Reagan presidency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Even prior to becoming president, Reagan was the leader of a dramatic conservative shift that undercut many of the domestic and foreign policies that had dominated the national agenda for decades. A major factor in the rise of conservatism was the growing distrust of government in the aftermath of the Watergate scandal. While distrust of high officials had been an American characteristic for two centuries, Watergate engendered heightened levels of suspicion and encouraged the media to engage in a vigorous search for scandals. An unexpected new factor was the emergence of the religious right as a cohesive political force that gave strong support to conservatism.
Other factors in the rise of the conservative movement were the emergence of a " culture war" as a triangular battle among conservatives, traditional liberals, and the
Even prior to becoming president, Reagan was the leader of a dramatic conservative shift that undercut many of the domestic and foreign policies that had dominated the national agenda for decades. A major factor in the rise of conservatism was the growing distrust of government in the aftermath of the Watergate scandal. While distrust of high officials had been an American characteristic for two centuries, Watergate engendered heightened levels of suspicion and encouraged the media to engage in a vigorous search for scandals. An unexpected new factor was the emergence of the religious right as a cohesive political force that gave strong support to conservatism.
Other factors in the rise of the conservative movement were the emergence of a " culture war" as a triangular battle among conservatives, traditional liberals, and the
 Reagan, who had served as
Reagan, who had served as
 Reagan tapped James Baker, who had run Bush's 1980 campaign, as his first
Reagan tapped James Baker, who had run Bush's 1980 campaign, as his first
 Reagan made four successful appointments to the
Reagan made four successful appointments to the
Statement on Signing the Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986.
Collected Speeches, Ronald Reagan Presidential Library. Retrieved August 15, 2007. The bill was largely unsuccessful at halting illegal immigration, and the population of illegal immigrants rose from 5 million in 1986 to 11.1 million in 2013.

 Not long after being sworn into office, Reagan declared more militant policies in the " War on Drugs". He promised a "planned, concerted campaign" against all drugs, in hopes of decreasing drug use, particularly among adolescents. The " crack epidemic," which saw a large number of individuals become addicted to
Not long after being sworn into office, Reagan declared more militant policies in the " War on Drugs". He promised a "planned, concerted campaign" against all drugs, in hopes of decreasing drug use, particularly among adolescents. The " crack epidemic," which saw a large number of individuals become addicted to
 Reagan escalated the Cold War, accelerating a reversal from the policy of détente which had begun in 1979 after the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. Reagan feared that the Soviet Union had gained a military advantage over the United States, and the Reagan administration hoped that heightened military spending would grant the U.S. military superiority and weaken the Soviet economy. Reagan ordered a massive buildup of the United States Armed Forces, directing funding to the B-1 Lancer bomber, the B-2 Spirit bomber,
Reagan escalated the Cold War, accelerating a reversal from the policy of détente which had begun in 1979 after the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. Reagan feared that the Soviet Union had gained a military advantage over the United States, and the Reagan administration hoped that heightened military spending would grant the U.S. military superiority and weaken the Soviet economy. Reagan ordered a massive buildup of the United States Armed Forces, directing funding to the B-1 Lancer bomber, the B-2 Spirit bomber,  In March 1983, Reagan introduced the
In March 1983, Reagan introduced the
 The Reagan administration placed a high priority on the Central America and the Caribbean Sea, which it saw as a key front in the Cold War. Reagan and his foreign policy team were particularly concerned about the potential influence of Cuba on countries such as
The Reagan administration placed a high priority on the Central America and the Caribbean Sea, which it saw as a key front in the Cold War. Reagan and his foreign policy team were particularly concerned about the potential influence of Cuba on countries such as
 Three different Soviet leaders died between 1982 and 1985, leaving the Soviets with an unstable leadership until
Three different Soviet leaders died between 1982 and 1985, leaving the Soviets with an unstable leadership until
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over Democratic
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
incumbent President Jimmy Carter in the 1980 presidential election. Four years later, in the 1984 election, he defeated Democrat former vice president Walter Mondale to win re-election in a larger landslide. Reagan was succeeded by his vice president, George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
. Reagan's 1980 election resulted from a dramatic conservative shift to the right in American politics, including a loss of confidence in liberal, New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
, and Great Society programs and priorities that had dominated the national agenda since the 1930s.
Domestically, the Reagan administration enacted a major tax cut, sought to cut non-military spending, and eliminated federal regulations. The administration's economic policies, known as " Reaganomics", were inspired by supply-side economics
Supply-side economics is a macroeconomic theory that postulates economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-side economics, consumers will benefit fr ...
. The combination of tax cuts and an increase in defense spending led to budget deficits, and the federal debt increased significantly during Reagan's tenure. Reagan signed the Tax Reform Act of 1986 (which simplified the tax code by reducing rates and removing several tax breaks) and the Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986 (which enacted sweeping changes to U.S. immigration law and granted amnesty to three million illegal immigrants). Reagan also appointed more federal judges than any other president, including four Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
Justices.
Reagan's foreign policy
A State (polity), state's foreign policy or external policy (as opposed to internal or domestic policy) is its objectives and activities in relation to its interactions with other states, unions, and other political entities, whether bilaterall ...
stance was resolutely anti-communist
Anti-communism is Political movement, political and Ideology, ideological opposition to communism. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in the Russian Empire, and it reached global dimensions during the Cold War, w ...
; its plan of action, known as the Reagan Doctrine, sought to roll back
''Roll Back'' is an album by Irish rock band Horslips, their first since ''Short Stories/Tall Tales'' 25 years earlier. It is a collection of acoustic re-workings of various songs from the band's catalogue.
Background
In March 2004, three Ho ...
the global influence of the Soviet Union in an attempt to end the Cold War. Under this doctrine, the Reagan administration initiated a massive buildup of the United States military; promoted new technologies such as missile defense systems; and, in 1983, undertook an invasion of Grenada
The United States invasion of Grenada began at dawn on 25 October 1983. The United States and a coalition of six Caribbean nations invaded the island nation of Grenada, north of Venezuela. Codenamed Operation Urgent Fury by the U.S. military, ...
, the first major overseas action by U.S. troops since the end of the Vietnam War. The administration also created controversy by granting aid to paramilitary forces seeking to overthrow leftist governments, particularly in war-torn Central America and Afghanistan. Specifically, the Reagan administration engaged in covert arms sales to Iran to fund Contra rebels in Nicaragua that were fighting to overthrow their nation's socialist government; the resulting scandal led to the conviction or resignation of several administration officials. During Reagan's second term, he sought closer relations with Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
, and the two leaders signed a major arms control
Arms control is a term for international restrictions upon the development, production, stockpiling, proliferation and usage of small arms, conventional weapons, and weapons of mass destruction. Arms control is typically exercised through the u ...
agreement known as the INF Treaty.
Leaving office in 1989, Reagan held an approval rating of 68%. This rating matches the approval ratings of Franklin D. Roosevelt and later Bill Clinton as the highest rating for a departing president in the modern era. Historians and political scientists generally rank Reagan as an above-average president. Due to Reagan's impact on public discourse and advocacy of American conservatism, some historians have described the period during and after his presidency as the Reagan Era.
Conservative shift in politics
 Even prior to becoming president, Reagan was the leader of a dramatic conservative shift that undercut many of the domestic and foreign policies that had dominated the national agenda for decades. A major factor in the rise of conservatism was the growing distrust of government in the aftermath of the Watergate scandal. While distrust of high officials had been an American characteristic for two centuries, Watergate engendered heightened levels of suspicion and encouraged the media to engage in a vigorous search for scandals. An unexpected new factor was the emergence of the religious right as a cohesive political force that gave strong support to conservatism.
