferdinand, ''History of the City of Rome in the Middle Ages'', Vol. 1, (1894)
''Curiosum - Notitia''. 4th-century descriptions of the regions of Rome and their main buildings
from the original on 8 June 2019. Regions of Augustan Rome Subdivisions of Rome Topography of the ancient city of Rome