Other factors in the rise of the conservative movement were the emergence of a " culture war" as a triangular battle among conservatives, traditional liberals, and the
Even prior to becoming president, Reagan was the leader of a dramatic conservative shift that undercut many of the domestic and foreign policies that had dominated the national agenda for decades. A major factor in the rise of conservatism was the growing distrust of government in the aftermath of the Watergate scandal. While distrust of high officials had been an American characteristic for two centuries, Watergate engendered heightened levels of suspicion and encouraged the media to engage in a vigorous search for scandals. An unexpected new factor was the emergence of the religious right as a cohesive political force that gave strong support to conservatism.
Other factors in the rise of the conservative movement were the emergence of a " culture war" as a triangular battle among conservatives, traditional liberals, and the New Left
The New Left was a broad political movement mainly in the 1960s and 1970s consisting of activists in the Western world who campaigned for a broad range of social issues such as civil and political rights, environmentalism, feminism, gay rights, g ...
, involving such issues as individual freedom, divorce, sexual freedom, abortion, and homosexuality. A mass movement of population from the cities to the suburbs led to the creation of a new group of voters less attached to New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
economic policies and machine politics. Meanwhile, it became socially acceptable for conservative Southern whites, especially well educated suburbanites, to vote Republican. Though the civil rights legislation of the 1960s had been a triumphal issue for liberalism and had created a new, pro-Democratic black electorate, it had also destroyed the argument that whites had to vote Democratic to protect segregation in the South. Responding to these various trends, Reagan and other conservatives successfully presented conservative ideas as an alternative to a public that had grown disillusioned with New Deal liberalism and the Democratic Party. Reagan's charisma and speaking skills helped him frame conservatism as an optimistic, forward-looking vision for the country.
1980 election
Governor of California
The governor of California is the head of government of the U.S. state of California. The governor is the commander-in-chief of the California National Guard and the California State Guard.
Established in the Constitution of California, the g ...
from 1967 to 1975, narrowly lost the 1976 Republican presidential primaries to incumbent President Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected ...
. With the defeat of Ford by Democrat Jimmy Carter in the 1976 election, Reagan immediately became the front-runner for the 1980 Republican presidential nomination. A darling of the conservative movement, Reagan faced more moderate Republicans such as George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
, Howard Baker
Howard Henry Baker Jr. (November 15, 1925 June 26, 2014) was an American politician and diplomat who served as a United States Senator from Tennessee from 1967 to 1985. During his tenure, he rose to the rank of Senate Minority Leader and then ...
, and Bob Dole
Robert Joseph Dole (July 22, 1923 – December 5, 2021) was an American politician and attorney who represented Kansas in the United States Senate from 1969 to 1996. He was the Republican Leader of the Senate during the final 11 years of his te ...
in the 1980 Republican presidential primaries. After Bush won the Iowa caucuses, he became Reagan's primary challenger, but Reagan won the New Hampshire primary and most of the following primaries, gaining an insurmountable delegate lead by the end of March 1980. Ford was Reagan's first choice for his running mate, but Reagan backed away from the idea out of the fear of a "copresidency" in which Ford would exercise an unusual degree of power. Reagan instead chose Bush, and the Reagan-Bush ticket was nominated at the 1980 Republican National Convention
The 1980 Republican National Convention convened at Joe Louis Arena in Detroit, Michigan, from July 14 to July 17, 1980. The Republican National Convention nominated retired Hollywood actor and former Governor Ronald Reagan of California for pre ...
. Meanwhile, Carter won the Democratic nomination, defeating a primary challenge by Senator Ted Kennedy. Polls taken after the party conventions showed a tied race between Reagan and Carter, while independent candidate John B. Anderson
John Bayard Anderson (February 15, 1922 – December 3, 2017) was an American lawyer and politician who served in the United States House of Representatives, representing Illinois's 16th congressional district from 1961 to 1981. A member o ...
had the support of many moderates.
The 1980 general campaign between Reagan and Carter was conducted amid a multitude of domestic concerns and the ongoing Iran hostage crisis. After winning the Republican nomination, Reagan pivoted to the center. Though he continued to champion a major tax cut, Reagan backed off of his support for free trade and the privatization of Social Security, and promised to consider arms control
Arms control is a term for international restrictions upon the development, production, stockpiling, proliferation and usage of small arms, conventional weapons, and weapons of mass destruction. Arms control is typically exercised through the u ...
treaties with the Soviet Union. He instead sought to focus the race on Carter's handling of the economy. Mired with an approval rating in the low 30s, Carter also waged a negative campaign, focusing on the supposed risk of war if Reagan took office.
Reagan and Carter met in one presidential debate, held just one week before election day. Reagan delivered an effective performance, asking voters, "Are you better off today than you were four years ago?" In response to a characterization by Carter of his record regarding Medicare, Reagan replied with a phrase that would help define the election and endure in the American political lexicon: " There you go again."
Though the race had been widely regarded as a close contest, Reagan won over the large majority of undecided voters. Reagan took 50.7% of the popular vote and 489 of the 538 electoral votes. Carter won 41% of the popular vote and 49 electoral votes, while Anderson won 6.6% of the popular vote. In the concurrent congressional elections, Republicans took control of the Senate for the first time since the 1950s, while Democrats retained control of the House of Representatives.
Administration
 Reagan tapped James Baker, who had run Bush's 1980 campaign, as his first
Reagan tapped James Baker, who had run Bush's 1980 campaign, as his first chief of staff
The title chief of staff (or head of staff) identifies the leader of a complex organization such as the armed forces, institution, or body of persons and it also may identify a principal staff officer (PSO), who is the coordinator of the supporti ...
. Baker, Deputy Chief of Staff Michael Deaver, and Counselor Edwin Meese formed the "troika," the key White House staffers early in Reagan's presidency. Baker quickly established himself as the most powerful member of the troika and the overseer of day-to-day operations, while Meese had nominal leadership of policy development and Deaver orchestrated Reagan's public appearances. Aside from the troika, other important White House staffers included Richard Darman
Richard Gordon "Dick" Darman (May 10, 1943January 25, 2008) was an American businessman and government official who served in senior positions during the presidencies of Ronald Reagan and George H. W. Bush.
Early life
Darman was born in Charlotte ...
and David Gergen.
Reagan chose Alexander Haig, a former general who had served as chief of staff to Richard Nixon, as his first secretary of state. Other major Cabinet appointees included Secretary of Defense Caspar Weinberger, a former Nixon cabinet official who would preside over an increase in defense spending, and Secretary of the Treasury Donald Regan, a bank executive. Reagan selected David Stockman, a young congressman from Michigan, as the Director of the Office of Management and Budget. CIA director William J. Casey
William Joseph Casey (March 13, 1913 – May 6, 1987) was the Director of Central Intelligence from 1981 to 1987. In this capacity he oversaw the entire United States Intelligence Community and personally directed the Central Intelligence Agency ...
emerged as an important figure in the administration, as the CIA would figure prominently into Reagan's Cold War initiatives. Reagan downgraded the importance of the national security advisor A national security advisor serves as the chief advisor to a national government on matters of security. The advisor is not usually a member of the government's cabinet but is usually a member of various military or security councils.
National secu ...
, and six different individuals held that position during Reagan's presidency.
Haig left the cabinet in 1982 after clashing with other members of the Reagan administration, and was replaced by another former Nixon administration official, George P. Shultz
George Pratt Shultz (; December 13, 1920February 6, 2021) was an American economist, businessman, diplomat and statesman. He served in various positions under two different Republican presidents and is one of the only two persons to have held fou ...
. By 1982, National Security Advisor William P. Clark Jr., Ambassador to the United Nations Jeane Kirkpatrick, and CIA Director Casey had established themselves as the major figures in the formulation of the administration's foreign policy. Shultz eventually emerged as the administration's most influential foreign policy figure, moving the administration towards a less confrontational policy with the Soviet Union.
Baker and Treasury Secretary Regan switched positions at the beginning of Reagan's second term. Regan centralized power within his office, and he took on the responsibilities that had been held by Baker, Deaver, and Meese, the latter of whom succeeded William French Smith as attorney general in 1985. Regan frequently clashed with First Lady Nancy Reagan
Nancy Davis Reagan (; born Anne Frances Robbins; July 6, 1921 – March 6, 2016) was an American film actress and First Lady of the United States from 1981 to 1989. She was the second wife of president Ronald Reagan.
Reagan was born in N ...
, and he left the administration in the wake of the Iran–Contra affair and Republican losses in the 1986 mid-term elections. Regan was replaced by former Senate Majority Leader Howard Baker
Howard Henry Baker Jr. (November 15, 1925 June 26, 2014) was an American politician and diplomat who served as a United States Senator from Tennessee from 1967 to 1985. During his tenure, he rose to the rank of Senate Minority Leader and then ...
.
Judicial appointments
Supreme Court
 Reagan made four successful appointments to the
Reagan made four successful appointments to the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
during his eight years in office. In 1981, he successfully nominated Sandra Day O'Connor
Sandra Day O'Connor (born March 26, 1930) is an American retired attorney and politician who served as the first female associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1981 to 2006. She was both the first woman nominated and th ...
to succeed Associate Justice Potter Stewart, fulfilling a campaign promise to name the first woman to the Supreme Court. Democrats, who had planned to vigorously oppose Reagan's nominations to the Supreme Court, approved of the nomination of O'Connor. However, the Christian right was astonished and dismayed with O'Connor, whom they feared would not overturn the Supreme Court's decision in '' Roe v. Wade'', which had established the constitutional right to have an abortion without undue government interference. O'Connor served on the Supreme Court until 2006, and was generally considered to be a centrist conservative.
In 1986, Reagan elevated Associate Justice William Rehnquist to the position of Chief Justice of the United States after Warren Burger chose to retire. Rehnquist, a member of the conservative wing of the Court, was the third sitting associate justice to be elevated to chief justice, after Edward Douglass White and Harlan F. Stone
Harlan Fiske Stone (October 11, 1872 – April 22, 1946) was an American attorney and jurist who served as an associate justice of the U.S. Supreme Court from 1925 to 1941 and then as the 12th chief justice of the United States from 1941 un ...
. Reagan successfully nominated Antonin Scalia
Antonin Gregory Scalia (; March 11, 1936 – February 13, 2016) was an American jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1986 until his death in 2016. He was described as the intellectu ...
to fill Rehnquist's position as an associate justice of the Supreme Court. Scalia became a member of the Court's conservative wing.
Reagan faced greater difficulties in filling the final Supreme Court vacancy, which arose due to the retirement of Lewis F. Powell Jr. Reagan nominated Robert Bork in July 1987, but the nomination was rejected by the Senate in October 1987. Later that month, Reagan announced the nomination of Douglas H. Ginsburg
Douglas Howard Ginsburg (born May 25, 1946) is an American jurist and academic who serves as a senior judge on the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit. He was appointed to that court in October 1986 by President Ro ...
, but Ginsburg withdrew from consideration in November 1987. Finally, Reagan nominated Anthony Kennedy, who won Senate confirmation in February 1988. Along with O'Connor, Kennedy served as the key swing vote on the Supreme Court in the decades after Reagan left office.
Other courts
Reagan appointed a combined total of 368 judges to the United States courts of appeals and the United States district courts, more than any other president. The vast majority of his judicial appointees were conservative white men, and many of the appointees were affiliated with the conservative Federalist Society. Partly because Congress passed a law creating new federal judicial positions in 1984, Reagan had appointed nearly half of the federal judiciary by the time he left office in 1989.Rossinow, p. 178Assassination attempt
On March 30, 1981, only 69 days into the new administration, Reagan, his press secretaryJames Brady
James Scott Brady (August 29, 1940 – August 4, 2014) was an American public official who served as assistant to the U.S. president and the seventeenth White House Press Secretary, serving under President Ronald Reagan. In 1981, Brady b ...
, Washington police officer Thomas Delahanty, and Secret Service agent Tim McCarthy were struck by gunfire from would-be assassin John Hinckley Jr.
John Warnock Hinckley Jr. (born May 29, 1955) is an American man who attempted to assassinate U.S. President Ronald Reagan in Washington, D.C. on March 30, 1981, two months after Reagan's first inauguration. Using a .22 caliber revolver, Hinck ...
outside the Washington Hilton Hotel. Although Reagan was initially reported to be "close to death", he recovered and was released from the hospital on April 11, becoming the first serving president to survive being wounded in an assassination attempt. The failed assassination attempt had great influence on Reagan's popularity; polls indicated his approval rating to be around 73%.Leuchtenberg, pp. 597–598 Many pundits and journalists later described the failed assassination as a critical moment in Reagan's presidency, as his newfound popularity provided critical momentum in passing his domestic agenda.
Domestic affairs
Reagan used his White House staff to shape major domestic policies. His Chief of Staff made heavy use of the Office of Policy Development in supervising cabinet action on the Reagan initiatives."Reaganomics" and taxation

Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981
Reagan implementedneoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent fa ...
economic policies based on supply-side economics
Supply-side economics is a macroeconomic theory that postulates economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-side economics, consumers will benefit fr ...
, advocating a '' laissez-faire'' philosophy and free-market fiscal policy. Reagan's taxation policies resembled those instituted by President Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge (born John Calvin Coolidge Jr.; ; July 4, 1872January 5, 1933) was the 30th president of the United States from 1923 to 1929. Born in Vermont, Coolidge was a History of the Republican Party (United States), Republican lawyer ...
and Treasury Secretary Andrew Mellon in the 1920s. Reagan's team was also strongly influenced by contemporary economists such as Arthur Laffer, who rejected the then-dominant views of Keynesian economists
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output a ...
. Reagan relied on Laffer and other economists to argue that tax cuts would reduce inflation, which went against the prevailing Keynesian view. Supply-side advocates also asserted that cutting taxes would ultimately lead to higher government revenue due to economic growth, a proposition that was challenged by many economists.
Republican Congressman Jack Kemp
Jack French Kemp (July 13, 1935 – May 2, 2009) was an American politician and a professional football player. A member of the Republican Party from New York, he served as Housing Secretary in the administration of President George H. W. Bu ...
and Republican Senator William Roth had nearly won passage of a major tax cut during Carter's presidency, but Carter had prevented passage of the bill due to concerns about the deficit. Reagan made passage of the Kemp-Roth bill his top domestic priority upon taking office. As Democrats controlled the House of Representatives, passage of any bill would require the support of some House Democrats in addition to the support of congressional Republicans. Reagan's victory in the 1980 presidential campaign had united Republicans around his leadership, while conservative Democrats like Phil Gramm
William Philip Gramm (born July 8, 1942) is an American economist and politician who represented Texas in both chambers of Congress. Though he began his political career as a Democrat, Gramm switched to the Republican Party in 1983. Gramm was ...
of Texas (who would later switch parties) were eager to back some of Reagan's conservative policies. Throughout 1981, Reagan frequently met with members of Congress, focusing especially on winning support from conservative Southern Democrats. Reagan also benefited from a conservative majority in the House during his first two years as president, with an estimated 230 votes during the 97th Congress, although this changed after the Democratic gains in the 1982 election, with House control switching to liberals within the Democratic caucus.
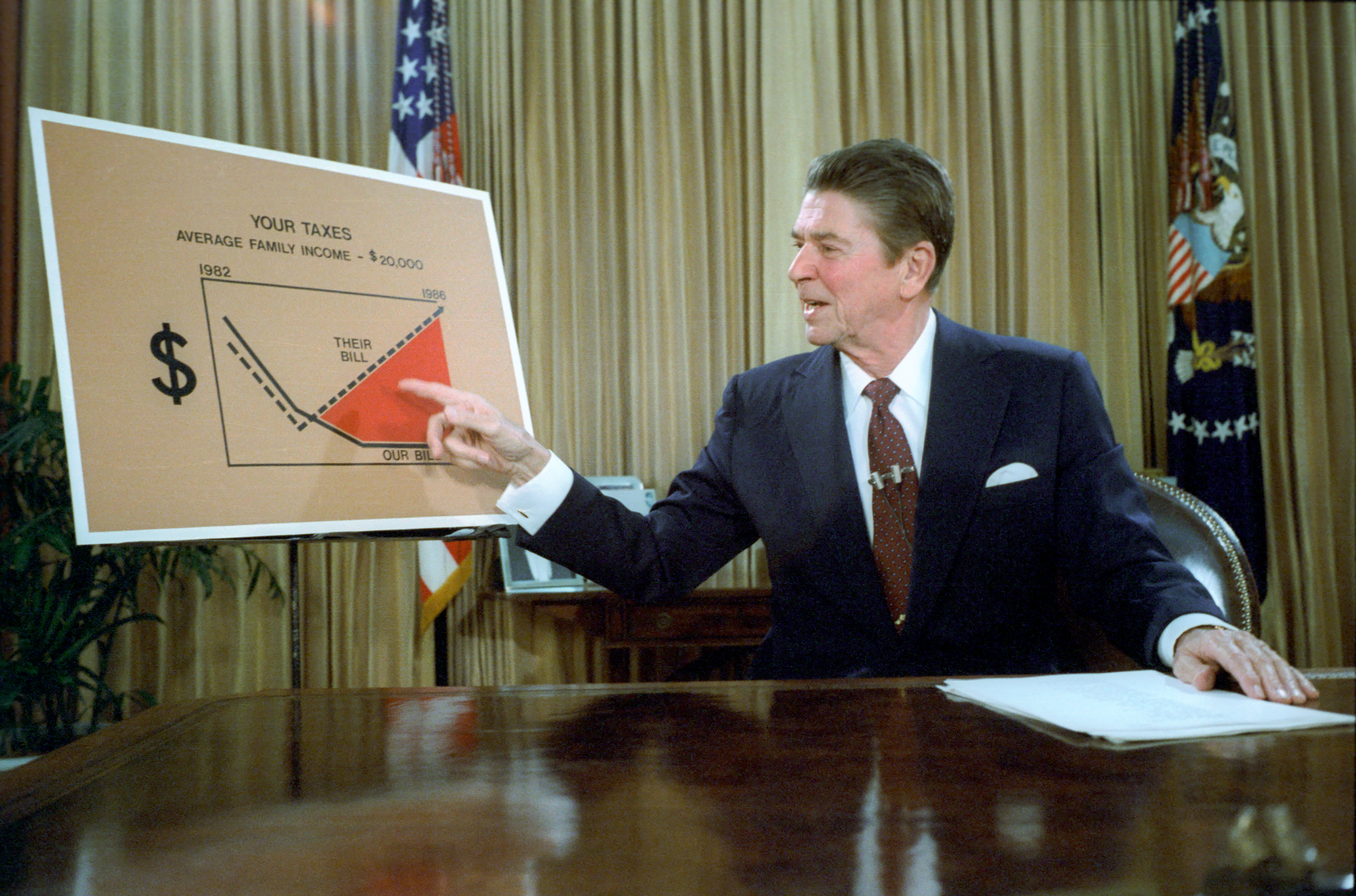
In July 1981, the Senate voted 89–11 in favor of the tax cut bill favored by Reagan, and the House subsequently approved the bill in a 238–195 vote.Rossinow, pp. 61–62 The Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981 cut the top marginal tax rate from 70% to 50%, lowered the capital gains tax from 28% to 20%, more than tripled the amount of inherited money exempt from the estate tax, and cut the corporate tax
A corporate tax, also called corporation tax or company tax, is a direct tax imposed on the income or capital of corporations or analogous legal entities. Many countries impose such taxes at the national level, and a similar tax may be imposed at ...
.Leuchtenberg, pp. 599–601 Reagan's success in passing a major tax bill and cutting the federal budget was hailed as the "Reagan Revolution" by some reporters; one columnist wrote that the Reagan's legislative success represented the "most formidable domestic initiative any president has driven through since the Hundred Days
The Hundred Days (french: les Cent-Jours ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration ...
of Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
."Patterson, p. 157
Later tax acts
Faced with concerns about the mounting federal debt, Reagan agreed to raise taxes, signing the Tax Equity and Fiscal Responsibility Act of 1982 (TEFRA). Many of Reagan's conservative supporters condemned TEFRA, but Reagan argued that his administration would be unable to win further budget cuts without the tax hike. Among other provisions, TEFRA doubled the federal cigarette tax and rescinded a portion of the corporate tax cuts from the 1981 tax bill. By 1983, the amount of federal tax had fallen for all or almost all American taxpayers, but most strongly affected the wealthy; the proportion of income paid in taxes by the richest one percent fell from 29.8 percent to 24.8 percent. Partly due to the poor economy, Reagan's legislative momentum dissipated after his first year in office, and his party lost several seats in the House in the 1982 congressional elections.Patterson, pp. 162–163 Compared to other midterm elections, the losses were relatively small for the party holding the presidency, but conservative Democrats were less open to Reagan's initiatives after 1982. As deficits continued to be an issue, Reagan signed another bill that raised taxes, the Deficit Reduction Act of 1984. With Donald Regan taking over as Chief of Staff in 1985, the Reagan administration made simplification of the tax code the central focus of its second term domestic agenda. Working withSpeaker of the House
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hunger ...
Tip O'Neill, a Democrat who also favored tax reform, Reagan overcame significant opposition from members of Congress in both parties to pass the Tax Reform Act of 1986. The act simplified the tax code by reducing the number of tax brackets to four and slashing a number of tax breaks. The top rate was dropped to 28%, but capital gains taxes were increased on those with the highest incomes from 20% to 28%. The increase of the lowest tax bracket from 11% to 15% was more than offset by expansion of the personal exemption, standard deduction
Under United States tax law, the standard deduction is a dollar amount that non- itemizers may subtract from their income before income tax (but not other kinds of tax, such as payroll tax) is applied. Taxpayers may choose either itemized deducti ...
, and earned income tax credit. The net result was the removal of six million poor Americans from the income tax roll and a reduction of income tax liability at all income levels. The net effect of Reagan's tax bills was that overall tax burden held steady at roughly 19 percent of gross national product.
Government spending
Reagan prioritized tax cuts over spending cuts, arguing that lower revenue would eventually require lower spending. Nonetheless, Reagan was determined to decrease government spending and roll back or dismantle Great Society programs such as Medicaid and the Office of Economic Opportunity. In August 1981, Reagan signed the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1981, which cut federal funding for social programs likefood stamps
In the United States, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as the Food Stamp Program, is a federal program that provides food-purchasing assistance for low- and no-income people. It is a federal aid program, ad ...
, school lunch programs, and Medicaid. The Comprehensive Employment and Training Act, which had provided for the employment of 300,000 workers in 1980, was also repealed, and the administration tightened eligibility for unemployment benefits.Rossinow, p. 85 Notably absent from the budget cuts was the Department of Defense, which saw its budget bolstered.
Reagan experienced several legislative successes in his first year in office, but his attempts to cut federal domestic spending after 1981 met increasing congressional resistance. Spending on programs like Supplemental Security Income
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is a means-tested program that provides cash payments to disabled children, disabled adults, and individuals aged 65 or older who are citizens or nationals of the United States. SSI was created by the Social Se ...
, Medicaid, the earned income tax credit, and Aid to Families with Dependent Children all increased after 1982. The number of federal civilian employees rose during Reagan's tenure, from 2.9 million to 3.1 million. Reagan's policy of New Federalism, which sought to shift the responsibility for most social programs to state governments, found little support in Congress.
In 1981, OMB Director David Stockman won Reagan's approval to seek cuts to Social Security in 1981, but this plan was poorly-received in Congress. In 1982, Reagan established the bipartisan National Commission on Social Security Reform to make recommendations to secure the long-term integrity of Social Security. The commission rejected Social Security privatization and other major changes to the program, but recommended expanding the Social Security base (by including exempt federal and nonprofit employees), raising Social Security taxes, and reducing some payments. These recommendations were enacted in the Social Security Amendments of 1983, which received bipartisan support. While Reagan avoided cuts to Social Security and Medicare for most individuals, his administration attempted to purge many people from the Social Security disability rolls. Reagan's inability to implement major cuts to Social Security solidified its status as the " third rail" of U.S. politics, and future administrations would be reluctant to propose cuts to the popular program.
Deficits
As Reagan was unwilling to match his tax cuts with cuts to defense spending or Social Security, rising deficits became an issue. These deficits were exacerbated by the early 1980s recession, which cut into federal revenue. Unable to win further domestic spending cuts, and pressured to address the deficit, Reagan was forced to raise taxes after 1981. Nonetheless, the national debt more than tripled between fiscal year 1980 and fiscal year 1989, going from $914 billion to $2.7 trillion, while national debt as a percentage of GDP rose from 33 percent in 1981 to 53 percent in 1989. Reagan never submitted a balanced budget during his time in office. In an effort to lower the national debt, Congress passed the Gramm–Rudman–Hollings Balanced Budget Act, which called for automatic spending cuts if Congress was unable to eliminate deficits through the regular budget-making process. However, Congress found ways around the automatic cuts and deficits continued to rise, ultimately leading to the passage of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990.Economy
Reagan took office in the midst of poor economic conditions, as the country experienced stagflation, a phenomenon in which both inflation and unemployment were high. The economy experienced a brief period of growth early in Reagan's first year in office, but plunged into a recession in July 1981. As the recession continued in the first two years of Reagan's presidency, many within Reagan's administration blamed the policies of Paul Volcker, the Chair of the Federal Reserve. But Reagan himself never criticized Volcker. Volcker sought to fight inflation by pursuing a policy of "tight money" in which interest rates were set at a high level. High interest rates would restrict lending and investment, which would in turn lower inflation, raise unemployment and, at least in the short term, reduce economic growth. Unemployment reached a high of nearly 11% in 1982,Brands, pp. 317–319poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
rate rose from 11.7 percent to 15 percent. The country emerged from recession in 1983,Brands, pp. 452–453 but not all shared equally in the economic recovery, and economic inequality and the number of homeless
Homelessness or houselessness – also known as a state of being unhoused or unsheltered – is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and adequate housing. People can be categorized as homeless if they are:
* living on the streets, also kn ...
individuals both increased during the 1980s. Fearful of damaging confidence in the economic recovery, Reagan nominated Volcker to a second term in 1983, and Volcker remained in office until 1987. Inflation dropped to approximately 3.5% in 1985, while the unemployment rate fell to about 5% in 1988. In 1987, Reagan appointed conservative economist Alan Greenspan to succeed Volcker, and Greenspan would lead the Federal Reserve until 2006. Greenspan raised interest rates in another attempt to curb inflation, setting off a stock market crash in October 1987 known as " Black Monday," but the markets stabilized and recovered in the following weeks.Brands, pp. 668–671
Labor
In August 1981, the Professional Air Traffic Controllers Organization (PATCO), which consisted of federal employees, voted to go on alabor strike
Strike action, also called labor strike, labour strike, or simply strike, is a work stoppage caused by the mass refusal of employees to work. A strike usually takes place in response to employee grievances. Strikes became common during the I ...
in hopes of receiving better pay and benefits. After the vote, Reagan announced that the strikers would be fired if they did not return to work within forty-eight hours. After the deadline passed, Reagan fired over 10,000 air traffic controllers, while approximately 40 percent of the union members returned to work. Reagan's handling of the strike was strongly criticized by union leaders, but it won the approval of his conservative base of voters and others in the public. The breaking of the PATCO strike demoralized organized labor, and the number of strikes fell dramatically in the 1980s.Patterson, pp. 157–158 Many of the strikes that did occur, including the Arizona copper mine strike of 1983, the 1983 Greyhound bus driver strike, and the 1985–86 Hormel strike, ended with dismissal of the strikers. With the assent of Reagan's sympathetic National Labor Relations Board appointees, many companies also won wage and benefit cutbacks from unions, especially in the manufacturing sector.Rossinow, p. 87–88 During Reagan's time in office, the share of employees who were part of a labor union dropped from approximately one-fourth of the total workforce to approximately one-sixth of the total workforce.
Deregulation
Reagan sought to loosen federal regulation of economic activities, and he appointed key officials who shared this agenda. According to historian William Leuchtenburg, by 1986, the Reagan administration eliminated almost half of the federal regulations that had existed in 1981. The Federal Communications Commission aggressively deregulated the broadcasting industry, eliminating the Fairness Doctrine and other restrictions. The 1982 Garn–St. Germain Depository Institutions Act deregulated savings and loan associations and allowed banks to provide adjustable-rate mortgages. Reagan also eliminated numerous government positions and dismissed numerous federal employees, including the entire staff of the Employment and Training Administration. Secretary of the Interior James G. Watt implemented policies designed to open up federal territories to oil drilling andsurface mining
Surface mining, including strip mining, open-pit mining and mountaintop removal mining, is a broad category of mining in which soil and rock overlying the mineral deposit (the overburden) are removed, in contrast to underground mining, in which ...
. Under EPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
Director Anne Gorsuch
Anne Irene McGill Gorsuch Burford ( ; April 21, 1942 – July 18, 2004), also known as Anne M. Gorsuch, was an American attorney and politician. Between 1981 and 1983, while known as Anne M. Gorsuch, she served under President Ronald Reagan as the ...
, the EPA's budget was dramatically reduced and the EPA loosely enforced environmental regulations.Leuchtenberg, pp. 601–604
Savings and loan crisis
After the passage of the Garn–St. Germain Depository Institutions Act, savings and loans associations engaged in riskier activities, and the leaders of some institutions embezzled funds. In what became known as the Savings and loan crisis, a total of 747 financial institutions failed and needed to be rescued with $160 billion in taxpayer dollars. As an indication of this scandal's size,Martin Mayer
Martin Prager Mayer (January 14, 1928 – August 1, 2019) was the writer of 35 non-fiction books, including ''Madison Avenue, U.S.A.'' (1958), ''The Schools'' (1961), ''The Lawyers'' (1967), ''About Television'' (1972), ''The Bankers'' (1975), ''Th ...
wrote at the time, "The theft from the taxpayer by the community that fattened on the growth of the savings and loan (S&L) industry in the 1980s is the worst public scandal in American history...Measuring by money, rby the misallocation of national resources...the S&L outrage makes Teapot Dome and Credit Mobilier seem minor episodes."
Immigration
The 1980s saw the highest rate of immigration to the United States since the 1910s, and the proportion of the foreign-born population reached its highest level since the 1940s. Reagan did not make immigration a focus of his administration, but he came to support a package of reforms sponsored by Republican Senator Alan Simpson and Democratic Congressman Romano Mazzoli, which he signed into law as the Immigration Reform and Control Act in November 1986. The act made it illegal to knowingly hire or recruit illegal immigrants, required employers to attest to their employees' immigration status, and granted amnesty to approximately three million illegal immigrants who had entered the United States before January 1, 1982, and had lived in the country continuously. The bill was also contained provisions designed to enhance security measures at the Mexico–United States border. Upon signing the act at a ceremony held beside the newly refurbishedStatue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World''; French: ''La Liberté éclairant le monde'') is a List of colossal sculpture in situ, colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the U ...
, Reagan said, "The legalization provisions in this act will go far to improve the lives of a class of individuals who now must hide in the shadows, without access to many of the benefits of a free and open society. Very soon many of these men and women will be able to step into the sunlight and, ultimately, if they choose, they may become Americans."Reagan, Ronald. (November 6, 1986Statement on Signing the Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986.
Collected Speeches, Ronald Reagan Presidential Library. Retrieved August 15, 2007. The bill was largely unsuccessful at halting illegal immigration, and the population of illegal immigrants rose from 5 million in 1986 to 11.1 million in 2013.
Criminal and anti-drug policy

 Not long after being sworn into office, Reagan declared more militant policies in the " War on Drugs". He promised a "planned, concerted campaign" against all drugs, in hopes of decreasing drug use, particularly among adolescents. The " crack epidemic," which saw a large number of individuals become addicted to
Not long after being sworn into office, Reagan declared more militant policies in the " War on Drugs". He promised a "planned, concerted campaign" against all drugs, in hopes of decreasing drug use, particularly among adolescents. The " crack epidemic," which saw a large number of individuals become addicted to crack cocaine
Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant cocaine that can be smoked. Crack offers a short, intense high to smokers. The ''Manual of Adolescent Substance Abuse Treatment'' calls ...
and may have played a role in numerous murders, emerged as a major area of public concern. First Lady
First lady is an unofficial title usually used for the wife, and occasionally used for the daughter or other female relative, of a non-monarchical
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state fo ...
Nancy Reagan made the War on Drugs her main cause as First Lady, founding the " Just Say No" drug awareness campaign.
Concerns about drug use prompted Congress to pass legislation such as the Comprehensive Crime Control Act of 1984
Comprehensive may refer to:
*Comprehensive layout, the page layout of a proposed design as initially presented by the designer to a client.
*Comprehensive school, a state school that does not select its intake on the basis of academic achievement o ...
and the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1986, the latter of which granted $1.7 billion to fight drugs and established a mandatory minimum penalties for drug offenses. Reagan also signed the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988, which further increased criminal penalties for drug use and established the Office of National Drug Control Policy
The Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) is a component of the Executive Office of the President of the United States.
The Director of the ONDCP, colloquially known as the Drug Czar, heads the office. "Drug Czar" was a term first used ...
. Critics charged that Reagan's policies promoted significant racial disparities in the prison population, were ineffective in reducing the availability of drugs or crime on the street, and came at a great financial and human cost for American society. Supporters argued that the numbers for adolescent drug users declined during Reagan's years in office.
Social policies and civil rights
Reagan was largely unable to enact his ambitious social policy agenda, which included a federal ban onabortions
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregnan ...
and an end to desegregation busing. With Reagan's support, conservative Republican Senator Jesse Helms
Jesse Alexander Helms Jr. (October 18, 1921 – July 4, 2008) was an American politician. A leader in the conservative movement, he served as a senator from North Carolina from 1973 to 2003. As chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee ...
led an effort to prevent the Supreme Court from reviewing state and local laws mandating school prayer
School prayer, in the context of religious liberty, is state-sanctioned or mandatory prayer by students in public schools. Depending on the country and the type of school, state-sponsored prayer may be required, permitted, or prohibited. Countries ...
, but Republican senators like Lowell Weicker and Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater (January 2, 1909 – May 29, 1998) was an American politician and United States Air Force officer who was a five-term U.S. Senator from Arizona (1953–1965, 1969–1987) and the Republican Party nominee for presiden ...
blocked passage of Helms' bill. Despite the lack of major social policy legislation, Reagan was able to influence social policy through regulations and the appointment of conservative Supreme Court Justices.
In 1982, Reagan signed a bill extending the Voting Rights Act for 25 years after a grass-roots lobbying and legislative campaign forced him to abandon his plan to ease that law's restrictions. He also reluctantly accepted the continuation of affirmative action programs and the establishment of Martin Luther King Jr. Day as a federal holiday. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission and the Justice Department both prosecuted far fewer civil rights cases per year than they had under Carter. In 1988, Reagan vetoed the Civil Rights Restoration Act
The Civil Rights Restoration Act of 1987, or Grove City Bill, is a US, United States legislative act that specifies that entities receiving federal funds must comply with civil rights legislation in all of their operations, not just in the pro ...
, but his veto was overridden by Congress. Reagan had argued that the legislation infringed on states' rights and the rights of churches and business owners.
No civil rights legislation for gay individuals passed during Reagan's tenure. Many in the Reagan administration, including Communications Director Pat Buchanan
Patrick Joseph Buchanan (; born November 2, 1938) is an American paleoconservative political commentator, columnist, politician, and broadcaster. Buchanan was an assistant and special consultant to U.S. Presidents Richard Nixon, Gerald Ford, an ...
, were hostile to the gay community, as were many religious leaders who were important allies to the administration. Gay rights and the growing HIV/AIDS emerged as an important matter of public concern in 1985 after it was disclosed that actor Rock Hudson, a personal friend of President Reagan, was receiving treatment for AIDS. As public anxiety over AIDS rose, the Supreme Court upheld a state law that criminalized homosexuality in the case of ''Bowers v. Hardwick
''Bowers v. Hardwick'', 478 U.S. 186 (1986), was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court that upheld, in a 5–4 ruling, the constitutionality of a Georgia sodomy law criminalizing oral and anal sex in private between consenting adults, in ...
''. Though Surgeon General C. Everett Koop advocated for a public health campaign designed to reduce the spread of AIDS by raising awareness and promoting the use of condoms, Reagan rejected Koop's proposals in favor of abstinence-only sex education. By 1989, approximately 60,000 Americans had died of AIDS, and liberals strongly criticized Reagan's response to the HIV/AIDS crisis. On the 1980 campaign trail, Reagan spoke of the gay rights movement:
Environmental policy
Reagan's strong preferences for limited federal involvement and deregulation extended to the environment. His main goal was to lessen the burden of regulation on businesses to promote more economic activity in the United States. Because of this policy, Reagan refused to renew the Clean Air Act during his administration. Reagan lessened existing regulations on pollution, cut funding to government environmental agencies, and appointed known anti-environmentalist individuals to key positions presiding over these organizations. When Reagan took office in 1981, he "attempted to reduce" money that was directed towards studying the burgeoning field of global warming and human-driven climate change. In the early 1980s, the study of the intersection between human activity and climate change was still in its infancy and scientists were far from a consensus on the topic. In 1987, the Reagan administration signed the Montreal Protocol in an effort to reduce emissions that damage theozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in rela ...
.
Mass surveillance
Citingnational security
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military atta ...
concerns, the president's national security team pressed for more surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as c ...
power early during Reagan's first term. Their recommendations were based upon the premise that the federal government's intelligence and counterintelligence capabilities had been weakened by presidents Carter and Ford. On December 4, 1981, Reagan signed Executive Order 12333
Executive Order 12333, signed on December 4, 1981 by U.S. President Ronald Reagan, was an Executive Order intended to extend powers and responsibilities of U.S. intelligence agencies and direct the leaders of U.S. federal agencies to co-operate ...
. This presidential directive broadened the power of the government's intelligence community; mandated rules for spying on United States citizens, permanent residents, and on anyone within the United States; and also directed the Attorney General and others to create further policies and procedures for what information intelligence agencies can collect, retain, and share.
Foreign affairs
Escalation of the Cold War
 Reagan escalated the Cold War, accelerating a reversal from the policy of détente which had begun in 1979 after the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. Reagan feared that the Soviet Union had gained a military advantage over the United States, and the Reagan administration hoped that heightened military spending would grant the U.S. military superiority and weaken the Soviet economy. Reagan ordered a massive buildup of the United States Armed Forces, directing funding to the B-1 Lancer bomber, the B-2 Spirit bomber,
Reagan escalated the Cold War, accelerating a reversal from the policy of détente which had begun in 1979 after the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. Reagan feared that the Soviet Union had gained a military advantage over the United States, and the Reagan administration hoped that heightened military spending would grant the U.S. military superiority and weaken the Soviet economy. Reagan ordered a massive buildup of the United States Armed Forces, directing funding to the B-1 Lancer bomber, the B-2 Spirit bomber, cruise missile
A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhe ...
s, the MX missile, and the 600-ship Navy. In response to Soviet deployment of the SS-20, Reagan oversaw NATO's deployment of the Pershing missile in West Germany. The president also strongly denounced the Soviet Union and Communism in moral terms, describing the Soviet Union as an "evil empire
An evil empire is a speculative fiction trope in which a major antagonist of the story is a technologically advanced nation, typically ruled by an evil emperor or empress, that aims to control the world or conquer some specific group. They a ...
."Cannon (1991), pp. 314–317. Despite this heavy rhetoric, the Reagan administration continued arms control talks with the Soviet Union in the form of "START
Start can refer to multiple topics:
*Takeoff, the phase of flight where an aircraft transitions from moving along the ground to flying through the air
* Starting lineup in sports
*Standing start, and rolling start, in an auto race
Acronyms
*St ...
". Unlike the " SALT" treaties of the 1970s, which set upper limits on the size of nuclear arsenals, the proposed START treaty would require both sides to reduce their existing nuclear arsenals.
 In March 1983, Reagan introduced the
In March 1983, Reagan introduced the Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons (intercontinental ballistic ...
(SDI), a defense project that would have used ground- and space-based systems to protect the United States from attack by strategic nuclear ballistic missiles. Reagan believed that this defense shield could make nuclear war impossible. Many scientists and national security experts criticized the project as costly and technologically infeasible, and critics dubbed SDI as "Star Wars" in reference to a popular film series of the same name. Ultimately, the SDI would be canceled in 1993 due to concerns about its cost and effectiveness as well as a changing international situation. However, the Soviets became concerned about the possible effects SDI would have and viewed its development as a violation of the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. In protest of SDI, the Soviet Union broke off arms control talks, and U.S.-Soviet relations descended to their lowest point since the early 1960s. The Cold War tensions influenced works of popular culture such as the films '' The Day After'' and '' WarGames'' (both 1983), and the song " 99 Luftballons" (1983) by Nena, each of which exhibited the rising public anxiety for the possibility of a nuclear war.
Reagan Doctrine
Under a policy that came to be known as the Reagan Doctrine, the Reagan administration provided overt and covert aid to anti-communist resistance movements in an effort to " rollback" Soviet-backed communist governments in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. In Eastern Europe, the CIA provided support to the Polish opposition group,Solidarity
''Solidarity'' is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. It is based on class collaboration.''Merriam Webster'', http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictio ...
, ensuring that it stayed afloat during a period of martial law.Herring, pp. 883–884 Reagan deployed the CIA's Special Activities Division to Afghanistan and Pakistan, and the CIA was instrumental in training, equipping, and leading Mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term th ...
forces against the Soviet Army in the Soviet–Afghan War. By 1987, the United States was sending over $600 million a year, as well as weapons, intelligence, and combat expertise to Afghanistan. The Soviet Union announced it would withdraw from Afghanistan in 1987, but the U.S. was subjected to blowback in the form of the Taliban and al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
, two groups that arose out of the Mujahideen and that would oppose the United States in future conflicts.
Central America and the Caribbean
 The Reagan administration placed a high priority on the Central America and the Caribbean Sea, which it saw as a key front in the Cold War. Reagan and his foreign policy team were particularly concerned about the potential influence of Cuba on countries such as
The Reagan administration placed a high priority on the Central America and the Caribbean Sea, which it saw as a key front in the Cold War. Reagan and his foreign policy team were particularly concerned about the potential influence of Cuba on countries such as Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
, Nicaragua, and El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south b ...
. To counter the influence of Cuba and the Soviet Union, Reagan launched the Caribbean Basin Initiative, an economic program designed to aid countries opposed to Communism. He also authorized covert measures, such as the arming of Nicaragua's Contras
The Contras were the various U.S.-backed and funded right-wing rebel groups that were active from 1979 to 1990 in opposition to the Marxist Sandinista Junta of National Reconstruction Government in Nicaragua, which came to power in 1979 fol ...
, to minimize Cuban and Soviet influence in the region. The administration provided support to right-wing governments throughout Latin America, disregarding humans rights abuses in countries like Argentina and El Salvador.
Tensions rose between the left-wing Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
n government of Maurice Bishop and the U.S because Cuban construction workers were building an airfield on the island. On October 16, 1983, pro-Communist forces of Hudson Austin
Hudson Austin (26 April 1938 – 24 September 2022) was a general in the People's Revolutionary Army of Grenada. After the killing of Maurice Bishop, he formed a military government with himself as chairman to rule Grenada.
History Early life ...
led a coup against Bishop, who was subsequently arrested and executed. Reagan dispatched approximately 5,000 U.S. soldiers to invade Grenada nine days after. After two days of fighting that resulted in the deaths of nineteen Americans, forty-five Grenadans, and twenty-four Cubans, Austin's government was overthrown. While the invasion enjoyed public support in the United States and Grenada, it was criticized by the United Kingdom, Canada and the United Nations General Assembly as "a flagrant violation of international law".
Iran–Contra affair
In 1979, a group of left-wing rebels in Nicaragua known as the Sandinistas overthrew the president of Nicaragua and installedDaniel Ortega
José Daniel Ortega Saavedra (; born 11 November 1945) is a Nicaraguans, Nicaraguan revolutionary and politician serving as President of Nicaragua since 2007. Previously he was leader of Nicaragua from 1979 to 1990, first as coordinator of the ...
as the country's leader. Fearing that Communists would take over Nicaragua if it remained under the leadership of the Sandinistas, the Reagan administration authorized CIA Director William J. Casey to arm the right-wing Contras
The Contras were the various U.S.-backed and funded right-wing rebel groups that were active from 1979 to 1990 in opposition to the Marxist Sandinista Junta of National Reconstruction Government in Nicaragua, which came to power in 1979 fol ...
. Congress, which favored negotiations between the Contras and Sandinista, passed the 1982 Boland Amendment
The Boland Amendment is a term describing three U.S. legislative amendments between 1982 and 1984, all aimed at limiting U.S. government assistance to the Contras in Nicaragua. The first Boland Amendment was part of the House Appropriations Bill ...
, prohibiting the CIA and Defense Department from using their budgets to provide aid to the Contras. Still intent on supporting the Contras, the Reagan administration raised funds for the Contras from private donors and foreign governments. When Congress learned that the CIA had secretly placed naval mines in Nicaraguan harbors, Congress passed a second Boland Amendment that barred granting any assistance to the Contras.
During his second term, Reagan sought to find a way procure the release of seven American hostages held by Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
, a Lebanese paramilitary group supported by Iran. The Reagan administration decided to sell American arms to Iran, then engaged in the Iran–Iraq War, in hopes that Iran would pressure Hezbollah to release the hostages. Secretary of Defense Weinberger and Secretary of State Shultz both opposed the arrangement, so it was handled by National Security Advisor Robert McFarlane and McFarlane's successor, John Poindexter. The Reagan administration sold over 2000 missiles to Iran without informing Congress; Hezbollah released four hostages but captured an additional six Americans. On the initiative of Oliver North, an aide on the National Security Council, the Reagan administration redirected the proceeds from the missile sales to the Contras.Weisberg, pp. 129–134 The transactions became public knowledge by early November 1986. Reagan initially denied any wrongdoing, but on November 25 he announced that Poindexter and North had left the administration and that he would form the Tower Commission to investigate the transactions. A few weeks later, Reagan asked a panel of federal judges to appoint a special prosecutor who would conduct a separate investigation, and the panel chose Lawrence Walsh.
The Tower Commission, chaired by former Republican Senator John Tower, released a report in February 1987 that confirmed that the administration had traded arms for hostages and sent the proceeds of the weapons sales to the Contras. The report laid most of the blame for the operation on North, Poindexter, and McFarlane, but it was also critical of Regan and other White House staffers. In response to the Tower Commission report, Reagan stated, "Its findings are honest, convincing and highly critical...As angry as I may be about activities undertaken without my knowledge, I am still accountable for those activities." The Iran–Contra scandal, as it became known, did serious damage to the Reagan presidency, raising questions about Reagan's competency and the wisdom of conservative policies. A poll taken in March 1987 showed that 85 percent of respondents believed that the Reagan administration had engaged in an organized cover-up, and half of the respondents believed that Reagan had been personally involved. The administration's credibility was also badly damaged on the international stage, as it had violated its own arms embargo on Iran.Brands, pp. 653, 674 Congressional Democrats considered impeaching, but decided that it would be an unwise use of political capital against a weakened president; Democrats were also somewhat mollified by Reagan's decision to replace Chief of Staff Regan with Howard Baker.
The investigations into the Iran–Contra scandal continued after Reagan left office, but were effectively halted when President George H. W. Bush pardoned Secretary of Defense Caspar Weinberger before his trial began. Investigators did not find conclusive proof that Reagan had known about the aid provided to the Contras, but Walsh's report noted that Reagan had "created the conditions which made possible the crimes committed by others" and had "knowingly participated or acquiesced in covering up the scandal."
End of the Cold War
 Three different Soviet leaders died between 1982 and 1985, leaving the Soviets with an unstable leadership until
Three different Soviet leaders died between 1982 and 1985, leaving the Soviets with an unstable leadership until Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
came to power in 1985.Herring, p. 894 Although the Soviet Union had not accelerated military spending during Reagan's military buildup, their large military expenses, in combination with collectivized agriculture and inefficient planned manufacturing, were a heavy burden for the Soviet economy. Gorbachev was less ideologically rigid than his predecessors, and he believed that the Soviet Union urgently needed economic and political reforms. In 1986, he introduced his twin reforms of perestroika
''Perestroika'' (; russian: links=no, перестройка, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg) was a political movement for reform within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s widely associated wit ...
and glasnost
''Glasnost'' (; russian: link=no, гласность, ) has several general and specific meanings – a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information, the inadmissibility of hushing up problems, ...
, which would change the political and economic conditions of the Soviet Union. Seeking to reduce military expenditures and minimize the possibility of nuclear war, he also sought to re-open negotiations with the United States over arms control.
As his influence on domestic affairs waned during his second term, Reagan increasingly focused on relations with the Soviet Union. Reagan recognized the change in the direction of the Soviet leadership under Gorbachev, and shifted to diplomacy, with a view to encourage the Soviet leader to pursue substantial arms agreements. Reagan's personal mission was to achieve a world free of nuclear weapons, which according to Jack F. Matlock Jr.
Jack Foust Matlock Jr. (born October 1, 1929) is an American former ambassador, career Foreign Service Officer, a teacher, a historian, and a linguist. He was a Soviet and Communist studies, specialist in Soviet affairs during some of the most tu ...
, Reagan's ambassador to Moscow, he regarded as "totally irrational, totally inhumane, good for nothing but killing, possibly destructive of life on earth and civilization." Gorbachev and Reagan agreed to meet at the 1985 Geneva Summit, where they issued a joint statement indicating that neither the U.S. nor the Soviet Union would "seek to achieve military superiority." The two leaders began a private correspondence after the summit, and each became increasingly optimistic about arms control negotiations. Reagan's willingness to negotiate with the Soviets was opposed by many conservatives, including Weinberger; conservative columnist George Will wrote that Reagan was "elevating wishful thinking to the status of a political philosophy."
Various issues, including intelligence operations performed by both countries and tensions in Germany and Afghanistan, threatened to forestall the possibility of an agreement between the United States and the Soviet Union. Nonetheless, both Gorbachev and Reagan agreed to continue arms control negotiations at the October 1986 Reykjavík Summit. At the summit, Gorbachev and Reagan closed in on an agreement to greatly reduce or eliminate the nuclear stockpiles of both the U.S. and the Soviet Union over a ten-year period, but the deal collapsed due to disagreements regarding SDI development. Reagan attacked Gorbachev in a 1987 speech delivered in West Berlin, but negotiations continued.Patterson, p. 215 Gorbachev and Reagan broke the impasse by agreeing to negotiate separate treaties on intermediate nuclear forces (such as intermediate-range ballistic missile
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range of 3,000–5,500 km (1,864–3,418 miles), between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying ba ...
s) and strategic arms (such as intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
s).
With the fr